3.1. Analysis of Economic Development and Environmental Pollution Issues
According to
Figure 1,
Figure 2,
Figure 3 and
Figure 4, it can be seen that the rapid economic growth in Shanxi Province in the past 20 years has brought serious environmental problems, which can be summarized as follows:
(1) Excessive energy consumption exacerbates resource dependence. From 2.2, it can be seen that during the “Tenth Five Year Plan” and “Eleventh Five Year Plan” periods, the environmental pollution intensity in Shanxi Province was relatively severe. Shanxi Province has abundant coal reserves, with a proven coal reserve of 27 billion tons, second only to Xinjiang and Inner Mongolia, ranking third in the country, and coal production accounting for about 1/4 of the country. At the same time, there are abundant mineral resources, and 120 types of minerals have been discovered, including 63 minerals with proven resource reserves and 230.4 billion cubic meters of coalbed methane recoverable reserves [
16]. At the same time, Shanxi Province is a famous heavy industry base in China, and the steel industry is one of the important pillar industries. There are many large iron and steel enterprises in the province, such as Taiyuan Iron and Steel Group, Shougang Changzhi Iron and Steel Company, etc. The scale of iron and steel production capacity ranks in the forefront of the country, focusing on the development of iron and steel, metallurgy, electricity, coke and other industries. These traditional “three high” (high pollution, high energy consumption, high emissions) industries bring high industrial output, but also bring serious environmental problems, mainly air pollution, soil pollution, and water pollution. According to statistics, the average annual growth rate of energy consumption in Shanxi Province from 2007 to 2017 reached 3.52%, increasing from 146.1976 million tons of standard coal to 200.5723 million tons of standard coal [
