Submitted:
21 June 2023
Posted:
23 June 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
1.1. Background
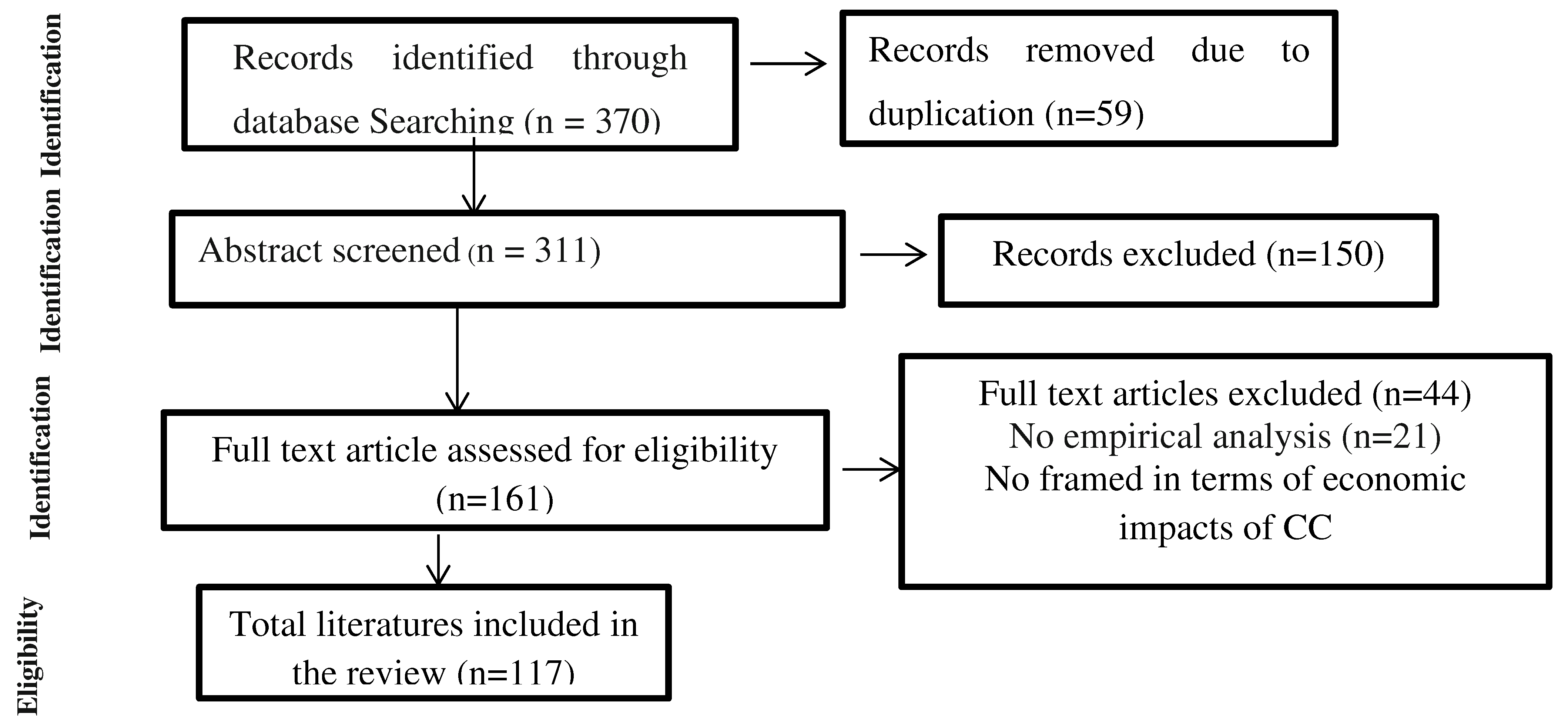
2. Methodology
3. Literature Review
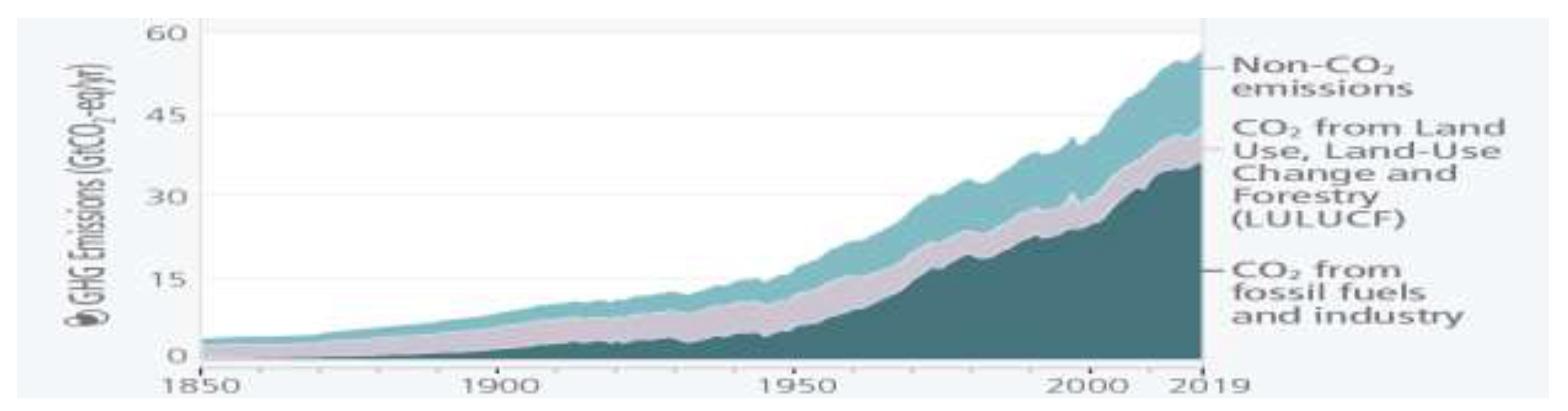
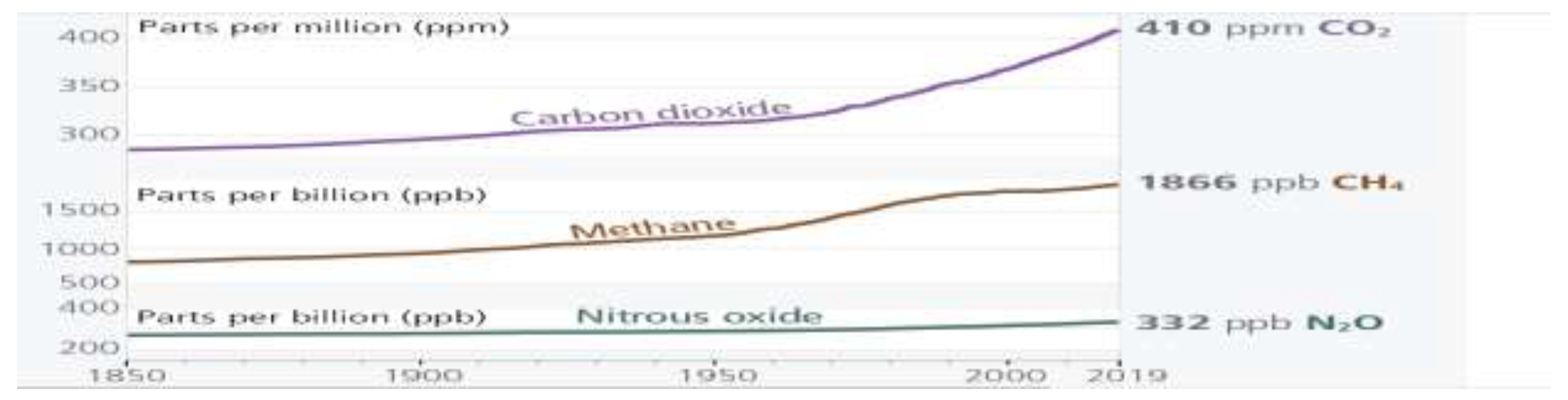
