1. Introduction
Flos daturae, a well-known medicinal herb, is widely distributed across East India, North America, and China [
1]. It has been traditionally utilized as anti-cholinergic, anti-spasmodic, mydriatic, and preanesthetic agents [
2]. Recent studies have highlighted the presence of tropane alkaloids in
Flos daturae, including scopolamine, hyoscyamine, anisodamine, and anisodine [
3]. Among them, scopolamine exhibits various bioactivities, such as mydriatic, antispasmodic, anticholinergic, anesthesia, analgesic, and sedative properties. Thus it has received increasing attention during the past few decades [
4]. Compared to hyoscyamine or atropine (the racemic form of hyoscyamine), scopolamine possesses fewer adverse reactions and stronger efficacy. Based on preliminary statistics, the market demand for scopolamine is ten times higher than that for the total of hyoscyamine and atropine [
5]. Therefore, a lot of efforts have been devoted to the production of scopolamine.
Currently, scopolamine is primarily obtained through chemical synthesis [
6], biosynthesis [7, 8], and extraction from plants [
9]. However, due to technical difficulties and complex processes, chemical synthesis and biosynthesis are challenging to scale up for industrial production. The extraction method of scopolamine from plants has gained more and more attention due to abundant species, low toxicity, and high efficiency. The common preparation process includes alkalization, extraction with non-polar solvents [10-15], polar solvents or acid water [16-21], and purification by multiple liquid-liquid extraction (LLE). Unfortunately, the use of a large amount of toxic organic solvents in multiple LLE causes several problems, such as human safety, environmental pollution and low efficiency. Recently, new separation methods have been adopted as a clean-up step, like Extrelut (Merck) cartridges, solid phase extraction (SPE) [13, 21, 22], dispersive solid phase extraction (d-SPE) [
23], supercritical extraction [
24], capillary electrophoresis [
25] and molecularly imprinted polymers (MIPs) [
26]. Although these methods have been successfully applied in the pretreatment of chromatographic analysis or small-scale preparation, further research, including bio-activity tests and clinical research, is still seriously restricted by the lack of adequate supply of raw materials. Therefore, it is urgent to develop a fast, reliable and effective preparation method for scopolamine with high purity and considerable quantity.
Crystallization is a commonly used method for the separation and enrichment of natural products [27, 28]. However, traditional crystallization methods have limitations, such as long induction time, low product yield, various influencing factors, and difficulty in controlling crystal form. To address these issues, external fields have been applied to control or improve the crystallization process. For example, electric field [
29], sound field [30-32], microwave [
33], light field [
34], pressure field [
35], and magnetic field [29, 36-38] have been introduced to shorten the induction time, control crystal growth and improve the crystal quality. Among them, the application of magnetic field has gained increasing attention. However, according to previous reports, we have noticed that the magnetic field was mainly employed in the crystallization of protein or inorganic small molecules. Few research works have been carried out for the preparation of natural products, especially for alkaloids. In our previous studies, the effect of magnetic field on the crystallization process of puerarin and menthol has been investigated [39, 40]. During the experiments, it was found that the induction time shortened and regular crystals were obtained after magnetic field treatment. Therefore, magnetic field is potential to be used for the promotion of scopolamine preparation.
The aim of this study was to establish a fast and efficient method for the preparation of high-purity scopolamine hydrobromide using magnetic field induced crystallization. After scopolamine successfully transformed to its slat form (scopolamine hydrobromide), the effect of crystallization solvent and magnetic field intensity on the crystallization process of scopolamine hydrobromide, as well as the effect of magnetic field on the crystal growth direction were investigated. Additionally, we evaluated the influence of magnetic field on the physical properties of the solution and clarified the mechanism of magnetic field induced crystallization.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and reagents
The dried flowers of Flos daturae were supplied by Anhui Dexinjia Biopharm Co., Ltd (Anhui, China). Standards of scopolamine and scopolamine hydrobromide (purity ≥ 99.8%) were bought from Yihe Biotechnology Co., Ltd (Shanghai, China). The extracts of scopolamine (purity ≥ 83%) were offered by Shanxi Yuning Biological Science and Technology Co., Ltd (Shanxi, China). High performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) grade methanol was purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA). Other reagents, including methanol, ethanol, isopropanol, n-butyl alcohol, ethyl acetate, sodium acetate, hydrobromic acid, acetic acid, and triethylamine, were analytical grade and obtained from Sinopharm Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd (Shanghai, China). Watson's distilled water (Guangzhou, China) was used throughout the experiment as deionized water.
2.2. HPLC analysis
A standard stock solution of scopolamine was prepared in methanol (4.0 mg/mL) and serially diluted with methanol to produce working solutions (0.125, 0.25, 0.5, 1.0, and 2.0 mg/mL). The standard curve was plotted with the concentration of scopolamine standard as the abscissa (X) and the peak area determined by HPLC as the ordinate (Y). HPLC analysis was performed on an Agilent 1260 chromatographic system (Agilent Technologies Inc., Santa Clara, USA) equipped with a G1311A quaternary pump, an online G1322A degasser, and a G1315A diode array detector (DAD). The separation was achieved on an SGE protecol C18 column (4.6 × 250 mm i.d., 5.0 µm) at 35 °C. The mobile phase consisted of methanol and 0.02 mol/L sodium acetate solution containing 0.02% triethylamine (40:60, v/v) and was eluted at a flow rate of 1.0 mL/min. After injecting 20 μL of the sample into the system, the DAD detector was set at 215 nm to acquire chromatograms.
