Submitted:
21 June 2023
Posted:
23 June 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
Drugs targeting the key signalling pathway
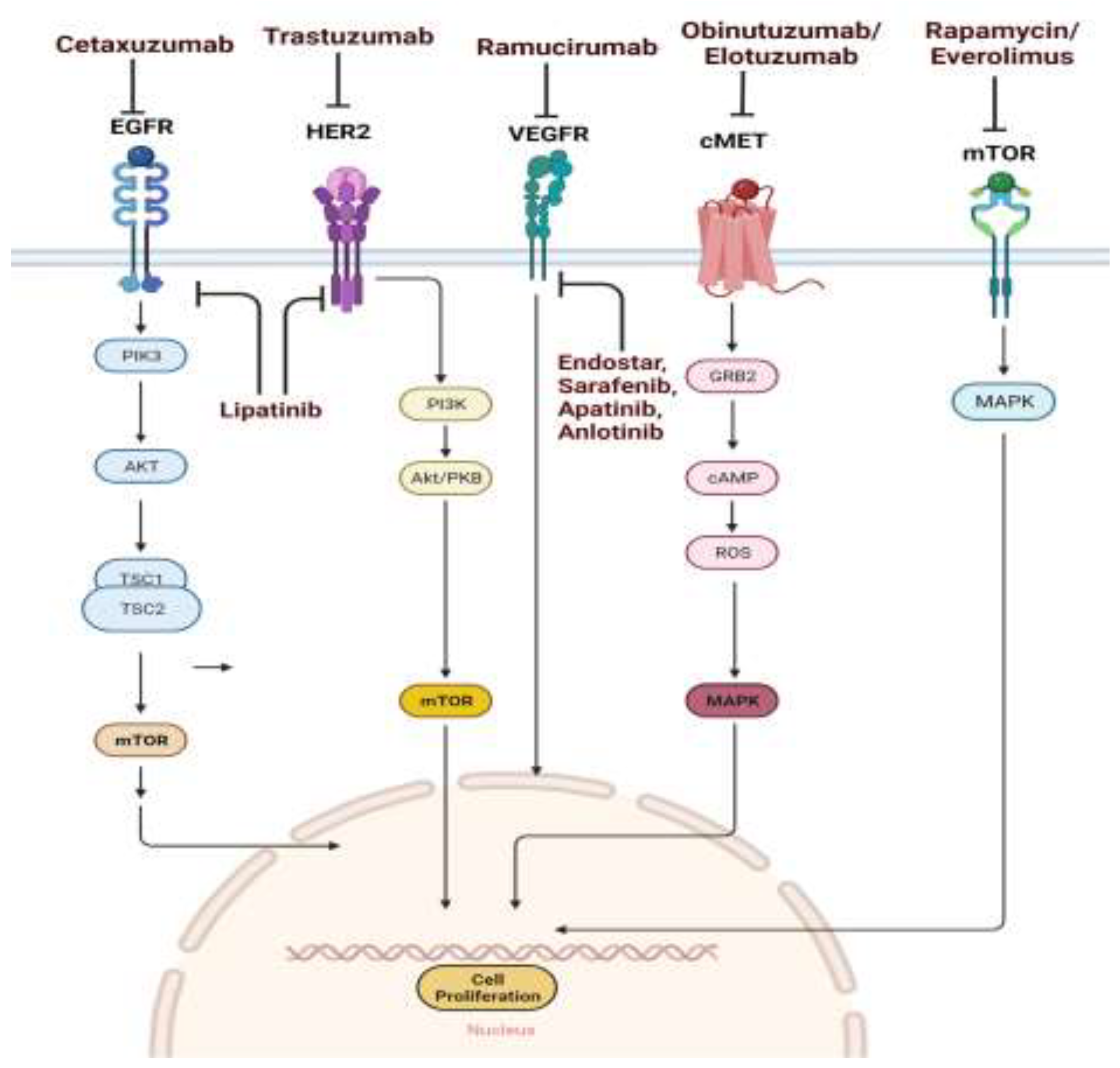
Drug targeting EGFR pathway
Anti EGFR monoclonal antibody
Cetuximab
Nimotuzumab
Anti EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor
Gefitinib
Icotinib
Drug targeting HER2 pathway
Trastuzumab
Lapatinib
Drug targeting VEGF / VEGFR pathway
Ramucirumab
HGF/c-MET pathway
Rilotumumab and Obinutuzumab
mTOR Pathway
Factor associated with targeted therapy
Cancer heterogeneity
Drug resistance
Cellular components involved in drug resistance
Cancer Stem Cells
Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts
Inflammatory Immune cells
Non-cellular components
Cytokines
Hypoxia
Growth factors
Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Collaboration, G.B.o.D.C., Global, Regional, and National Cancer Incidence, Mortality, Years of Life Lost, Years Lived With Disability, and Disability-Adjusted Life-years for 32 Cancer Groups, 1990 to 2015: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study. JAMA Oncology, 2017. 3(4): p. 524-548.
