Breast cancer (BC) is the most common tumour in women. It is a multifactorial disease with a high grade of heterogeneity often contributing to making breast cancer difficult to treat. Different methods of classification, such as immunohistochemical technique, molecular characteristic and gene expression have been used to frame this high heterogeneity in order to foresee the prognosis and to choose the best treatment options [
22,
23]. Immunohistochemically, BC can be classified by the expression of oestrogen receptors (ERs), progesterone receptors (PRs) and receptor tyrosine-protein kinase erbB-2 (HER2) [
1,
2,
3]. The clinical guidelines for immunohistochemical (IHC) quantitation of steroid receptors in BC recommend that ER and PR assays be considered positive if at least one per cent of nuclei are stained [
2]. Although the two groups of BC identified in this way (ER-positive/ER-negative) are not completely homogeneous, the two BC groups can be differentiated by biological characteristics and clinical behaviour [
24]. It is noteworthy that the tumour ER expression is considered an element of high cellular differentiation and has a very important role in prognosis and therapy [
3]. In fact, breast cancer prognosis progressively worsens in ER-negative subtypes due to their high aggressiveness, hormonal therapies insensitivity and chemoresistance and a subset of patients will progress to relapse after CT remission, which subsequently leads to metastasis. Furthermore, in patients with ER-positive BC, the relapses have molecular characteristics similar to those of ER-negative BC [
