Submitted:
15 June 2023
Posted:
16 June 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Mechanistic target of rapamycin (mTOR)
2.1. mTORC1 and mTORC2 structure
2.2. Upstream regulation of mTORC1
2.3. Substrates and functions of mTORC1
2.4. Upstream regulation of mTORC2
2.5. Substrates and functions of mTORC2
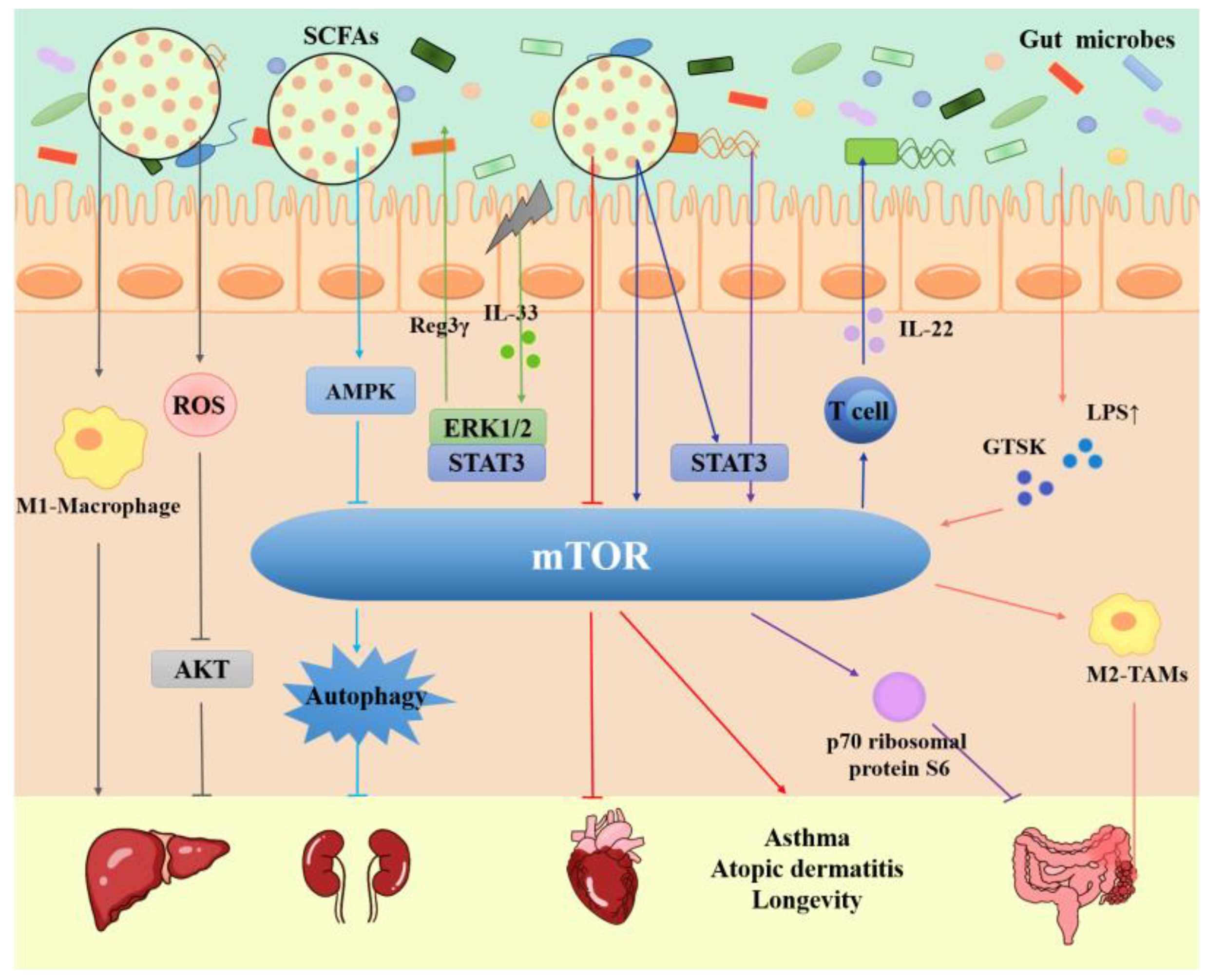
3. Gut microbiota
3.1. Gut microbiota, mTOR and Intestinal Diseases
3.2. Gut microbiota, mTOR and Liver Diseases
3.3. Gut microbiota, mTOR and Heart disease
3.4. Gut microbiota, mTOR and Other Diseases
3.5. Gut microbes and mTOR in the analysis of big data
4. Application of multiple drugs affecing gut microbes and mTOR in the treatment of different diseases
4.1. Treatment of Intestinal diseases
4.2. Treatment of Liver Diseases
4.3. Treatment of Other Diseases
5. Conclusions and Future Perspective
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 4E-BPs | 4E-binding proteins |
| AB23A | Alisol B 23-acetate |
| AD | Alzheimer’s disease |
| AMP | Aronia melanocarpa polysaccharide |
| AMPK | AMP-activated protein kinase |
| AMPK | AMP-activated protein kinase |
| AOM | Azomethane |
| ASD | Autism spectrum disorder |
| ATF4 | Activating transcription factor 4 |
| BMMSCs | Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells |
| BMMSCs | Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells |
| BO | Bruceae fructus oil |
| CASTOR1 | GTPase-activating protein activity toward Rags-1 |
| CD | Crohn's disease |
| CTSK | Cathepsin K |
| DAP1 | Death-associated protein 1 |
| DDiT4L | DNA-damage-inducible transcript 4-like |
| DEPTOR | DEP domain-containing mTOR-interacting protein |
| DSS | Dextran sodium sulfate |
| eIF4E | Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E |
| ERS | Engineered Resistant-Starch |
| FLCN | Folliculin |
| FoxO1/3a | Forkhead box O1/3a |
| FVP | Flammulina velutipes polysaccharide |
| GAP | GTPase-activating protein |
| GI | Gastrointestinal tract |
| Grb10 | Growth factor receptor-bound protein 10 |
| GSK3 | Glycogen synthase kinase 3 |
| HCC | Hepatocellular Carcinoma |
| HK-II | Hexokinase-II |
| HMB | β-hydroxy-β-methylbutyrate |
| HQD | Huangqin decoction |
| IBD | Inflammatory bowel disease |
| IEC | Intestinal epithelial cells |
| IGF1 | Insulin and insulin-like growth factor 1 |
| IKKβ | IκB kinase β |
| L. reuteri | Lactobacillus reuteri DSM 17938 |
| LGG-s | Lactobacillus rhamnosus culture supernatant |
| LI | Large intestine |
| LPS | Lipopolysaccharide |
| METS | Metabolic syndrome |
| mLST8 | Mammalian lethal with SEC13 protein 8 |
| MogV | MogrosideV |
| mSIN1 | Mammalian stress-activated protein kinase interacting protein 1 |
| MST1 | Mammalian sterile 20-like kinase |
| MTF | Metformin |
| MTHFD2 | Methylenetetrahydrofolate dehydrogenase 2 |
| mTOR | The mammalian or mechanistic target of rapamycin |
| mTORC | mTOR complex |
| NAFLD | Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease |
| NDRG1 | N-myc downstream regulated gene 1 |
| NKB | Natural killer B cell |
| OPD | Ophiopogonin D |
| P. ginseng | Polysaccharides from Panax ginseng C. A. Meyer |
| PC | Pancreatic cancer |
| PDCD4 | Programmed cell death 4 |
| PFT | Probiotics fermentation technology |
| PGC-1α | Proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1-alpha |
| PI3K | Phosphoinositide 3-kinase |
| PIKK | Phosphoinositide 3-kinase related protein kinase |
| PKC-α | Protein kinase C-α |
| PPAR-γ | Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ |
| PRAS40 | Proline-rich substrate of 40 kDa |
| PROTOR1/2 | Protein observed with RICTOR 1/2 |
| Rags | Ras-related GTPases |
| RAPTOR | Regulatory-associated protein of mTOR |
| Redd1 | Regulation of DNA damage response 1 |
| Rheb | Ras homolog enriched in the brain |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| RSK | Ribosomal S6 kinase |
| S6K1 | S6 kinase 1 |
| SAM | S-adenosylmethionine |
| SCFAs | Short chain fatty acids |
| SGK1 | Serum and glucocorticoid-induced protein kinase 1 |
| SI | Small intestine |
| SREBP1/2 | Sterol regulatory element binding protein 1/2 |
| SRPK2 | SR protein kinase 2 |
| STZ | Streptozotocin |
| T-ALL | T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia |
| TB | Theabrownin |
| TFH | Follicular helper T cell |
| TLR4 | Toll-like receptor 4 |
| TNBC | Triple-negative breast cancer |
| TNF-α | Tumor necrosis factor-α |
| Trx1 | Thioredoxin 1 |
| TSC | Tuberous sclerosis complexes |
| UC | Ulcerative colitis |
| UCP-2 | Uncoupling protein-2 |
| ULK1 | Unc-51-like autophagy-activating kinase 1 |
| XXT | Xiexin Tang |
References
- Laplante, M.; Sabatini, D. M. , mTOR signaling in growth control and disease. Cell 2012, 149, 274–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxton, R. A.; Sabatini, D. M. , mTOR Signaling in Growth, Metabolism, and Disease. Cell 2017, 168, 960–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, G. Y.; Sabatini, D. M. , mTOR at the nexus of nutrition, growth, ageing and disease. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2020, 21, 183–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, T.; Li, X.; Zhang, J. , mTOR Signaling in Cancer and mTOR Inhibitors in Solid Tumor Targeting Therapy. Int J Mol Sci 2019, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sciarretta, S.; Forte, M.; Frati, G.; Sadoshima, J. , The complex network of mTOR signalling in the heart. Cardiovasc Res 2022, 118, 424–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruth, E. Ley, P. J. T., Samuel Klein, Jeffrey I. Gordon, Human gut microbes associated with obesity. NATURE 2006, 444. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, J.; Li, Y.; Cai, Z.; Li, S.