Submitted:
15 June 2023
Posted:
16 June 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Objectives and Contributions
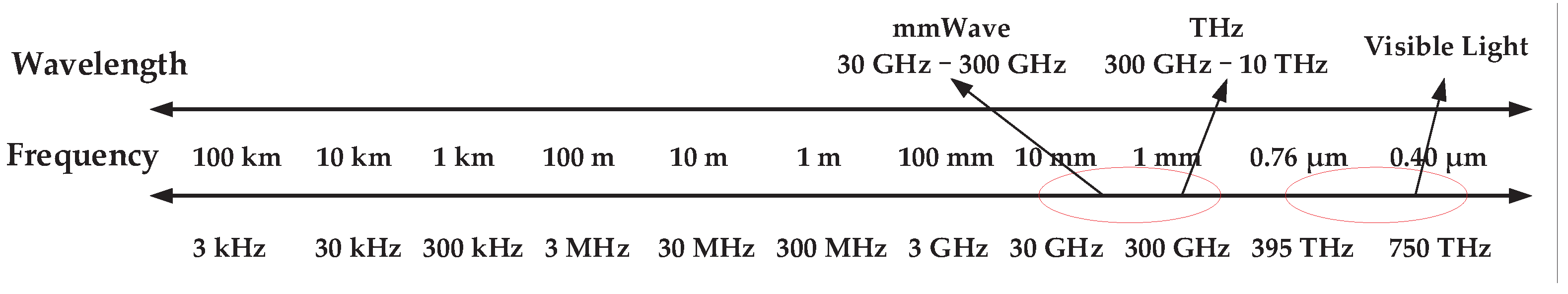
3. Channel Estimation in Different Frequency Bands
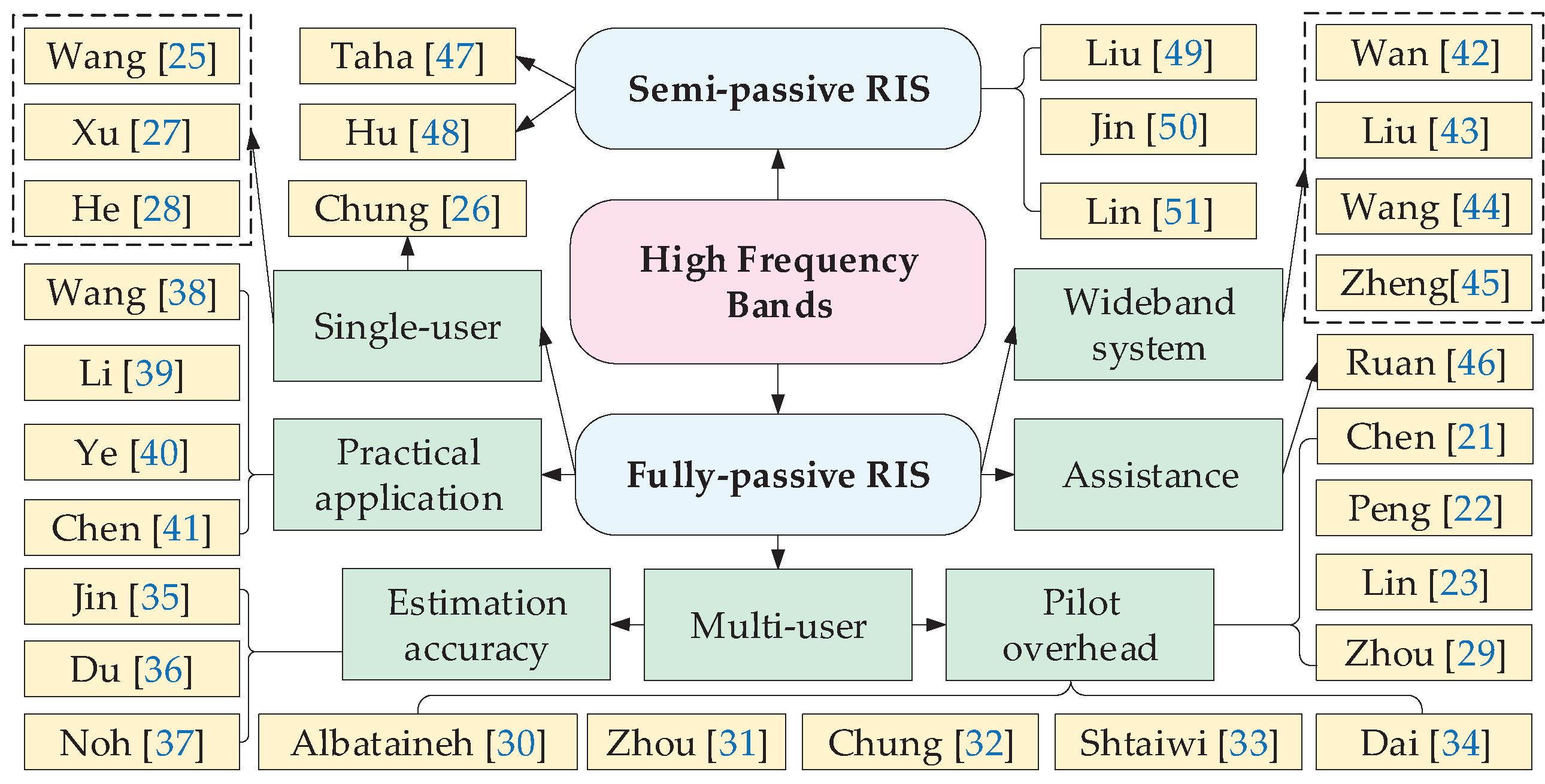
3.1. Channel Estimation for RIS Systems in High Frequency Bands
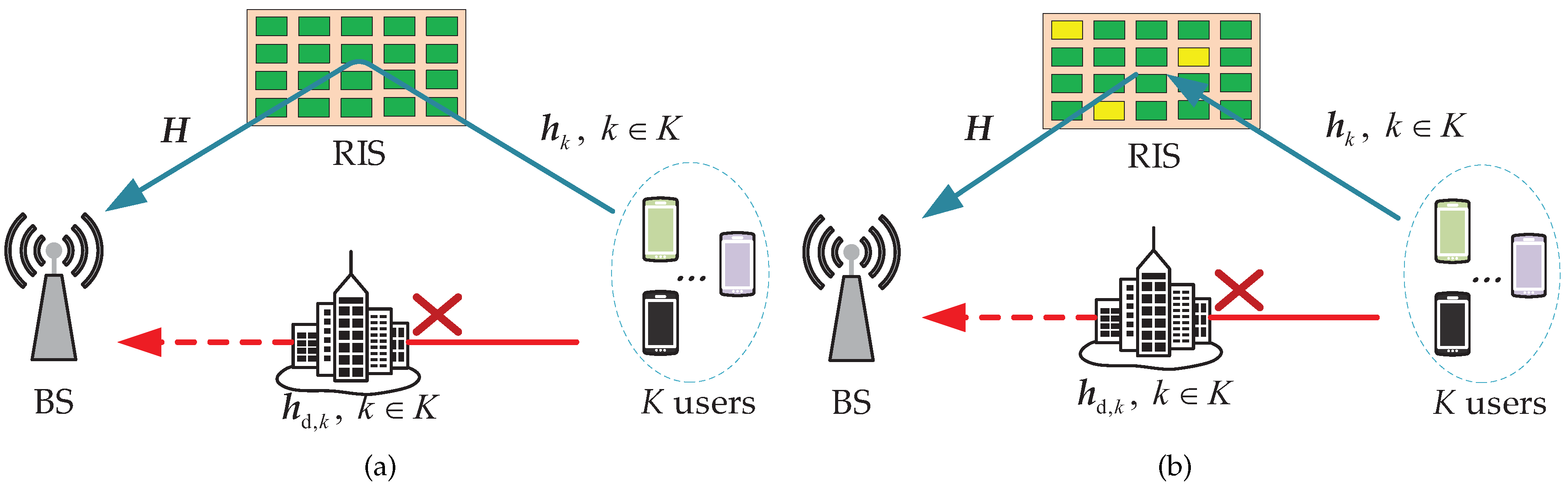
3.1.1. Channel Estimation for Fully-Passive RIS
3.1.2. Channel Estimation for Semi-Passive RIS
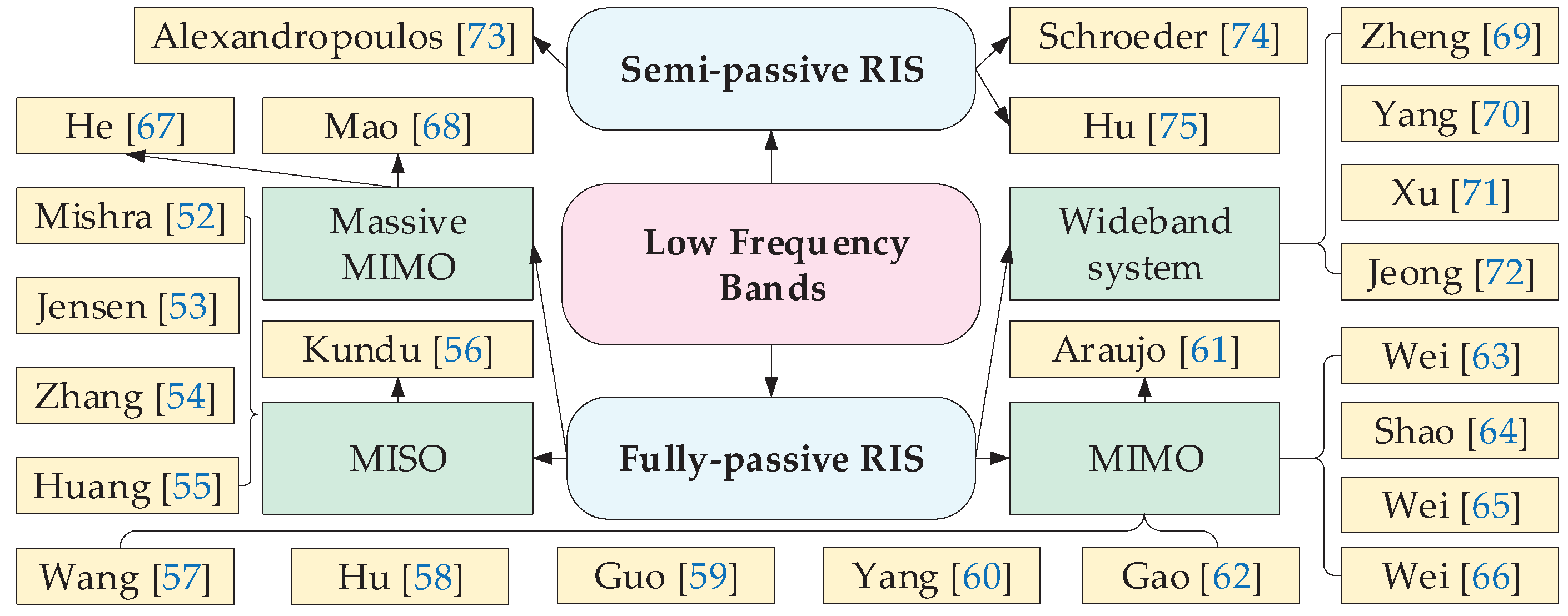
3.2. Channel Estimation for RIS Systems in Low Frequency Bands
3.2.1. Channel Estimation for Fully-Passive RIS
3.2.2. Channel Estimation for Semi-Passive RIS
4. Signal Processing Algorithms for RIS Channel Estimation
4.1. The Conventional Algorithms for RIS Channel Estimation
4.2. Compressed Sensing-Based Algorithms for RIS Channel Estimation
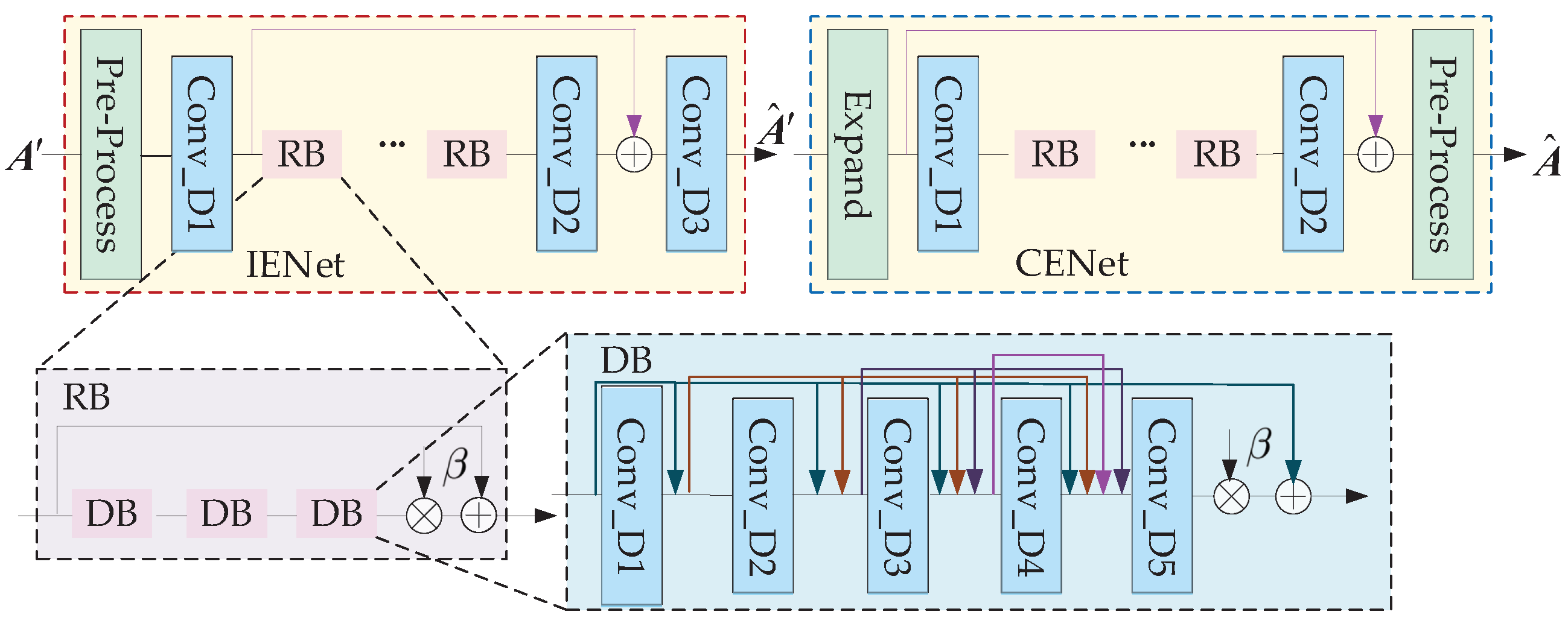
4.3. Deep Learning-Based Algorithms for RIS Channel Estimation
4.4. Composition-based Algorithms for RIS Channel Estimation
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, Y.; Liu, X.; Mu, X.; Hou, T.; Xu, J.; Di Renzo, M.; Al-Dhahir, N. Reconfigurable intelligent surfaces: Principles and opportunities. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2021, 23, 1546–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dajer, M.; Ma, Z.; Piazzi, L.; Prasad, N.; Qi, X.F.; Sheen, B.; Yang, J.; Yue, G. Reconfigurable intelligent surface: Design the channel – A new opportunity for future wireless networks. Digit. Commun. Netw. 2022, 8, 87–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Lv, X. Network coexistence analysis of RIS-assisted wireless communications. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 63442–63454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Zhang, S.; Zheng, B.; You, C.; Zhang, R. Intelligent reflecting surface-aided wireless communications: A tutorial. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2021, 69, 3313–3351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papazafeiropoulos, A.; Abdullah, Z.; Kourtessis, P.; Kisseleff, S.; Krikidis, I. Coverage probability of STAR-RIS-assisted massive MIMO systems with correlation and phase errors. IEEE Wirel. Commun. Lett. 2022, 11, 1738–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noh, S.; Lee, J.; Lee, G.; Seo, K.; Sung, Y.; Yu, H. Channel estimation techniques for RIS-assisted communication: Millimeter-wave and sub-THz systems. IEEE Veh. Technol. Mag. 2022, 17, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elzwawi, G.H.; Elzuwawi, H.H.; Tahseen, M.M.; Denidni, T.A. Frequency selective surface-based switched-beamforming antenna. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 48042–48050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Chen, X.Q.; Liu, S.; Zhang, Q.; Zhao, J.; Dai, J.Y.; Bai, G.D.; Wan, X.; Cheng, Q.; Castaldi, G.; et al. Space-time-coding digital metasurfaces. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 4334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.; Sun, Z.; Jornet, J.M.; Pados, D. Increasing indoor spectrum sharing capacity using smart reflect-array. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Communications; IEEE: Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 2016; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Chen, W.; Cao, H. Beamforming design and power allocation for transmissive RMS-Based transmitter architectures. IEEE Wirel. Commun. Lett. 2022, 11, 53–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Renzo, M.; Ntontin, K.; Song, J.; Danufane, F.H.; Qian, X.; Lazarakis, F.; de Rosny, J.; Phan-Huy, D.T.; Simeone, O.; Zhang, R.; et al. Reconfigurable intelligent surfaces vs. relaying: Differences, similarities, and performance comparison, 2020; arXiv:cs, eess, math/1908.08747]. [Google Scholar]
- Pradhan, C.; Li, A.; Song, L.; Li, J.; Vucetic, B.; Li, Y. Reconfigurable intelligent surface (RIS)-enhanced two-way OFDM communications. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2020, 69, 16270–16275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Al-Dhahir, N. Machine learning for user partitioning and phase shifters design in RIS-aided NOMA networks. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2021, 69, 7414–7428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, B.; You, C.; Mei, W.; Zhang, R. A survey on channel estimation and practical passive beamforming design for intelligent reflecting surface aided wireless communications. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2022, 24, 1035–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, C.; Zhou, G.; Zhi, K.; Hong, S.; Wu, T.; Pan, Y.; Ren, H.; Renzo, M.D.; Swindlehurst, A.L.; Zhang, R.; et al. An overview of signal processing techniques for RIS/IRS-aided wireless systems. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Signal Process. 2022, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, M.; Alexandropoulos, G.C.; Basar, E.; Huang, C.; Liu, R.; Liu, Y.; Yuen, C. Reconfigurable intelligent surfaces for wireless communications: Overview of hardware designs, channel models, and estimation techniques. Intelligent and Converged Networks 2022, 3, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.C.; Chen, J.; Long, R.; He, Z.Q.; Lin, X.; Huang, C.; Liu, S.; Shen, X.S.; Di Renzo, M. Reconfigurable intelligent surfaces for smart wireless environments: Channel estimation, system design and applications in 6G networks. Sci. China-Inf. Sci. 2021, 64, 200301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Ma, X.; Han, C.; Wen, Q. Towards intelligent reflecting surface empowered 6G terahertz communications: A survey. China Commun. 