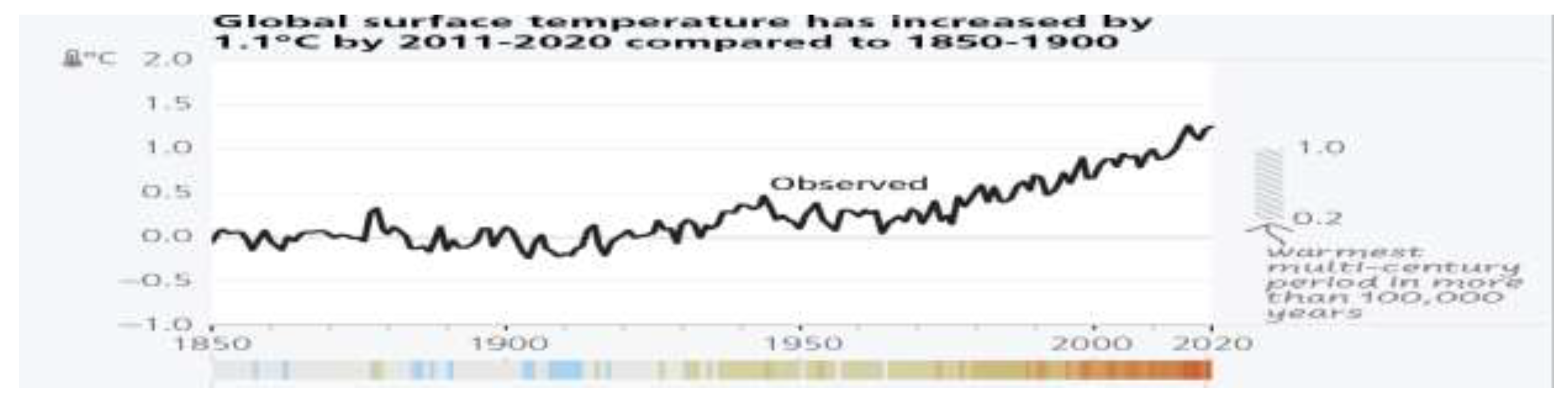
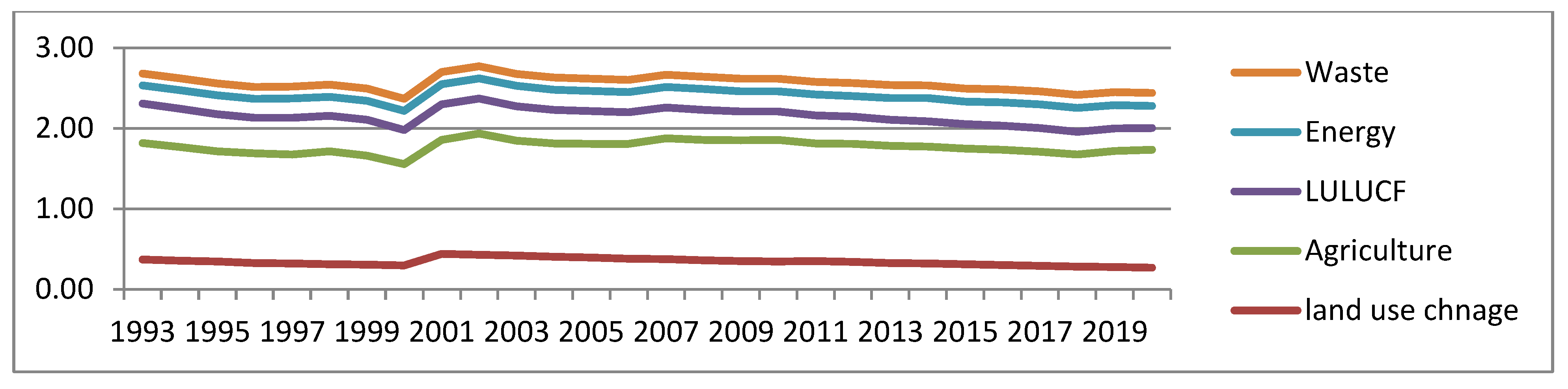
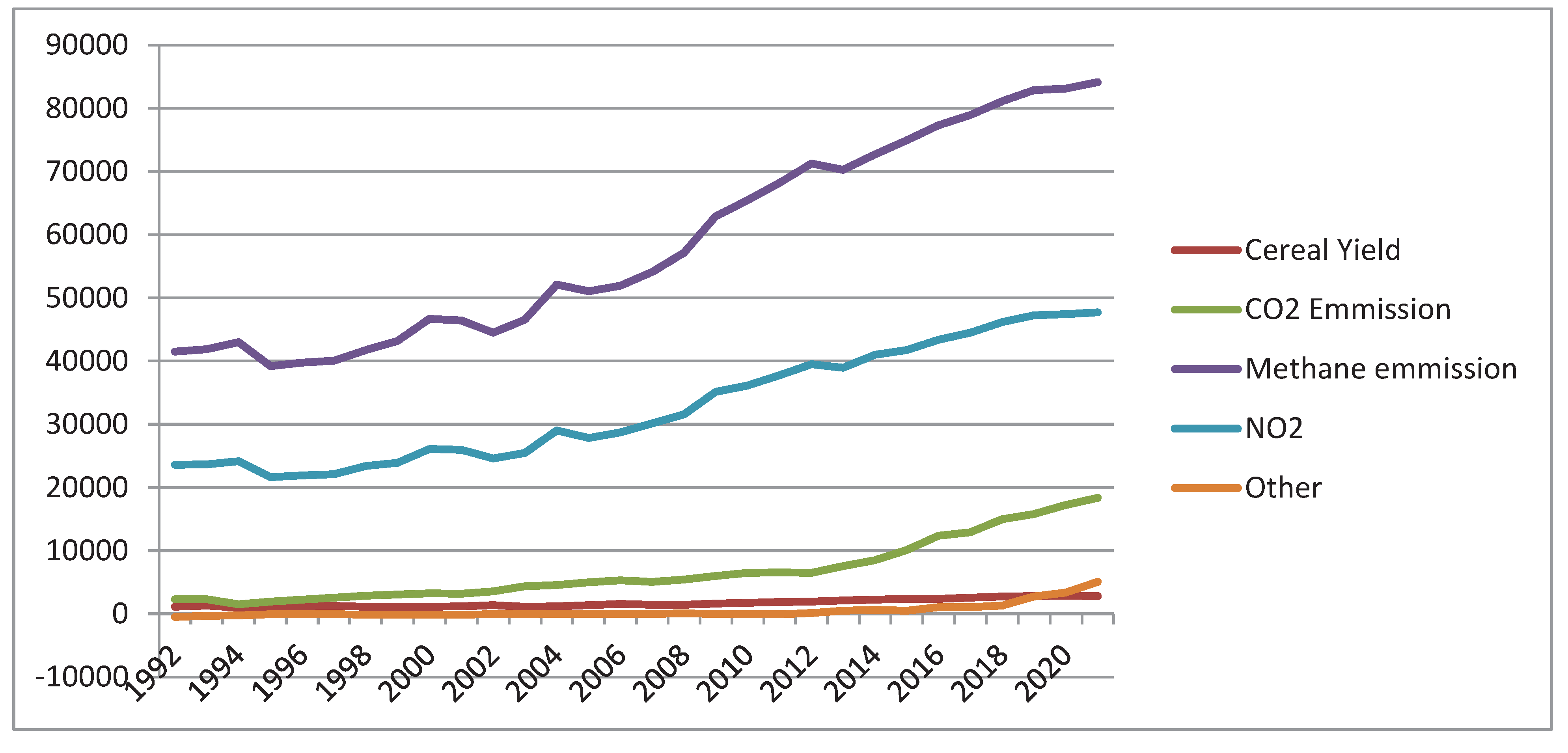
3.1. Emission of Green-House Gases
3.2. Trend of climate change in Ethiopia
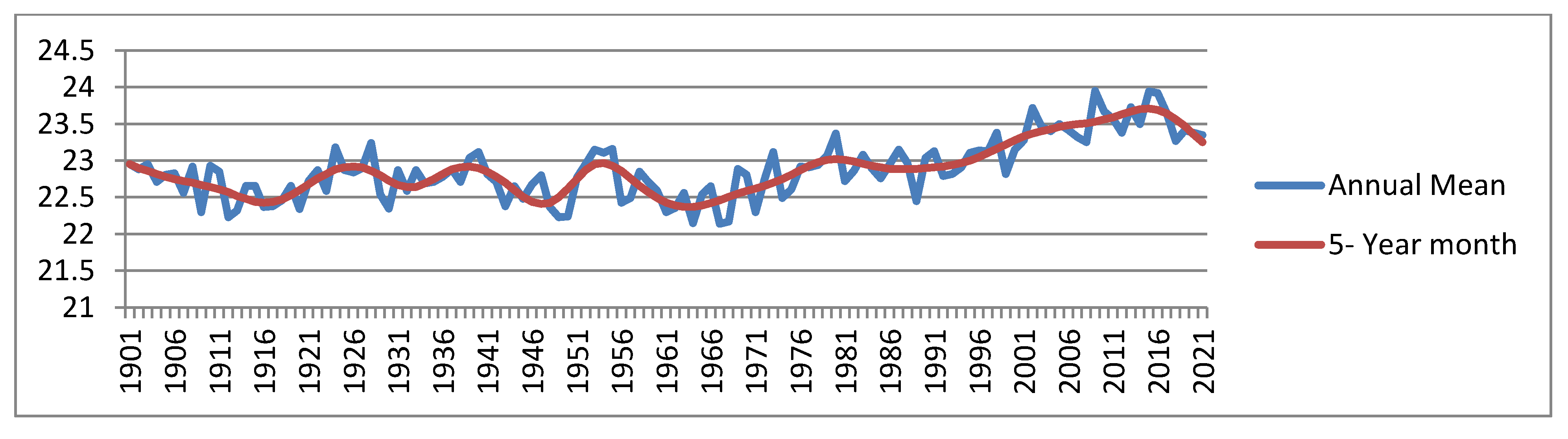
