Submitted:
24 June 2023
Posted:
25 June 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
Introduction
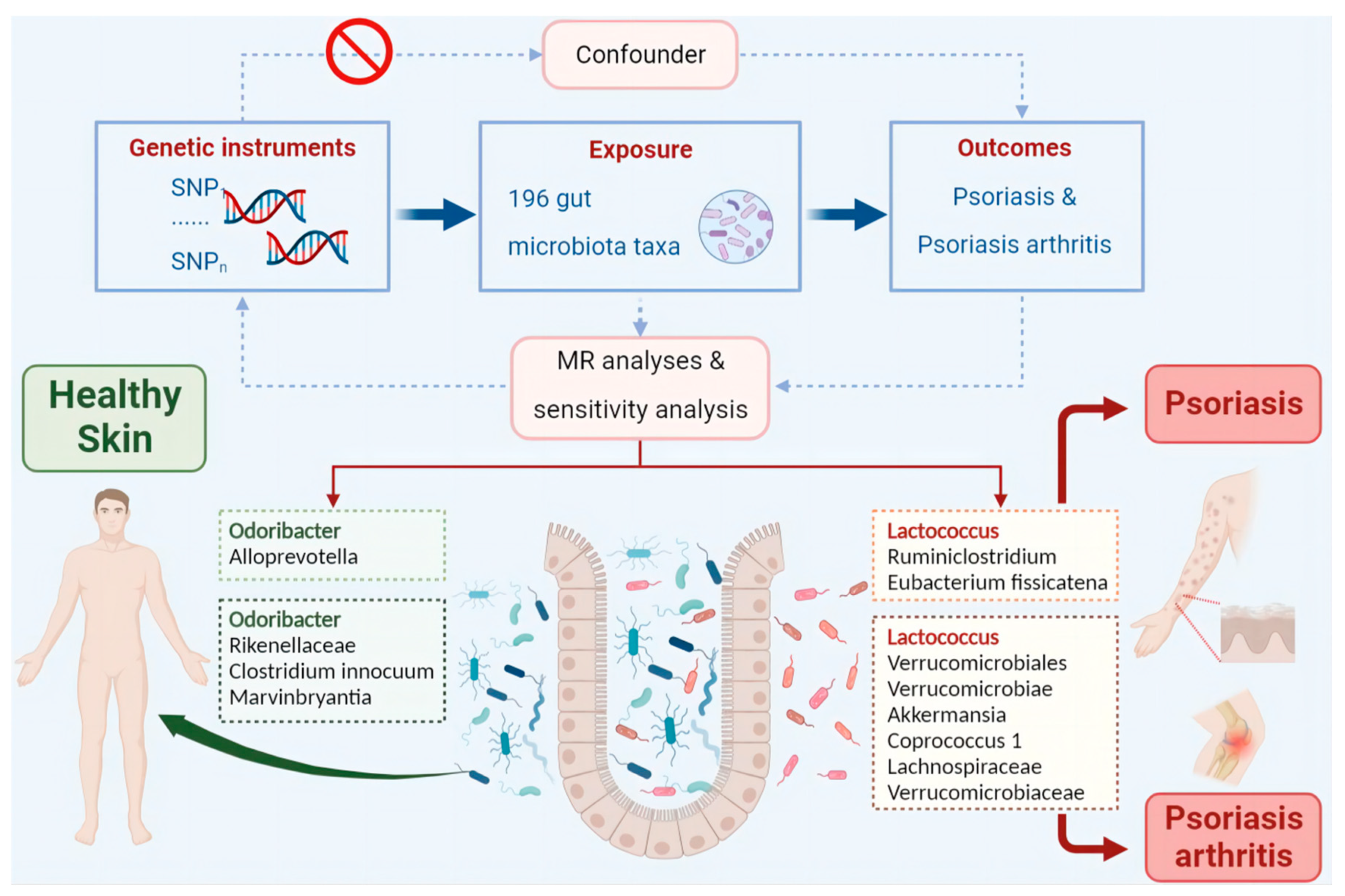
Materials and Methods
Data Sources and Filter Instrumental Variables
Mendelian Randomization Analysis
Sensitivity Analysis
Results
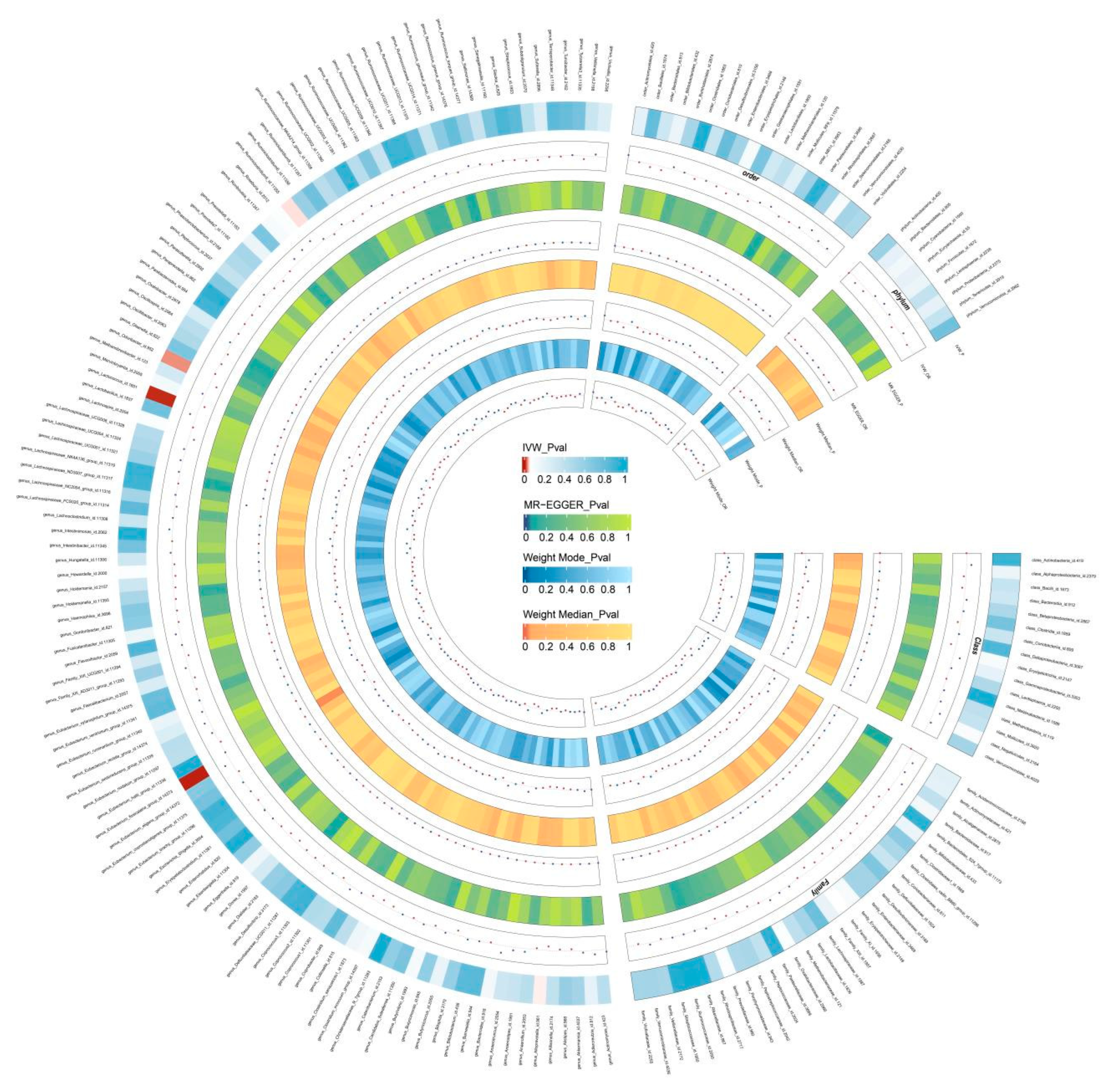
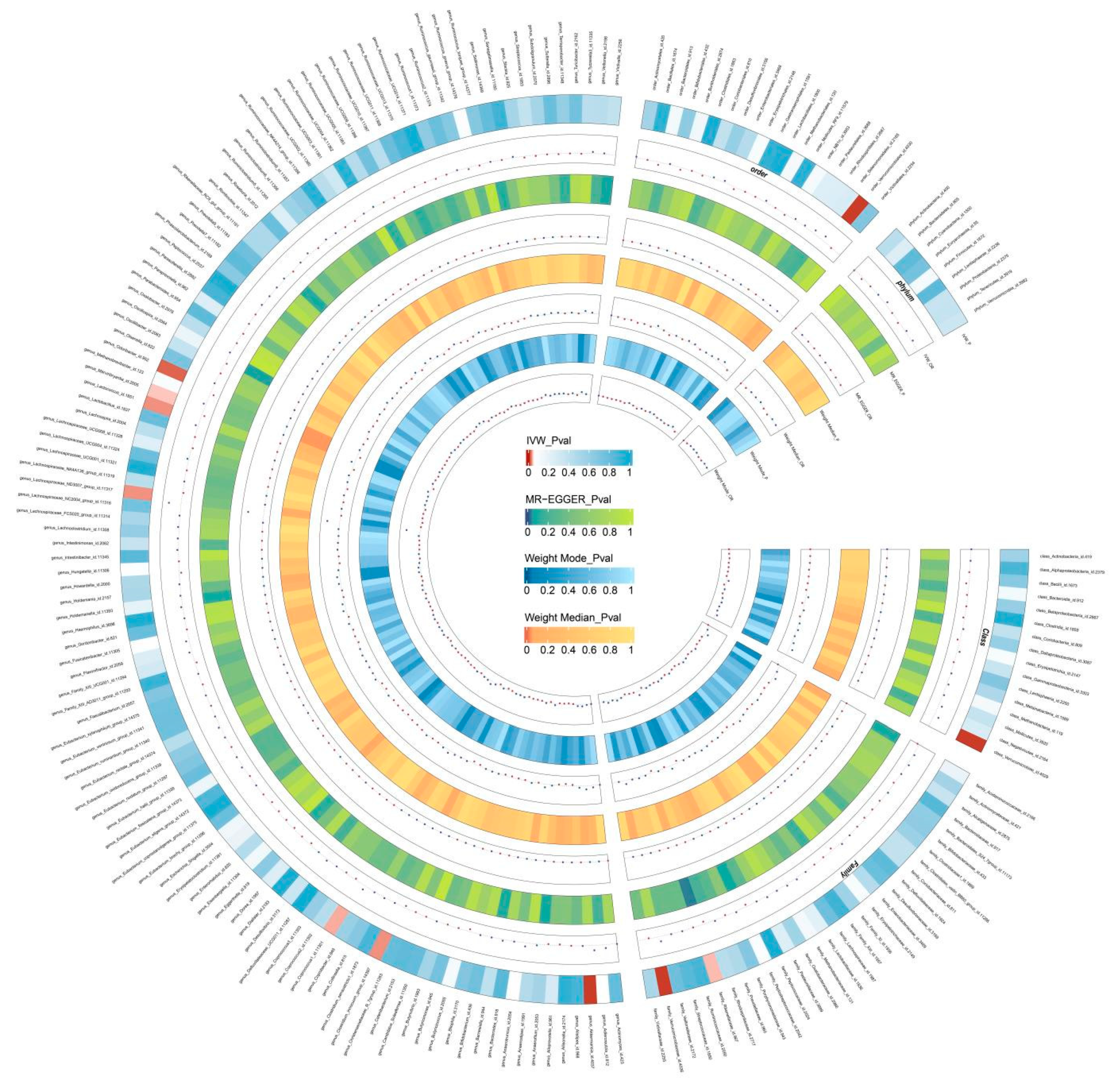
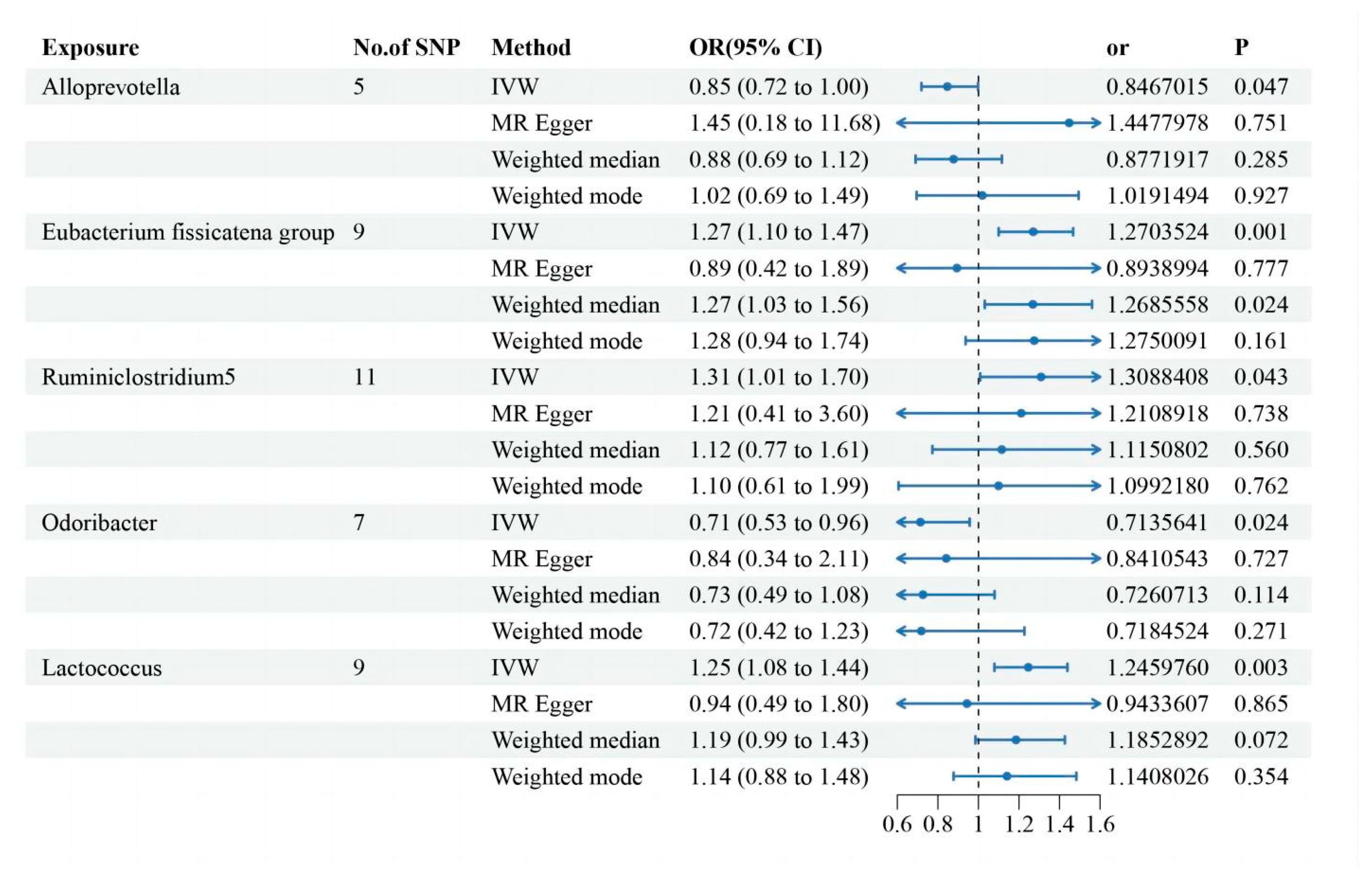
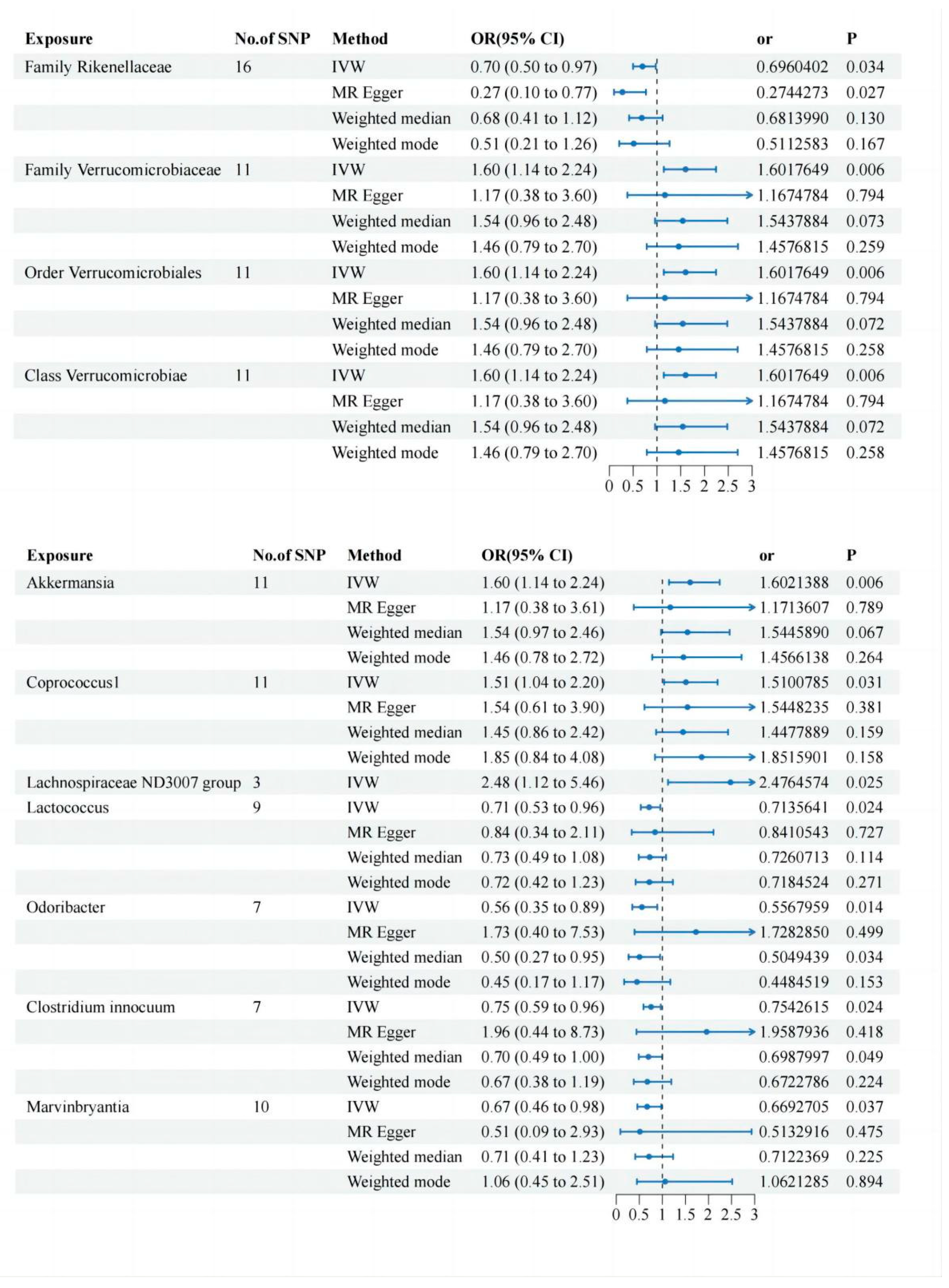
Two-Sample MR Analysis of Intestinal Flora Taxa to Ps and PsA
Sensitivity Analysis
Reverse MR Analysis
Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Ethics Statement
Disclosure Statement of Financial Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Ni, X.; Lai, Y. Keratinocyte: A trigger or an executor of psoriasis? J Leukoc Biol 2020, 108, 485–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffiths, C.; Armstrong, A.; Gudjonsson, J.; Barker, J. Psoriasis. Lancet (London, England) 2021, 397, 1301–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mou, Y.; Li, F.; Xu, Y.; Jin, X.; Dong, S.; Xia, J. Global trends in the incidence of psoriasis from 1990 to 2019. Eur J Dermatol 2022, 32, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coates, L.; Soriano, E.; Corp, N.; Bertheussen, H.; Callis Duffin, K.; Campanholo, C.; Chau, J.; Eder, L.; Fernández-Ávila, D.; FitzGerald, O.; et al. Group for Research and Assessment of Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis (GRAPPA): updated treatment recommendations for psoriatic arthritis 2021. Nature reviews. Rheumatology 2022, 18, 