Submitted:
06 May 2023
Posted:
08 May 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Participants and Clinical Examination
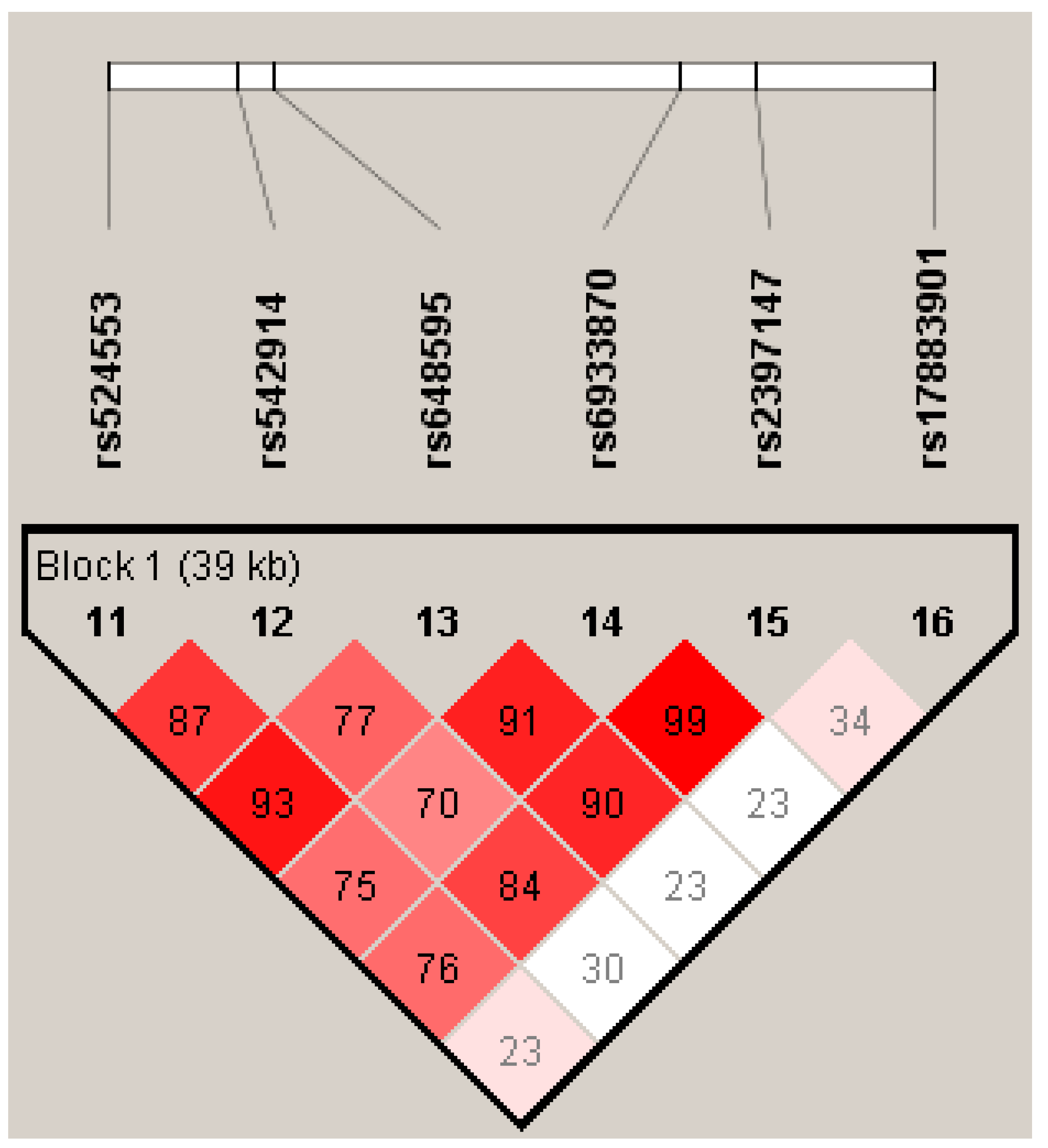
2.2. Selection of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs)
2.3. Genetic Analysis
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Baseline and clinical characteristics of the study patients
3.2. Association of GCLC Gene Polymorphisms with the Risk of Psoriasis
3.3. Joint Effects of GCLC Gene Polymorphisms on the Risk of Psoriasis
3.4. Gene-Environment Interactions and Psoriasis risk
3.5. Replication of Associations between GCLC Gene Polymorphisms Psoriasis Risk in a population of UK Biobank
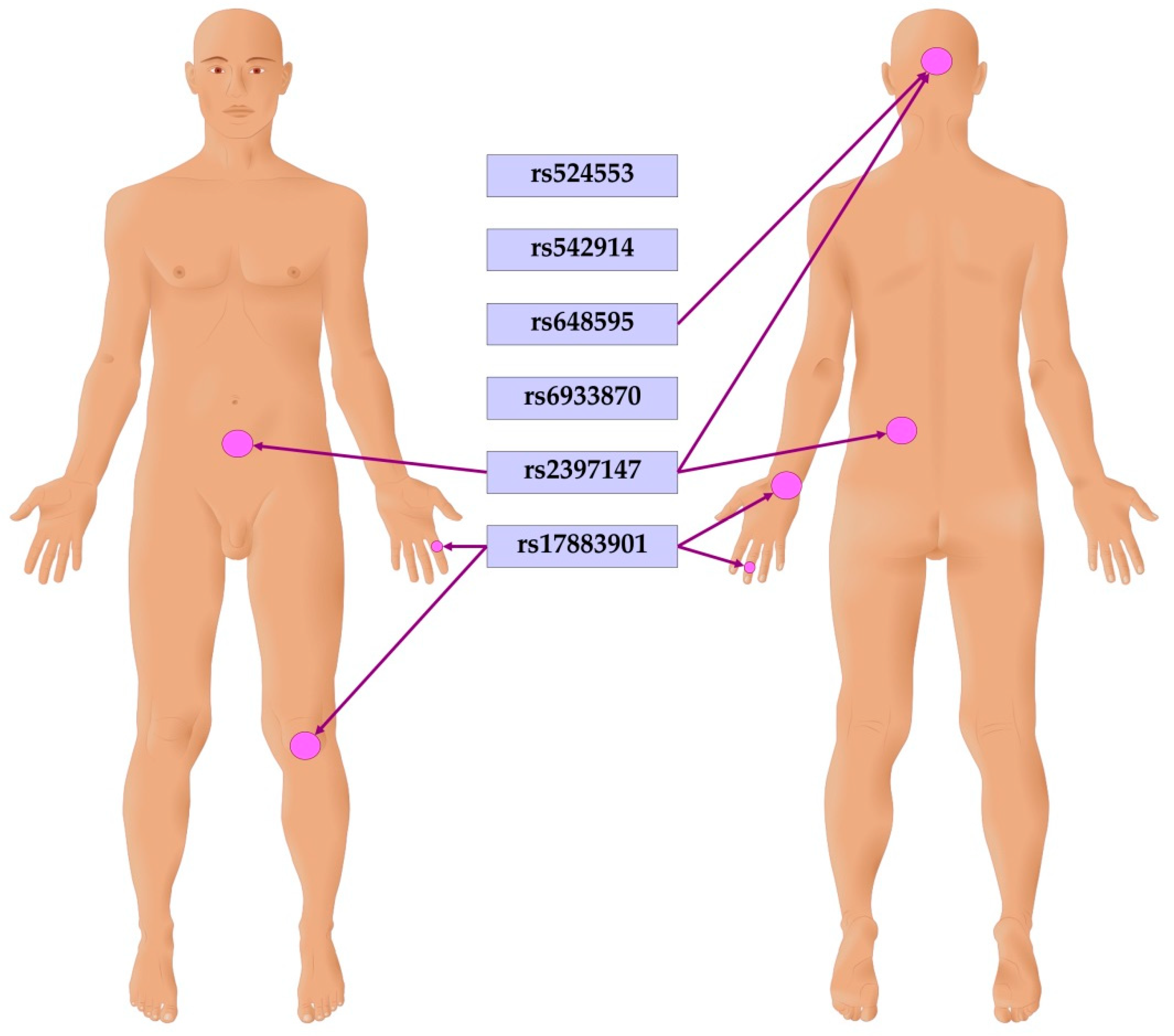
3.6. Association of GCLC Gene Polymorphisms with Clinical Features of Psoriasis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gudjonsson JE, Elder JT. Psoriasis: epidemiology. Clin Dermatol. 2007 Nov-Dec;25(6):535-46. [CrossRef]
- Campanati A, Marani A, Martina E, Diotallevi F, Radi G, Offidani A. Psoriasis as an Immune-Mediated and Inflammatory Systemic Disease: From Pathophysiology to Novel Therapeutic Approaches. Biomedicines. 2021 Oct 21;9(11):1511. [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Global report on psoriasis. World Health Organization. 2016.