- Liu, K., et al., Etiology, cancer stem cells and potential diagnostic biomarkers for esophageal cancer. Cancer Lett, 2019. 458: p. 21-28. [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.M., et al., Advances in targeted therapy for esophageal cancer. Signal Transduct Target Ther, 2020. 5(1): p. 229. [CrossRef]
- Edgren, G., et al., A global assessment of the oesophageal adenocarcinoma epidemic. Gut, 2013. 62(10): p. 1406. [CrossRef]
- Xie, S.-H. and J. Lagergren, A global assessment of the male predominance in esophageal adenocarcinoma. Oncotarget, 2016. 7(25): p. 38876-38883. [CrossRef]
- Lagergren, J. and P. Lagergren, Oesophageal cancer. 2010. 341: p. c6280.
- Smyth, E.C., et al., Oesophageal cancer. Nat Rev Dis Primers, 2017. 3: p. 17048.
- Tong, C., et al., Causes, Risk Factors and Outcomes of Patients Readmitted to the Intensive Care Unit After Esophageal Cancer Surgery: A Retrospective Cohort Study. World J Surg, 2021. 45(7): p. 2167-2175. [CrossRef]
- Lagergren, J., et al., Oesophageal cancer. The Lancet, 2017. 390(10110): p. 2383-2396.
- Secrier, M., et al., Mutational signatures in esophageal adenocarcinoma define etiologically distinct subgroups with therapeutic relevance. Nat Genet, 2016. 48(10): p. 1131-41. [CrossRef]
- Rahmani, H., et al., Burden of esophageal cancer in Iran during 1995-2015: Review of findings from the Global Burden of Disease studies. Medical journal of the Islamic Republic of Iran, 2018. 32: p. 55-55. [CrossRef]
- Lagergren, J., et al., Oesophageal cancer. Lancet, 2017. 390(10110): p. 2383-2396.
- Schweigert, M., A. Dubecz, and H.J. Stein, Oesophageal cancer--an overview. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2013. 10(4): p. 230-44.
- Fatehi Hassanabad, A., et al., Esophageal carcinoma: Towards targeted therapies. Cell Oncol (Dordr), 2020. 43(2): p. 195-209. [CrossRef]
- Lu, R.-M., et al., Development of therapeutic antibodies for the treatment of diseases. Journal of Biomedical Science, 2020. 27(1): p. 1. [CrossRef]
- van Hagen, P., et al., Preoperative chemoradiotherapy for esophageal or junctional cancer. N Engl J Med, 2012. 366(22): p. 2074-84. [CrossRef]
- Tong, Y., et al., Tumor-Secreted Exosomal lncRNA POU3F3 Promotes Cisplatin Resistance in ESCC by Inducing Fibroblast Differentiation into CAFs. Mol Ther Oncolytics, 2020. 18: p. 1-13. [CrossRef]
- Mao, C., et al., Mechanisms of Pharmaceutical Therapy and Drug Resistance in Esophageal Cancer. 2021. 9(22). [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y. and Z.Y. Ding, PD-1 Inhibitors in the Advanced Esophageal Cancer. Front Pharmacol, 2019. 10: p. 1418. [CrossRef]
- Aref, D. and S. Croul, Medulloblastoma: recurrence and metastasis. CNS oncology, 2013. 2: p. 377-385. [CrossRef]
- Kang, X., et al., Personalized targeted therapy for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol, 2015. 21(25): p. 7648-58. [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.-M., et al., Advances in targeted therapy for esophageal cancer. Signal Transduct Target Ther, 2020. 5(1): p. 229. [CrossRef]
- Lyons, T.G. and G.Y. Ku, Systemic therapy for esophagogastric cancer: targeted therapies. Chin Clin Oncol, 2017. 6(5): p. 48. [CrossRef]
- Chong, C.R. and P.A. Jänne, The quest to overcome resistance to EGFR-targeted therapies in cancer. Nat Med, 2013. 19(11): p. 1389-400. [CrossRef]
- Ciardiello, F. and G. Tortora, EGFR Antagonists in Cancer Treatment. 2008. 358(11): p. 1160-1174. [CrossRef]
- Martinelli, E., et al., Anti-epidermal growth factor receptor monoclonal antibodies in cancer therapy. Clinical and experimental immunology, 2009. 158(1): p. 1-9. [CrossRef]
- Verma, H.K., et al., A Retrospective Look at Anti-EGFR Agents in Pancreatic Cancer Therapy. Curr Drug Metab, 2019. 20(12): p. 958-966. [CrossRef]