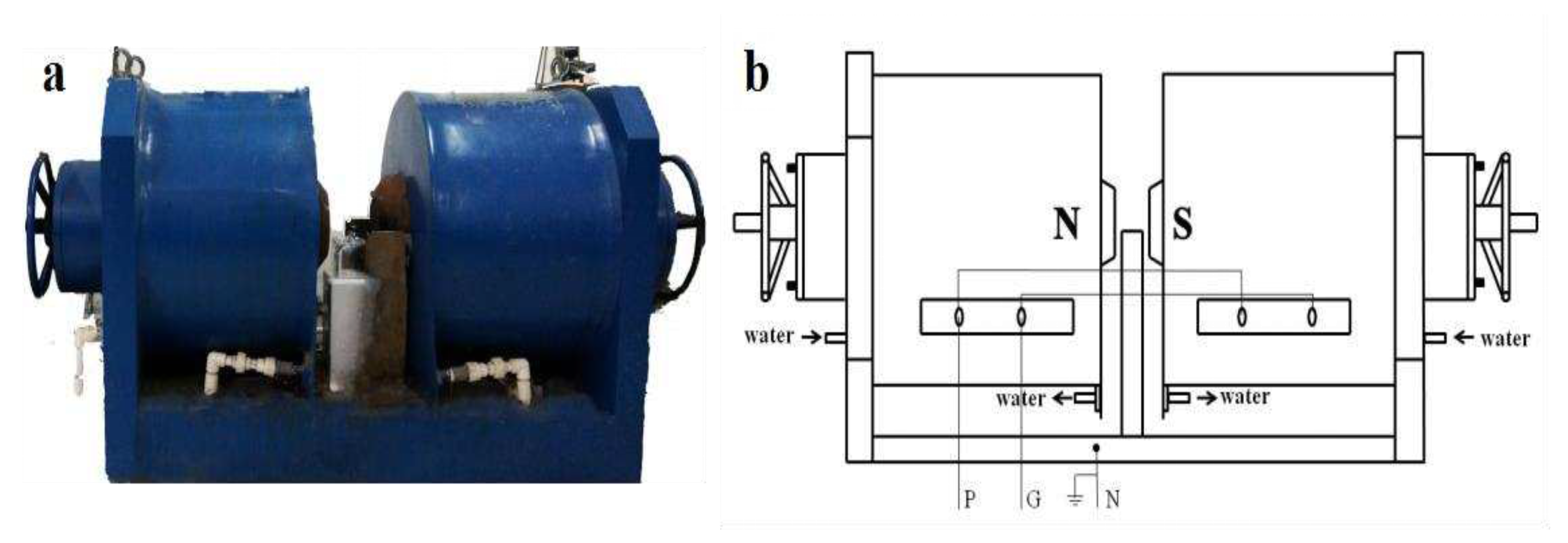
2.3. Device used for magnetic field generation
Figure 1 illustrates the device used for generating magnetic field. Two cylindrical electromagnets were positioned in opposite directions with a flat-type electromagnetic pole face having a diameter of 14.5 cm. The air gap between the poles can be adjusted by the hand-wheel equipped at the back of each magnetic pole, with a range of 0-18 cm. A water cooling system was installed outside the magnetic poles to dissipate heat generated during the experiment. The rated excitation voltage and current were 0-340 V and 0-28 A, respectively. The intensity and direction of the magnetic field were measured by using a Tesla meter (HT-20, Shanghai Hengtong magneto Electricity Technology Co., Ltd.). This device is similar to the one described in a previous article [
41]. Therefore, we can assume that the magnetic field gradient is also similar to that described in the above article. In our experiment, the gap between two poles was 15 cm and the magnetic field intensity was controlled by adjusting the magnitude of the voltage and current. When the device was turned on, the magnetic field intensity increased from the center of the surface of magnetic pole to the boundary. Furthermore, the magnetic field intensity was highest when closest to the magnet and stronger at both ends of the magnet than that at the center. The crystallizer was placed at the center position between two poles, and then the strength and direction of magnetic field were measured. Although the magnetic field intensity increased along the center toward the electromagnet, the influence of magnetic force induced by magnetic field gradient on the results of our experiment was relatively small, due to the small size of the crystallizer (r = 5 mm).
Figure 1.
(a) Prototype of the device used for magnetic field generation; (b) Schematic diagram of the device.
Figure 1.
(a) Prototype of the device used for magnetic field generation; (b) Schematic diagram of the device.
2.4. Effect of different solvents on the crystallization
Five different solvents, including methanol, ethanol, isopropanol, n-butanol, and a mixed solution of ethyl acetate and water (v/v=9:1), were selected as crystallization solvents. First, scopolamine solution with a concentration of 100 mg/mL was respectively prepared with each of the above solvents. Then, excessive hydrobromic acid was added to each solution in a molar ratio of 1.2:1. Next, each solution was divided into two equal portions, one portion was placed under magnetic field with an intensity of 0.4 T for 3 h, while the other portion was used as a blank control, crystallized without magnetic field at 20 ± 2 °C. After samples were taken out from the magnetic field, the crystal growth in different crystallization bottles was observed and the effect of magnetic field on the crystal growth direction was compared. Additionally, after the sample bottles were removed from magnetic field for 24 h and the solution was filtered using suction filtration, the crystals were washed three times with ice ethanol, and then placed in a vacuum oven at 40 °C for 24 h to remove the solvent and water. The dried crystals were accurately weighed and their purity was determined by HPLC.
2.5. Effect of magnetic field intensity on crystallization
The effect of magnetic field intensity on crystallization was investigated from four aspects, including induction time, crystal purity, and recovery rate of crystals. Five portions of scopolamine solution with a concentration of 100 mg/mL were prepared with ethanol, and added with excessive hydrobromic acid at a molar ratio of 1.2:1. The prepared solutions were then placed in a magnetic field with intensities of 0, 0.2, 0.4, 0.6, 0.8 T for 3 h, respectively (20 ± 2 °C). After the sample bottles were removed from the magnetic field for 24 h, 20 uL of crystallization solution was taken, dried under vacuum, dissolved in a mixed solution composed of methanol and water (v/v= 40: 60) under ultrasound treatment, and used for HPLC determination. The remaining solution was filtered using suction filtration, and the crystals were washed three times with ice ethanol, and then placed in a vacuum oven at 40 °C for 24 h to remove solvent and water. The dried crystals were accurately weighed and their purity was determined by HPLC. The recovery rate (R) was calculated according to the following formula:
where
R was the recovery rate, %;
mcrystal was the weight of crystals, g;
P was the purity of sample, %;
mraw was the weight of raw materials, g; 1.445 was the molar mass ratio of scopolamine hydrobromide to scopolamine; 0.83 was the purity of scopolamine in raw materials.