24,
25]. The underlying mechanisms of BC heterogeneity features and mechanisms that drive to therapy resistance (both hormonal and chemotherapeutic) are conundrums that have still to be completely solved and efforts have to be made in order to better understand the biology of BC and stratify patients to effective treatments [
24].
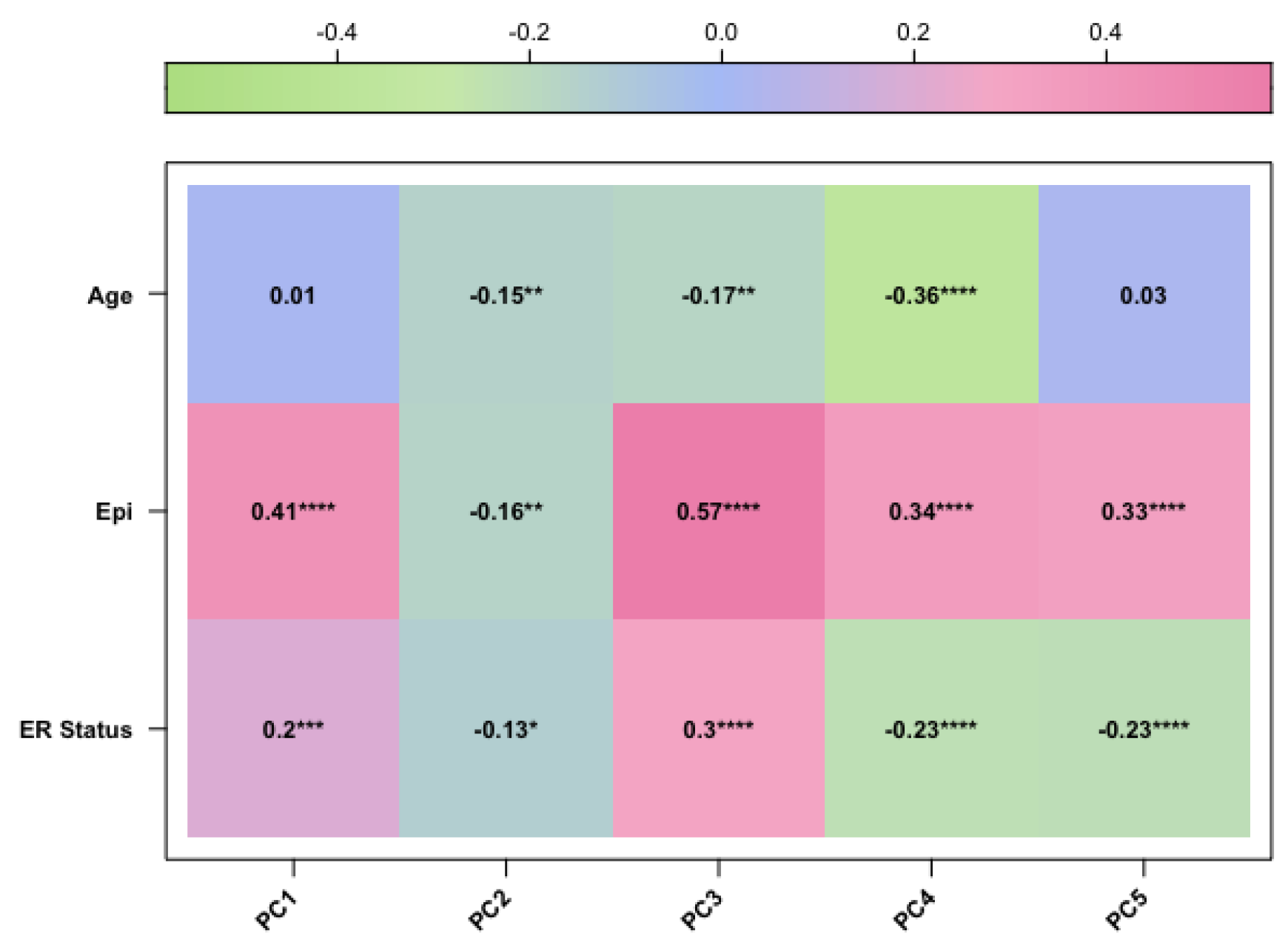
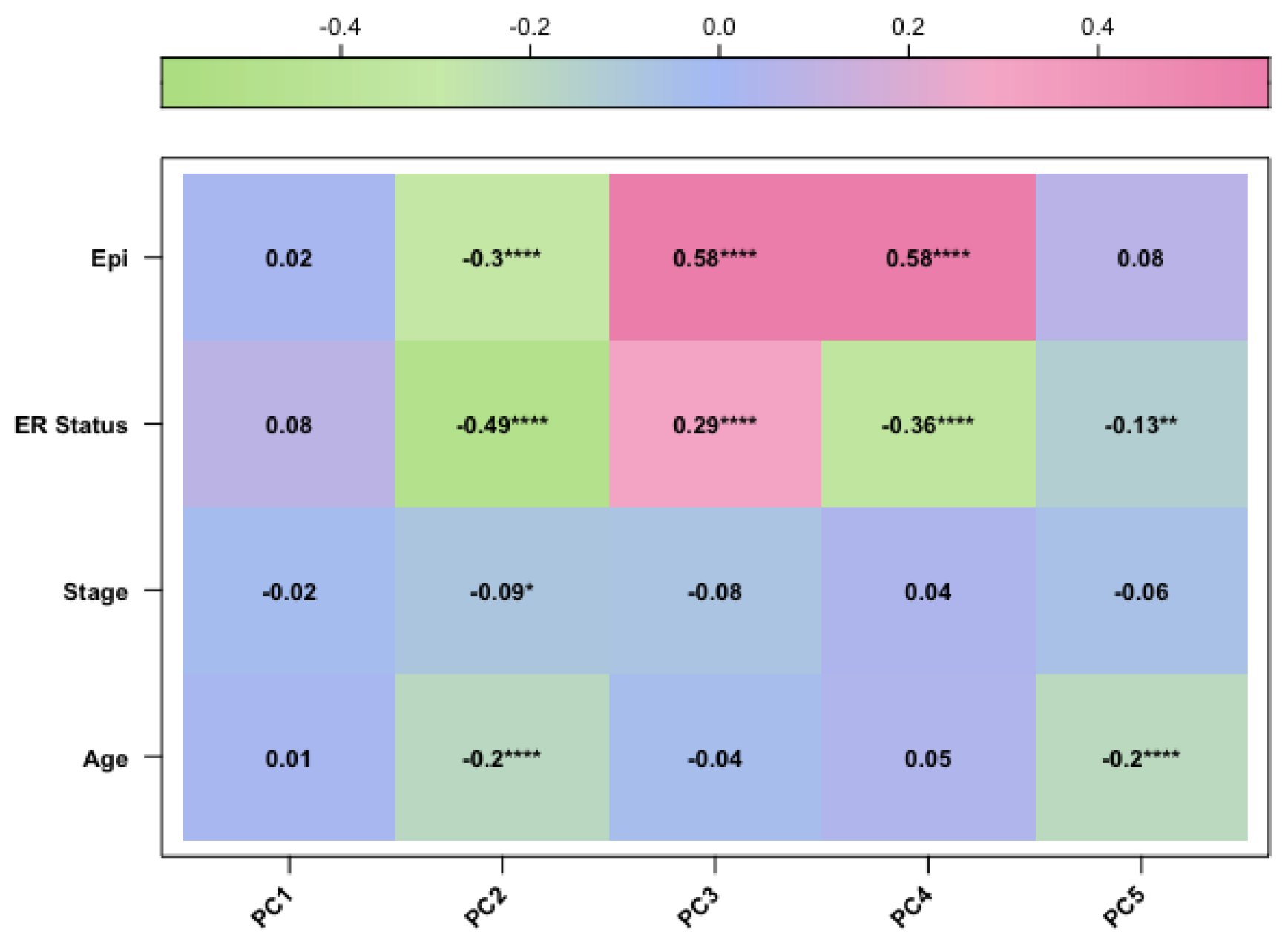
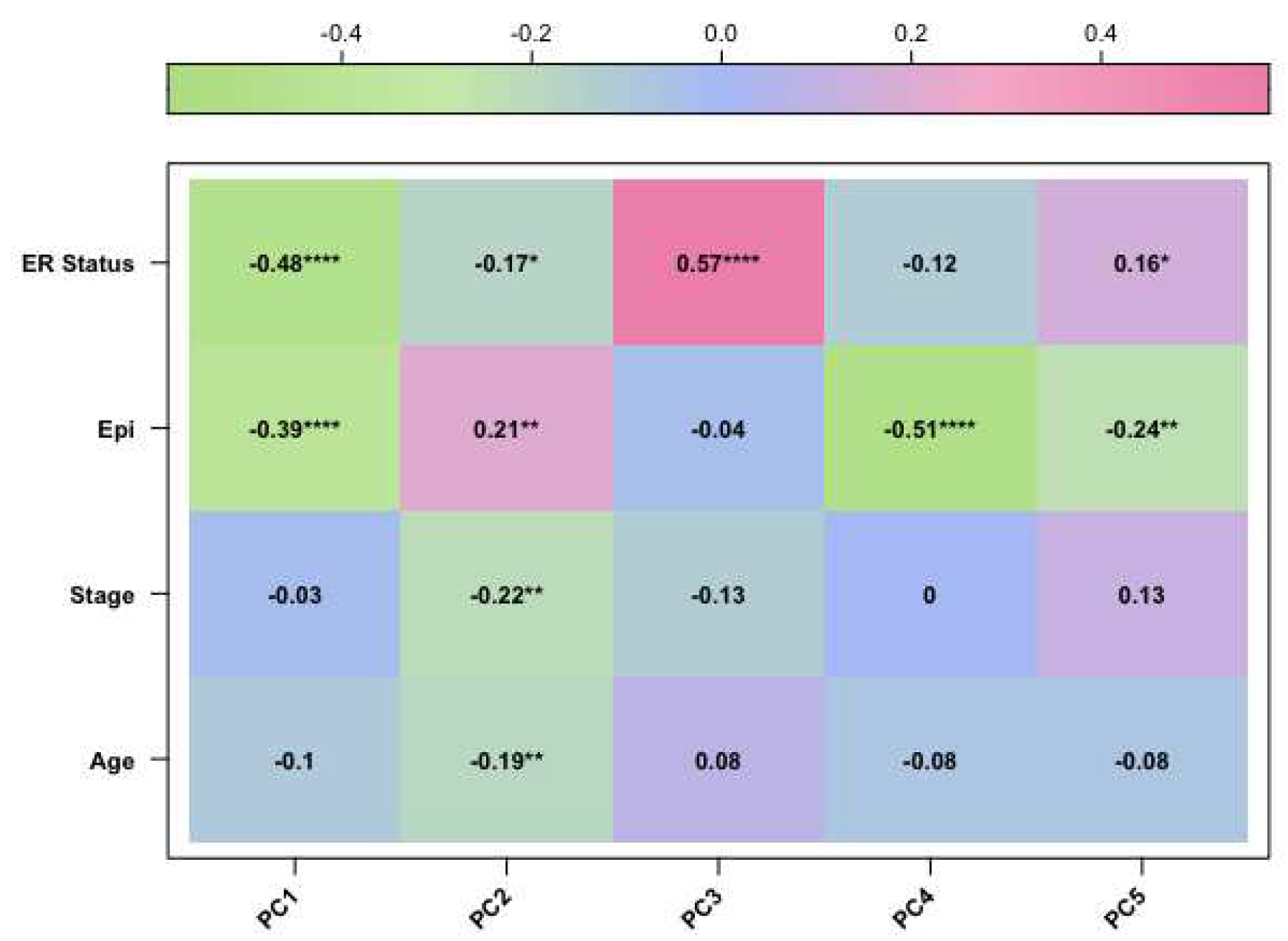
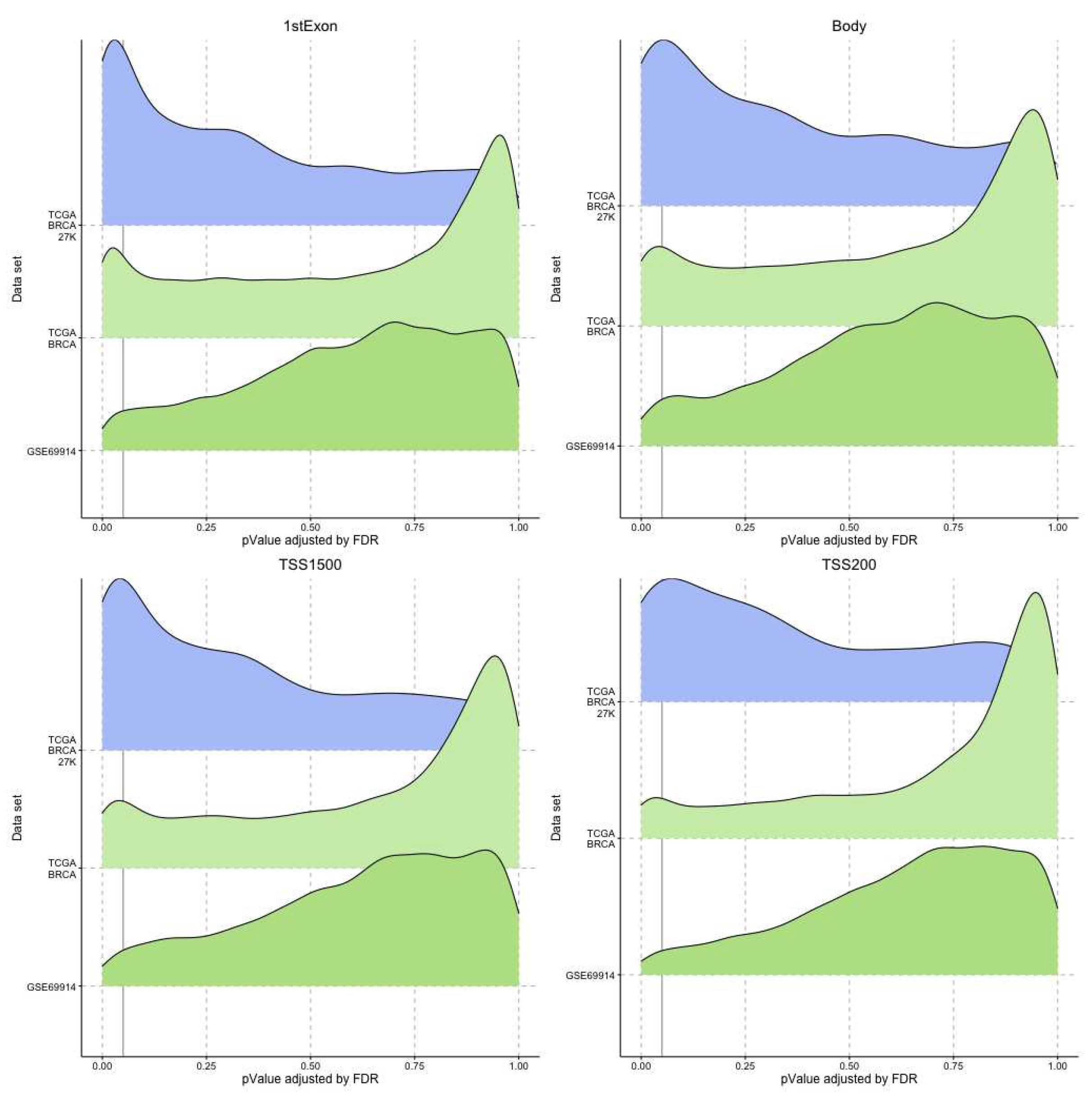
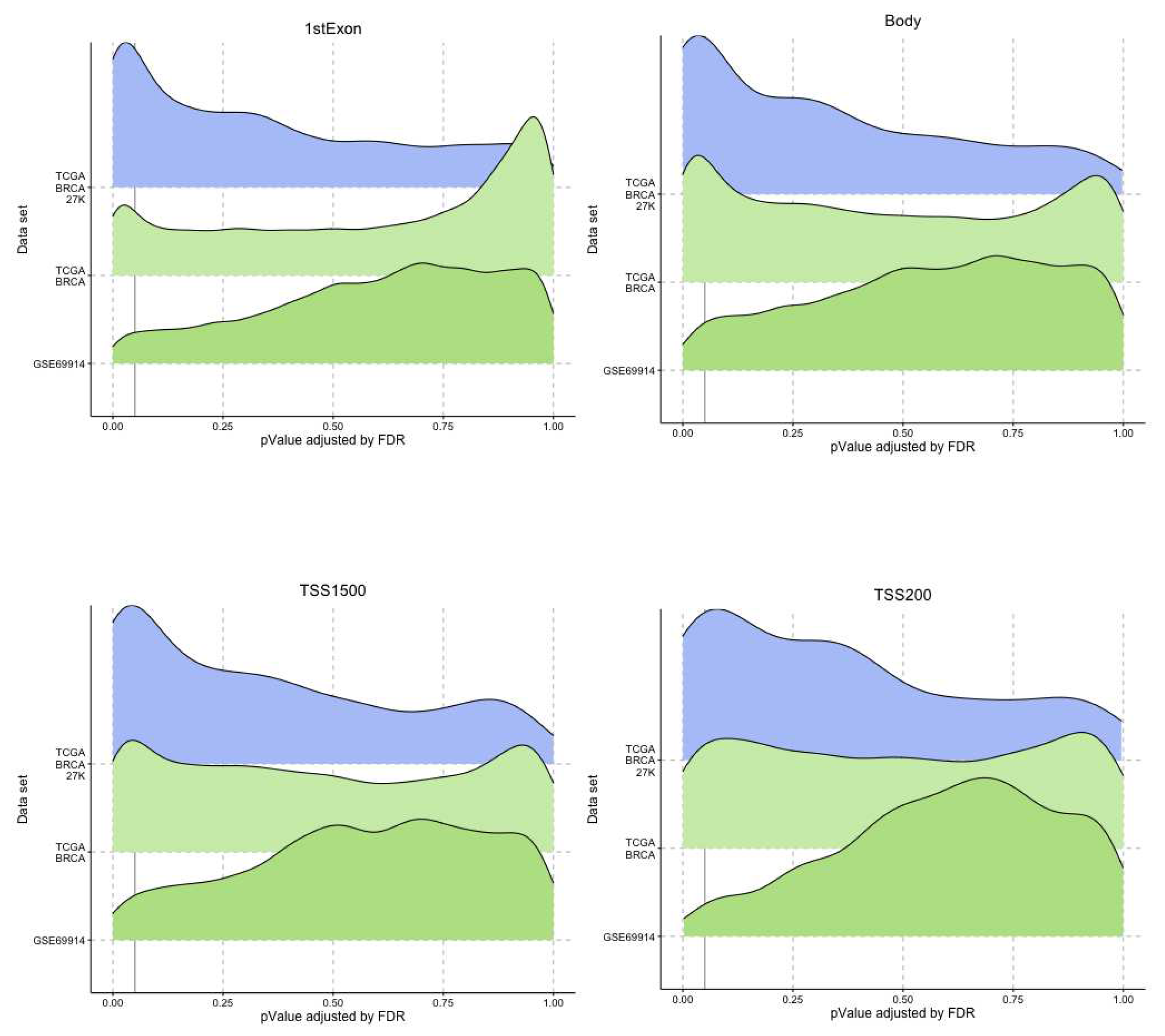
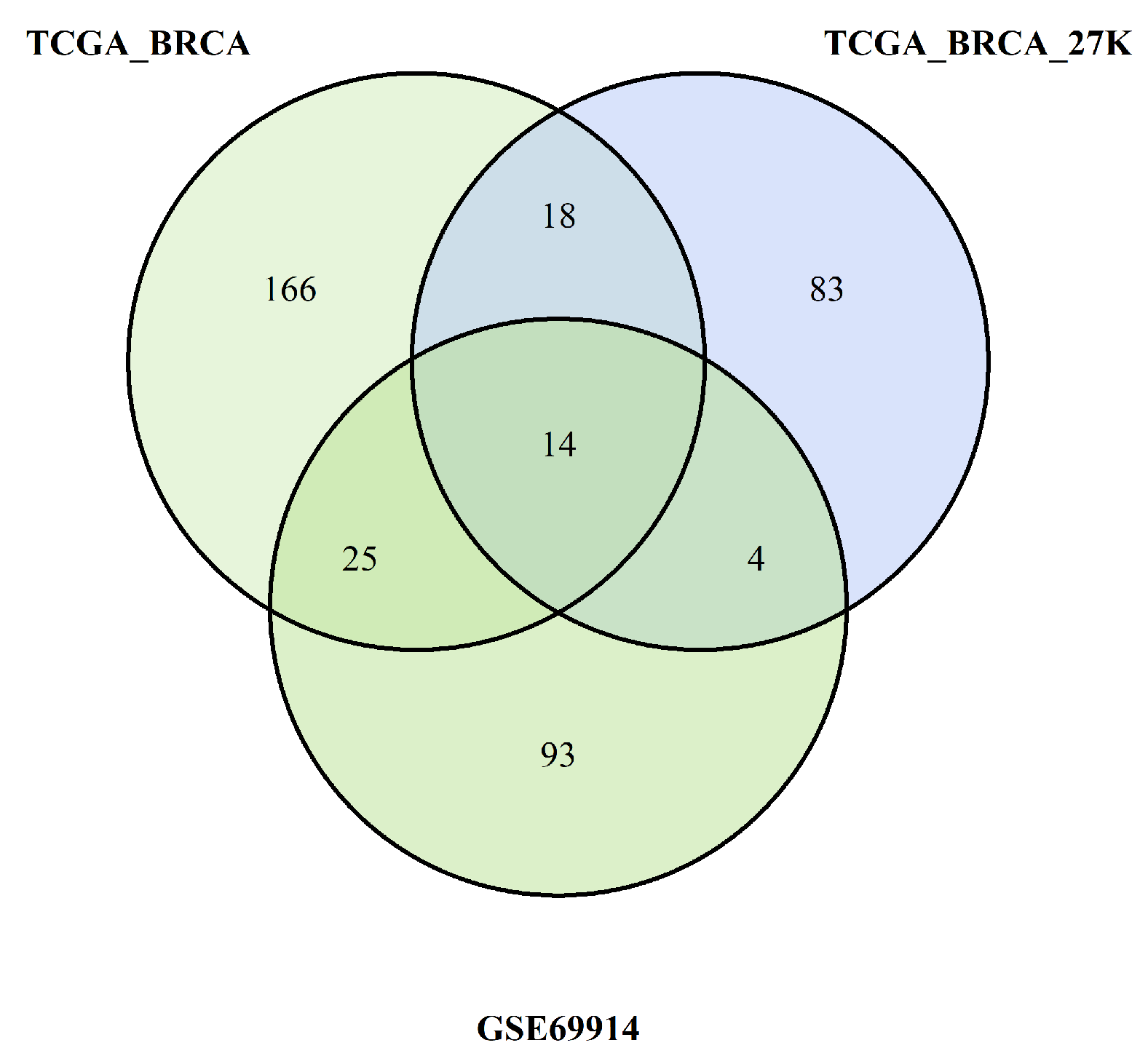
In our study, we tried to characterise these two groups of breast cancers (ER-positive and negative) by applying an epigenetic score based on the identification of different epigenetic outliers (defined as epimutations). An epimutation, at a given CpG site, could be defined as an extreme outlier of DNA methylation value distribution across individuals [
14]. Previous studies evaluated the presence of epigenetic outliers in BC but they compared BC tumour samples vs normal breast tissue or blood samples from BC patients vs control women without BC [
14,
15,
27]. Teschendorff AE et al., [