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, F.; Liang, S.; Zhang, W.; Guan, Y.; Shen, D.; Peng, Y.; Zhang, D.; Jie, Z.; Wu, W.; Qin, Y.; Xue, W.; Li, J.; Han, L.; Lu, D.; Wu, P.; Dai, Y.; Sun, X.; Li, Z.; Tang, A.; Zhong, S.; Li, X.; Chen, W.; Xu, R.; Wang, M.; Feng, Q.; Gong, M.; Yu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Hansen, T.; Sanchez, G.; Raes, J.; Falony, G.; Okuda, S.; Almeida, M.; LeChatelier, E.; Renault, P.; Pons, N.; Batto, J. M.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, H.; Yang, R.; Zheng, W.; Li, S.; Yang, H.; Wang, J.; Ehrlich, S. D.; Nielsen, R.; Pedersen, O.; Kristiansen, K.; Wang, J. , A metagenome-wide association study of gut microbiota in type 2 diabetes. Nature 2012, 490, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Wang, T.; Jin, F. , Alzheimer's disease and gut microbiota. Sci China Life Sci 2016, 59, 1006–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephen, B. Helliwell, P. W., Jeannette Kunz, Maja Deuter-Reinhard, Ruben Henriquez, and Michael N. Hall, TOR1 and TOR2 Are Structurally and Functionally Similar but not Identical Phosphatidylinositol Kinase Homologues in Yeast. Molecular biology of the cell 1994, 5, 105–118. [Google Scholar]
- Schreiber, C. T. K. a. S. L. , PIK-Related Kinases: DNA Repair, Recombination, and Cell Cycle Checkpoints. Science 1995, 270, 50–50. [Google Scholar]
- Loewith, R.; Jacinto, E.; Wullschleger, S.; Lorberg, A.; Crespo, J. L.; Bonenfant, D.; Oppliger, W.; Jenoe, P.; Hall, M. N. , Two TOR Complexes, Only One of which Is Rapamycin Sensitive, Have Distinct Roles in Cell Growth Control. Mol Cell 2002, 10, 457–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Rudge, D. G.; Koos, J. D.; Vaidialingam, B.; Yang, H. J.; Pavletich, N. P. , mTOR kinase structure, mechanism and regulation. Nature 2013, 497, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baretic, D.; Berndt, A.; Ohashi, Y.; Johnson, C. M.; Williams, R. L. , Tor forms a dimer through an N-terminal helical solenoid with a complex topology. Nat Commun 2016, 7, 11016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chao, L. H.; Avruch, J. , Cryo-EM insight into the structure of MTOR complex 1 and its interactions with Rheb and substrates. F1000Res 2019, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, T. R.; Laplante, M.; Thoreen, C. C.; Sancak, Y.; Kang, S. A.; Kuehl, W. M.; Gray, N. S.; Sabatini, D. M. , DEPTOR is an mTOR inhibitor frequently overexpressed in multiple myeloma cells and required for their survival. Cell 2009, 137, 873–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sancak, Y.; Thoreen, C. C.; Peterson, T. R.; Lindquist, R. A.; Kang, S. A.; Spooner, E.; Carr, S. A.; Sabatini, D. M. , PRAS40 is an insulin-regulated inhibitor of the mTORC1 protein kinase. Mol Cell 2007, 25, 903–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarbassov, D. D.; Ali, S. M.; Kim, D. H.; Guertin, D. A.; Latek, R. R.; Erdjument-Bromage, H.; Tempst, P.; Sabatini, D. M. , Rictor, a novel binding partner of mTOR, defines a rapamycin-insensitive and raptor-independent pathway that regulates the cytoskeleton. Curr Biol 2004, 14, 1296–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearce, L. R.; Sommer, E. M.; Sakamoto, K.; Wullschleger, S.; Alessi, D. R. , Protor-1 is required for efficient mTORC2-mediated activation of SGK1 in the kidney. Biochem J 2011, 436, 169–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frias, M. A.; Thoreen, C. C.; Jaffe, J. D.; Schroder, W.; Sculley, T.; Carr, S. A.; Sabatini, D. M. , mSin1 is necessary for Akt/PKB phosphorylation, and its isoforms define three distinct mTORC2s. Curr Biol 2006, 16, 1865–1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scaiola, A.; Mangia, F.; Imseng, S.; Boehringer, D.; Berneiser, K.; Shimobayashi, M.; Stuttfeld, E.; Hall, M. N.; Ban, N.; Maier, T. , The 3.2-Å resolution structure of human mTORC2. Sci Adv 2020, 6, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatebe, H.; Murayama, S.; Yonekura, T.; Hatano, T.; Richter, D.; Furuya, T.; Kataoka, S.; Furuita, K.; Kojima, C.; Shiozaki, K. , Substrate specificity of TOR complex 2 is determined by a ubiquitin-fold domain of the Sin1 subunit. Elife 2017, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berchtold, D.; Walther, T. C. , TORC2 plasma membrane localization is essential for cell viability and restricted to a distinct domain. Mol Biol Cell 2009, 20, 1565–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, P.; Gan, W.; Chin, Y. R.; Ogura, K.; Guo, J.; Zhang, J.; Wang, B.; Blenis, J.; Cantley, L. C.; Toker, A.; Su, B.; Wei, W. , PtdIns(3,4,5)P3-Dependent Activation of the mTORC2 Kinase Complex. Cancer Discov 2015, 5, 1194–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, X. M.; Blenis, J. , Molecular mechanisms of mTOR-mediated translational control. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2009, 10, 307–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauvin, C.; Koka, V.; Nouschi, A.; Mieulet, V.; Hoareau-Aveilla, C.; Dreazen, A.; Cagnard, N.; Carpentier, W.; Kiss, T.; Meyuhas, O.; Pende, M. , Ribosomal protein S6 kinase activity controls the ribosome biogenesis transcriptional program. Oncogene 2014, 33, 474–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holz, M. K.; Ballif, B. A.; Gygi, S. P.; Blenis, J. , mTOR and S6K1 mediate assembly of the translation preinitiation complex through dynamic protein interchange and ordered phosphorylation events. Cell 2005, 123, 569–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorrello, N. V.; Peschiaroli, A.; Guardavaccaro, D.; Colburn, N. H.; Sherman, N. E.; Pagano, M. , S6K1- and betaTRCP-mediated degradation of PDCD4 promotes protein translation and cell growth. Science 2006, 314, 467–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porstmann, T.; Santos, C. R.; Griffiths, B.; Cully, M.; Wu, M.; Leevers, S.; Griffiths, J. R.; Chung, Y. L.; Schulze, A. , SREBP