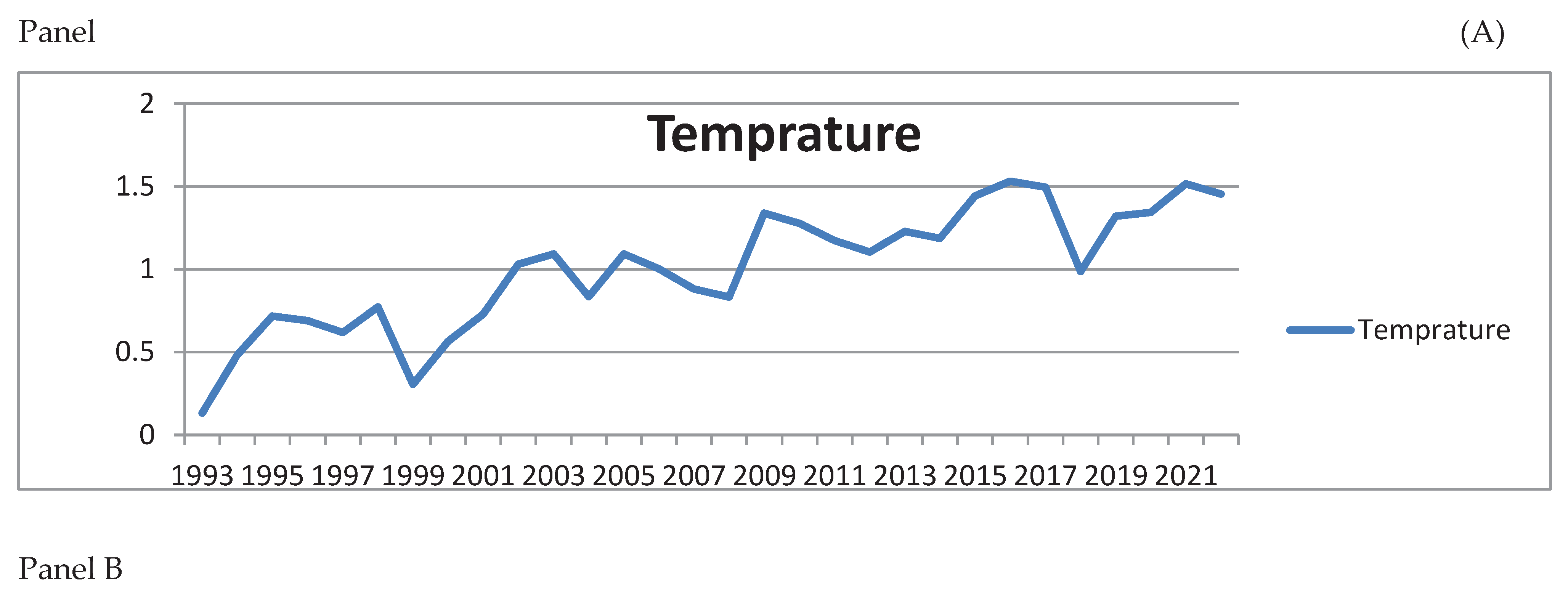
3.2.1. Trend of Mean daily temperature in Ethiopia
3.2.2. Trend of rainfall in Ethiopia
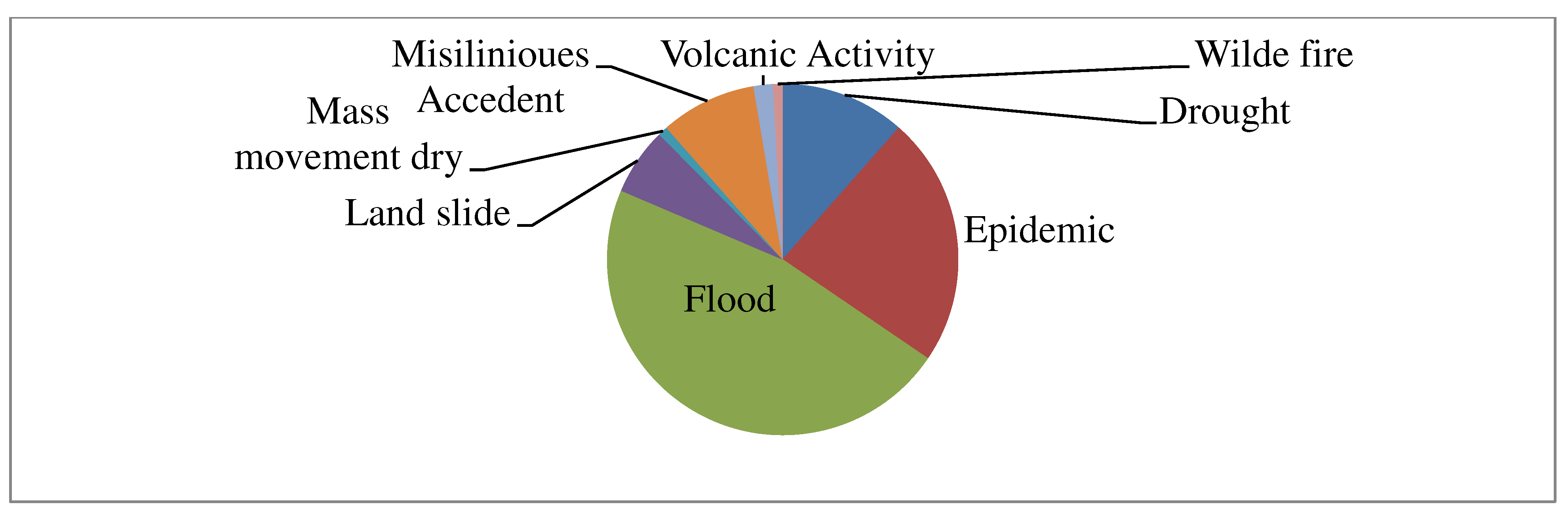
3.2.3. Trend of Extreme weather in Ethiopia
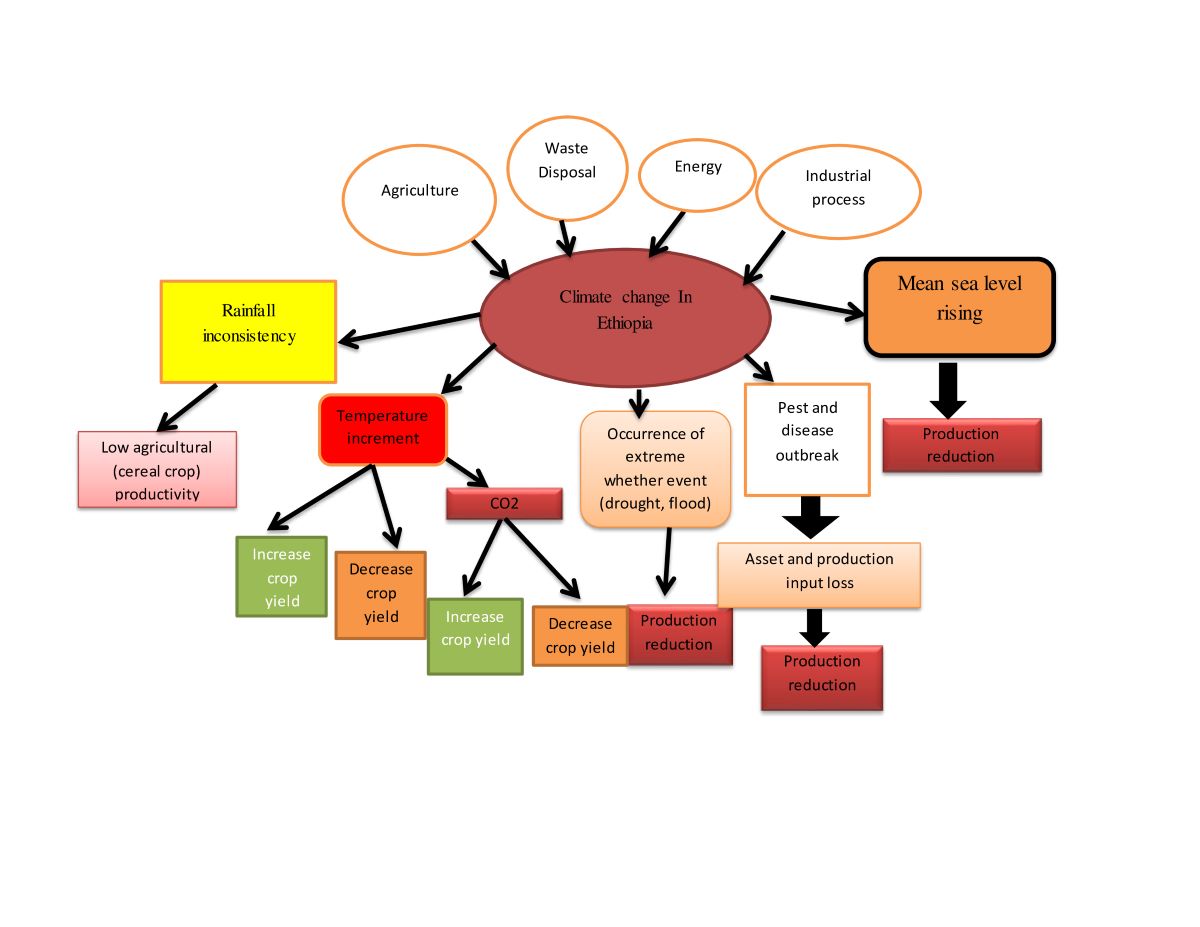
3.2.4. Major contributor/driver of climate change in Ethiopia
3.3. Impacts of Climate Change on cereal crop yield in Ethiopia
4. Conclusion
References
- McGill, T. In the Hot Seat: Climate Change and Agriculture in Ethiopia and Malawi. Global Majority E-Journal, 2022, 112.
