1. Introduction
The demand for dietary supplements containing collagen has been growing for years. The collagen market, including hydrolysed collagen, is expected to continue to grow [
1]. Collagen is the most abundant protein found in mammals. (30% of the total protein mass) It has a structural role, contributing to the mechanical, conformational and organisational properties of our tissues [
2]. Collagen, being a protein, is made up of amino acids. Our body can produce it if we have sufficient protein-rich foods in our diet. However, vitamin C is essential for its synthesis, helping to bind collagen-forming amino acids. Collagen can be extracted from pork, beef, chicken and various seafood. Its consumption also affects the skin, eyes, hair, nails, gums, ligaments, muscles, cartilage, bones, digestion and heart health. The demand for dietary supplements containing collagen has been growing for years. The collagen market, including hydrolysed collagen, is expected to continue to grow [
1].
The main types of collagen:
Type I: the most common type of collagen. It is found in connective tissues, including tendon, ligament, dermis and blood vessels. Its main sources are marine fish and, to a lesser extent, pigs [
3].
Type II: in adults, it is the main structural component of the hyaline cartilage of joint surfaces, thus affecting joint function. It can also be found in other tissues such as the nucleus of the intervertebral disc, retina, sclera and lens of the eye. It is used as a dietary supplement for the treatment of joint pain and inflammation and as a source of dietary protein [
4].
Type III: the second most common type of collagen in tissues. It is usually found in tissues that have elastic properties, such as the skin, lungs, intestinal walls and blood vessel walls. It is also found in fibrous proteins in bone, cartilage, dentin, tendons and other connective tissues. Its main sources are pigs and cattle [
3].
The effects, role, and benefits of collagen supplements, based on the results in the literature, are limited to the areas of our research:
The skin undergoes structural changes with age. There is a deterioration in neurosensory perception, permeability and the ability to recover from injury. The skin's natural ability to retain water is reduced as a result of the amino acid composition of aged skin changing. The amount of hyaluronic acid produced by fibroblasts decreases and collagen synthesis slows down [
5]. Collagen peptide supplementation can also increase lean body mass and muscle fibre diameter [
6]. Researchers have shown that taking collagen can promote the synthesis of muscle proteins such as creatine and stimulate muscle growth after exercise [
7]. Collagen is a major component of connective tissues, including tendons, ligaments, skin and muscles [
8]. Collagen peptide supplementation is also useful in relieving the symptoms of osteoarthritis. There is a significant improvement in pain, stiffness and physical function [
9]. The glycine content of collagen reduces the risk of stomach ulcers [
10]. Collagen synthesis is important in the process of intestinal wall repair and healing. [
11]. A link has been shown between inflammatory bowel disease and reduced serum collagen levels [
12]. Oral collagen supplementation has been shown to have a positive effect on blood lipids, with regular use, the LDL/HDL ratio is reduced [
13], high blood pressure is reduced [
14], and arterial stiffness is reduced [
15].
In research, only pre-digested (hydrolysed) collagens are used, which contain peptides and not whole proteins [
16].
Collagen supplements are in increasing demand due to the need to delay age and stay youthful, as they have been shown to have positive effects on skin, joints and bones. The hydrolysed collagen market is expected to grow fastest, supported by its increasing use in the healthcare sector [
17].
The speciality and uniqueness of dietary supplement used in the study is the high levels of L-arginine and hyaluronic acid, in addition to collagen and vitamin C.
The individual mechanisms of action and physiological role of these ingredients are well understood, but have not yet been uniformly tested in the pairing and amounts of the dietary supplement used in this study.
The aim of the research: To investigate the effectiveness of the tested dietary supplement in elderly patients with musculoskeletal complaints. On the one hand, we wanted to demonstrate that the dietary supplement under investigation could reduce musculoskeletal complaints, and on the other hand, that the effectiveness of the supplement could be enhanced by regular, intense exercise in addition to consumption.
Thirdly, we have used laboratory tests to refute the common misconception that dietary supplements can cause liver and kidney damage.
2. Materials and Methods
The research was conducted at the Faculty of Health Sciences of University of Miskolc, during a 60-day study period. 30 elderly people aged 60 years and over were included in the study, who live an active life, with musculoskeletal complaints (permanent or recurrent degenerative musculoskeletal complaints affecting at least two body parts or joints), and randomly divided into two groups (study and control).
All participants took part in blood tests, body composition measurements, somatometric tests, joint range of motion and endurance tests at the beginning and at the end of the study period, and consumed 25 ml of the study supplement dissolved in 2 dl of water every morning throughout the study period.
The experimental group - contrary to the control group - participated in three guided physiotherapy sessions per week throughout the study.
The dietary supplement tested in our study (one dose: 500 mg Vitamin C (625%RIV), 10000 mg Collagen, 40 mg Hyaluronic acid (molecular weight Da (0.8-1.5)×10 6), 1075 mg L-Arginine, 1074 mg Glycine) have been formulated taking into account international research on collagen.
Socio-demographic data: data from 13-13 individuals in both study and control groups were analysed. There were 1 man in the test group and 2 men in the control group. The average age was 68.9 +/- 4.6 years in the study group and 69.9 +/- 4.9 years in the control group. The participants were mostly retired, with 2 people in the study group working in intellectual jobs and three in the control group, also in intellectual jobs.
Somatometric tests: body height was measured using an Inbody BSM 270, waist and hip, thigh and upper arm circumferences were measured manually using a tape measure and tabulated.
Extensive anthropometric and body composition analysis: was performed by using InBody 270 (InBody Co., Ltd., South Korea) in accordance with the manufacturers’ protocol. During the analysis, the following parameters were determined: weight (kg), total body water (l), body fat mass (kg), soft lean mass (kg), fat-free mass (kg), skeletal muscle mass (kg), percent body fat (%), visceral fat area (kg), body cell mass (kg), total body water (l), extracellular water (l), intracellular water (l), mineral mass (kg), bone mineral content (kg), protein mass (kg), basal metabolic rate (kcal), and overall fitness score (InBody Score).
Passive Range of Motion (PROM): Movement applied to a joint solely by another person or persons or a passive motion machine. When passive range of motion is applied, the joint of an individual receiving exercise is completely relaxed while the outside force moves the body part, such as a leg or arm, throughout the available range [
18].
Stamina test: determination of voluntary time, 3-minute step bench test - resting, maximum, 1, 3 and 5 minute relaxation heart rate data, fatigue rate at the end of the test with Modified Borg scale. (The Modified Borg Dyspnea Scale (MBS) is a 0 to 10 rated numerical score used to measure dyspnea as reported by the patient during submaximal exercise and is routinely administered during six-minute walk testing (6MWT), one of the most common and frequently used measures to assess disease severity in pulmonary arterial hypertension) [
19].
Garmin Vivoactive 4 activity watch: continuous monitoring of activity, heart rate, calorie consumption of the persons during the entire duration of the physical training;
Lab results: blood glucose; liver function (GPT, GOT, GGT), kidney function (urea, creatinine, GFR), vitamin B12 and D, ions (Na, K, Mg, Ca, Fe, transferrin, iron binding capacity, inflammatory parameters (red blood cell sedimentation, CRP, LDH, AST), blood lipids (cholesterol, HDL, LDL, triglyceride).
Our research is cross-sectional and prospective. The research will be longitudinal in duration and qualitative in method.
The methods used in this research provide valid and reliable results, as we examine the subjects' somatometric data, body composition, laboratory results, activity during physical exercises, musculoskeletal complaints, in several dimensions.
For descriptive statistical evaluation,mathematical mean, standard deviation (SD), number of items, minimum and maximum values were calculated; normality was checked by Shapiró-Wilk test, and the difference between sample means was tested by t-test.
Statistical analyses were performed by using IBPM SPSS Statistics Version 25 software packages.
Weeks 1-4 (Part A): Each training session started with a warm-up, about 5 minutes apart. This was followed by mobilisation exercises to improve the movement of the "stem" joints and spine in a relieved position. Elements of a standard series of posture correction exercises, stretching and strengthening of antigravity muscles followed.
Weeks 5-8 (Part B): Elements: low-intensity cardio-pulmonary training, postural correction, stretching and strengthening of antigravity muscles, even in loaded positions.
From week 5 onwards, part B was introduced, and thereafter fewer and fewer exercises were gradually phased out of part A, and more and more only elements of part B were used. Each time the exercise programme was pulse controlled.
3. Results
3.1. Results of the comparative analysis of laboratory results
Pre- and post-intervention blood laboratory results from the experimental and control groups were compared using statistical methods (normality was tested by Shapiró-Wilk test, and the difference between sample means was tested by t-test).
The laboratory analysis included the results of 26 constituents, of which 20 showed no measurable change.
It is important to note that liver function parameters (GOT, GPT, GGT) and renal function values (urea, creatinine, eGFR) also fell into this category.
In cases of for 4 items, the experimental group showed a significant change based on the t-test:
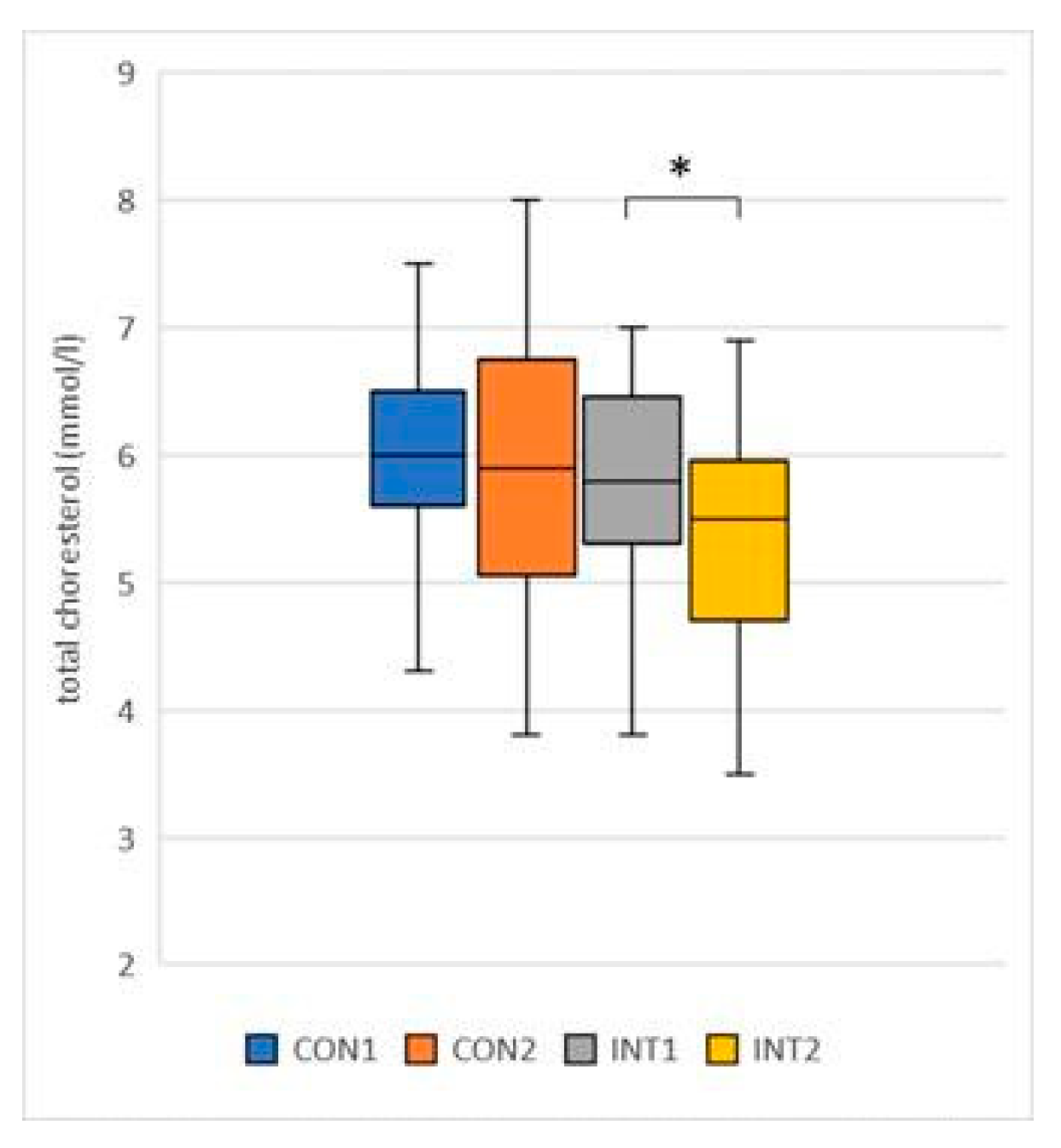
total cholesterol (mmol/l): the mean decreased in both groups, with -0.14 in the control group from 6.02 to 5.88, but the change was not significant (p=0.636), while the change in the experimental group (-0.44) was significant (p=0.018), with a decrease from 5.81 to 5.37 (
Figure 1);
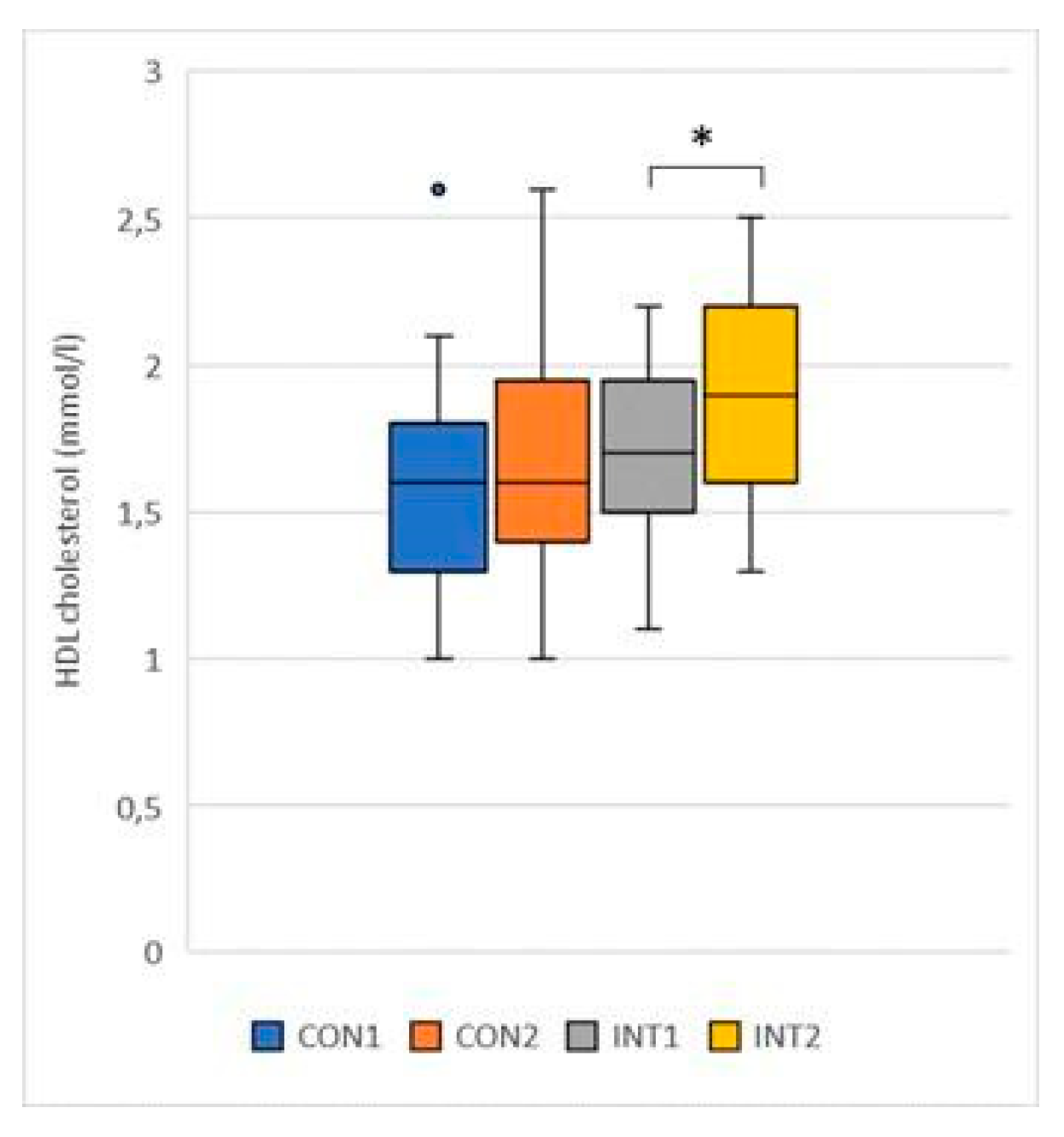
HDL cholesterol (mmol/l): the mean of both groups showed an increase, in the control group by 0.07 from 1.59 to 1.66, the change was not significant (p=0.121), in the experimental group the change increased by 0.23 from 1.69 to 1.92, which was significant (p=0.004) (
Figure 2);
Figure 2.