465–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myers, B.; Brownstone, N.; Reddy, V.; Chan, S.; Thibodeaux, Q.; Truong, A.; Bhutani, T.; Chang, H.W.; Liao, W. The gut microbiome in psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol 2019, 33, 101494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olejniczak-Staruch, I.; Ciazynska, M.; Sobolewska-Sztychny, D.; Narbutt, J.; Skibinska, M.; Lesiak, A. Alterations of the Skin and Gut Microbiome in Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis. Int J Mol Sci 2021, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikora, M.; Stec, A.; Chrabaszcz, M.; Knot, A.; Waskiel-Burnat, A.; Rakowska, A.; Olszewska, M.; Rudnicka, L. Gut Microbiome in Psoriasis: An Updated Review. Pathogens 2020, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stehlikova, Z.; Kostovcikova, K.; Kverka, M.; Rossmann, P.; Dvorak, J.; Novosadova, I.; Kostovcik, M.; Coufal, S.; Srutkova, D.; Prochazkova, P. , et al. Crucial Role of Microbiota in Experimental Psoriasis Revealed by a Gnotobiotic Mouse Model. Front Microbiol 2019, 10, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuber, V.; Grinberg, N.; Gill, D.; Manipur, I.; Slob, E.; Patel, A.; Wallace, C.; Burgess, S. Combining evidence from Mendelian randomization and colocalization: Review and comparison of approaches. American journal of human genetics 2022, 109, 767–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurilshikov, A.; Medina-Gomez, C.; Bacigalupe, R.; Radjabzadeh, D.; Wang, J.; Demirkan, A.; Le Roy, C.I.; Raygoza Garay, J.A.; Finnicum, C.T.; Liu, X. , et al. Large-scale association analyses identify host factors