activity is regulated by mTORC1 and contributes to Akt-dependent cell growth. Cell Metab 2008, 8, 224–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duvel, K.; Yecies, J. L.; Menon, S.; Raman, P.; Lipovsky, A. I.; Souza, A. L.; Triantafellow, E.; Ma, Q.; Gorski, R.; Cleaver, S.; Vander Heiden, M. G.; MacKeigan, J. P.; Finan, P. M.; Clish, C. B.; Murphy, L. O.; Manning, B. D. , Activation of a metabolic gene regulatory network downstream of mTOR complex 1. Mol Cell 2010, 39, 171–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, T. R.; Sengupta, S. S.; Harris, T. E.; Carmack, A. E.; Kang, S. A.; Balderas, E.; Guertin, D. A.; Madden, K. L.; Carpenter, A. E.; Finck, B. N.; Sabatini, D. M. , mTOR complex 1 regulates lipin 1 localization to control the SREBP pathway. Cell 2011, 146, 408–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J. E. K. a. J. , Regulation of Peroxisome Proliferator–Activated Receptor-γ Activity by Mammalian Target of Rapamycin and Amino Acids in Adipogenesis. Diabetes 2004, 53, 2748–2756. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H. H.; Huang, J.; Duvel, K.; Boback, B.; Wu, S.; Squillace, R. M.; Wu, C. L.; Manning, B. D. , Insulin stimulates adipogenesis through the Akt-TSC2-mTORC1 pathway. PLoS One 2009, 4, e6189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, G.; Zheng, Y.; Cho, S.; Jang, C.; England, C.; Dempsey, J. M.; Yu, Y.; Liu, X.; He, L.; Cavaliere, P. M.; Chavez, A.; Zhang, E.; Isik, M.; Couvillon, A.; Dephoure, N. E.; Blackwell, T. K.; Yu, J. J.; Rabinowitz, J. D.; Cantley, L. C.; Blenis, J. , Post-transcriptional Regulation of De Novo Lipogenesis by mTORC1-S6K1-SRPK2 Signaling. Cell 2017, 171, 1545–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aaron, M. Robitaille; Stefan Christen; Mitsugu Shimobayashi; Marion Cornu; Luca L. Fava; Suzette Moes; Cristina Prescianotto-Baschong; Uwe Sauer; Paul Jenoe; Hall, M. N., Quantitative Phosphoproteomics Reveal mTORC1 Activates de Novo Pyrimidine Synthesis. Science 2013, 339, 1320–1323. [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Sahra, I.; Howell, J. J.; Asara, J. M.; Manning, B. D. , Stimulation of de novo pyrimidine synthesis by growth signaling through mTOR and S6K1. Science 2013, 339, 1323–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Sahra, I.; Hoxhaj, G.; Ricoult, S. J. H.; Asara, J. M.; Manning, B. D. , mTORC1 induces purine synthesis through control of the mitochondrial tetrahydrofolate cycle. Science 2016, 351, 728–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunningham, J. T.; Rodgers, J. T.; Arlow, D. H.; Vazquez, F.; Mootha, V. K.; Puigserver, P. , mTOR controls mitochondrial oxidative function through a YY1-PGC-1alpha transcriptional complex. Nature 2007, 450, 736–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zid, B. M.; Rogers, A. N.; Katewa, S. D.; Vargas, M. A.; Kolipinski, M. C.; Lu, T. A.; Benzer, S.; Kapahi, P. , 4E-BP extends lifespan upon dietary restriction by enhancing mitochondrial activity in Drosophila. Cell 2009, 139, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dikic, I.; Elazar, Z. , Mechanism and medical implications of mammalian autophagy. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2018, 19, 349–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganley, I. G.; Lam du, H.; Wang, J.; Ding, X.; Chen, S.; Jiang, X. , ULK1.ATG13.FIP200 complex mediates mTOR signaling and is essential for autophagy. J Biol Chem 2009, 284, 12297–12305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosokawa, N.; Hara, T.; Kaizuka, T.; Kishi, C.; Takamura, A.; Miura, Y.; Iemura, S.; Natsume, T.; Takehana, K.; Yamada, N.; Guan, J. L.; Oshiro, N.; Mizushima, N. , Nutrient-dependent mTORC1 association with the ULK1-Atg13-FIP200 complex required for autophagy. Mol Biol Cell 2009, 20, 1981–1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Kundu, M.; Viollet, B.; Guan, K. L. , AMPK and mTOR regulate autophagy through direct phosphorylation of Ulk1. Nat Cell Biol 2011, 13, 132–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y. M.; Jung, C. H.; Seo, M.; Kim, E. K.; Park, J. M.; Bae, S. S.; Kim, D. H. , mTORC1 phosphorylates UVRAG to negatively regulate autophagosome and endosome maturation. Mol Cell 2015, 57, 207–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martina, J. A.; Chen, Y.; Gucek, M.; Puertollano, R. , MTORC1 functions as a transcriptional regulator of autophagy by preventing nuclear transport of TFEB. Autophagy 2012, 8, 903–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roczniak-Ferguson, A.; Petit, C. S.; Froehlich, F.; Qian, S.; Ky, J.; Angarola, B.; Walther, T. C.; Ferguson, S. M. , The transcription factor TFEB links mTORC1 signaling to transcriptional control of lysosome homeostasis. Sci Signal 2012, 5, ra42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Settembre, C.; Zoncu, R.; Medina, D. L.; Vetrini, F.; Erdin, S.; Erdin, S.; Huynh, T.; Ferron, M.; Karsenty, G.; Vellard, M. C.; Facchinetti, V.; Sabatini, D. M.; Ballabio, A. , A lysosome-to-nucleus signalling mechanism senses and regulates the lysosome via mTOR and TFEB. EMBO J 2012, 31, 1095–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martina, J. A.; Diab, H. I.; Lishu, L.; Jeong, A. L.; Patange, S.; Raben, N.; Puertollano, R. , The nutrient-responsive transcription factor TFE3 promotes autophagy, lysosomal biogenesis, and clearance of cellular debris. Sci Signal 2014, 7, ra9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, Q.; Liu, R. , MTOR-mediates hepatic lipid metabolism through an autophagic SNARE complex. Autophagy 2022, 18, 1467–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koren, I.; Reem, E.; Kimchi, A. , DAP1, a novel substrate of mTOR, negatively regulates autophagy. Curr Biol 2010, 20, 