- 2. IPCC. SYNTHESIS REPORT OF THE IPCC SIXTH ASSESSMENT REPORT (AR6) Summary for Policymakers, 2023; pp. 1–36.
- Pörtner, H.-O.; Roberts, D.C.; Adams, H.; Adler, C.; Aldunce, P.; Ali, E.; Begum, R.A.; Betts, R.; Kerr, R.B.; Biesbroek, R. Climate change 2022: Impacts, adaptation and vulnerability; IPCC Geneva, Switzerland:: 2022.
- Piao, S.; Ciais, P.; Huang, Y.; Shen, Z.; Peng, S.; Li, J.; Zhou, L.; Liu, H.; Ma, Y.; Ding, Y. The impacts of climate change on water resources and agriculture in China. Nature 2010, 467, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mall, R.K.; Gupta, A.; Sonkar, G. Effect of climate change on agricultural crops. In Current developments in biotechnology and bioengineering; Elsevier: 2017; pp. 23-46.
- Diez, J.M.; D'Antonio, C.M.; Dukes, J.S.; Grosholz, E.D.; Olden, J.D.; Sorte, C.J.; Blumenthal, D.M.; Bradley, B.A.; Early, R.; Ibáñez, I. Will extreme climatic events facilitate biological invasions? Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment 2012, 10, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Aalst, M.K. The impacts of climate change on the risk of natural disasters. Disasters 2006, 30, 5–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bale, J.S.; Masters, G.J.; Hodkinson, I.D.; Awmack, C.; Bezemer, T.M.; Brown, V.K.; Butterfield, J.; Buse, A.; Coulson, J.C.; Farrar, J. Herbivory in global climate change research: direct effects of rising temperature on insect herbivores. Global change biology 2002, 8, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viste, E.; Korecha, D.; Sorteberg, A. Recent drought and precipitation tendencies in Ethiopia. Theoretical and Applied Climatology 2013, 112, 535–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haile, G.G.; Tang, Q.; Sun, S.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Liu, X. Droughts in East Africa: Causes, impacts and resilience. Earth-science reviews 2019, 193, 146–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melketo, T.; Schmidt, M.; Bonatti, M.; Sieber, S.; Müller, K.; Lana, M. Determinants of pastoral household resilience to food insecurity in Afar region, northeast Ethiopia. Journal of Arid Environments 2021, 188, 104454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tessema, I.; Simane, B. Vulnerability analysis of smallholder farmers to climate variability and change: an agro-ecological system-based approach in the Fincha’a sub-basin of the upper Blue Nile Basin of Ethiopia. Ecological Processes 2019, 8, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tofu, D.A.; Fana, C.; Dilbato, T.; Dirbaba, N.B.; Tesso, G. Pastoralists’ and agro-pastoralists’ livelihood resilience to climate change-induced risks in the Borana zone, south Ethiopia: Using resilience index measurement approach. Pastoralism 2023, 13, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conway, D.; Schipper, E.L.F. Adaptation to climate change in Africa: Challenges and opportunities identified from Ethiopia. Global environmental change 2011, 21, 227–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gemeda, D.O.; Sima, A.D. The impacts of climate change on African continent and the way forward. Journal of Ecology and the Natural environment 2015, 7, 256–262. [Google Scholar]
- Palmer, P.I.; Wainwright, C.M.; Dong, B.; Maidment, R.I.; Wheeler, K.G.; Gedney, N.; Hickman, J.E.; Madani, N.; Folwell, S.S.; Abdo, G. Drivers and impacts of Eastern African rainfall variability. Nature Reviews Earth & Environment, 2023, 1-17 .
- Tofu, D.A.; Wolka, K. Climate change induced progressive shift of livelihood from cereal towards Khat (Chata edulis) production in eastern Ethiopia. Heliyon 2023, e12790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alemu, T.; Mengistu, A. Impacts of climate change on food security in Ethiopia: adaptation and mitigation options: a review. Climate Change-Resilient Agriculture and Agroforestry: Ecosystem Services and Sustainability, 2019, 397-412.
- Deressa, T.T.; Hassan, R.M. Economic impact of climate change on crop production in Ethiopia: Evidence from cross-section measures. Journal of African economies 2009, 18, 529–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awika, J.M. Major Cereal Grains Production and Use around the World. Joseph M. Awika, V.P., Scott Bean, Ed.; American Chemical Society: Washington, DC, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- McKevith, B. Nutritional aspects of cereals. Nutrition Bulletin 2004, 29, 111–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amine, E.; Baba, N.; Belhadj, M.; Deurenberg-Yap, M.; Djazayery, A.; Forrestre, T.; Galuska, D.; Herman, S.; James, W.; Kabangu, J.M.B. Diet, nutrition and the prevention of chronic diseases. World Health Organization technical report series 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, P.; Sahu, N.C.; Kumar, S.; Ansari, M.A. Impact of climate change on cereal production: evidence from lower-middle-income countries. Environmental Science and Pollution Research 2021, 28, 51597–51611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Vanga, S.K.; Saxena, R.; Orsat, V.; Raghavan, V. Effect of climate change on the yield of cereal crops: a review. Climate 2018, 6, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poudel, M.R.; Ghimire, S.; Dhakal, K.H.; Thapa, D.B.; Poudel, H.K. Evaluation of wheat genotypes under irrigated, heat stress and drought conditions. Journal of Biology and Today's World 2020, 9, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Leng, G.; Hall, J. Crop yield sensitivity of global major agricultural countries to droughts and the projected changes in the future. Science of the Total Environment 2019, 654, 811–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassaye, A.Y.; Shao, G.; Wang, X.; Shifaw, E.; Wu, S. Impact of climate change on the staple food crops yield in Ethiopia: implications for food security. Theoretical and Applied Climatology 2021, 145, 327–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearson, R.G.; Dawson, T.P. Predicting the impacts of climate change on the distribution of species: are bioclimate envelope models useful? Global ecology and biogeography 2003, 12, 361–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seaward, C. El Niño in Ethiopia: Programme observations on the impact of the Ethiopia drought and recommendations for action; Oxfam International: 2016.
- Gizaw, M.S.; Gan, T.Y. Impact of climate change and El Niño episodes on droughts in sub-Saharan Africa. Climate Dynamics 2017, 49, 665–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.M.; Yaseen, M.; Saqib, S.E. Climate change impacts of drought on the livelihood of dryland smallholders: Implications of adaptation challenges. International Journal of Disaster Risk Reduction 2022, 80, 103210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, K. Global environmental change II: From adaptation to deliberate transformation. Progress in human geography 2012, 36, 667–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas-Downing, M.M.; Nejadhashemi, A.P.; Harrigan, T.; Woznicki, S.A. Climate change and livestock: Impacts, adaptation, and mitigation. Climate risk management 2017, 16, 145–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kane, S.; Shogren, J.F. Linking adaptation and mitigation in climate change policy; Springer: 2000.