- Lv, Z.-C., J.-Y. Ning, and H.-B. Chen, Efficacy and toxicity of adding cetuximab to chemotherapy in the treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer: a meta-analysis from 12 randomized controlled trials. Tumour biology : the journal of the International Society for Oncodevelopmental Biology and Medicine, 2014. 35. [CrossRef]
- Sotelo, M.J., et al., Role of cetuximab in first-line treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer. World J Gastroenterol, 2014. 20(15): p. 4208-19. [CrossRef]
- Cunningham, D., et al., Cetuximab Monotherapy and Cetuximab plus Irinotecan in Irinotecan-Refractory Metastatic Colorectal Cancer. New England Journal of Medicine, 2004. 351(4): p. 337-345. [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.H., et al., Cetuximab for esophageal cancer: an updated meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. BMC Cancer, 2018. 18(1): p. 1170. [CrossRef]
- Xu, S., et al., Treatment outcome of nimotuzumab plus chemotherapy in advanced cancer patients: a single institute experience. Oncotarget, 2016. 7(22): p. 33391-407. [CrossRef]
- Han, X., et al. Nimotuzumab Combined with Chemotherapy is a Promising Treatment for Locally Advanced and Metastatic Esophageal Cancer. Medical science monitor : international medical journal of experimental and clinical research, 2017. 23, 412-418. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.-l., et al., A phase I dose escalation study of Nimotuzumab in combination with concurrent chemoradiation for patients with locally advanced squamous cell carcinoma of esophagus. Investigational New Drugs, 2012. 30(4): p. 1585-1590. [CrossRef]
- Bai, S.-X., et al., Clinical efficacy and safety of nimotuzumab plus chemotherapy in patients with advanced colorectal cancer: a retrospective analysis. The Journal of international medical research, 2020. 48(1): p. 300060519895858. [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y., et al., Nimotuzumab, an EGFR-targeted antibody, promotes radiosensitivity of recurrent esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Oncol, 2020. 56(4): p. 945-956. [CrossRef]
- Cui, G., et al., Galectin-3 knockdown increases gefitinib sensitivity to the inhibition of EGFR endocytosis in gefitinib-insensitive esophageal squamous cancer cells. Med Oncol, 2015. 32(4): p. 124. [CrossRef]
- Petty, R.D., et al., Gefitinib and EGFR Gene Copy Number Aberrations in Esophageal Cancer. J Clin Oncol, 2017. 35(20): p. 2279-2287. [CrossRef]
- Liu, W., et al., Galectin-3 regulates intracellular trafficking of EGFR through Alix and promotes keratinocyte migration. The Journal of investigative dermatology, 2012. 132(12): p. 2828-2837. [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y., et al., Gefitinib single drug in treatment of advanced esophageal cancer. J Cancer Res Ther, 2016. 12(Supplement): p. C295-c297. [CrossRef]
- Drenckhan, A., et al., Esophageal carcinoma cell line with high EGFR polysomy is responsive to gefitinib. Langenbeck's Archives of Surgery, 2014. 399(7): p. 879-888. [CrossRef]
- Huang, J., et al., Icotinib in Patients with Pretreated Advanced Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma with EGFR Overexpression or EGFR Gene Amplification: A Single-Arm, Multicenter Phase 2 Study. Journal of Thoracic Oncology, 2016. 11(6): p. 910-917. [CrossRef]
- Sun, J., et al., Icotinib inhibits the proliferation of hepatocellular carcinoma cells in vitro and in vivo dependently on EGFR activation and PDL1 expression. Onco Targets Ther, 2018. 11: p. 8227-8237. [CrossRef]
- Wang, X., et al., Predictive value of EGFR overexpression and gene amplification on icotinib efficacy in patients with advanced esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Oncotarget, 2016. 7(17): p. 24744-51. [CrossRef]
- Luo, H., et al., Icotinib With Concurrent Radiotherapy vs Radiotherapy Alone in Older Adults With Unresectable Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Phase II Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Netw Open, 2020. 3(10): p. 19440.