17]. In the energy structure, coal consumption accounts for over 88% of the energy consumption in the industrial industry, forming a typical feature of Shanxi Province in the process of economic development, which is dominated by coal. It can be seen from
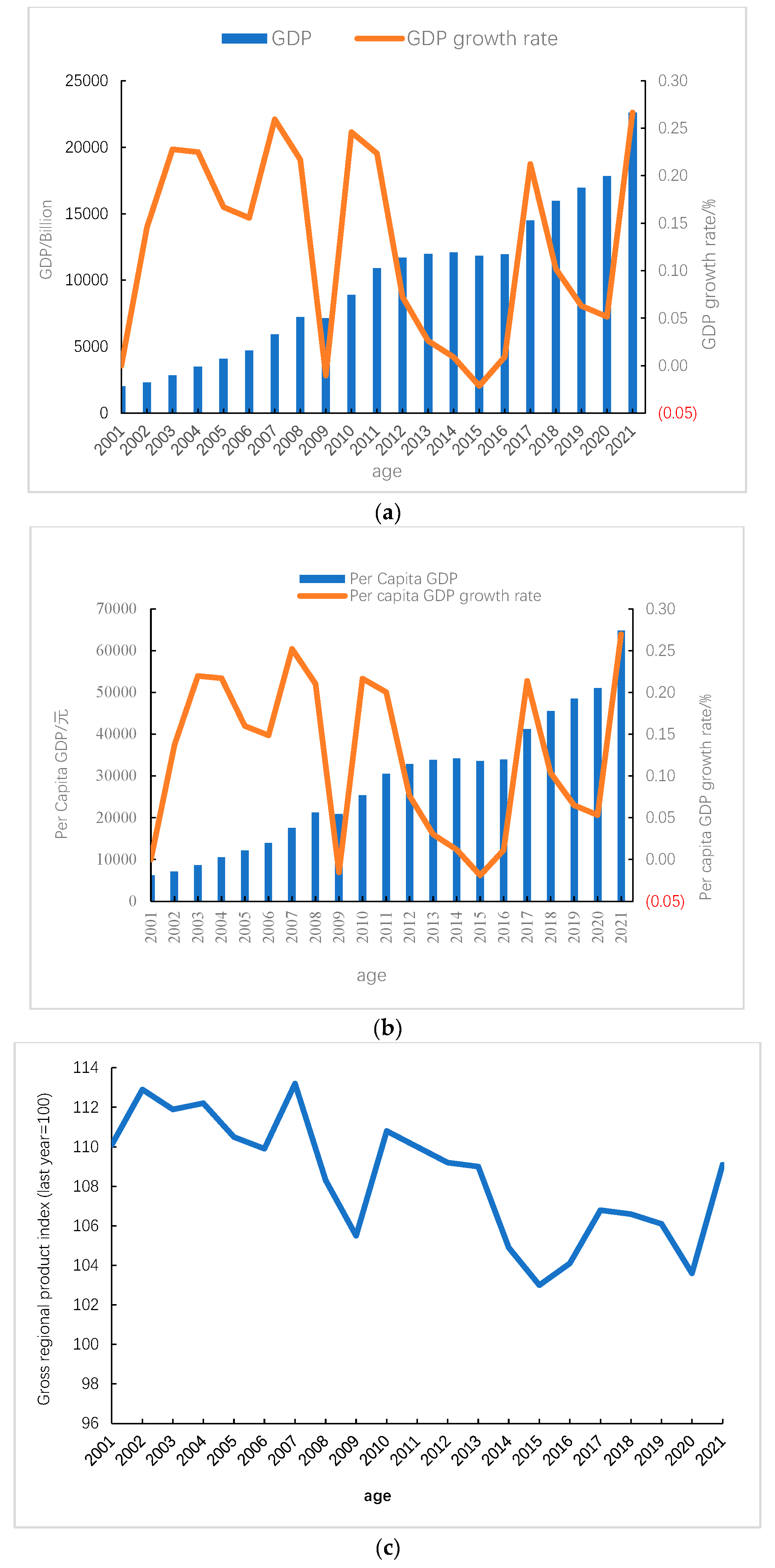
Figure 1a that the Gross regional product (1552.84 billion yuan) of Shanxi Province in 2017 ranked 23 among the 31 provinces and cities in China, while the per capita Gross regional product (40557 yuan) ranked 18, indicating that the per capita income level of residents in Shanxi Province is not high, and the level of economic development is relatively backward, reducing the expectations of environmental quality.
(2) The industrial structure is single and the economic structure is fragile. With the acceleration of industrialization, the proportion of Tertiary sector of the economy in GDP will inevitably surpass that of Primary sector of the economy and Secondary sector of the economy, and become the main force leading the healthy development of the national economy. It can be seen from
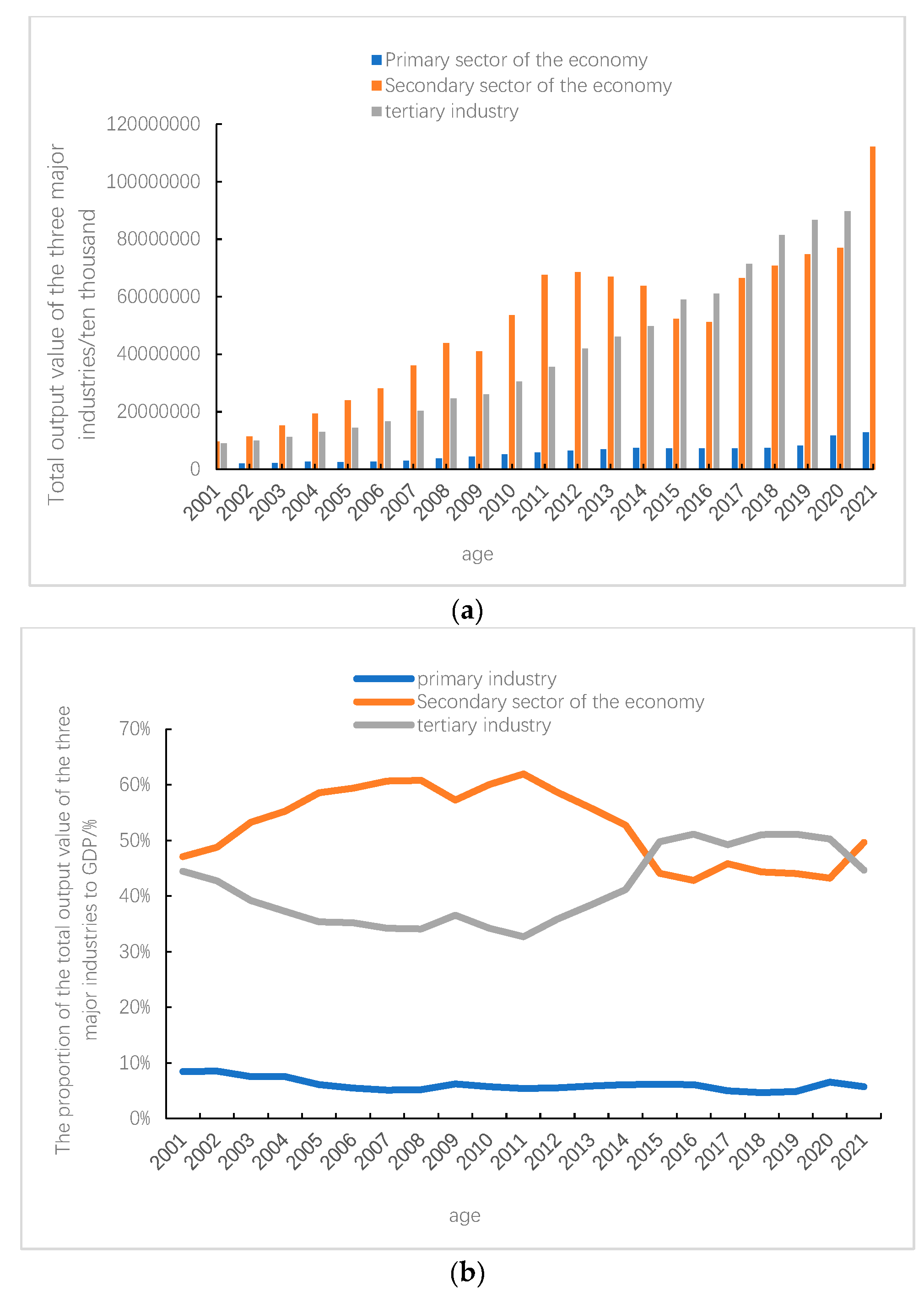
Figure 2 that during the period from the “Tenth Five Year Plan” to the “Twelfth Five Year Plan”, among the three major industrial output values of Shanxi Province, the Secondary sector of the economy>Tertiary sector of the economy output value>Primary sector of the economy output value, and the proportion of the