influencing human gut microbiome composition. Nat Genet 2021, 53, 156–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurki, M.I.; Karjalainen, J.; Palta, P.; Sipila, T.P.; Kristiansson, K.; Donner, K.M.; Reeve, M.P.; Laivuori, H.; Aavikko, M.; Kaunisto, M.A.; et al. FinnGen provides genetic insights from a well-phenotyped isolated population. Nature 2023, 613, 508–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuber, V.; Grinberg, N.F.; Gill, D.; Manipur, I.; Slob, E.A.W.; Patel, A.; Wallace, C.; Burgess, S. Combining evidence from Mendelian randomization and colocalization: Review and comparison of approaches. Am J Hum Genet 2022, 109, 767–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, M.; Raffler, J.; Pfeufer, A.; Suhre, K.; Kastenmuller, G. SNiPA: an interactive, genetic variant-centered annotation browser. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 1334–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Fu, R.; Li, R.; Zeng, J.; Liu, T.; Li, X.; Jiang, W. Causality of gut microbiome and hypertension: A bidirectional mendelian randomization study. Front Cardiovasc Med 2023, 10, 1167346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, K.; Zhang, J.J.; Xu, Y.Y.; Zhong, X.; Ni, J.; Pan, H.F. Genetically Predicted Causality of 28 Gut Microbiome Families and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Risk. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 2022, 13, 780133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamat, M.A.; Blackshaw, J.A.; Young, R.; Surendran, P.; Burgess, S.; Danesh, J.; Butterworth, A.S.; Staley, J.R. PhenoScanner V2: an expanded tool for searching human genotype-phenotype associations. Bioinformatics 2019, 35, 4851–4853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nast, A.; Smith, C.; Spuls, P.; Avila Valle, G.; Bata-Csörgö, Z.; Boonen, H.; De Jong, E.; Garcia-Doval, I.; Gisondi, P.; Kaur-Knudsen, D.; et al. EuroGuiDerm Guideline on the systemic treatment of Psoriasis vulgaris - Part 2: specific clinical and comorbid situations. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology : JEADV 2021, 35, 281–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowden, J.; Davey Smith, G.; Burgess, S. Mendelian randomization with invalid instruments: effect estimation and bias detection through Egger regression. International journal of epidemiology 2015, 44, 512–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgess, S.; Thompson, S. Avoiding bias from weak instruments in Mendelian randomization studies. International journal of epidemiology 2011, 40, 755–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verbanck, M.; Chen, C.; Neale, B.; Do, R. Detection of widespread horizontal pleiotropy in causal relationships inferred from Mendelian randomization between complex traits and diseases. Nature genetics 2018, 50, 693–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Wan, B.; Sun, M. Mendelian randomization identifies age at menarche as an independent causal effect factor for gestational diabetes mellitus. Diabetes, obesity & metabolism 2023, 25, 248–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogdie, A.; Weiss, P. The Epidemiology of Psoriatic Arthritis. Rheum Dis