Submitted:
12 June 2023
Posted:
14 June 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
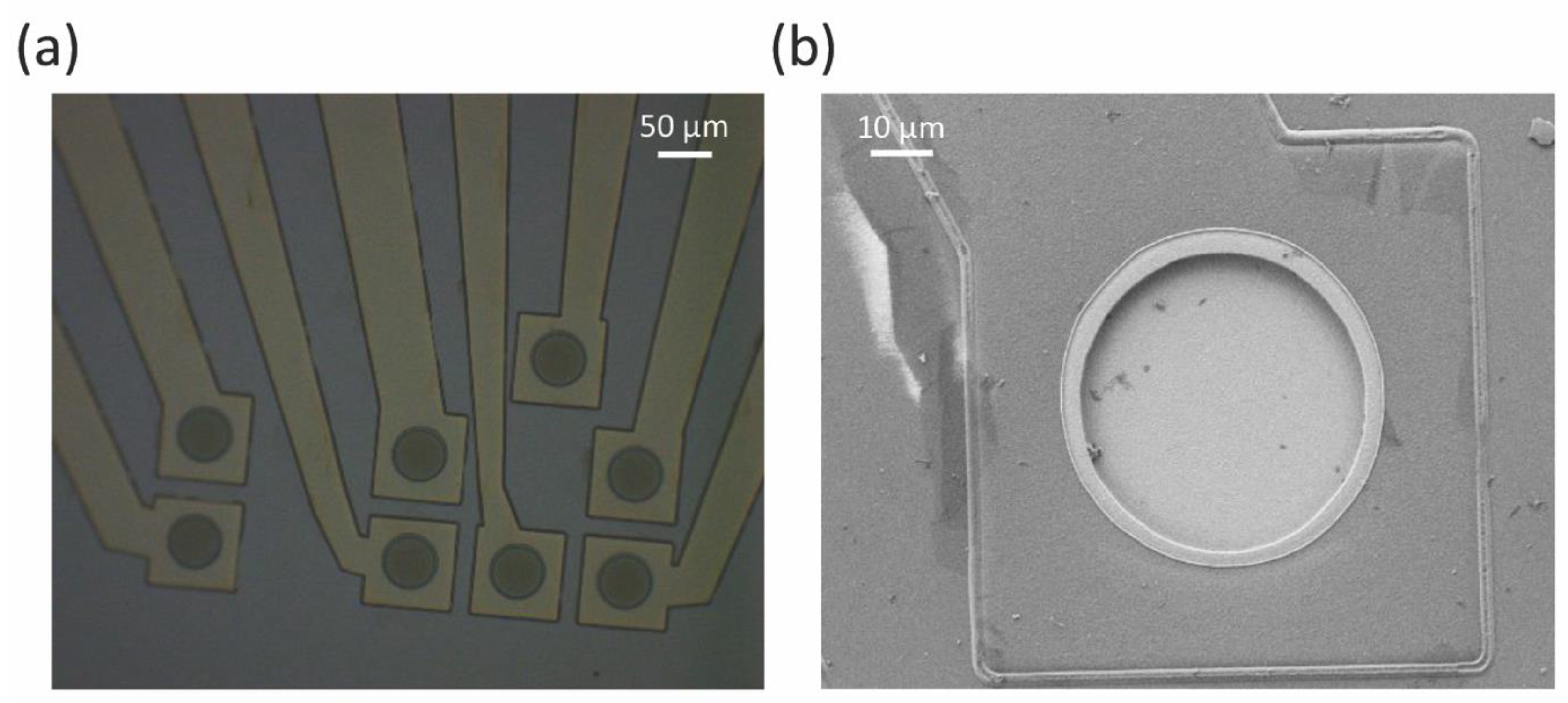
2.1. Planar Microelectrode Fabrication
2.2. Electrolyte Preparation
2.3. Cyclic Voltammetry
2.4. Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy
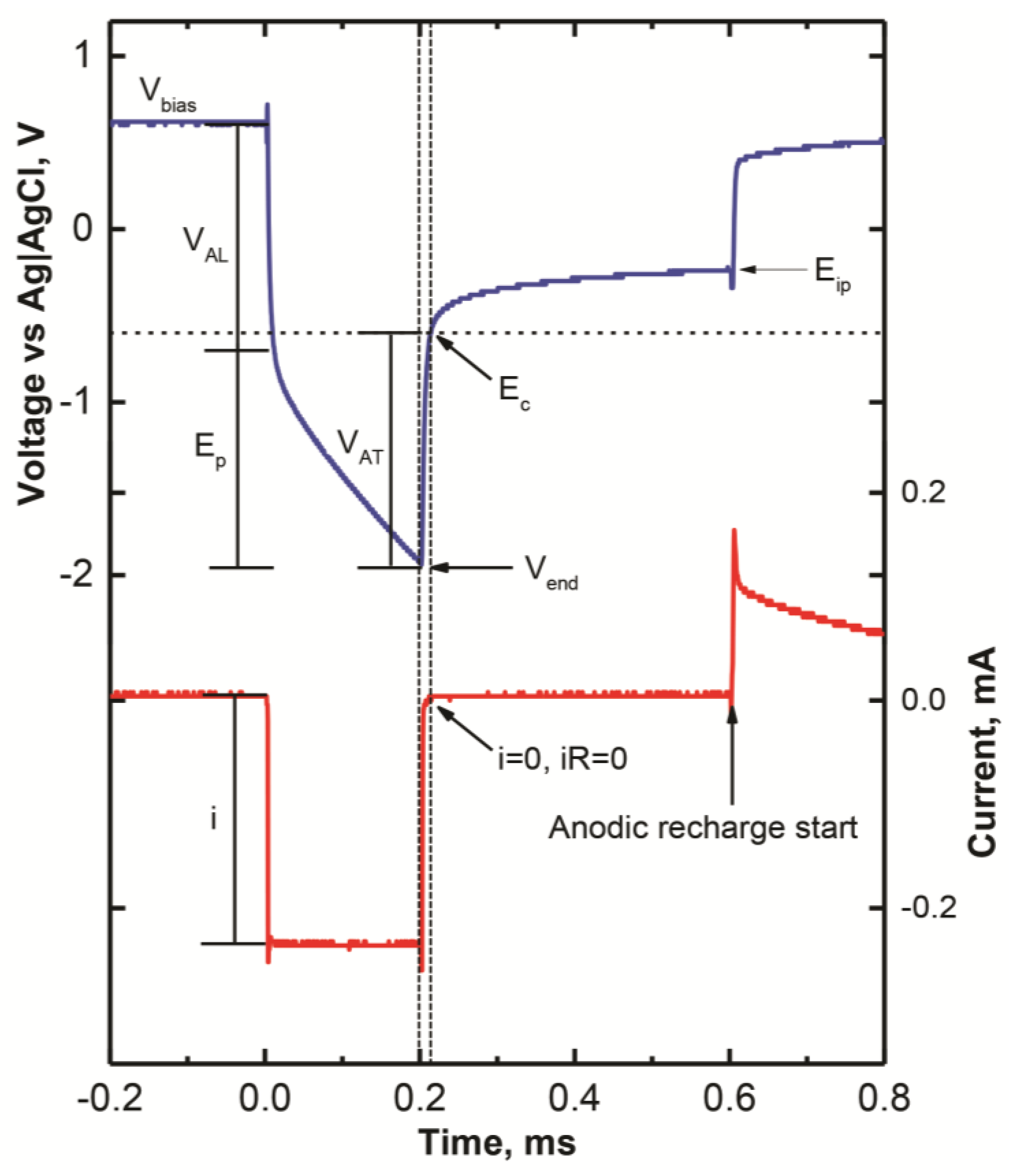
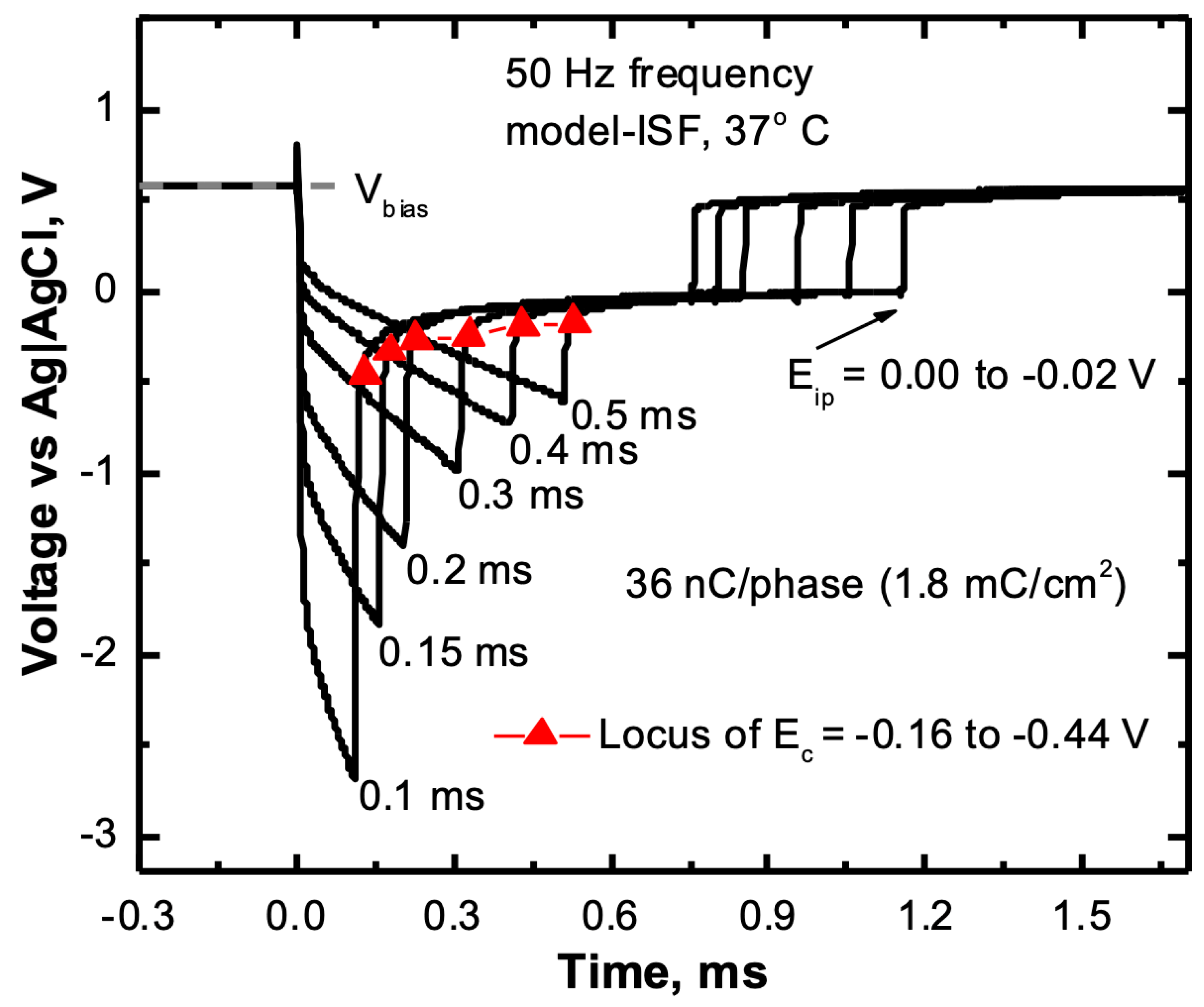
2.5. Voltage Transient Measurements
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Cyclic Voltammetry
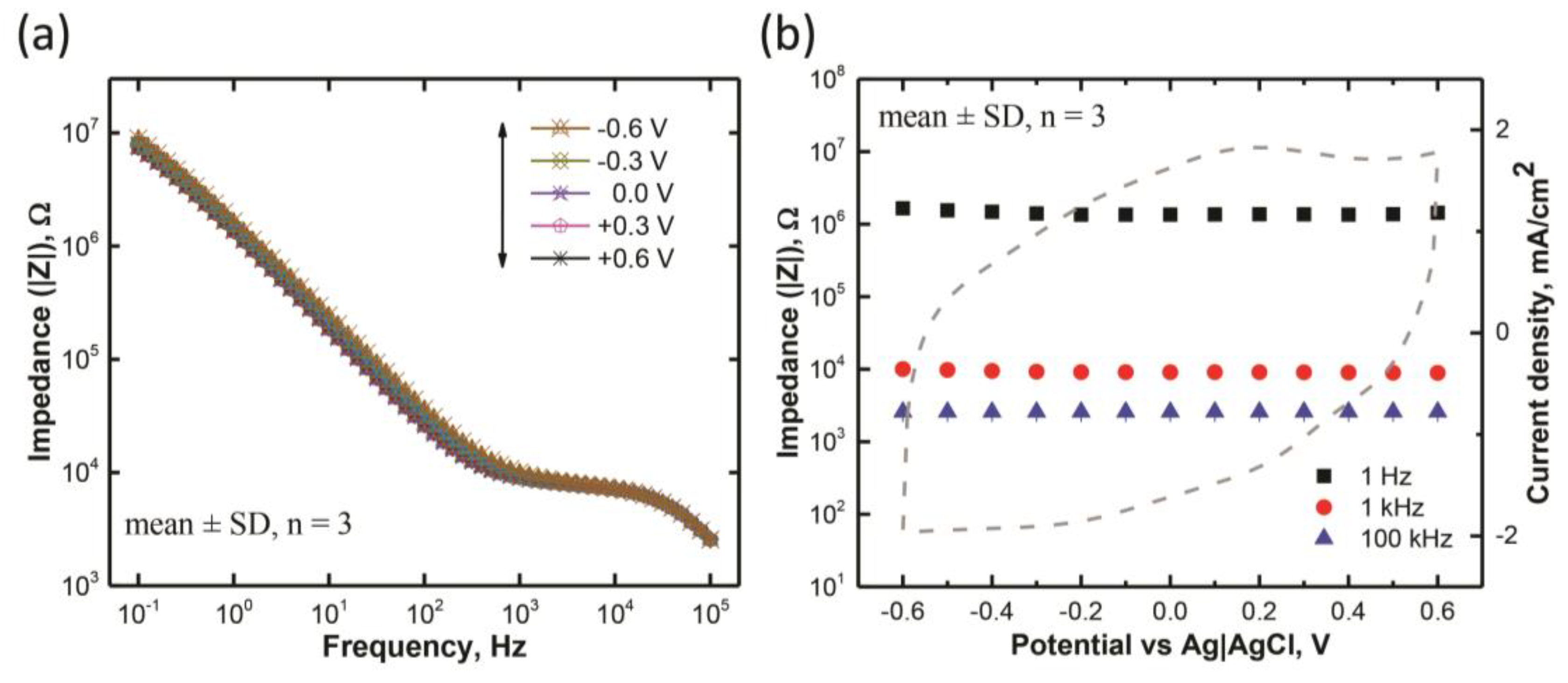
3.2. Electrochemical Impedance Characteristics
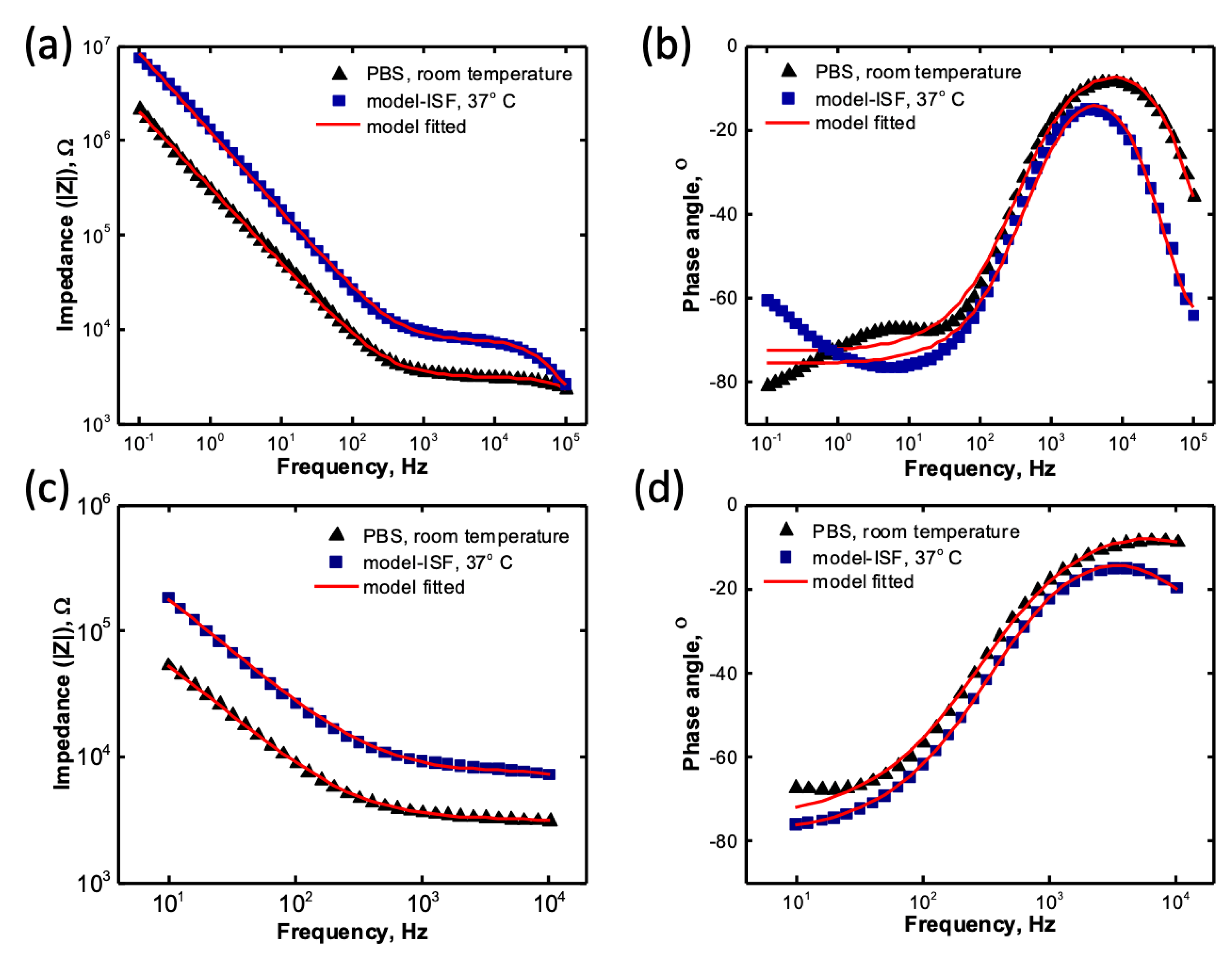
3.3. Impedance Modelling Study
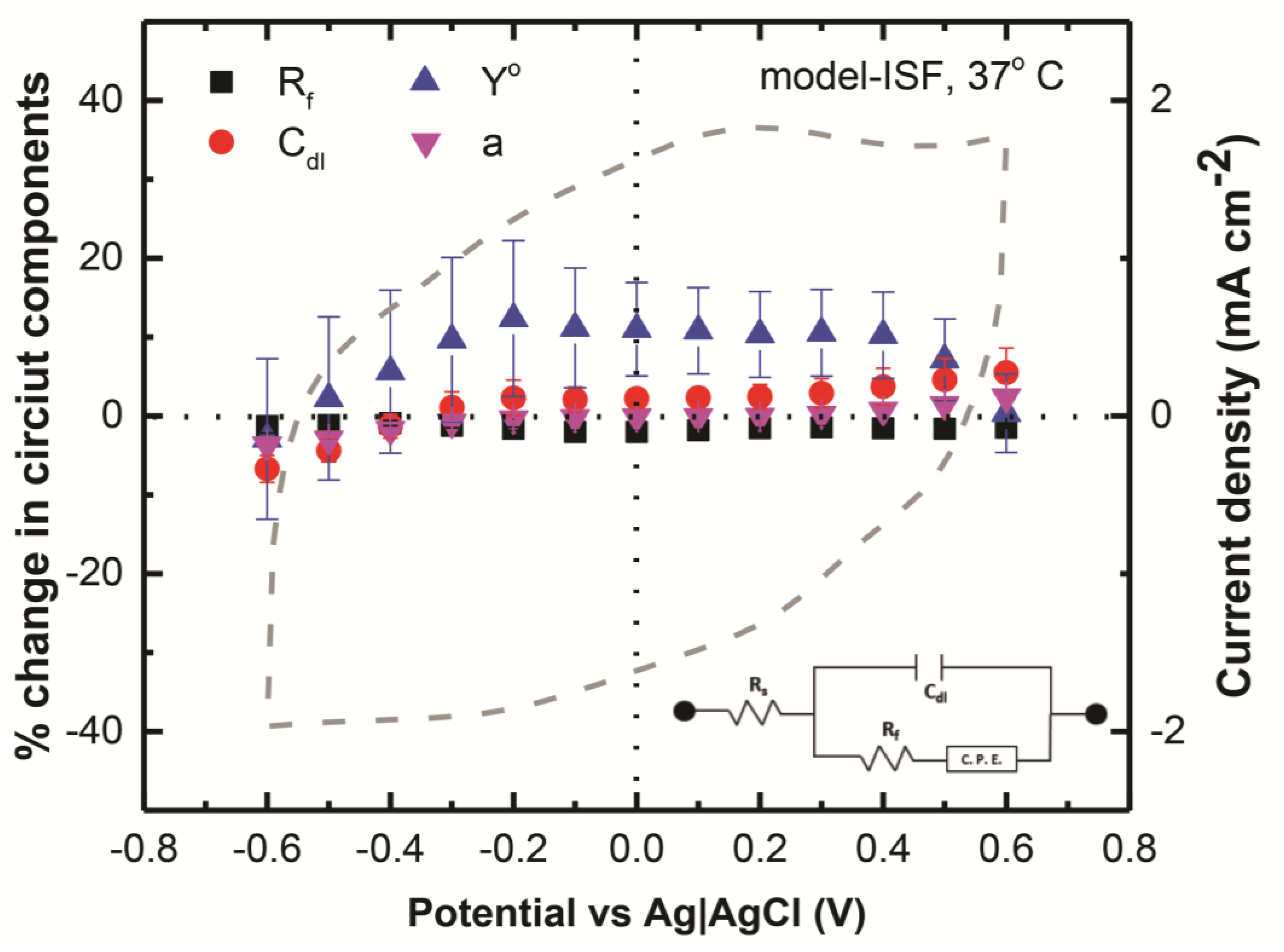
3.4. Contribution of Circuit Componenets in Charge Injection
3.5. Charge Injection Reversibility
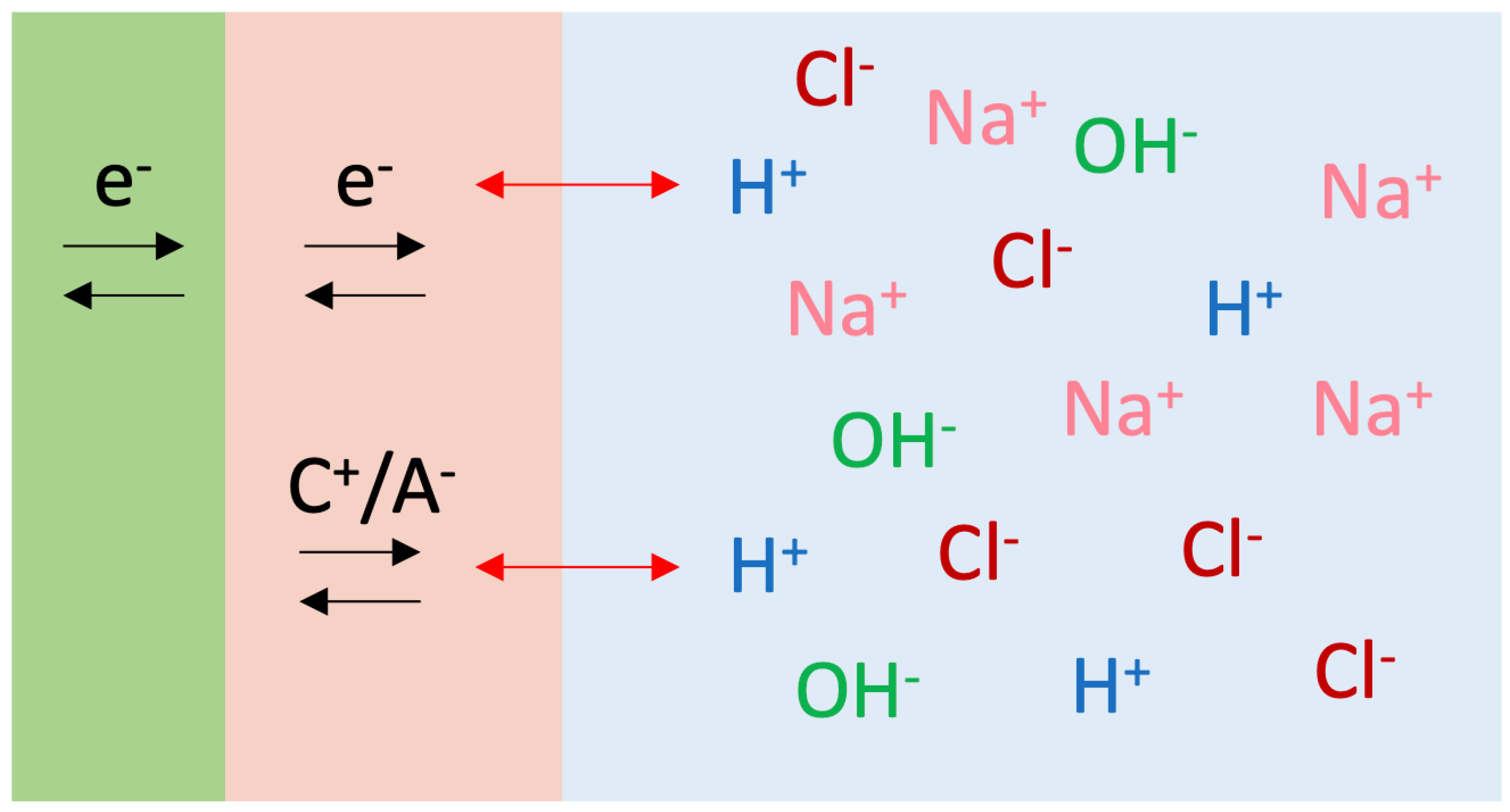
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Flesher, S.N.; Collinger, J.L.; Foldes, S.T.; Weiss, J.M.; Downey, J.E.; Tyler-Kabara, E.C.; Bensmaia, S.J.; Schwartz, A.B. , Boninger; M.L.; Gaunt, R.A. Intracortical microstimulation of human somatosensory cortex. Science translational medicine 2016, 