Secondary sector of the economy in GDP exceeded 50%. The economic development was mainly driven by the Secondary sector of the economy. Until the beginning of 2015, the proportion of the Tertiary sector of the economy in GDP was overtaking, becoming the pillar of social economy in Shanxi Province. From the perspective of the proportion of the three industries in GDP, the contribution rate of the Primary sector of the economy has been basically stable. Before 2015, the change trend of the contribution rate of the Secondary sector of the economy and the Tertiary sector of the economy was basically stable. Since the “13th Five Year Plan”, the contribution rate of the Tertiary sector of the economy in Shanxi Province has continued to grow, and exceeded the contribution rate of the Secondary sector of the economy in 2015. The industrial structure is gradually changing from “two, three, one” to “three, two, one”. The main reason for this change is that the Shanxi Provincial Government took the initiative to vigorously develop the cultural service industry [
18], adjust the proportion of the three major industries, optimize industrial layout, upgrade and transform industrial structure, in order to gradually reverse the traditional extensive economic development model. Nevertheless, the extensive development approach still leads to an unreasonable industrial structure, with a high proportion of resource based industries with high energy consumption and pollution such as coal, steel, and electricity. There are fewer green and low-carbon emerging strategic projects, and there is still a severe situation where environmental protection lags behind economic and social development.
