Submitted:
26 June 2023
Posted:
26 June 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
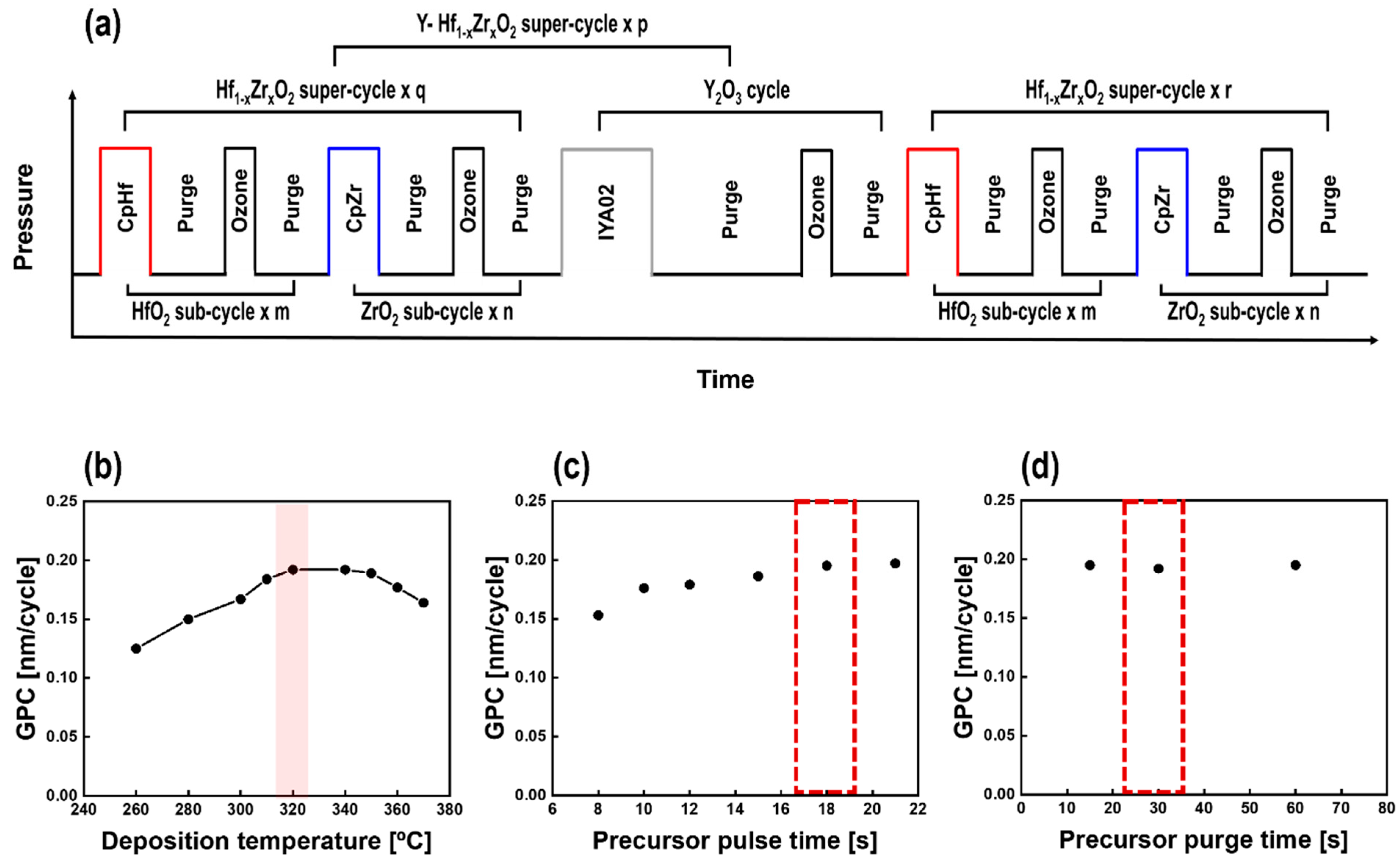
2.1. Sample Fabrication Process
2.2. Characterizations
3. Results
3.1. ALD Characteristics of Y2O3 Thin Films
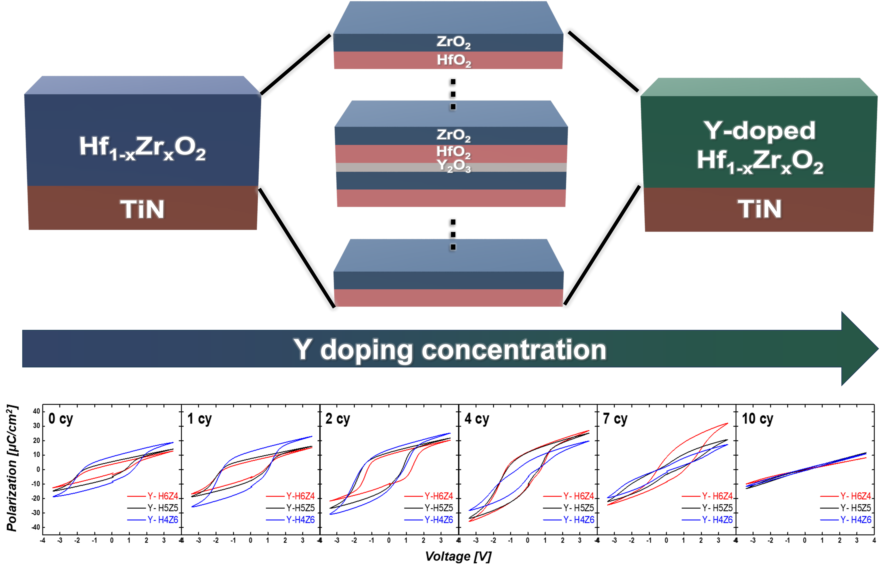
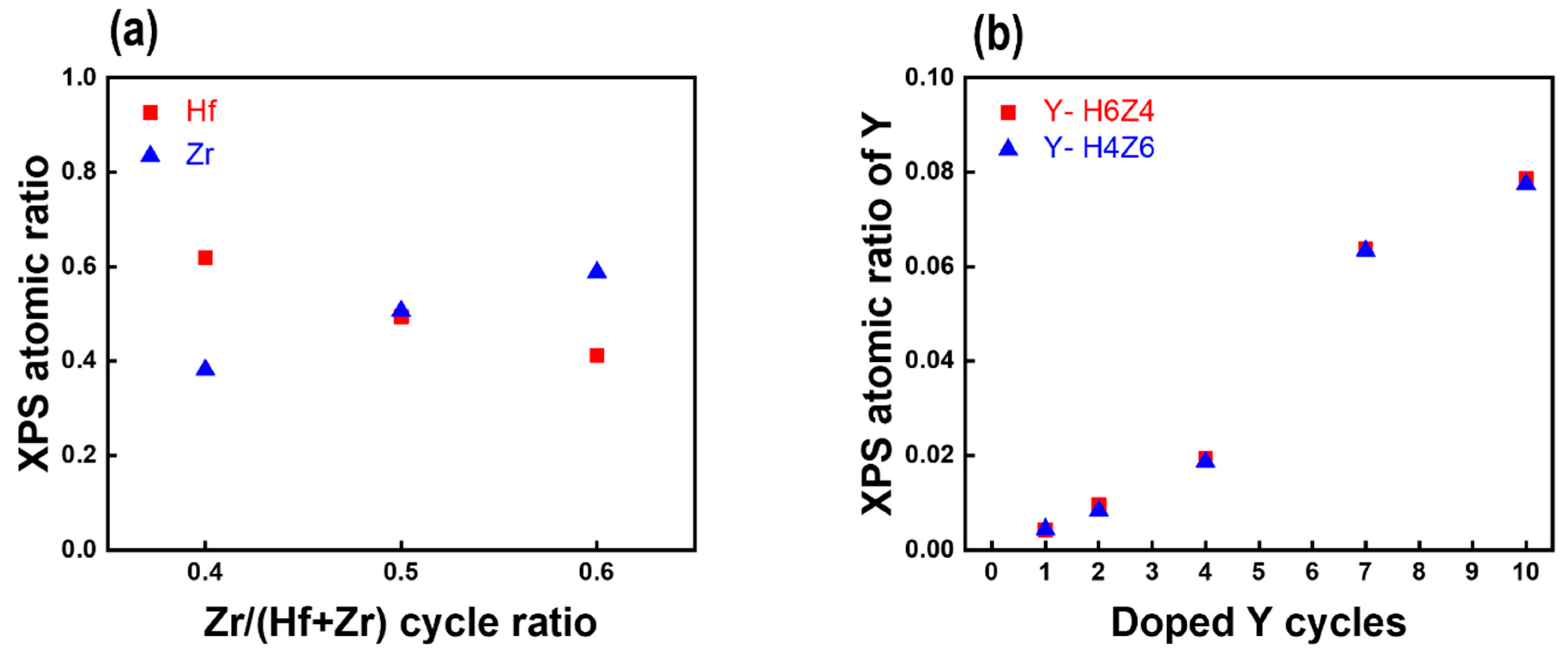
3.2. Chemical composition of as-Deposited Y-HZO Thin Films
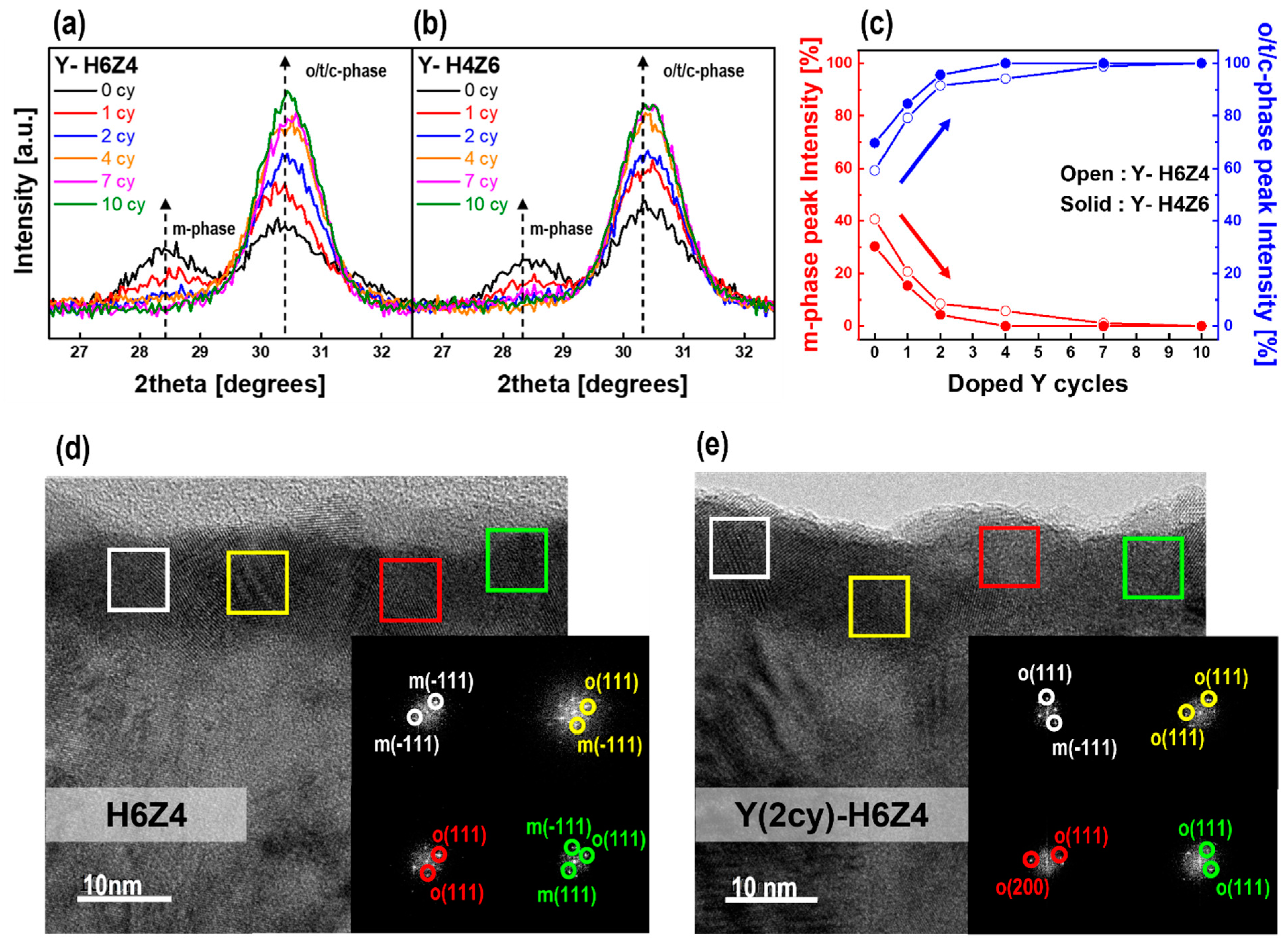
3.3. Crystallinity of As-Deposited Y-HZO Thin Films
3.4. Electrical Properties of As-Deposited Y-HZO Thin Films
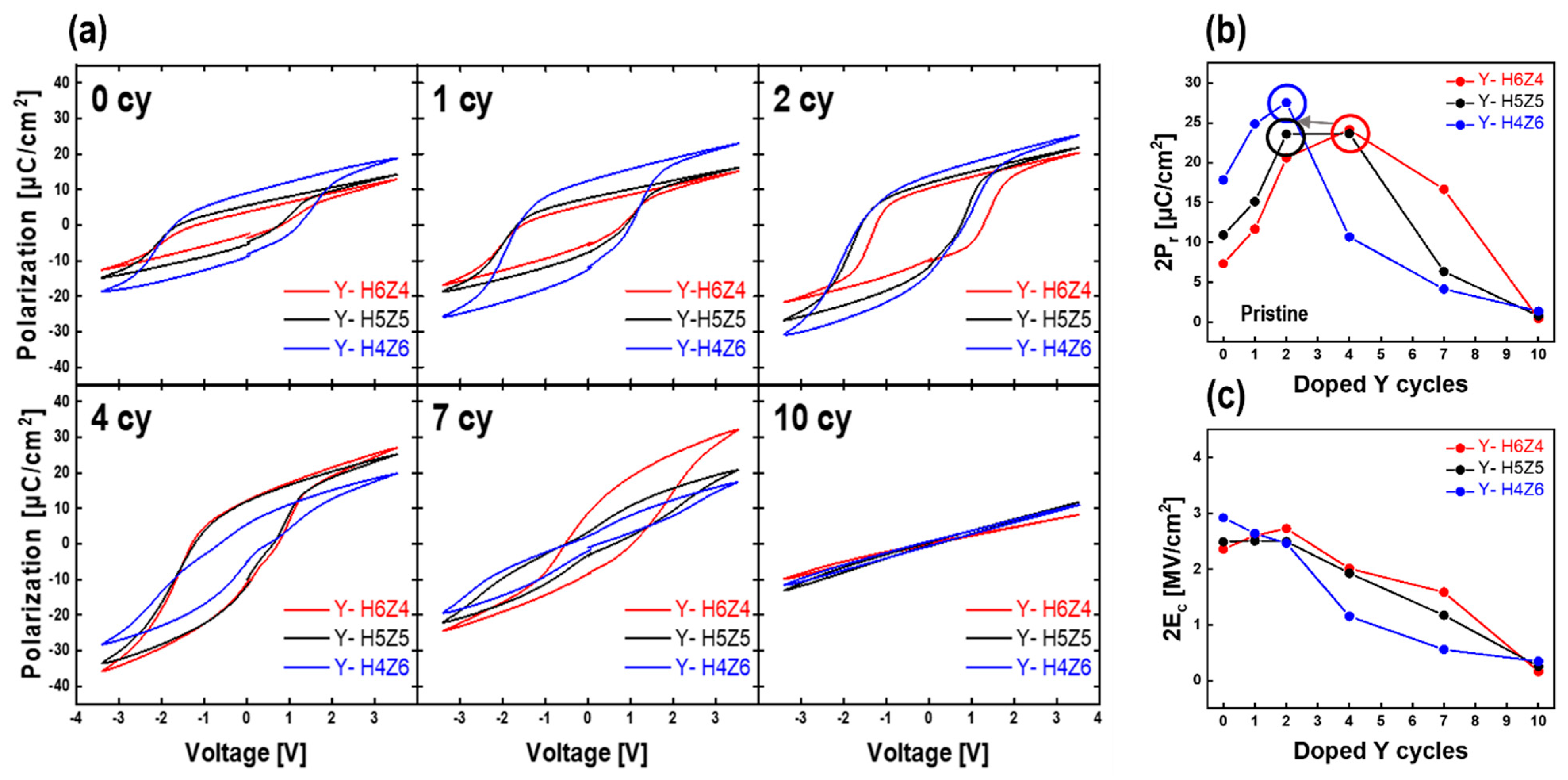
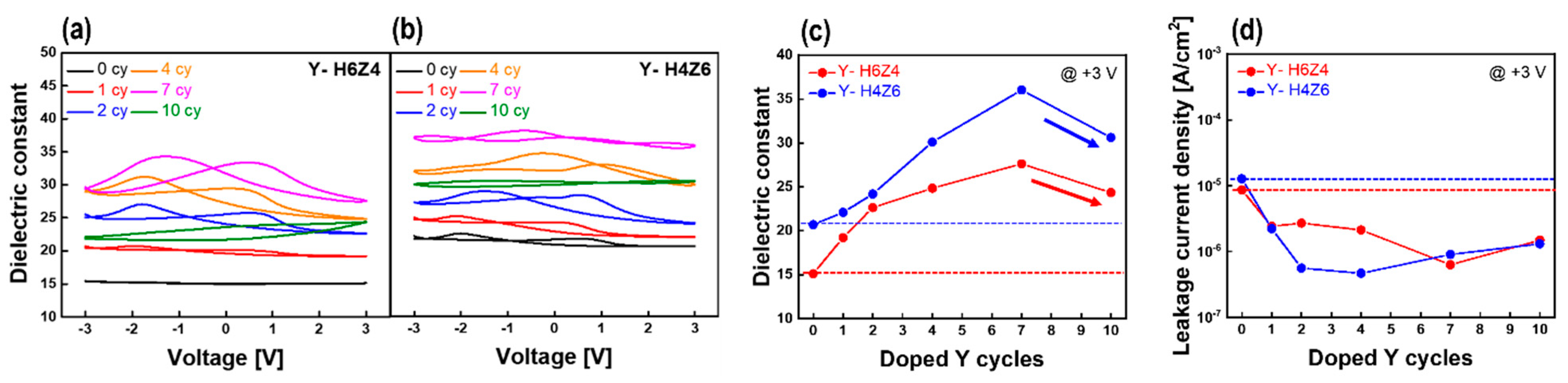
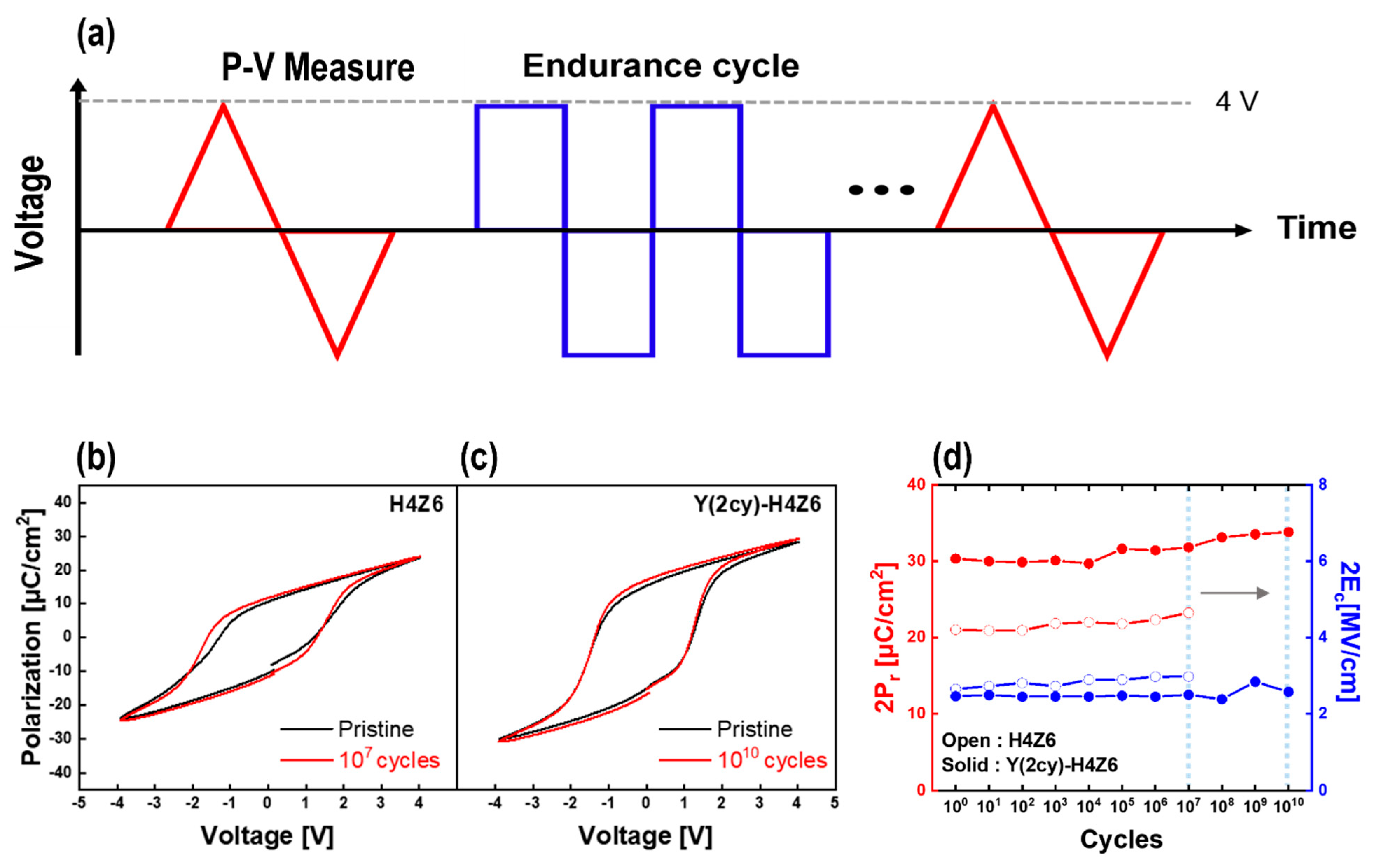
3.5. Reliability Test of As-Deposited Y-HZO Thin Films
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Muller, J.; Boscke, T.S.; Schroder, U.; Mueller, S.; Brauhaus, D.; Bottger, U.; Frey, L.; Mikolajick, T. Ferroelectricity in simple binary ZrO2 and HfO2. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 4318–4323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böscke, T.; Müller, J.; Bräuhaus, D.; Schröder, U.; Böttger, U. Ferroelectricity in hafnium oxide thin films. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2011, 99, 102903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohr, M.T.; Chau, R.S.; Ghani, T.; Mistry, K. The high-k solution. IEEE spectr. 2007, 44, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sang, X.; Grimley, E.D.; Schenk, T.; Schroeder, U.; LeBeau, J.M. On the structural origins of ferroelectricity in HfO2 thin films. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2015, 106, 162905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Materlik, R.; Künneth, C.; Falkowski, M.; Mikolajick, T.; Kersch, A. Al-, Y-, and La-doping effects favoring intrinsic and field induced ferroelectricity in HfO2: A first principles study. J. Appl. Phys. 2018, 123, 164101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starschich, S.; Boettger, U. An extensive study of the influence of dopants on the ferroelectric properties of HfO 2. J. Mater. Chem. C 2017, 5, 333–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, J.; Schröder, U.; Böscke, T.; Müller, I.; Böttger, U.; Wilde, L.; Sundqvist, J.; Lemberger, M.; Kücher, P.; Mikolajick, T. Ferroelectricity in yttrium-doped hafnium oxide. J. Appl. Phys. 2011, 110, 114113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, S.; Mueller, J.; Singh, A.; Riedel, S.; Sundqvist, J.; Schroeder, U.; Mikolajick, T. Incipient ferroelectricity in Al-doped HfO2 thin films. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2012, 22, 2412–2417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, J.; Böscke, T.; Müller, S.; Yurchuk, E.; Polakowski, P.; Paul, J.; Martin, D.; Schenk, T.; Khullar, K.; Kersch, A. Ferroelectric hafnium oxide: A CMOS-compatible and highly scalable approach to future ferroelectric memories. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Electron Devices Meeting; 2013; pp. 10.18. 11–10.18. 14. [Google Scholar]
- Popovici, M.I.; Walke, A.M.; Bizindavyi, J.; Meersschaut, J.; Banerjee, K.; Potoms, G.; Katcko, K.; Van den Bosch, G.; Delhougne, R.; Kar, G.S. High-endurance ferroelectric (La, Y) and (La, Gd) Co-doped hafnium zirconate grown by atomic layer deposition. ACS Appl. Electron. Mater. 