Clin North Am 2015, 41, 545–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, L.; Gao, R.; Yu, N.; Zhu, Y.; Ding, Y.; Qin, H. Dysbiosis of gut microbiota was closely associated with psoriasis. Sci China Life Sci 2019, 62, 807–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shapiro, J.; Cohen, N.A.; Shalev, V.; Uzan, A.; Koren, O.; Maharshak, N. Psoriatic patients have a distinct structural and functional fecal microbiota compared with controls. J Dermatol 2019, 46, 595–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Chen, Y.; Stanton, C.; Ross, R.P.; Zhao, J.; Chen, W.; Yang, B. Dose-Response Efficacy and Mechanisms of Orally Administered Bifidobacterium breve CCFM683 on IMQ-Induced Psoriasis in Mice. Nutrients 2023, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, S.; Zhang, G.; Jiang, C.; Liu, X.; Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Cheng, M.; Lv, H.; Xian, F.; Guo, X. , et al. Deciphering Gut Microbiota Dysbiosis and Corresponding Genetic and Metabolic Dysregulation in Psoriasis Patients Using Metagenomics Sequencing. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 2021, 11, 605825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, T.T.; Ye, X.L.; Li, R.R.; Chen, H.; Wang, Y.Y.; Yong, H.J.; Pan, M.L.; Lu, W.; Tang, Y.; Miao, H. , et al. Resveratrol Modulates the Gut Microbiota and Inflammation to Protect Against Diabetic Nephropathy in Mice. Front Pharmacol 2020, 11, 1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kjaer, T.N.; Thorsen, K.; Jessen, N.; Stenderup, K.; Pedersen, S.B. Resveratrol ameliorates imiquimod-induced