15] demonstrated that DNA methylation outliers in pre-neoplastic lesions define epigenetic field defects, marking cells which become enriched in invasive breast cancer and cervix cancer and which may therefore contribute casually to cancer progression. In another study, the same group highlights that the identification of outlier methylation profiles allows more reliable identification of risk-associated CpGs than statistics based on differences in mean methylation levels [
27].
4.1. Cancer cells, epigenetic mechanisms and DNA methylation
Cancer cells acquire the ability to divide and grow uncontrollably [
17]. Though it is well established that this could be due to both genomic and epigenetic alterations, the process through which cells acquire this characteristic is not completely understood [
26]. Several studies have demonstrated the importance of epigenetic alterations in multiple aspects of cancer biology (tumour pathogenesis and immuno-modulation), cancer diagnosis and prognosis and, finally, treatment response and therapy resistance [
26,
28]. DNA methylation is one the most commonly occurring epigenetic events, in which there is the addition of a methyl group to the carbon 5-position of cytosine within a cytosine guanine (CpG) dinucleotide by enzyme DNA methyltransferase. DNA methylation can be stable and heritable through cell divisions but in the meanwhile, it is reversible and modifiable by specific enzymes [
26]. Many studies report how breast cancer cells show disrupted methylation patterns in their DNA [
24,
29]. Moreover, DNA methylation pattern can be very specific not only for different types of tumours (inter-tumour heterogeneity) but also for different tumour subgroups (intra-tumour heterogeneity) and therefore has been used also to identify different cancer types and to trace the primary origin of metastatic tumours [
26,
29].
In general, global DNA hypomethylation has been associated with cancer. DNA hypomethylation can determine chromosomal instabilities and gene activation, thus leading to the upregulation or overexpression of proto-oncogenes, increased recombination and mutation rates [
29]. Hypomethylation contributes to oncogenesis also by activation of latent retrotransposons or mobile DNA, such as long interspersed nuclear elements, that can determine disruption of expression of the adjacent gene, for example, homeobox [
26].
DNA hypermethylation in cancer, instead, is associated with a direct gene repression effect (of tumour-suppressor genes, for example), but also with compaction of chromatin that in turn modifies its accessibility and, finally, determines instability and alteration of gene expression (silencing of DNA repair genes, for example) [
29]. However, the inhibition or activation of transcription by methylation is dependent on the analyzed DNA gene’s segment (promoter, TSS or gene body).