- Verchot, L.V.; Van Noordwijk, M.; Kandji, S.; Tomich, T.; Ong, C.; Albrecht, A.; Mackensen, J.; Bantilan, C.; Anupama, K.; Palm, C. Climate change: linking adaptation and mitigation through agroforestry. Mitigation and adaptation strategies for global change 2007, 12, 901–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharifi, A. Co-benefits and synergies between urban climate change mitigation and adaptation measures: A literature review. Science of the total environment 2021, 750, 141642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osaka, S.; Bellamy, R.; Castree, N. Framing “nature-based” solutions to climate change. Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews: Climate Change 2021, 12, e729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, L.; Jaspars, S.; Pavanello, S.; Ludi, E.; Slater, R.; Grist, N.; Mtisi, S. Responding to a changing climate: Exploring how disaster risk reduction, social protection and livelihoods approaches promote features of adaptive capacity. 2010.
- STRATEGY, C.R.G.E. Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia. Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, 2011.
- FDRE. Ethiopia’s climate resilient green economy: National adaptation plan. Addis Ababa, Ethiopia: Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia, 2019.
- Marie, M.; Yirga, F.; Haile, M.; Tquabo, F. Farmers' choices and factors affecting adoption of climate change adaptation strategies: evidence from northwestern Ethiopia. Heliyon 2020, 6, e03867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reviva Hasson, Å.L.a.M.V. Climate Change in a Public Goods Game: Investment Decision in Mitigation versus Adaptation. Environment for Development Initiative is collaborating with JSTOR to digitize, preserve and extend access to this content. 2009.
- Rosa, E.A.; Dietz, T. Human drivers of national greenhouse-gas emissions. Nature Climate Change 2012, 2, 581–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shivanna, K. Climate change and its impact on biodiversity and human welfare. Proceedings of the Indian National Science Academy 2022, 88, 160–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bretschger, L.; Karydas, C. Economics of climate change: introducing the Basic Climate Economic (BCE) model. Environment and development economics 2019, 24, 560–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Bhattacharya, S.; Garg, A. Greenhouse gas emissions from India: A perspective. Current science 2006, 326–333. [Google Scholar]
- Kiros, G.; Shetty, A.; Nandagiri, L. Analysis of variability and trends in rainfall over northern Ethiopia. Arabian Journal of Geosciences 2016, 9, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malede, D.A.; Agumassie, T.A.; Kosgei, J.R.; Linh, N.T.T.; Andualem, T.G. Analysis of rainfall and streamflow trend and variability over Birr River watershed, Abbay basin, Ethiopia. Environmental Challenges 2022, 7, 100528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degefu, M.A.; Bewket, W. Variability and trends in rainfall amount and extreme event indices in the Omo-Ghibe River Basin, Ethiopia. Regional environmental change 2014, 14, 799–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebi, K.L.; Bowen, K. Extreme events as sources of health vulnerability: Drought as an example. Weather and climate extremes 2016, 11, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teshome, A.; Zhang, J. Increase of extreme drought over Ethiopia under climate warming. Advances in Meteorology 2019, 2019, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, S.K.; Ranjan, R.K.; Misra, A.K.; Wanjari, N.; Vishwakarma, S. Variability of precipitation extremes and drought intensity over the Sikkim State, India, during 1950–2018. Theoretical and Applied Climatology 2022, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, G.J.-Y.; Ringler, C. Hydro-economic modeling of climate change impacts in Ethiopia; Citeseer: 2010; Volume 960.
- Margulis, S.; Hughes, G.; Schneider, R.; Pandey, K.; Narain, U.; Kemeny, T. Economics of adaptation to climate change: Synthesis report. 2010.
- Tareke, K.A.; Awoke, A.G. Hydrological drought analysis using streamflow drought index (SDI) in Ethiopia. Advances in Meteorology 2022, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeleke, T.T.; Giorgi, F.; Diro, G.; Zaitchik, B. Trend and periodicity of drought over Ethiopia. International journal of climatology 2017, 37, 4733–4748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teshager Abeje, M.; Tsunekawa, A.; Adgo, E.; Haregeweyn, N.; Nigussie, Z.; Ayalew, Z.; Elias, A.; Molla, D.; Berihun, D. Exploring drivers of livelihood diversification and its effect on adoption of sustainable land management practices in the Upper Blue Nile Basin, Ethiopia. Sustainability 2019, 11, 2991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mera, G.A. Drought and its impacts in Ethiopia. Weather and climate extremes 2018, 22, 24–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tongwane, M.I.; Moeletsi, M.E. A review of greenhouse gas emissions from the agriculture sector in Africa. Agricultural Systems 2018, 166, 124–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanc, E.; Reilly, J. Approaches to assessing climate change impacts on agriculture: an overview of the debate. Review of Environmental Economics and Policy 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antle, J.M.; Stöckle, C.O. Climate impacts on agriculture: insights from agronomic-economic analysis. Review of Environmental Economics and Policy 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Falco, S.; Veronesi, M.; Yesuf, M. Does adaptation to climate change provide food security? A micro-perspective from Ethiopia. American Journal of Agricultural Economics 2011, 93, 829–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Falco, S.; Yesuf, M.; Kohlin, G.; Ringler, C. Estimating the impact of climate change on agriculture in low-income countries: Household level evidence from the Nile Basin, Ethiopia. Environmental and Resource Economics 2012, 52, 457–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanc, E.; Schlenker, W. The use of panel models in assessments of climate impacts on agriculture. Review of Environmental Economics and Policy 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginbo, T. Heterogeneous impacts of climate change on crop yields across altitudes in Ethiopia. Climatic Change 2022, 170, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelbore, Z.G. An analysis of the impacts of climate change on crop yield and yield variability in Ethiopia. 2012.
- Kassie, B.T.; Asseng, S.; Rotter, R.P.; Hengsdijk, H.; Ruane, A.C.; Van Ittersum, M.K. Exploring climate change impacts and adaptation options for maize production in the Central Rift Valley of Ethiopia using different climate change scenarios and crop models. Climatic change 2015, 129, 145–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gbetibouo, G.A.; Hassan, R.M. Measuring the economic impact of climate change on major South African field crops: a Ricardian approach. Global and Planetary change 2005, 47, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabubo-Mariara, J.; Karanja, F.K. The economic impact of climate change on Kenyan crop agriculture: A Ricardian approach. Global and planetary change 2007, 57, 319–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eid, H.M.; El-Marsafawy, S.M.; Ouda, S.A. Assessing the economic impacts of climate change on agriculture in Egypt: a Ricardian approach. World Bank Policy Research Working Paper 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Mano, R.; Nhemachena, C. Assessment of the economic impacts of climate change on agriculture in Zimbabwe: A Ricardian approach. World Bank Policy Research Working Paper 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Huong, N.T.L.; Bo, Y.S.; Fahad, S. Economic impact of climate change on agriculture using Ricardian approach: A case of northwest Vietnam. Journal of the Saudi Society of Agricultural Sciences 2019, 18, 449–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouedraogo, M.; Some, L.; Dembele, Y. Economic impact assessment of climate change on agriculture in Burkina Faso: A Ricardian Approach. Centre for Environmental Economics and Policy in Africa (CEEPA), University of Pretoria, 2006.