- Lebwohl M. Psoriasis. Lancet. 2003 Apr 5;361(9364):1197-204. [CrossRef]
- Kubanov AA, Bakulev AL, Fitileva TV, Novoderezhkina E, Gilloteau I, Tian H, Howe T, Pietri G. Disease Burden and Treatment Patterns of Psoriasis in Russia: A Real-World Patient and Dermatologist Survey. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2018 Dec;8(4):581-592. [CrossRef]
- Di Meglio P, Villanova F, Nestle FO. Psoriasis. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2014 Aug 1;4(8):a015354. [CrossRef]
- Rendon A, Schäkel K. Psoriasis Pathogenesis and Treatment. Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Mar 23;20(6):1475. [CrossRef]
- Harden JL, Krueger JG, Bowcock AM. The immunogenetics of Psoriasis: A comprehensive review. J Autoimmun. 2015 Nov;64:66-73. [CrossRef]
- Grjibovski AM, Olsen AO, Magnus P, Harris JR. Psoriasis in Norwegian twins: contribution of genetic and environmental effects. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2007 Nov;21(10):1337-43. [CrossRef]
- Gupta R, Debbaneh MG, Liao W. Genetic Epidemiology of Psoriasis. Curr Dermatol Rep. 2014 Mar;3(1):61-78. [CrossRef]
- Capon F. The Genetic Basis of Psoriasis. Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Nov 25;18(12):2526. [CrossRef]
- Fan X, Yang S, Huang W, Wang ZM, Sun LD, Liang YH, Gao M, Ren YQ, Zhang KY, Du WH, Shen YJ, Liu JJ, Zhang XJ. Fine mapping of the psoriasis susceptibility locus PSORS1 supports HLA-C as the susceptibility gene in the Han Chinese population. PLoS Genet. 2008 Mar 21;4(3):e1000038. [CrossRef]
- Trouba KJ, Hamadeh HK, Amin RP, Germolec DR. Oxidative stress and its role in skin disease. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2002 Aug;4(4):665-73. [CrossRef]
- Cannavò SP, Riso G, Casciaro M, Di Salvo E, Gangemi S. Oxidative stress involvement in psoriasis: a systematic review. Free Radic Res. 2019 Aug;53(8):829-840. [CrossRef]
- Pleńkowska J, Gabig-Cimińska M, Mozolewski P. Oxidative Stress as an Important Contributor to the Pathogenesis of Psoriasis. Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Aug 27;21(17):6206. [CrossRef]
- Dobrică EC, Cozma MA, Găman MA, Voiculescu VM, Găman AM. The Involvement of Oxidative Stress in Psoriasis: A Systematic Review. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 Jan 29;11(2):282. [CrossRef]
- Yang S, Yan KL, Zhang XJ, Xiao FL, Fan X, Gao M, Cui Y, Wang PG, Zhang GL, Sun LD, Wang ZM, Wang DZ, Zhang KY, Huang W, Liu JJ. Systematic evaluation of association between the microsomal glutathione S-transferase 2 common variation and psoriasis vulgaris in Chinese population. Arch Dermatol Res. 2006 Aug;298(3):107-12. [CrossRef]
- Solak B, Karkucak M, Turan H, Ocakoğlu G, Özemri Sağ Ş, Uslu E, Yakut T, Erdem T. Glutathione S-Transferase M1 and T1 Gene Polymorphisms in Patients with Chronic Plaque-Type Psoriasis: A Case-Control Study. Med Princ Pract. 2016;25(2):155-8. [CrossRef]
- Srivastava DSL, Jain VK, Verma P, Yadav JP. Polymorphism of glutathione S-transferase M1 and T1 genes and susceptibility to psoriasis disease: A study from North India. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2018 Jan-Feb;84(1):39-44. [CrossRef]
- Guarneri F, Sapienza D, Papaianni V, Marafioti I, Guarneri C, Mondello C, Roccuzzo S, Asmundo A, Cannavò SP. Association between genetic polymorphisms of glutathione S-transferase M1/T1 and psoriasis in a population from the area of the strict of messina (Southern Italy). Free Radic Res. 2020 Jan;54(1):57-63. [CrossRef]
- Wu G, Fang YZ, Yang S, Lupton JR, Turner ND. Glutathione metabolism and its implications for health. J Nutr 2004; 134(3):489–492. [CrossRef]
- Sies H. Glutathione and its role in cellular functions. Free Radic Biol Med. 1999 Nov;27(9-10):916-21. [CrossRef]
- Sipos K, Lange H, Fekete Z, Ullmann P, Lill R, Kispal G. Maturation of cytosolic iron-sulfur proteins requires glutathione. J Biol Chem. 2002 Jul 26;277(30):26944-9. [CrossRef]
- Jacquoilleot S, Sheffield D, Olayanju A, Sison-Young R, Kitteringham NR, Naisbitt DJ, Aleksic M. Glutathione metabolism in the HaCaT cell line as a model for the detoxification of the model sensitisers 2,4-dinitrohalobenzenes in human skin. Toxicol Lett. 2015 Aug 19;237(1):11-20. [CrossRef]
- Telorack M, Meyer M, Ingold I, Conrad M, Bloch W, Werner S. A Glutathione-Nrf2-Thioredoxin Cross-Talk Ensures Keratinocyte Survival and Efficient Wound Repair. PLoS Genet. 2016 Jan 25;12(1):e1005800. [CrossRef]
- Prussick R, Prussick L, Gutman J. Psoriasis Improvement in Patients Using Glutathione-enhancing, Nondenatured Whey Protein Isolate: A Pilot Study. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2013 Oct;6(10):23-6.
- Zhou Q, Mrowietz U, Rostami-Yazdi M. Oxidative stress in the pathogenesis of psoriasis. Free Radic Biol Med. 2009 Oct 1;47(7):891-905. [CrossRef]
- Medovic MV, Jakovljevic VL, Zivkovic VI, Jeremic NS, Jeremic JN, Bolevich SB, Ravic Nikolic AB, Milicic VM, Srejovic IM. Psoriasis between Autoimmunity and Oxidative Stress: Changes Induced by Different Therapeutic Approaches. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022 Mar 12;2022:2249834. [CrossRef]
- Franklin CC, Backos DS, Mohar I, White CC, Forman HJ, Kavanagh TJ. Structure, function, and post-translational regulation of the catalytic and modifier subunits of glutamate cysteine ligase. Mol Aspects Med. 2009 Feb-Apr;30(1-2):86-98. [CrossRef]
- Klyosova E, Azarova I, Polonikov A. A Polymorphism in the Gene Encoding Heat Shock Factor 1 (HSF1) Increases the Risk of Type 2 Diabetes: A Pilot Study Supports a Role for Impaired Protein Folding in Disease Pathogenesis. Life (Basel). 2022 Nov 20;12(11):1936. [CrossRef]
- Lazarenko V, Churilin M, Azarova I, Klyosova E, Bykanova M, Ob'edkova N, Churnosov M, Bushueva O, Mal G, Povetkin S, Kononov S, Luneva Y, Zhabin S, Polonikova A, Gavrilenko A, Saraev I, Solodilova M, Polonikov A. Comprehensive Statistical and Bioinformatics Analysis in the Deciphering of Putative Mechanisms by Which Lipid-Associated GWAS Loci Contribute to Coronary Artery Disease. Biomedicines. 2022 Jan 25;10(2):259. [CrossRef]
- Kobzeva KA, Shilenok IV, Belykh AE, et al. C9orf16 (BBLN) gene, encoding a member of Hero proteins, is a novel marker in ischemic stroke risk. Research Results in Biomedicine. 2022;8(3):278-292. [CrossRef]
- Griffiths CE, Barker JN. Pathogenesis and clinical features of psoriasis. Lancet. 2007 Jul 21;370(9583):263-271. [CrossRef]
- Fredriksson T, Pettersson U. Severe psoriasis--oral therapy with a new retinoid. Dermatologica. 1978;157(4):238-44. [CrossRef]
- Klyosova, E.Y.; Azarova, I.E.; Sunyaykina, O.A.; Polonikov, A.V. Validity of a brief screener for environmental risk factors of age-related diseases using type 2 diabetes and coronary artery disease as examples. Res. Results Biomed. 2022, 8, 130–137.