DNA hypermethylation of promoters transcription start sites (TSS) or enhancers contributes to reducing gene expression or silencing by interfering with the binding of specific transcription factors to their recognition sites or by binding of transcriptional repressors specific for the methylated sequence [
28]. Estecio and Issa [
30] underlined that CpG island promoters are the most straightforward compartment to evaluate when searching for aberrant DNA methylation in cancer, above all considering that these CpG islands usually are unmethylated in normal cells (except for imprinted and X-chromosome inactivated genes). Therefore, they speculate that these abnormally methylated gene promoters (along with other regions with regulatory function) will likely reveal important players in tumour biology. They reported examples of promoter hypermethylation of the CDKN2A and MLH1 genes.
On the contrary, hypermethylation at gene bodies is associated with active transcription and gene expression, as a result of mRNA expression studies (as the case of homeobox) [
26]. It has been suggested that the sliding of RNA polymerase over the gene body attracts DNA methyltransferase enzymes and therefore that DNA methylation in a gene body is a consequence of transcription, rather than an active agent promoting it. Others suggested that methylation marks embedded in coding sequences are associated with the timing of transcription initiation events [
31]. Moreover, differences in CpG methylation between exon and intron regions raise the possibility that gene body methylation participates in splicing regulation [
30]. Finally, the biological meaning of gene body methylation remains still unclear and more studies are needed to address this issue.
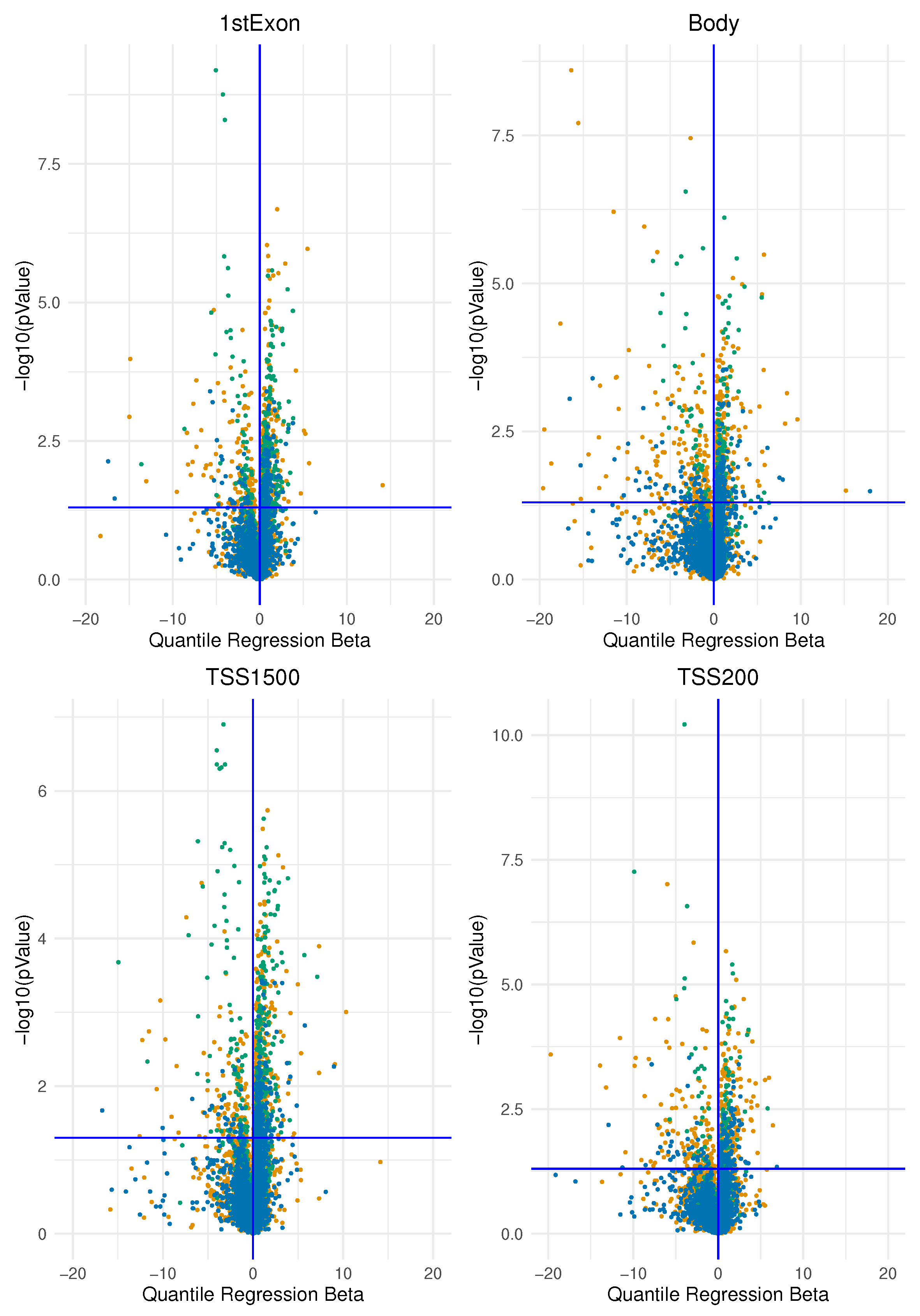
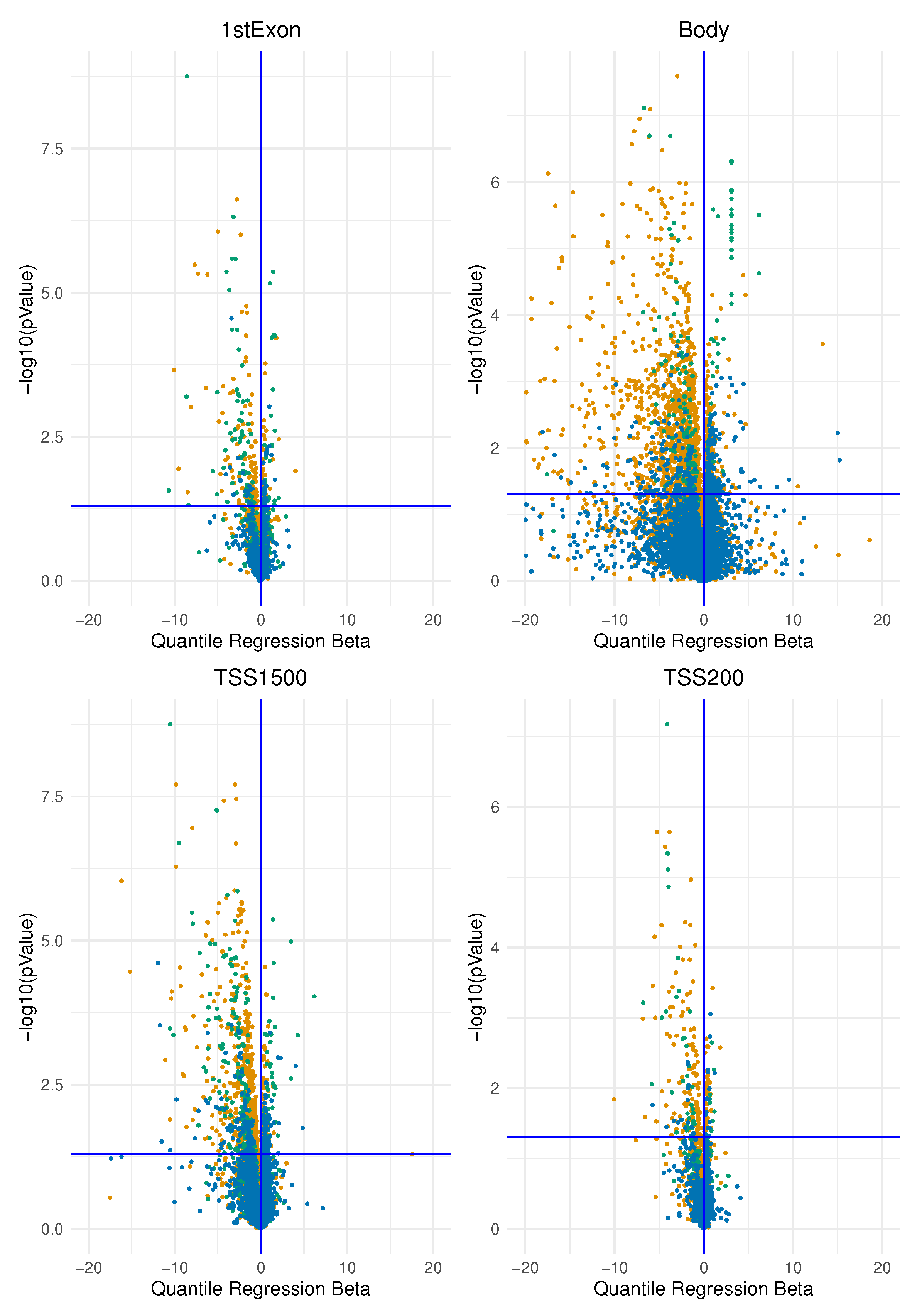
Methylate marks in intergenic regions are thought to have little impact on genome activity [
31]. In this study, according to previous studies, we found the most important differences of epimutation score between the two groups of ER-positive and ER-negative breast cancer precisely in the promoters of specific genes belonging to few pathways.
4.2. Main pathways identified by our analysis
Pathway-centric analysis, as opposed to gene-centric one, allows to identify of recurrent altered signalling or function in cancer, based on alterations found in different genes belonging to the same pathway but not altered at equal frequencies [
17]. Moreover, evaluating the burden of epimutations per gene region (TSS200, TSS1500, promoter, gene body and first exon) and then using these data for gene enrichment pathway analysis, permits to capture the biological process involved by these variations avoiding to treat individual occurrences of epigenetic marks like nucleotide polymorphisms (i.e., as epialleles), since it was observed that the methylation state of any particular nucleotide in the promoter, for example, is usually irrelevant and could represent statistically significant alterations but functionally uninformative differences [
31].
The ESR-mediated signalling was identified as the pathway whose genes are overcharged by higher epimutation score due to hypomethylation of TSS1500 gene region (corresponding at least in part to promoter region) in ER-positive BC vs ER-negative BC. In light of the fact that a hypomethylated promoter could permit gene expression (even if it is not the unique condition), we interpreted this result as coherent with a higher activation of this pathway in the BC group that expresses ER. In this sense, previous studies centred on the role of epigenetic control of ER function, confirm our results. This is indirectly suggested by many studies that report higher hypermethylation status of ER-promoter in the group of ER-negative BC and that ER gene hypermethylation is associated with lacking ER gene expression [
32,
33,
34,
35]. Moreover, other studies confirm, for example, that inhibition of the DNA methyltransferase (DNMT) in ER-negative BC cells induces re-expression of oestrogen receptor-alpha [
36,
37].