- Budi, H.S., et al., Human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2)-specific chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) for tumor immunotherapy; recent progress. Stem Cell Research & Therapy, 2022. 13(1): p. 40. [CrossRef]
- Won, E., Y.J. Janjigian, and D.H. Ilson, HER2 directed therapy for gastric/esophageal cancers. Curr Treat Options Oncol, 2014. 15(3): p. 395-404. [CrossRef]
- Swain, S.M., M. Shastry, and E. Hamilton, Targeting HER2-positive breast cancer: advances and future directions. Nature Reviews Drug Discovery, 2023. 22(2): p. 101-126. [CrossRef]
- Gerson, J.N., et al., Perspectives of HER2-targeting in gastric and esophageal cancer. Expert Opin Investig Drugs, 2017. 26(5): p. 531-540. [CrossRef]
- Swain, S.M., et al., Pertuzumab, trastuzumab, and docetaxel in HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer. N Engl J Med, 2015. 372(8): p. 724-34. [CrossRef]
- Won, E., Y. Janjigian, and D.J.C.T.O.i.O. Ilson, HER2 Directed Therapy for Gastric/Esophageal Cancers. 2014. 15(3): p. 395-404. [CrossRef]
- Bang, Y.J., et al., Trastuzumab in combination with chemotherapy versus chemotherapy alone for treatment of HER2-positive advanced gastric or gastro-oesophageal junction cancer (ToGA): a phase 3, open-label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet, 2010. 376(9742): p. 687-97. [CrossRef]
- Tabernero, J., et al., Pertuzumab plus trastuzumab and chemotherapy for HER2-positive metastatic gastric or gastro-oesophageal junction cancer (JACOB): final analysis of a double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled phase 3 study. Lancet Oncol, 2018. 19(10): p. 1372-1384. [CrossRef]
- Mimura, K., et al., Lapatinib inhibits receptor phosphorylation and cell growth and enhances antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity of EGFR- and HER2-overexpressing esophageal cancer cell lines. Int J Cancer, 2011. 129(10): p. 2408-16. [CrossRef]
- Shiraishi, K., et al., Lapatinib acts on gastric cancer through both antiproliferative function and augmentation of trastuzumab-mediated antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity. Gastric cancer : official journal of the International Gastric Cancer Association and the Japanese Gastric Cancer Association, 2012. 16. [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.-f., et al., Lapatinib in combination with paclitaxel plays synergistic antitumor effects on esophageal squamous cancer. Cancer Chemotherapy and Pharmacology, 2018. 82(3): p. 383-394. [CrossRef]
- Hassan, M.S., et al., Combination effect of lapatinib with foretinib in HER2 and MET co-activated experimental esophageal adenocarcinoma. Sci Rep, 2019. 9(1): p. 019-54129.
- Chai, J., M.K. Jones, and A.S. Tarnawski, Serum response factor is a critical requirement for VEGF signaling in endothelial cells and VEGF-induced angiogenesis. Faseb j, 2004. 18(11): p. 1264-6. [CrossRef]
- Meng, L., et al., Survivin is critically involved in VEGFR2 signaling-mediated esophageal cancer cell survival. Biomed Pharmacother, 2018. 107: p. 139-145. [CrossRef]
- Whittaker, S., R. Marais, and A.X. Zhu, The role of signaling pathways in the development and treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncogene, 2010. 29(36): p. 4989-5005. [CrossRef]
- Cheung, A., W. Xu, and B. Li, The potential of targeted antiangiogenesis therapies in the treatment of esophageal cancer. Gastrointestinal Cancer: Targets and Therapy, 2015. 2015. [CrossRef]
- Khan, U. and M.A. Shah, Ramucirumab for the treatment of gastric or gastro-esophageal junction cancer. Expert Opin Biol Ther, 2019. 19(11): p. 1135-1141. [CrossRef]
- Spratlin, J.L., et al., Phase I pharmacologic and biologic study of ramucirumab (IMC-1121B), a fully human immunoglobulin G1 monoclonal antibody targeting the vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2. J Clin Oncol, 2010. 28(5): p. 780-7.