2021, 18, 93–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basharat, S.; Khan, M.; Iqbal, M.; Hashmi, U.S.; Zaidi, S.A.R.; Robertson, I. Exploring reconfigurable intelligent surfaces for 6G: State-of-the-art and the road ahead. IET Communications 2022, 16, 1458–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babiker, J.M.S.D.; Huang, X. A survey channel estimation for intelligent reflecting surface (IRS). In Cognitive Radio Oriented Wireless Networks and Wireless Internet; 2022; Vol. 427, pp. 169–180. [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Liang, Y.C.; Cheng, H.V.; Yu, W. Channel estimation for reconfigurable intelligent surface aided multi-user mmWave MIMO systems. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2023, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Z.; Zhou, G.; Pan, C.; Ren, H.; Swindlehurst, A.L.; Popovski, P.; Wu, G. Channel estimation for RIS-aided multi-user mmWave systems with uniform planar arrays. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2022, 70, 8105–8122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.; Yu, X.; Zhu, Y.; Schober, R. Channel estimation for IRS-assisted millimeter-wave MIMO systems: Sparsity-inspired approaches. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2022, 70, 4078–4092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Yuan, X.; Zhang, Y.J.A. Matrix-calibration-based cascaded channel estimation for reconfigurable intelligent surface assisted multiuser MIMO. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2020, 38, 2621–2636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Fang, J.; Duan, H.; Li, H. Compressed channel estimation for intelligent reflecting surface-assisted millimeter wave systems. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2020, 27, 905–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, H.; Kim, S. Efficient two-stage beam training and channel estimation for RIS-aided mwave systems via fast alternating least squares. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing; IEEE:, Singapore, Singapore; 2022; pp. 5188–5192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Zhang, S.; Ma, J.; Dobre, O.A. Deep learning-based time-varying channel estimation for RIS assisted communication. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2022, 26, 94–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Wymeersch, H.; Di Renzo, M.; Juntti, M. Learning to estimate RIS-aided mmWave channels. IEEE Wirel. Commun. Lett. 2022, 11, 841–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Pan, C.; Ren, H.; Popovski, P.; Swindlehurst, A.L. Channel estimation for RIS-aided multiuser millimeter-wave systems. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2022, 70, 1478–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albataineh, Z.; Hayajneh, K.F.; Shakhatreh, H.; Athamneh, R.A.; Anan, M. Channel estimation for reconfigurable intelligent surface-assisted mmWave based on Re`nyi entropy function. Sci Rep 2022, 12, 22301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Cai, B.; Chen, J.; Liang, Y.C. Dictionary learning-based channel estimation for RIS-aided MISO communications. IEEE Wirel. Commun. Lett. 2022, 11, 2125–2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, H.; Kim, S. Location-aware channel estimation for RIS-aided mmWave MIMO systems via atomic norm minimization, 2021, [arXiv:eess/2107.09222]. 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Shtaiwi, E.; Zhang, H.; Abdelhadi, A.; Han, Z. RIS-assisted mmWave channel estimation using convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference Workshops; IEEE: Nanjing, China, 2021; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, L.; Wei, X. Distributed machine learning based downlink channel estimation for RIS assisted wireless communications. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2022, 70, 4900–4909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Zhang, J.; Huang, C.; Yang, L.; Xiao, H.; Ai, B.; Wang, Z. Multiple residual dense networks for reconfigurable intelligent surfaces cascaded channel estimation. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2022, 71, 2134–2139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Luo, X.; Li, X.; Zhu, M.; Rabie, K.M.; Kara, F. Semi-blind joint channel estimation and symbol detection for RIS-empowered multiuser mmWave systems. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2023, 27, 362–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noh, S.; Yu, H.; Sung, Y. Training signal design for sparse channel estimation in intelligent reflecting surface-assisted millimeter-wave communication. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2022, 21, 2399–2413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Ren, H.; Pan, C.; Fang, J.; Dong, M.; Dobre, O.A. Channel estimation for RIS-aided mmWave massive MIMO system using few-bit ADCs. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2023, 27, 961–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B. Sparse channel estimation for reconfigurable intelligent surface assisted millimeter wave massive MIMO system. PhD thesis, University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, J.; Kammoun, A.; Alouini, M.S. Reconfigurable intelligent surface enabled interference nulling and signal power maximization in mmWave bands. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2022, 21, 9096–9113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, Y.; Jiao, L. Robust transmission for reconfigurable intelligent surface aided millimeter wave vehicular communications with statistical CSI. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2022, 21, 928–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Z.; Gao, Z.; Alouini, M.S. Broadband channel estimation for intelligent reflecting surface aided mmWave massive MIMO systems. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Communications; IEEE: Dublin, Ireland, 2020; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, S.; Gao, F.; Tang, J.; Dobre, O.A. Cascaded channel estimation for RIS assisted mmWave MIMO transmissions. IEEE Wirel. Commun. Lett. 2021, 10, 2065–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Lu, H.; Sun, H. Channel estimation in IRS-enhanced mmWave system with super-resolution network. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2021, 25, 2599–2603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Wang, P.; Fang, J.; Li, H. Compressed channel estimation for IRS-assisted millimeter wave OFDM systems: A low-rank tensor decomposition-based approach. IEEE Wirel. Commun. Lett. 2022, 11, 1258–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, C.; Zhang, Z.; Jiang, H.; Dang, J.; Wu, L.; Zhang, H. Approximate message passing for channel estimation in reconfigurable intelligent surface aided MIMO multiuser systems. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2022, 70, 5469–5481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taha, A.; Alrabeiah, M.; Alkhateeb, A. Enabling large intelligent surfaces with compressive sensing and deep learning. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 44304–44321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Yin, H.; Bjornson, E. MmWave MIMO communication with semi-passive RIS: A low-complexity channel estimation scheme. In Proceedings of the IEEE Global Communications Conference; IEEE: Madrid, Spain, 2021; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Gao, Z.; Zhang, J.; Renzo, M.D.; Alouini, M.S. Deep denoising neural network assisted compressive channel estimation for mmWave intelligent reflecting surfaces. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2020, 69, 9223–9228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, X.; Xiao, H.; Ai, B.; Ng, D.W.K. Channel estimation for semi-passive reconfigurable intelligent surfaces with enhanced deep residual networks. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2021, 70, 11083–11088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Jin, S.; Matthaiou, M.; You, X. Tensor-based algebraic channel estimation for hybrid IRS-assisted MIMO-OFDM. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2021, 20, 3770–3784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, D.; Johansson, H. Channel estimation and low-complexity beamforming design for passive intelligent surface assisted MISO wireless energy transfer. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing; IEEE: , Brighton, United Kingdom; 2019; pp. 4659–4663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, T.L.; De Carvalho, E. An optimal channel estimation scheme for intelligent reflecting surfaces based on a minimum variance unbiased estimator. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing; IEEE: Barcelona, Spain; 2020; pp. 5000–5004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Tay, W.P. Cost-efficient RIS-aided channel estimation via rank-one matrix factorization. IEEE Wirel. Commun. Lett. 2021, 10, 2562–2566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Xu, J.; Zhang, W.; Xu, W.; Ng, D.W.K. Semi-blind channel estimation for RIS-assisted MISO systems using expectation maximization. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2022, 71, 10173–10178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundu, N.K.; McKay, M.R. Channel estimation for reconfigurable intelligent surface aided MISO communications: From LMMSE to deep learning solutions. IEEE Open Journal of the Communications Society 2021, 2, 471–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, L.; Cui, S. Channel estimation for intelligent reflecting surface assisted multiuser communications: Framework, algorithms, and analysis. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2020, 19, 6607–6620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Dai, L.; Han, S.; Wang, X. Two-timescale channel estimation for reconfigurable intelligent surface aided wireless communications. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2021, 69, 7736–7747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Lau, V.K.N. Uplink cascaded channel estimation for intelligent reflecting surface assisted multiuser MISO systems. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2022, 70, 3964–3977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Li, M.; Liu, Q. A novel anchor-assisted channel estimation for RIS-aided multiuser communication systems. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2022, 26, 2740–2744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Araujo, G.T.; de Almeida, A.L.F.; Boyer, R. Channel estimation for intelligent reflecting surface assisted MIMO systems: A tensor modeling approach. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Signal Process. 2021, 15, 789–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Dong, P.; Pan, Z.; Li, G.Y. Deep multi-stage CSI acquisition for reconfigurable intelligent surface aided MIMO systems. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2021, 25, 2024–2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Shen, D.; Dai, L. Channel estimation for RIS assisted wireless communications—Part II: An improved solution based on double-structured sparsity. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2021, 25, 1403–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, X.; Cheng, L.; Chen, X.; Huang, C.; Ng, D.W.K. Reconfigurable intelligent surface-aided 6G massive access: Coupled tensor modeling and sparse Bayesian learning. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2022, 21, 10145–10161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Huang, C.; Alexandropoulos, G.C.; Yang, Z.; Yuen, C.; Zhang, Z. Joint channel estimation and signal recovery in RIS-assisted multi-user MISO communications. In Proceedings of the IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference; IEEE: Nanjing, China, 2021; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Huang, C.; Guo, Q.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Alexandropoulos, G.C.; Debbah, M.; Yuen, C. Joint channel estimation and signal recovery for RIS-empowered multiuser communications. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2022, 70, 4640–4655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.Q.; Yuan, X. Cascaded channel estimation for large intelligent metasurface assisted massive MIMO. IEEE Wirel. Commun. Lett. 2020, 9, 210–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Z.; Liu, X.; Peng, M. Channel estimation for intelligent reflecting surface assisted massive MIMO systems—A deep learning approach. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2022, 26, 798–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, B.; Zhang, R. Intelligent reflecting surface-enhanced OFDM: Channel estimation and reflection optimization. IEEE Wirel. Commun. Lett. 2020, 9, 518–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zheng, B.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, R. Intelligent reflecting surface meets OFDM: Protocol design and rate maximization. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2020, 68, 4522–4535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Zhang, S.; Gao, F.; Wang, J. Sparse Bayesian learning based channel extrapolation for RIS assisted MIMO-OFDM. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2022, 70, 5498–5513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, S.; Farhang, A.; Perovic, N.S.; Flanagan, M.F. Low-complexity joint CFO and channel estimation for RIS-aided OFDM systems. IEEE Wirel. Commun. Lett. 2022, 11, 203–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexandropoulos, G.C.; Vlachos, E. A hardware architecture for reconfigurable intelligent surfaces with minimal active elements for explicit channel estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing; IEEE: Barcelona, Spain; 2020; pp. 9175–9179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroeder, R.; He, J.; Juntti, M. Channel estimation for hybrid RIS aided MIMO communications via atomic norm minimization. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Communications Workshops; IEEE: Seoul, Republic of Korea, 2022; pp. 1219–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Zhang, R.; Zhong, C. Semi-passive elements assisted channel estimation for intelligent reflecting surface-aided communications. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2022, 21, 1132–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Pan, C.; Ren, H.; Wang, K. Channel estimation for RIS-aided millimeter-wave massive MIMO systems. In Proceedings of the 55th Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems, and Computers; IEEE: Pacific Grove, CA, USA, 2021; pp. 698–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, B.; You, C.; Zhang, R. Intelligent reflecting surface assisted multi-user OFDMA: Channel estimation and training design. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2020, 19, 8315–8329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abeywickrama, S.; You, C.; Zhang, R.; Yuen, C. Channel estimation for intelligent reflecting surface assisted backscatter communication. IEEE Wirel. Commun. Lett. 2021, 10, 2519–2523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demir, O.T.; Bjornson, E.; Sanguinetti, L. Exploiting array geometry for reduced-subspace channel estimation in RIS-aided communications. In Proceedings of the IEEE 12th Sensor Array and Multichannel Signal Processing Workshop; IEEE: Trondheim, Norway, 2022; pp. 455–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; An, J.; Bai, T.; Xiang, L.; Sugiura, S.; Maunder, R.G.; Yang, L.L.; Hanzo, L. Reconfigurable intelligent surface assisted multi-carrier wireless systems for doubly selective high-mobility Ricean channels. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2022, 71, 4023–4041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; An, J.; Bai, T.; Sugiura, S.; Maunder, R.G.; Wang, Z.; Yang, L.L.; Hanzo, L. Channel estimation for reconfigurable intelligent surface assisted high-mobility wireless systems. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2023, 72, 718–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shtaiwi, E.; Zhang, H.; Vishwanath, S.; Youssef, M.; Abdelhadi, A.; Han, Z. Channel estimation approach for RIS assisted MIMO systems. IEEE Trans. Cogn. Commun. Netw. 2021, 7, 452–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, C.; Zheng, B.; Zhang, R. Channel estimation and passive beamforming for intelligent reflecting surface: Discrete phase shift and progressive refinement. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2020, 38, 2604–2620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Z.; Peng, M.; Liu, X. Channel estimation for reconfigurable intelligent surface assisted wireless communication systems in mobility scenarios. China Commun. 2021, 18, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, P.; Zong, J.; Luo, X.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, S.; Qian, H. Downlink channel tracking for intelligent reflecting surface-aided FDD MIMO systems. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2021, 70, 3341–3353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, S.; Chen, Y.; Li, Q.; Li, P.; Xia, X.; Wen, M. Anchor-aided channel estimation for RIS-assisted multiuser broadband communications. IEEE Wirel. Commun. Lett. 2023, 12, 89–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Wang, C.X.; Zhou, Z.; Feng, R.; Xin, L.; Huang, J. A novel SAGE-based channel parameter estimation scheme for 6G RIS-assisted wireless channel measurements. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Communications; IEEE: Seoul, Republic of Korea, 2022; pp. 3305–3310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Jiang, Y. Over-the-air phase calibration of reconfigurable intelligent surfaces. IEEE Wirel. Commun. Lett. 2023, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardah, K.; Gherekhloo, S.; de Almeida, A.L.F.; Haardt, M. TRICE: A channel estimation framework for RIS-aided millimeter-wave MIMO systems. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2021, 28, 513–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, C.; Cheng, J.; Gao, H.; Xu, W. High-resolution channel estimation for intelligent reflecting surface-assisted mmWave communications. In Proceedings of the IEEE 31st Annual International Symposium on Personal, Indoor and Mobile Radio Communications; IEEE:, London, UK; 2020; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Chen, Z.; Chen, W.; Li, Z.; Chi, Y.; Han, C.; Li, S. Joint channel estimation and data rate maximization for intelligent reflecting surface assisted terahertz MIMO communication systems. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 99565–99581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirza, J.; Ali, B. Channel estimation method and phase shift design for reconfigurable intelligent surface assisted MIMO networks. IEEE Trans. Cogn. Commun. Netw. 2021, 7, 441–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayraktar, M.; Palacios, J.; Gonzalez-Prelcic, N.; Zhang, C.J. Multidimensional orthogonal matching pursuit-based RIS-aided joint localization and channel estimation at mmWave. In Proceedings of the IEEE 23rd International Workshop on Signal Processing Advances in Wireless Communication; IEEE: Oulu, Finland, 2022; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Qin, L.; Sun, S.; Liu, L.; Mao, S.; Zhang, Z.; Wei, N. Joint effective channel estimation and data detection for RIS-aided massive MIMO systems with low-resolution ADCs. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2023, 27, 721–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Dai, J.; Xu, W.; Chang, C. Sparse channel estimation for intelligent reflecting surface assisted massive MIMO systems. IEEE Trans. Green Commun. Netw. 2022, 6, 208–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Li, Y.; Xin, L. Joint channel estimation for RIS-assisted wireless communication system. In Proceedings of the IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference; IEEE: Austin, TX, USA, 2022; pp. 1087–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Mo, R.; Yuen, C. Reconfigurable intelligent surface assisted multiuser MISO systems exploiting deep reinforcement learning. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2020, 38, 1839–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yerzhanova, M.; Kim, Y.H. Channel estimation via model and learning for monostatic multiantenna backscatter communication. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 165341–165350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Dai, L.; Hao, M.; MacKenzie, R. End-to-end learning for RIS-aided communication systems. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2022, 71, 6778–6783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Jiang, T.; Yu, W. Learning based user scheduling in reconfigurable intelligent surface assisted multiuser downlink. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Signal Process. 2022, 16, 1026–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Ai, B. When mmWave high-speed railway networks meet reconfigurable intelligent surface: A deep reinforcement learning method. IEEE Wirel. Commun. Lett. 2022, 11, 533–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Zhang, S.; Zhong, C.; Ma, J.; Dobre, O.A. Ordinary differential equation-based CNN for channel extrapolation over RIS-assisted communication. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2021, 25, 1921–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmet M., E.; Papazafeiropoulos, A.; Kourtessis, P.; Chatzinotas, S. Deep channel learning for large intelligent surfaces aided mm-wave massive MIMO systems. IEEE Wirel. Commun. Lett. 2020, 9, 1447–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Tang, J.; Zhang, X.Y.; Wu, Q.; Wang, Y.; So, D.K.C.; Jin, S.; Wong, K.K. Offset learning based channel estimation for intelligent reflecting surface-assisted indoor communication. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Signal Process. 2022, 16, 41–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Liu, X.; Ng, D.W.K.; Yuan, J. Deep residual learning for channel estimation in intelligent reflecting surface-assisted multi-user communications. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2022, 21, 898–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tekbiyik, K.; Kurt, G.K.; Huang, C.; Ekti, A.R.; Yanikomeroglu, H. Channel estimation for full-duplex RIS-assisted HAPS backhauling with graph attention networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Communications; IEEE: Montreal, QC, Canada, 2021; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhang, S.; Gao, F.; Ma, J.; Dobre, O.A. Deep learning-based RIS channel extrapolation with element-grouping. IEEE Wirel. Commun. Lett. 2021, 10, 2644–2648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Ai, B.; Quek, T.Q.S.; Liuc, Y. Deep reinforcement learning for interference suppression in RIS-aided high-speed railway networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Communications Workshops; IEEE: Seoul, Republic of Korea, 2022; pp. 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Huang, C.; Gong, Y.; Chen, G. Double deep learning for joint phase-shift and beamforming based on cascaded channels in RIS-assisted MIMO networks. IEEE Wirel. Commun. Lett. 2023, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; An, J.; Xu, Y.; Huang, C.; Gan, L.; Yuen, C. Time-varying channel prediction for RIS-assisted MU-MISO networks via deep learning. IEEE Trans. Cogn. Commun. Netw. 2022, 8, 1802–1815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, S.; Li, Y.; Tian, Y.; Yu, F.R. Intelligent reflecting surface enhanced wireless communications with deep-learning-based channel prediction. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2022, 71, 1049–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, W.C.; Chen, C.W.; Teng, C.F.; Wu, A.Y. Low-complexity compressive channel estimation for IRS-aided mmWave systems with hypernetwork-assisted LAMP network. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2022, 26, 1883–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Ref. | Year | Main Direction | Major Contribution |
