Submitted:
21 June 2023
Posted:
21 June 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
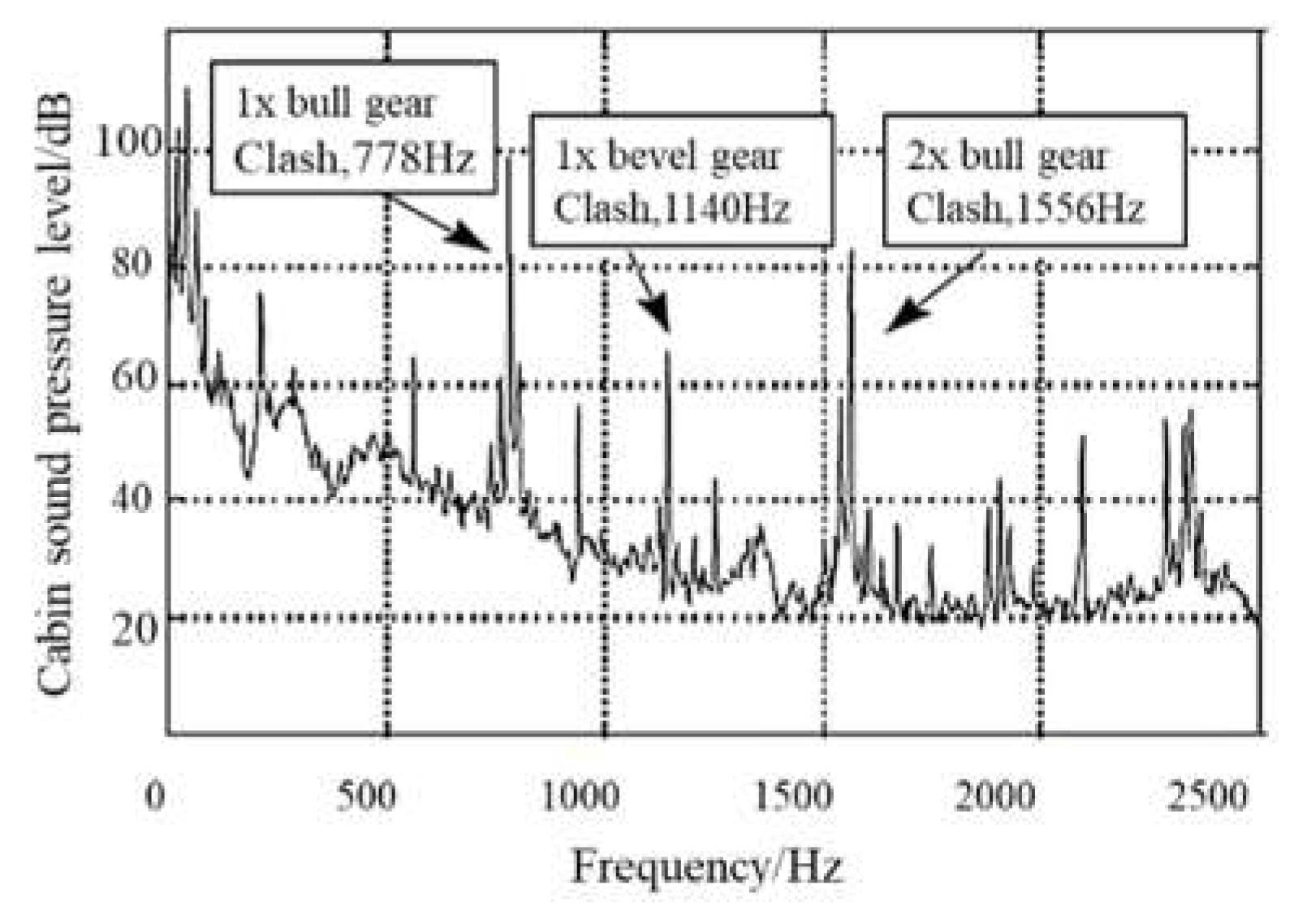
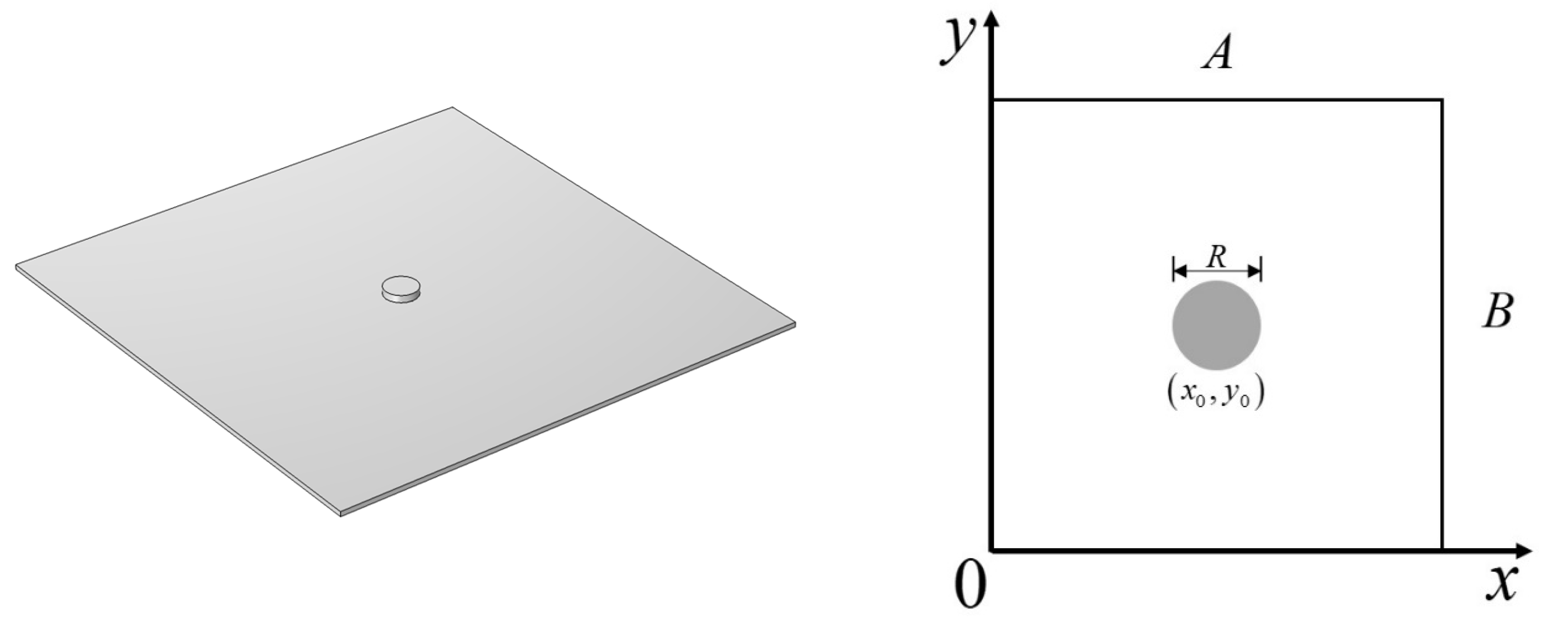
2.1. Mathematical model of MPP
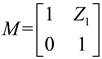
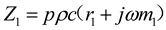
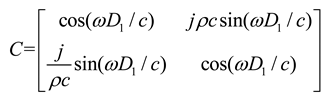
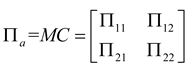