- Tun Oo, A.; Van Huylenbroeck, G.; Speelman, S. Measuring the economic impact of climate change on crop production in the dry zone of Myanmar: A Ricardian Approach. Climate 2020, 8, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.U.; Shah, A.H.; Iftikhar-ul-Husnain, M. Impact Of Climate Change On The Net Revenue Of Major Crop Growing Farmers In Pakistan: A Ricardian Approach. Climate change economics 2021, 12, 2150006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, C.T.; Scrimgeour, F. Measuring the impact of climate change on agriculture in Vietnam: A panel Ricardian analysis. Agricultural Economics 2022, 53, 37–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimmerer, C. The Impact of Climate Change on Canadian Agriculture: A Parcel Level Ricardian Analysis. University of Guelph, 2022.
- Xiang, T.; Malik, T.H.; Hou, J.W.; Ma, J. The Impact of Climate Change on Agricultural Total Factor Productivity: A Cross-Country Panel Data Analysis, 1961–2013. Agriculture 2022, 12, 2123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendelsohn, R.O.; Massetti, E. The use of cross-sectional analysis to measure climate impacts on agriculture: theory and evidence. Review of Environmental Economics and Policy 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evangelista, P.; Young, N.; Burnett, J. How will climate change spatially affect agriculture production in Ethiopia? Case studies of important cereal crops. Climatic change 2013, 119, 855–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, R.; Dixit, G.; Dwivedi, S.; Adhikari, B.; Chakrabarty, D.; Trivedi, P.; Pandey, V.; Tewari, S.; Mishra, A.; Nautiyal, C. Climate change affects cereal crop production and mitigation strategies. SATSA Mukhaptra Annual Technical Issue 2012, 16, 30–40. [Google Scholar]
- Ketema, A.M.; Negeso, K.D. Effect of climate change on agricultural output in Ethiopia. Jurnal Perspektif Pembiayaan Dan Pembangunan Daerah 2020, 8, 195–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alemayehu, A.; Bewket, W. Local climate variability and crop production in the central highlands of Ethiopia. Environmental Development 2016, 19, 36–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Wang, G.; Ahmed, K.F.; Adugna, B.; Eggen, M.; Atsbeha, E.; You, L.; Koo, J.; Anagnostou, E. The role of climate in the trend and variability of Ethiopia's cereal crop yields. Science of The Total Environment 2020, 723, 137893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tembo, F.M. The impact of climate change on teff production in southeast Tigray, Ethiopia. Journal of Agricultural Economics and Rural Development 2018, 4, 389–396. [Google Scholar]
- Asfaw, A.; Simane, B.; Hassen, A.; Bantider, A. Variability and time series trend analysis of rainfall and temperature in northcentral Ethiopia: A case study in Woleka sub-basin. Weather and climate extremes 2018, 19, 29–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.; Liu, Y.; Ishaq, M.; Shah, T.; Ilyas, A.; Din, I.U. Climate change and its impact on the yield of major food crops: Evidence from Pakistan. Foods 2017, 6, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenzweig, C.; Iglesius, A.; Yang, X.-B.; Epstein, P.R.; Chivian, E. Climate change and extreme weather events-Implications for food production, plant diseases, and pests. 2001.
- Velásquez, A.C.; Castroverde, C.D.M.; He, S.Y. Plant–pathogen warfare under changing climate conditions. Current biology 2018, 28, R619–R634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- St. Clair, S.B.; Lynch, J.P. The opening of Pandora’s Box: climate change impacts on soil fertility and crop nutrition in developing countries. Plant and Soil 2010, 335, 101–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, T.W.; Waddington, S.R.; Anderson, C.L.; Chew, A.; True, Z.; Cullen, A. Environmental impacts and constraints associated with the production of major food crops in Sub-Saharan Africa and South Asia. Food Security 2015, 7, 795–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mcgrath, J.M.; Lobell, D.B. Reduction of transpiration and altered nutrient allocation contribute to nutrient decline of crops grown in elevated CO2 concentrations. Plant, Cell & Environment 2013, 36, 697–705. [Google Scholar]
- Ziska, L.H. The role of climate change and increasing atmospheric carbon dioxide on weed management: herbicide efficacy. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment 2016, 231, 304–309. [Google Scholar]
- Dukes, J.S.; Pontius, J.; Orwig, D.; Garnas, J.R.; Rodgers, V.L.; Brazee, N.; Cooke, B.; Theoharides, K.A.; Stange, E.E.; Harrington, R. Responses of insect pests, pathogens, and invasive plant species to climate change in the forests of northeastern North America: what can we predict? Canadian journal of forest research 2009, 39, 231–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singer, A.; Travis, J.M.; Johst, K. Interspecific interactions affect species and community responses to climate shifts. Oikos 2013, 122, 358–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posch, B.C.; Kariyawasam, B.C.; Bramley, H.; Coast, O.; Richards, R.A.; Reynolds, M.P.; Trethowan, R.; Atkin, O.K. Exploring high temperature responses of photosynthesis and respiration to improve heat tolerance in wheat. Journal of experimental botany 2019, 70, 5051–5069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tol, R.S. The economic impacts of climate change. Review of Environmental Economics and Policy 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brouder, S.M.; Volenec, J.J. Impact of climate change on crop nutrient and water use efficiencies. Physiologia Plantarum 2008, 133, 705–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimball, B.; Idso, S. Increasing atmospheric CO2: effects on crop yield, water use and climate. Agricultural water management 1983, 7, 55–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatfield, J.L.; Dold, C. Water-use efficiency: advances and challenges in a changing climate. Frontiers in plant science 2019, 10, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Araya, A.; Prasad, P.; Gowda, P.; Djanaguiraman, M.; Kassa, A. Potential impacts of climate change factors and agronomic adaptation strategies on wheat yields in central highlands of Ethiopia. Climatic Change 2020, 159, 461–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, M.R.; Friedlingstein, P.; Girardin, C.A.; Jenkins, S.; Malhi, Y.; Mitchell-Larson, E.; Peters, G.P.; Rajamani, L. Net zero: science, origins, and implications. Annual Review of Environment and Resources 2022, 47, 849–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carraro, C. Climate change: scenarios, impacts, policy, and development opportunities. Agricultural Economics 2016, 47, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andres, R.J.; Gregg, J.S.; Losey, L.; Marland, G.; Boden, T.A. Monthly, global emissions of carbon dioxide from fossil fuel consumption. Tellus B: Chemical and Physical Meteorology 2011, 63, 309–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakjira, M.T.; Peleg, N.; Anghileri, D.; Molnar, D.; Alamirew, T.; Six, J.; Molnar, P. Rainfall seasonality and timing: implications for cereal crop production in Ethiopia. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology 2021, 310, 108633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aberra, K. The impact of climate variability on crop production in Ethiopia: which crop is more vulnerable to rainfall variability. In Proceedings of the ninth Conference of EEA; 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Asfew, M.; Bedemo, A. Impact of climate change on cereal crops production in Ethiopia. Advances in Agriculture 2022, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deressa, T.T. Measuring the economic impact of climate change on Ethiopian agriculture: Ricardian approach. World Bank Policy Research Working Paper 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Shumetie, A.; Alemayehu Yismaw, M. Effect of climate variability on crop income and indigenous adaptation strategies of households. International Journal of Climate Change Strategies and Management 2018, 10, 580–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tembo, F. The impact of climate change on teff production in southeast Tigray, Ethiopia. Journal of Agricultural Economics and Rural Development 2018, 4, 389–396. [Google Scholar]
- Demissie, B.; Teklemariam, D.; Haile, M.; Meaza, H.; Nyssen, J.; Billi, P.; Abera, W.; Gebrehiwot, M.; Haug, R.; Van Eetvelde, V. Flood hazard in a semi-closed basin in northern Ethiopia: Impact and resilience. Geo: Geography and Environment 2021, 8, e00100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toulotte, J.M.; Pantazopoulou, C.K.; Sanclemente, M.A.; Voesenek, L.A.; Sasidharan, R. Water stress resilient cereal crops: Lessons from wild relatives. Journal of Integrative Plant Biology 2022, 64, 412–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eze, E.; Girma, A.; Zenebe, A.; Okolo, C.C.; Kourouma, J.M.; Negash, E. Predictors of drought-induced crop yield/losses in two agroecologies of southern Tigray, Northern Ethiopia. Scientific Reports 2022, 12, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gebrehiwot, T.; van der Veen, A. Farmers’ drought experience, risk perceptions, and behavioural intentions for adaptation: Evidence from Ethiopia. Climate and Development 2021, 13, 493–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayalew, D.; Tesfaye, K.; Mamo, G.; Yitaferu, B.; Bayu, W. Variability of rainfall and its current trend in Amhara region, Ethiopia. African Journal of Agricultural Research 2012, 7, 1475–1486. [Google Scholar]
- Etana, D.; Snelder, D.J.; van Wesenbeeck, C.F.; de Cock Buning, T. Trends of climate change and variability in three agro-ecological settings in central Ethiopia: contrasts of meteorological data and farmers’ perceptions. Climate 2020, 8, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belachew, K.Y.; Maina, N.H.; Dersseh, W.M.; Zeleke, B.; Stoddard, F.L. Yield Gaps of Major Cereal and Grain Legume Crops in Ethiopia: A Review. Agronomy 2022, 12, 2528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A.; Mohamed, N.S.; Siddig, E.E.; Algaily, T.; Sulaiman, S.; Ali, Y. The Journal of Climate Change and Health. 2021.

| Year | Extreme event |
| 1920-22 | Drought |
| 1957-58 | Drought |
| 1962-63 | Drought |
| 1968 | Flood |
| 1971-75 | Drought |
| 1978-79 | Drought |
| 1982 | Drought |
| 1984-85 | Drought |
| 1987-88 | Drought |
| 1990-92 | Both |
| 1996 | Drought |
| 1996 | Drought |
| 2002 | Drought |
| 2005 | Flood |
| 2006 | Flood |
| 2009 | Drought |
| 2015 | Drought |
| 2016 | Drought |
| 2021-22 | Drought |
| S/No. | Author(s) | Time | Types of crop | Econometric model(s) | Results |
| 1 | Wakjira, et al. [105] | 1981-2010 | maize, teff, sorghum, wheat, barley, millet, oats and rice | Univariate linear regression model | Late-onset of rainy seasons=> - Cereals |
| 2 | Yang, Wang, Ahmed, Adugna, Eggen, Atsbeha, You, Koo and Anagnostou [84] | 1979-2014 | barley, maize, millet, sorghum, and wheat | DSSAT |
Solar radiation and day time temperature => + Cereals Production Solar radiation and day time temperature =>- Cereals in eastern Ethiopia |
| 3 | Tofu and Wolka [17] |
Multinomial Logit |
extreme reduction in rainfall => - Cereals | ||
| 4 | Aberra [106] | 1970-2010 | Stable cereal crops | rainfall variability=> - Cereals Rainfall, Temperature => - Cereals Production CO2 => + Cereals Production |
|
| 5 | Kassaye, Shao, Wang, Shifaw and Wu [27] | 1988 -2018 | teff, maize, wheat, and sorghum | FGLS | Rise in maximum Temperature =>+cereal Rise in minimum temperature => - Cereals |
| 6 | Asfew and Bedemo [107] | 1990-2020 | Teff, maize, wheat, and sorghum | ARDL | Precipitation=>+cereal both in SR and LR Temperature => - Cereals |
| 7 | Deressa and Hassan [19] | 1977-2009 | Ricardian approach | Temperature => - Cereals Precipitation =>+cereal |
|
| 8 | [108] | Ricardian approach | increasing temperature => - Cereals decreasing precipitation=> - Cereals |
||
| 9 | Shumetie and Alemayehu Yismaw [109] | Insufficient rainfall=> - Cereals increase in summer temperature=> -Cereals |
|||
| 10 | Tembo [110] | Teff | Ricardian model | Temperature =>-cereal Decrease in rainfall => - Cereals |
| Climate change event | Effect on crop production | Crop affected | Source |
| Flood | Pollution (carrying debris, pollutants, and nutrients) inundation of croplands and destruction of irrigation canals |
Maize , wheat, rice, barley, Teff | [111] [111] |
| crop losses, the upsurge of water-borne diseases | Maize , wheat, rice, barley, Teff | ||
| Drought | Diminution of leaf water potential and a turgor loss. Leaf curling, partial, or complete stomatal closure, decrease in cell enlargement and growth, and a decrease of internal CO2 causing a decrease of photosynthetic activity complete crop failure, reduced yields, drying up of crops, increased pest damage [112] | Wheat | [113,114] |
| variability in the amount and duration of rainfall | brought a loss of crop in both kiremt and belg seasons | Maize , wheat, rice, barley, Teff | [115] |
| Extreme/intensive/ heavy rainfall |
reduced yields, cut-off roads, soil erosion, reduced labo | Maize , wheat, rice, barley, Teff | [116] |
| Storms (strong winds and/or hailstones) | destroyed leaves, broke shoots and flowers, broke house, reduce leaf quality |
Maize , wheat, rice, barley, Teff | [117,118] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