(3) Backward development level and insufficient investment in environmental protection funds. According to statistics [
19], during the 11th Five Year Plan period in Shanxi Province, the total amount of environmental protection investment was 16.51 billion yuan. However, within 7 years after entering the 12th Five Year Plan and 13th Five Year Plan periods, the total amount of environmental protection investment in Shanxi Province has reached 18.59 billion yuan, of which only 15% is used to treat industrial waste pollutants, and the majority is used for environmental infrastructure construction. Obviously, the investment is far from enough. For typical energy regions, The space for improving environmental pollution control is becoming increasingly small, and tackling challenges is becoming increasingly difficult. In the past 10 years of the new era, China’s industrial added value has doubled, from 20.9 trillion yuan to 45.1 trillion yuan. During the epidemic period, the output value is increasing, and China has been the world’s largest manufacturing country for 12 consecutive years [
20]. From
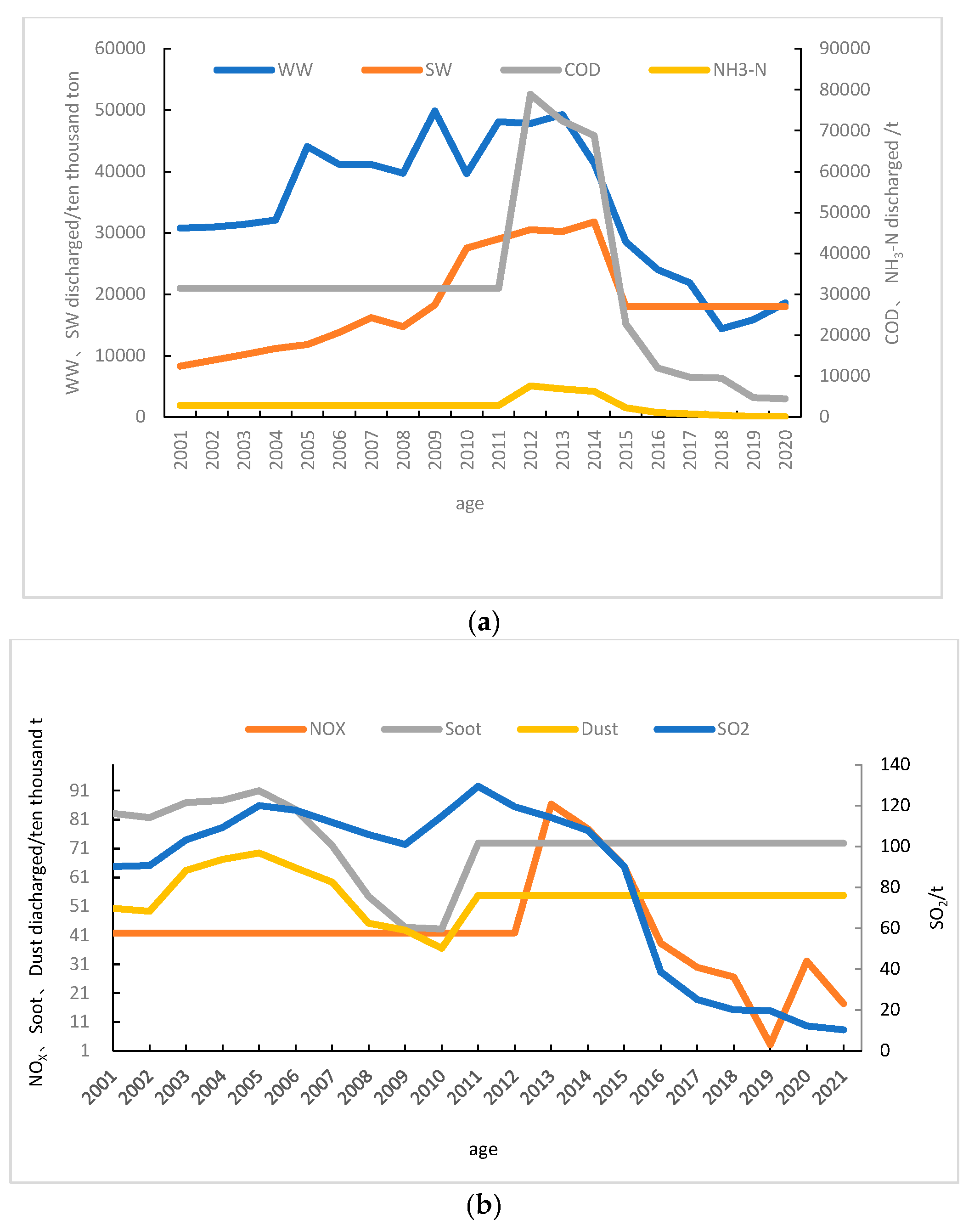
Figure 3, it can be seen that the discharge of solid waste in Shanxi Province has significantly decreased since 2012. After taking control measures, the discharge of industrial wastewater and sulfur dioxide in Shanxi Province has been decreasing year by year, and the compliance rate and sulfur dioxide removal rate of industrial wastewater discharge treatment have been increasing year by year. After 2012, industrial sulfur dioxide emissions significantly decreased, mainly due to the government’s significantly higher investment in exhaust gas treatment compared to other pollution control fields [
21]. At the same time, during the “12th Five Year Plan” period, Shanxi Province actively transformed its economic development mode from extensive to intensive, eliminated excess production capacity, seized the construction opportunity of the “Yellow River Golden Triangle Demonstration Area” [
22], further optimized the industrial structure, strengthened regional economic cooperation between Shanxi, Shaanxi and Henan, gave full play to the advantages of Cultural resource management, and actively explored new development models focusing on culture, tourism, finance, real estate, etc.