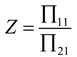
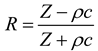
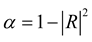
2.2. Mathematical model of MPP+Porous
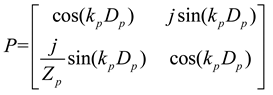
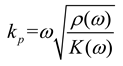
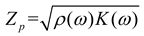
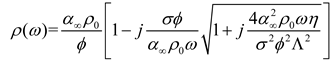

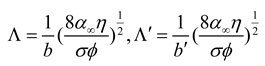

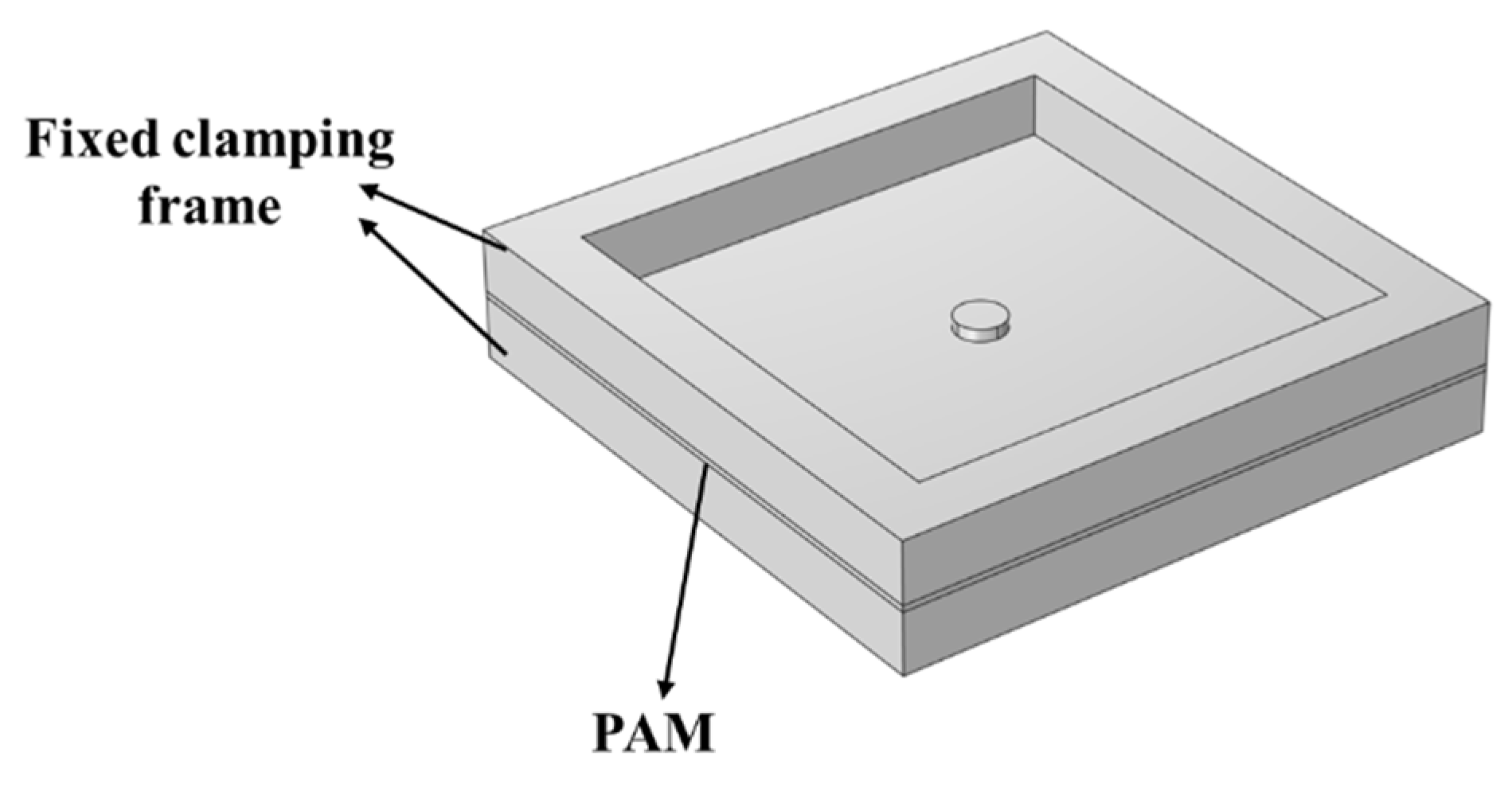
2.3. Mathematical model of MPP+PAM
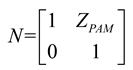
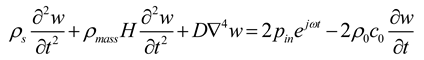
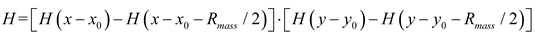
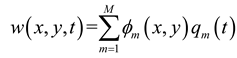
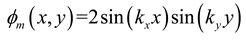
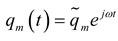

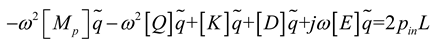