2.6. Effect of magnetic field on the absorbance of the solution
With pure water as the reference, the UV absorbance of five solvents including methanol, ethanol, isopropanol, n-butanol and ethyl acetate was measured at wavelengths of 220, 220, 220, 250 and 260 nm, respectively, at 20 ± 2 °C. Then all the solvents were placed under a magnetic field with an intensity of 0.4 T for 0.5, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 and 6 h. The UV absorbance of each solvent was then measured at the corresponding wavelength after each interval.
Scopolamine solutions with a concentration of 0.125 mg/mL were prepared using methanol, ethanol, isopropanol, n-butanol and ethyl acetate as the solvent, respectively, at 20 ± 2 °C, and then the UV absorbance of five solutions was measured at the corresponding wavelength. Next, all the solutions were placed under a magnetic field with an intensity of 0.4 T for 0.5, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 and 6 h, and the UV absorbance of five solutions was subsequently measured.
2.7. Effect of magnetic field on the interfacial tension of the solution
Scopolamine solutions with a concentration of 2 mg/mL were prepared with methanol, ethanol, isopropanol, n-butanol and ethyl acetate as the solvent, respectively, at 20 ± 2 °C, and then added with excessive hydrobromic acid at a molar ratio of 1.2:1. Thereafter, each solution was divided into two equal portions, one portion was placed under a magnetic field with an intensity of 0.4 T for 3 h, and the other portion was used as a blank control in the absence of magnetic field. The interfacial tension of each solution was measured using an interfacial tension meter (BZY-3B, Shanghai Hengping Instrument and Meter Factory, Shanghai, China).
2.8. Effect of magnetic field on viscosity and density
Scopolamine solutions with a concentration of 1 mg/mL were prepared with methanol, ethanol, isopropanol, n-butanol and ethyl acetate as the solvent, respectively, at 20 ± 2 °C, and then added with excessive hydrobromic acid at a molar ratio of 1.2:1. Thereafter, each solution was divided into two equal portions, one portion was placed under a magnetic field with an intensity of 0.4 T for 3 h, and the other portion was placed without magnetic field. The viscosity of different solutions was measured with a kinematic viscometer (PXSYD-265B, Shanghai Pingxuan Scientific Instrument Co., LTD., Shanghai, China), and the density was calculated by measuring the volume and quantity of the solvent.
3. Results and discussion
3.1. Effect of magnetic field on the crystal growth direction
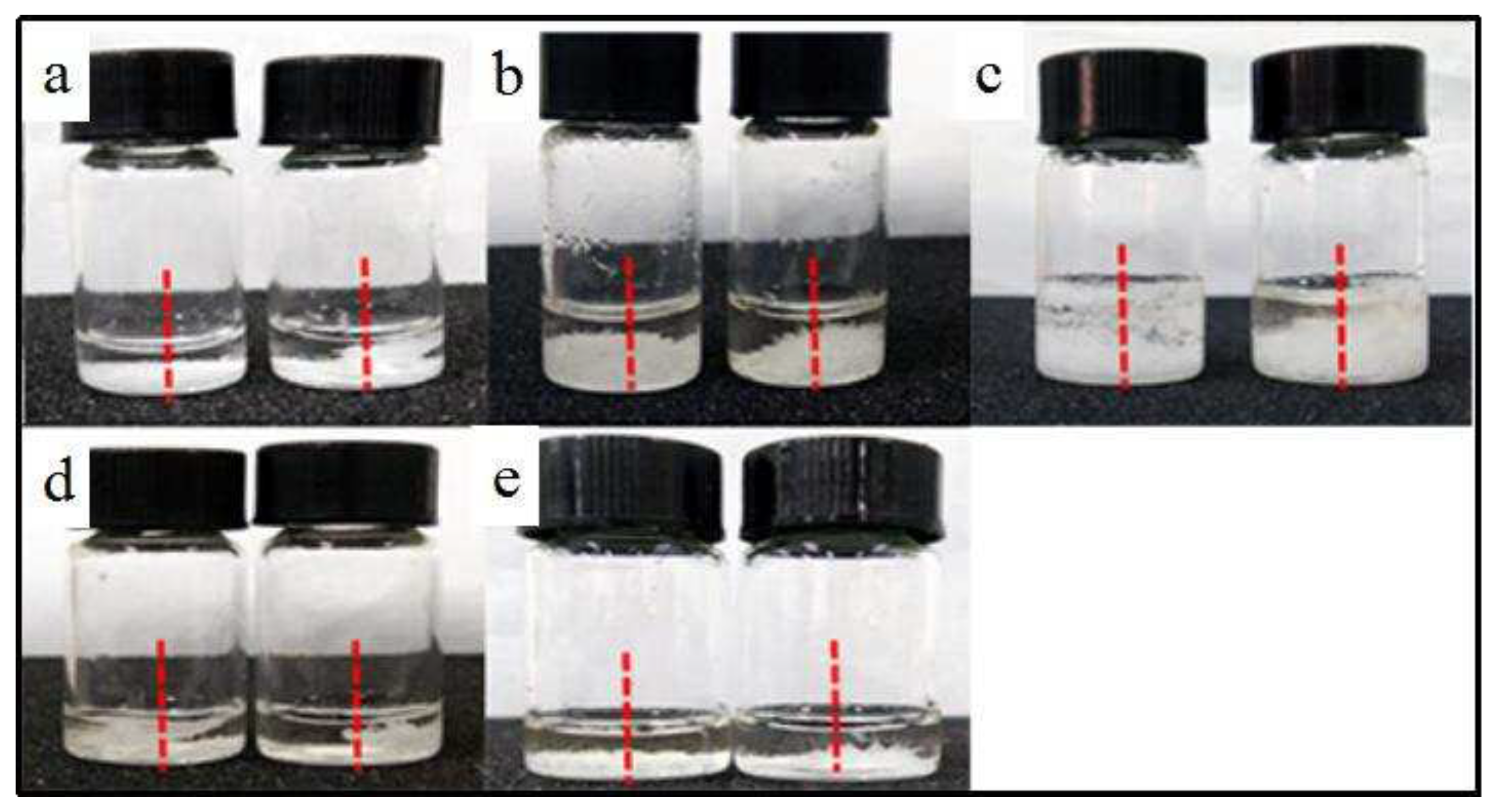
In comparison to control samples, more crystals grew against the wall on the S-pole side under a magnetic field of 0.4T (
Figure 2). Similar results were reported by Yin [
37] and Pareja-Rivera [
42] in their respective studies on lysozyme crystals and protein crystal growth, highlighting the directing effect of the magnetic field. The crystallization process can be affected by the wall effect of the container, as the solution surface tension at the wall of a container is lower than that in the center of the solution. According to classical nucleation formula, positions with low surface tension are beneficial for crystal precipitation. Furthermore, through comparison with the wall on the N-pole side, it was confirmed that preferential growth of crystals on the S-pole side, indicating that the movement of molecules in the solution was influenced by the magnetic field, leading to the gathering of scopolamine hydrobromide molecules to the S-pole side. As scopolamine hydrobromide concentration increased in the S-pole side, supersaturation of the solution increased, subsequently accelerating crystal nucleus formation and crystal growth.