- Armstrong AW, Harskamp CT, Dhillon JS, Armstrong EJ. Psoriasis and smoking: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Br J Dermatol. 2014 Feb;170(2):304-14. [CrossRef]
- Brenaut E, Horreau C, Pouplard C, Barnetche T, Paul C, Richard MA, Joly P, Le Maître M, Aractingi S, Aubin F, Cribier B, Jullien D, Ortonne JP, Misery L. Alcohol consumption and psoriasis: a systematic literature review. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2013 Aug;27 Suppl 3:30-5. [CrossRef]
- Polonikov AV, Ivanov VP, Solodilova MA. CYP2E1 gene promoter polymorphism -1293G>C increases the risk of essential hypertension in men with alcohol abuse. Bull Exp Biol Med. 2013 Oct;155(6):734-7. [CrossRef]
- Polonikov AV, Samgina TA, Nazarenko PM, Bushueva OY, Ivanov VP. Alcohol Consumption and Cigarette Smoking are Important Modifiers of the Association Between Acute Pancreatitis and the PRSS1-PRSS2 Locus in Men. Pancreas. 2017 Feb;46(2):230-236. [CrossRef]
- Purcell S, Neale B, Todd-Brown K, Thomas L, Ferreira MA, Bender D, Maller J, Sklar P, de Bakker PI, Daly MJ, Sham PC. PLINK: a tool set for whole-genome association and population-based linkage analyses. Am J Hum Genet. 2007 Sep;81(3):559-75. [CrossRef]
- Barrett JC, Fry B, Maller J, Daly MJ. Haploview: analysis and visualization of LD and haplotype maps. Bioinformatics. 2005 Jan 15;21(2):263-5. [CrossRef]
- Neale BM, Sham PC. The future of association studies: gene-based analysis and replication. Am J Hum Genet. 2004 Sep;75(3):353-62. [CrossRef]
- Kraft P, Zeggini E, Ioannidis JP. Replication in genome-wide association studies. Stat Sci. 2009 Nov 1;24(4):561-573. [CrossRef]
- Belonogova NM, Zorkoltseva IV, Tsepilov YA, Axenovich TI. Gene-based association analysis identifies 190 genes affecting neuroticism. Sci Rep. 2021 Jan 28;11(1):2484. [CrossRef]
- Manevski N, Swart P, Balavenkatraman KK, Bertschi B, Camenisch G, Kretz O, Schiller H, Walles M, Ling B, Wettstein R, Schaefer DJ, Itin P, Ashton-Chess J, Pognan F, Wolf A, Litherland K. Phase II metabolism in human skin: skin explants show full coverage for glucuronidation, sulfation, N-acetylation, catechol methylation, and glutathione conjugation. Drug Metab Dispos. 2015 Jan;43(1):126-39. [CrossRef]
- Azevedo Martins TE, Sales de Oliveira Pinto CA, Costa de Oliveira A, Robles Velasco MV, Gorriti Guitiérrez AR, Cosquillo Rafael MF, Tarazona JPH, Retuerto-Figueroa MG. Contribution of Topical Antioxidants to Maintain Healthy Skin—A Review. Scientia Pharmaceutica. 2020; 88(2):27. https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm88020027.
- Le TM, Willis AS, Barr FE, Cunningham GR, Canter JA, Owens SE, Apple RK, Ayodo G, Reich D, Summar ML. An ethnic-specific polymorphism in the catalytic subunit of glutamate-cysteine ligase impairs the production of glutathione intermediates in vitro. Mol Genet Metab. 2010 Sep;101(1):55-61. [CrossRef]
- Nichenametla SN, Lazarus P, Richie JP Jr. A GAG trinucleotide-repeat polymorphism in the gene for glutathione biosynthetic enzyme, GCLC, affects gene expression through translation. FASEB J. 2011 Jul;25(7):2180-7. [CrossRef]
- Butticaz C, Gysin R, Cuénod M, Do KQ. Interaction of GAG trinucleotide repeat and C-129T polymorphisms impairs expression of the glutamate-cysteine ligase catalytic subunit gene. Free Radic Biol Med. 2011 Mar 1;50(5):617-23. [CrossRef]
- Wang D, Curtis A, Papp AC, Koletar SL, Para MF. Polymorphism in glutamate cysteine ligase catalytic subunit (GCLC) is associated with sulfamethoxazole-induced hypersensitivity in HIV/AIDS patients. BMC Med Genomics. 2012 Jul 23;5:32. [CrossRef]
- Azarova I, Klyosova E, Lazarenko V, Konoplya A, Polonikov A. Genetic variants in glutamate cysteine ligase confer protection against type 2 diabetes. Mol Biol Rep. 2020 Aug;47(8):5793-5805. [CrossRef]
- Koide S, Kugiyama K, Sugiyama S, Nakamura S, Fukushima H, Honda O, Yoshimura M, Ogawa H. Association of polymorphism in glutamate-cysteine ligase catalytic subunit gene with coronary vasomotor dysfunction and myocardial infarction. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2003 Feb 19;41(4):539-45. [CrossRef]
- Skvortsova L, Perfelyeva A, Khussainova E, Mansharipova A, Forman HJ, Djansugurova L. Association of GCLM -588C/T and GCLC -129T/C Promoter Polymorphisms of Genes Coding the Subunits of Glutamate Cysteine Ligase with Ischemic Heart Disease Development in Kazakhstan Population. Dis Markers. 2017;2017:4209257. [CrossRef]
- Polonikov A, Bocharova I, Azarova I, Klyosova E, Bykanova M, Bushueva O, Polonikova A, Churnosov M, Solodilova M. The Impact of Genetic Polymorphisms in Glutamate-Cysteine Ligase, a Key Enzyme of Glutathione Biosynthesis, on Ischemic Stroke Risk and Brain Infarct Size. Life (Basel). 2022 Apr 18;12(4):602. [CrossRef]
- Bekris LM, Shephard C, Janer M, Graham J, McNeney B, Shin J, Zarghami M, Griffith W, Farin F, Kavanagh TJ, Lernmark A. Glutamate cysteine ligase catalytic subunit promoter polymorphisms and associations with type 1 diabetes age-at-onset and GAD65 autoantibody levels. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes. 2007 Apr;115(4):221-8. [CrossRef]
- Vieira SM, Monteiro MB, Marques T, Luna AM, Fortes MA, Nery M, Queiroz M, Dib SA, Vendramini MF, Azevedo MJ, Canani LH, Parisi MC, Pavin EJ, Giannella-Neto D, Corrêa-Giannella ML. Association of genetic variants in the promoter region of genes encoding p22phox (CYBA) and glutamate cysteine ligase catalytic subunit (GCLC) and renal disease in patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus. BMC Med Genet. 2011 Sep 30;12:129. [CrossRef]
- Yang C, Xi M, Liu H, Bai H, Jiang C, Liu Q, Fan P. Association of Polymorphisms of Glutamate Cysteine Ligase Genes GCLC C-129 T and GCLM C-588 T with Risk of Polycystic Ovary Syndrome in Chinese Women. Reprod Sci. 2022 Jun;29(6):1790-1800. [CrossRef]
- Macaluso FS, Maida M, Petta S. Genetic background in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A comprehensive review. World J Gastroenterol. 2015 Oct 21;21(39):11088-111. [CrossRef]
- Polonikov AV, Ivanov VP, Solodilova MA, Khoroshaya IV, Kozhuhov MA, Panfilov VI. The relationship between polymorphisms in the glutamate cysteine ligase gene and asthma susceptibility. Respir Med. 2007 Nov;101(11):2422-4. [CrossRef]
- Yuniastuti A, Susanti R, Mustikaningtyas D. Polymorphism of Glutamate-Cysteine Ligase Subunit Catalytic (GCLC) Gene in Pulmonary Tuberculosis Patients. Pak J Biol Sci. 2017;20(8):397-402. [CrossRef]
- Bykanova MA, Solodilova MA, Azarova IE, Klyosova EY, Bushueva OY, Polonikova AA, Churnosov MI, Polonikov AV. Genetic variation at the catalytic subunit of glutamate cysteine ligase contributes to the susceptibility to sporadic colorectal cancer: a pilot study. Mol Biol Rep. 2022 Jul;49(7):6145-6154. [CrossRef]
- Hägg D, Sundström A, Eriksson M, Schmitt-Egenolf M. Severity of Psoriasis Differs Between Men and Women: A Study of the Clinical Outcome Measure Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI) in 5438 Swedish Register Patients. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2017 Aug;18(4):583-590. [CrossRef]
- Murer C, Sgier D, Mettler SK, Guillet C, Maul JT, Djamei V, Navarini AA, Anzengruber F. Gender differences in psoriasis: a Swiss online psoriasis survey. Arch Dermatol Res. 2021 Mar;313(2):89-94. [CrossRef]
- Dvornyk V, Ponomarenko I, Belyaeva T, Reshetnikov E, Churnosov M. Filaggrin gene polymorphisms are associated with atopic dermatitis in women but not in men in the Caucasian population of Central Russia. PLoS One. 2021 Dec 9;16(12):e0261026. [CrossRef]
- Bayaraa B, Imafuku S. Relationship between environmental factors, age of onset and familial history in Japanese patients with psoriasis. J Dermatol. 2018 Jun;45(6):715-718. [CrossRef]
- Temellini A, Castiglioni M, Giuliani L, Mussi A, Giulianotti PC, Pietrabissa A, Angeletti CA, Mosca F, Pacifici GM. Glutathione conjugation with 1-chloro-2,4-dinitrobenzene (CDNB): interindividual variability in human liver, lung, kidney and intestine. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1995 Sep;33(9):498-503.