|---|---|---|---|
| Wu et al. [4] | 2021 | Reflection optimization and channel estimation | Reflection channel models, practical constraint, and hardware architecture |
| Noh et al. [6] | 2022 | Channel estimation for RIS-assisted mmWave/sub-terahertz (THz) communication | Technical challenges, channel estimation frameworks, and training signal design |
| Zheng et al. [14] | 2022 | Channel estimation and passive beamforming design | Discussed emerging RIS architectures, applications and practical design problems |
| Pan et al. [15] | 2022 | Channel estimation, transmission design, and radio localization | Channel estimation, transmission design, radio localization, etc. |
| Jian et al. [16] | 2022 | Channel estimation | Wireless communication standards, the current and future standardization activities |
| Liang et al. [17] | 2021 | Channel estimation and system design | Reflection principle, channel estimation, system designs, etc. |
| Chen et al. [18] | 2021 | Hardware design, channel estimation, etc. | Channel modeling, new material exploration, etc. |
| Basharat et al. [19] | 2022 | CSI acquisition, passive beamforming optimization, etc. | Phase-shift optimization and resource allocation |
| Babiker et al. [20] | 2022 | Channel estimation | Main recent techniques and various strategies |
| Ref. | Year | System Setup | Problem | Method | Results Analysis |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wang et al. [25] | 2020 | MISO | High training overhead | Conversion to sparse channel recovery problem | Approximate NMSE of 0.04 obtained using the GAMP algorithm |
| Wan et al. [42] | 2020 | MIMO | Wideband system estimation issues | DOMP algorithm and redundant dictionary | Pilot design and redundant dictionaries can improve performance significantly |
| Liu et al. [49] | 2020 | MIMO | High training overhead | The deep denoising neural network assisted compressive channel estimation | 4 dB performance gain over initial estimation |
| Chung et al. [32] | 2021 | MIMO | High training overhead | Location-aware channel estimation based on ANM | 2D ANM location awareness was only at 32 training symbols, 3D ANM maximum training symbols was 32, both better than 1D ANM |
| Shtaiwi et al. [33] | 2021 | MIMO | High training overhead | Estimate active users and use CNN’s STS framework to estimate inactive users | The larger the number of active users, the smaller the NMSE |
| Li. [39] | 2021 | MIMO | High cost/array block | An EM-NNL-GAMP method/Joint array diagnosis and channel estimation algorithm | Outperformed other algorithms at 2 bit/Different methods for different situations were effective for array diagnosis and channel estimation |
| Liu et al. [43] | 2021 | MIMO | High pilot overhead | Convert a parameter recovery problem and use NOMP algorithm | Low SNR and small number of pilots had better performance than OMP |
| Wang et al. [44] | 2021 | SISO | High training overhead | SR method in images | 10% rate improvement compared to LS (SNR = 35 dB) |
| Taha et al. [47] | 2021 | MIMO | High training overhead | Reconstruction of the full channel from subsampled channels using CS and deep learning | Achieved 90% of the best rates |
| Hu et al. [48] | 2021 | MIMO | High hardware cost and energy consumption | The semi-passive RIS equipped with a partial 1-bit quantization, ADMM and GAMP algorithms | Better than baseline at high SNR |
| Jin et al. [50] | 2021 | MIMO | Low estimation accuracy | Reshape the channel matrix into a two-dimensional image | As the proportion of active cells increases, EDSR had better NMSE performance and MDSR reduced complexity |
| Lin et al. [51] | 2021 | MIMO | The problem of time-varying channels | Modeling as a CPD problem and solving tensor problems with algebraic algorithm | Reduced complexity and great results at high SNR |
| Chung et al. [26] | 2022 | MISO | High training overhead | Two-stage beam training and FALS | FALS required 45% fewer training symbols compared to the OMP and ANM algorithms (NMSE = 0.1) |
| Xu et al. [27] | 2022 | MISO | High training overhead | Deep DNN assisted compressed channel estimation algorithm | NMSE decreased with increasing spatial and temporal sampling |
| Zhou et al. [29] | 2022 | MISO | High training overhead | Multi-user correlation, channel sparsity, invariance of channel coherence blocks | 60% reduction in pilot overhead compared to baseline scheme (NMSE = ) |
| Peng et al. [22] | 2022 | MIMO | High training overhead | A three-stage estimation protocol using the correlation between typical users and normal users | 50% reduction in pilot overhead compared to OMP (NMSE = ) |
| Albataineh et al. [30] | 2022 | MIMO | High Pilot overhead | Extends the Re‘nyi entropy function as the sparsity-promoting regularizer | An improvement over the OMP |
| Lin et al. [23] | 2022 | MIMO | Inefficient method | A MO and AM based method and a three-stage algorithm | The MO method had good results when the overhead was higher than 130. The CS method proposed in this paper is better than GAMP |
| Zhou et al. [31] | 2022 | MISO | Grid mismatch issues and estimation performance degradation | Dictionary is optimized to adapt to channel characteristics | Better than the predefined dictionary method when the training overhead was small |
| He et al. [28] | 2022 | SIMO | High training overhead | The model-driven deep unfolding neural network | Achieved the same NMSE with 25% less training overhead than LS |
| Dai et al. [34] | 2022 | MIMO | High training overhead | The DML algorithm | Used in different scenarios |
| Jin et al. [35] | 2022 | MIMO | Low estimation accuracy | GAN-CBD, CBDNet and MRDNet | MRDNet achieved better NMSE performance than GAN-CBD and CBDNet, with improvements of 5.63 dB and 4.51 dB, respectively |
| Du et al. [36] | 2022 | MIMO | Low estimation accuracy | Semi-blind joint channel estimation and symbol detection algorithm | Better NMSE and BER performance |