Figure 2.
Effect of magnetic field on the crystal growth direction. (a-e) Crystal samples obtained by using different solvents, in which the right and left side represent crystallization with and without magnetic field, respectively. (a) methanol, (b) ethanol, (c) isopropanol, (d) n-butanol, and (e) ethyl acetate/water (v/v=9:1).
Figure 2.
Effect of magnetic field on the crystal growth direction. (a-e) Crystal samples obtained by using different solvents, in which the right and left side represent crystallization with and without magnetic field, respectively. (a) methanol, (b) ethanol, (c) isopropanol, (d) n-butanol, and (e) ethyl acetate/water (v/v=9:1).
3.2. Effect of different solvents on crystallization
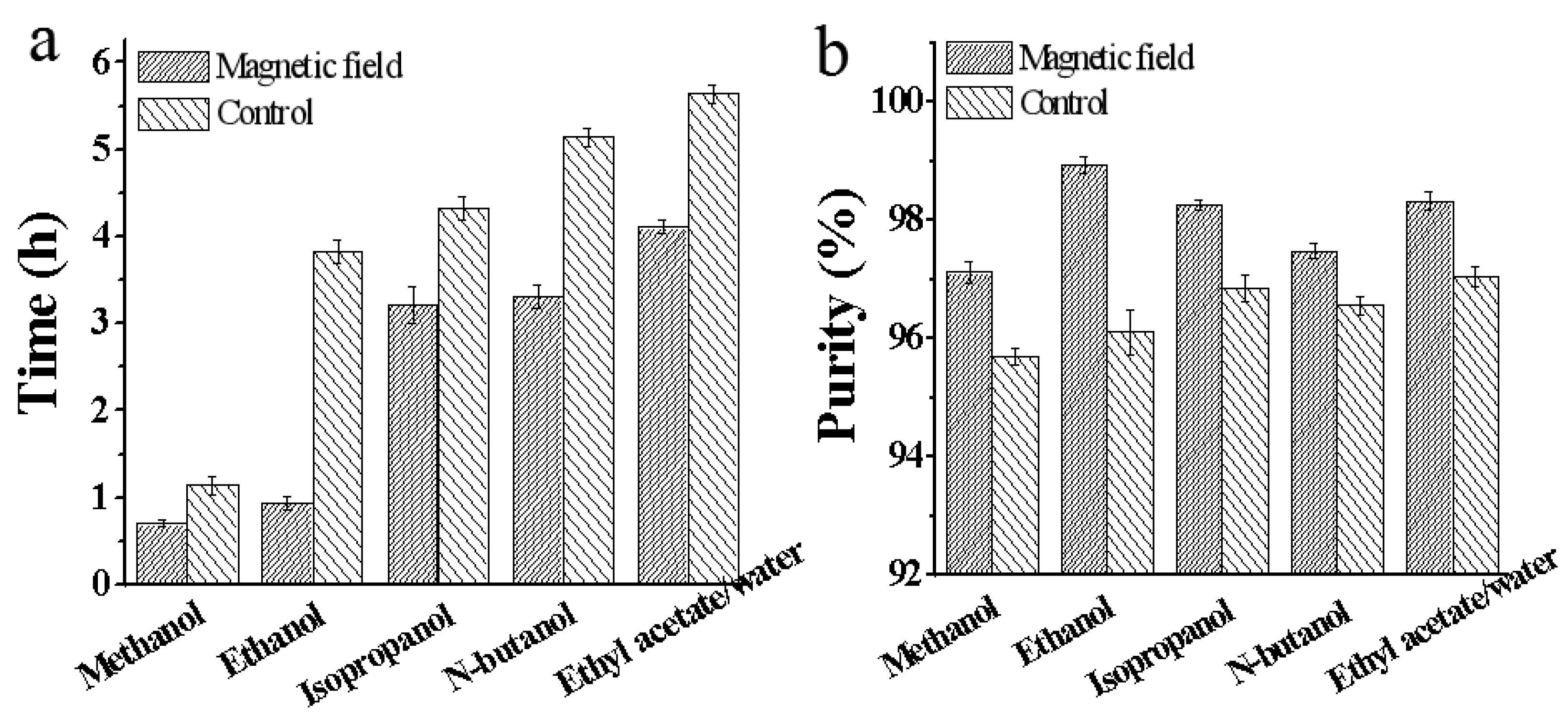
In this study, induction time was defined as the period from the moment when a well-prepared crystalline solution was quickly placed into the magnetic field until the first appearance of crystals. The effect of five different solvents on the crystallization process are shown in
Figure 3. All the induction time of scopolamine hydrobromide was shortened after magnetic field treatment at 0.4 T (
Figure 3a). The order of shortening was listed as follows: ethanol (75.5%) > methanol (38.6%) > n-butanol (35.6%) > ethyl acetate / water (27.1%) > isopropanol (25.6%). These findings indicated that magnetic field accelerated the formation of nuclei and promoted the crystallization process of scopolamine hydrobromide. According to our results described in Section 3.1.1, the directed effect of magnetic field caused molecules to move in a specific direction and orderly manner, leading to an increase in concentration in some regions of the solution, thereby enhancing the supersaturation of solution here. A certain degree of supersaturation can stimulate the nuclei formation and crystal growth.
Figure 3.
Effect of five different solvents on the crystallization. (a) Effect of five different solvents on the induction time. (b) Effect of five different solvents on the purity of crystals.
Figure 3.
Effect of five different solvents on the crystallization. (a) Effect of five different solvents on the induction time. (b) Effect of five different solvents on the purity of crystals.
