1. Introduction
Conventional metals have a crystalline structure with ordered atoms and grain boundaries, which makes the metal prone to dislocations and other defects, reducing the strength of the material. Amorphous alloys are relative to crystalline alloys, which are usually cooled down rapidly to suppress the generation of grains inside the material. Amorphous alloys are characterized by long-range disorder, which is disordered in three-dimensional space, without composition segregation and inclusions, and have a denser internal structure compared to crystals, which gives them excellent physical properties, chemical properties and biocompatibility, such as high strength, high hardness, high ductility, and good corrosion resistance [
1,
2]. Moreover, amorphous alloys have superplasticity in the supercooled liquid region and this makes them easy to process. These properties earn them application potential in the field of medical devices [
3,
4,
5]. For instance, excellent hardness makes it very suitable for use as various surgical blade (scalpel) materials; excellent biocompatibility and corrosion resistance make it suitable for manufacturing implantable orthopedic prostheses; superplasticity makes it very suitable for forming minimally invasive medical devices with small volumes and complex structures. However, the widespread use of amorphous alloys has been limited by their glass-forming ability. At present, amorphous alloys are generally made by rapid cooling. However, this method can only be used to produce samples in the form of thin plates, powder, filaments, and cylinders. It is difficult to produce complicated and precise shapes. In order to break this limitation, researchers have made many efforts [
6,
7,
8], one of which is welding.
Amorphous alloys have been successfully connected by friction welding [
9,
10], explosive welding [
11,
12], electron beam welding [
13], and laser welding [
14,
15]. Compared with other welding methods, laser welding has great advantages [
16,
17]. Laser welding is a method of welding two parts together by using the radiation energy of a laser to bring the temperature of the welded part to the melting point. Because laser welding produces a small spot area, its influence around the weld is also small, and it does not require the filling of other materials during the welding process, so laser welding is highly efficient, fast, and the weld surface is continuous and uniform with few defects such as porosity and cracks, making it ideal for precision welding and micro welding to obtain complex and precise parts [
18]. Therefore, in this study, we use laser welding to connect amorphous alloys. Vit1 is one of the Zr-based amorphous alloys with promising applications. It has a large supercooled liquid region and good glass-forming ability. At a heating rate of 30 K/min, the glass-transition temperature of Vit1 is T
g = 633 K, and the crystallization temperature is T
x = 724 K. Vit1 can be made by low cooling rate (1–100 K/s) [
19,
20,
21]. In this study, we use Vit1 to produce samples.
In laser welding, the temperature field of the welding area is difficult to obtain, which means it is hard to determine the power and laser moving speed in laser welding. Therefore, crystallization often occurs during the laser welding of amorphous alloys, reducing the amorphous alloys’ mechanical properties [
22]. So, it is necessary to simulate the temperature field of the welding area by computer and then determine the power and laser moving speed of laser welding [
23]. In this study, the temperature field of the welding area is simulated using the software SYSWELD, and the continuous heating transformation (CHT) curve of Vit1 is obtained using the Vogel-Fulcher-Tammann (VFT) equation and the Kissinger equation to predict the crystallization of amorphous alloy under given welding parameters. During laser welding, the temperature field curve shouldn't intersect with the CHT curve, or crystallization will happen in the welding area [
24]. The simulation results are verified by experiments.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of original specimens
The amorphous alloy used in this paper is Vit1, in which the purity of Zr is 90% (atomic percentage), and the purity of Ti, Cu, Ni, and Be are over 99%. The raw materials were mixed proportionally, put into an ultrasonic cleaning machine to remove impurities from the raw materials, dried, and then put into a vacuum induction arc furnace to repeatedly melt the master alloy ingots four times to obtain a uniform mixture of each element. Then the master alloy ingots are broken to obtain fragmented master alloy. The master alloy pieces are put into the pressure-casting machine for die-casting to obtain amorphous alloy sample strips. Four sample strips can be obtained in one die-casting, with dimensions of 2 x 100mm x 10mm x 1mm³, 1 x 100mm x 10mm x 2mm³, and 1 x 100mm x 10mm x 3mm³ respectively. The sample strips were continued to be cut to obtain the experimental amorphous alloy sample strips with dimensions of 50mm×10mm×2mm³ as shown in
Figure 1. In this paper, the sample strip with the size of 50mm×10mm×2mm³ is selected for the experiment.
2.2. Detection method
First of all, the X-ray diffraction (XRD, Rigaku Corporation, Tokyo, Japan) test should be performed on the experimental amorphous alloy samples to ensure that they are amorphous so as not to interfere with the subsequent experiments. The test is mainly divided into two parts: first, to detect whether the welded part is crystallized; second, to detect the mechanical properties of the welded parts. For detecting whether crystallization occurs, scanning electron microscope (SEM, FEI Company, Hillsboro, USA) observation and XRD inspection are mainly used. After welding, the welded parts will be cut into small pieces, and sample making, the sample made as shown in
Figure 2. The surface of the sample was then polished to a mirror finish and the microscopic morphology of the welded area was observed with a scanning electron microscope to see if crystallization was produced. Next, XRD testing was performed to determine whether the welded area was crystallized. For mechanical properties, the maximum flexural strength of the welded part was obtained using a three-point bending test to analyze the effect of changes in welding parameters on the flexural strength of the sample.