The pathways identified by a higher epimutation score due to hypermethylation of the TSS1500 gene region in ER-positive BC vs. ER-negative BC belong to the following main groups: the Notch pathway, the SUMOylation pathway, the signalling and the ubiquitination protease signalling. Other studies confirm that, generally, the hypermethylated loci in ER-negative tumours were clustered closer to the transcriptional start site compared to ER-positive tumours[
38] and that the cumulative effect of a very large number of epigenetic perturbations to be correlated specifically and in cis with hundreds of additional transcriptional changes [
39].
Interestingly, the SUMOylation pathway and ubiquitination protease signalling belong to the same kind of protein post-translational modifications.
The data about the role of signalling in BC are few and contrasting. Todorović-Raković found that raised serum IFN-
levels associate independently with favourable disease outcomes in hormonally dependent breast cancer [
40]. On the other side, Yu and colleagues found that IFN-
induces tumour resistance to anti-PD-1 immunotherapy in BC [
41] and experiments on BC cells demonstrated that IFN-
could up-regulate the expression of PD-L1, promote cell migration and transmission and facilitate the epithelial-mesenchymal transformation of breast cancer cells [
42].
The SUMOylation and the Notch signalling are the other two pathways whose genes emerged as characterised by a higher epimutation score due to hypermethylation in the TSS1500 gene region in the ER-positive vs ER-negative BCs. Since we performed a direct comparison of the two BC groups, we hypothesized that the presence of a higher hypermethylation of the gene region that overlaps to the gene promoters, correspond to a general reduced gene expression (as discussed before) and, consequently, to a reduced activity of these two pathways in the ER-positive BCs. Moreover, based on the direct comparison between the two groups of BC, we speculated that the relative hypomethylation in the ER-negative BC and could justify the hypothesis of a presence of a state of hyper-activation of these two pathways in ER-negative BC. The presence of a significant activity of these two pathways in the ER-negative BC group does not lack as discussed thereafter [
43].
4.3. About the role of SUMOylation and NOTCH pathways in ER-negative BC and their correlation with epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) and breast cancer stem cells (BCSC)
Many studies suggest the existence of complex and intricate relations among the biological process of Epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT) and cancer stem cells (CSC) phenotype. The EMT is characterized by the acquisition of phenotypic plasticity and stem cell-like properties of the tumour cells, including cytoskeleton adjustment, loss of cell polarity and loss of cell adhesion. During EMT, cells lose their epithelial features and markers - like cobblestone shape and E-cadherin expression - to acquire a mesenchymal phenotype - assuming spindle shape and mesenchymal markers, like vimentin and fibronectin [
23,
44]. These mesenchymal attributes permit cancer cells to develop new capabilities, such as migratory and invasiveness, pro-survival ability, stemness, immunosuppression and chemoresistance [
45]. These characteristics can lead to the formation of CSCs, maintenance of aggressiveness, initiation of metastasis, and tumour relapse [
46].
CSCs have been identified for the first time in 2003 in human breast tumours (BCSCs) and since then a growing number of evidence has supported their role in breast cancer initiation, intratumoral heterogeneity, progression, disease recurrence, metastasis and resistance to therapy [
47]. Actually, it is not clear the origin of CSC. In particular, the two main hypotheses are that they are cells already present in the tumour since its origin but in a state of quiescence or, in alternative, that they originate in a second moment through a process of de-differentiation (for example, through a process of partial/total EMT). Finding a set of markers to identify and target these partial/total EMT cells could lead to understanding the origin of CSCs and their deregulated pathways and could be a strategy for therapeutics development blocking cancer invasion and dissemination [
45].