HDL cholesterol.
Figure 2.
HDL cholesterol.
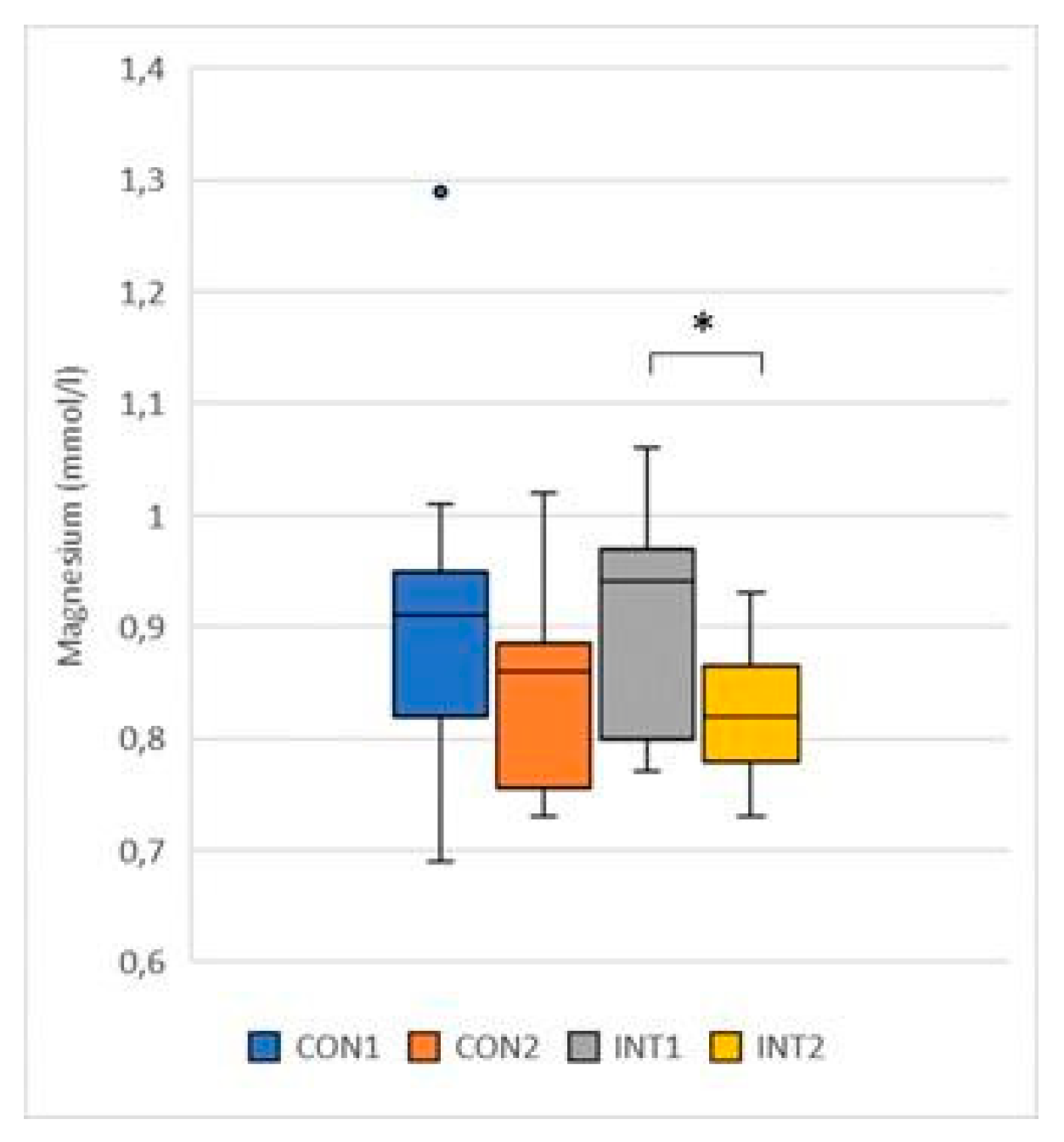
Magnesium (mmol/l): the mean decreased in both groups, in the control group by -0.07, from 0.90 to 0.84, showing no significant change (p=0.096), in the experimental group the decrease was -0.07, from 0.90 to 0.83, reaching significance (p=0.002) (
Figure 3);
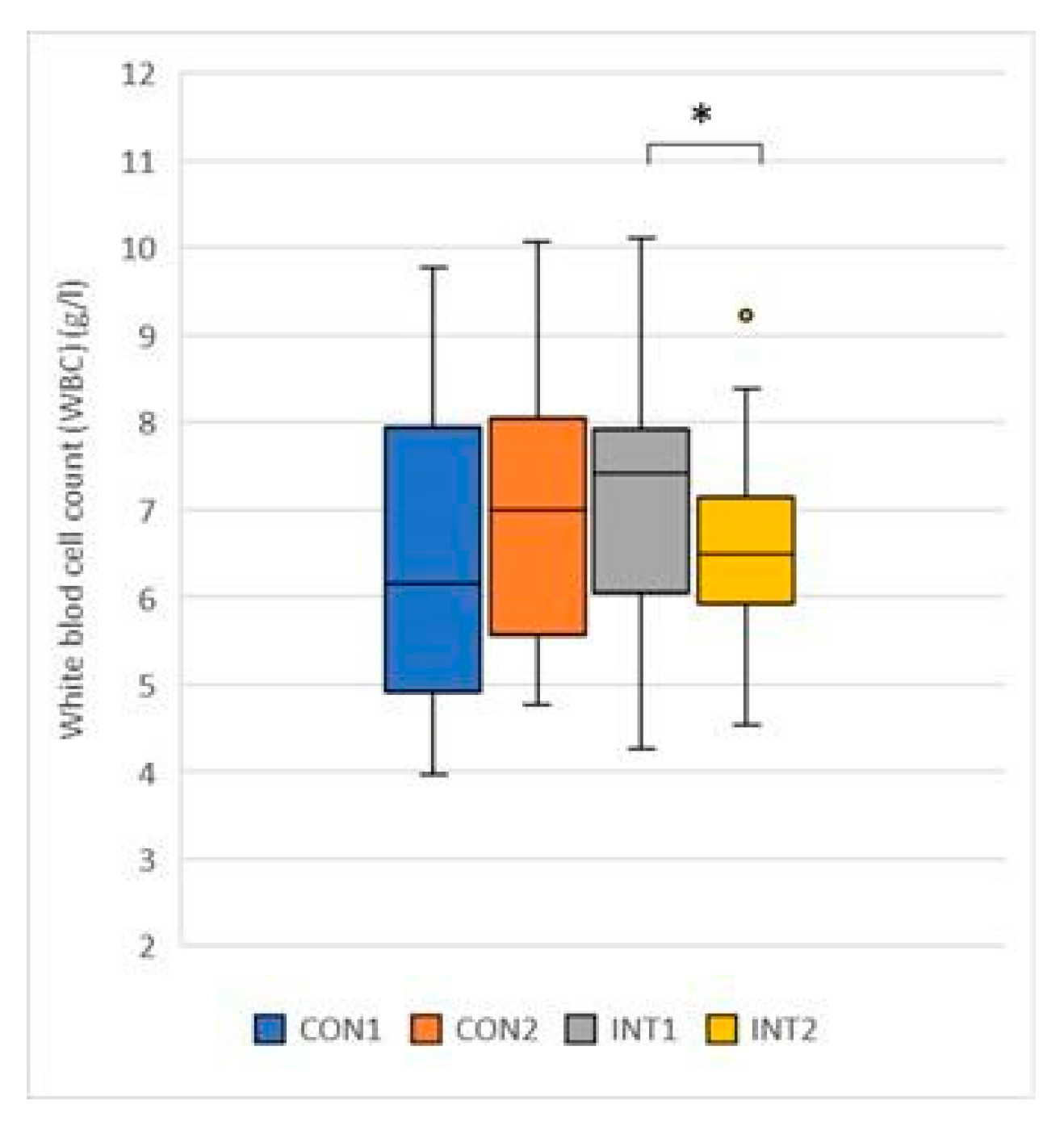
White blood cell count (G/L): the mean showed an opposite trend, although neither group was outside the normal range at the beginning or at the end of the study. While it increased by 0.49 from 6.47 to 6.96 in the control group to a non-significant extent (p=0.232), it decreased significantly in the experimental group by -0.46 from 6.96 to 6.67 (p=0.030) (
Figure 4).
Figure 4.
White blood cell.
Figure 4.
White blood cell.
for 2 items, the change was significant for both groups according to the t-test (Table xy):
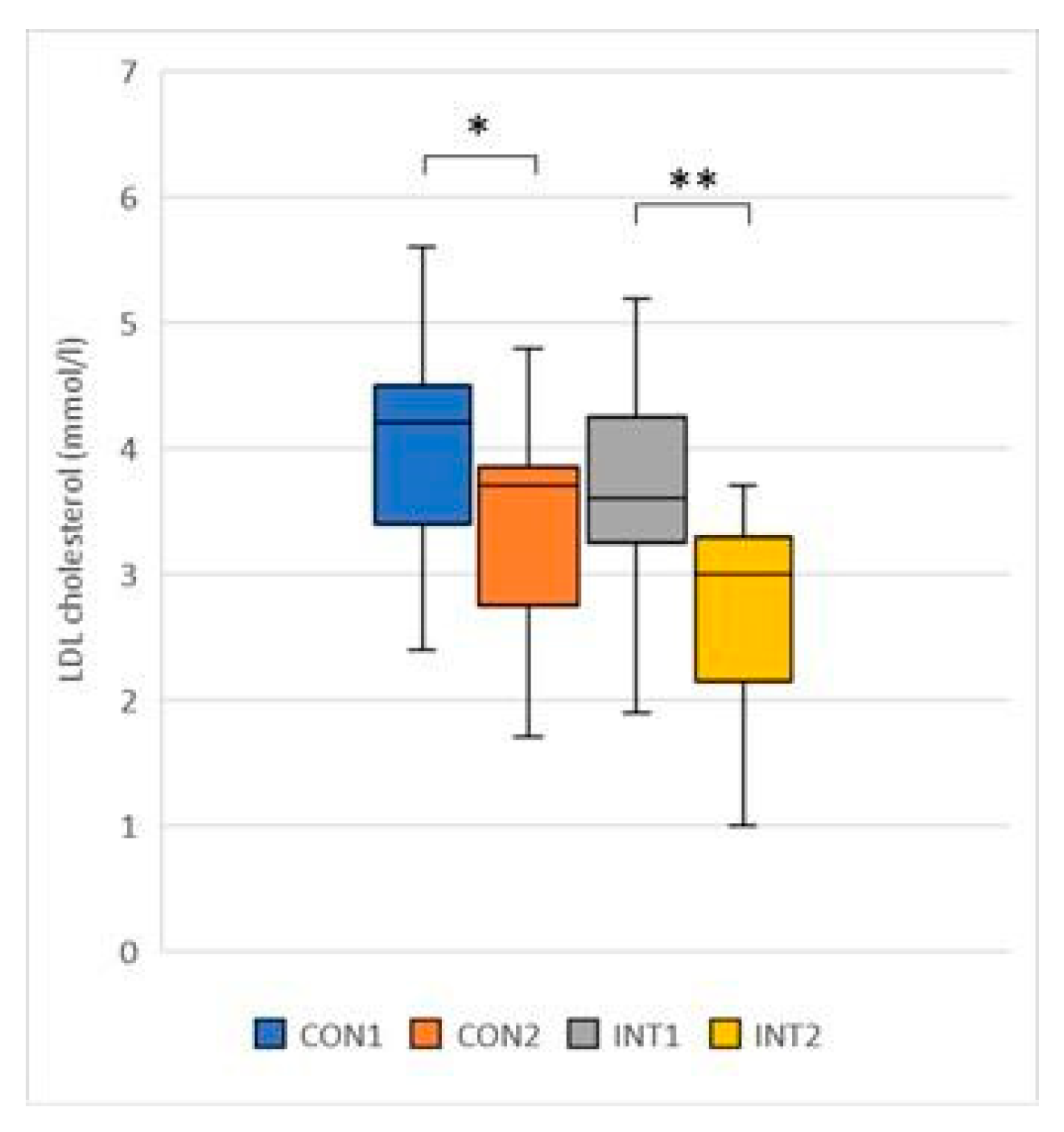
LDL (mmol/l): the mean of both groups showed a significant decrease, with the control group decreasing by -0.74 from 4.08 to 3.35 (p=0.003) and the experimental group decreasing by -0.98 from 3.71 to 2.72 (p=0.000) (
Figure 5);
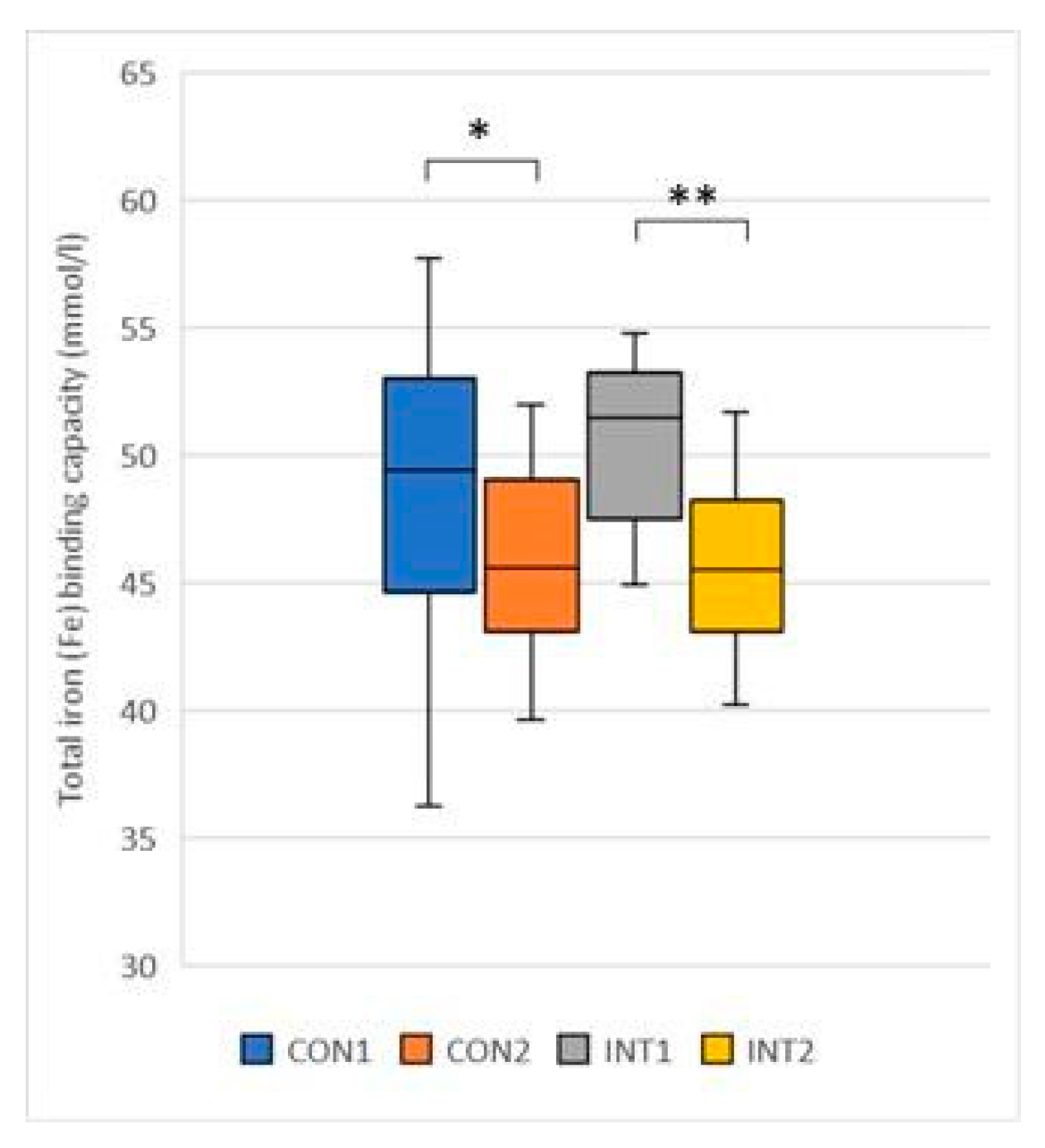
Total iron-binding capacity: a significant decrease was observed in both groups, with a decrease of -3.67 from 49.38 to 45.71 in the control group (p=0.018) and -4.53 from 50.39 to 45.86 in the experimental group (p=0.000) (
Figure 6).