- Dilokthornsakul W, Dhippayom T, Dilokthornsakul P. The clinical effect of glutathione on skin color and other related skin conditions: A systematic review. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2019 Jun;18(3):728-737. [CrossRef]
- Hess J, Angel P, Schorpp-Kistner M. AP-1 subunits: quarrel and harmony among siblings. J Cell Sci. 2004 Dec 1;117(Pt 25):5965-73. [CrossRef]
- Local A, Huang H, Albuquerque CP, Singh N, Lee AY, Wang W, Wang C, Hsia JE, Shiau AK, Ge K, Corbett KD, Wang D, Zhou H, Ren B. Identification of H3K4me1-associated proteins at mammalian enhancers. Nat Genet. 2018 Jan;50(1):73-82. [CrossRef]
- Creyghton MP, Cheng AW, Welstead GG, Kooistra T, Carey BW, Steine EJ, Hanna J, Lodato MA, Frampton GM, Sharp PA, Boyer LA, Young RA, Jaenisch R. Histone H3K27ac separates active from poised enhancers and predicts developmental state. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010 Dec 14;107(50):21931-6. [CrossRef]
- Lauberth SM, Nakayama T, Wu X, Ferris AL, Tang Z, Hughes SH, Roeder RG. H3K4me3 interactions with TAF3 regulate preinitiation complex assembly and selective gene activation. Cell. 2013 Feb 28;152(5):1021-36. [CrossRef]
- Karmodiya K, Krebs AR, Oulad-Abdelghani M, Kimura H, Tora L. H3K9 and H3K14 acetylation co-occur at many gene regulatory elements, while H3K14ac marks a subset of inactive inducible promoters in mouse embryonic stem cells. BMC Genomics. 2012 Aug 24;13:424. [CrossRef]
- Vogt BL, Richie JP Jr. Glutathione depletion and recovery after acute ethanol administration in the aging mouse. Biochem Pharmacol. 2007 May 15;73(10):1613-21. [CrossRef]
- Guerri C, Grisolía S. Changes in glutathione in acute and chronic alcohol intoxication. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 1980;13 Suppl 1:53-61. [CrossRef]
- Lauterburg BH, Velez ME. Glutathione deficiency in alcoholics: risk factor for paracetamol hepatotoxicity. Gut. 1988 Sep;29(9):1153-7. [CrossRef]
- Kimura T, Kawasaki Y, Okumura F, Sone T, Natsuki R, Isobe M. Ethanol-induced expression of glutamate-cysteine ligase catalytic subunit gene is mediated by NF-kappaB. Toxicol Lett. 2009 Mar 10;185(2):110-5. [CrossRef]
- Haramaki N, Ikeda H, Takajo Y, Katoh A, Kanaya S, Shintani S, Haramaki R, Murohara T, Imaizumi T. Long-term smoking causes nitroglycerin resistance in platelets by depletion of intraplatelet glutathione. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2001 Nov;21(11):1852-6. [CrossRef]
- van der Toorn M, Smit-de Vries MP, Slebos DJ, de Bruin HG, Abello N, van Oosterhout AJ, Bischoff R, Kauffman HF. Cigarette smoke irreversibly modifies glutathione in airway epithelial cells. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2007 Nov;293(5):L1156-62. [CrossRef]
- Bazzini C, Rossetti V, Civello DA, Sassone F, Vezzoli V, Persani L, Tiberio L, Lanata L, Bagnasco M, Paulmichl M, Meyer G, Garavaglia ML. Short- and long- term effects of cigarette smoke exposure on glutathione homeostasis in human bronchial epithelial cells. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2013;32(7):129-45. [CrossRef]
- Ghezzi P. Role of glutathione in immunity and inflammation in the lung. Int J Gen Med. 2011 Jan 25;4:105-13. [CrossRef]
- Dröge W, Breitkreutz R. Glutathione and immune function. Proc Nutr Soc. 2000 Nov;59(4):595-600. [CrossRef]
- Diotallevi M, Checconi P, Palamara AT, Celestino I, Coppo L, Holmgren A, Abbas K, Peyrot F, Mengozzi M, Ghezzi P. Glutathione Fine-Tunes the Innate Immune Response toward Antiviral Pathways in a Macrophage Cell Line Independently of Its Antioxidant Properties. Front Immunol. 2017 Sep 29;8:1239. [CrossRef]
- Perricone C, De Carolis C, Perricone R. Glutathione: a key player in autoimmunity. Autoimmun Rev. 2009 Jul;8(8):697-701. [CrossRef]
- Hirai A, Minamiyama Y, Hamada T, Ishii M, Inoue M. Glutathione metabolism in mice is enhanced more with hapten-induced allergic contact dermatitis than with irritant contact dermatitis. J Invest Dermatol. 1997 Sep;109(3):314-8. [CrossRef]
- Azarova I, Klyosova E, Polonikov A. The Link between Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and the Polymorphisms of Glutathione-Metabolizing Genes Suggests a New Hypothesis Explaining Disease Initiation and Progression. Life (Basel). 2021 Aug 28;11(9):886. [CrossRef]
- International HapMap 3 Consortium; Altshuler DM, Gibbs RA, Peltonen L, Altshuler DM, Gibbs RA, Peltonen L, Dermitzakis E, Schaffner SF, Yu F, Peltonen L, Dermitzakis E, Bonnen PE, Altshuler DM, Gibbs RA, de Bakker PI, Deloukas P, Gabriel SB, Gwilliam R, Hunt S, Inouye M, Jia X, Palotie A, Parkin M, Whittaker P, Yu F, Chang K, Hawes A, Lewis LR, Ren Y, Wheeler D, Gibbs RA, Muzny DM, Barnes C, Darvishi K, Hurles M, Korn JM, Kristiansson K, Lee C, McCarrol SA, Nemesh J, Dermitzakis E, Keinan A, Montgomery SB, Pollack S, Price AL, Soranzo N, Bonnen PE, Gibbs RA, Gonzaga-Jauregui C, Keinan A, Price AL, Yu F, Anttila V, Brodeur W, Daly MJ, Leslie S, McVean G, Moutsianas L, Nguyen H, Schaffner SF, Zhang Q, Ghori MJ, McGinnis R, McLaren W, Pollack S, Price AL, Schaffner SF, Takeuchi F, Grossman SR, Shlyakhter I, Hostetter EB, Sabeti PC, Adebamowo CA, Foster MW, Gordon DR, Licinio J, Manca MC, Marshall PA, Matsuda I, Ngare D, Wang VO, Reddy D, Rotimi CN, Royal CD, Sharp RR, Zeng C, Brooks LD, McEwen JE. Integrating common and rare genetic variation in diverse human populations. Nature. 2010 Sep 2;467(7311):52-8. [CrossRef]
- Kinney N, Kang L, Bains H, Lawson E, Husain M, Husain K, Sandhu I, Shin Y, Carter JK, Anandakrishnan R, Michalak P, Garner H. Ethnically biased microsatellites contribute to differential gene expression and glutathione metabolism in Africans and Europeans. PLoS One. 2021 Mar 25;16(3):e0249148. [CrossRef]