The EMT and the CSC have been correlated to alterations of NOTCH and SUMOylation pathway in ER-negative BC in many studies [
23,
47,
58,
59,
60,
61].
Numerous studies found that the Notch signalling activation and protein SUMOylation may promote breast cancer tumorigenesis and progression by accelerating cell cycle transition and proliferation and facilitating tumor cell EMT in breast epithelial cells in vivo and in vitro [
23,
47,
58,
59,
60,
61,
70].
Notch1 knockdown in breast cancer cells suppressed the EMT process, tumour growth, migration, and invasion using in vitro and in vivo models. Jagged1-mediated Notch signalling activation was able to activate the EMT process and increase migration and invasion in breast cancer mainly through upregulation of N1ICD. Notch1 signalling is able to reverse the epithelial cobblestone morphology cells to the spindle mesenchymal one, to induce switching of epithelial markers like E-cadherin by the up-regulation of SNAIL, SIP1/ZEB2 and SLUG (which are E-cadherin direct transcriptional repressors) and the acquisition of mesenchymal markers such as vimentin, N-cadherin and fibronectin to reduce invasion and migration [
47,
59,
60,
61]. On the contrary, activation of Notch signalling can be suppressed by EMT-inhibiting microRNAs such as miR-34 and miR-200 [
60] The role of Notch signalling in EMT corresponds to its promotion of invasive and metastatic phenotypes. Activation of Notch signalling in non-invasive breast cancer cells promotes cell invasion and migration, while inhibition of Notch in invasive cells reduces their invasive and migratory capacity [
47,
59,
60,
61]and Notch signalling is correlated with metastasis in vivo [
62].
On the same way, SUMOylation participates directly in modifications of many transcription factors (TFs) and in activation of various signalling involved in the control of EMT [
23,
44]. Several transcriptional factors activity - including ZEB1, SNAIL and TWIST - that regulate mesenchymal cell marker expression, such as CDH1 (the E-cadherin gene) and promote EMT - is directly or indirectly influenced by SUMOylation pathway. ZEB1, one of the main TFs involved in EMT, has been reported to be regulated by SUMOylation through different mechanisms. SUMOylation of ZEB1, as well as its homologue ZEB2, inhibits E-cadherin expression and induces EMT. Moreover, silencing of SENP1 (which has also the function of peptidase that causes hydrolysis of SUMO bonds) decreases ZEB1 protein level, suggesting that deSUMOylation of ZEB has a role in activating the TF [
44]. By regulating numerous oncoproteins, ZEB1 plays an important role in metastasis. In the ER-negative basal-like breast cancer (BLBC), a breast cancer subtype enriched with expression of mesenchymal genes and reduced expression of epithelial ones including E-cadherin [
73], downregulation of CDH1 is mediated by ZEB1, which recruits DNMT1 (a DNA metil-transferase enzyme) to the CDH1 promoter to maintain the methylation status in the promoter. These results suggest that ZEB1 could act as a transcriptional repressor and an epigenetic modulator to induce EMT in breast cancer [
72]. A recent study demonstrates that also ZNF451, a SUMO2/3-specific E3 ligase, is a positive regulator of EMT through the SUMOylation of TWIST2 at the K129 residue. SUMOylation stabilizes TWIST2 by inhibiting its ubiquitination and degradation, and, consequently, promotes EMT [
44]. Two prominent mesenchymal transcription factors, Slug and Twist1, are up-regulated in cells that present mesenchymal characteristics. Expression levels of Slug and Twist1 are highest in ER-negative claudin-low tumors and both genes identify letrozole-resistant disease. Slug accumulation in basal-like tumours is also associated with BRCA1 mutations [
63]
Moreover, a direct correlation between aberrant Notch and SUMOylation pathway and the triple negative phenotype BC has been found in many studies.
Notch signalling has been seen hyperactivated in TNBC and in ER-positive BC with poor prognosis or with a higher risk of relapse (which have many features in common with ER-negative BC). It was suggested that this hyperactivation could have an important role in EMT induction and BCSCs proliferation in TNBC [
24], while in ER-positive BC could induce hormone-therapy resistance [
64]. Clinical analyses showed that JAG1 as well as NOTCH1, NOTCH3, and NOTCH4 are overexpressed at high levels in TNBC and correlated with the aggressive, metastatic and therapy resistance phenotype characteristic of TNBC and are associated with poor clinical prognosis. Moreover, expression of the Notch target, HES4, was correlated with poor prognosis outcomes in TNBC patients [
59]. Reedijk and colleague [
64] observed that patients with tumours expressing high levels of JAG1 or NOTCH1 had a significantly poorer overall survival compared with patients expressing low levels of these genes and moreover, a synergistic effect of high-level JAG1 and high-level NOTCH1 coexpression on overall survival was observed. Therefore, they suggest a mechanism whereby Notch is activated in aggressive and poor prognosis breast tumours (since JAG1 is a ligand of Notch-receptor-1) and that the basal breast cancer subgroup (belonging to ER-negative BC) shows poor overall survival as a result of JAG1-induced Notch activation in some of these tumours [
65] performed exome sequencing analysis to identify Notch mutations in various solid tumours, revealing that constitutive receptor activation induced by NOTCH1 and NOTCH2 mutations is limited to TNBC. A TNBC cell line with NOTCH1 rearrangement also exhibited high-level N1ICD (notch-1 intracellular domain) accumulation with subsequent upregulated target gene expression. In addition, NOTCH1 or NOTCH2 mutations can synergistically act with EZH2 to inhibit the tumour suppressor PTEN transcription at the promoter in TNBC [
66].
In a gene expression study, Orzechowska M. and colleagues evaluate [
67] the effect of differential expression of Notch members on DF) in luminal type A (lumA) and triple-negative (TN) BC. This study highlights significant differences in the biology of the two tumours and indicates differences in the signals activating the Notch pathway and particularly suggests a role of Notch signalling in BRCA progression through triggering EMT. From their analysis emerges that aberrant expression and regulation of Notch receptors have the most significant influence on the course of the disease. Notably, their results indicate that while there are subgroups of patients who will probably never experience disease relapse, other subgroups exist within the ER-positive lumA subtype which have a higher risk of recurrence due to potential transition into mesenchymal cell type. Moreover, their findings indicate that the expression profiles of Notch pathway members can be used to differentiate the DFS in lumA and TNBC subtypes, and so may serve as novel prognostic biomarkers. Finally, they highlight that MMP11, TAGLN and THB2, three genes involved in acquiring mesenchymal phenotype and which are regulated by the Notch pathway, can be used as potential therapeutic targets.