3.2. Results of a comparative study of Inbody results
The results of the pre- and post-intervention Inbody body composition analyser of the experimental and control groups were compared using statistical methods (normality was tested by Shapiró-Wilk test, the difference between sample means was tested by t-test).
We analysed 13 different measures of body composition, 2 of which showed no measurable change: ECW (Extracellular Water), BMC (Bone Mineral Content).
for 8 test items, the experimental group showed a significant change based on the t-test:
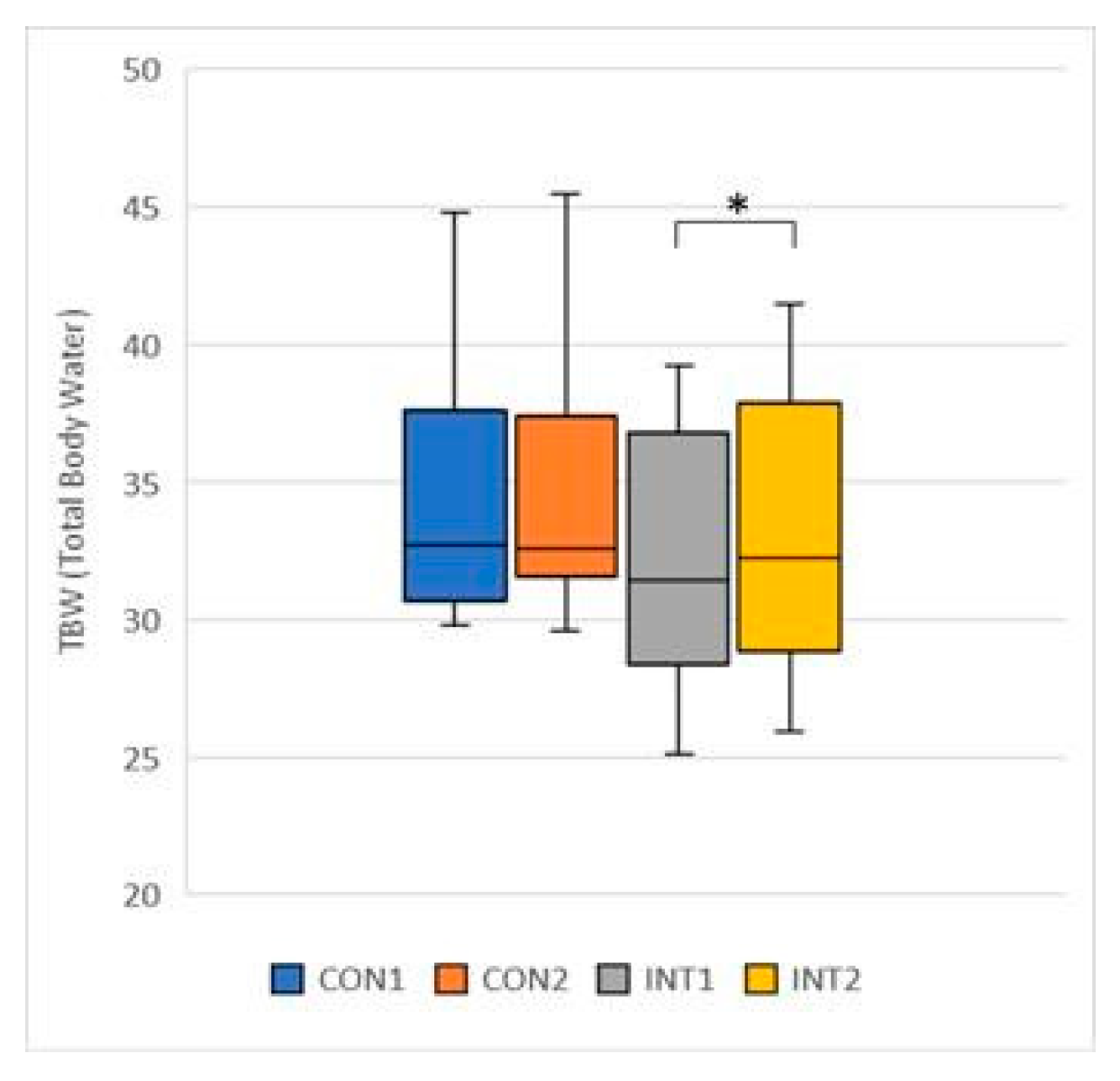
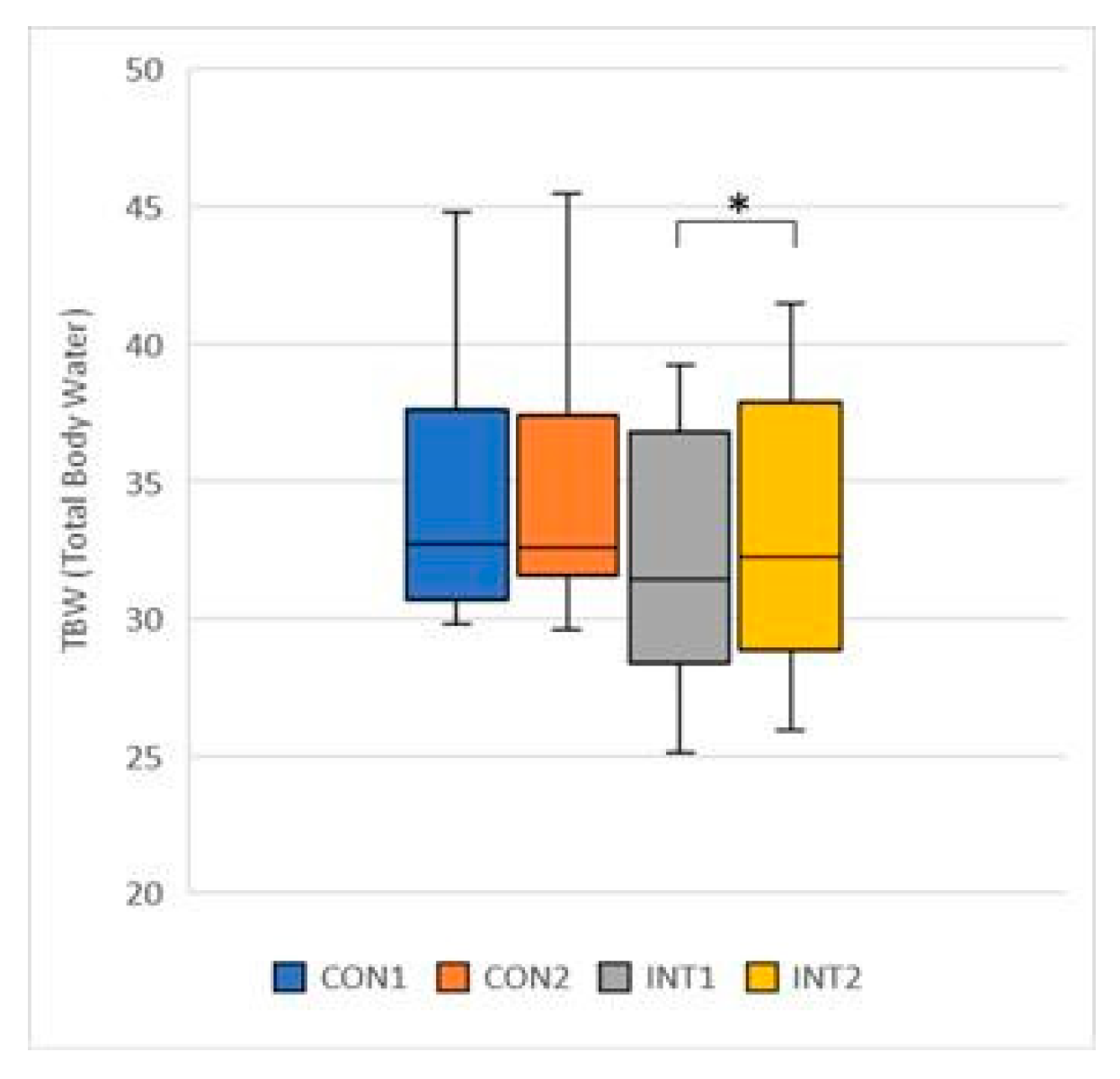
TBW (Total Body Water): the mean increased for both groups, by 0.10 for the control group from 34.26 to 34.36, a change that was not significant (p=0.744), but by 0.72 for the experimental group from 32.26 to 32.98, a significant change (p=0.003) (
Figure 7);
ICW (Intracellular Water): the change of the mean for the control group was negligible, increasing by 0.06 from 20.88 to 20.95, (p=0.809), but for the experimental group the increase was 0.82, from 19.84 to 20.65, a significant increase (p=0.013) (
Figure 8);
Figure 8.
Intracellular Water.
Figure 8.
Intracellular Water.