- Wilke, H., et al., Ramucirumab plus paclitaxel versus placebo plus paclitaxel in patients with previously treated advanced gastric or gastro-oesophageal junction adenocarcinoma (RAINBOW): a double-blind, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol, 2014. 15(11): p. 1224-35. [CrossRef]
- Konstorum, A. and J.S. Lowengrub, Activation of the HGF/c-Met axis in the tumor microenvironment: A multispecies model. Journal of theoretical biology, 2018. 439: p. 86-99. [CrossRef]
- Boromand, N., et al., Clinical and prognostic value of the C-Met/HGF signaling pathway in cervical cancer. J Cell Physiol, 2018. 233(6): p. 4490-4496. [CrossRef]
- Granito, A., E. Guidetti, and L. Gramantieri, c-MET receptor tyrosine kinase as a molecular target in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatocell Carcinoma, 2015. 2: p. 29-38. [CrossRef]
- Arnold, L., J. Enders, and S.M. Thomas, Activated HGF-c-Met Axis in Head and Neck Cancer. Cancers (Basel), 2017. 9(12). [CrossRef]
- Stanley, A., et al., Synergistic effects of various Her inhibitors in combination with IGF-1R, C-MET and Src targeting agents in breast cancer cell lines. Sci Rep, 2017. 7(1): p. 3964. [CrossRef]
- Lam, B.Q., L. Dai, and Z. Qin, The role of HGF/c-MET signaling pathway in lymphoma. J Hematol Oncol, 2016. 9(1): p. 135. [CrossRef]
- Krause, D.S. and R.A. Van Etten, Tyrosine kinases as targets for cancer therapy. N Engl J Med, 2005. 353(2): p. 172-87. [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.M., et al., Advances in targeted therapy for esophageal cancer. Signal Transduct Target Ther, 2020. 5(1): p. 020-00323. [CrossRef]
- Van Der Steen, N., et al., Chapter 2 - Targeting the Hepatocyte Growth Factor Receptor to Overcome Resistance to Targeted Therapies, in Targeting Cell Survival Pathways to Enhance Response to Chemotherapy, D.E. Johnson, Editor 2019, Academic Press. p. 25-60.
- Shah, M., et al., METGastric: A phase III study of onartuzumab plus mFOLFOX6 in patients with metastatic HER2-negative (HER2-) and MET-positive (MET+) adenocarcinoma of the stomach or gastroesophageal junction (GEC). J Clin Oncol, 2015. 33. [CrossRef]
- Catenacci, D.V.T., et al., Rilotumumab plus epirubicin, cisplatin, and capecitabine as first-line therapy in advanced MET-positive gastric or gastro-oesophageal junction cancer (RILOMET-1): a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol, 2017. 18(11): p. 1467-1482. [CrossRef]
- Pópulo, H., J.M. Lopes, and P. Soares, The mTOR signalling pathway in human cancer. International journal of molecular sciences, 2012. 13(2): p. 1886-1918. [CrossRef]
- Hirashima, K., et al., Phosphorylated mTOR Expression is Associated with Poor Prognosis for Patients with Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Annals of Surgical Oncology, 2010. 17(9): p. 2486-2493. [CrossRef]
- Harrison, D.E., et al., Rapamycin fed late in life extends lifespan in genetically heterogeneous mice. Nature, 2009. 460(7253): p. 392-395. [CrossRef]
- Hasskarl, J., Everolimus. Recent Results Cancer Res, 2018. 211: p. 101-123.
- Huang, Z.-H., et al., Cetuximab for esophageal cancer: an updated meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. BMC Cancer, 2018. 18. [CrossRef]
- Yang, X., et al., Radiotherapy combined with nimotuzumab for elderly esophageal cancer patients: A phase II clinical trial. Chinese journal of cancer research = Chung-kuo yen cheng yen chiu, 2021. 33(1): p. 53-60. [CrossRef]
- Guan, Y.-S., Q. He, and M. Li, Icotinib: Activity and clinical application in Chinese patients with lung cancer. Expert opinion on pharmacotherapy, 2014. 15. [CrossRef]
- Soularue, É., et al., Efficacy and safety of trastuzumab in combination with oxaliplatin and fluorouracil-based chemotherapy for patients with HER2-positive metastatic gastric and gastro-oesophageal junction adenocarcinoma patients: A retrospective study. Bulletin du cancer, 2015. 102. [CrossRef]
- Nolting, M., T. Schneider-Merck, and M. Trepel, Lapatinib. Recent Results Cancer Res, 2014. 201: p. 125-43.
- Kawai, S., et al., Retrospective observational study of salvage line ramucirumab monotherapy for patients with advanced gastric cancer. BMC Cancer, 2020. 20. [CrossRef]
- Han, H.S., et al., Ramucirumab plus paclitaxel as second-line treatment in patients with advanced gastric or gastroesophageal junction adenocarcinoma: a nationwide real-world outcomes in Korea study (KCSG-ST19-16). Ther Adv Med Oncol, 2021. 13: p. 17588359211042812. [CrossRef]
- Ling, Y., et al., Endostar, a novel recombinant human endostatin, exerts antiangiogenic effect via blocking VEGF-induced tyrosine phosphorylation of KDR/Flk-1 of endothelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2007. 361: p. 79-84. [CrossRef]
- Li, Y., et al., Efficacy and Safety of Endostar Combined with Chemotherapy in Patients with Advanced Solid Tumors. Asian Pacific journal of cancer prevention : APJCP, 2010. 11: p. 1119-23.