- Sychev DA, Malova EU. Evidence-based pharmacogenetics: Is it possible? Int J Risk Saf Med. 2015;27 Suppl 1:S97-8. [CrossRef]
- Johansson Å, Andreassen OA, Brunak S, Franks PW, Hedman H, Loos RJF, Meder B, Melén E, Wheelock CE, Jacobsson B. Precision medicine in complex diseases-Molecular subgrouping for improved prediction and treatment stratification. J Intern Med. 2023 Apr 24. [CrossRef]
| Characteristics | Patients with psoriasis n=474 |
Healthy controls n=470 |
P-value* |
| Baseline characteristics | |||
| Age, mean ± standard deviation | 44.3 ± 13.6 | 55.3 ± 6.7 | <0.0001 |
| Males, n (%) | 252 (53.2) | 234 (49.8) | 0.30 |
| Females, n (%) | 222 (46.8) | 236 (50.2) | |
| Risk factors | |||
| Smokers, (ever/never), n (%) | 168 (35.4) | 148 (31.5) | 0.20 |
| Alcohol abusers1, n (%) | 105 (21.2) | 7 (3.2) | <0.0001 |
| Locations of psoriatic lesions | |||
| Psoriatic triad | 256 (54.0) | - | - |
| Scalp | 227 (47.9) | - | |
| Trunk | 160 (33.08) | - | - |
| Hands | 379 (80.0) | - | - |
| Legs | 272 (57.4) | - | - |
| Joints | 128 (27.0) | - | - |
| Low back | 24 (5.1) | - | - |
| Knees | 59 (12.4) | - | - |
| Hips | 21 (4.4) | - | - |
| Elbows | 33 (7.0) | - | - |
| Fingers | 60 (12.6) | - | - |
| Ankles | 24 (5.1) | - | - |
| Feet/toes | 23 (4.9) | - | - |
| Thumbs | 18 (3.8) | - | - |
| Shoulders | 11 (2.3) | - | - |
| Wrists | 33 (7.0) | - | - |
| Nails | 123 (25.9) | - | - |
| Comorbidities | |||
| Type 2 diabetes, n (%) | 15 (3.2) | - | - |
| Arterial hypertension, n (%) | 106 (22.6) | - | - |
| Coronary artery disease, n (%) | 27 (5.7) | - | - |
| Cerebral stroke, n (%) | 9 (1.9) | - | - |
| Chronic thyroid disease, n (%) | 7 (1.5) | - | - |
| Chronic renal disease, n (%) | 30 (6.4) | - | - |
| Chronic gastric disease, n (%) | 33 (7.0) | - | - |
| Chronic pulmonary disease, n (%) | 7 (1.5) | - | - |
| Oncological disease, n (%) | 8 (1.7) | - | - |
|
1 Data on alcohol intake were available from 220 subjects of the control group. *Bold is statistically significant P-value. | |||
| SNP ID | Minor allele | N | Permutation P-values (Pperm) estimated for genetic models of SNP-disease associations* | |||
| Allelic | Additive | Dominant | Recessive | |||
| Entire groups | ||||||
| rs524553 | T | 939 | 0.36 | 0.28 | 0.42 | 0.20 |
| rs542914 | A | 941 | 0.18 | 0.23 | 0.67 | 0.11 |
| rs648595 | G | 941 | 0.21 | 0.58 | 1.00 | 0.13 |
| rs6933870 | G | 942 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.86 |
| rs2397147 | C | 940 | 0.48 | 0.29 | 0.86 | 0.40 |
| rs17883901 | A | 810 | 0.63 | 0.78 | 1.00 | 0.15 |
| Males | ||||||
| rs524553 | T | 485 | 0.38 | 0.43 | 0.50 | 0.20 |
| rs542914 | A | 485 | 0.55 | 0.41 | 1.00 | 0.28 |
| rs648595 | G | 484 | 0.048 | 0.23 | 0.86 | 0.017 |
| rs6933870 | G | 485 | 0.25 | 0.13 | 0.32 | 0.09 |
| rs2397147 | C | 484 | 0.11 | 0.11 | 0.31 | 0.05 |
| rs17883901 | A | 418 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.33 |
| Females | ||||||
| rs524553 | T | 454 | 0.78 | 0.67 | 0.58 | 0.78 |
| rs542914 | A | 456 | 0.59 | 0.32 | 0.59 | 0.48 |
| rs648595 | G | 457 | 1.00 | 0.64 | 0.52 | 0.78 |
| rs6933870 | G | 457 | 0.32 | 0.45 | 0.55 | 0.22 |
| rs2397147 | C | 456 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.59 | 0.43 |
| rs17883901 | A | 392 | 0.58 | 0.78 | 0.67 | 0.06 |
| Significance of SNP-disease associations was assessed by adaptive permutations using the PLINK software, v.1.9. | ||||||
| SNP | Genotype/ allele |
Healthy Controls n (%)1 |
Patients with psoriasis n (%)1 |
OR2 (95% CI) | Pperm3 |
| Entire groups | |||||
| rs524553 | C/C | 273 (58.3) | 285 (60.5) | 0.67 (0.34-1.30) | 0.20R |
| C/T | 173 (37.0) | 171 (36.3) | |||
| T/T | 22 (4.7) | 15 (3.2) | |||
| T | 217 (23.2) | 201 (21.3) | 0.90 (0.72-1.12) | 0.36 | |
| rs542914 | C/C | 168 (35.8) | 174 (36.9) | 0.75 (0.52-1.08) | 0.11R |
| C/A | 227 (48.4) | 240 (50.9) | |||
| A/A | 74 (15.8) | 58 (12.3) | |||
| A | 375 (40.0) | 356 (37.7) | 0.91 (0.76-1.09) | 0.18 | |
| rs648595 | T/T | 147 (31.4) | 144 (30.4) | 0.75 (0.54-1.05) | 0.13R |
| T/G | 225 (48.1) | 252 (53.3) | |||
| G/G | 96 (20.5) | 77 (16.3) | |||
| G | 417 (44.6) | 406 (42.9) | 0.94 (0.78-1.12) | 0.21 | |
| rs6933870 | C/C | 160 (34.0) | 163 (34.5) | 0.93 (0.65-1.33) | 0.86R |
| C/G | 237 (50.4) | 240 (50.9) | |||
| G/G | 73 (15.5) | 69 (14.6) | |||
| G | 383 (40.7) | 378 (40.0) | 0.97 (0.81-1.17) | 0.99 | |
| rs2397147 | T/T | 183 (39.2) | 198 (41.9) | 0.90 (0.74-1.09) | 0.29A |
| T/C | 231 (49.5) | 230 (48.6) | |||
| C/C | 53 (11.3) | 45 (9.5) | |||
| C | 337 (36.1) | 320 (33.8) | 0.91 (0.75-1.09) | 0.48 | |
| rs17883901 | G/G | 334 (89.1) | 388 (89.2) | 0.43 (0.11-1.72) | 0.15R |
| G/A | 35 (9.3) | 44 (10.1) | |||
| A/A | 6 (1.6) | 3 (0.7) | |||
| A | 47 (6.3) | 50 (5.7) | 0.91 (0.60-1.38) | 0.63 | |
| Males | |||||
| rs524553 | C/C | 137 (58.5) | 152 (60.6) | 0.56 (0.23-1.38) | 0.20R |
| C/T | 84 (35.9) | 91 (36.2) | |||
| T/T | 13 (5.6) | 8 (3.2) | |||
| T | 110 (23.5) | 107 (21.3) | 0.88 (0.65-1.19) | 0.38 | |
| rs542914 | C/C | 81 (34.6) | 87 (34.7) | 0.75 (0.44-1.26) | 0.28R |
| C/A | 117 (50.0) | 134 (53.4) | |||
| A/A | 36 (15.4) | 30 (11.9) | |||
| A | 189 (40.4) | 194 (38.6) | 0.93 (0.72-1.20) | 0.55 | |
| rs648595 | T/T | 71 (30.5) | 78 (31.1) | 0.56 (0.35-0.90) | 0.017R |
| T/G | 110 (47.2) | 138 (55.0) | |||
| G/G | 52 (22.3) | 35 (13.9) | |||
| G | 214 (45.9) | 208 (41.4) | 0.83 (0.65-1.07) | 0.048 | |
| rs6933870 | C/C | 73 (31.2) | 87 (34.7) | 0.64 (0.38-1.06) | 0.09R |
| C/G | 120 (51.3) | 134 (53.4) | |||
| G/G | 41 (17.5) | 30 (11.9) | |||
| G | 202 (43.2) | 194 (38.6) | 0.83 (0.64-1.07) | 0.25 | |
| rs2397147 | T/T | 85 (36.5) | 101 (40.2) | 0.54 (0.30-0.98) | 0.05R |
| T/C | 116 (49.8) | 130 (51.8) | |||