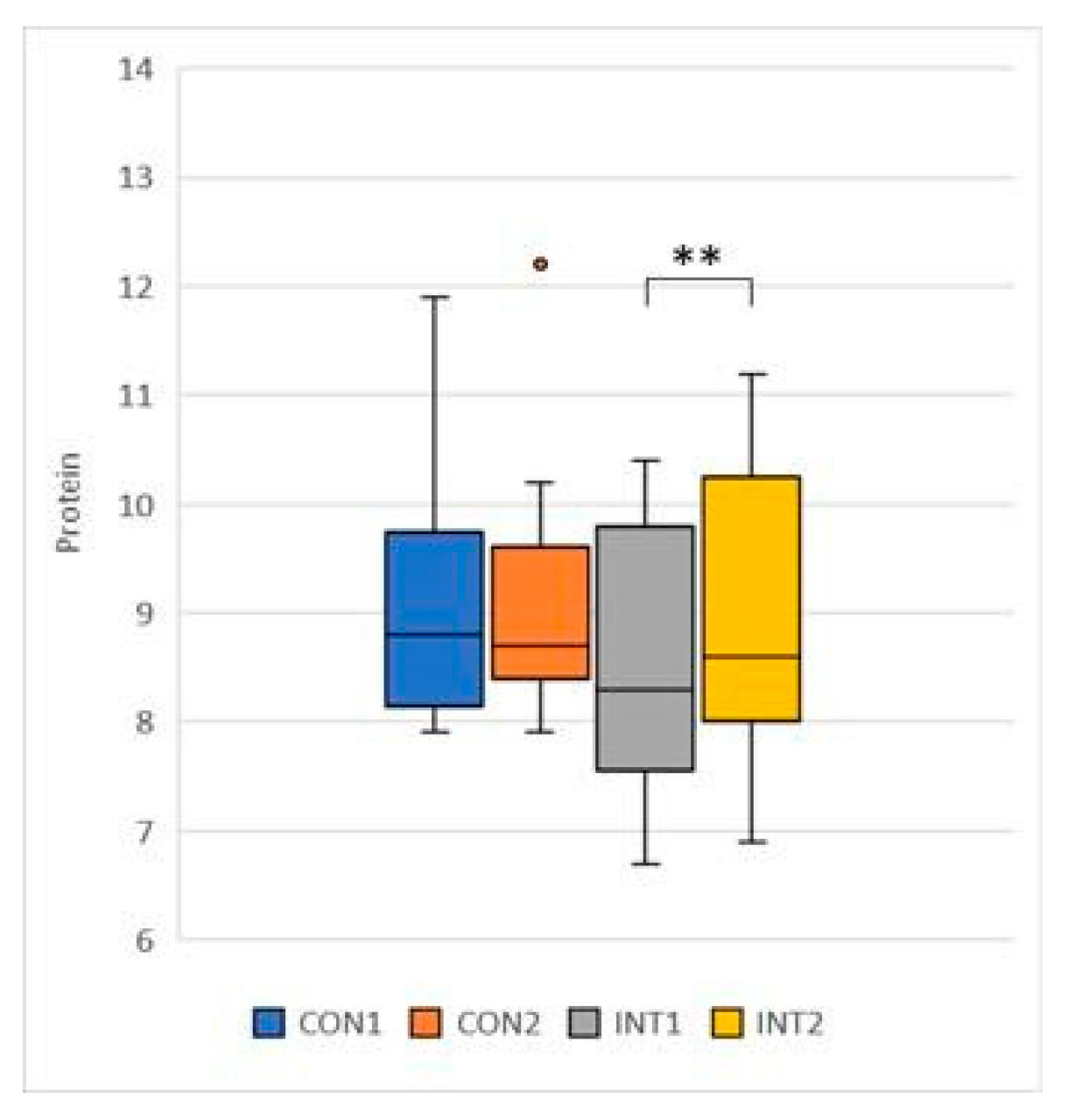
Protein: the mean of the control group was 0.05, increasing from 9.04 to 9.08 by a non-significant amount (p=.0666), while for the experimental group the results increased by 0.48 from 8.58 to 9.06, a significant change (p=0.000) (
Figure 9);
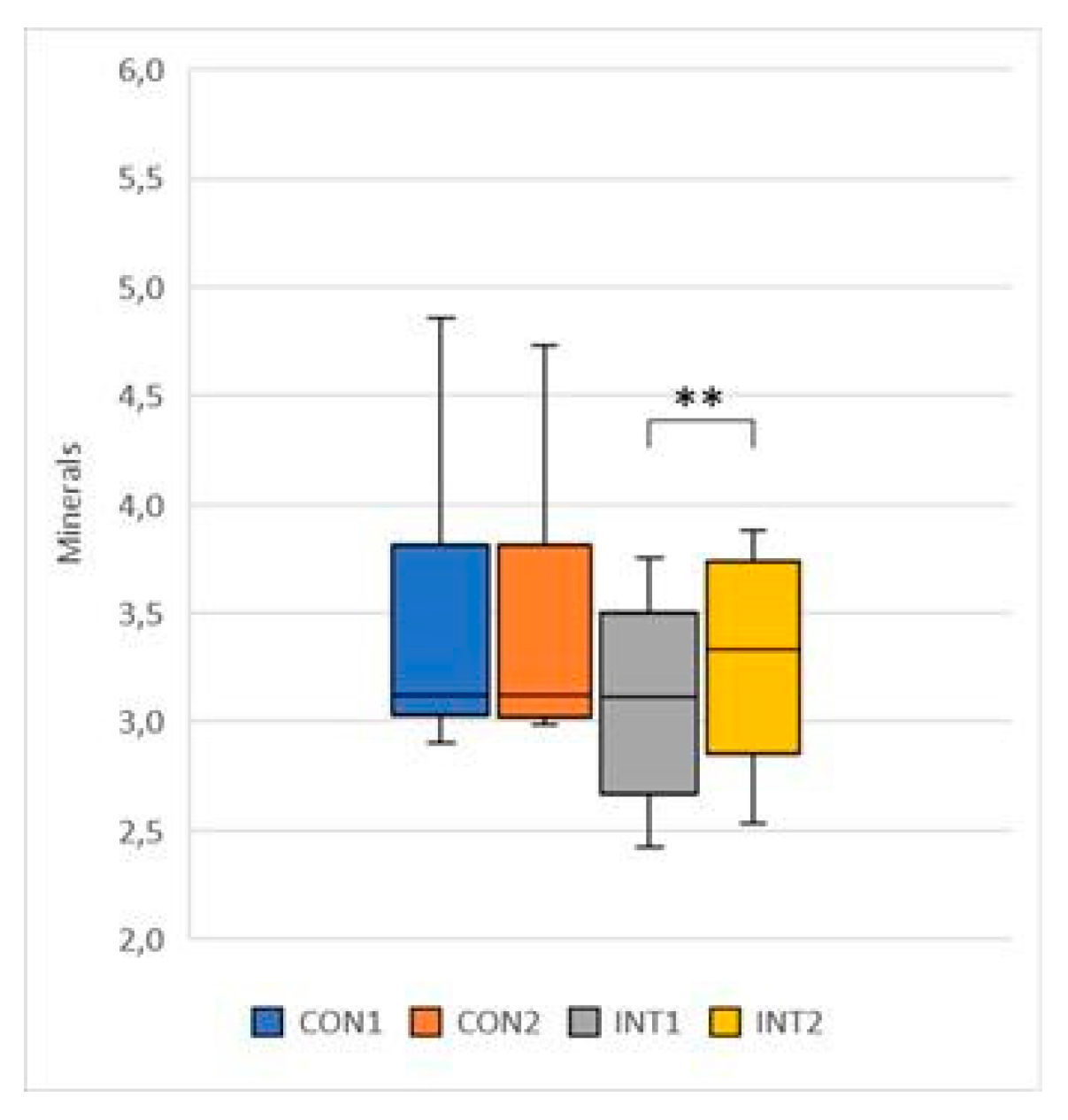
Minerals: mean increased by 0.03 in the control group, from 3.39 to 3.42, with no significant change (p=0.286), and by 0.19 in the study group, from 3.10 to 3.30, with a significant change (p=0.000) (
Figure 10);
SMM (Skeletal Muscle Mass): the mean of both groups showed an increase. For the control group, the increase in muscle mass was 0.09 from 25.25 to 25.34, which was not significant (p=0.773), while for the experimental group, the increase in muscle mass was significant, with a significant result of 0.67 from 23.88 to 24.55, which was a significant change (p=0.002) (
Figure 11);
Figure 11.
Skeletal Muscle Mass.
Figure 11.
Skeletal Muscle Mass.
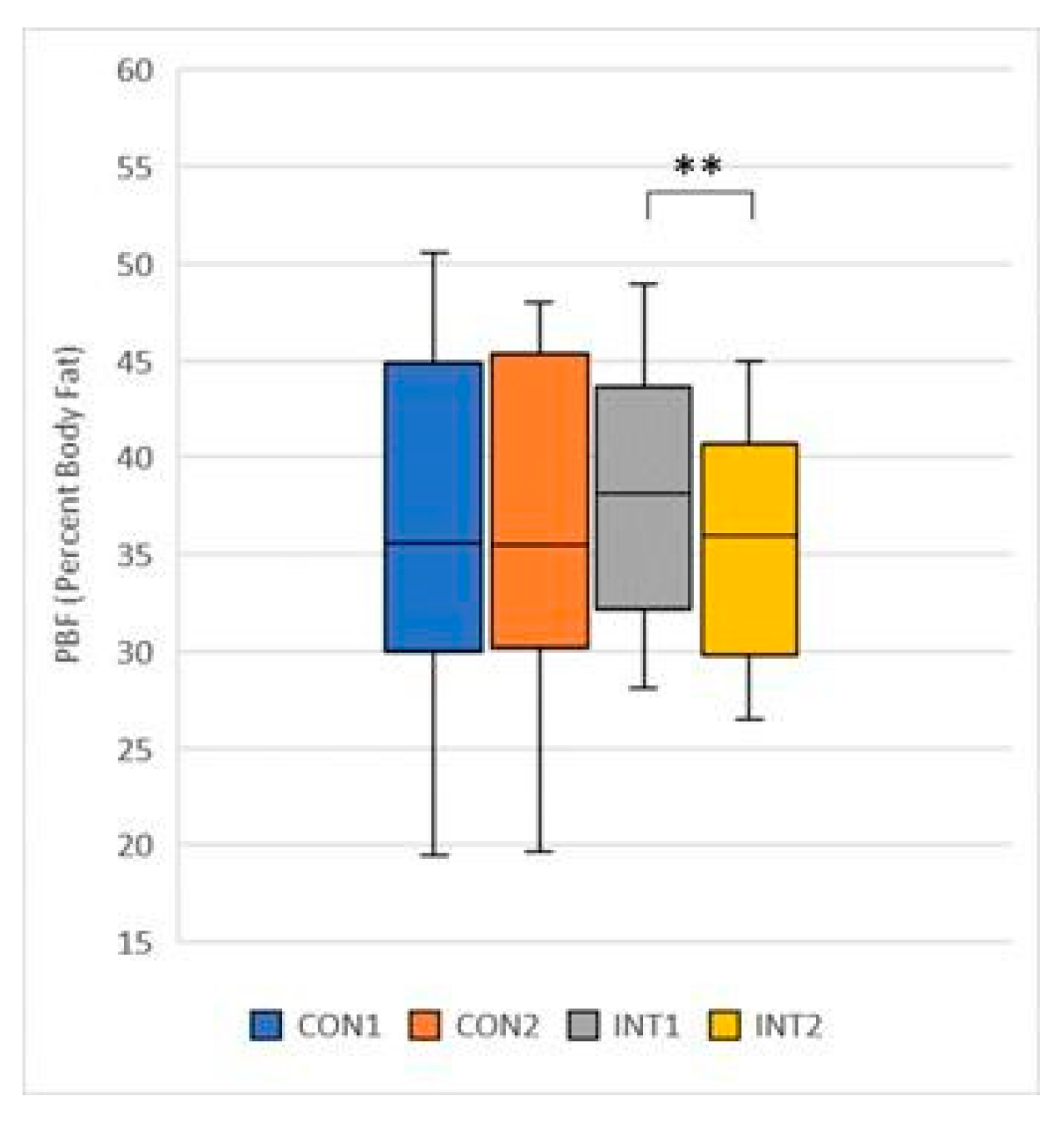
PBF (Percent Body Fat): its mean decreased in both groups, in the control group by -0.98 from 37.55 to 36.57, which was not significant (p=0.068), in the experimental group the decrease was significant (p=0.000) by -2.57 from 38.30 to 35.73 (
Figure 12);
Figure 12.
Percent Body Fat.
Figure 12.
Percent Body Fat.
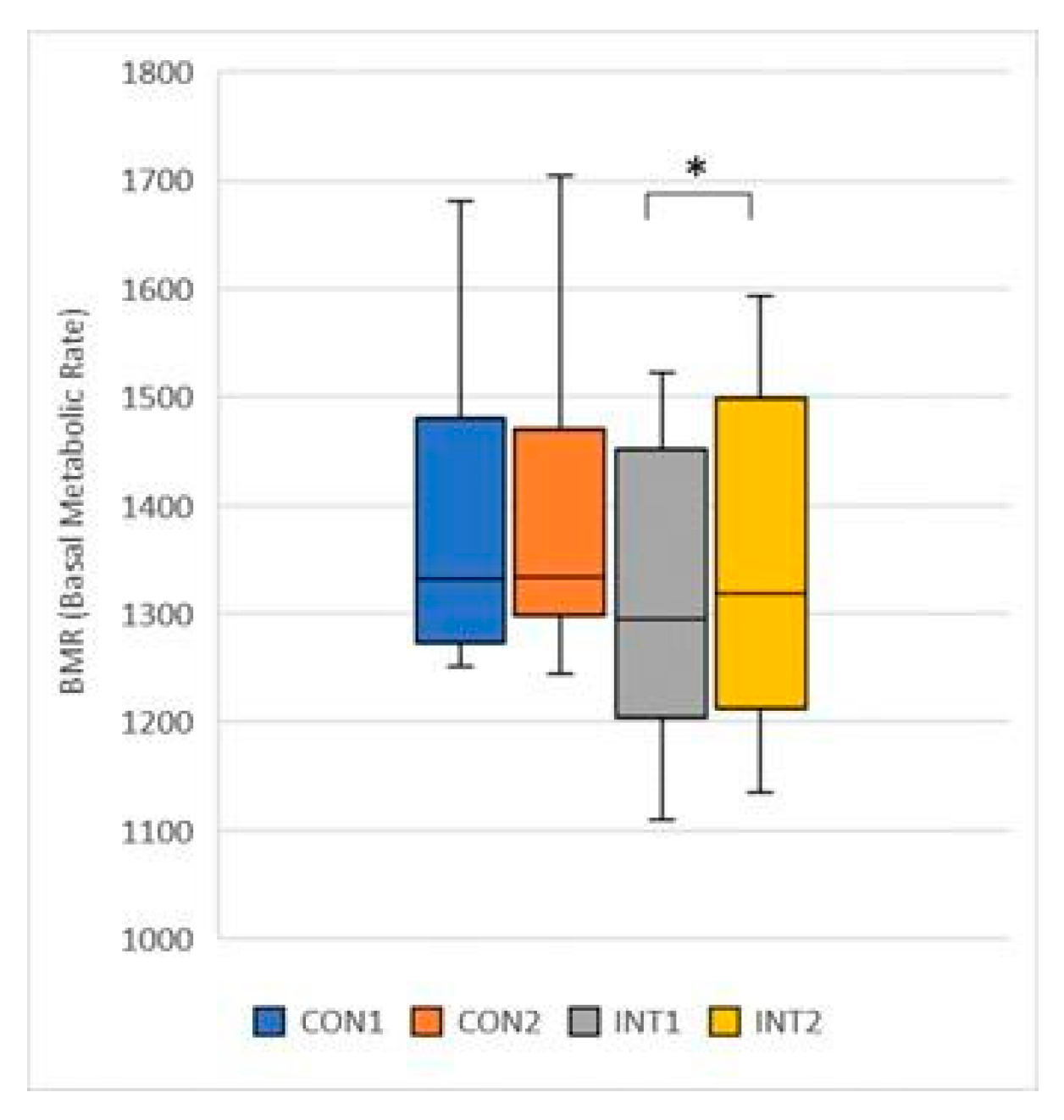
BMR (Basal Metabolic Rate): the mean increased in both groups, in the control group by 3.38 from 1378.54 to 1381, with a non-significant increase (p=0.717), and in the experimental group by 26.08 from 1319.08 to 1345.15, with a significant change (p=0.022) (
Figure 13);
Figure 13.
Basal Metabolic Rate.
Figure 13.
Basal Metabolic Rate.