3. Simulation
3.1. CHT Curve Fitting
The crystallization temperature and the range of supercooled liquid region are often used to evaluate the stability of amorphous alloys. However, the crystallization temperature and the range of supercooled liquid region vary with the change in heating rate, so they cannot be used to describe the crystallization process of amorphous alloys. The CHT curve can be used to describe the crystallization of amorphous alloys [
25,
26,
27]. However, the measurement of the CHT curve takes a long time, so it is necessary to find a simple way to fit the CHT curve.
The Kissinger [
28,
29] equation and the VFT equation [
27,
30] are often used to study the phase transition of a material. It is convenient to fit the CHT curve by the Kissinger equation and the VFT equation using the characteristic temperature of amorphous alloys. However, for different alloy systems, the fitting ability of the Kissinger equation and the VFT equation are different [
30,
31]. Therefore, in this section, we use both the Kissinger equation and the VFT equation to fit the CHT curve of Vit1, and then investigate which equation can be used to better predict crystallization by experiments.
Ding et al [
31] obtained the CHT curve of Cu
50.3Zr
49.7 by the Kissinger equation. It was found that the fitted CHT curve was in good agreement with the experimental data. The dependence of T on heating rate α is described by
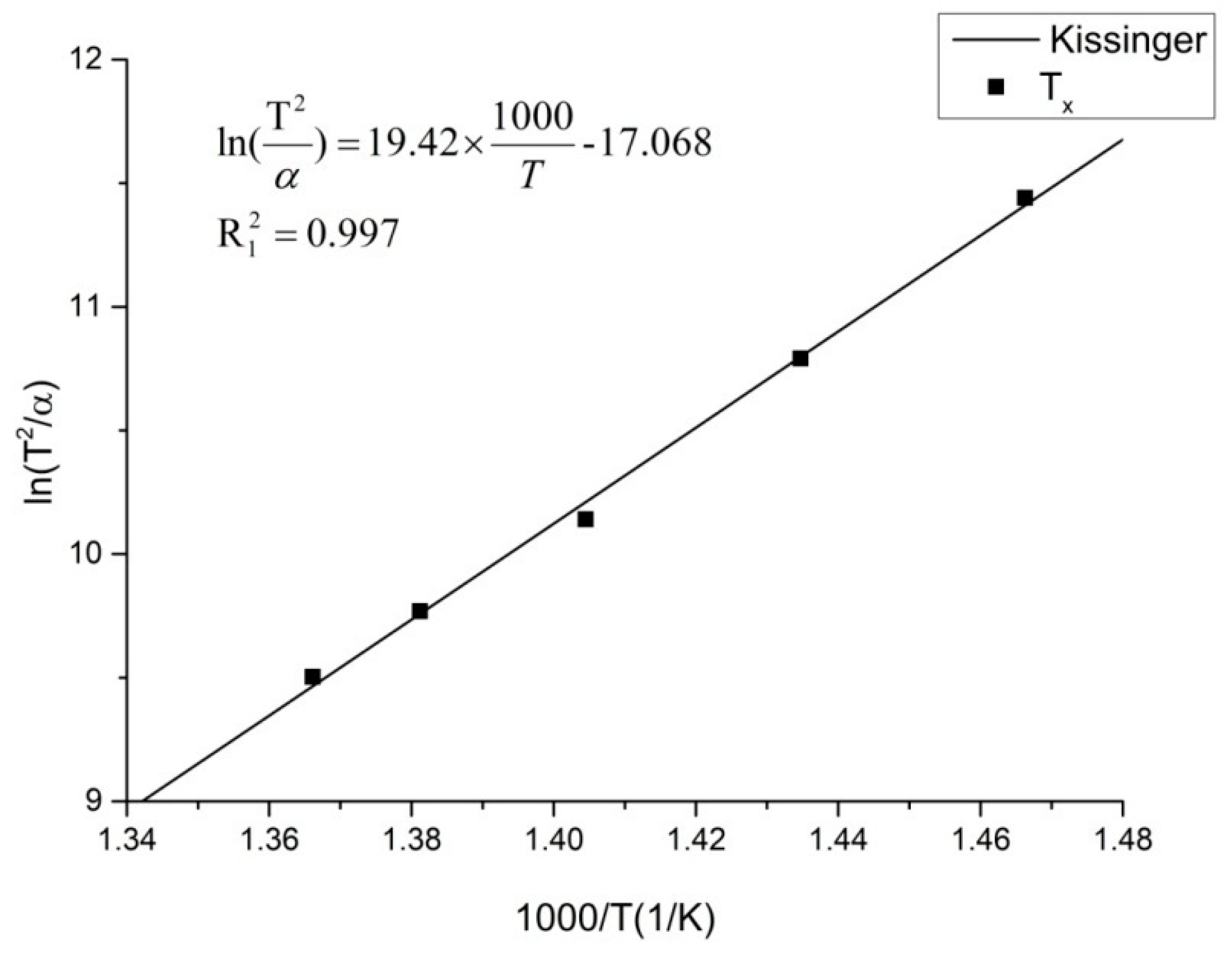
Where T is the characteristic temperature, α is the heating rate, R is the gas constant, E is the apparent activation energy, and C is a constant. The Kissinger equation describes the linear relationship between ln(T2/α) and 1/T.