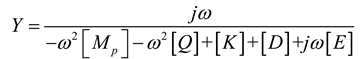
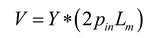
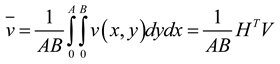
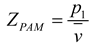
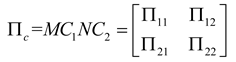
3. Simulation
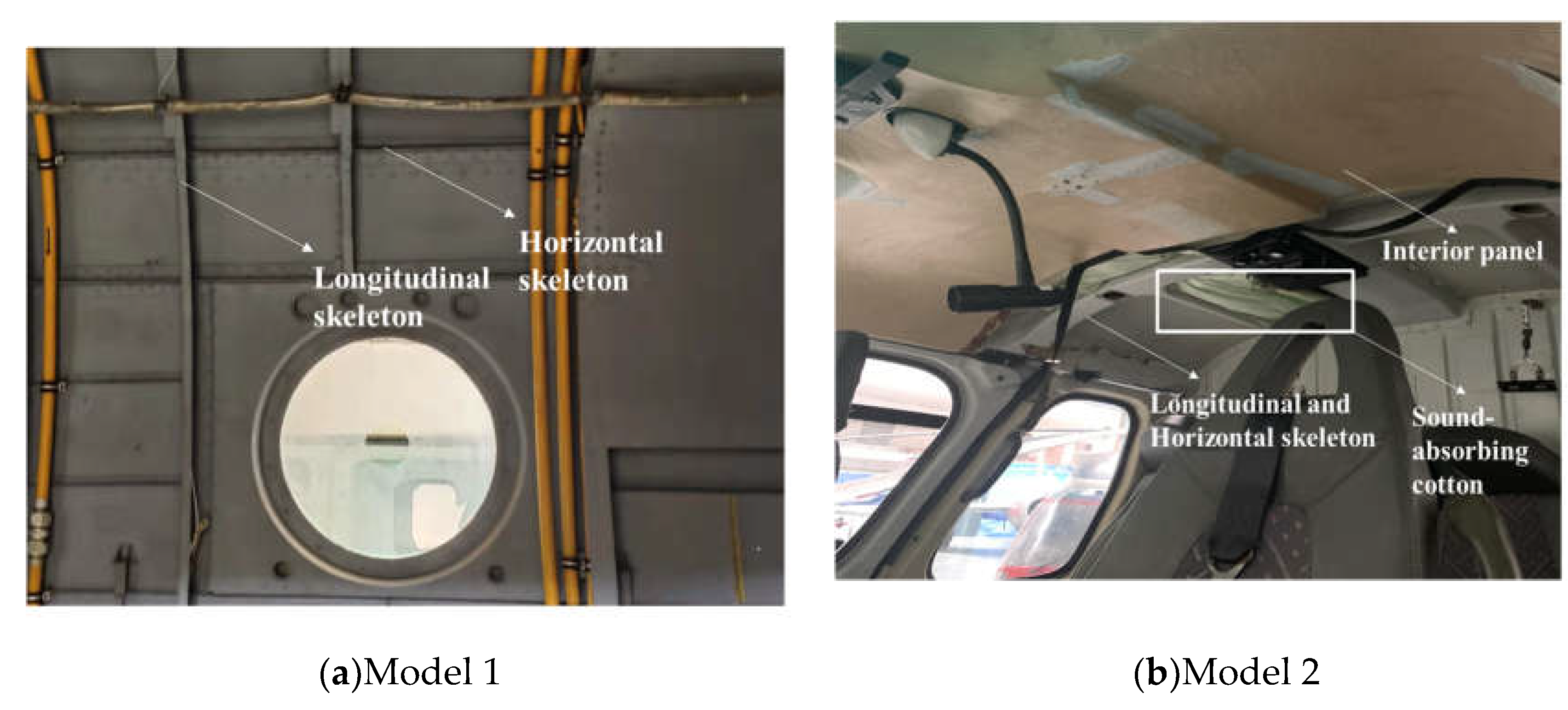
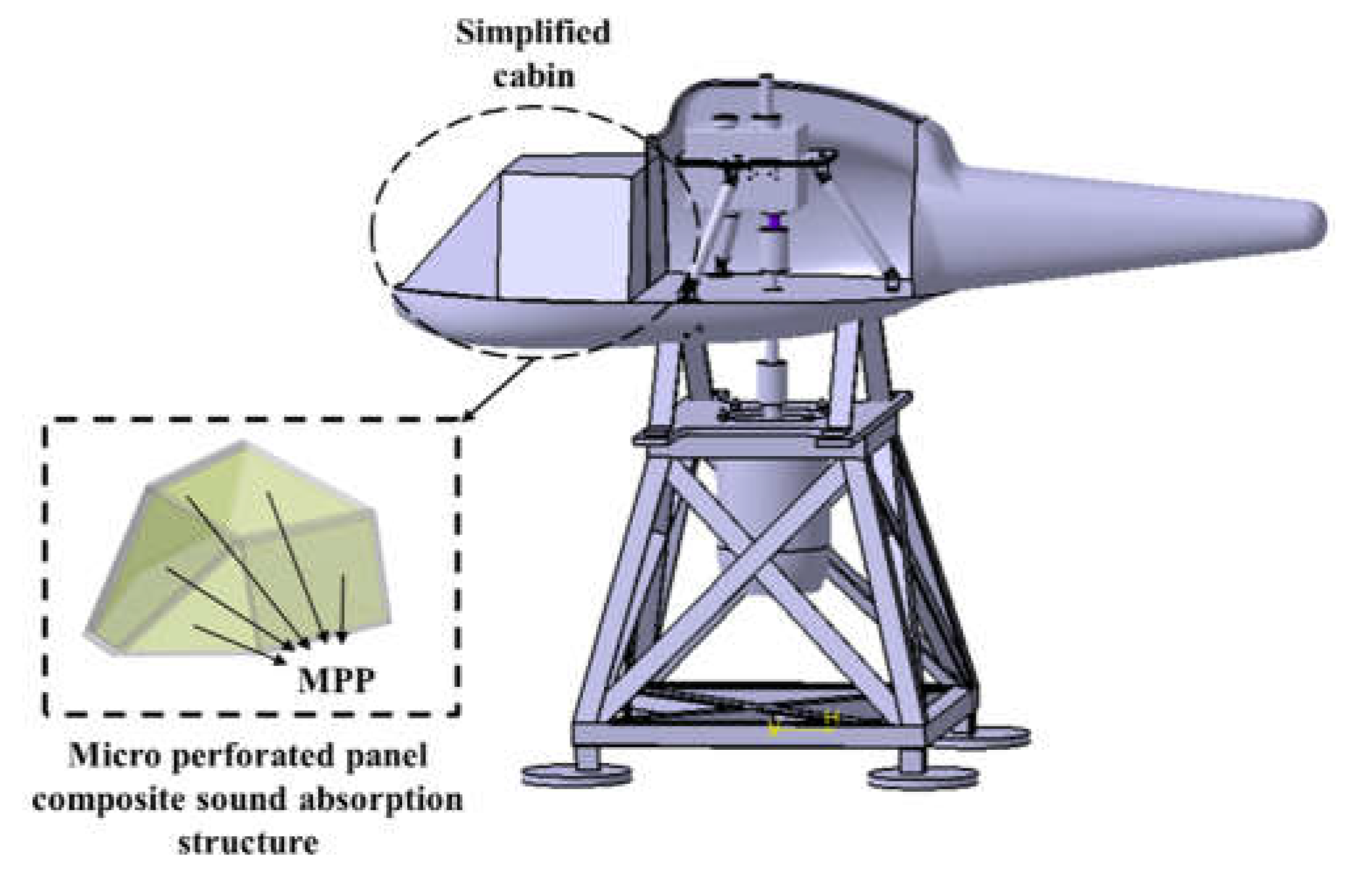
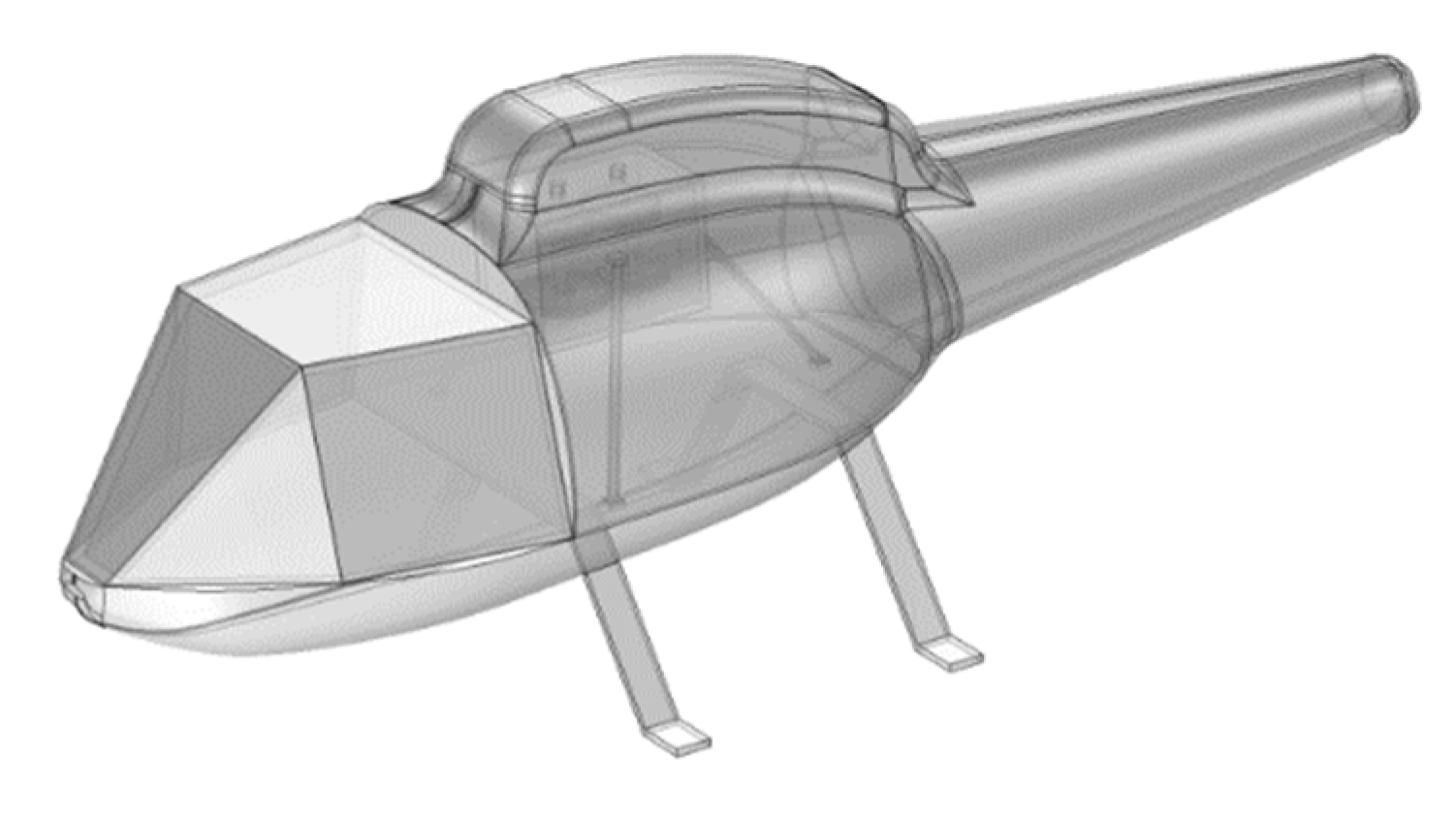
3.1. Simulation object