8, 361ra141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhillon, G.S. and Horch, K.W. Direct neural sensory feedback and control of a prosthetic arm. IEEE transactions on neural systems and rehabilitation engineering 2005, 13, 468–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomlinson, T.; Miller, L.E. Toward a proprioceptive neural interface that mimics natural cortical activity. Progress in Motor Control: Theories and Translations 2016, 367–388. [Google Scholar]
- Humayun, M.S.; Weiland, J.D.; Fujii, G.Y.; Greenberg, R.; Williamson, R.; Little, J.; Mech, B.; Cimmarusti, V.; Van Boemel, G.; Dagnelie, G.; de Juan Jr, E. Visual perception in a blind subject with a chronic microelectronic retinal prosthesis. Vision research 2003, 43, 2573–2581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradley, D.C.; Troyk, P.R.; Berg, J.A.; Bak, M.; Cogan, S.; Erickson, R.; Kufta, C.; Mascaro, M.; McCreery, D.; Schmidt, E.M.; Towle, V.L. Visuotopic mapping through a multichannel stimulating implant in primate V1. Journal of neurophysiology 2005, 93, 1659–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cogan, S.F. Neural stimulation and recording electrodes. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2008, 10, 275–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merrill, D.R. , Bikson, M. and Jefferys, J.G. Electrical stimulation of excitable tissue: design of efficacious and safe protocols. Journal of neuroscience methods 2005, 141, 171–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrese, J.C.; Rao, N.; Paroo, K.; Triebwasser, C.; Vargas-Irwin, C.; Franquemont, L.; Donoghue, J.P. Failure mode analysis of silicon-based intracortical microelectrode arrays in non-human primates. Journal of neural engineering 2013, 10, 066014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negi, S.; Bhandari, R.; Rieth, L.; Solzbacher, F. In vitro comparison of sputtered iridium oxide and platinum-coated neural implantable microelectrode arrays. Biomedical materials 2010, 5, 015007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, T.L.; Robblee, L.S. Electrical stimulation with Pt electrodes. VIII. Electrochemically safe charge injection limits with 0.2 ms pulses (neuronal application). IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering 1990, 37, 1118–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiland, J.D.; Anderson, D.J.; Humayun, M.S. In vitro electrical properties for iridium oxide versus titanium nitride stimulating electrodes. IEEE transactions on biomedical engineering 2002, 49, 1574–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beebe, X.; Rose, T.L. Charge injection limits of activated iridium oxide electrodes with 0.2 ms pulses in bicarbonate buffered saline (neurological stimulation application). IEEE transactions on biomedical engineering 1988, 35, 494–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Z.J.; Luo, X.; Weaver, C.L.; Cui, X.T. Poly (3, 4-ethylenedioxythiophene)-ionic liquid coating improves neural recording and stimulation functionality of MEAs. Journal of Materials Chemistry C 2015, 3, 6515–6524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakraborty, B.; Joshi-Imre, A.; Maeng, J.; Cogan, S.F. Sputtered ruthenium oxide coatings for neural stimulation and recording electrodes. Journal of Biomedical Materials Research Part B: Applied Biomaterials 2021, 109, 643–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakraborty, B.; Joshi-Imre, A.; Cogan, S.F. Charge injection characteristics of sputtered ruthenium oxide electrodes for neural stimulation and recording. Journal of Biomedical Materials Research Part B: Applied Biomaterials 2022, 110, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakraborty, B.; Joshi-Imre, A.; Cogan, S.F. Sputtered Ruthenium Oxide Neural Stimulation Electrodes. 43rd Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine & Biology Society (EMBC) 2021, 6655–6658. [Google Scholar]
- Randles, J.E.B. Kinetics of rapid electrode reactions. Discussions of the faraday society 1947, 1, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeng, J.; Chakraborty, B.; Geramifard, N.; Kang, T.; Rihani, R.T.; Joshi-Imre, A.; Cogan, S.F. High-charge-capacity sputtered iridium oxide neural stimulation electrodes deposited using water vapor as a reactive plasma constituent. Journal of Biomedical Materials Research Part B: Applied Biomaterials 2020, 108, 880–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cogan, S.F.; Troyk, P.R.; Ehrlich, J.; Gasbarro, C.M.; Plante, T.D. The