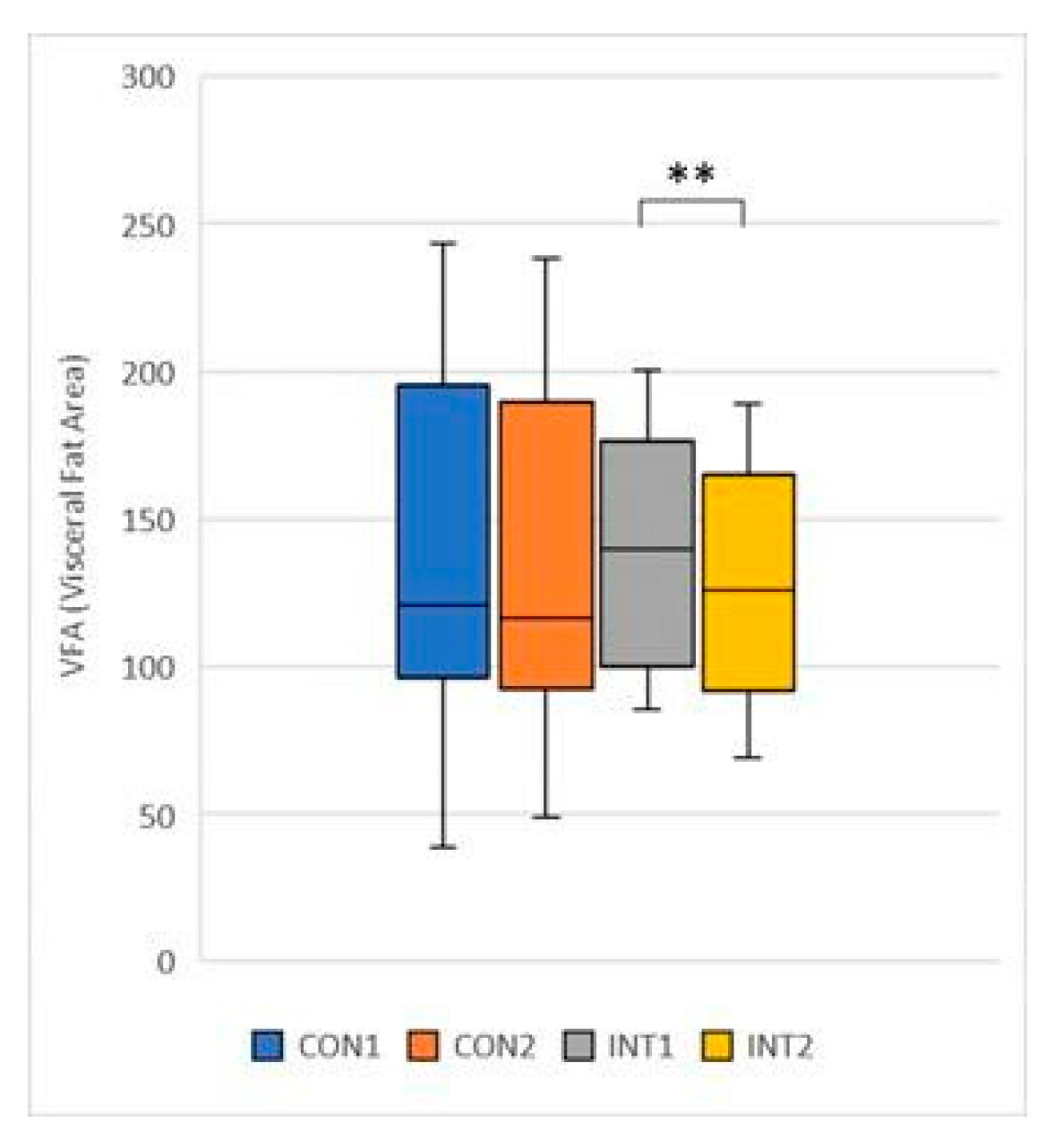
VFA (Visceral Fat Area): its mean decreased in both groups, the control group by 2.65 from 140.89 to 138.25, non-significantly (p=0.353), while the experimental group showed a decrease of -10.33 from 138.12 to 127.79, significant (p=0.000) (
Figure 14).
Figure 14.
Visceral Fat Area.
Figure 14.
Visceral Fat Area.
for 3 test items, the change was significant for both groups according to the t-test:
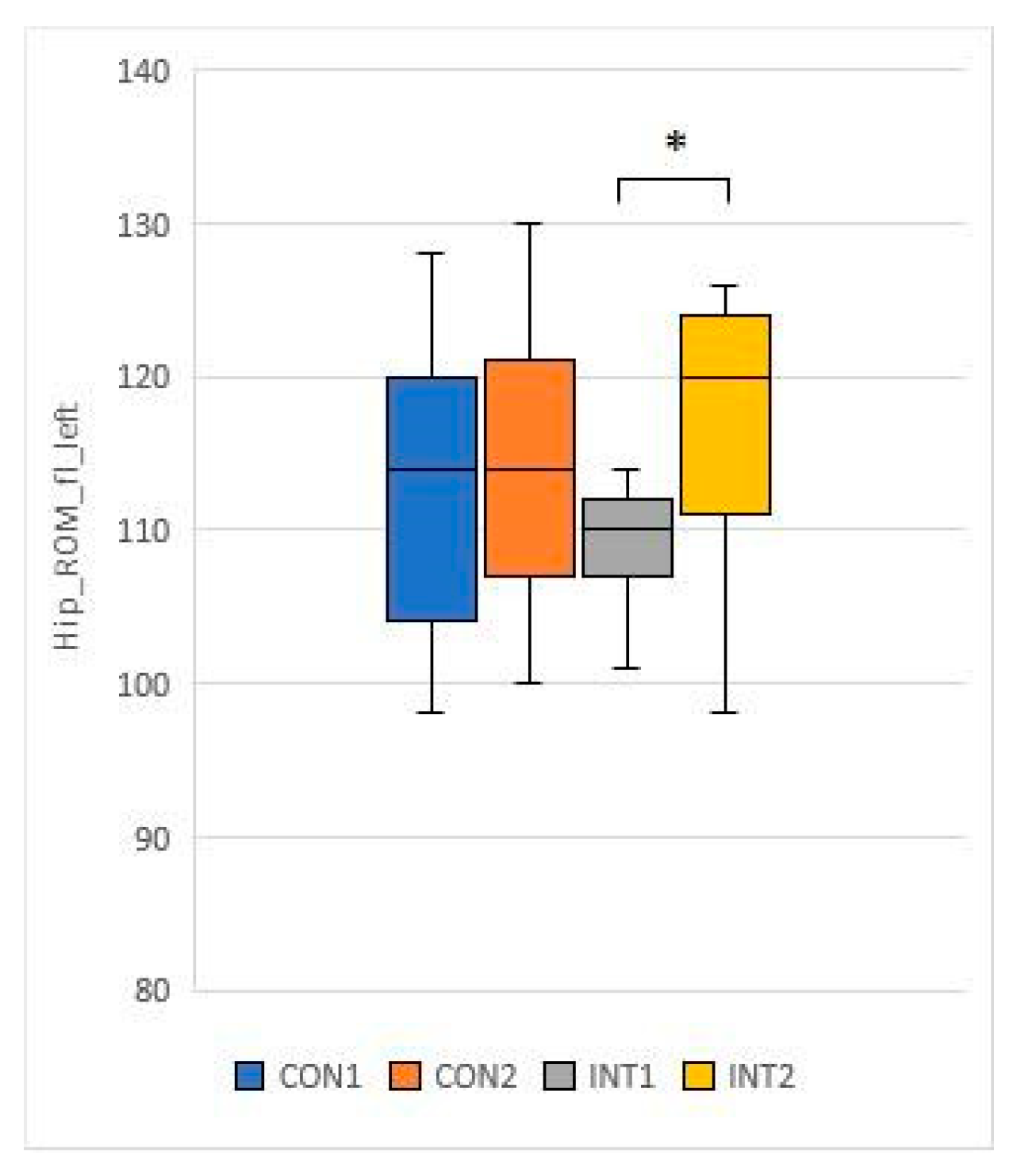
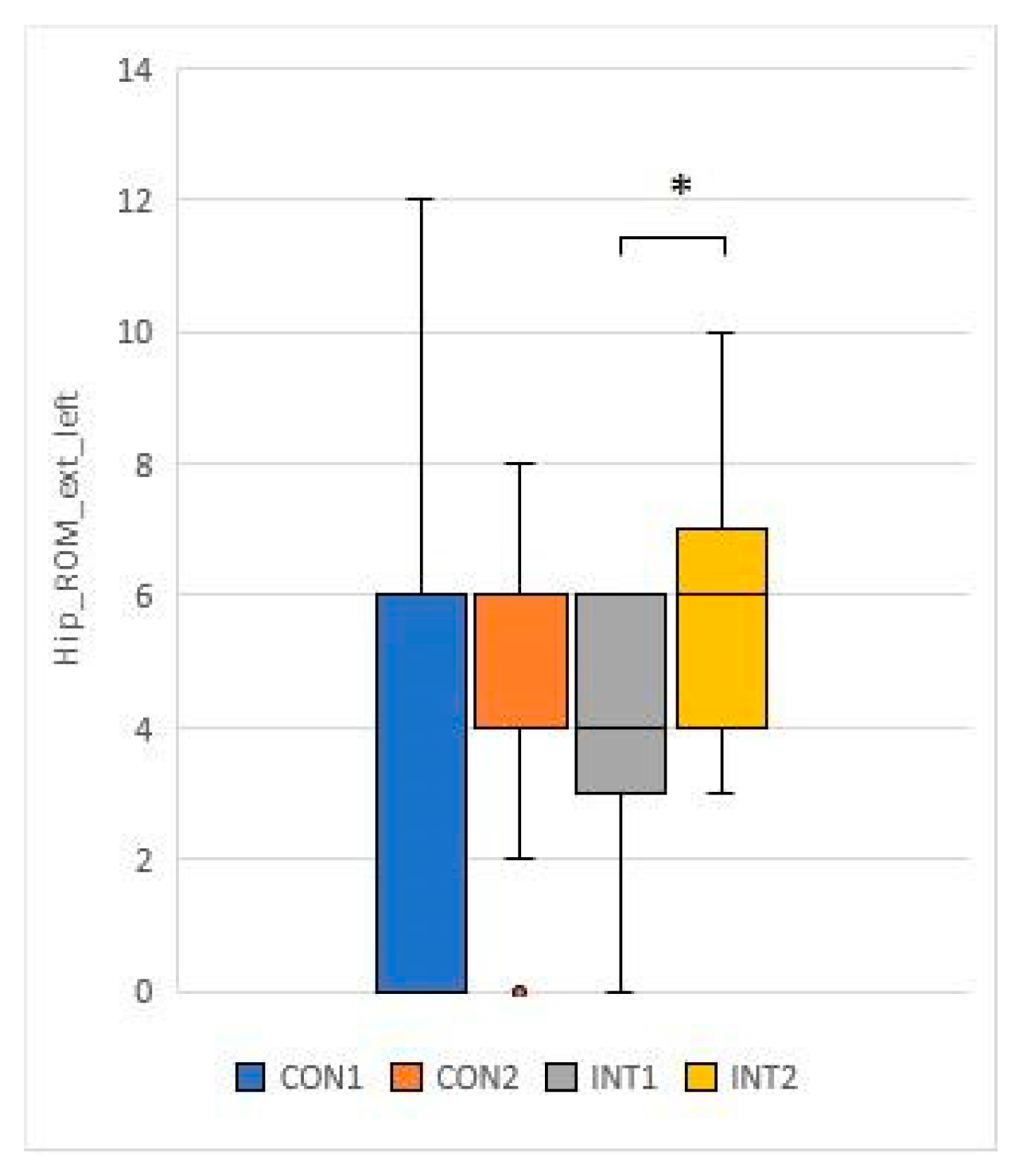
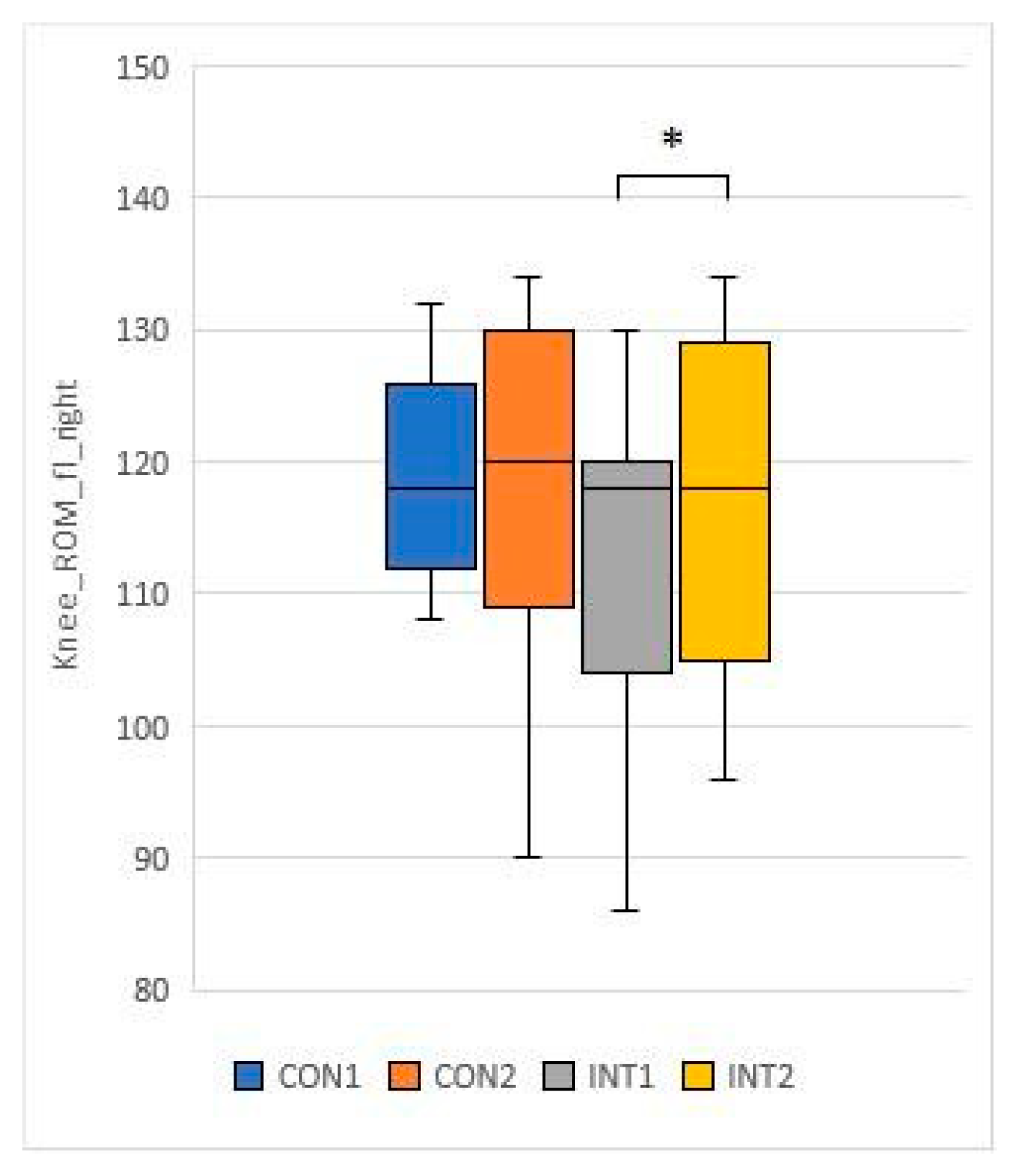
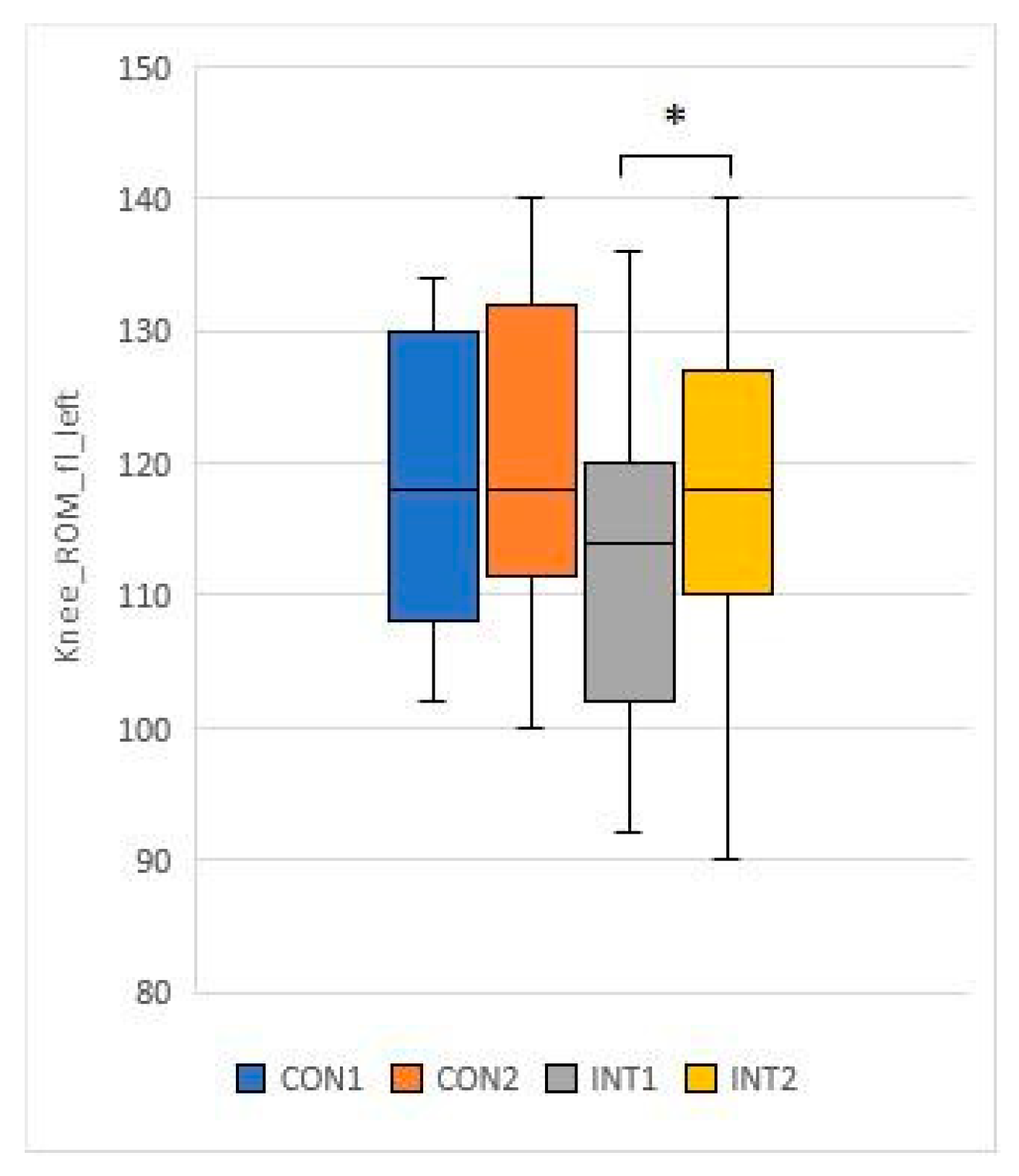
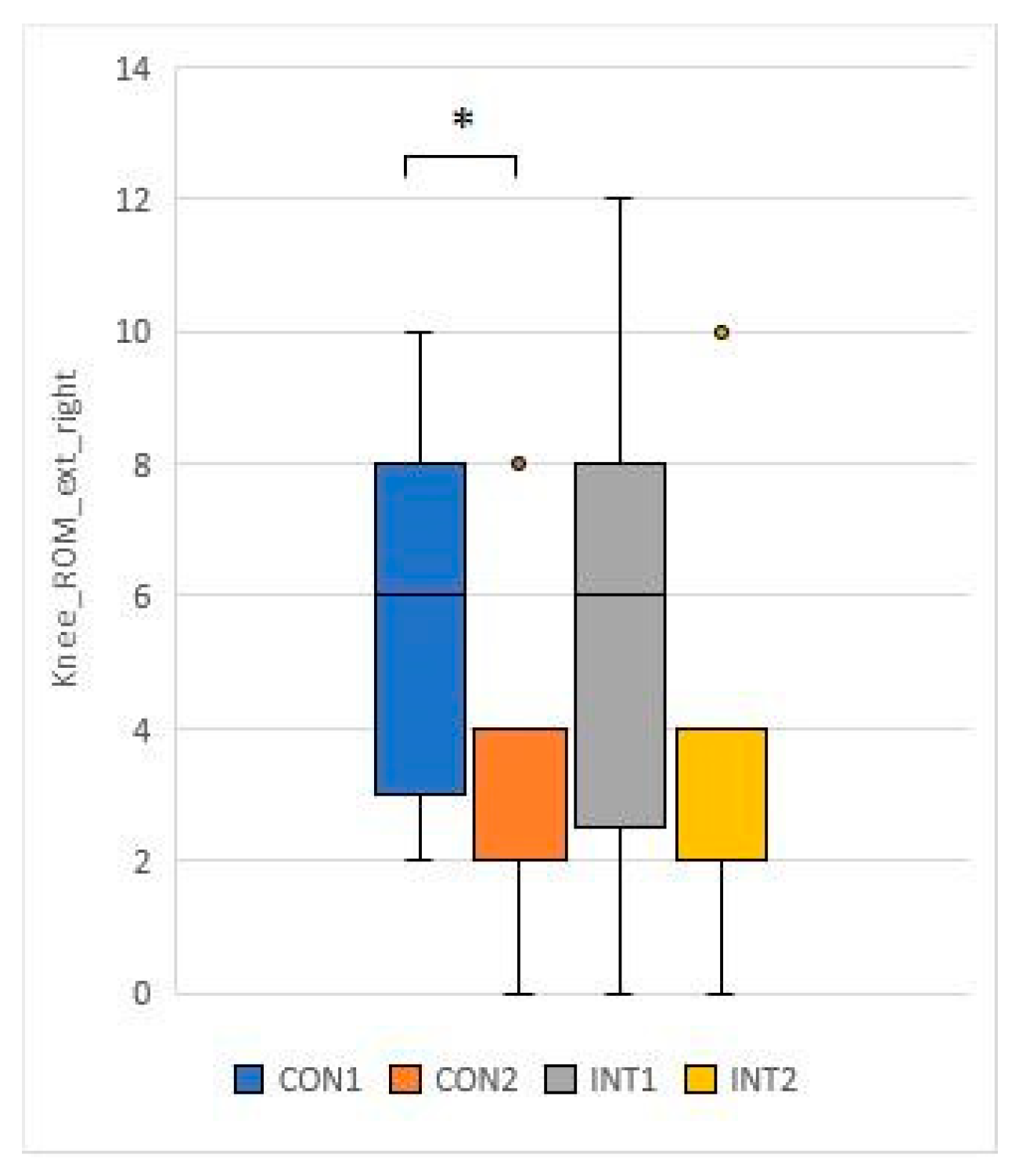