In summary, in the past 20 years, the main pollutants have shown a trend of increasing first and then decreasing steadily, with a turning point occurring during the “12th Five Year Plan” period. It can be seen that the environmental policies and investments of the Chinese and Shanxi provincial governments in the new era have been effective in the past 10 years, and the environmental pollution problem has been effectively improved.
3.2. Correlation Analysis
Correlation analysis refers to the analysis of multiple variables related to the quality of economic development and the intensity of environmental pollution, in order to measure the degree of correlation between economic development and environmental pollution. From
Figure 5, it can be seen that there are different degrees of correlation between economic development quality data and environmental pollution intensity data.
In terms of the quality of economic development, there is a positive correlation between GDP and per capita GDP, permanent population, and per capita disposable income. Among these data, the correlation between GDP and per capita GDP is the strongest, with a correlation coefficient of 0.981 with per capita disposable income and 0.742 with permanent population. This means that population growth has a significant impact on GDP, and the level of economic development is closely related to per capita disposable income.
In terms of environmental pollution intensity, it can be seen that there is a strong positive correlation between wastewater discharge and Chemical oxygen demand, ammonia nitrogen discharge and sulfur dioxide discharge, with correlation coefficients of 0.757, 0.764 and 0.855 respectively. This indicates that the amount of wastewater discharge may affect the level of these pollutant emissions. There is no significant correlation between the amount of wastewater discharge and the amount of solid waste generated or exhaust gas emissions. There is a strong correlation between the amount of solid waste generated and Chemical oxygen demand emissions, ammonia nitrogen emissions, with coefficients of 0.519 and 0.513 respectively. The correlation coefficient between Chemical oxygen demand and ammonia nitrogen emissions reached 0.998, indicating that the higher the concentration of ammonia nitrogen, the higher the COD; The correlation coefficient between Chemical oxygen demand and sulfur dioxide emissions is 0.642, showing a certain correlation, and the change trend is basically the same under certain conditions. The correlation coefficient between ammonia nitrogen emissions and solid waste emissions and sulfur dioxide emissions is greater than 0.5, showing a certain positive correlation.