The main characteristic temperatures of Vit1 at different heating rates (5–40 K/min) are shown in
Table 1 according to the reference [
32], which indicates that the characteristic temperature of Vit1 increases as the heating rate increases. Therefore we can obtain Kissinger’s linear relationship between ln(T
2/α) and 1/T for T
x as follow:
The correlation coefficient
= 0.997 indicates that the glass-transition temperature meets the Kissinger fitting well. The fitting line is shown in
Figure 3.
Although plotting ln(T
2/α) as a function of 1/T enables the estimation of the apparent activation energy E. Some researchers believe that the dependence of T on the heating rate agrees with the nonlinear VFT equation [
25,
30]:
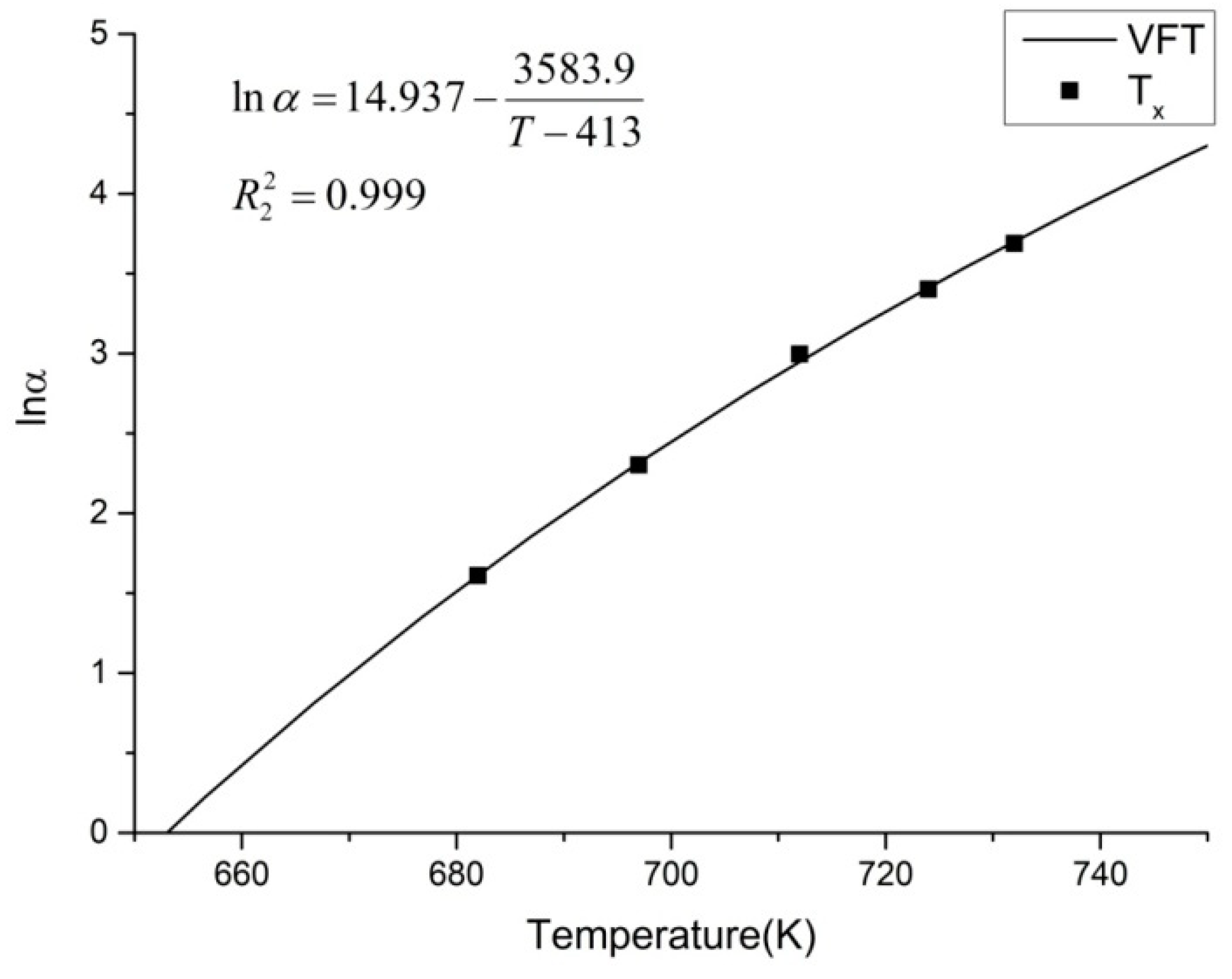
where T is the characteristic temperature, α is the heating rate, T
0 is the hypothetical value of T at the limit of indefinitely slow cooling and heating rate, and A, B is constant.
We can obtain VFT’s nonlinear relationship between lnα and T for T
x as follow:
The correlation coefficient
= 0.999. The fitting line is shown in
Figure 4.
It can be seen that the Tx meets both the Kissinger fitting and the VFT fitting very well at the heating rate of 5–40 K/min. And the correlation coefficient and are very close.