| C/C | 32 (13.7) | 20 (8.0) | |||
| C | 180 (38.6) | 170 (33.9) | 0.81 (0.63-1.06) | 0.11 | |
| rs17883901 | G/G | 167 (89.3) | 204 (88.3) | 0.54 (0.09-3.24) | 0.33R |
| G/A | 17 (9.1) | 25 (10.8) | |||
| A/A | 3 (1.6) | 2 (0.9) | |||
| A | 23 (6.1) | 29 (6.3) | 1.02 (0.58-1.80 | 0.99 | |
| Females | |||||
| rs524553 | C/C | 136 (58.1) | 133 (60.5) | 0.91 (0.62-1.32) | 0.58D |
| C/T | 89 (38.0) | 80 (36.4) | |||
| T/T | 9 (3.8) | 7 (3.2) | |||
| T | 107 (22.9) | 94 (21.4) | 0.92 (0.67-1.25) | 0.78 | |
| rs542914 | C/C | 87 (37.0) | 87 (39.4) | 0.88 (0.68-1.15) | 0.32A |
| C/A | 110 (46.8) | 106 (48) | |||
| A/A | 38 (16.2) | 28 (12.7) | |||
| A | 186 (39.6) | 162 (36.7) | 0.88 (0.68-1.15) | 0.59 | |
| rs648595 | T/T | 76 (32.3) | 66 (29.7) | 1.13 (0.76-1.68) | 0.52D |
| T/G | 115 (48.9) | 114 (51.4) | |||
| G/G | 44 (18.7) | 42 (18.9) | |||
| G | 203 (43.2) | 198 (44.6) | 1.06 (0.82-1.37) | 0.99 | |
| rs6933870 | C/C | 87 (36.9) | 76 (34.4) | 1.37 (0.82-2.27) | 0.22R |
| C/G | 117 (49.6) | 106 (48.0) | |||
| G/G | 32 (13.6) | 39 (17.6) | |||
| G | 181 (38.3) | 184 (41.6) | 1.15 (0.88-1.49) | 0.32 | |
| rs2397147 | T/T | 98 (41.9) | 97 (43.7) | 1.29 (0.70-2.37) | 0.43R |
| T/C | 115 (49.1) | 100 (45) | |||
| C/C | 21 (9.0) | 25 (11.3) | |||
| C | 157 (33.5) | 150 (33.8) | 1.01 (0.77-1.33) | 0.99 | |
| rs17883901 | G/G | 167 (88.8) | 184 (90.2) | 0.30 (0.03-2.95) | 0.06R |
| G/A | 18 (9.6) | 19 (9.3) | |||
| A/A | 3 (1.6) | 1 (0.5) | |||
| A | 24 (6.4) | 21 (5.1) | 0.80 (0.44-1.45) | 0.58 | |
|
* The table shows the best genetic models for SNP-disease associations. 1 Absolute number and percentage of individuals/chromosomes with a particular genotype/allele. 2 Odds ratio with 95% confidence intervals (crude analysis) estimated for the best association model. 3 P-value estimated for the best association model through adaptive permutations. Superscripts denote SNP association models: R, recessive; D, dominant; A, additive. Bold depicts statistically significant P-values and odds ratios. | |||||
| Haplotypes | SNP | Patients with psoriasis | Healthy Controls | Chi Square | P-value | |||||
| rs524553 | rs542914 | rs648595 | rs6933870 | rs2397147 | rs17883901 | |||||
| Entire groups | ||||||||||
| H1 | C | C | T | C | T | G | 0.482 | 0.463 | 0.635 | 0.426 |
| H2 | T | A | G | G | C | G | 0.154 | 0.162 | 0.192 | 0.661 |
| H3 | C | A | G | G | C | G | 0.121 | 0.128 | 0.186 | 0.666 |
| H4 | C | C | G | G | T | G | 0.056 | 0.043 | 1.681 | 0.195 |
| H5 | C | A | T | C | T | G | 0.043 | 0.042 | 0.017 | 0.898 |
| H6 | C | C | G | C | T | G | 0.032 | 0.027 | 0.422 | 0.516 |
| H7 | C | C | T | C | T | A | 0.019 | 0.026 | 0.940 | 0.332 |
| H8 | T | A | G | C | T | G | 0.017 | 0.027 | 2.247 | 0.134 |
| H9 | T | A | G | G | C | A | 0.023 | 0.020 | 0.133 | 0.715 |
| H10 | C | C | T | G | C | G | 0.018 | 0.018 | 0.016 | 0.900 |
| H11 | C | A | G | G | C | A | 0.010 | 0.013 | 0.301 | 0.583 |
| H12 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Males | ||||||||||
| H1 | C | C | T | C | T | G | 0.495 | 0.457 | 1.407 | 0.236 |
| H2 | T | A | G | G | C | G | 0.160 | 0.175 | 0.357 | 0.550 |
| H3 | C | A | G | G | C | G | 0.115 | 0.136 | 0.989 | 0.320 |
| H4 | C | C | G | G | T | G | 0.045 | 0.043 | 0.017 | 0.896 |
| H5 | C | A | T | C | T | G | 0.048 | 0.030 | 2.040 | 0.153 |
| H6 | C | C | G | C | T | G | 0.026 | 0.024 | 0.040 | 0.842 |
| H7 | C | C | T | C | T | A | 0.020 | 0.024 | 0.223 | 0.637 |
| H8 | T | A | G | C | T | G | 0.016 | 0.022 | 0.456 | 0.499 |
| H9 | T | A | G | G | C | A | 0.025 | 0.018 | 0.604 | 0.437 |
| H10 | C | C | T | G | C | G | 0.015 | 0.023 | 0.839 | 0.359 |
| H11 | C | A | G | G | C | A | 0.013 | 0.014 | 0.030 | 0.863 |
| H12 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Females | ||||||||||
| H1 | C | C | T | C | T | G | 0.463 | 0.464 | 0.001 | 0.981 |
| H2 | T | A | G | G | C | G | 0.150 | 0.158 | 0.109 | 0.741 |
| H3 | C | A | G | G | C | G | 0.130 | 0.119 | 0.243 | 0.622 |
| H4 | C | C | G | G | T | G | 0.069 | 0.045 | 2.445 | 0.118 |
| H5 | C | A | T | C | T | G | 0.037 | 0.052 | 1.155 | 0.283 |
| H6 | C | C | G | C | T | G | 0.034 | 0.027 | 0.418 | 0.518 |
| H7 | C | C | T | C | T | A | 0.023 | 0.028 | 0.321 | 0.571 |
| H8 | T | A | G | C | T | G | 0.018 | 0.031 | 1.511 | 0.219 |
| H9 | T | A | G | G | C | A | 0.017 | 0.017 | 0.010 | 0.919 |
| H10 | C | C | T | G | C | G | 0.021 | 0.013 | 0.761 | 0.383 |
| H11 | C | A | G | G | C | A | - | - | - | - |
| H12 | T | C | G | G | C | G | 0.010 | 0.010 | 0.001 | 0.983 |
| Estimation of haplotype frequencies and significance of haplotype-disease associations was done using the Haploview software, v.4.2. | ||||||||||
| Genotype combination | Patients | Controls | P-value | OR (95% CI)3 | ||
| n1 | %2 | n1 | %2 | |||
| Entire groups | ||||||
| rs542914-C/C × rs648595-G/T | 55 | 11.7 | 35 | 7.5 | 0.03 | 1.63 (1.04-2.54) |
| rs648595-G/G × rs6933870-C/G | 13 | 2.8 | 28 | 6.0 | 0.016 | 0.45 (0.23-0.87) |
| Males | ||||||
| rs524553-C/C ×rs648595-G/G | 7 | 2.8 | 18 | 7.7 | 0.025 | 0.36 (0.15-0.85) |
| rs524553-C/C× rs6933870-G/G | 6 | 2.4 | 15 | 6.4 | 0.05 | 0.37 (0.15-0.95) |
| rs542914-A/A × rs648595-G/G | 19 | 7.6 | 31 | 13.3 | 0.038 | 0.54 (0.30-0.98) |
| rs648595-G/G × rs17883901-G/G | 21 | 9.1 | 33 | 17.7 | 0.009 | 0.47 (0.26-0.84) |
| rs6933870-G/G × rs2397147-C/C | 20 | 8.0 | 32 | 13.7 | 0.042 | 0.55 (0.30-0.99) |
| rs6933870-G/G × rs17883901-G/G | 19 | 8.2 | 27 | 14.4 | 0.044 | 0.53 (0.29-0.99) |
| rs2397147-C/C ×rs17883901-G/G | 11 | 4.8 | 21 | 11.2 | 0.014 | 0.40 (0.19-0.85) |
| Females | ||||||
| rs6933870-G/G × rs17883901-G/G | 32 | 15.8 | 17 | 9.0 | 0.045 | 1.88 (1.01-3.52) |
|