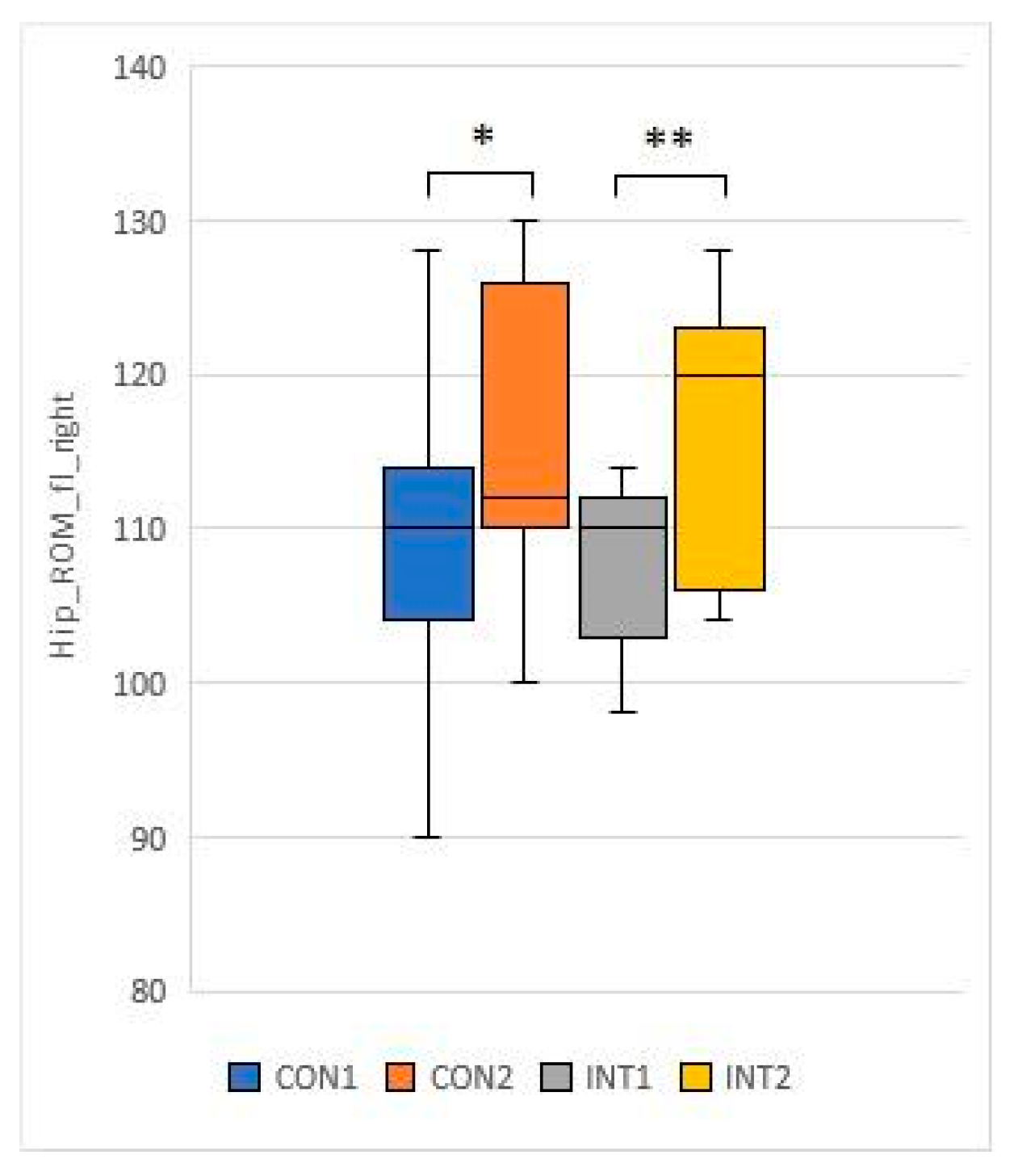
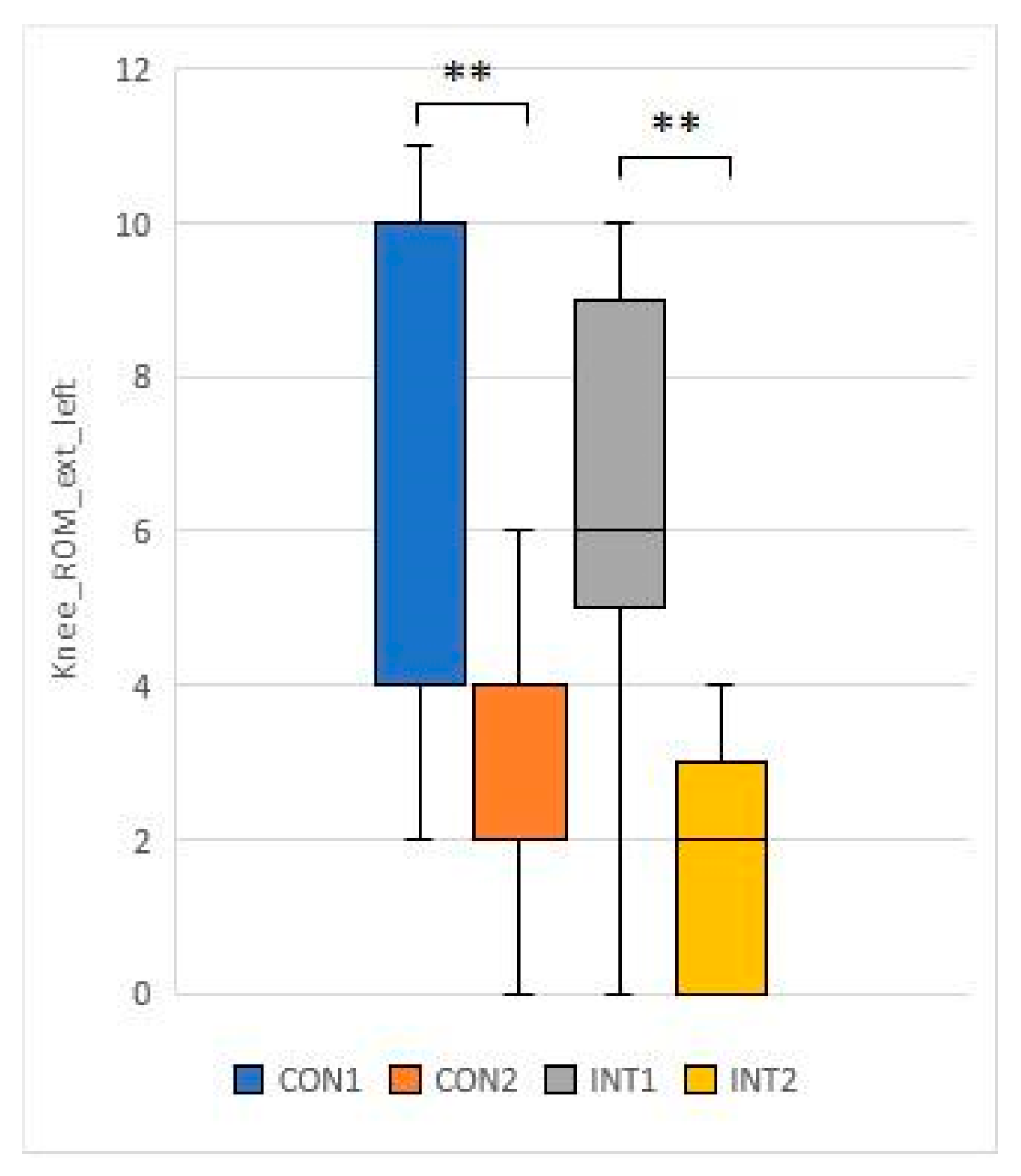
3.3. Range of motion testing of hip and knee joints (passive range of motion - PROM)
for 5 test items, the experimental group showed a significant change based on the t-test:
for 2 test items, the change was significant for both groups according to the t-test:
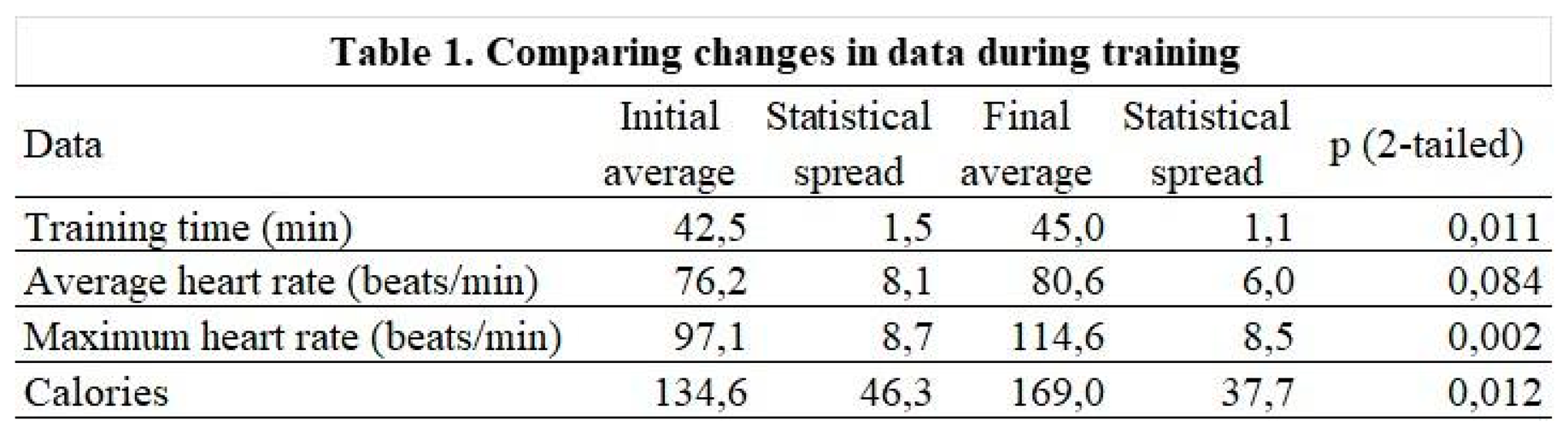
3.4. Results of the parameters measured during the physiotherapy session
Among the parameters tested, exercise time (p=0.011), maximum heart rate (0.002) and calories burned during exercise (p=0.012) showed significant changes (Table 1).