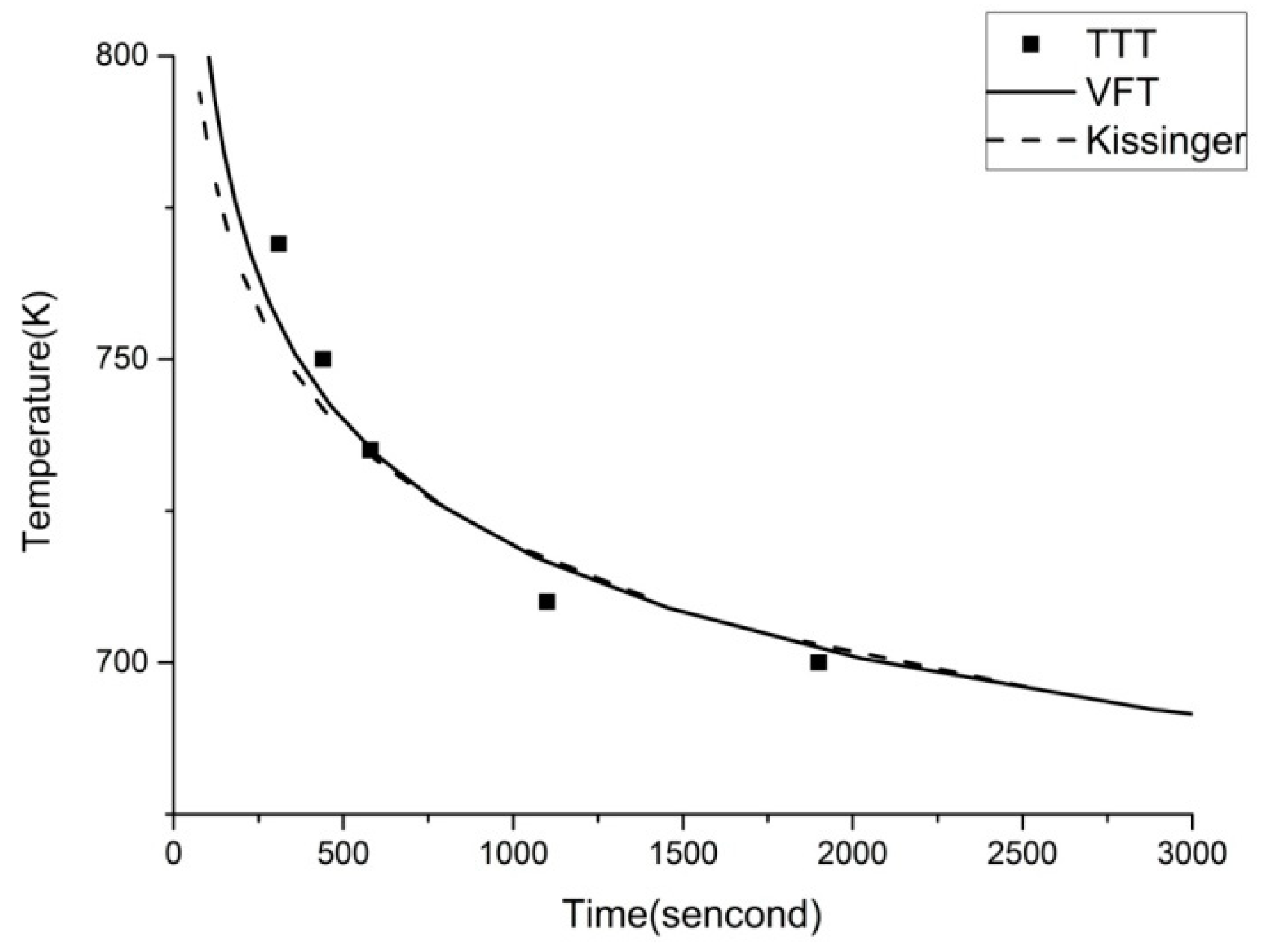
The heating rates can be calculated by (T-293)/t, and put into Equations (2) and (4) to construct the CHT curve, as shown in
Figure 5.
It can be seen from
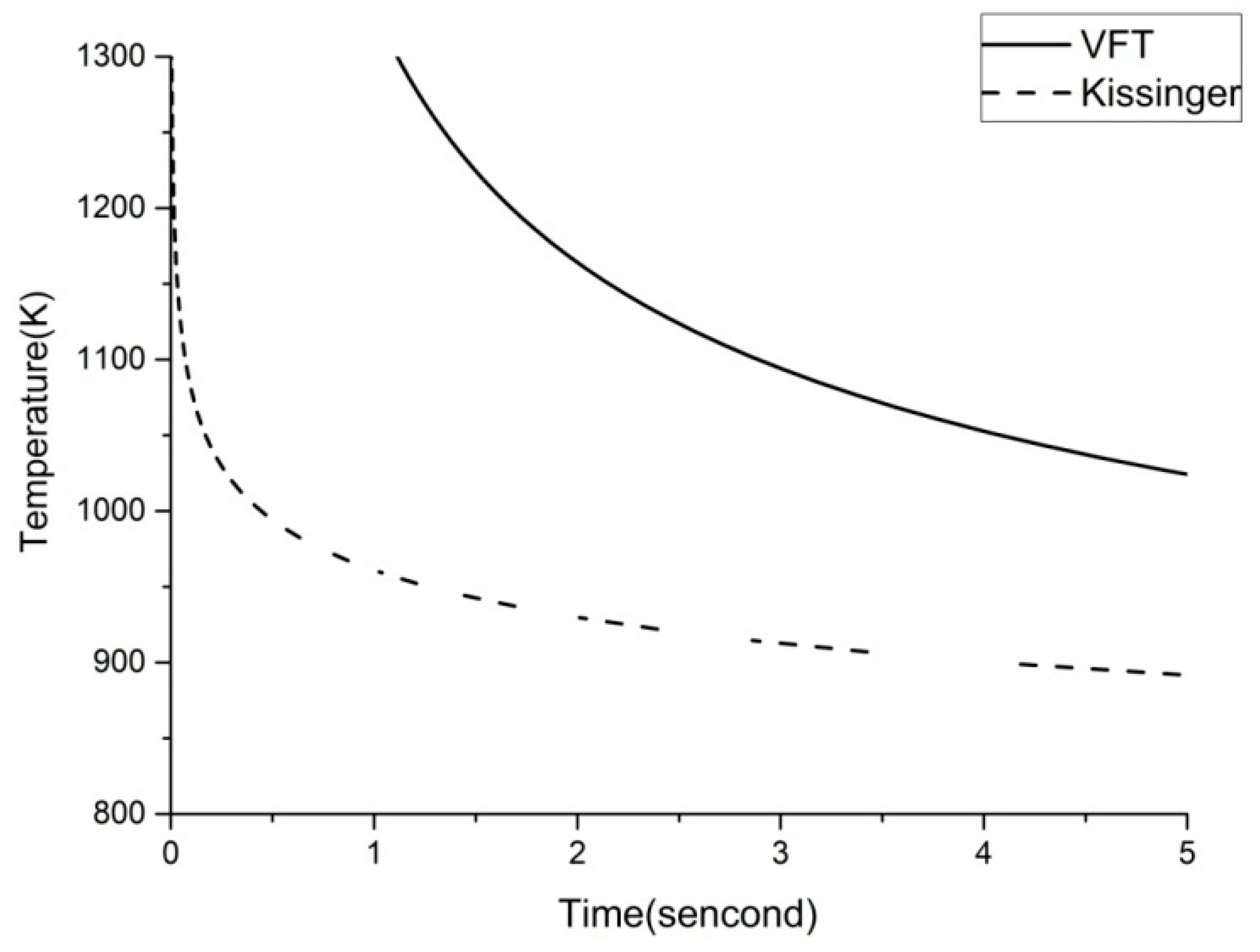
Figure 5 that the VFT fitting and the Kissinger fitting almost coincide, and the TTT data meets the fittings very well. Thus, there is no significant difference between the VFT equation and the Kissinger equation in the ability of CHT curve fitting of Vit1. In laser welding, the welding speed is high, which leads to short welding time, no more than one second in one spot. So we reduce the range of time, and the result is shown in
Figure 6. It can be seen that the two curves are far apart in the short time interval. Therefore, it is necessary to analyze both the VFT fitting and the Kissinger fitting in laser welding.
3.2. Simulation of Temperature Field