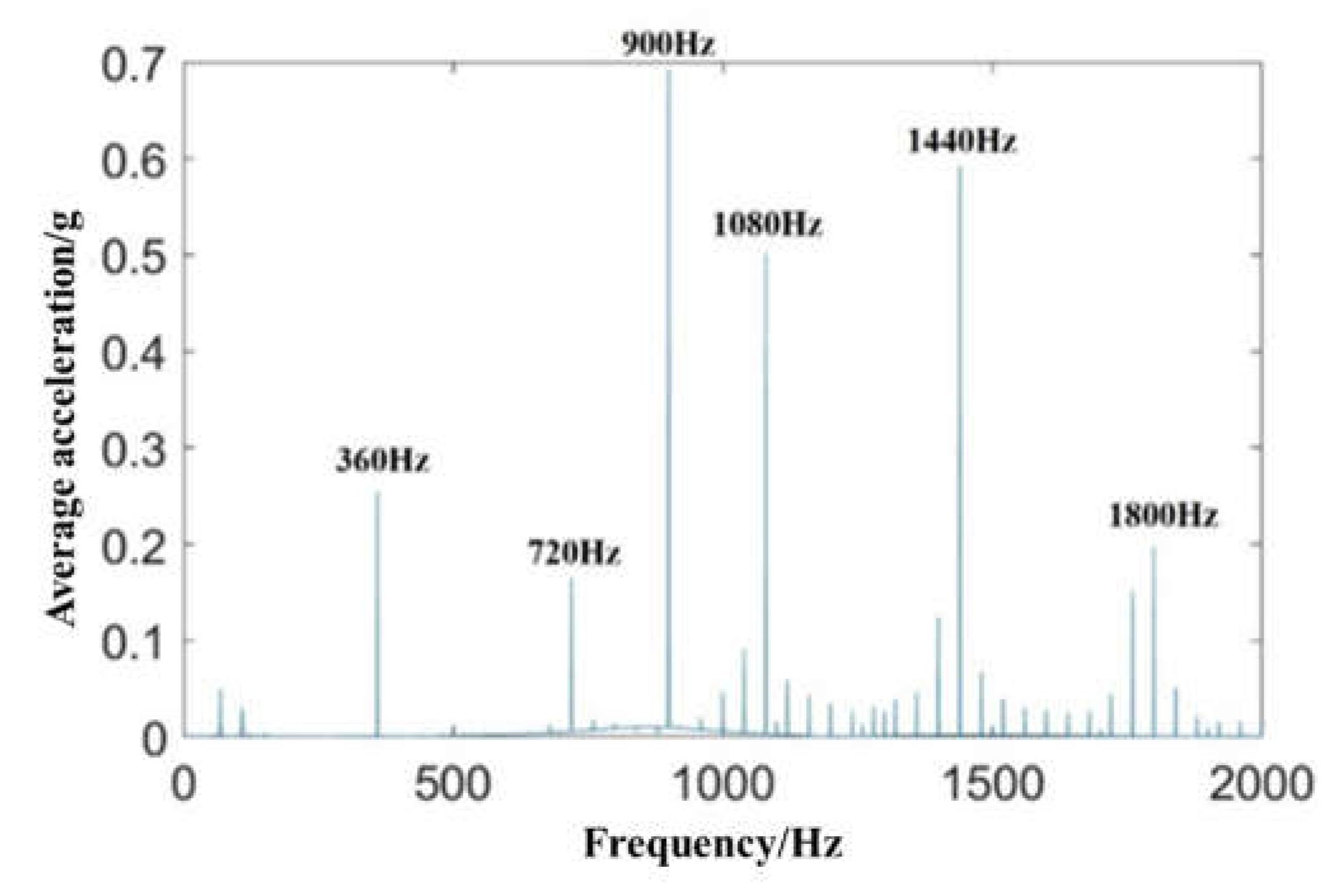
3.2. Main reducer vibration source simulation
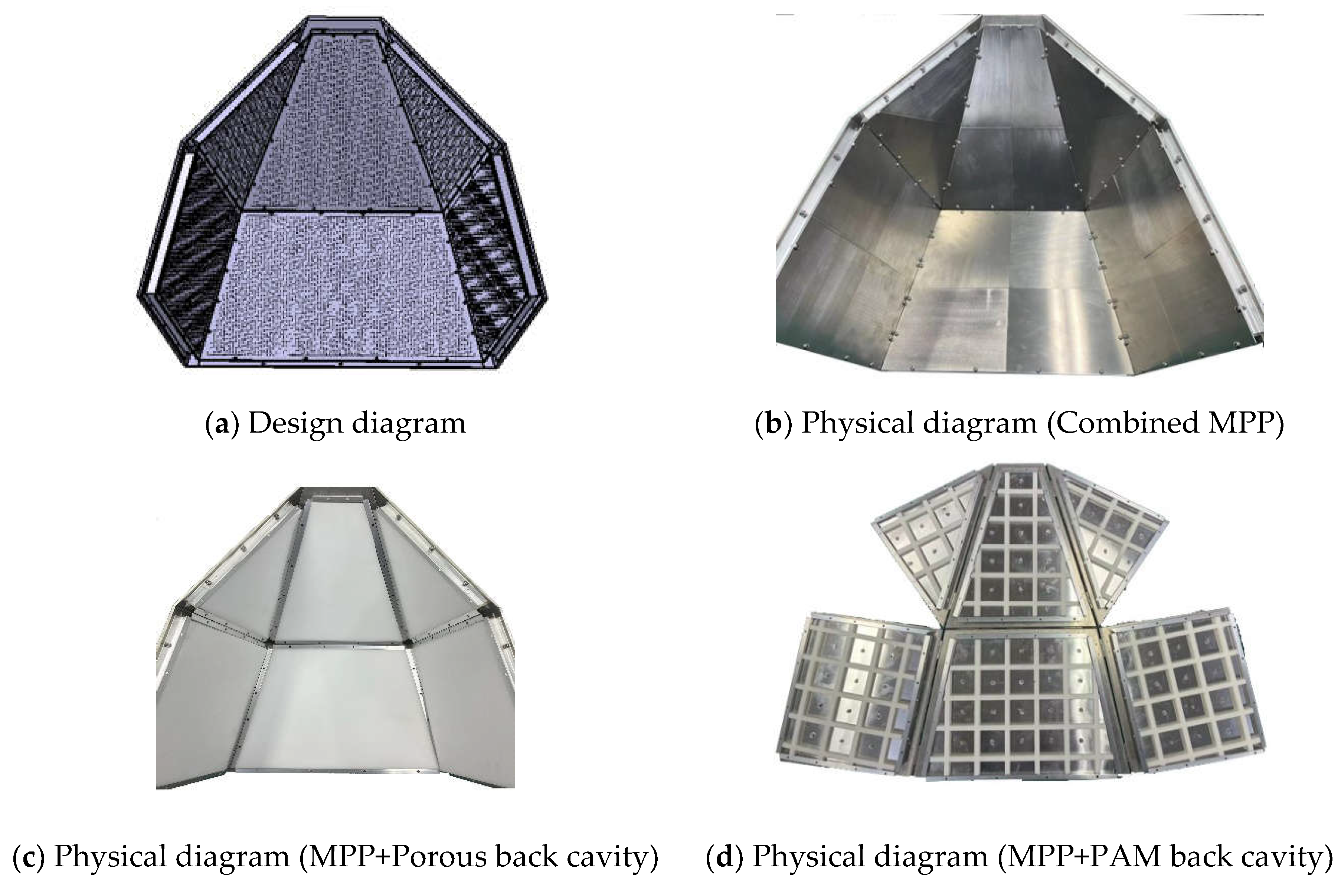
3.3. Design parameters
3.4. Model cabin sound field simulation
4. Experiment
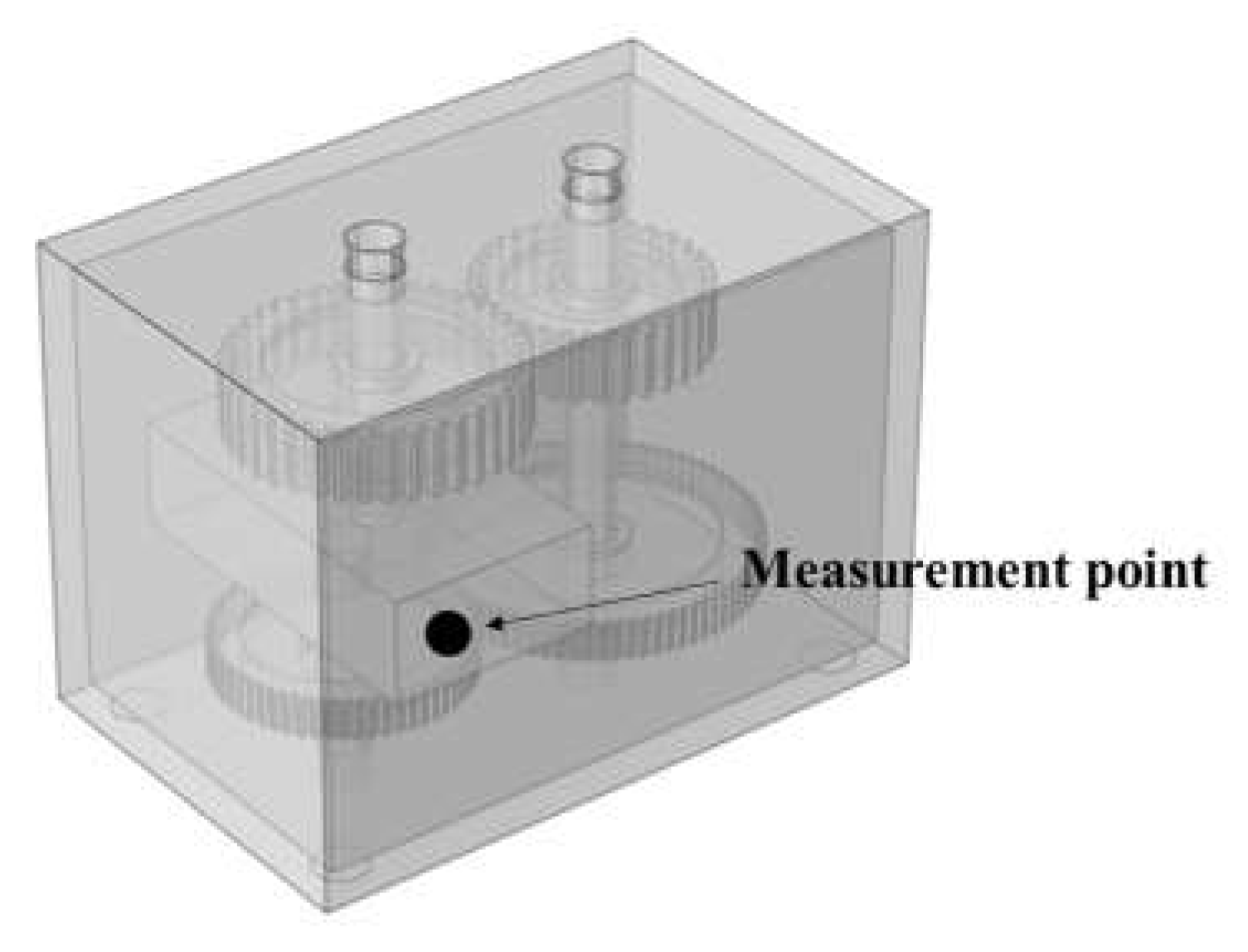
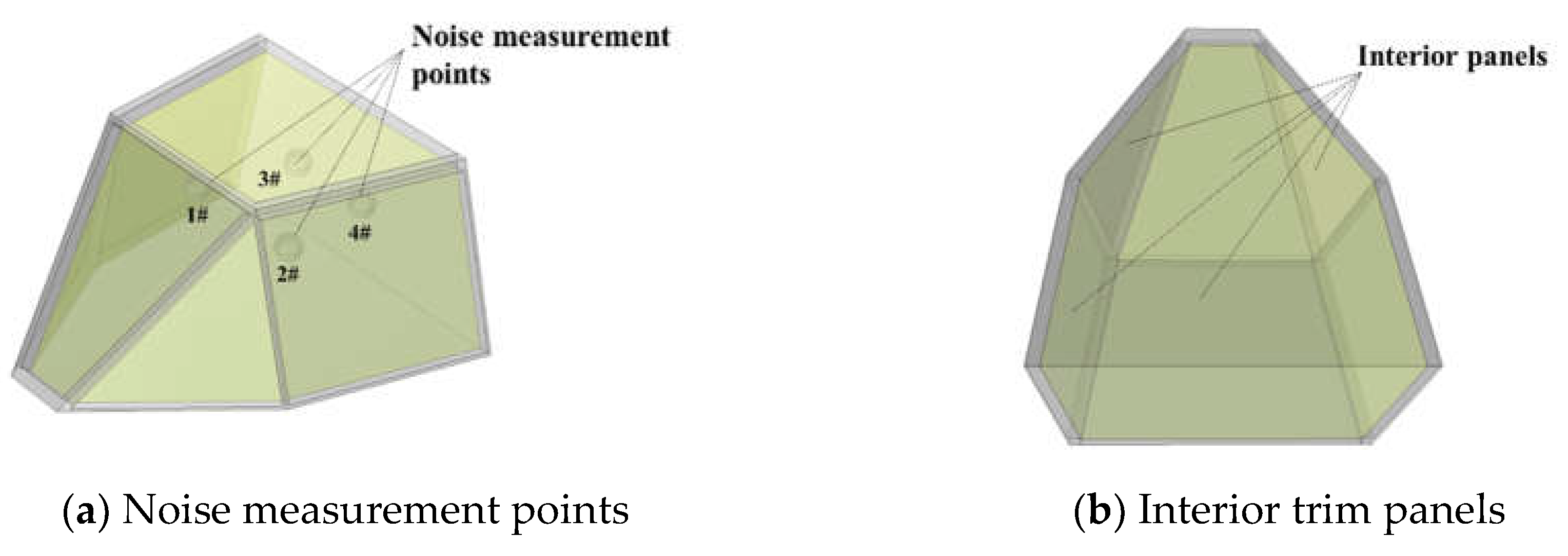
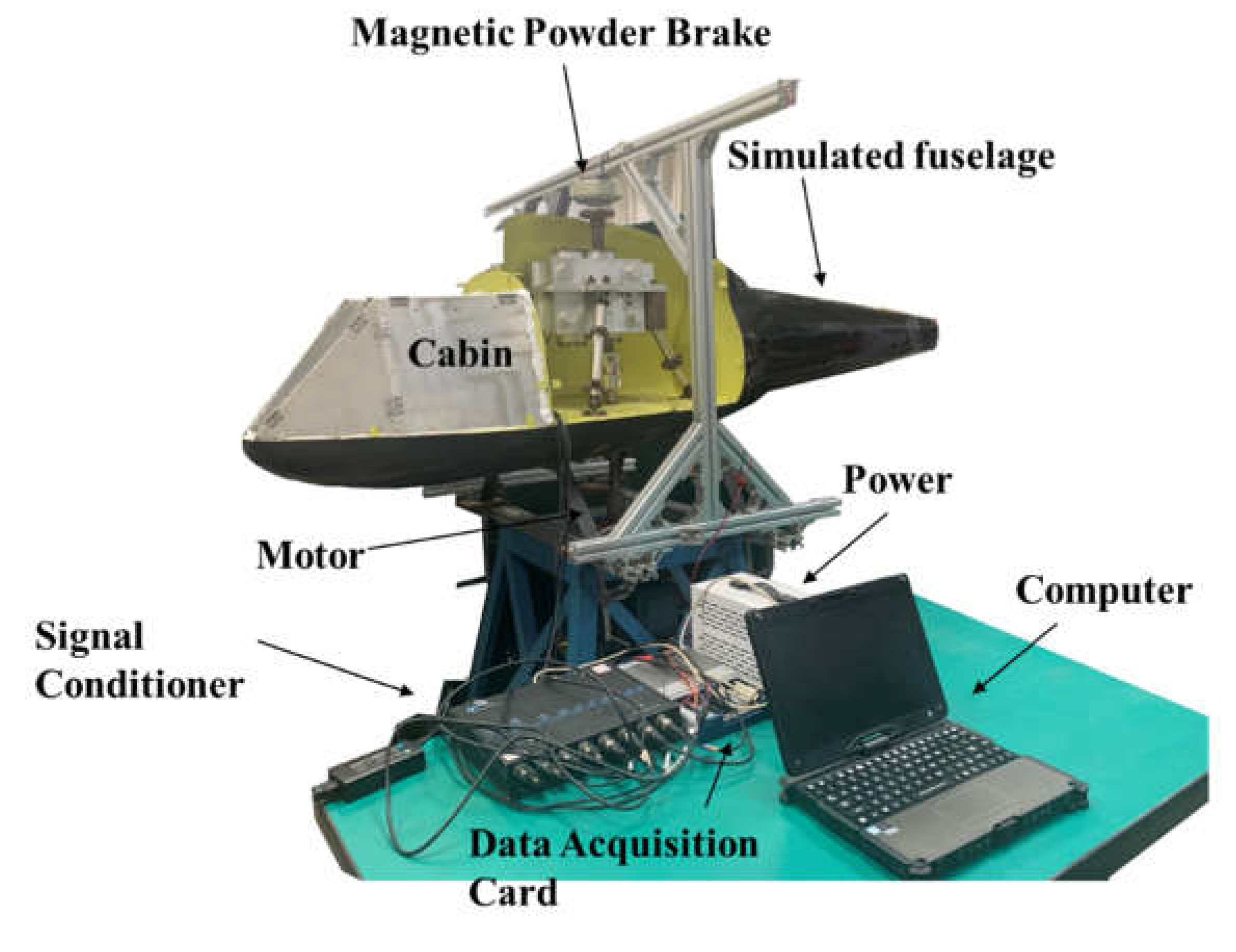
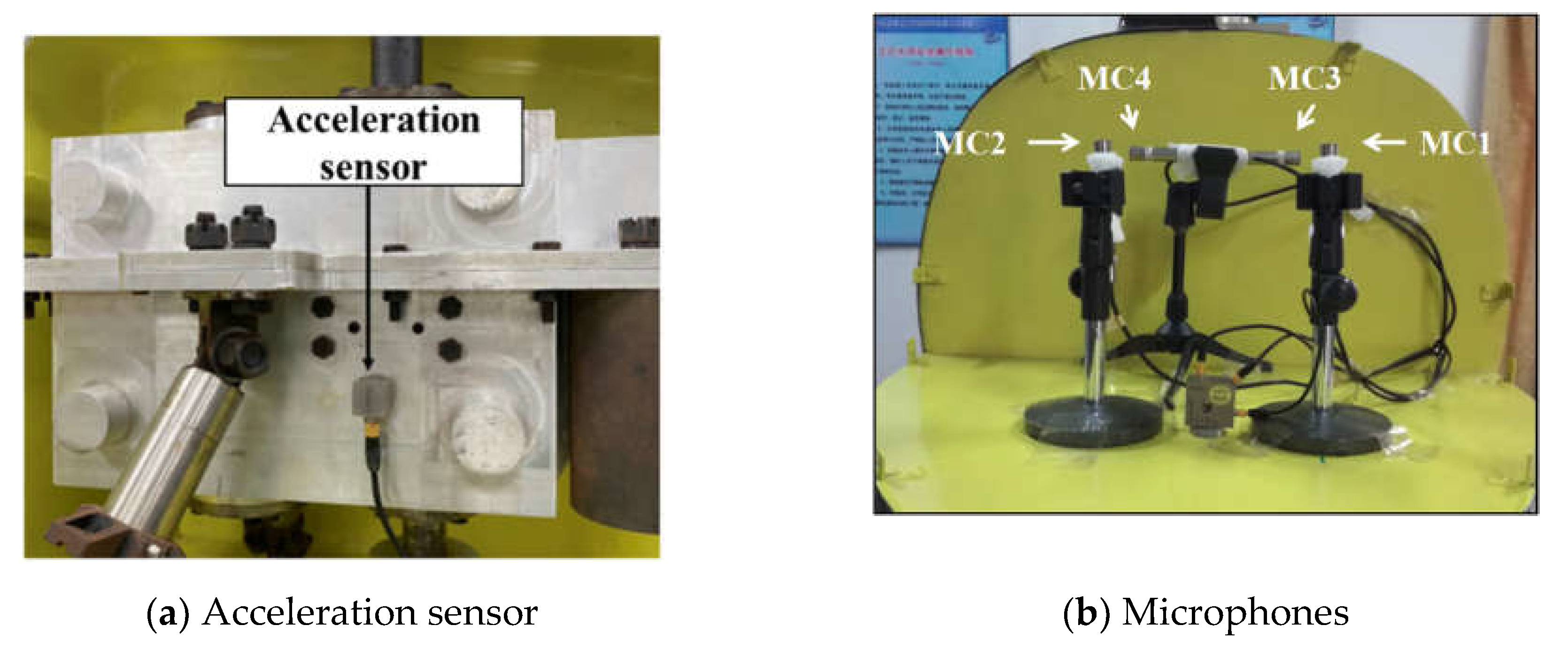