psoriasis-like skin inflammation in mice. PLoS One 2015, 10, e0126599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elgewelly, M.A.; Elmasry, S.M.; Sayed, N.S.E.; Abbas, H. Resveratrol-Loaded Vesicular Elastic Nanocarriers Gel in Imiquimod-Induced Psoriasis Treatment: In Vitro and In Vivo Evaluation. J Pharm Sci 2022, 111, 417–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinget, G.V.; Tan, J.K.; Ni, D.; Taitz, J.; Daien, C.I.; Mielle, J.; Moore, R.J.; Stanley, D.; Simpson, S.; King, N.J.C.; et al. Dysbiosis in imiquimod-induced psoriasis alters gut immunity and exacerbates colitis development. Cell Rep 2022, 40, 111191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.Y.; Hsu, C.Y.; He, H.R.; Chiang, W.Y.; Lin, S.H.; Huang, Y.L.; Kuo, Y.H.; Su, Y.J. Gut microbiota differences between psoriatic arthritis and other undifferentiated arthritis: A pilot study. Medicine (Baltimore) 2022, 101, e29870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, L.; Zhao, S.; Zhu, W.; Wu, L.; Li, J.; Shen, M.; Lei, L.; Chen, X.; Peng, C. The Akkermansia muciniphila is a gut microbiota signature in psoriasis. Exp Dermatol 2018, 27, 144–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ritchlin, C.T.; Colbert, R.A.; Gladman, D.D. Psoriatic Arthritis. N Engl J Med 2017, 376, 957–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.J.; Ho, H.J.; Tseng, C.H.; Lai, Z.L.; Shieh, J.J.; Wu, C.Y. Intestinal microbiota profiling and predicted metabolic dysregulation in psoriasis patients. Exp Dermatol 2018, 27, 