- Adnane, L., et al., Sorafenib (BAY 43-9006, Nexavar), a dual-action inhibitor that targets RAF/MEK/ERK pathway in tumor cells and tyrosine kinases VEGFR/PDGFR in tumor vasculature. Methods Enzymol, 2006. 407: p. 597-612.
- Janjigian, Y., et al., Phase II Trial of Sorafenib in Patients with Chemotherapy Refractory Metastatic Esophageal and Gastroesophageal (GE) Junction Cancer. PloS one, 2015. 10(8):e0134731. [CrossRef]
- Roviello, G., et al., Apatinib: A novel receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor for the treatment of gastric cancer. Cancer Lett, 2016. 372(2): p. 187-91. [CrossRef]
- Hu, L., et al., Apatinib enhances the radiosensitivity of the esophageal cancer cell line KYSE-150 by inducing apoptosis and cell cycle redistribution. Oncol Lett, 2019. 17(2): p. 1609-1616. [CrossRef]
- Metibemu, D.S., et al., Exploring receptor tyrosine kinases-inhibitors in Cancer treatments. Egyptian Journal of Medical Human Genetics, 2019. 20(1): p. 35. [CrossRef]
- Huang, J., et al., Anlotinib for previously treated advanced or metastatic esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: A double-blind randomized phase 2 trial. Cancer medicine, 2021. 10. [CrossRef]
- Shen, G., et al., Anlotinib: a novel multi-targeting tyrosine kinase inhibitor in clinical development. Journal of Hematology & Oncology, 2018. 11(1): p. 120. [CrossRef]
- Paplomata, E., A. Zelnak, and R. O'Regan, Everolimus: side effect profile and management of toxicities in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat, 2013. 140(3): p. 453-62. [CrossRef]
- Xie, J., X. Wang, and C.G. Proud, mTOR inhibitors in cancer therapy. F1000Research, 2016. 5: p. F1000 Faculty Rev-2078. [CrossRef]
- Meacham, C.E. and S.J. Morrison, Tumour heterogeneity and cancer cell plasticity. Nature, 2013. 501(7467): p. 328-337. [CrossRef]
- Dinh, H.Q., et al., Integrated single-cell transcriptome analysis reveals heterogeneity of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma microenvironment. Nature Communications, 2021. 12(1): p. 7335. [CrossRef]
- Alfarouk, K.O., et al., Resistance to cancer chemotherapy: failure in drug response from ADME to P-gp. Cancer Cell International, 2015. 15(1): p. 71. [CrossRef]
- Luan, S., et al., Advances in Drug Resistance of Esophageal Cancer: From the Perspective of Tumor Microenvironment. 2021. 9(623). [CrossRef]
- Yang, W., et al., Molecular mechanisms and clinical implications of miRNAs in drug resistance of esophageal cancer. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2017. 11(12): p. 1151-1163. [CrossRef]
- Hanahan, D. and R.A. Weinberg, Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell, 2011. 144(5): p. 646-74. [CrossRef]
- Adhikari, S., et al., The paradigm of drug resistance in cancer: an epigenetic perspective. Biosci Rep, 2022. 42(4). [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z., et al., Cancer stem cells. The International Journal of Biochemistry & Cell Biology, 2012. 44(12): p. 2144-2151.
- Walcher, L., et al., Cancer Stem Cells—Origins and Biomarkers: Perspectives for Targeted Personalized Therapies. 2020. 11(1280). 1280. [CrossRef]
- Batlle, E. and H. Clevers, Cancer stem cells revisited. Nat Med, 2017. 23(10): p. 1124-1134. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J., Cancer stem cells and chemoresistance: The smartest survives the raid. Pharmacol Ther, 2016. 160: p. 145-58. [CrossRef]
- Luan, S., et al., Advances in Drug Resistance of Esophageal Cancer: From the Perspective of Tumor Microenvironment. Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology, 2021. 9. [CrossRef]
- Li, H., et al., The PTEN/PI3K/Akt pathway regulates stem-like cells in primary esophageal carcinoma cells. Cancer biology & therapy, 2011. 11(11): p. 950-958. [CrossRef]
- Tong, D., et al., p75 neurotrophin receptor: A potential surface marker of tongue squamous cell carcinoma stem cells. Molecular medicine reports, 2017. 15(5): p. 2521-2529. [CrossRef]
- Galluzzi, L., et al., Molecular mechanisms of cisplatin resistance. Oncogene, 2012. 31(15): p. 1869-1883. [CrossRef]
- Sahai, E., et al., A framework for advancing our understanding of cancer-associated fibroblasts. Nature Reviews Cancer, 2020. 20(3): p. 174-186. [CrossRef]
- Hanahan, D. and Robert A. Weinberg, Hallmarks of Cancer: The Next Generation. Cell, 2011. 144(5): p. 646-674. [CrossRef]
- Kalluri, R., The biology and function of fibroblasts in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer, 2016. 16(9): p. 582-98. [CrossRef]