4.1. Test system
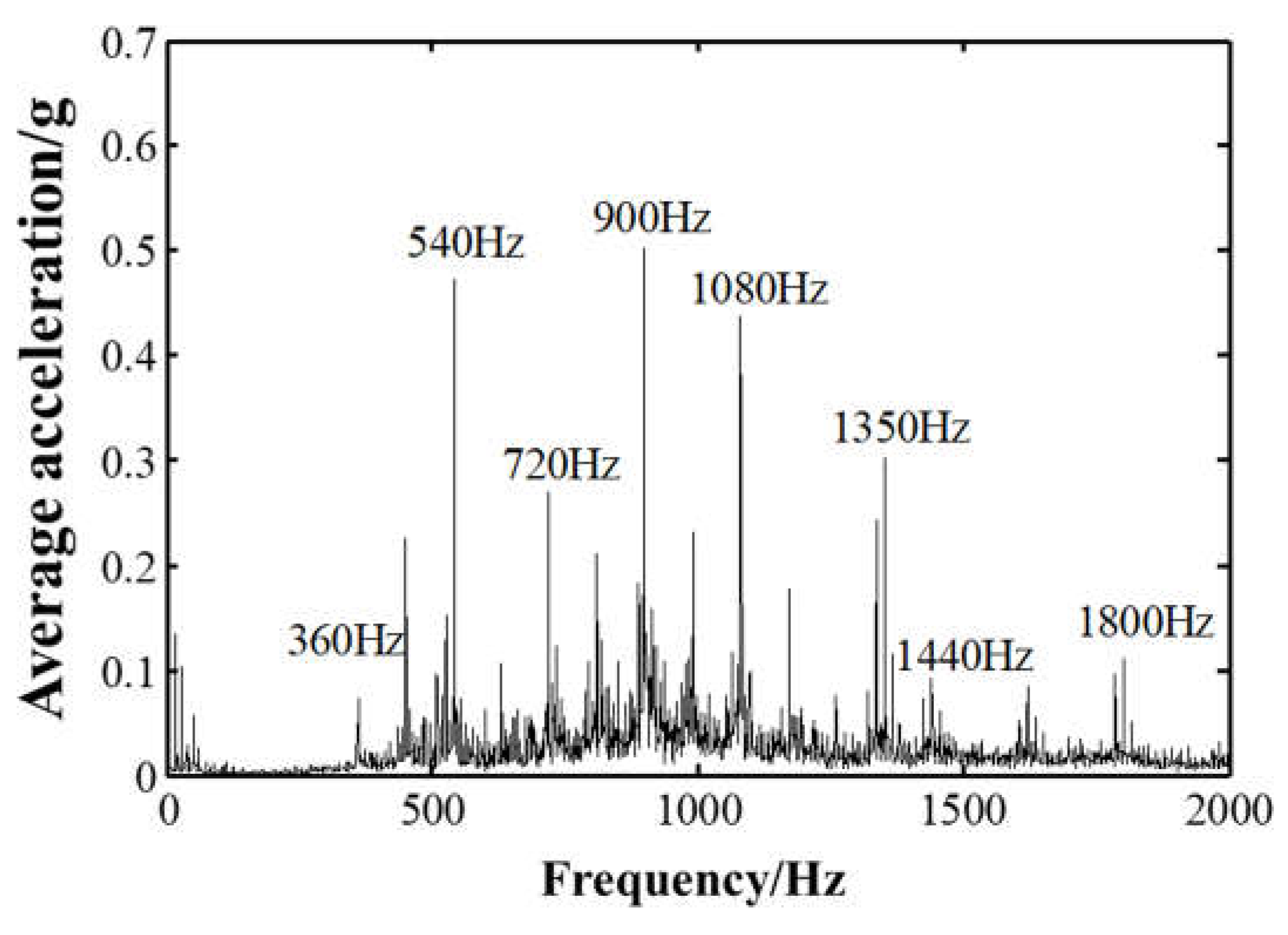
4.2. Vibration level test results
4.3. Cabin noisel test results
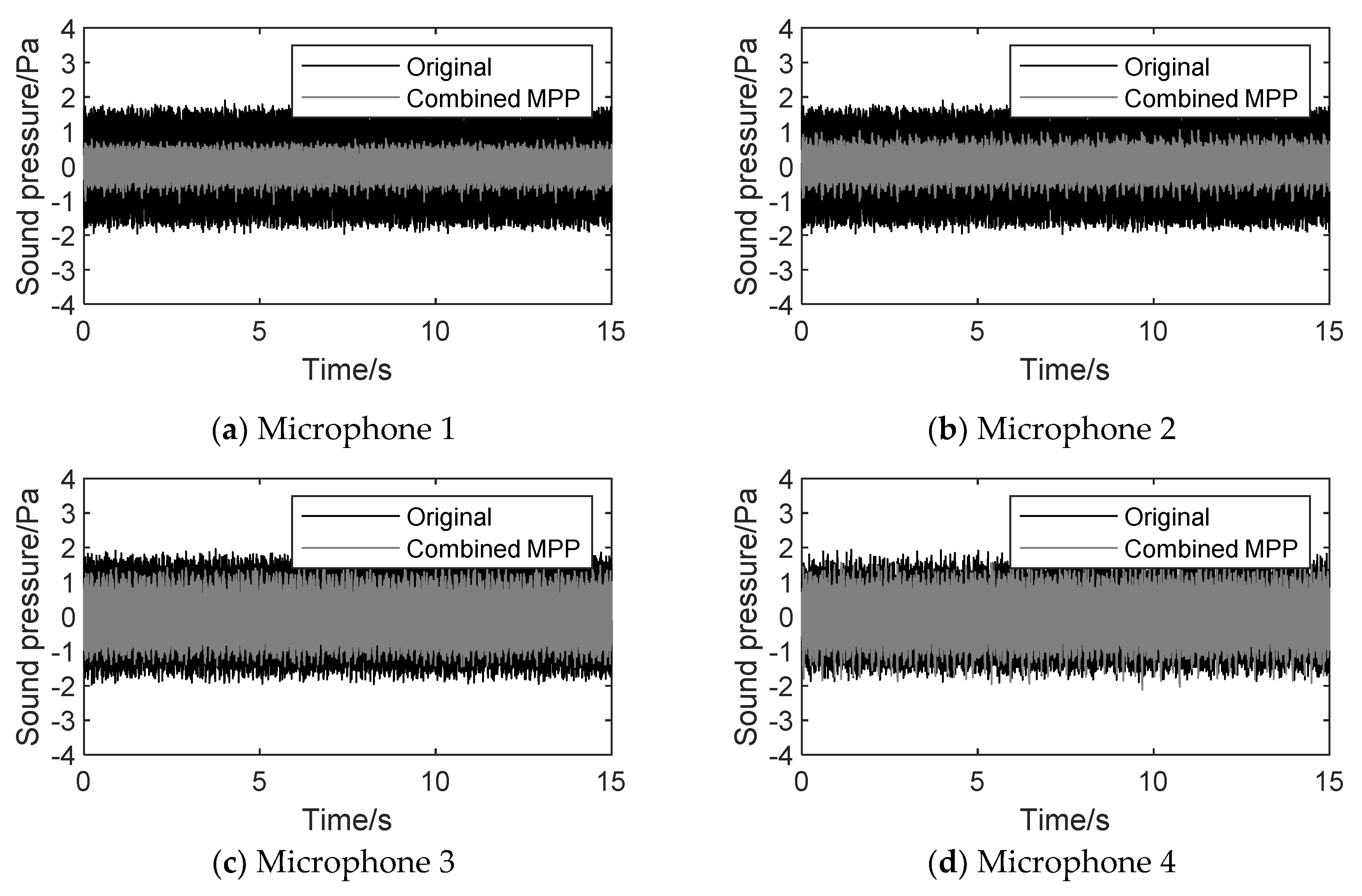
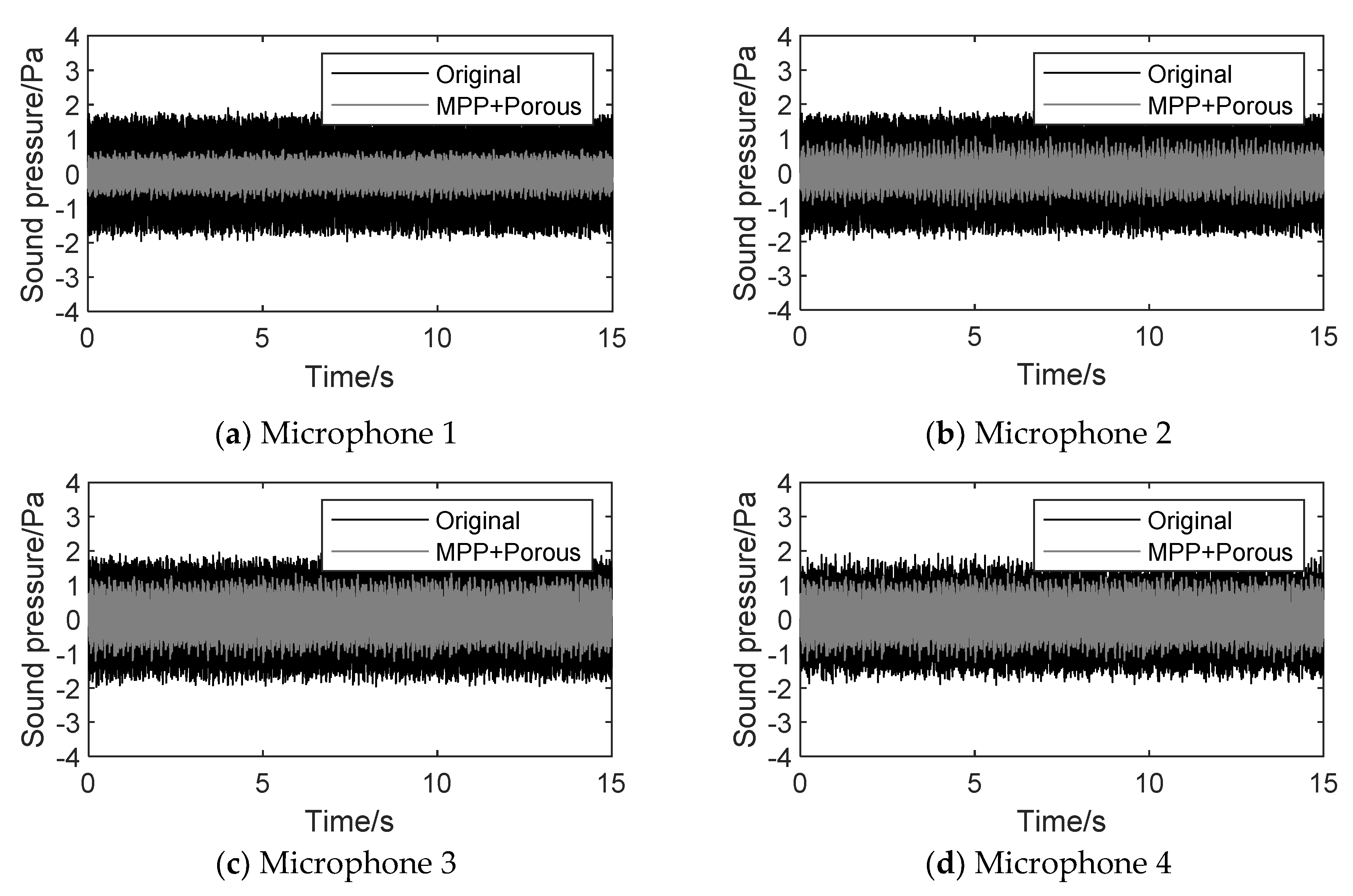
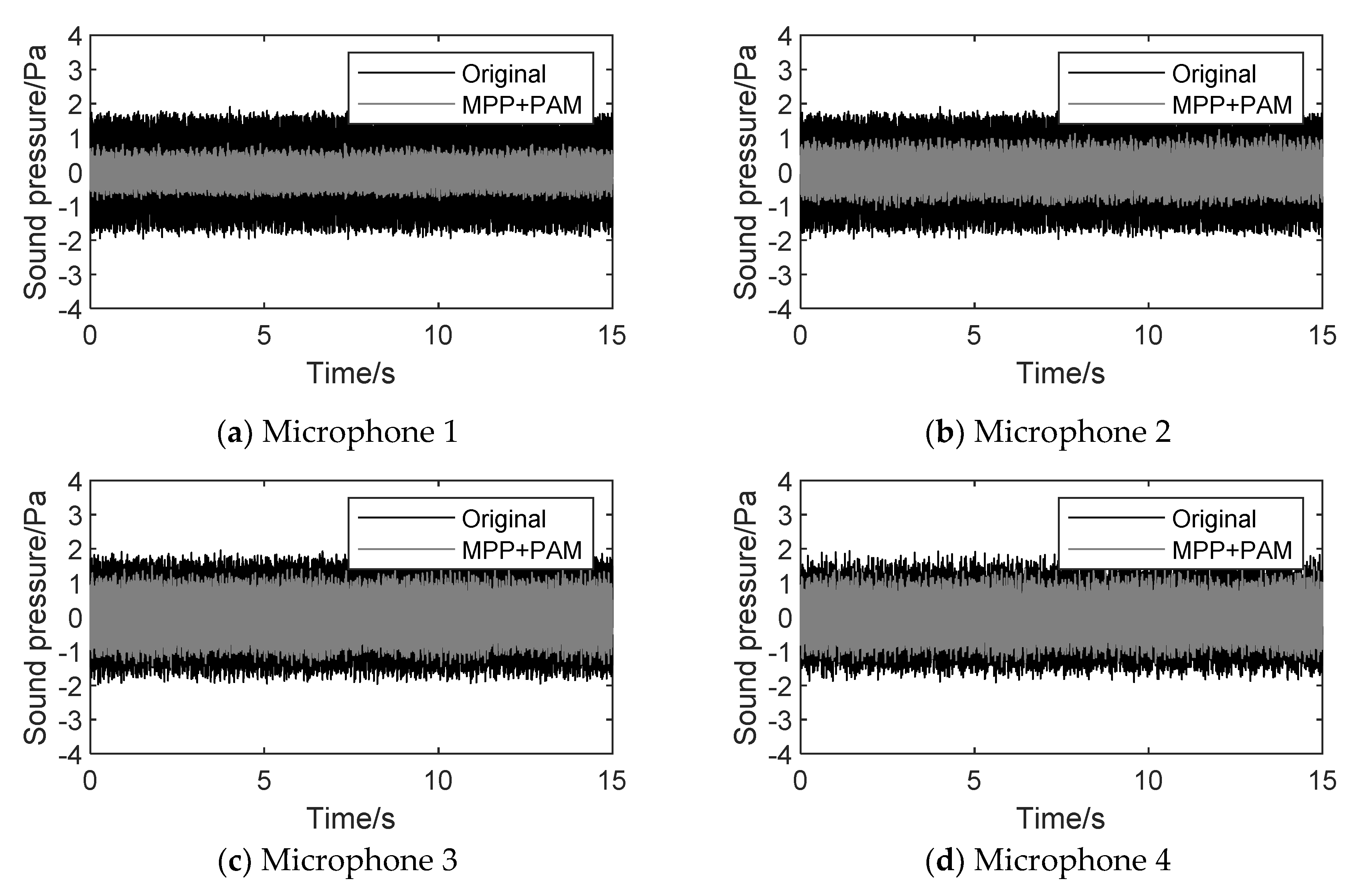
4.3.1. Time domain analysis
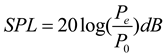
4.3.2. Frequency domain analysis