1093–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, W.; You, Z.; Zhou, L.; Xu, Y.; Peng, C.; Zhou, T.; Yi, C.; Shi, Y.; Liu, W. , mTORC1-Regulated and HUWE1-Mediated WIPI2 Degradation Controls Autophagy Flux. Mol Cell 2018, 72, 303–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinzalla, V.; Stracka, D.; Oppliger, W.; Hall, M. N. , Activation of mTORC2 by association with the ribosome. Cell 2011, 144, 757–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Dibble, C. C.; Matsuzaki, M.; Manning, B. D. , The TSC1-TSC2 complex is required for proper activation of mTOR complex 2. Mol Cell Biol 2008, 28, 4104–4115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, O. J.; Wang, Z.; Hunter, T. , Inappropriate activation of the TSC/Rheb/mTOR/S6K cassette induces IRS1/2 depletion, insulin resistance, and cell survival deficiencies. Curr Biol 2004, 14, 1650–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung Hee Um, F. F. M. W.; Fre De Ric Picard, M. J. M. S.; Peter, R. Allegrini, S. C. K. J., Absence of S6K1 protects against age- and diet-induced obesity while enhancing insulin sensitivity. Nature 2004, 431, 200–205. [Google Scholar]
- Yoneyama, Y.; Inamitsu, T.; Chida, K.; Iemura, S. I.; Natsume, T.; Maeda, T.; Hakuno, F.; Takahashi, S. I. , Serine Phosphorylation by mTORC1 Promotes IRS-1 Degradation through SCFbeta-TRCP E3 Ubiquitin Ligase. iScience 2018, 5, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, P. P.; Kang, S. A.; Rameseder, J.; Zhang, Y.; Ottina, K. A.; Lim, D.; Peterson, T. R.; Choi, Y.; Gray, N. S.; Yaffe, M. B.; Marto, J. A.; Sabatini, D. M. , The mTOR-regulated phosphoproteome reveals a mechanism of mTORC1-mediated inhibition of growth factor signaling. Science 2011, 332, 1317–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Yoon, S. O.; Poulogiannis, G.; Yang, Q.; Ma, X. M.; Villen, J.; Kubica, N.; Hoffman, G. R.; Cantley, L. C.; Gygi, S. P.; Blenis, J. , Phosphoproteomic analysis identifies Grb10 as an mTORC1 substrate that negatively regulates insulin signaling. Science 2011, 332, 1322–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julien, L. A.; Carriere, A.; Moreau, J.; Roux, P. P. , mTORC1-activated S6K1 phosphorylates Rictor on threonine 1135 and regulates mTORC2 signaling. Mol Cell Biol 2010, 30, 908–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Gan, W.; Inuzuka, H.; Lazorchak, A. S.; Gao, D.; Arojo, O.; Liu, D.; Wan, L.; Zhai, B.; Yu, Y.; Yuan, M.; Kim, B. M.; Shaik, S.; Menon, S.; Gygi, S. P.; Lee, T. H.; Asara, J. M.; Manning, B. D.; Blenis, J.; Su, B.; Wei, W. , Sin1 phosphorylation impairs mTORC2 complex integrity and inhibits downstream Akt signalling to suppress tumorigenesis. Nat Cell Biol 2013, 15, 1340–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazyken, D.; Magnuson, B.; Bodur, C.; Acosta-Jaquez, H. A.; Zhang, D.; Tong, X.; Barnes, T. M.; Steinl, G. K.; Patterson, N. E.; Altheim, C. H.; Sharma, N.; Inoki, K.; Cartee, G. D.; Bridges, D.; Yin, L.; Riddle, S. M.; Fingar, D. C. , AMPK directly activates mTORC2 to promote cell survival during acute energetic stress. Sci Signal 2019, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betz, C.; Hall, M. N. , Where is mTOR and what is it doing there? J Cell Biol 2013, 203, 563–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarbassov, D. D.; Guertin, D. A.; Ali, S. M.; Sabatini, D. M. , Phosphorylation and regulation of Akt/PKB by the rictor-mTOR complex. FEBRUARY 2005, 307, 1098–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacinto, E.; Facchinetti, V.; Liu, D.; Soto, N.; Wei, S.; Jung, S. Y.; Huang, Q.; Qin, J.; Su, B. , SIN1/MIP1 maintains rictor-mTOR complex integrity and regulates Akt phosphorylation and substrate specificity. Cell 2006, 127, 125–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guertin, D. A.; Stevens, D. M.; Thoreen, C. C.; Burds, A. A.; Kalaany, N. Y.; Moffat, J.; Brown, M.; Fitzgerald, K. J.; Sabatini, D. M. , Ablation in mice of the mTORC components raptor, rictor, or mLST8 reveals that mTORC2 is required for signaling to Akt-FOXO and PKCalpha, but not S6K1. Dev Cell 2006, 11, 859–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakker, W. J.; Harris, I. S.; Mak, T. W. , FOXO3a is activated in response to hypoxic stress and inhibits HIF1-induced apoptosis via regulation of CITED2. Mol Cell 2007, 28, 941–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Martinez, J. M.; Alessi, D. R. , mTOR complex 2 (mTORC2) controls hydrophobic motif phosphorylation and activation of serum- and glucocorticoid-induced protein kinase 1 (SGK1). Biochem J 2008, 416, 375–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiler, M.; Blaes, J.; Pusch, S.; Sahm, F.; Czabanka, M.; Luger, S.; Bunse, L.; Solecki, G.; Eichwald, V.; Jugold, M.; Hodecker, S.; Osswald, M.; Meisner, C.; Hielscher, T.; Rubmann, P.; Pfenning, P. N.; Ronellenfitsch, M.; Kempf, T.; Schnolzer, M.; Abdollahi, A.; Lang, F.; Bendszus, M.; von Deimling, A.; Winkler, F.; Weller, M.; Vajkoczy, P.; Platten, M.; Wick, W. , mTOR target NDRG1 confers MGMT-dependent resistance to alkylating chemotherapy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2014, 111, 409–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sciarretta, S.; Zhai, P.; Maejima, Y.; Del Re, D. P.; Nagarajan, N.; Yee, D.; Liu, T.; Magnuson, M. A.; Volpe, M.; Frati, G.; Li, H.; Sadoshima, J. , mTORC2 regulates cardiac response to stress by inhibiting MST1. Cell Rep 2015, 11, 125–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Meng, Z.; Chen, R.; Guan, K. L. , The Hippo Pathway: Biology and Pathophysiology. Annu Rev Biochem 2019, 88, 577–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacinto, E.; Loewith, R.; Schmidt, A.; Lin, S.; Ruegg, M. A.; Hall, A.; Hall, M. N. , Mammalian TOR complex 2 controls