- Tong, Y., et al., Tumor-Secreted Exosomal lncRNA POU3F3 Promotes Cisplatin Resistance in ESCC by Inducing Fibroblast Differentiation into CAFs. Molecular therapy oncolytics, 2020. 18: p. 1-13. [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, K., et al., miR-27 is associated with chemoresistance in esophageal cancer through transformation of normal fibroblasts to cancer-associated fibroblasts. Carcinogenesis, 2015. 36(8): p. 894-903. [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Y., et al., IL6 derived from cancer-associated fibroblasts promotes chemoresistance via CXCR7 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Oncogene, 2018. 37(7): p. 873-883. [CrossRef]
- Verma, H.K., G. Falco, and L.V.K.S. Bhaskar, Molecular Signaling Pathways Involved in Gastric Cancer Chemoresistance, in Theranostics Approaches to Gastric and Colon Cancer, G.S.R. Raju and L.V.K.S. Bhaskar, Editors. 2020, Springer Singapore: Singapore. p. 117-134. [CrossRef]
- Juneja, V.R., et al., PD-L1 on tumor cells is sufficient for immune evasion in immunogenic tumors and inhibits CD8 T cell cytotoxicity. J Exp Med, 2017. 214(4): p. 895-904. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J. and J. Huang, Breast cancer immunology and immunotherapy: targeting the programmed cell death protein-1/programmed cell death protein ligand-1. Chin Med J (Engl), 2020. 133(7): p. 853-862.
- Huang, T.-X. and L. Fu, The immune landscape of esophageal cancer. Cancer communications (London, England), 2019. 39(1): p. 79-79. [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y. and Z.-Y.J.F.i.p. Ding, PD-1 inhibitors in the advanced esophageal cancer. 2019. 10: p. 1418. [CrossRef]
- Dhupar, R., et al., Targeting Immune Checkpoints in Esophageal Cancer: A High Mutational Load Tumor. Ann Thorac Surg, 2017. 103(4): p. 1340-1349. [CrossRef]
- Yagi, T., et al., Tumour-associated macrophages are associated with poor prognosis and programmed death ligand 1 expression in oesophageal cancer. Eur J Cancer, 2019. 111: p. 38-49. [CrossRef]
- Däster, S., et al., Low expression of programmed death 1 (PD-1), PD-1 Ligand 1 (PD-L1), and Low CD8+ T Lymphocyte infiltration identify a subgroup of patients with gastric and esophageal adenocarcinoma with severe prognosis. 2020. 7: p. 144. [CrossRef]
- Bielenberg, D.R. and B.R.J.C.J. Zetter, The contribution of angiogenesis to the process of metastasis. 2015. 21(4): p. 267. [CrossRef]
- Nisar, S., et al., Exploring dysregulated signaling pathways in cancer. 2020. 26(4): p. 429-445. [CrossRef]
- Leu, C.-M., et al., Interleukin-6 acts as an antiapoptotic factor in human esophageal carcinoma cells through the activation of both STAT3 and mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways. 2003. 22(49): p. 7809-7818. [CrossRef]
- Ebbing, E.A., et al., Stromal-derived interleukin 6 drives epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and therapy resistance in esophageal adenocarcinoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2019. 116(6): p. 2237-2242. [CrossRef]
- Sugimura, K., et al., Let-7 expression is a significant determinant of response to chemotherapy through the regulation of IL-6/STAT3 pathway in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res, 2012. 18(18): p. 5144-53.
- Hatata, T., et al., Immunohistochemical study of nuclear factor-κB expression in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: prognostic significance and sensitivity to treatment with 5-FU. 2012. 25(8): p. 716-722.
- Chen, S., et al., IL-1RA suppresses esophageal cancer cell growth by blocking IL-1α. 2019. 33(6): p. e22903.
- Muz, B., et al., The role of hypoxia in cancer progression, angiogenesis, metastasis, and resistance to therapy. Hypoxia (Auckland, N.Z.), 2015. 3: p. 83-92. [CrossRef]
- Brown, A., S. Kumar, and P.B. Tchounwou, Cisplatin-Based Chemotherapy of Human Cancers. J Cancer Sci Ther, 2019. 11(4).
- Kimura, S., et al., Expression of hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1alpha is associated with vascular endothelial growth factor expression and tumour angiogenesis in human oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Eur J Cancer, 2004. 40(12): p. 1904-12. [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.J., et al., Hypoxia induces chemoresistance of esophageal cancer cells to cisplatin through regulating the lncRNA-EMS/miR-758-3p/WTAP axis. Aging (Albany NY), 2021. 13(13): p. 17155-17176.