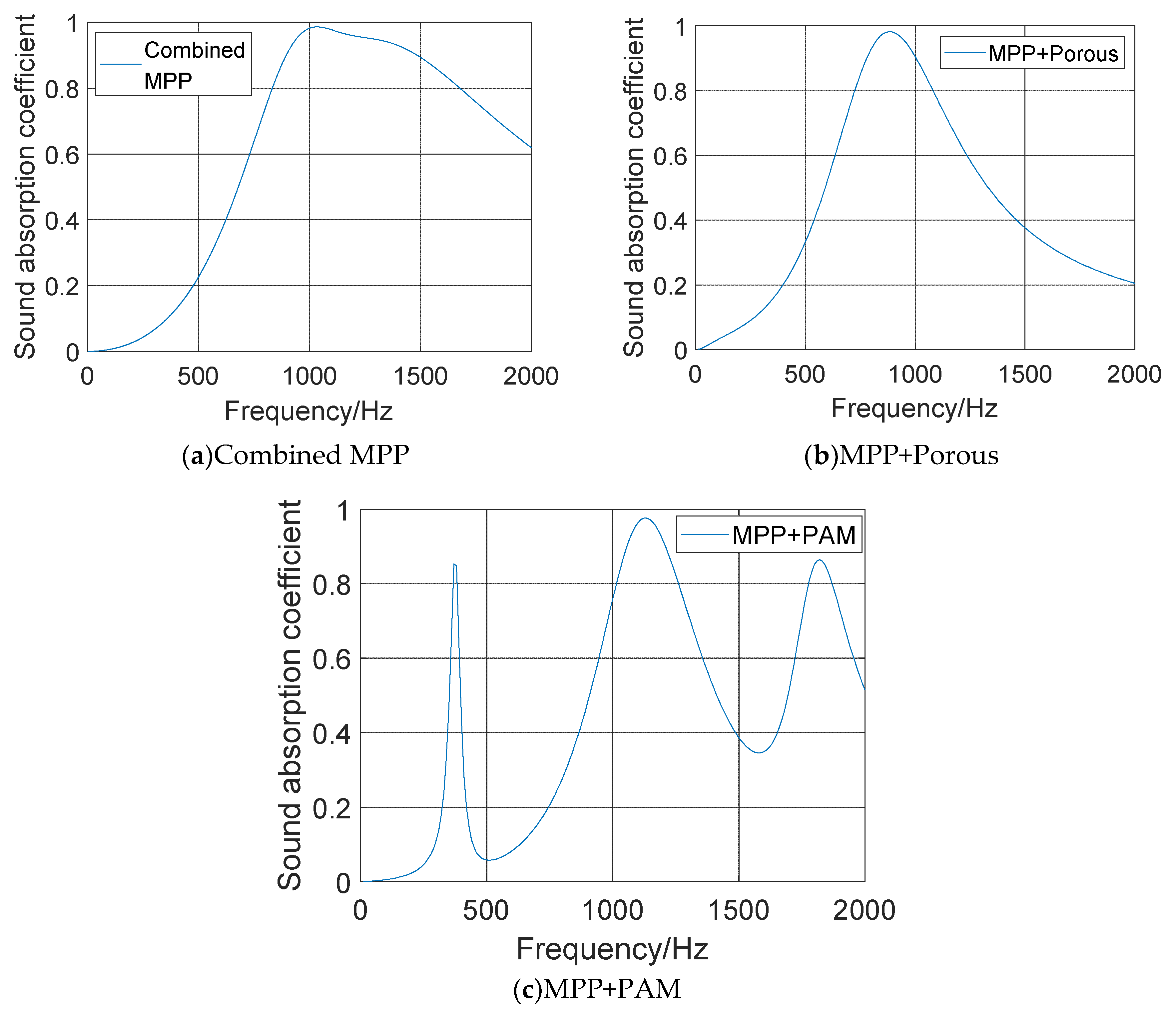
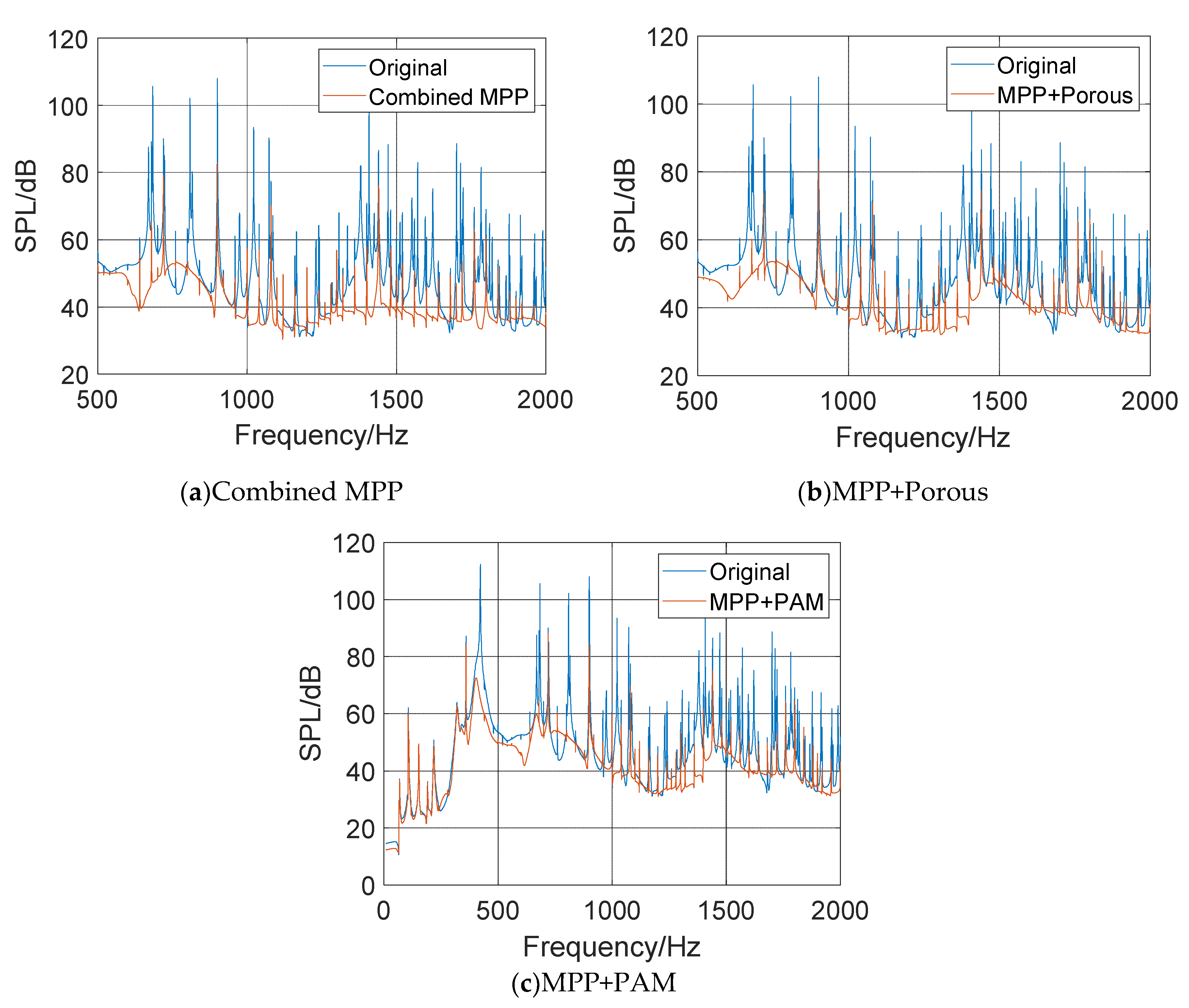
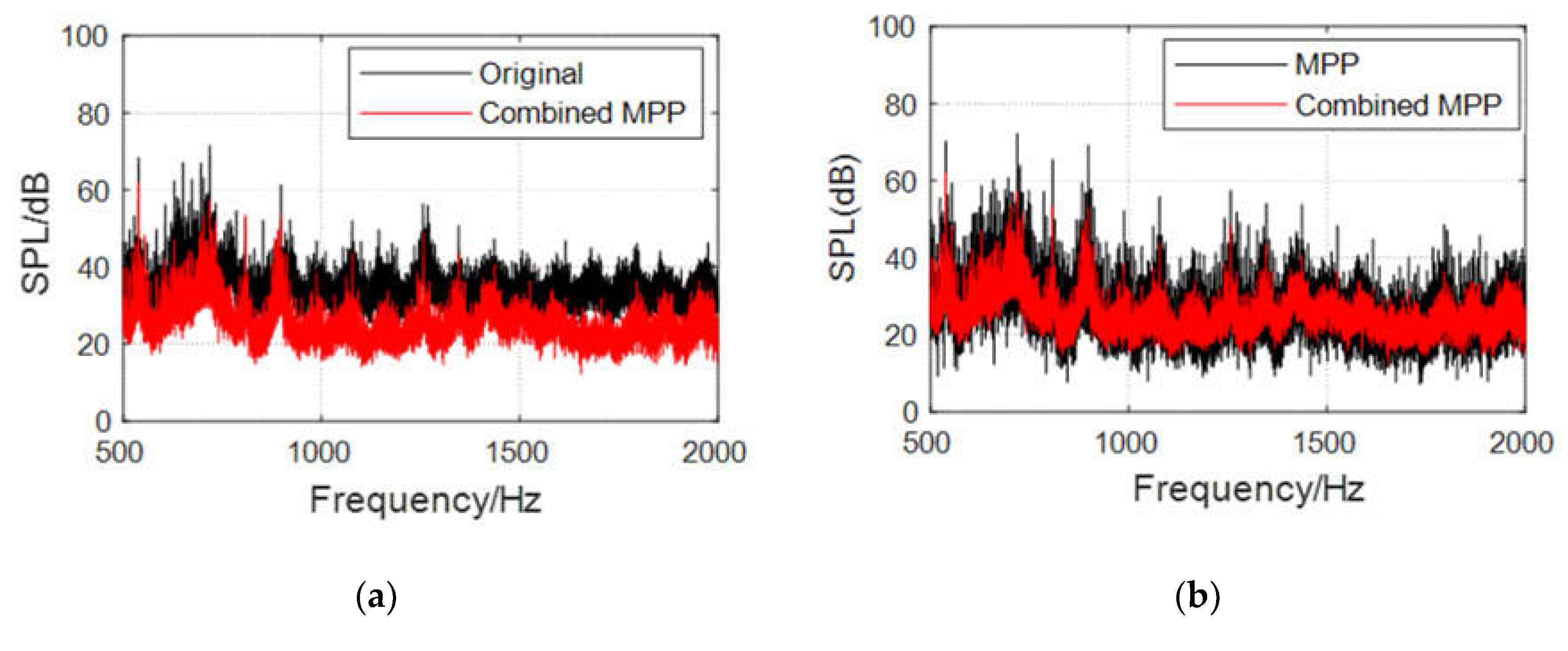
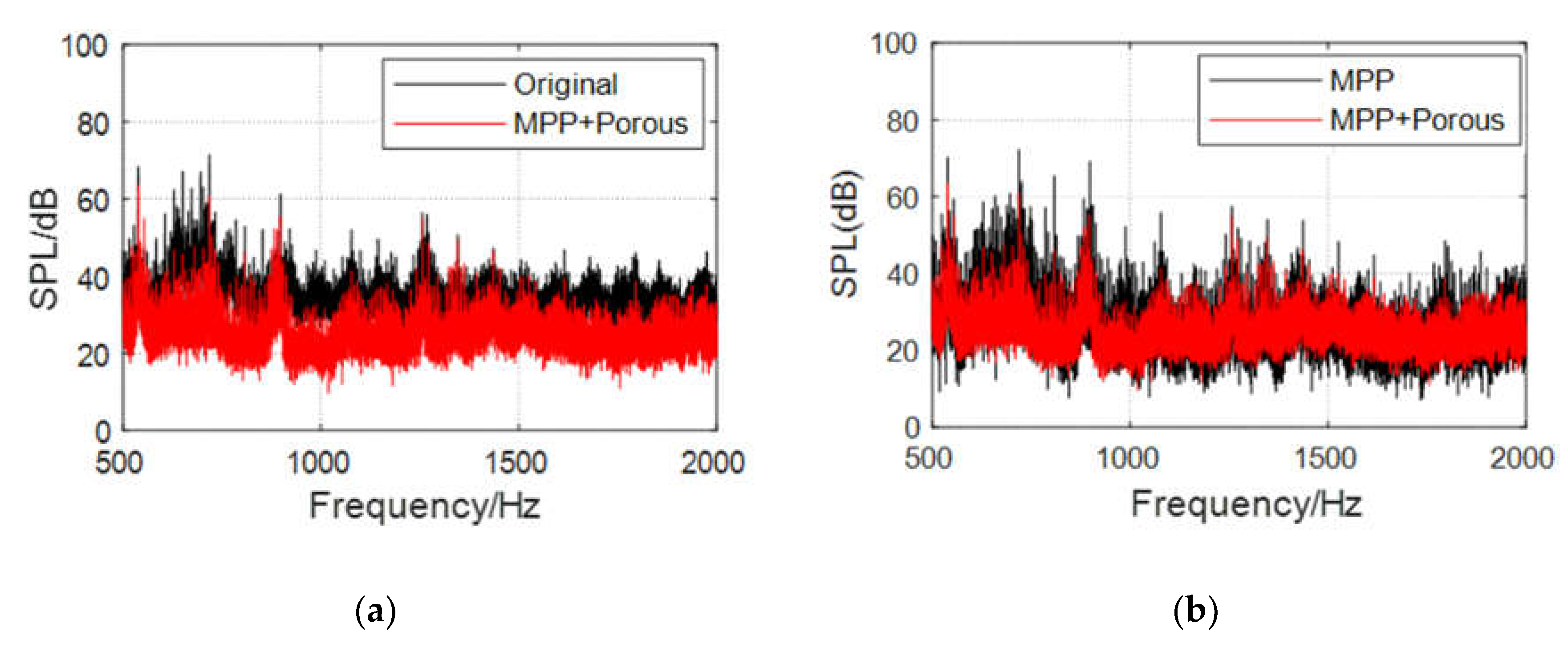
- Compared with the original wall panel, the three structures evidently attenuate the cabin SPL in the range of the resonance peak and its nearby frequency band, with a maximum attenuation greater than 20 dB.