the actin cytoskeleton and is rapamycin insensitive. Nat Cell Biol 2004, 6, 1122–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozupone, C. A.; Stombaugh, J. I.; Gordon, J. I.; Jansson, J. K.; Knight, R. , Diversity, stability and resilience of the human gut microbiota. Nature 2012, 489, 220–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adak, A.; Khan, M. R. , An insight into gut microbiota and its functionalities. Cell Mol Life Sci 2019, 76, 473–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rampelli, S.; Schnorr, S. L.; Consolandi, C.; Turroni, S.; Severgnini, M.; Peano, C.; Brigidi, P.; Crittenden, A. N.; Henry, A. G.; Candela, M. , Metagenome Sequencing of the Hadza Hunter-Gatherer Gut Microbiota. Curr Biol 2015, 25, 1682–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adak, A.; Maity, C.; Ghosh, K.; Mondal, K. C. , Alteration of predominant gastrointestinal flora and oxidative damage of large intestine under simulated hypobaric hypoxia. Z Gastroenterol 2014, 52, 180–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adak, A.; Maity, C.; Ghosh, K.; Pati, B. R.; Mondal, K. C. , Dynamics of predominant microbiota in the human gastrointestinal tract and change in luminal enzymes and immunoglobulin profile during high-altitude adaptation. Folia Microbiol (Praha) 2013, 58, 523–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nardone, G.; Compare, D. , The human gastric microbiota: Is it time to rethink the pathogenesis of stomach diseases? United European Gastroenterol J 2015, 3, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Aidy, S.; van den Bogert, B.; Kleerebezem, M. , The small intestine microbiota, nutritional modulation and relevance for health. Curr Opin Biotechnol 2015, 32, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollister, E. B.; Gao, C.; Versalovic, J. , Compositional and functional features of the gastrointestinal microbiome and their effects on human health. Gastroenterology 2014, 146, 1449–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belkaid, Y.; Hand, T. W. , Role of the microbiota in immunity and inflammation. Cell 2014, 157, 121–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerard, P. , Gut microbiota and obesity. Cell Mol Life Sci 2016, 73, 147–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, Z.; Liu, X.; Cheng, Y.; Yan, X.; Wu, S. , Gut microbiota and aging. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 2022, 62, 3509–3534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, J.; Wu, G. D.; Albenberg, L.; Tomov, V. T. , Gut microbiota and IBD: causation or correlation? Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 2017, 14, 573–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jameson, K. G.; Olson, C. A.; Kazmi, S. A.; Hsiao, E. Y. , Toward Understanding Microbiome-Neuronal Signaling. Mol Cell 2020, 78, 577–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J. Y.; Liu, M. T.; Tao, T.; Zhu, X.; Fei, F. Q. , The role of gut microbiota in tumorigenesis and treatment. Biomed Pharmacother 2021, 138, 111444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, D.; Albenberg, L.; Compher, C.; Baldassano, R.; Piccoli, D.; Lewis, J. D.; Wu, G. D. , Diet in the pathogenesis and treatment of inflammatory bowel diseases. Gastroenterology 2015, 148, 1087–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuoka, K.; Kanai, T. , The gut microbiota and inflammatory bowel disease. Semin Immunopathol 2015, 37, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloyd-Price, J.; Arze, C.; Ananthakrishnan, A. N.; Schirmer, M.; Avila-Pacheco, J.; Poon, T. W.; Andrews, E.; Ajami, N. J.; Bonham, K. S.; Brislawn, C. J.; Casero, D.; Courtney, H.; Gonzalez, A.; Graeber, T. G.; Hall, A. B.; Lake, K.; Landers, C. J.; Mallick, H.; Plichta, D. R.; Prasad, M.; Rahnavard, G.; Sauk, J.; Shungin, D.; Vazquez-Baeza, Y.; White, R. A., 3rd; Investigators, I.; Braun, J.; Denson, L. A.; Jansson, J. K.; Knight, R.; Kugathasan, S.; McGovern, D. P. B.; Petrosino, J. F.; Stappenbeck, T. S.; Winter, H. S.; Clish, C. B.; Franzosa, E. A.; Vlamakis, H.; Xavier, R. J.; Huttenhower, C. , Multi-omics of the gut microbial ecosystem in inflammatory bowel diseases. Nature 2019, 569, 655–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Shi, L.; Li, W.; Chen, K.; Li, M.; Chen, X.; Zhang, H.; Li, T.; Matsuzawa-Ishimoto, Y.; Yao, X.; Shao, D.; Ke, Z.; Li, J.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, X.; Cui, J.; Cui, S.; Leng, Q.; Cadwell, K.; Li, X.; Wei, H.; Zhang, H.; Li, H.; Xiao, H. , Gut epithelial TSC1/mTOR controls RIPK3-dependent necroptosis in intestinal inflammation and cancer. J Clin Invest 2020, 130, 2111–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Y.; Huang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, F.; Sun, M.; Yang, W.; Chen, L.; Yao, S.; Peniche, A.; Dann, S. M.; Sun, J.; Golovko, G.; Fofanov, Y.; Miao, Y.; Liu, Z.; Chen, D.; Cong, Y. , Interleukin-33 Promotes REG3gamma Expression in Intestinal Epithelial Cells and Regulates Gut Microbiota. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol 2019, 8, 21–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.; Yu, T.; Huang, X.; Bilotta, A. J.; Xu, L.; Lu, Y.; Sun, J.; Pan, F.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, W.; Yao, S.; Maynard, C. L.; Singh, N.; Dann, S. M.; Liu, Z.; Cong, Y. , Intestinal microbiota-derived short-chain fatty acids regulation of immune cell IL-22 production and gut immunity. Nat Commun 2020, 11, 4457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qing Zhao; W., L.; Duck1 Fengyuan Huang; Katie L.Alexander; L., C.; Maynard; J., P.; Mannon; Elson, C. O., CD4+T cell activation and concomitant mTOR metabolic inhibition can ablate microbiota-specific memory cells and prevent colitis. SCIENCE IMMUNOLOGY.