4. Discussion
The world is undergoing a huge age shift. According to the UN Population Profile, the number of people over 60 in high-income countries is projected to reach 366 million by 2030. Most of us can expect to live many years longer than our parents' and grandparents' generation. This longer life expectancy is a huge achievement, driven by improvements in public health and healthcare [
20]. Health promotion-oriented and prevention-oriented research thinking has led to the emergence of a wide range of research aimed at maintaining health at a high level over the long term. Proper nutrition and carefully used dietary supplements can help maintain health.
Consumption of collagen is beneficial for the skin, eyes, hair, nails, gums, ligaments, muscles, cartilage, joints, digestion and heart health. The demand for dietary supplements containing collagen has been growing for years. The collagen market, including hydrolysed collagen, is expected to continue to grow [
1].
The speciality and uniqueness of the supplement used in this study is the high levels of L-arginine and hyaluronic acid in addition to collagen and vitamin C. The individual mechanisms of action and physiological role of these ingredients are well understood, but have not yet been uniformly tested in the pairing and amounts included in the dietary supplement under investigation. It is biologically known that high LDL and triglyceride levels are pro-atherogenic and lead to endothelial dysfunction. Many indicators of early atherosclerosis have been described. The LDL to HDL ratio (LDL-C/HDL-C ratio) indicates the balance between the two types of cholesterol associated with cardiovascular events, LDL/HDL higher than 2.5 is high risk, lower than 2.5 is low risk [
21]. In a study similar in some respects to ours, healthy adults (30) who consumed 16 grams of collagen per day for 6 months had a reduction in their LDL/HDL cholesterol ratio. They also had significantly lower levels of a marker of atherosclerosis risk in their bloodstream at the end of the study [
13].
These associations were confirmed in our study, with patients who regularly exercised (study group) showing a significant increase in HLD cholesterol, a decrease in total cholesterol and a decrease in mean LDL cholesterol. However, the control group who did not exercise also had non-significant decreases in total cholesterol, increases in HDL cholesterol, and significant decreases in LDL cholesterol.
In our study, the initial LDL/HDL ratio of the randomly assigned control group was 2.66, which showed a significant decrease to 2.01 by the end of the two-month study period (p: 0,006). This reduced the cardiovascular risk from high to low. The mean LDL/HDL ratio of patients in the study group was 2.19 for low-risk, but this also fell significantly to 1.41 by the end of the study (p:0.000). Although the intake of 16 mg of collagen per day for 6 months by Tomosugi et al. reduced the LDL/HDL ratio of all subjects (p:0.253), the high cardiovascular risk group (p: 0.025), for high risk (0, 458).
We attribute the strong improvement in the LDL/HDL ratio, a marker of cardiovascular risk, to the fact that the supplement also contains other ingredients with antiatherogenic effects, such as L-arginine and vitamin C. So in virtually a third of the time, less collagen intake (16 grams instead of 10 grams per day), with these additional supplemental ingredients, works significantly more effectively.
Similar studies have been carried out in the literature. For example, in a small study, 15 adult subjects had mild hypertension reduced by consuming 5.2 grams of collagen per day for 4 weeks [
14]. consuming 2.5 grams of collagen per day for 12 weeks reduced arterial stiffness [
15].
In the last decades, there have been numerous studies aimed at identifying anti-atherogenic substances (e.g: Vitamin C, L-Arginine) or different forms of exercise on blood fat levels [
21]. Regular physical activity can lead to a reduction in blood lipids, with both triglyceride and total cholesterol levels showing a downward trend [
22]. In addition to total cholesterol, a breakdown of HLD and LDL cholesterol levels shows increasing values for HDL cholesterol and decreasing values for LDL cholesterol with exercise [
23]. One study found that physically active women had significantly higher HDL cholesterol levels than women with a sedentary lifestyle [
24]. It has been found that high-intensity exercise alone can be used to modify lipoproteins in a cardiovascularly beneficial manner in a population of healthy older women [
25].
These associations were confirmed in our study, with patients who regularly exercised (study group) showing a significant increase in HLD cholesterol, a decrease in total cholesterol and a decrease in mean LDL cholesterol. However, the control group who did not exercise also had non-significant decreases in total cholesterol, increases in HDL cholesterol, and significant decreases in LDL cholesterol.
It can therefore be concluded that while these changes are significant in patients who are both physically active and taking a dietary supplement, the results are also better in those taking a dietary supplement alone, although significant levels are only achieved in the case of LDL reduction.
Other exercise-related contexts have also emerged in the literature. Research has shown that exercise triggers the redistribution of magnesium in the body to meet metabolic needs.
Exertive exercise appears to increase urine and sweat losses, which can increase magnesium requirements by 10-20% [26]. Another study draws attention to the role of L-arginine as a means of reducing blood lipids. It found that watermelon consumption and L-arginine supplementation improved lipid profiles by reducing serum concentrations of triglycerides, total cholesterol and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol [27]. L-arginine administration has been shown to inhibit visceral fat accumulation [28]. A similar study has also demonstrated the anti-atherogenic effects of L-Arginine and vitamin C [29]. L-arginine is one of the most versatile metabolic amino acids with pronounced anti-aging effects. Such effects include reduced risk of vascular and heart disease, reduced erectile dysfunction, improved immune response and inhibition of gastric acidosis [30]. Other research suggests that oral hyaluronic acid supplementation also has anti-obesity effects.
Oral administration of hyaluronic acid (200 mg/kg bw for 8 weeks) reduced body weight, adipose tissue, serum lipids (LDL, triglyceride) and leptin levels [
31].
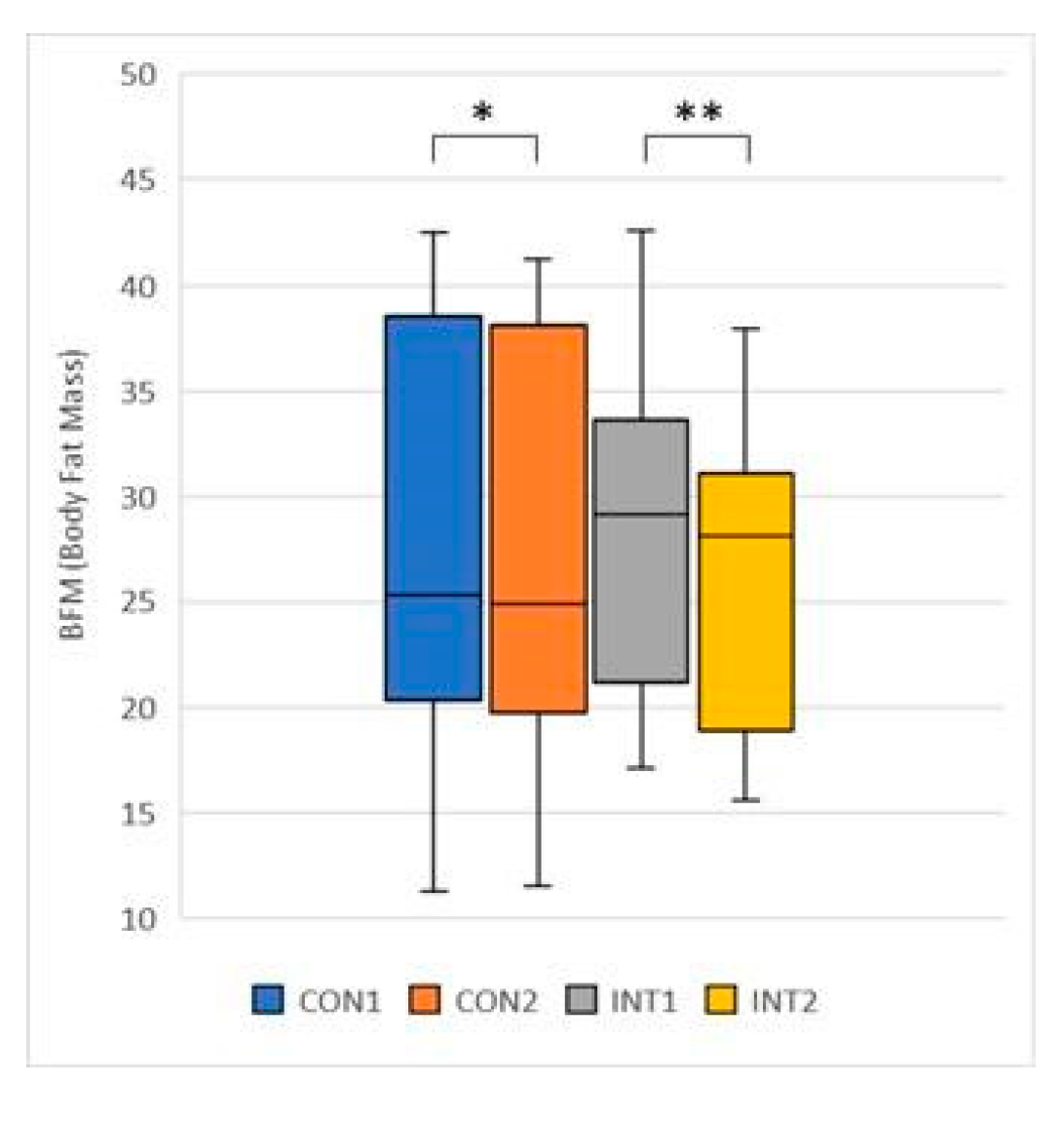
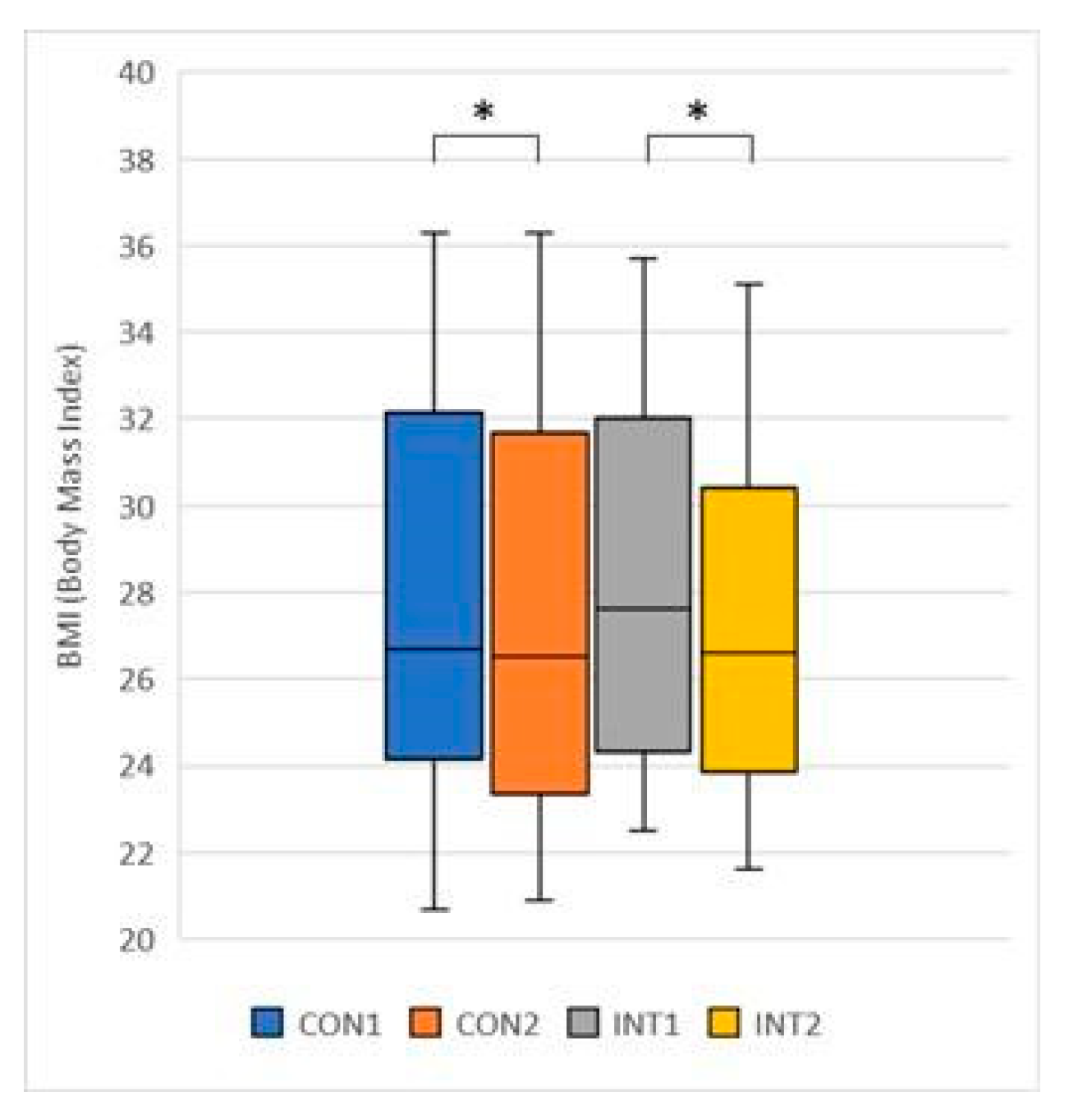
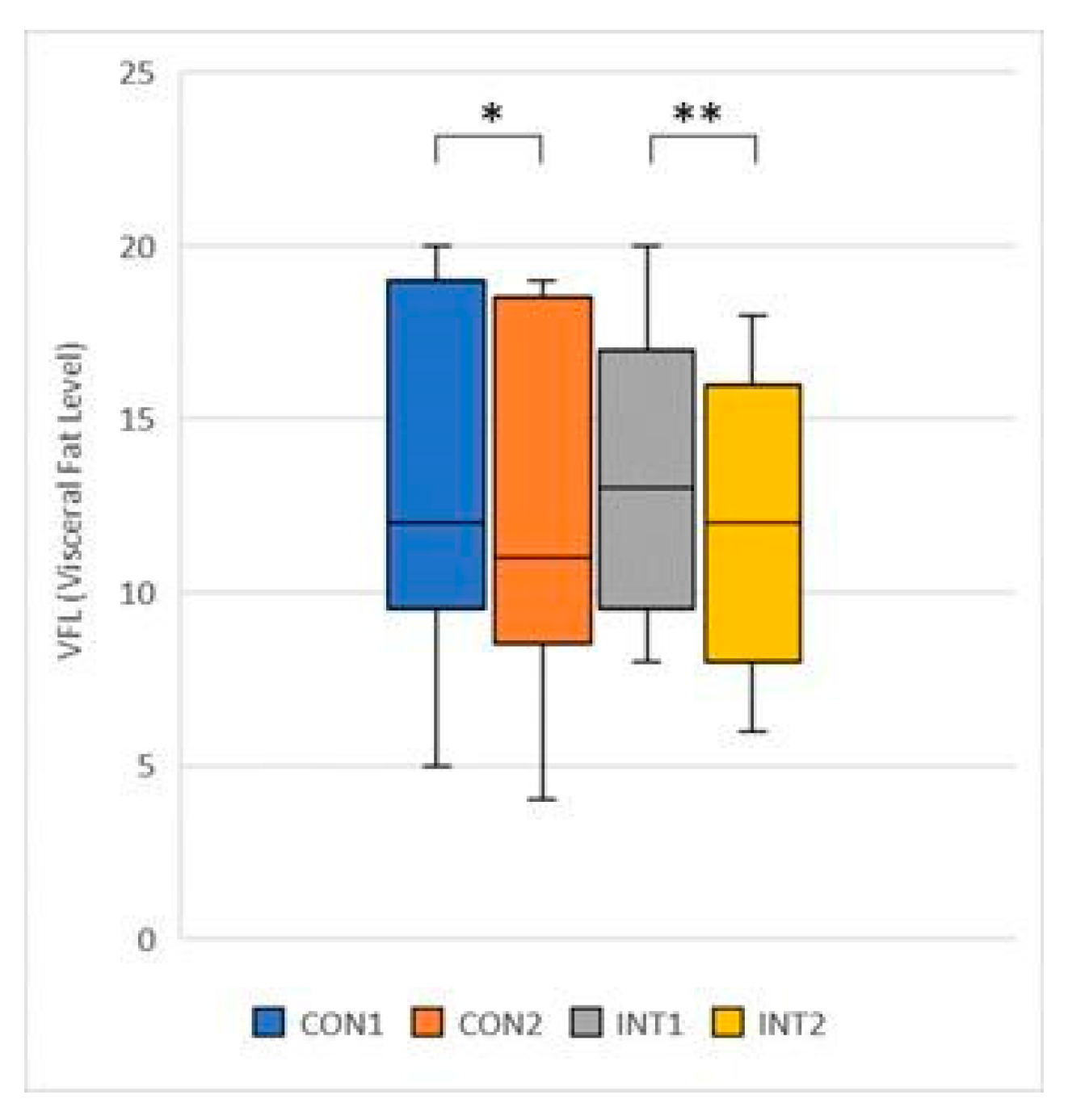
In our study, Body Fat Mass, Body Mass Index and Visceral Fat Level were significantly reduced in both groups, which we attribute to the combined anti-adipogenic and metabolism-enhancing effects of the ingredients in the supplement.