influence of electrolyte composition on the in vitro charge-injection limits of activated iridium oxide (AIROF) stimulation electrodes. Journal of neural engineering 2007, 4, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deku, F.; Joshi-Imre, A.; Mertiri, A.; Gardner, T.J.; Cogan, S.F. Electrodeposited iridium oxide on carbon fiber ultramicroelectrodes for neural recording and stimulation. Journal of The Electrochemical Society 2018, 165, D375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiland, J.D.; Anderson, D.J. Chronic neural stimulation with thin-film, iridium oxide electrodes. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering 2000, 47, 911–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franks, W.; Schenker, I.; Schmutz, P.; Hierlemann, A. Impedance characterization and modeling of electrodes for biomedical applications. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering 2005, 52, 1295–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brug, G.J.; van den Eeden, A.L.; Sluyters-Rehbach, M.; Sluyters, J.H. The analysis of electrode impedances complicated by the presence of a constant phase element. Journal of electroanalytical chemistry and interfacial electrochemistry 1984, 176, 275–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dellis, J.L.; Carpentier, J.L. Nelder and Mead algorithm in impedance spectra fitting. Solid state ionics 1993, 62, 119–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunde, S.; Lervik, I.A.; Tsypkin, M.; Owe, L.E. Impedance analysis of nanostructured iridium oxide electrocatalysts. Electrochimica Acta 2010, 55, 7751–7760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontes, M.B.A. Electrodes for bio-application: recording and stimulation. Journal of Physics: Conference Series 2013, 421, 012019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frederick, R.A.; Meliane, I.Y.; Joshi-Imre, A.; Troyk, P.R.; Cogan, S.F. Activated iridium oxide film (AIROF) electrodes for neural tissue stimulation. Journal of Neural Engineering 2020, 17, 056001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauporté, T.; Durand, R. Impedance spectroscopy study of electrochromism in sputtered iridium oxide films. Journal of applied electrochemistry 2000, 30, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKeown, D.A.; Hagans, P.L.; Carette, L.P.; Russell, A.E. , Swider, K.E.; Rolison, D.R. Structure of hydrous ruthenium oxides: implications for charge storage. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B 1999, 103, 4825–4832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atmaramani, R.; Chakraborty, B.; Rihani, R.T.; Usoro, J.; Hammack, A.; Abbott, J.; Nnoromele, P.; Black, B.J.; Pancrazio, J.J.; Cogan, S.F. Ruthenium oxide based microelectrode arrays for in vitro and in vivo neural recording and stimulation. Acta biomaterialia 2020, 101, 565–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Electrolyte | Rs (kΩ) Mean ± SD |
Rf (kΩ) Mean ± SD |
Cdl (nF) Mean ± SD |
Yo (nS sa) Mean ± SD |
a Mean ± SD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PBS | 2.32 ± 0.12 | 1.08 ± 0.14 | 6.54 ± 1.05 | 601.70 ± 30.90 | 0.85 ± 0.00 |
| model-ISF | 4.95 ± 0.62 | 2.96 ± 0.31 | 8.86 ± 3.75 | 328.90 ± 33.40 | 0.87 ± 0.01 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