- Sakai, K.; De Velasco, M. A.; Kura, Y.; Nishio, K. , Transcriptome Profiling and Metagenomic Analysis Help to Elucidate Interactions in an Inflammation-Associated Cancer Mouse Model. Cancers (Basel) 2021, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Xie, W.; Wan, X.; Deng, T. , Clostridium butyricum protects intestinal barrier function via upregulation of tight junction proteins and activation of the Akt/mTOR signaling pathway in a mouse model of dextran sodium sulfate-induced colitis. Exp Ther Med 2020, 20, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, L.; Shan, Y.-J.; He, C.-X.; Ren, M.-H.; Tian, P.-J.; Song, W. , Effects of L. paracasei subp. paracasei X12 on cell cycle of colon cancer HT-29 cells and regulation of mTOR signalling pathway. Journal of Functional Foods 2016, 21, 431–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorgensen, S. F.; Troseid, M.; Kummen, M.; Anmarkrud, J. A.; Michelsen, A. E.; Osnes, L. T.; Holm, K.; Hoivik, M. L.; Rashidi, A.; Dahl, C. P.; Vesterhus, M.; Halvorsen, B.; Mollnes, T. E.; Berge, R. K.; Moum, B.; Lundin, K. E.; Fevang, B.; Ueland, T.; Karlsen, T. H.; Aukrust, P.; Hov, J. R. , Altered gut microbiota profile in common variable immunodeficiency associates with levels of lipopolysaccharide and markers of systemic immune activation. Mucosal Immunol 2016, 9, 1455–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.; Zhou, R.; Wang, H.; Li, W.; Pan, M.; Yao, X.; Zhan, W.; Yang, S.; Xu, L.; Ding, Y.; Zhao, L. , Gut microbiota-stimulated cathepsin K secretion mediates TLR4-dependent M2 macrophage polarization and promotes tumor metastasis in colorectal cancer. Cell Death Differ 2019, 26, 2447–2463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassard, A. M.; Ciocan, D. , Microbiota, a key player in alcoholic liver disease. Clin Mol Hepatol 2018, 24, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miura, K.; Ohnishi, H. , Role of gut microbiota and Toll-like receptors in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. World J Gastroenterol 2014, 20, 7381–7391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrin, G.; Guerrero, M.; Amado, V.; Rodriguez-Peralvarez, M.; De la Mata, M. , Activation of mTOR Signaling Pathway in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Int J Mol Sci 2020, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, C. C.; Ching, Y. H.; Li, Y. P.; Liu, J. Y.; Huang, Y. T.; Huang, Y. W.; Yang, S. S.; Huang, W. C.; Chuang, H. L. , Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Is Exacerbated in High-Fat Diet-Fed Gnotobiotic Mice by Colonization with the Gut Microbiota from Patients with Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. Nutrients 2017, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Jiang, W.; Xu, J.; Wu, N.; Wang, Y.; Lin, T.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y., E. coli NF73-1 Isolated From NASH Patients Aggravates NAFLD in Mice by Translocating Into the Liver and Stimulating M1 Polarization. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 2020, 10, 535940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, F.; Xiang, S.; Chen, Z.; Song, L.; Li, Y.; Liao, Z.; Ge, B.; Zhou, B. , The probiotic effects of AB23A on high-fat-diet-induced non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in mice may be associated with suppressing the serum levels of lipopolysaccharides and branched-chain amino acids. Arch Biochem Biophys 2021, 714, 109080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chao Cai1*, D.-Z. C. , Li-Chao Ge1, Wen-Kai Chen1, Sha-Sha Ye1, Wei-Wei Ye1,3, Ying Tao1, Rui Wang1, Ji Li1, Zhuo Lin1, Xiao-Dong Wang1, Lan-Man Xu1,4,5, Yong-Ping Chen1, Synergistic effects of Lactobacillus rhamnosus culture supernatant and bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells on the development of alcoholic steatohepatitis in mice. Am J Transl Res 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Pant, K.; Saraya, A.; Venugopal, S. K. , Oxidative stress plays a key role in butyrate-mediated autophagy via Akt/mTOR pathway in hepatoma cells. Chem Biol Interact 2017, 273, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, C.-M.; Sun, M.-F.; Jia, X.-B.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, B.-P.; Zhou, Z.-L.; Zhao, L.-P.; Cui, C.; Shen, Y.-Q. , Sodium butyrate causes α-synuclein degradation by an Atg5-dependent and PI3K/Akt/mTOR-related autophagy pathway. Experimental Cell Research 2020, 387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Bari, M. A. A.; Xu, P. , Molecular regulation of autophagy machinery by mTOR-dependent and -independent pathways. Ann N Y Acad Sci 2020, 1467, 3–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, D.; Liu, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Hou, N.; Yan, W.; Qin, Y.; Ye, Q.; Cheng, X.; Xiao, Q.; Bao, Y.; Luo, J.; Wu, X. , Urolithin B, a gut microbiota metabolite, protects against myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury via p62/Keap1/Nrf2 signaling pathway. Pharmacol Res 2020, 153, 104655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Gao, H.; Jiang, X.; Zheng, Z. , Urolithin B, a Gut Microbiota Metabolite, Reduced Susceptibility to Myocardial Arrhythmic Predisposition after Hypoxia. Dis Markers 2022, 2022, 6517266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, K.; Ma, Y.; Cai, F.; Huang, X.; Xiao, L.; Zhong, C.; Ren, P.; Luo, Q.; Chen, J.; Han, F. , Changes of gut microbiota in diabetic nephropathy and its effect on the progression of kidney injury. Endocrine 2022, 76, 294–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, S.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, M.; Zou, J.; Jiang, S.; Qian, D.; Duan, J. , Xiexin Tang ameliorates dyslipidemia in high-fat diet-induced obese rats via elevating gut microbiota-derived short chain fatty acids production and adjusting energy metabolism. J Ethnopharmacol 2019, 241, 112032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, T.; Sun, X.; Zhu, J.; Hon, K. L.; Jiang, P.; Chu, I. M.; Tsang, M. S.; Lam, C. W.; Zeng, H.; Wong, C. K. , IL-37 Ameliorating Allergic Inflammation in Atopic Dermatitis Through Regulating Microbiota and AMPK-mTOR Signaling Pathway-Modulated Autophagy Mechanism. Front Immunol 2020, 11, 752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S. K.; Ma, L. B.; Yuan, Y.; Ji, X. Y.; Sun, W. J.; Duan, J. X.; Zeng, Q. P.; Wasti, B.; Xiao, B.; Zheng, J. F.; Chen, P.; Xiang, X. D. , Alanylglutamine Relieved Asthma Symptoms by Regulating Gut Microbiota and the Derived Metabolites in Mice. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2020, 2020, 7101407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ju, Z.; Guo, P.; Xiang, J.; Lei, R.; Ren, G.; Zhou, M.; Yang, X.; Zhou, P.; Huang, R. , Low-dose radiation exaggerates HFD-induced metabolic dysfunction by gut microbiota through PA-PYCR1 axis. Communications Biology 2022, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, M. J.; Lee, J.; Shin, N. R.; Kim, M. S.; Hyun, D. W.; Yun, J. H.; Kim, P. S.; Whon, T. W.; Bae, J. W. , Chronic Repression of mTOR Complex 2 Induces Changes in the Gut Microbiota of Diet-induced Obese Mice. Sci Rep 2016, 6, 30887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hurez, V.; Dao, V.; Liu, A.; Pandeswara, S.; Gelfond, J.; Sun, L.; Bergman, M.; Orihuela, C. J.; Galvan, V.; Padrón, Á.; Drerup, J.; Liu, Y.; Hasty, P.; Sharp, Z. D.; Curiel, T. J. , Chronic mTOR inhibition in mice with rapamycin alters T, B, myeloid, and innate lymphoid cells and gut flora and prolongs life of immune-deficient mice. Aging Cell 2015, 14, 945–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Fang, S.; Wei, H.; He, M.; Fu, H.; Xiong, X.; Zhou, Y.; Wu, J.; Gao, J.; Yang, H.; Huang, L. , Prevotella copri increases fat accumulation in pigs fed with formula diets. Microbiome 2021, 9, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinstock, G. M. , Genomic approaches to studying the human microbiota. Nature 2012, 489, 250–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, J.; Li, R.; Raes, J.; Arumugam, M.; Burgdorf, K. S.; Manichanh, C.; Nielsen, T.; Pons, N.; Levenez, F.; Yamada, T.; Mende, D. R.; Li, J.; Xu, J.; Li, S.; Li, D.; Cao, J.; Wang, B.; Liang, H.; Zheng, H.; Xie, Y.; Tap, J.; Lepage, P.; Bertalan, M.; Batto, J. M.; Hansen, T.; Le Paslier, D.; Linneberg, A.; Nielsen, H. B.; Pelletier, E.; Renault, P.; Sicheritz-Ponten, T.; Turner, K.; Zhu, H.; Yu, C.; Li, S.; Jian, M.; Zhou, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, X.; Li, S.; Qin, N.; Yang, H.; Wang, J.; Brunak, S.; Dore, J.; Guarner, F.; Kristiansen, K.; Pedersen, O.; Parkhill, J.; Weissenbach, J.; Meta, H. I. T. C.; Bork, P.; Ehrlich, S. D.; Wang, J. , A human gut microbial gene catalogue established by metagenomic sequencing. Nature 2010, 464, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.; Chen, B.; Zhai, X.; Qian, Q.; Gui, R.; Jiang, C. , Integrated analysis of the gut microbiome and metabolome in a mouse model of inflammation-induced colorectal tumors. Front Microbiol 2022, 13, 1082835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.; You, H. J.; Lee, G.; Lee, S. H.; Yoo, T.; Choi, M.; Joo, S. K.; Park, J. H.; Chang, M. S.; Lee, D. H.; Kim, W.; Ko, G.; Innovative Target Exploration of, N. c. , Interaction effect between NAFLD severity and high carbohydrate diet on gut microbiome alteration and hepatic de novo lipogenesis. Gut Microbes 2022, 14, 2078612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M. X.; Li, M. Y.; Lei, J. X.; Wu, Y. Z.; Li, Z. H.; Chen, L. M.; Zhou, C. L.; Su, J. Y.; Huang, G. X.; Huang, X. Q.; Zheng, X. B. , Huangqin decoction ameliorates DSS-induced ulcerative colitis: Role of gut microbiota and amino acid metabolism, mTOR pathway and intestinal epithelial barrier. Phytomedicine 2022, 100, 154052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Shao, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, D.; Wang, M. , Insight Into Polysaccharides From Panax ginseng C. A. Meyer in Improving Intestinal Inflammation: Modulating Intestinal Microbiota and Autophagy. Front Immunol 2021, 12, 683911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qing Zhao; Lennard W. Duck; Fengyuan Huang; Katie L. Alexander; Craig L. Maynard; Peter J. Mannon; Elson, C. O., CD4+ T cell activation and concomitant mTOR metabolic inhibition can ablate microbiota-specific memory cells and prevent colitis. SCIENCE IMMUNOLOGY 2020, 5.
- Seif El-Din, S. H.; Salem, M. B.; El-Lakkany, N. M.; Hammam, O. A.; Nasr, S. M.; Okasha, H.; Ahmed, L. A.; Saleh, S.; Botros, S. S. , Early intervention with probiotics and metformin alleviates liver injury in NAFLD rats via targeting gut microbiota dysbiosis and p-AKT/mTOR/LC-3II pathways. Hum Exp Toxicol 2021, 40, 1496–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chao Cai; Da-Zhi Chen; Ge,, L. -C.; Chen,, W.-K.; Ye,, S.-S.; Ye,, W.-W.; Tao,, Y.; Rui Wang; Ji Li; Zhuo Lin; Xiao-Dong Wang; Xu, L.-M.; Chen, Y.-P., Synergistic effects of Lactobacillus rhamnosus culture supernatant and bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells on the development of alcoholic steatohepatitis in mice. Am J Transl Res 2019, 11, 5703–5715. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, Z.; Wu, N.; Wang, J.; Geng, L.; Yue, Y.; Wang, F.; Zhang, Q. , Low molecular weight fucoidan fraction LF2 improves metabolic syndrome via up-regulating PI3K-AKT-mTOR axis and increasing the abundance of Akkermansia muciniphila in the gut microbiota. Int J Biol Macromol 2021, (Pt A), 789–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Yang, M.; Ericsson, A. C. , The Potential Gut Microbiota-Mediated Treatment Options for Liver Cancer. Front Oncol 2020, 10, 524205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, M.; Kong, L.; Han, Y.; Zhang, S. , Gut microbiota enhances the chemosensitivity of hepatocellular carcinoma to 5-fluorouracil in vivo by increasing curcumin bioavailability. Phytother Res 2021, 35, 5823–5837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Sayed, N. S.; Kandil, E. A.; Ghoneum, M. H. , Enhancement of Insulin/PI3K/Akt Signaling Pathway and Modulation of Gut Microbiome by Probiotics Fermentation Technology, a Kefir Grain Product, in Sporadic Alzheimer's Disease Model in Mice. Front Pharmacol 2021, 12, 666502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Liu, X.; Zheng, Y.; Liu, W.; Ding, C. , Aronia melanocarpa polysaccharide ameliorates inflammation and aging in mice by modulating the AMPK/SIRT1/NF-kappaB signaling pathway and gut microbiota. Sci Rep 2021, 11, 20558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, P.; Ding, W.; Chen, J.; Cheng, Y.; Yang, B.; Huang, L.; Zhou, Q.; Zhu, C.; Li, X.; Wang, M.; Chen, J. , The protective effects of Mogroside V and its metabolite 11-oxo-mogrol of intestinal microbiota against MK801-induced neuronal damages. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 2020, 237, 1011–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y. X.; Qu, S. S.; Zhang, L. H.; Gu, Y. Y.; Chen, Y. H.; Huang, Z. Y.; Liu, M. H.; Zou, W.; Jiang, J.; Chen, J. Q.; Wang, Y. J.; Zhou, F. H. , The Role of Ophiopogonin D in Atherosclerosis: Impact on Lipid Metabolism and Gut Microbiota. Am J Chin Med 2021, 49, 1449–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, J.; Zheng, C.; Song, B.; Guo, Q.; Zhong, Y.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, L.; Duan, G.; Li, F.; Duan, Y. , HMB Improves Lipid Metabolism of Bama Xiang Mini-Pigs via Modulating the Bacteroidetes-Acetic Acid-AMPKalpha Axis. Front Microbiol 2021, 12, 736997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, Y.; Liao, X.; Wang, X.; Lao, S.; Liao, W. , The biological regulatory activities of Flammulina velutipes polysaccharide in mice intestinal microbiota, immune repertoire and heart transcriptome. Int J Biol Macromol 2021, 185, 582–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, J.; Chen, X.; Xiao, Y.; Li, D.; Li, M.; Li, H.; Huang, J.; Lai, Z.; Su, Z.; Xie, Y.; Zhu, D.; Chen, Q.; Lu, H.; He, J.; Xia, C. , Bruceae Fructus Oil Inhibits Triple-Negative Breast Cancer by Restraining Autophagy: Dependence on the Gut Microbiota-Mediated Amino Acid Regulation. Front Pharmacol 2021, 12, 727082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, T.; Zhang, B.; Li, Y.; Fang, B.; Zhu, X.; Xu, B.; Zhang, J.; Wang, M.; Fang, J. , New insight into 20(S)-ginsenoside Rh2 against T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia associated with the gut microbiota and the immune system. Eur J Med Chem 2020, 203, 112582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panebianco, C.; Adamberg, K.; Adamberg, S.; Saracino, C.; Jaagura, M.; Kolk, K.; Di Chio, A. G.; Graziano, P.; Vilu, R.; Pazienza, V. , Engineered Resistant-Starch (ERS) Diet Shapes Colon Microbiota Profile in Parallel with the Retardation of Tumor Growth in In Vitro and In Vivo Pancreatic Cancer Models. Nutrients 2017, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Liang, J.; Fu, N.; Han, Y.; Qin, J. , A Ketogenic Diet and the Treatment of Autism Spectrum Disorder. Front Pediatr 2021, 9, 650624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hurez, V.; Dao, V.; Liu, A.; Pandeswara, S.; Gelfond, J.; Sun, L.; Bergman, M.; Orihuela, C. J.; Galvan, V.; Padron, A.; Drerup, J.; Liu, Y.; Hasty, P.; Sharp, Z. D.; Curiel, T. J. , Chronic mTOR inhibition in mice with rapamycin alters T, B, myeloid, and innate lymphoid cells and gut flora and prolongs life of immune-deficient mice. Aging Cell 2015, 14, 945–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Chen, F.; Wu, W.; Sun, M.; Bilotta, A. J.; Yao, S.; Xiao, Y.; Huang, X.; Eaves-Pyles, T. D.; Golovko, G.; Fofanov, Y.; D'Souza, W.; Zhao, Q.; Liu, Z.; Cong, Y. , GPR43 mediates microbiota metabolite SCFA regulation of antimicrobial peptide expression in intestinal epithelial cells via activation of mTOR and STAT3. Mucosal Immunol 2018, 11, 752–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, H. K. M.; Lo, E. K. K.; El-Nezami, H. , Theabrownin Alleviates Colorectal Tumorigenesis in Murine AOM/DSS Model via PI3K/Akt/mTOR Pathway Suppression and Gut Microbiota Modulation. Antioxidants (Basel) 2022, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Name | Disease | Pathway affected | Changes of gut microbiota | Cell response |
|
HQD [121] |
UC | ↑PI3K/AKT/mTOR |
↑Firmicutes, Bacteroidetes, |
↑amino acid metabolism, p-S6 and p-4EBP1 ↓Apoptosis |
|
P.ginseng [122] |
IBD | ↓mTOR, TLR4, NF-kB |
↓Gram-negative bacteria | ↑Autophagy ↓p62 |
|
SCFAs [90] |
CD and UC | ↑mTOR, STAT3 |
against enteric infection of Citrobacter rodentium |
↑HIF1α, AhR, IL-22 ↓Gpr41, HDAC |
|
TB [141] |
CRC | ↓PI3K/AKT/mTOR |
↓Bacteroidceae and Bacteroides ↑Prevotellaceae and Alloprevotella |
↑cyclin D1 protein, cleaved caspase 3 |
|
SCFAs [140] |
—— | ↑mTOR, STAT3 |
—— | ↑AMP, RegIIIγ, β-defensins |
| L. reuteri + MTZ [124] | NAFLD |
↓mTOR, AKT |
↑Akkermansia muciniphila, Firmicutes, butyrate |
↑Autophagy, LC-3II ↓LPS, NF-kB, TNF-α |
|
AB23A [102] |
NAFLD |
↓mTOR, TLR4, NF-kB |
↓Firmicutes/Bacteroidaeota, Actinobacteriota/Bacteroidaeota | ↑ZO-1, occludin |
|
LGG-s and BMMSC [125] |
Alcoholic liver disease | ↓PI3K/mTOR, PI3K/NF-kB |
—— | ↑Autophagy ↓NKB cells, TFH cells |
|
LF2 [126] |
METS |
↓PI3K/AKT/mTOR |
↑Verrucomicrobia, Akkermansia muciniphila |
↓SREBP-1c, PPARγ |
|
Butyrate [104] |
HCC | ↓mTOR, AKT |
—— | ↑ROS, Autophagy: beclin 1, ATG 5, LC3-II |
|
Curcumin [128] |
HCC | ↓PI3K/AKT/mTOR |
↑family Helicobacteraceaeorder, order Campylobacterales, and genus Helicobacter and Campylobacteria |
↑apoptosis |
|
PFT [129] |
AD | ↑PI3K/AKT ↓mTOR, GSK-3β |
—— | ↓oxidative stress, inflammation |
|
AMP [130] |
Brain aging | ↑PI3K/AKT/mTOR ↓AMPK/SIRT1/NF-κB |
↑Bacteroides ↓Firmicutes |
↓apoptosis, NLRP3 |
| MogV and 11-oxo-mogrol [131] | neuronal damages | ↑AKT/mTOR | —— | ↑neurite outgrowth ↓apoptosis, [Ca2+]i release |
|
OPD [132] |
atherosclerosis | ↓mTOR/SREBP1/SCD1 | ↑Bacteroidetes, Faecalibaculum ↓Firmicutes, Ileibacterium |
↑insulin resistance ↓lipid metabolism |
|
HMB [133] |
Obesity | ↑AMPKα, Sirt1, and FoxO1 ↓mTOR |
↑Bacteroidetes, acetic acid | ↓lipid metabolism |
|
XXT [110] |
Obesity | ↑AMPK ↓mTOR |
↑key synthetic enzymes of SCFAs | ↑energy expenditure:PGC-1α, UCP-2 ↓energy intake |
|
FVP [134] |
Heart | ↑mTOR, etc ↓AMPK, PI3K-Akt, etc |
↑Bacteroidetes, Muribaculaceae | ↑Immunity |
|
BO [135] |
TNBC | ↑mTOR | ↑Candidatus Melainabacteria bacterium MEL.A1, Ndongobacter massiliensis, Prevotella ruminicola | ↓Autophagy Regulate amino acid metabolism |
|
GRh2 [136] |
T-ALL | ↓PI3K/AKT/mTOR |
↑Bacteroidetes, Verrucomicrobia ↓Firmicutes, Proteobacteria |
↑Immunity, tight junction proteins, antimicrobial peptides, IgA |
|
ERS Diet [137] |
PC | ↓mTOR, ERK1/2 | ↑diversity of microbiota ↑Formate, Lactate ↓Propionate |
↓Proliferation |
|
Resveratrol [114] |
Obesity and Diabetes |
↓mTOR |
↓Lactococcus, Clostridium XI, Oscillibacter, and Hydrogenoanaerobacterium | ↑insulin resistance |
|
ERapa [115] |
Longevity | ↓mTOR | Alteration of gut metagenomes | Regulate T, B, myeloid, and innate lymphoid cells |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