1336–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scher, J.U.; Ubeda, C.; Artacho, A.; Attur, M.; Isaac, S.; Reddy, S.M.; Marmon, S.; Neimann, A.; Brusca, S.; Patel, T.; et al. Decreased bacterial diversity characterizes the altered gut microbiota in patients with psoriatic arthritis, resembling dysbiosis in inflammatory bowel disease. Arthritis Rheumatol 2015, 67, 128–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnas, J.L.; Ritchlin, C.T. Etiology and Pathogenesis of Psoriatic Arthritis. Rheum Dis Clin North Am 2015, 41, 643–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ocampo, D.V.; Gladman, D. Psoriatic arthritis. F1000Res 2019, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciccia, F.; Guggino, G.; Ferrante, A.; Raimondo, S.; Bignone, R.; Rodolico, V.; Peralta, S.; Van Tok, M.; Cannizzaro, A.; Schinocca, C.; et al. Interleukin-9 Overexpression and Th9 Polarization Characterize the Inflamed Gut, the Synovial Tissue, and the Peripheral Blood of Patients With Psoriatic Arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol 2016, 68, 1922–1931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mielants, H.; Veys, E.M.; Cuvelier, C.; De Vos, M.; Goemaere, S.; De Clercq, L.; Schatteman, L.; Elewaut, D. The evolution of spondyloarthropathies in relation to gut histology. II. Histological aspects. J Rheumatol 1995, 22, 2273–2278. [Google Scholar]
- Scarpa, R.; Manguso, F.; D'Arienzo, A.; D'Armiento, F.P.; Astarita, C.; Mazzacca, G.; Ayala, F. Microscopic inflammatory changes in colon of patients with both active psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis without bowel symptoms. J Rheumatol 2000, 27, 1241–1246. [Google Scholar]