Positive changes in Visceral Fat Area, Basal Metabolic Rate, Percent Body Fat, Skeletal Muscle Mass were also recorded, which were not significant compared to the control group, but positive in terms of body composition. Significant levels of positive changes were measured for the test group for the same test data. We believe that the change with significant strength was due to regular exercise, but it is encouraging that the group that only used a dietary supplement also improved their results. As far as somatometric studies are concerned, it is a known fact that there is a direct correlation between waist circumference and visceral fat [
32]. In our study, a significant reduction in abdominal volume was also observed in the study group, correlated with significantly reduced VFA and VFL.
With collagen supplementation, patients diagnosed with chronic knee pain had reduced knee pain and improved ROM test [
33]. In our study, the knee and hip joint range of motion (ROM) showed significant improvement in the study group, while the control group also showed significant improvement in joint range of motion in the passive condition.
5. Conclusions
The dietary supplement under investigation can be used for joint, cardiovascular and nutritional health promotion and prophylactic purposes.
In the future, we plan to study its effects in other groups, such as younger patients and athletes.
Author Contributions
PF, RF, contributed to the original idea, study design and the conception of the work. PF, LM, and AM supervised the study, performed measurements. PB performed the statistical analysis. PF, RF wrote the main manuscript text. PF, RF, PB, LM, and AM revised and edited the manuscript. All authors approved the final version of the article.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted according to the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the the Regional/Institutional Science and Research Ethics Committee (BAZ County Central Hospital and University Teaching Hospital (BORS – 10/2022).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
All data generated and analyzed during the current study are included in this published article [and its supplementary information file]. The raw datasets are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request. (Dr. Péter Fritz;
peter.fritz@uni-miskolc.hu)
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the Superfoods Ltd.
Conflicts of Interest
The sponsors had no role in the design, execution, interpretation, or writing of the study.
Competing Interests
The authors report there are no competing interests to declare.
Consent for Publication
Not applicable.
References
- Fritz, P.; Mayer, L.; Pető, A.; Németh, B. A kollagén szerepe és hatása az emberi szervezetre = The role and effect of collagen on the human body. Recreation 2020, 10, 8–11. ISSN 2064-4981. [CrossRef]
- Ricard-Blum, S. The collagen family. Cold Spring Harbor perspectives in biology 2011, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- León-López, A.; Morales-Peñaloza, A.; Martínez-Juárez, V. M.; Vargas-Torres, A.; Zeugolis, D. I.; Aguirre-Álvarez, G. Hydrolyzed Collagen-Sources and Applications. Molecules (Basel, Switzerland) 2019, 24, 4031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Line, S.; Rhodes, C.; Yamada, Y. Molecular Biology of Cartilage Matrix. In Cellular and Molecular Biology of Bone.; Noda, M.; Academic press, Cambridge, Massachusetts, USA, 1993; pp. 539–555. ISBN: 9780080925004. 9, 9780. [Google Scholar]
- Farage, M. A.; Miller, K. W.; Elsner, P.; Maibach, H. I. Characteristics of the Aging Skin. Advances in wound care 2013, 2, 5–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirmse, M.; Oertzen-Hagemann, V.; de Marées, M.; Bloch, W.; Platen, P. Prolonged Collagen Peptide Supplementation and Resistance Exercise Training Affects Body Composition in Recreationally Active Men. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zdzieblik, D.; Oesser, S.; Baumstark, M. W.; Gollhofer, A.; König, D. Collagen peptide supplementation in combination with resistance training improves body composition and increases muscle strength in elderly sarcopenic men: a randomised controlled trial. The British journal of nutrition 2015, 114, 1237–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lodish, H.; Berk, A.; Matsudaira, P.; Kaiser, C.A.; Krieger, M.; Scott, M.P.; Zipursky, L.; Darnell, J. Molecular Cell Biology, 5th ed.; W. H. Freeman, New York, USA, 2005; 15. ISBN: 9780716743668.
- Lugo, J. P.; Saiyed, Z. M.; Lane, N. E. Efficacy and tolerability of an undenatured type II collagen supplement in modulating knee osteoarthritis symptoms: a multicenter randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Nutritional journal 2016, 15, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tariq, M.; Al Moutaery, A. R. Studies on the antisecretory, gastric anti-ulcer and cytoprotective properties of glycine. Research communications in molecular pathology and pharmacology, 1997; 97, 185–198. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Graham, M. F.; Drucker, D. E.; Diegelmann, R. F.; Elson, C. O. Collagen synthesis by human intestinal smooth muscle cells in culture. Gastroenterology 1987, 92, 400–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koutroubakis, I. E.; Petinaki, E.; Dimoulios, P.; Vardas, E.; Roussomoustakaki, M.; Maniatis, A. N.; Kouroumalis, E. A. Serum laminin and collagen IV in inflammatory bowel disease. Journal of clinical pathology 2003, 56, 817–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomosugi, N.; Yamamoto, S.; Takeuchi, M.; Yonekura, H.; Ishigaki, Y.; Numata, N.; Katsuda, S.; Sakai, Y. Effect of Collagen Tripeptide on Atherosclerosis in Healthy Humans. Journal of atherosclerosis and thrombosis 2017, 24, 530–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saiga-Egusa, A.; Iwai, K.; Hayakawa, T.; Takahata, Y.; Morimatsu, F. Antihypertensive effects and endothelial progenitor cell activation by intake of chicken collagen hydrolysate in pre- and mild-hypertension. Bioscience, biotechnology, and biochemistry 2009, 73, 422–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igase, M.; Kohara, K.; Okada, Y.; Ochi, M.; Igase, K.; Inoue, N.; Kutsuna, T.; Miura, H.; Ohyagi, Y. A double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomised clinical study of the effect of pork collagen peptide supplementation on atherosclerosis in healthy older individuals. Bioscience, biotechnology, and biochemistry 2018, 82, 893–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, F.D.; Sung, C.T.; Juhasz, M.; Mesinkovsk, N.A. Oral Collagen Supplementation: A Systematic Review of Dermatological Applications. Journal of drugs in dermatology: JDD 2019, 18, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Collagen Market Size, Share & Trends Analysis Report By Source (Bovine, Porcine), By Product (Gelatin), By Application (Food & Beverages, Healthcare), By Region, And Segment Forecasts 2020-2027. Available online: https://www.grandviewresearch.com/industry-analysis/collagen-market (accessed on 24 October 2020).
- Range of Motion. Available online: https://www.physio-pedia.com/Range_of_Motion (accessed on 19 May 2023).
- Debasree Banerjee, Jane Kamuren, Grayson L. Baird, Amy Palmisciano, Ipsita Krishnan, Mary Whittenhall, James R. Klinger,and Corey E. Ventetuolo, The Modified Borg Dyspnea Scale does not predict hospitalization in pulmonary arterial hypertension, Published online 2017 Mar 16. [CrossRef]
- Dixon, A. The United Nations Decade of Healthy Ageing requires concerted global action. Nature Aging 2021, 1, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enomoto M, Adachi H, Hirai Y, Fukami A, Satoh A, Otsuka M, Kumagae S, Nanjo Y, Yoshikawa K, Esaki E, Kumagai E, Ogata K, Kasahara A, Tsukagawa E, Yokoi K, Ohbu-Murayama K, Imaizumi T: LDL-C/HDL-C ratio predicts carotid intima-media thickness progression better than HDL-C or LDL-C alone. J Lipids, 2012; 21: 153-159. 1.
- Haskell, W.L. The influence of exercise on the concentrations of triglyceride and cholesterol in human plasma. Exercise and Sport Sciences Reviews 1984, 12, 205–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halverstadt, A.; Phares, D.A.; Wilund, K.R.; Goldberg, A.P.; Hagberg, J.M. Endurance exercise training raises high-density lipoprotein cholesterol and lowers small low-density lipoprotein and very low-density lipoprotein independent of body fat phenotypes in older men and women. Metabolism 2007, 56, 444–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokkinos, P.F.; Fernhall, B. Physical activity and high density lipoprotein cholesterol levels: what is the relationship? Sports Medicine 1999, 28, 307–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahlman, M.M.; Boardley, D.; Lambert, C.P.; Flynn, M.G. Effects of endurance training and resistance training on plasma lipoprotein profiles in elderly women. The Journals of Gerontology. Series A, Biological sciences and medical sciences 2002, 57, B54–B60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, F.H.; Lukaski, H.C. Update on the relationship between magnesium and exercise. Magnes Res 2006, 19, 180–189. [Google Scholar]
- Hadi, A.; Arab, A.; Moradi, S.; Pantovic, A.; Clark, C. C. T.; Ghaedi, E. The effect of l-arginine supplementation on lipid profile: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. The British journal of nutrition 2019, 122, 1021–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kujawska-Łuczak, M.; Suliburska, J.; Markuszewski, L.; Pupek-Musialik, D.; Jabłecka, A.; Bogdański, P. The effect of L-arginine and ascorbic acid on the visceral fat and the concentrations of metalloproteinases 2 and 9 in high-fat-diet rats. Endokrynologia Polska 2015, 66, 526–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogdański, P.; Suliburska, J.; Szulińska, M.; Sikora, M.; Walkowiak, J.; Jakubowski, H. L-Arginine and vitamin C attenuate pro-atherogenic effects of high-fat diet on biomarkers of endothelial dysfunction in rats. Biomedicine & pharmacotherapy = Biomedecine & pharmacotherapie 2015, 76, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gad, M.Z. Anti-aging effects of l-arginine. Journal of Advanced Research 2010, 1, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, B. G.; Park, Y. S.; Park, J. W.; Shin, E.; Shin, W. S. Anti-obesity potential of enzymatic fragments of hyaluronan on high-fat diet-induced obesity in C57BL/6 mice. Biochemical and biophysical research communications 2016, 473, 290–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, R.; Neeland, I. J.; Yamashita, S.; Shai, I.; Seidell, J.; Magni, P.; Santos, R. D.; Arsenault, B.; Cuevas, A.; Hu, F. B.; Griffin, B. A.; Zambon, A.; Barter, P.; Fruchart, J. C.; Eckel, R. H.; Matsuzawa, Y.; Després, J. P. Waist circumference as a vital sign in clinical practice: a Consensus Statement from the IAS and ICCR Working Group on Visceral Obesity. Nature reviews. Endocrinology 2020, 16, 177–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zdzieblik, D.; Oesser, S.; Gollhofer, A.; Koenig, D. Corrigendum: Improvement of activity-related knee joint discomfort following supplementation of specific collagen peptides. Applied physiology, nutrition, and metabolism = Physiologie appliquee, nutrition et metabolisme 2017, 42, 1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).