| Noh et al. [37] | 2022 | MIMO | Less training symbols | Two CRB-based training signal design algorithms for enhanced sparse channel estimation | Significant performance gain when the number of training symbols was less than the number of RIS reflection elements |
| Ye et al. [40] | 2022 | SISO | Interference problems | Maximize power at desired users and eliminate interference at undesired users | The reflector element changed from 8 to 16, achieved a power gain of approximately 10 dB |
| Chen et al. [41] | 2022 | MIMO | High mobility leads to CSI changes and requires high overhead | A reasonable configuration of the CSI acquisition time scale | The communication performance was improved in mobile vehicle scenarios |
| Zheng et al. [45] | 2022 | MIMO | High training overhead | The received signal is represented as a low-rank third-order tensor | Significantly reduced training overhead and better performance compared to SOMP algorithm |
| Ruan et al. [46] | 2022 | MIMO | High training overhead | Used reference points to aid estimation | NMSE was reduced by 2 dB compared to the best benchmark solution (SNR = 10 dB) |
| Chen et al. [21] | 2023 | MIMO | High training overhead | Two-stage channel estimation method using common sparse structure | 80% and 60% pilot overhead reduction in LS and MMV respectively (NMSE = ) |
| Wang et al. [38] | 2023 | MIMO | High cost | Low-resolution ADCs and Bayesian optimal estimation framework | The BiG AMP algorithm had better performance in few bit quantization, and 8 bit quantization was almost as good as infinite bit quantization |
| Ref. | Year | System Setup | Problem | Method | Results Analysis |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mishra et al. [52] | 2019 | MISO | Fully-passive RIS cannot handle signals | ON/OFF method | Binary channel estimation method |
| Jensen et al. [53] | 2020 | MISO | RIS increases the number of estimated links | MVU | Estimation accuracy was T (training periods) times better than the ON/OFF method |
| Wang et al. [57] | 2020 | MIMO | High training overhead | The relevance of typical user and other users | Improve estimation performance, more time slots should be allocated for the second stage to reduce error propagation |
| He et al. [67] | 2020 | MIMO | RIS can’t send and receive signals | Sparse matrix decomposition stage and matrix completion | Better than comparable matrix decomposition and matrix completion schemes. |
| Zheng et al. [69] | 2020 | SISO | High training overhead | Transmission protocol with sequential channel estimation and reflection optimization | 14 dB gain improvement over ON/OFF method at the same pilot overhead |
| Yang et al. [70] | 2020 | SISO | High training overhead | Elements grouping | Better achievable rates than methods without RIS component grouping |
| Alexandropoulos et al. [73] | 2020 | SISO | High training overhead | RIS architecture with a single RF | Produced best estimation performance with smaller training symbols than OMP and LS algorithms |
| Zhang et al. [54] | 2021 | MISO | High training overhead | Matrix factorization | Lower overhead and higher accuracy |
| Kun et al. [56] | 2021 | MISO | Low estimation accuracy | FFDNET and DNCNN | FFDNET outperformed DNCNN at low SNR but required noise variance information |
| Hu et al. [58] | 2021 | MIMO | High training overhead | BS-RIS quasi-static features | Reduced pilot overhead, but worse performance than MVU |
| Dearaujo et al. [61] | 2021 | MIMO | High training overhead | PARAFAC tensor modeling of the received signal | Robustness for amplitude and phase perturbations |
| Gao et al. [62] | 2021 | MIMO | High training overhead | Integrated DNN to estimate the direct channel, active RIS and inactive RIS sequentially | 50% reduction in pilot overhead compared to OMP (NMSE = ) |
| Wei et al. [63] | 2021 | MIMO | High training overhead | Cascaded channel estimation scheme based on DS-OMP | Improved NMSE performance as the number of common paths increased |
| Wei et al. [65] | 2021 | MIMO | Large complexity for both channel estimation and signal recovery | Joint channel estimation and signal recovery algorithm | Only about 2.5 dB performance difference compared to LS scheme assuming perfect channel knowledge |
| Huang et al. [55] | 2022 | MISO | High cost/array block | Iterative EM algorithm for semi-blind channel estimation | 85% reduction in pilot overhead compared to baseline scheme (NMSE = ) |
| Guo et al. [59] | 2022 | MIMO | High training overhead | Alternating optimization algorithms and cascaded channel covariance | Approximately 15 dB performance gain over ON/OFF method |
| Yang et al. [60] | 2022 | MIMO | High training overhead | Anchor-assisted channel estimation | Approximately 50 training symbols can be reduced for the same performance as the baseline scheme |
| Shan et al. [64] | 2022 | MIMO | High training overhead | A rank one decomposition-based message recovery and channel estimation algorithm for RIS-assisted URAs | Better separation than baseline solution for active devices |
| Wei et al. [66] | 2022 | MIMO | Large complexity for both channel estimation and signal recovery | Joint channel estimation and signal recovery method | Approximately 18 dB gap from baseline approach when pilot length = 100 |
| Mao et al. [68] | 2022 | MIMO | Grid mismatch issues and performance degradation | Residual networks to reduce NMSE | SN worked well at small training overheads, RS-OMP achieved better results at large training overheads |
| Xu et al. [71] | 2022 | MIMO | High training overhead | Subsampled information is extrapolated to the full channel | 12 dB performance gain compared to LS (The number of active RIS elements was 1/16 of the total RIS elements) |
| Jeong et al. [72] | 2022 | SISO | Carrier frequency offset | A joint CFO and CIR estimation | Up to 30 times higher performance relative to benchmark solutions |