1 Absolute number of individuals with particular genotype combination (minor alleles in genotypes are underlined). 2 Percentage of individuals with particular genotype combination. 3 OR, odds ratio; CI, confidence interval. Bold is statistically significant P-value after an adjustment for FDR of 0.05 (https://tools.carbocation.com/FDR). | ||||||
| SNP ID | Minor allele | Permutation P-values (Pperm) estimated for genetic models of SNP-disease associations | |||||||||
| N | Genetic models | N | Genetic models | ||||||||
| Allelic | Additive | Dominant | Recessive | Allelic | Additive | Dominant | Recessive | ||||
| Smokers | Non-smokers | ||||||||||
| rs524553 | T | 315 | 1.00 | 0.52 | 0.63 | 0.64 | 624 | 0.46 | 0.43 | 0.86 | 0.34 |
| rs542914 | A | 315 | 0.86 | 0.55 | 0.67 | 0.67 | 626 | 0.21 | 0.59 | 0.86 | 0.10 |
| rs648595 | G | 316 | 0.12 | 0.44 | 0.52 | 0.049 | 625 | 0.86 | 0.78 | 1.00 | 0.52 |
| rs6933870 | G | 315 | 0.65 | 0.52 | 0.86 | 0.59 | 627 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.86 | 0.67 |
| rs2397147 | C | 315 | 0.67 | 0.33 | 0.48 | 0.25 | 625 | 0.86 | 0.46 | 0.39 | 0.73 |
| rs17883901 | A | 275 | 0.24 | 0.16 | 0.09 | 1.00 | 535 | 0.18 | 0.11 | 0.18 | 0.002 |
| Alcohol abusers | Non-drinkers | ||||||||||
| rs524553 | T | 110 | 0.26 | 0.09 | 0.10 | NA | 580 | 0.24 | 0.08 | 0.20 | 0.15 |
| rs542914 | A | 112 | 0.11 | 0.053 | 0.06 | NA | 579 | 0.034 | 0.026 | 0.16 | 0.015 |
| rs648595 | G | 112 | 0.33 | 0.19 | 0.58 | NA | 580 | 0.05 | 0.04 | 0.26 | 0.03 |
| rs6933870 | G | 111 | 0.18 | 0.11 | 0.23 | NA | 581 | 0.29 | 0.14 | 0.18 | 0.27 |
| rs2397147 | C | 112 | 0.19 | 0.22 | 0.14 | NA | 579 | 0.20 | 0.09 | 0.14 | 0.25 |
| rs17883901 | A | 98 | 0.79 | NA | NA | NA | 498 | 0.55 | 0.48 | 0.67 | 0.09 |
| Significance of SNP-disease associations was assessed by adaptive permutations using the PLINK software, v.1.9. NA, not available. | |||||||||||
| Psoriasis phenotype2 | Variant | Eff, allele | beta | OR beta | P-value | MAF | HWE |
| psoriasis | rs524553 | T | 0.00030445 | 1.03 | 0.24054 | 0.248703 | 0.8257 |
| L40 Psoriasis | rs524553 | T | 0.00014144 | 1.03 | 0.43139 | 0.248703 | 0.8257 |
| psoriasis | rs542914 | A | 0.00031437 | 1.03 | 0.16739 | 0.409665 | 0.7591 |
| L40 Psoriasis | rs542914 | A | 0.00018358 | 1.03 | 0.24466 | 0.409665 | 0.7591 |
| psoriasis | rs648595 | G | 0.00034186 | 1.03 | 0.12131 | 0.485677 | 0.2804 |
| L40 Psoriasis | rs648595 | G | 0.00019125 | 1.04 | 0.21101 | 0.485677 | 0.2804 |
| psoriasis | rs6933870 | G | 0.00041555 | 1.04 | 0.062535 | 0.478105 | 0.1793 |
| L40 Psoriasis | rs6933870 | G | 0.00015391 | 1.03 | 0.3195 | 0.478105 | 0.1793 |
| psoriasis | rs2397147 | C | 0.00043391 | 1.04 | 0.057101 | 0.407803 | 0.6808 |
| L40 Psoriasis | rs2397147 | C | 0.000164 | 1.03 | 0.29943 | 0.407803 | 0.6808 |
| psoriasis | rs17883901 | G | -0.0001631 | 0.986 | 0.68281 | 0.0837 | 0.05018 |
| L40 Psoriasis | rs17883901 | G | -0.0002265 | 0.959 | 0.4129 | 0.0837 | 0.05018 |
|
1 The calculations were obtained from the Gene ATLAS web site (http://geneatlas.roslin.ed.ac.uk/). accessed by 28.04.2023 2 “Psoriasis” phenotype investigated in a cohort of 5175 cases and 447089 controls).: “L40 Psoriasis” phenotype investigated in a cohort of 2437 cases and 449827 controls; MAF. minor allele frequency; HWE. Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium P-value. | |||||||
| N | Variant | Position | Eff, Allele | Trait | Beta | P-value | MAF |
| Psoriasis phenotype: “psoriasis” (5175 cases and 447089 controls) | |||||||
| 1 | rs183555084 | 53463377 | A | psoriasis | 0.0054328 | 0.00048311 | 0.005415 |
| 2 | rs536001584 | 53491157 | A | psoriasis | 0.0069889 | 0.0037087 | 0.002296 |
| 3 | rs78863400 | 53507843 | G | psoriasis | 0.0020045 | 0.0049101 | 0.0245 |
| 4 | rs114919458 | 53478492 | A | psoriasis | 0.0020638 | 0.0077221 | 0.020874 |
| 5 | rs77162334 | 53473387 | A | psoriasis | 0.0015616 | 0.0084049 | 0.036438 |
| 6 | rs547541077 | 53524639 | A | psoriasis | 0.0083841 | 0.011327 | 0.001201 |
| 7 | rs55661362 | 53463674 | G | psoriasis | 0.0026909 | 0.012278 | 0.011041 |
| 8 | rs78331008 | 53489705 | G | psoriasis | 0.0014586 | 0.014341 | 0.036042 |
| 9 | rs115558853 | 53325654 | C | psoriasis | -0.0019831 | 0.016188 | 0.018765 |
| 10 | rs6902510 | 53493460 | T | psoriasis | -0.00052994 | 0.019054 | 0.405458 |
| 11 | rs62398116 | 53405203 | G | psoriasis | -0.0008575 | 0.019471 | 0.110262 |
| 12 | rs189491343 | 53341496 | G | psoriasis | -0.0019418 | 0.020189 | 0.01847 |
| 13 | rs7762921 | 53319569 | T | psoriasis | -0.00065758 | 0.021591 | 0.1828 |
| 14 | rs62398159 | 53490625 | A | psoriasis | -0.00051684 | 0.022213 | 0.406839 |
| 15 | rs56013020 | 53390696 | A | psoriasis | 0.00082793 | 0.022789 | 0.103296 |
| 16 | rs7739121 | 53510423 | C | psoriasis | -0.00049679 | 0.024997 | 0.467815 |
| 17 | rs72944719 | 53358473 | G | psoriasis | -0.0010805 | 0.025673 | 0.05524 |
| 18 | rs7761225 | 53315323 | C | psoriasis | -0.00064261 | 0.025687 | 0.179565 |
| 19 | rs6458936 | 53314296 | G | psoriasis | -0.00064298 | 0.025697 | 0.179334 |
| 20 | rs1914707 | 53311047 | G | psoriasis | -0.00063643 | 0.026486 | 0.181629 |
| 21 | rs563831 | 53327107 | G | psoriasis | 0.00063512 | 0.026486 | 0.183707 |
| 22 | rs4715409 | 53511015 | T | psoriasis | -0.00049168 | 0.02667 | 0.467022 |
| 23 | rs1518511 | 53313237 | C | psoriasis | -0.00063702 | 0.027149 | 0.179343 |
| 24 | rs6908614 | 53501678 | T | psoriasis | -0.00048943 | 0.027196 | 0.462606 |
| 25 | rs642103 | 53323152 | G | psoriasis | -0.00062689 | 0.028507 | 0.18174 |
| 26 | rs1914706 | 53311463 | T | psoriasis | -0.00062752 | 0.028627 | 0.181766 |
| 27 | rs72943672 | 53399516 | T | psoriasis | -0.00074715 | 0.028945 | 0.1182 |
| 28 | rs6933919 | 53313748 | G | psoriasis | -0.00062901 | 0.029059 | 0.179555 |