Through the analysis of molecular structure, it was discovered that scopolamine contains a seven-membered-ring, an ester group, a hydroxyl group and a nitrogen atom. Within the seven-membered-ring, there is an epoxy group. The oxygen atoms in the ester group, hydroxyl group and epoxy group possess negative charges, that can form hydrogen bonds with the hydrogen atoms having positive charge. For crystalline solvents except for ethyl acetate, the hydrogen atoms in the hydroxyl group of methanol, ethanol, isopropanol and n-butanol can also form intermolecular hydrogen bonds with the oxygen atoms. Additionally, the oxygen atoms in the hydroxyl groups of different solvents can form hydrogen bonds with the hydrogen atoms in the hydroxy of scopolamine. Moreover, hydrogen atom in water molecule can also form intermolecular hydrogen bonds with oxygen atom in scopolamine molecules. Therefore, extensive hydrogen bonds exist between the solute and solvent in the crystalline mother liquor. In addition, under the magnetic field, electrons in the hydrocarbon could easily jump from the pure spin state (S state) to the tripure spin state (T state) , whereas the transition from T state to S state was blocked. This increased the number of molecules in the T state and resulted in the breakdown of hydrogen bonds between molecules at a certain degree, the disintegration of the associated molecular group, as well as the changes of solution properties, such as viscosity, surface tension, solubility and so on. The spin state of electrons was influenced by magnetic field, causing the destruction of hydrogen bonds and affecting the crystallization process. As energy, magnetic field also promoted the vibration of scopolamine hydrobromide molecule themselves and destroyed the association between solute and solvent molecules [
43]. Therefore, it was hypothesized that magnetic field destroyed hydrogen bonds between solute and solvent, decreasing binding force between them, and then the crystallization was accelerated.
Moreover, crystals obtained under magnetic field exhibited higher purity compared to those without magnetic field. As depicted in Figure 3b, the crystalline purity was improved in various solvents, including methanol (95.7% to 97.12%), ethanol (96.12% to 98.93%), isopropanol (96.85% to 98.25%), n-butanol (95.56% to 97.48%) and ethyl acetate / water (97.05% to 98.32%). The increase in purity suggested that fewer impurities were present in the crystals. Generally, the main sources of impurities in the crystals can be divided into two aspects. Firstly, lattice defects cause impurities wrapped in the crystals during the crystallization process. Secondly, impurities exist in the mother liquor, and residuals on the crystal surface have not been completely washed away. Due to the directional effect of magnetic field on crystallization, more regular crystals were obtained, which facilitated removing residual impurities in the mother liquor during the washing process. Furthermore, treatment under magnetic field also reduced the impurities wrapped in the crystals and improved their quality.
3.3. Effect of magnetic field intensity on crystallization
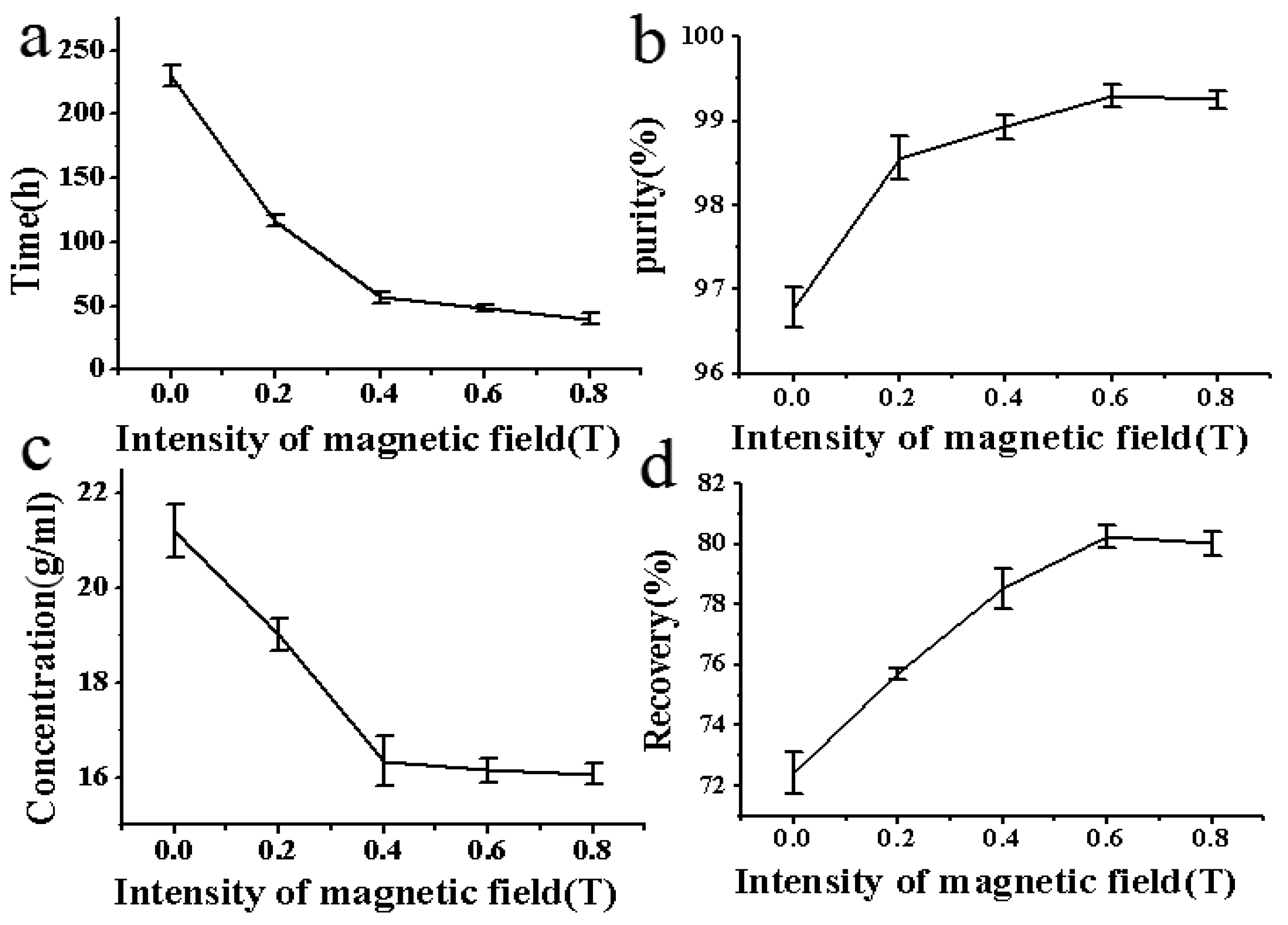
In the absence of a magnetic field, crystals began to appear after approximately 230 min (Figure 4a). However, when subjected to a magnetic field with an intensity of 0.2 T, crystallization could be observed only after about 116.7 min. As the magnetic field intensity increased from 0 to 0.8 T, the induction time gradually shortened from 230 to 40 min, indicating a 82.6% reduction in the duration. Additionally, the shortening effect slowed down as the magnetic field intensity was adjusted to 0.4 T, possibly due to the saturation effect of the magnetic field on the solution. In other words, when the magnetic field intensity was higher than 0.4 T, the reduced influence of the magnetic field on the induction time was not obvious, i.e., the influence was saturated [44, 45]. The magnetic field accelerated the formation of crystal nuclei and shortened the induction time by affecting molecular movement and the intermolecular hydrogen bonds. However, this effect is limited due to the limited number of molecules in the solution. That is to say, to some extent, the influence of the magnetic field on crystallization is effective. If the magnetic field intensity increases beyond this range, the influence of the magnetic field on the crystallization process does not significantly increase, reaching saturation.