- Ritchlin, C.T.; Haas-Smith, S.A.; Li, P.; Hicks, D.G.; Schwarz, E.M. Mechanisms of TNF-alpha- and RANKL-mediated osteoclastogenesis and bone resorption in psoriatic arthritis. J Clin Invest 2003, 111, 821–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luelmo, J.; Gratacos, J.; Moreno Martinez-Losa, M.; Ribera, M.; Romani, J.; Calvet, J.; Leal, L.; Larrosa, M. A report of 4 years of experience of a multidisciplinary unit of psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis. Reumatol Clin 2014, 10, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abji, F.; Pollock, R.A.; Liang, K.; Chandran, V.; Gladman, D.D. Brief Report: CXCL10 Is a Possible Biomarker for the Development of Psoriatic Arthritis Among Patients With Psoriasis. Arthritis Rheumatol 2016, 68, 2911–2916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cretu, D.; Gao, L.; Liang, K.; Soosaipillai, A.; Diamandis, E.P.; Chandran, V. Differentiating Psoriatic Arthritis From Psoriasis Without Psoriatic Arthritis Using Novel Serum Biomarkers. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken) 2018, 70, 454–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cretu, D.; Liang, K.; Saraon, P.; Batruch, I.; Diamandis, E.P.; Chandran, V. Quantitative tandem mass-spectrometry of skin tissue reveals putative psoriatic arthritis biomarkers. Clin Proteomics 2015, 12, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burgess, S.; Thompson, S.G. Interpreting findings from Mendelian randomization using the MR-Egger method. Eur J Epidemiol 2017, 32, 377–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