| 29 | rs4712030 | 53317469 | A | psoriasis | -0.00062437 | 0.029102 | 0.181758 |
| 30 | rs1467408 | 53351289 | A | psoriasis | -0.00052426 | 0.029222 | 0.361091 |
| 31 | rs9382209 | 53311804 | G | psoriasis | -0.00062389 | 0.02952 | 0.18191 |
| 32 | rs149644917 | 53519358 | A | psoriasis | -0.010751 | 0.029585 | 0.000499 |
| 33 | rs1401155 | 53312629 | C | psoriasis | -0.00062709 | 0.029593 | 0.17955 |
| 34 | rs9357769 | 53508264 | C | psoriasis | 0.00048131 | 0.029829 | 0.4664 |
| 35 | rs6908786 | 53494357 | A | psoriasis | -0.00047818 | 0.03092 | 0.466556 |
| 36 | rs587178 | 53325255 | T | psoriasis | 0.00061535 | 0.031491 | 0.182191 |
| 37 | rs6901352 | 53500138 | C | psoriasis | -0.0004754 | 0.031615 | 0.466514 |
| 38 | rs6908860 | 53494615 | T | psoriasis | -0.00047638 | 0.031652 | 0.464814 |
| 39 | rs681682 | 53440021 | C | psoriasis | -0.0072738 | 0.032871 | 0.001361 |
| 40 | rs543473 | 53439524 | T | psoriasis | -0.0072796 | 0.032941 | 0.001359 |
| 41 | rs681585 | 53439958 | G | psoriasis | -0.0072742 | 0.033023 | 0.00136 |
| 42 | rs9474608 | 53505134 | A | psoriasis | -0.00047139 | 0.033072 | 0.466612 |
| 43 | rs681635 | 53439987 | A | psoriasis | -0.0072632 | 0.033272 | 0.001359 |
| 44 | rs2397146 | 53360119 | A | psoriasis | -0.00053256 | 0.033642 | 0.273716 |
| 45 | rs607285 | 53326491 | T | psoriasis | 0.00060766 | 0.033745 | 0.182155 |
| 46 | rs62416866 | 53398370 | A | psoriasis | -0.00077679 | 0.033936 | 0.100838 |
| 47 | rs742528 | 53360191 | A | psoriasis | -0.00052981 | 0.034548 | 0.273993 |
| 48 | rs623928 | 53335695 | T | psoriasis | 0.00061135 | 0.034551 | 0.180506 |
| 49 | rs629162 | 53326283 | G | psoriasis | 0.00060422 | 0.034685 | 0.182369 |
| 50 | rs676637 | 53335353 | C | psoriasis | 0.00061072 | 0.03473 | 0.180538 |
| 51 | rs624432 | 53335555 | G | psoriasis | 0.00061046 | 0.034804 | 0.180555 |
| 52 | rs642625 | 53333732 | T | psoriasis | 0.00061027 | 0.034833 | 0.180511 |
| 53 | rs618033 | 53339289 | T | psoriasis | 0.00061046 | 0.034957 | 0.180357 |
| 54 | rs600722 | 53332887 | T | psoriasis | 0.00060973 | 0.034961 | 0.180513 |
| 55 | rs631783 | 53338531 | A | psoriasis | 0.00060876 | 0.035396 | 0.180454 |
| 56 | rs619955 | 53338845 | T | psoriasis | 0.00060877 | 0.035396 | 0.180457 |
| 57 | rs485371 | 53341627 | T | psoriasis | 0.00060874 | 0.035527 | 0.180356 |
| 58 | rs12196344 | 53457292 | A | psoriasis | -0.00048763 | 0.036061 | 0.404087 |
| 59 | rs9367538 | 53506487 | G | psoriasis | -0.00046273 | 0.036479 | 0.466245 |
| 60 | rs7764361 | 53492467 | C | psoriasis | 0.00046427 | 0.037421 | 0.456163 |
| 61 | rs663087 | 53342704 | T | psoriasis | 0.00060223 | 0.037659 | 0.180217 |
| 62 | rs646403 | 53347484 | T | psoriasis | 0.00059431 | 0.040381 | 0.180136 |
| 63 | rs12194171 | 53464937 | C | psoriasis | 0.00046011 | 0.041523 | 0.3968 |
| 64 | rs11756739 | 53316777 | A | psoriasis | 0.0029885 | 0.04429 | 0.006094 |
| 65 | rs4712031 | 53320273 | G | psoriasis | -0.00056517 | 0.04448 | 0.190022 |
| 66 | rs2092421 | 53473076 | A | psoriasis | -0.00045072 | 0.045589 | 0.398208 |
| 67 | rs4269374 | 53461179 | G | psoriasis | -0.00044872 | 0.04647 | 0.397012 |
| 68 | rs9349679 | 53470507 | A | psoriasis | -0.00044669 | 0.047497 | 0.39642 |
| 69 | rs34997452 | 53518439 | T | psoriasis | -0.0027868 | 0.047543 | 0.006643 |
| 70 | rs10807461 | 53472150 | T | psoriasis | -0.00044608 | 0.047762 | 0.398057 |
| 71 | rs738472 | 53477038 | C | psoriasis | -0.00045789 | 0.048043 | 0.353182 |
| 72 | rs6458946 | 53472830 | T | psoriasis | -0.00044442 | 0.048672 | 0.397982 |
| 73 | rs114749455 | 53489865 | G | psoriasis | 0.0022206 | 0.048751 | 0.0103 |
| 74 | rs2143399 | 53461749 | A | psoriasis | -0.00044292 | 0.049341 | 0.397029 |
| 75 | rs74357476 | 53476523 | T | psoriasis | 0.0014009 | 0.050596 | 0.025311 |
| Psoriasis phenotype: “L40 Psoriasis” (2437 cases and 449827 controls) | |||||||
| 1 | rs185956124 | 53496212 | C | L40 Psoriasis | 0.0026856 | 0.0036274 | 0.00747649 |
| 2 | rs547541077 | 53524639 | A | L40 Psoriasis | 0.0065265 | 0.0044446 | 0.00120121 |
| 3 | rs189622943 | 53509408 | T | L40 Psoriasis | 0.0035101 | 0.0095446 | 0.00341133 |
| 4 | rs183043870 | 53509634 | G | L40 Psoriasis | 0.0035128 | 0.0095673 | 0.00341141 |
| 5 | rs78735978 | 53360036 | C | L40 Psoriasis | 0.0012576 | 0.015913 | 0.0231714 |
| 6 | rs41271287 | 53370147 | T | L40 Psoriasis | 0.0011902 | 0.018795 | 0.0236652 |
| 7 | rs17215384 | 53510321 | T | L40 Psoriasis | 0.00039365 | 0.02118 | 0.28084 |
| 8 | rs77516417 | 53373662 | A | L40 Psoriasis | -0.001175 | 0.021204 | 0.02313 |
| 9 | rs574202 | 53481989 | G | L40 Psoriasis | 0.00035417 | 0.021427 | 0.489829 |
| 10 | rs12661112 | 53486714 | A | L40 Psoriasis | 0.00037194 | 0.021838 | 0.343991 |
| 11 | rs563699 | 53479410 | C | L40 Psoriasis | 0.00035124 | 0.022359 | 0.490659 |
| 12 | rs558026 | 53478773 | A | L40 Psoriasis | 0.00035803 | 0.022979 | 0.392597 |
| 13 | rs583513 | 53477688 | T | L40 Psoriasis | 0.00034605 | 0.024098 | 0.491525 |
| 14 | rs7759126 | 53484485 | C | L40 Psoriasis | 0.00035645 | 0.028105 | 0.343339 |
| 15 | rs12665537 | 53509452 | G | L40 Psoriasis | 0.00035343 | 0.030008 | 0.33107 |
| 16 | rs67228890 | 53511814 | G | L40 Psoriasis | 0.00034794 | 0.034841 | 0.327456 |
| 17 | rs74449072 | 53521238 | G | L40 Psoriasis | 0.00061918 | 0.039019 | 0.0749875 |
| 18 | rs7764361 | 53492467 | C | L40 Psoriasis | 0.00031881 | 0.039179 | 0.456163 |
| 19 | rs9382225 | 53511696 | T | L40 Psoriasis | -0.00033714 | 0.039962 | 0.328914 |
| 20 | rs5020412 | 53349885 | C | L40 Psoriasis | 0.00084548 | 0.041197 | 0.0354 |
| 21 | rs4715412 | 53511836 | T | L40 Psoriasis | -0.00033138 | 0.044253 | 0.328611 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