2022, 4, 1823–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haga, K.-i.; Tokumitsu, E. Electrical properties of yttrium-doped hafnium-zirconium dioxide thin films prepared by solution process for ferroelectric gate insulator TFT application. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2020, 59, SMMB02. [Google Scholar]
- Lomenzo, P.D.; Chung, C.-C.; Zhou, C.; Jones, J.L.; Nishida, T. Doped Hf0. 5Zr0. 5O2 for high efficiency integrated supercapacitors. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2017, 110, 232904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chernikova, A.G.; Kozodaev, M.G.; Negrov, D.V.; Korostylev, E.V.; Park, M.H.; Schroeder, U.; Hwang, C.S.; Markeev, A.M. Improved ferroelectric switching endurance of La-doped Hf0. 5Zr0. 5O2 thin films. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 2701–2708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozodaev, M.G.; Chernikova, A.G.; Korostylev, E.V.; Park, M.H.; Khakimov, R.R.; Hwang, C.S.; Markeev, A.M. Mitigating wakeup effect and improving endurance of ferroelectric HfO2-ZrO2 thin films by careful La-doping. J. Appl. Phys. 2019, 125, 034101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, T.; Haga, K.-i.; Tokumitsu, E. Impact of annealing environment on electrical properties of yttrium-doped hafnium zirconium dioxide thin films prepared by the solution process. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2020, 59, SPPB03. [Google Scholar]
- Miyasako, T.; Tokumitsu, E. Indium oxide and indium-tin-oxide channel ferroelectric gate thin film transistors with yttrium doped hafnium-zirconium dioxide gate insulator prepared by chemical solution process. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2021, 60, SBBM02. [Google Scholar]
- Hoffmann, M.; Schroeder, U.; Schenk, T.; Shimizu, T.; Funakubo, H.; Sakata, O.; Pohl, D.; Drescher, M.; Adelmann, C.; Materlik, R. Stabilizing the ferroelectric phase in doped hafnium oxide. J. Appl. Phys. 2015, 118, 072006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitz, J. Low temperature thin films for next-generation microelectronics. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2018, 343, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.-B.; Jung, M.; Oh, Y.; Lee, S.W.; Suh, D.; Ahn, J.-H. Superior and stable ferroelectric properties of hafnium-zirconium-oxide thin films deposited via atomic layer deposition using cyclopentadienyl-based precursors without annealing. Nanoscale 2021, 13, 8524–8530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, Y.; Kim, H.-B.; Lee, S.W.; Jeong, M.J.; Park, T.J.; Ahn, J.-H. Effects of Zr content and annealing on ferroelectricity of as-grown crystalline Hf1-xZrxO2 thin films using Hf [Cp (NMe2) 3] and Zr [Cp (NMe2) 3] precursors via atomic layer deposition. Ceram. Int. 2022, 48, 25661–25665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yurchuk, E.; Müller, J.; Müller, S.; Paul, J.; Pešić, M.; van Bentum, R.; Schroeder, U.; Mikolajick, T. Charge-trapping phenomena in HfO 2-based FeFET-type nonvolatile memories. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 2016, 63, 3501–3507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chanthbouala, A.; Crassous, A.; Garcia, V.; Bouzehouane, K.; Fusil, S.; Moya, X.; Allibe, J.; Dlubak, B.; Grollier, J.; Xavier, S. Solid-state memories based on ferroelectric tunnel junctions. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2012, 7, 101–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knoops, H.C.; Potts, S.E.; Bol, A.A.; Kessels, W. Atomic layer deposition. In Handbook of Crystal Growth; Elsevier: 2015; pp. 1101-1134.
- Chen, H.; Luo, H.; Yuan, X.; Yang, J.; Zhang, D. Effects of doping concentration and annealing temperatures on the ferroelectric memory properties of yttrium doped HfO2. Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics 2022, 55, 394001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.-M.; Kwon, H.-J. Ferroelectrics based on HfO2 film. Electronics 2021, 10, 2759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozodaev, M.; Chernikova, A.; Korostylev, E.; Park, M.; Schroeder, U.; Hwang, C.; Markeev, A. Ferroelectric properties of lightly doped La: HfO2 thin films grown by plasma-assisted atomic layer deposition. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2017, 111, 132903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Shieh, J.; Tsai, F. Induction of ferroelectricity in nanoscale ZrO2/HfO2 bilayer thin films on Pt/Ti/SiO2/Si substrates. Acta Materialia 2016, 115, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, B.-E.; Oh, I.-K.; Mahata, C.; Lee, C.W.; Thompson, D.; Maeng, W.J.; Kim, H. Atomic layer deposition of Y-stabilized ZrO2 for advanced DRAM capacitors. Journal of Alloys and Compounds 2017, 722, 307–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pramana, S.S. Crystal Structure of Electroceramics; MDPI AG-Multidisciplinary Digital Publishing Institute: 2017.
- Chen, G.; Hou, Z.; Gong, X.; Li, Q. Effects of Y doping on the structural stability and defect properties of cubic HfO 2. J. Appl. Phys. 2008, 104, 074101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouaziz, J.; Romeo, P.R.; Baboux, N.; Vilquin, B. Huge reduction of the wake-up effect in ferroelectric HZO thin films. ACS Appl. Electron. Mater. 2019, 1, 1740–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