- Li, B., et al., Id1-induced IGF-II and its autocrine/endocrine promotion of esophageal cancer progression and chemoresistance--implications for IGF-II and IGF-IR-targeted therapy. Clin Cancer Res, 2014. 20(10): p. 2651-62.
- Chan, D., et al., Expression of Insulin-Like Growth Factor Binding Protein-5 (IGFBP5) Reverses Cisplatin-Resistance in Esophageal Carcinoma. Cells, 2018. 7(10). [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y., et al., Resistance to cetuximab in EGFR-overexpressing esophageal squamous cell carcinoma xenografts due to FGFR2 amplification and overexpression. J Pharmacol Sci, 2014. 126(1): p. 77-83. [CrossRef]
- Saito, S., et al., The role of HGF/MET and FGF/FGFR in fibroblast-derived growth stimulation and lapatinib-resistance of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. 2015. 15(1): p. 1-12. [CrossRef]
| Drugs Name | Targeting Pathway | Mode of Action | Findings | Side Effects | Reference | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cetuximab | EGFR | Anti EGFR monoclonal antibody | Effective in combination with chemotherapy, Increase survival rate in resectable ESCC patient | Hypomagnesamia | [31,80] | |
| Nimotazumab | EGFR | Anti EGFR monoclonal antibody | Nimotazumab + radiotherapy= used in phage I clinical trial,Stop G2 phasr of ESCC cell cycle | esophagitis, pneumonitis, leukopenia, gastrointestinal reaction, thrombocytopenia, radiothermitis and fever | [36,81] | |
| Gefinitib | EGFR | Anti EGFR-RTK inhibitor | Gefinitib + 5-FU= increase survival rate of advance ESCC patient | Dry skin, Itching, rash, acne, mouth sores, and weakness,diarrhoea skin toxicity,fatigue | [40] | |
| Icotinib | EGFR | Anti EGFR-RTK inhibitor | Rash and diarrhea | [42,82] | ||
| Transtuzumab | HER2 | Monoclonal anti HER2 antibody | used in combination with cisplatin + fluopyrimidine (either capecitabine or 5-fluorouracil) for patient with HER2-positive metastatic gastric or GE adenocarcinoma | Fever and chills, cough,and.headache | [47,83] | |
| Lapatinib | Dual RTK inhibitor. Bind to ATP binding site and inhibit kinase activity | Lapatinib + paclitaxel = supress cell prlifetation and decrease ESCC cell migration,invasion | Face redness, dizziness, headache, shortness of breath, and anxiety | [56,84] | ||
| Ramucirumab | VEGF | Monoclonal antibody,block binding of VEGF to VEGFR | Ramucirumab + paclitaxel = used in 2nd line treatment of advanced GEJ adenocarcinoma | Hypertension, thromboembolism, rash, diarrhoea, and myelosuppression | [85,86] | |
| Endastar | VEGF | Supress the signaling of VEGFR and inhibit endothelial growth and migration | Endostar in combination with chemotherapy decline tumour weight | Nausea, vomiting, fever etc. | [87,88] | |
| sarofenib | VEGF | Inhibit VEGFR2 | Reduce development of EAC and GEJ in phase II clinical trial | fatigue, weakness, redness of the skin, hair loss, itching, dry or peeling skin, and a lack of appetite etc. | [89,90] | |
| Apatinib | VEGF | Inhibit RTK-VEGFR2 receptor | Having anti esohageal cancer effect | Diarrhea ,nausea, vomiting, dry skin etc | [91,92] | |
| Anlotinib | VEGF | Inhibit RTK-VEGFR2/3 receptor | Increase disease controle rate in pretreated advanced ESCC patients | thrombocytopenia and neutropenia,hypercholesterolemia, dermal toxicity hypertriglyceridemia | [93,94,95] | |
| Rilotumumab | HGF-c-MET | Inhibit interaction of HGF with c-MET | rilotumumab cant not effectively treat the pateients | Nausea, vomiting, fever etc. | [75] | |
| Obinautuzumab | HGF-c-MET | Block MET from binding to HGF | Obinutuzumab can not improve the patient survival rate | decrease in the number of WBC and platelets cause nfection and bleeding. Fever; Tiredness and weakness, headache; Hair loss | [22] | |
| Rapamysin and Everolimuzs | m-TOR | Inhibit m-TOR | Decrease cell proliferation and grwth | Stomatitis, rash, tiredness, hyperglycemia, hyperlipidemia,ect.. | [96,97] | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