For laser welding, simulating the temperature field in advance can guide the selection of welding parameters and reduce crystallization. We use finite element analysis in this part to simulate the temperature field curve of the welding area with the software SYSWELD (ESI SYSWELD 2019.0, Framatome, France), which has been proven effective in the simulation of temperature field [
24].
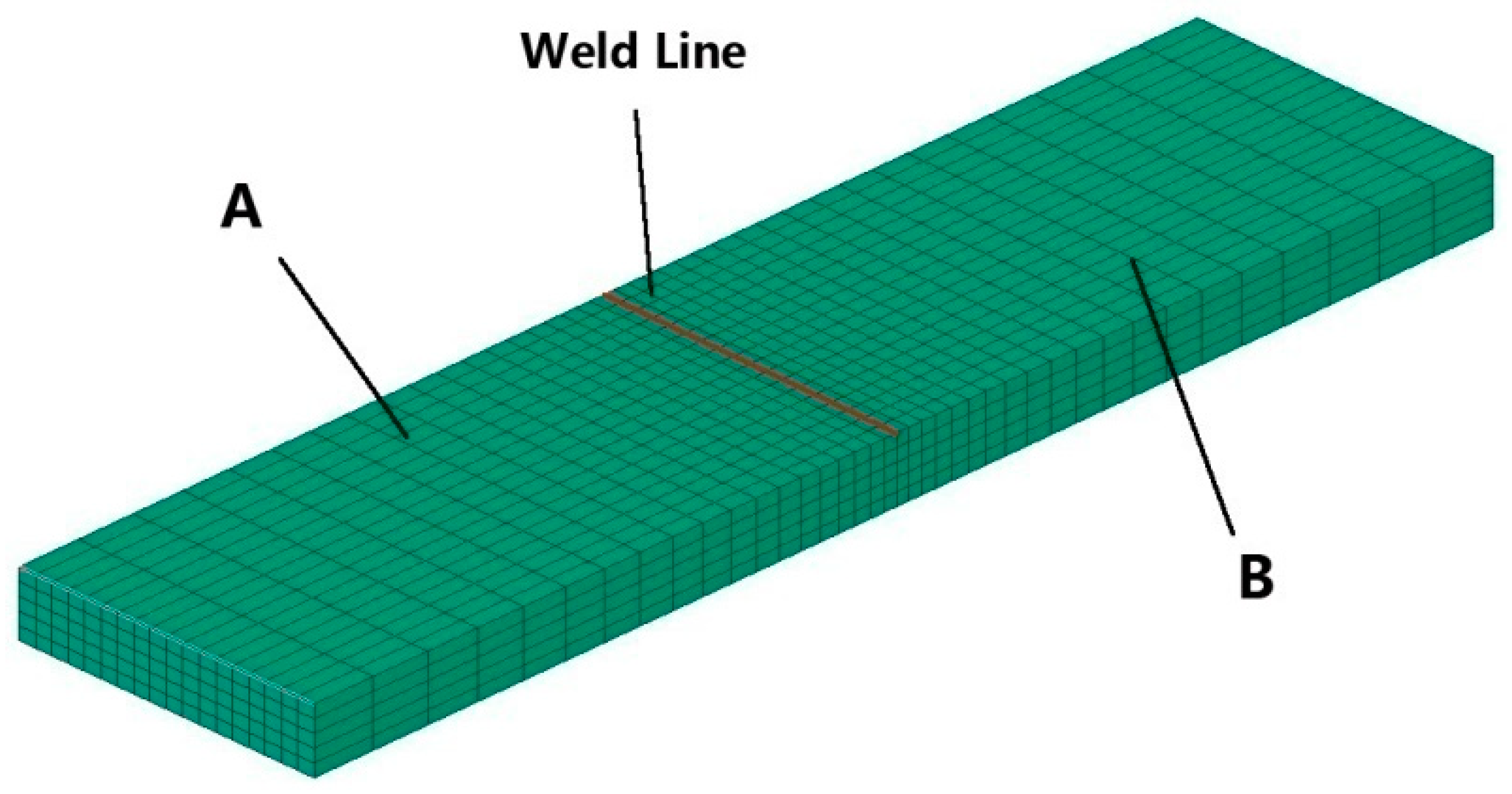
First, the sample was modelled by SYSWELD, as shown in
Figure 7. Then, the sample of amorphous alloy A and the sample of amorphous alloy B were welded virtually to get the temperature field curve. The dimension of samples A and B are all 50 × 5 × 2 mm
3 in size. The material parameters [
33] involved in the simulation are shown in
Table 2.
3.3. Results and Discussion
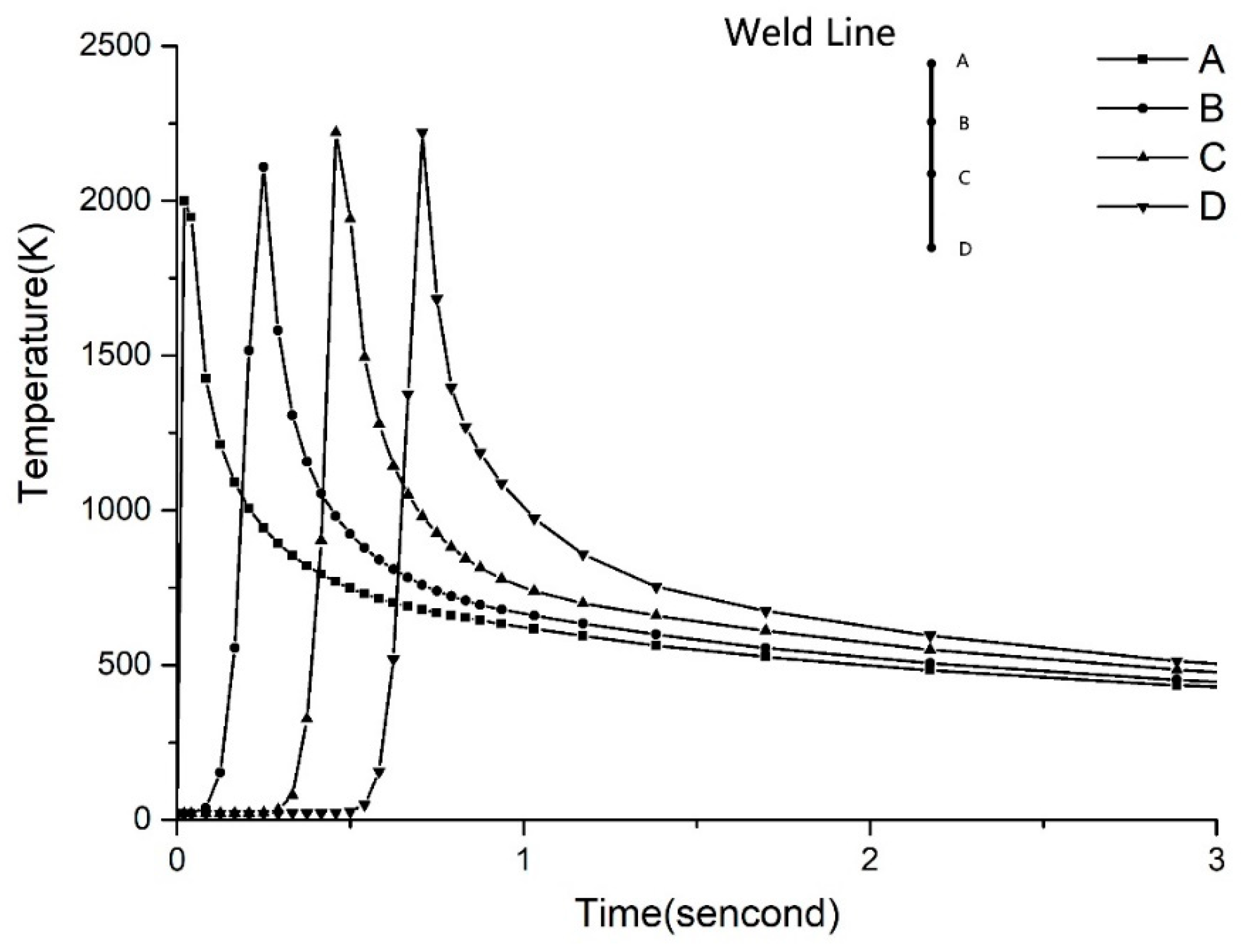
Firstly, the simulated welding runs under the parameter of 300 W-12 mm/s. The temperature field curves of points A, B, C and D, which are distributed evenly along the welding line, are shown in
Figure 8. It can be seen that the trends of the temperature field curve at all points are almost the same, and the highest temperature reaches about 2200 K. The maximum temperature at the starting point A is about 2000 K, which is lower than 2200 K. The reason is that the welding has just started and the temperature field has not been fully established. As the laser moves, the temperature rises rapidly, reaching the maximum temperature, and then decreases quickly. Such a temperature field curve makes it possible to avoid the intersection with the CHT curve, preventing the crystallization in laser welding. At the beginning of the welding, the temperature after point C does not change. The reason may be that the temperature field has not affected the point afterward so it remains at the initial temperature.