- Owing to the influence of the diffusion sound field, a new sound absorption band is formed, and the SPL with the three structures is attenuated by 10 dB, on average, over a wide frequency range of 1300–2000 Hz. The overall cabin noise level is effectively controlled.
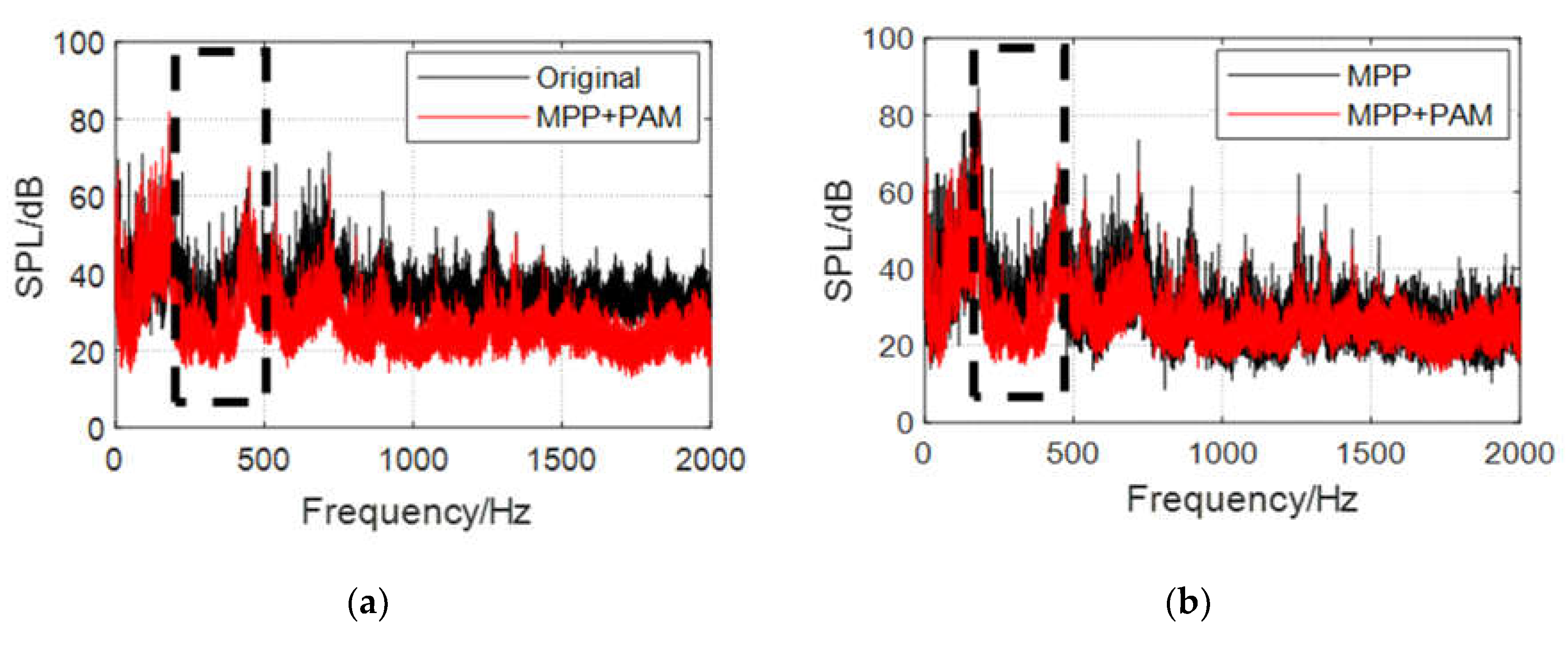
- MPP+PAM attains a significant cabin SPL attenuation in the range 300–450 Hz, with an average noise reduction effect of 45%. It also achieves a good low-frequency sound absorption effect and maintains satisfactory broadband noise reduction effects in the middle- and high-frequency bands.
- Compared with the sound absorption performance of the ordinary MPP, those of the three structures are optimized to a certain extent. Combined MPP substantially improves the sound absorption performance in the 600–1100 Hz and 1400–1800 Hz ranges. MPP+Porous enhances the sound absorption performance in the range 600–1200 Hz. The reason for the weak optimization effect of the porous material here is that this material needs to be filled with a certain thickness to obtain the best sound absorption performance. After coupling with the MPP, the sound absorption performance is significantly optimized only near the resonance frequency. The sound absorption performance of MPP+PAM is considerably improved in the 300–450, 600–900, and 1600–1800 Hz ranges.
5. Conclusion
- The proposed MPP composite sound absorption structures can satisfactorily suppress the noise from the main gearbox in the target frequency band.
- Based on the constructed finite element model of the helicopter main gear/body acoustic vibration coupling, the in-cabin noise reduction characteristics of the composite microperforated plate acoustic structures were obtained via simulation analysis. The simulation results show that Combined MPP and MPP+Porous significantly improve the acoustic bandwidth and acoustic performance and can effectively reduce the cabin noise level in the range 500–2000 Hz, with an attenuation amplitude of up to 35 dB. MPP+PAM achieves low-frequency noise control in the range 350–450 Hz and has a certain noise control effect in the middle- and high-frequency ranges.
- Based on the constructed model helicopter test platform, the cabin sound field conditions of composite acoustic structures equipped with microperforated panels were tested under real main gear vibration excitation. The cabin sound fields were compared with that of the original wall panel to verify the cabin noise reduction characteristics of the composite MPP acoustic structures. The test results show that Combined MPP and MPP+Porous realize an overall cabin SPL attenuation of 8–10 dB, on average, in the wide frequency range of 500–2000 Hz, with an amplitude of more than 20 dB. MPP+PAM achieves low-frequency sound absorption in the frequency range of 300–450 Hz; the sound absorption effect reaches 45% and it also has good noise reduction effects in the middle- and high-frequency bands.
References
- Yu H W, Sun D H, Li M Q, et al. Research on noise reduction technology in helicopter cabin[J]. Helicopter Technology, 2012(04):38-44.
- Scheidler J, J. A review of noise and vibration control technologies for rotorcraft transmissions[C]//Proceedings of INTER-NOISE and NOISE-CON Congress and Conference Proceedings. Hamburg, Germany: Institute of Noise Control Engineering, 2016, 253(5): 2986-2997.
- Szefi J, T. Helicopter gearbox isolation using periodically layered fluidic isolators [D]. The Pennsylvania State University. 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Lu Yang, Ma Xunjun, Wang Fengjiao. Research on active noise control technology in helicopter cabin[J]. Aviation manufacturing technology, 2016, 59(08):38-45.
- Millott T A, Yoerkie C A, Welsh W A, et al. Flight test of active gear-mesh noise control on the S-76 aircraft[C]//Proceedings of the American Helicopter Society Washinton, USA: The American Helicopter Society Inc, 1998.
- Caillet J, Marrot F, Unia Y, et al. Comprehensive approach for noise reduction in helicopter cabins[J]. Aerospace Science and Technology, 2012, 23(1): 17-25. [CrossRef]
- Ang L Y L, Tran L Q N, Phillips S, et al. Low-frequency noise reduction by earmuffs with flax fibre-reinforced polypropylene ear cups[J]. Advances in Acoustics and Vibration, 2018, 1: 1-10.
- Qin Datong. History and research progress of mechanical transmission science and technology[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2003, 39(12) : 37-43.
- He L, Zhu H-C, Qiu S-J, et al. Acoustic theory and engineering applications [M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2006.
- Ao QB, Wang JZ, Li Y, et al. Research progress of low-frequency sound-absorbing materials[J]. Functional Materials,2020,51(12):12045-12050.
- ZHA Xueqin. Transparent micro-perforated sound-absorbing material improves the sound quality of the newly built parliament hall[J]. Acoustic technology, 1994, 13(1):1-3.
- MAO Dongxing, XIA Junfeng, HONG Zonghui. Study on sound barrier based on micro-perforated panel structure with top absorbing cylinder[J]. Acoustic technology, 1999(1):26-29.
- Li, L.; Zhang, Z.; Huang, Q.; et al. A sandwich anechoic coating embedded with a micro-perforated panel in high-viscosity condition for underwater sound absorption[J]. Composite Structures, 2019, 235:111761. [CrossRef]
- WU Qu, LIU Yan, Li Yaozu, et al. Simulation Study on Acoustic Performance of Ventilation Muffler of STC-GV Supercharger[J]. Machinery, 2021, 48(06):8-13+19.
- Lee W, Y.; Kim J, C. ; Noh H M. Application of a micro-perforated panel absorber to reduce the curve squeal noise of railways[J]. Noise Control Engineering Journal, 2021, 69(06):507-517.
- Chen Hongshang. Research on noise reduction method of micro-perforated web face gear transmission based on Helmholtz theory[D]. Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics,2015.
- Ma, DY. Combined microperforated plate sound absorption structure[J]. Noise and Vibration Control, 1990(03):3-9.
- Ma, DY. Theory and design of microperforated plate sound absorption structures[J]. Chinese Science,1975(01):38-50.

| Parameters | σ(N·s·m-4) | ∅ | α∞ | Λ(μm) | Λ’(μm) |
| Numerical value | 10500 | 0.995 | 1.0059 | 240 | 470 |
| Structure | Parameters | Numerical value | Parameters | Numerical value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Combined MPP | Pore size d1 | 0.40 mm | Perforation rate p1 | 2.88% |
| Pore size d2 | 0.57 mm | Perforation rate p2 | 0.94% | |
| Plate thickness t | 1.00 mm | Dorsal cavity depth D | 20 mm |
| Structure | Parameters | Numerical value | Parameters | Numerical value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MPP+Porous | Pore size d | 0.52 mm | Perforation rate p | 1.11% |
| Plate thickness t | 1.00 mm | Dorsal cavity depth D | 20 mm |
| Structure | Parameters | Numerical value | Parameters | Numerical value |
| MPP+PAM | Pore size d | 0.53 mm | Perforation rate p | 0.96% |
| Depth of cavity in frontof thin plate D1 | 10 mm | Depth of cavitybehind thin plate D2 | 10 mm | |
| Thin plate thickness tp | 0.2 mm | Thin plate length B | 50 mm |
| Equipment | Model |
|---|---|
| Magnetic powder brake | PB-B2-0.6 |
| Acceleration sensor | LC0119 |
| Microphone | 378B11 |
| Signal conditioner | CM3508 |
| Data collector | NI USB6343 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