Figure 4.
Effect of magnetic field intensity on crystallization. (a) Effect of magnetic field intensity on induction time; (b) Effect of magnetic field intensity on the purity of crystals; (c) Concentration of scopolamine hydrobromide in crystallization mother liquor at 24 h; (d) Effect of magnetic field intensity on the recovery rate of crystals.
Figure 4.
Effect of magnetic field intensity on crystallization. (a) Effect of magnetic field intensity on induction time; (b) Effect of magnetic field intensity on the purity of crystals; (c) Concentration of scopolamine hydrobromide in crystallization mother liquor at 24 h; (d) Effect of magnetic field intensity on the recovery rate of crystals.
As illustrated in Figure 4b, the purity of crystals obtained in the absence of magnetic field was determined to be 96.78%. All the purities of crystals treated under magnetic field were more than 98%, and even more than 99% when intensity was 0.6 and 0.8 T. However, the crystal size decreased with the increase of magnetic field intensity. The above results could be attributed to that the increase of magnetic field intensity promoted the nucleation of solution, and too many nuclei could not fully grow, resulting in relatively small crystal sizes.
Another interesting finding was that the concentration of scopolamine hydrobromide in the solution decreased with the increase of magnetic field intensity (Figure 4c). After crystallization without magnetic field, the concentration of scopolamine hydrobromide in the solution was determined to be about 21.19 mg/mL. However, after treated under a magnetic field with an intensity of 0.8 T, the concentration of scopolamine hydrobromide reduced to 16.08 mg/mL, which was consistent with the theory that magnetic field could accelerate crystal growth and promote crystallization to reach equilibrium more quickly. At the same time, the magnetic field could affect the solubility, destroy hydrogen bonds formed between the substance and the solution, and decrease the solubility. According to mass balance theory, the concentration of scopolamine hydrobromide in the solution decreased after magnetic field treatment, which would also cause an increase of recovery rate.
In the absence of a magnetic field, the recovery rate of crystals was approximately 72.43%. However, after treatment with a magnetic field, the recovery rate gradually increased, and reached its maximum value of 80.24% when the magnetic field intensity was 0.6 T (Figure 4d). Nevertheless, the recovery rate slightly decreased from 0.6 T (80.24%) to 0.8T (80.02%). On one hand, as the magnetic field intensity increased, many crystal nucleus in the solution could not fully grow, resulting in the formation of smaller crystal particles and loss during the filtering and washing process. On the other hand, the saturated effect of the magnetic field on solubility would also lead to the stabilization of the recovery rate increase. Therefore, the recovery rate decreased during the process of magnetic field strength from 0.6T to 0.8T.
According to the theory of mass balance, the mass lost during the filtration and drying process is equal to the theoretically obtained mass minus the actually obtained mass. Meanwhile, the theoretically obtained mass is equal to the total amount of scopolamine minus the residual amount in the solution. Therefore, the loss rate during the filtration process was calculated and listed in order: 8.97% (0T) > 7.60% (0.2T) > 7.13% (0.4T) > 5.86% (0.8T) > 5.58% (0.6T), in which it can be found that the loss rate during the filtration and drying process decreased with the increase of magnetic field intensity. The results could be explained by the fact that crystals obtained under strong magnetic field were more regular and tightly arranged, causing fewer crystals to be lost during the washing process.