| Schroeder et al. [74] | 2022 | MIMO | Low estimated efficiency | Two-stage channel estimation scheme based on ANM | Better performance than passive RIS |
| Hu et al. [75] | 2022 | MIMO | High training overhead | ESPRIT, TLS, MUSIC | Better performance than OMP and LMMSE methods |
| Ref. | Year | Antenna/RIS Architecture | Channel Model | Major Algorithm | Performance Analysis |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zhou et al. [76] | 2021 | MIMO/Passive RIS | Static channel | AoA estimation and LS method | Improved estimation accuracy |
| Demir et al. [79] | 2022 | Passive RIS | Static channel | Reduced-subspace LS and array geometry | Reduced pliot overhead |
| Xu et al. [80] | 2022 | Passive RIS | Time-Varying and double selective Channel | MMSE and the end-to-end system model | Reduced computational complexity |
| Shtaiwi et al. [82] | 2021 | MIMO/Passive RIS | Static channel | SPD and Maximum-margin matrix factorization | Improved the estimation accuracy |
| You et al. [83] | 2020 | MIMO/Passive RIS | Time-varying channel | RIS-elements grouping and partition | Reduced computational complexity |
| Mao et al. [84] | 2021 | MIMO/Passive RIS | Time-varying channel | MMSE, KF and state-space model | Improved the estimation accuracy |
| Cai et al. [85] | 2021 | MIMO/Passive RIS | Time-varying channel | KF and codebook-based low complexity design | Reduced computational complexity and improved estimation accuracy |
| Xu et al. [81] | 2023 | Passive RIS | High-dimensional and high-Doppler reflected fading channels | MMSE interpolation and multiplicative concatenation of the channel coefficient | Improved estimation accuracy |
| Qian et al. [86] | 2023 | MIMO/Passive RIS | Static channel | Two-phase and anchor-aided channel estimation | Reduced polit overhead and improved estimation accuracy |
| Xu et al. [87] | 2022 | MIMO/Passive RIS | Static channel | Space-alternating GEM and ML estimation | Improved estimation accuracy |
| Zhang et al. [88] | 2023 | Passive RIS | Static channel | ML and CRB | Improved estimation accuracy |
| Ref. | Year | Antenna/RIS Architecture | Channel Model | Major Algorithm | Performance Analysis |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| He et al. [67] | 2020 | MIMO/Passive RIS | Time-varying channels | Sparse matrix factorization and completion | Improved channel estimation accuracy |
| Mirza et al. [92] | 2021 | MIMO/Passive RIS | Static channel | Bilinear generalized AMP | Balanced the quality of channel estimation with training overhead |
| Bayraktar et al. [93] | 2022 | Passive RIS | Static channel | Multidimensional OMP | Reduced computational complexity and improved estimation accuracy |
| Xiong et al. [94] | 2023 | MIMO/Passive RIS | Static channel | Bilinear generalized AMP | Reduced computational complexity |
| Zhou et al. [95] | 2022 | MIMO/Passive RIS | Static channel | Generalized-AMP | Reduced computational complexity and training overhead |
| Wu et al. [96] | 2022 | MIMO/Passive RIS | Static channel | Three-step OMP | Reduced pilot overhead |
| Ref. | Year | Antenna/RIS Architecture | Channel Model | Major Algorithm | Performance Analysis |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Xu et al. [27] | 2022 | Passive RIS | Time-varying Channel | Ordinary differential equation, recurrent neural network | Improved estimation accuracy and robustness |
| Jin et al. [35] | 2022 | Passive RIS | Static channel | GAN-CBD, CBDNet and MRDNet | Got better generalisation and fitting ability |
| Kundu et al. [56] | 2021 | Passive RIS | Static channel | Denoising CNN | Reduced computational complexity and improved estimation accuracy |
| Gao et al. [62] | 2021 | MIMO/ Semi-passive RIS | Static channel | Three-stage training strategy for RNN | Reduced pilot overhead and improved estimation accuracy |
| Ahmetm et al. [103] | 2020 | Passive RIS | Static channel | CNN | Improved channel estimation accuracy |
| Chen et al. [104] | 2022 | MIMO/Passive RIS | Static channel | Learning-based CNN | Reduced computational complexity and improved channel estimation accuracy |
| Tekbiyik et al. [106] | 2021 | Passive RIS | Static channel | Graph attention network | Enhanced system robustness and reduced pilot overhead |
| Liu et al. [105] | 2022 | MIMO/Passive RIS | Static channel | Deep residual network and CNN | Improved estimation accuracy |
| Zhang et al. [107] | 2021 | Passive RIS | Static channel | Deep learning, channel extrapolation | Improved estimation accuracy and enhanced network generalisation |
| Xu et al. [108] | 2020 | Passive RIS | Time-varying channels | Deep reinforcement learning | Increased system capacity and suppressed interference |
| Li et al. [109] | 2023 | MIMO/Passive RIS | Static channel | Double deep learning | Reduced computational complexity |
| Xu et al. [110] | 2022 | Passive RIS | Time-varying channel | Sparse-connected LSTM | Improved estimation accuracy, reduced time delay and pilot overhead |
| Ref. | Year | Antenna/RIS Architecture | Major Problem | Major Algorithm | Performance Analysis |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wang et al. [44] | 2021 | Passive RIS | High complexity of conventional algorithms | Proposed a high resolution network with low-precision by linear interpolation | Accuracy rate: 92% (SNR = 35 dB) |
| Mao et al. [68] | 2022 | Passive RIS | Insufficient estimation performance of the CS algorithm | Proposed residual network to improve the performance | Outperformed the OMP (SNR = 35 dB) |
| Tsai et al. [112] | 2022 | MIMO/Passive RIS | Insufficient performance of AMP algorithm estimation | Proposed a hypernetwork-assisted LAMP network with dynamic shrinkage parameters | Reduced memory overhead: 50% and execution time: 93% |
| Yin et al. [111] | 2022 | Passive RIS | Insufficient performance of conventional algorithm estimation | Designed an end to end deep learning model | Reduced channel estimation overhead |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