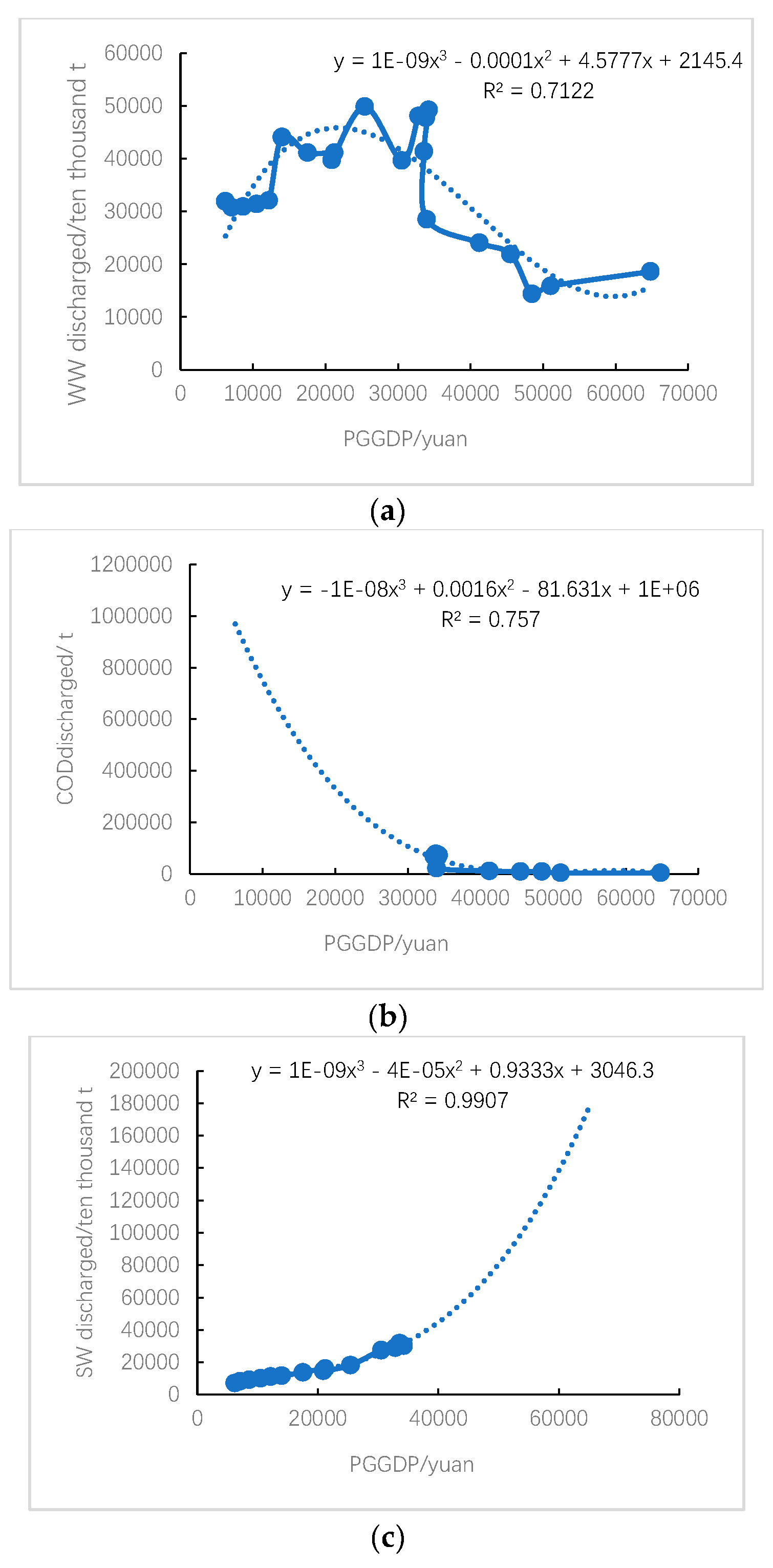
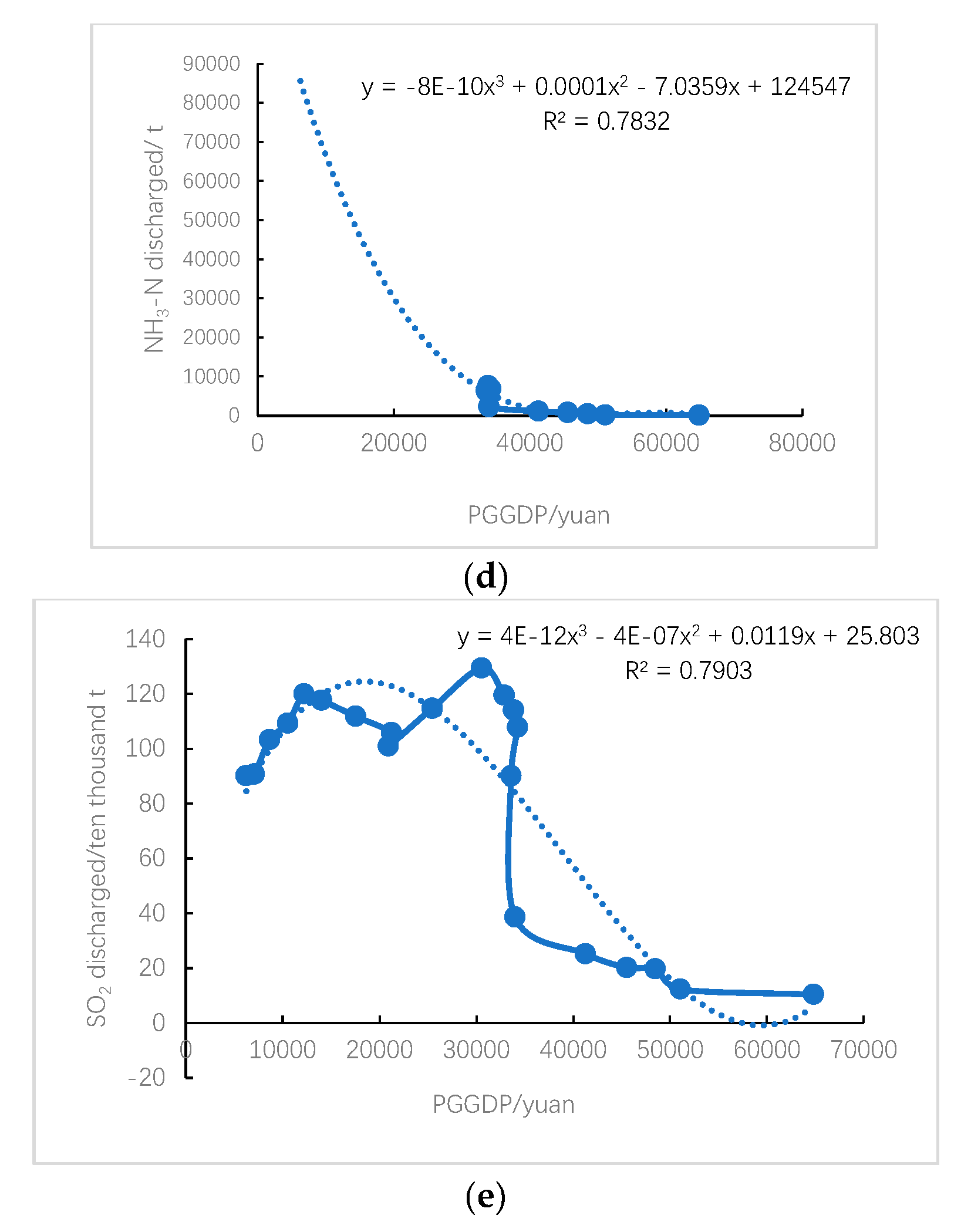
The correlation between economic development quality and environmental pollution intensity indicators shows that the correlation coefficients between GDP (per capita GDP) and wastewater emissions and sulfur dioxide emissions are -0.4 and -0.7, respectively. This indicates that as economic indicators increase, wastewater emissions and sulfur dioxide emissions gradually decrease, which is consistent with the curve fitting results in
Figure 4a,e; The correlation coefficient between GDP (per capita GDP) and COD emissions and ammonia nitrogen emissions is -0.3, while the correlation coefficient between COD and ammonia nitrogen emissions exceeds 0.9, indicating that with the continuous development of the economy, COD emissions and ammonia nitrogen emissions slowly decrease. The fitting curves in
Figure 4c,d further support this conclusion; The correlation coefficient between GDP (per capita GDP) and solid waste production exceeds 0.5, showing a positive correlation, which is consistent with the conclusion of the fitting curve in
Figure 4b, that is, the two show a monotonically increasing relationship. In addition, the correlation coefficient between GDP (per capita GDP) and exhaust emissions exceeds 0.7, indicating that the level of economic development is also closely related to exhaust emissions.