On the other hand, also the SUMOylation pathway seems to be involved in the maintenance of the characteristic of TNBC and basal BC subtype (belonging to the ER-negative BC group). Bogacheck and colleagues demonstrated that inhibition of the SUMOylation pathway reduced cell invasiveness and induced functional loss of CSCs in basal BC [
75]. Moreover, the same group in another study [
58] established that SUMOylation inhibitors induce a basal-to-luminal transition in BC cells and inhibit tumour outgrowth of basal cancer xenografts. Wang Q and colleagues reached similar conclusions about the relation of SUMOylation and ER-negative BC, evaluating the role of SUMO1-activating enzyme subunti1 (SAE1), an E1-ligase-activating enzyme, indispensable for protein SUMOylation in TNBC. They found that mRNA and protein SAE1 expression is increased in TNBC tissues compared to adjacent normal tissue and their expression levels are significantly associated with overall survival (OS) and disease-free survival (DFS) [
74]. In the review by Zhu et al., the multiple ways through which the SUMOylation pathway can influence stem cell functions in cancer are recapitulated [
76].
Finally, we discuss the role of epigenetic control on Notch and SUMOylation pathways. Interestingly, DNA methylation has been confirmed to have an important role in the regulation of Notch and SUMOylation pathways. Yousefi and colleagues, using the TCGA HumanMethylation450 Array data, determined that the epigenetic regulation of the Notch regulators contributes to their expression and suggested that Notch receptors and ligands expression is generally associated with the tumour subtype, grade, and stage [
68]. Aithal et al., focus on the methylation status of genes in the Notch signalling pathway from various cancers and highlight how this epigenetic alteration can be used as a biomarker for cancer diagnosis and subsequent treatment [
69]. Accordingly, to the important role of epigenetic reprogramming and DNA methylation, Hanif and colleagues highlight how these processes could be determinant specifically in TNBC in which we have seen that the Notch pathway could play fundamental regulatory functions [
24]. Finally, Kagara et al demonstrated that methylation is a significant mechanism regulating CD44, CD133, and Musashi-1 which are specific BCSC-related genes and that the hypomethylation of these genes correlates with a significant inverse correlation of mRNA expression in TNBC subtype [
71].
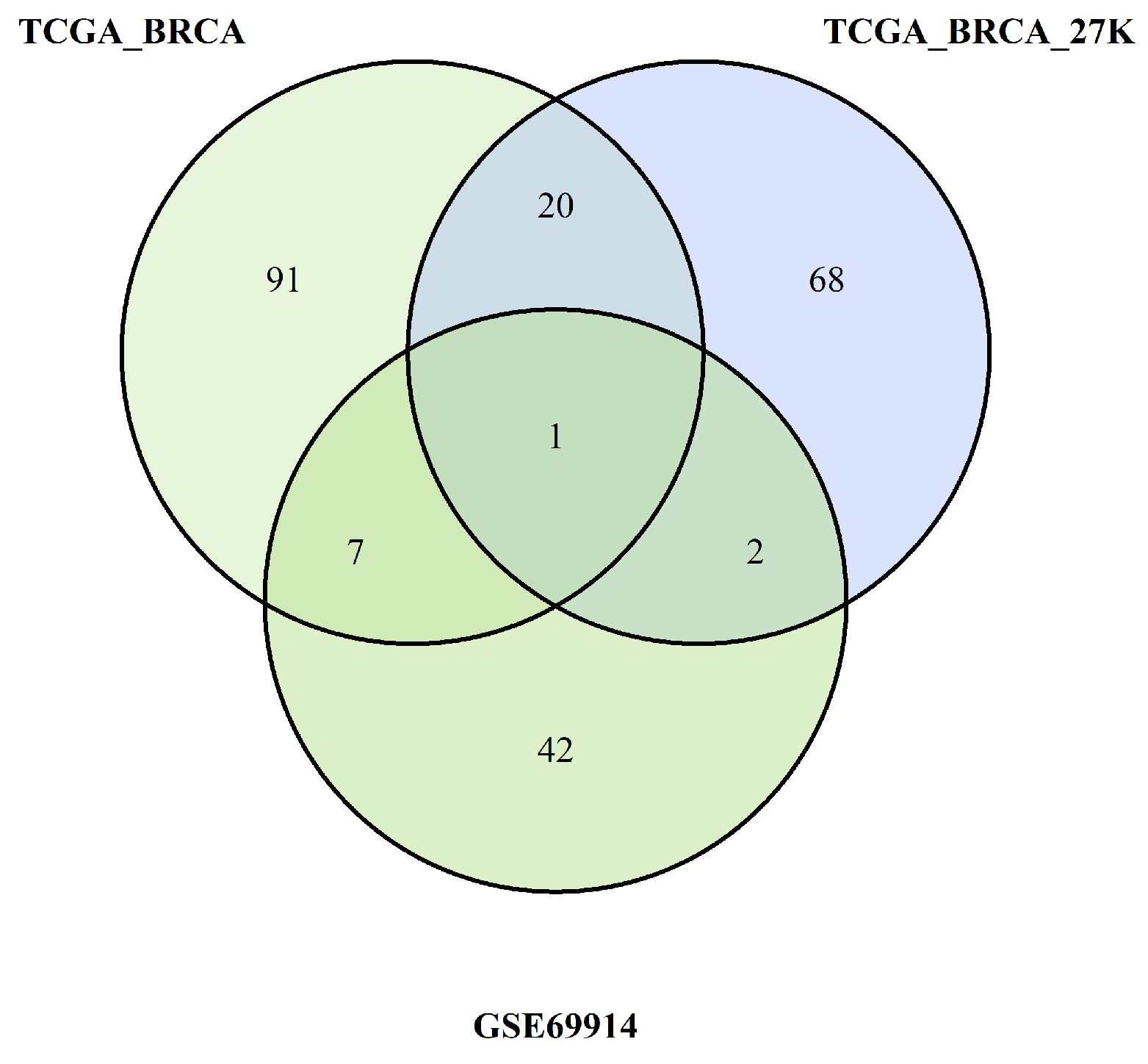
We want also discuss the limits of our study. First and foremost, for one dataset (GSE69914) the patients’ age and tumour stadiation were not available; therefore, age was inferred through methylation data, while tumour stadiation was omitted in the analysis of that dataset. Second, we introduce an epimutation score based on quantile ranking of the difference in the methylation levels; this is a new method of analysis that need to be validated with other studies. Finally, in the discussion we interpreted the results of hypomehtilatyion of the genes of ESR-mediated signaling in ER-positive BC as corresponding to an higher expression of the genes in this group of BC. Yet, we know that this condition of hypomethylation is not sufficient to draw this conclusion. An analogous consideration could be drawn when we considered hypermethylation promoter of genes belonging to Notch and SUMOyaltion pathways in the ER-positive BC. In this case, we concluded that the hypermethylation in the ER-positive BC corresponded to a reduced mehtylation in ER-negative BC (since we perfomed a direct comparison of methylation data between these two groups of BCs); we considered this condition potentially correlated to a higher expression of these genes in this group of ER-negative BC. We know that these are only indirect hypotheses that need to be confirmed.