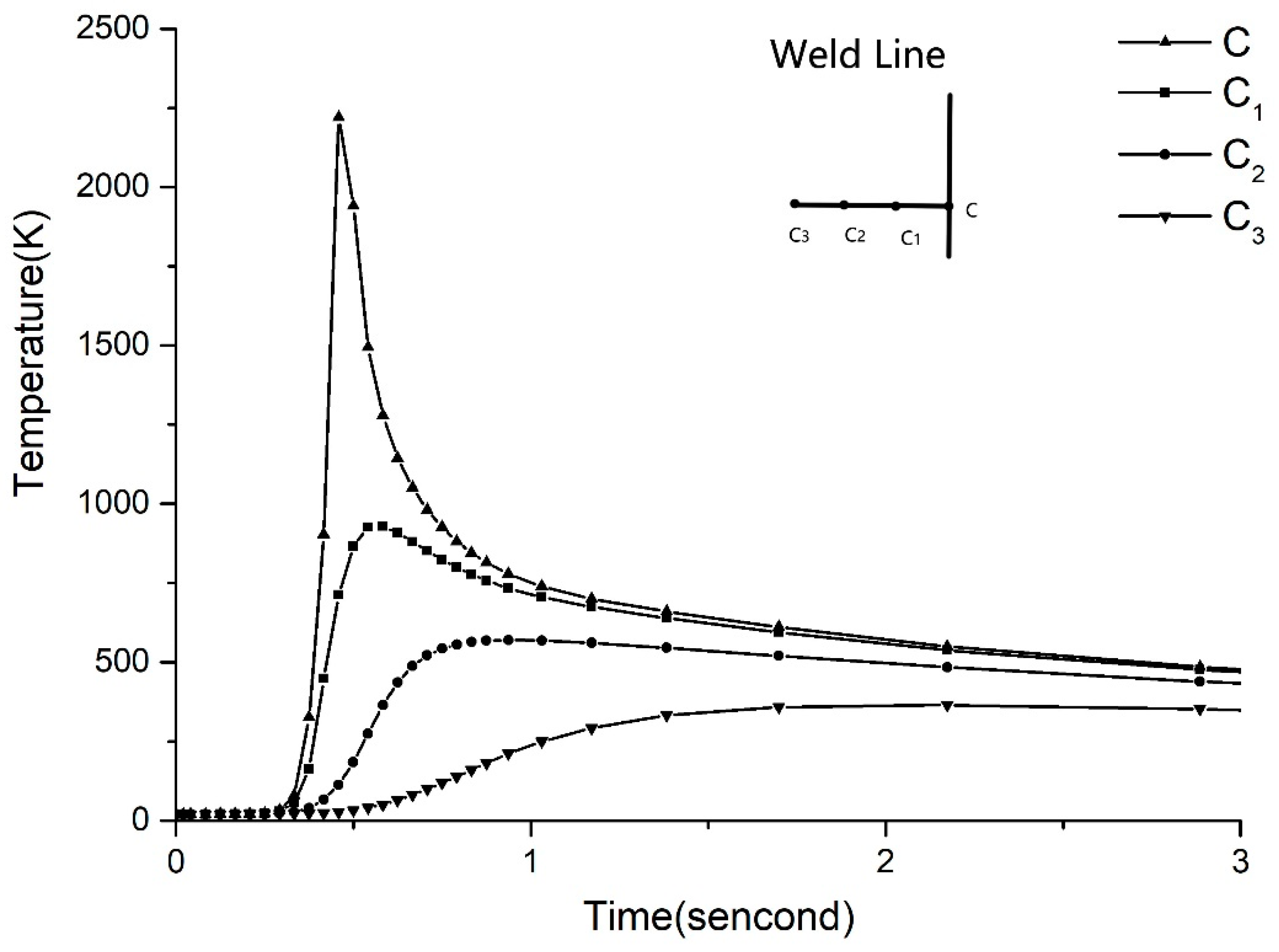
Figure 9 shows the temperature field curve normal to the welding line at the parameter of 300 W-12 mm/s. It can be seen from
Figure 9, the farther away from the weld line, the lower the maximum temperature and temperature changing rate.
Amorphous alloy is easier to crystallize in the heat-affected zone in laser welding [
34], so we choose a point in the heat-affected zone and simulate the temperature field curve of this point at different welding parameters.