In terms of other indicators, the resident population has the strongest correlation with the amount of solid waste generated, with a coefficient of 0.841 and a strong correlation with the amount of exhaust gas emissions, with a coefficient of 0.450. There is no obvious correlation with other pollutants (wastewater emissions, Chemical oxygen demand emissions, ammonia nitrogen emissions, sulfur dioxide emissions). The per capita disposable income has a strong correlation with the generation of solid waste and exhaust gas emissions, with coefficients of 0.513 and 0.714, respectively, while it has a significant negative correlation with sulfur dioxide (coefficient of -0.799), and has no strong or significant correlation with other pollutants (wastewater emissions, Chemical oxygen demand emissions, ammonia nitrogen emissions).
In summary, the trend of correlation between the quality of economic development and the intensity of environmental pollution is basically consistent, with GDP (per capita GDP) showing moderate and strong negative correlations with wastewater emissions and sulfur dioxide emissions; GDP (per capita GDP) shows a moderate negative correlation with COD emissions and ammonia nitrogen emissions, while GDP (per capita GDP) shows a strong positive correlation with solid waste production. The correlation analysis results further support the fitting curve results.
3.3. Comparison of Evolution Characteristics in Different Periods
From
Table 2, it can be seen that there are slight differences in the research conclusions of different researchers on the relationship between economic development and environmental pollution in Shanxi Province during different periods. The research results of Zhang Rongyan et al. [
23] indicate that the fitting curve of Shanxi is in an “N” shape. With economic growth, the industrial exhaust emissions in Shanxi will increase, and there has not yet been a turning point. The research results of Zhang Lin et al. [
24] show that wastewater discharge, soot dust discharge and sulfur dioxide are inverted “U” shaped, industrial solid waste and industrial waste gas are “U” shaped curves, and Chemical oxygen demand is “N” shaped curves. Zhu Weixin et al. [
25] found that 1998 was the year with the most severe pollution in Shanxi Province, with atmospheric and industrial solid waste pollution being the most severe; In 2011, water pollution reached its peak. The fitting curve shows that the curves of industrial exhaust emissions, SO
2 emissions, and COD emissions conform to the inverted “U” shape feature; The curve of NH
3-N emissions shows an inverted “N”shape; The curve of smoke and dust emissions and industrial solid waste emissions shows an “N”shaped characteristic.
In this study, it was found that the per capita GDP of Shanxi Province showed a classic inverted “U” shaped relationship between wastewater and SO2 emissions, with a turning point occurring around 20000 yuan per capita; It is monotonically decreasing with Chemical oxygen demand and ammonia nitrogen emissions, and monotonically increasing with solid waste generation. The reasons for the differences in the above research results may include the following: firstly, differences in the selection of data intervals and ranges: different researchers have chosen different research intervals and ranges, which may lead to different results. Secondly, differences in the selection of research variables: Researchers may choose different variables, such as some studies only studying exhaust and wastewater emissions, while others may also study solid waste production, which may lead to different results. Thirdly, differences in research methods: Researchers may adopt different research methods, using different statistical or computational methods, resulting in different results.
Therefore, for the evolution characteristics of economic development quality and environmental pollution intensity, it is necessary to select appropriate variables, research methods, and data intervals based on a thorough understanding of the research object, in order to obtain more accurate research results.