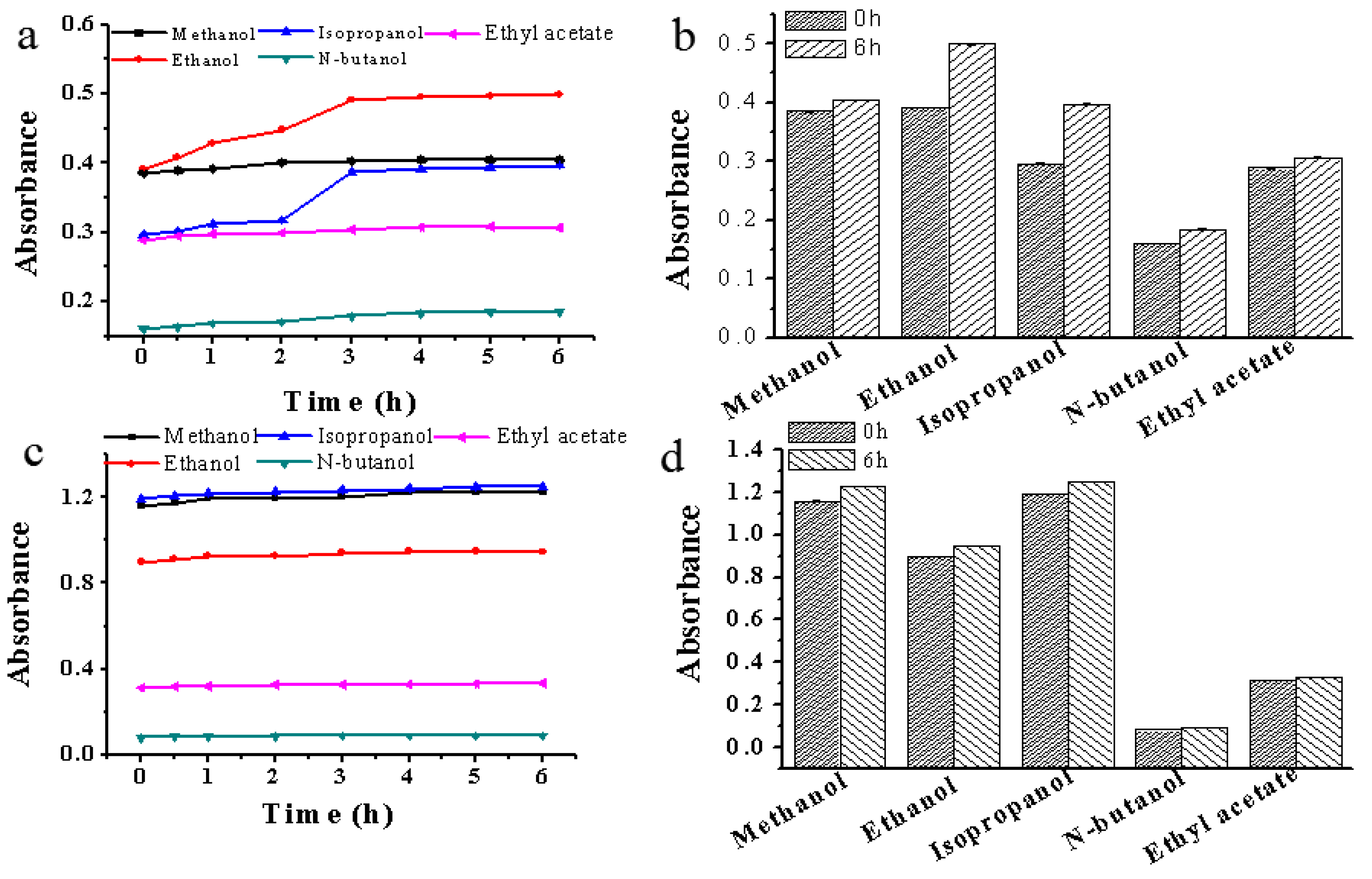
3.4. Effect of magnetic field on absorbance of solution
As shown in Figure 5, after treated under magnetic field within 6 h, the UV absorbance of five solvents increased, with ethanol (0.108) having the highest increase followed by isopropanol (0.101), n-butanol (0.023), methanol (0.019) and ethyl acetate (0.018). Similarly, the UV absorbance of five scopolamine solutions also increased after placed under magnetic field, with methanol (0.067) having the highest increase followed by isopropanol (0.058), ethanol (0.051), ethyl acetate (0.018) and n-butanol (0.009). These results suggested that the adsorbed energy of the hydrogen under magnetic field has reached the energy barrier required for the hydrogen bond cleavage, causing more broken hydrogen bonds in the solvent. Therefore, the increase in UV absorption was relatively obvious. Additionally, with the prolongation of magnetic field treatment time, the UV absorption of five solvents and solutions also gradually increased.
Figure 5.
Effect of magnetic field on the absorbance of solution. (a) Effect of magnetic field on the absorbance of five pure crystallization solvents; (b) The absorbance of five pure crystallization solvents without and with magnetic field treatment for 6 h; (c) Effect of magnetic field on the absorbance of five scopolamine solutions; (d) The absorbance of five scopolamine solutions without and with magnetic field treatment for 6 h.
Figure 5.
Effect of magnetic field on the absorbance of solution. (a) Effect of magnetic field on the absorbance of five pure crystallization solvents; (b) The absorbance of five pure crystallization solvents without and with magnetic field treatment for 6 h; (c) Effect of magnetic field on the absorbance of five scopolamine solutions; (d) The absorbance of five scopolamine solutions without and with magnetic field treatment for 6 h.
Generally, the absorption spectrum in the UV region depends on several factors, such as the excitation level of the electron layer outside the nucleus, the structure of the material bond and temperature. The UV absorbance of solvent increased with the increase of temperature, because heating can accelerate the thermal motion of solvent molecules and gradually destroy hydrogen bonds in the molecules, leading to smaller molecular clusters or individual solvent molecules. When the temperature is constant, magnetic treatment does not cause a change in the key structure, thus it might be due to changes in the structure of the molecular state. In our experiments, intermolecular interaction in the solution was found to be hydrogen bond. Based on these results, we hypothesize that hydrogen bonds between solvent molecules have been destroyed during magnetic field treatment. This is because only when the hydrogen bond is destroyed, it will cause changes in the internal structure of the solvent and achieve a series of physical and chemical properties changes.
3.5. Effect of magnetic field on interfacial tension of solution
According to a previous study [
34], the classical nucleation equation can be expressed as follows:
where
A is the pre-exponential factor,
γ is the interfacial tension between the solid and the solution phases;
Vm is the molar volume of the solid phase;
Δμ is the difference in the solute chemical potential between the solution and the solid phase; and
KB is Boltzmann constant.
Through several mathematical transformations and formula derivations, the equation can be re-written as follows:
where
A is the pre-exponential factor;
γ is the interfacial tension between the solid and the solution phases;
V is the molecular volume;
KB is Boltzmann constant;
T is the temperature and
S is the supersaturation.
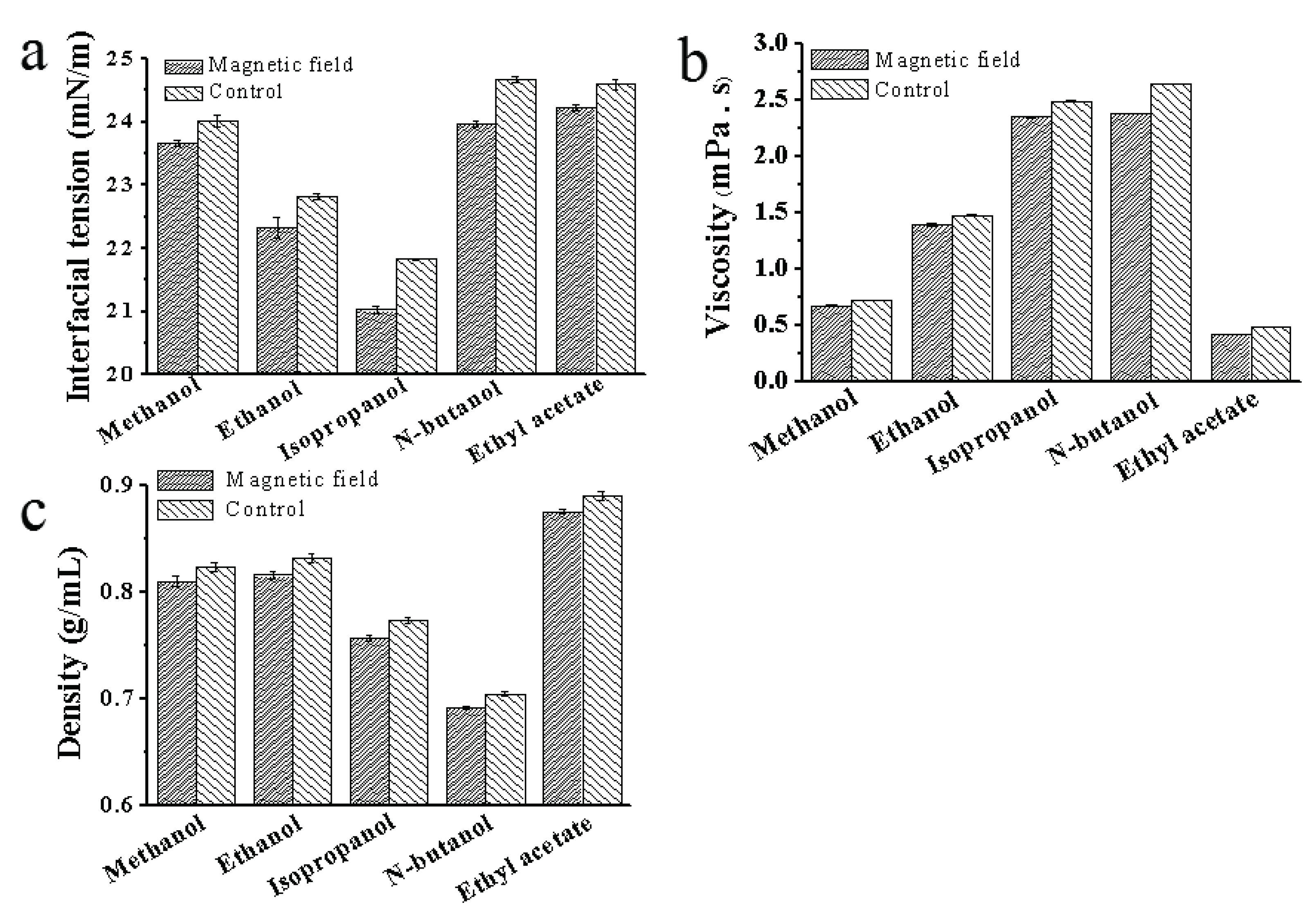
Figure 6.
Effect of magnetic field on the properties of solution. (a) Effect of magnetic field on interfacial tension; (b) Effect of magnetic field on viscosity; (c) Effect of magnetic field on density.
Figure 6.
Effect of magnetic field on the properties of solution. (a) Effect of magnetic field on interfacial tension; (b) Effect of magnetic field on viscosity; (c) Effect of magnetic field on density.
Based on the new equation, the rate of nucleation is related to temperature, degree of supersaturation and interfacial tension. Therefore, increasing temperature and supersaturation, as well as reducing interfacial tension are conducive to nucleation. According to Figure 6a, all five solutions showed decreased interfacial tension, with isopropanol (0.8 mN/m) having the greatest decrease followed by n-butanol (0.7 mN/m), ethanol (0.5 mN/m), ethyl acetate (0.37 mN/m) and methanol (0.36 mN/m). The decrease of interfacial tension suggested that treatment with magnetic field is favorable for crystal nuclei formation. The above findings that the crystals were preferentially precipitated at the inner wall of the container were also verified that the decrease in surface tension promoted nuclei formation.
As surface tension is a basic property of the solution, a decrease in surface tension indicates a change in the physical properties of the solution, when no new substance is added. Hydrogen bonding is an intermolecular force commonly found in solutions. The decrease in surface tension in the solution shows that the hydrogen bonds are broken under the magnetic field, reducing intermolecular interaction and the surface tension of the mixed solution. This means that the magnetic field reduces the surface tension of the mixed solution by breaking the intermolecular hydrogen bonds, promoting crystal nuclei formation, accelerating crystals formation, and shortening the induction time.
3.6. Effect of magnetic field on the viscosity and density of solution
As depicted in Figures. 6b-c, all the viscosity and density of solutions treated under magnetic field reduced in various degrees. The greater the viscosity of a solution was, the more obvious reduced degree became. Viscosity reduction is conducive to crystal precipitation from the solution. Viscosity and density are considered as basic properties of the solution and have a close relationship with hydrogen bonds in solution. When intermolecular hydrogen bonds are formed, molecular association may occur, resulting in an increase in viscosity and density of the solution. However, the formation of intramolecular hydrogen bonds do not cause an increase in viscosity and density. Therefore, the destructive effect of magnetic field on hydrogen bonding can be demonstrated by measuring viscosity and density. After treatment under magnetic field, the density and viscosity of the solution decreased, indicating that the intermolecular hydrogen bonds were destroyed by the magnetic field. Consequently, magnetic field destroyed the intermolecular hydrogen bonds in the solution and weakened the interaction between the solute and the solvent, making it easier for the solute to crystallize.
Author Contributions
Zeyu Wu: Conceptualization, Data curation, Writing – review and editing, Supervision, Funding acquisition; Pengpeng Chen: Investigation, Methodology, Formal analysis, Writing – original draft; Huixi Bian: Validation, Resources; An Zhou: Validation, Resources; Kun Xu: Conceptualization, Resources; Wencheng Zhang: Conceptualization, Methodology, Resources.