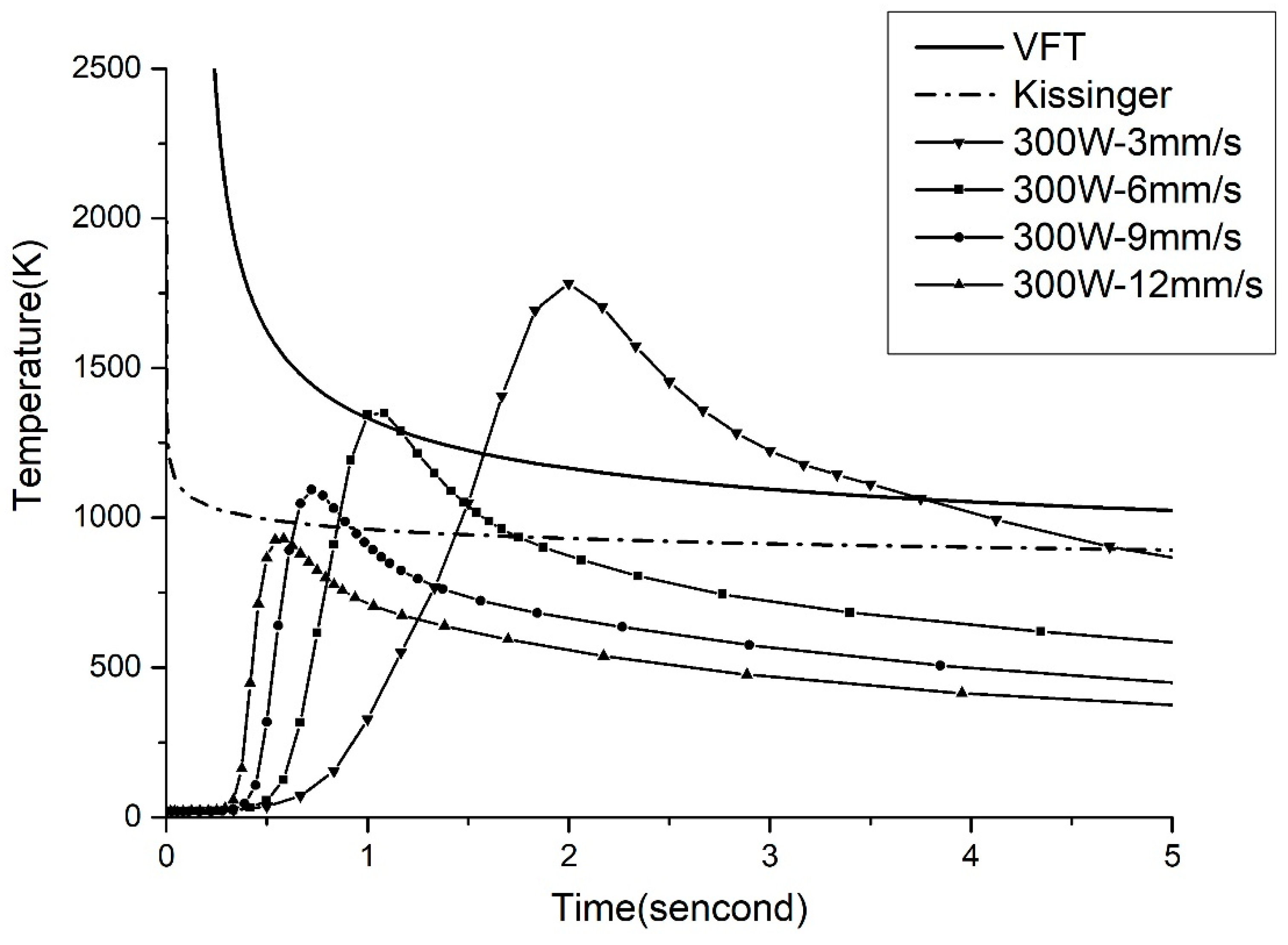
The welding power is kept at 300 W while the welding speed is changed to study its influence of it, as shown in
Figure 10. The welding parameters are shown in
Table 3. With the decrease in the welding speed, the welding time and the maximum temperature gradually increase, and the temperature field curve moves to the upper right. At the welding speed of 3 mm/s and 6 mm/s, the temperature field curves both intersect with the corresponding VFT fitting and the Kissinger fittings. According to the hypothesis mentioned above, the crystallization occurs in the welding area at 300 W-3 mm/s and 300 W-6 mm/s. At 9 mm/s, the temperature field curve intersects only with the Kissinger fitting, so it is hard to determine whether crystallization will occur or not at 300 W-9 mm/s. In this study, experiments are carried out to investigate which fitting can be used to better predict the crystallization in laser welding.
4. Laser Welding Experiments
4.1. Procedure
In order to verify the accuracy of crystallization prediction in simulated welding, laser welding tests of Vit1 amorphous alloy are performed in this section. As-received amorphous alloys were produced in EONTEC Co. Ltd.(Dongguan, Guangdong, China). To be consistent with the simulation, the amorphous alloy samples used for laser welding are 50 × 5 × 2 mm³ in size. Laser welding experiments were conducted by using a WF300 laser welder (GrandTech Laser Industry Group Co., Ltd., Shenzhen, China) with a pulse width of 3.0 ms, frequency of 40 Hz, and argon flow rate of 20 L/min. Welding parameters are shown in
Table 3. In laser welding, welding areas were protected by argon to reduce welding defects and increase the cooling rate. The surface morphology of the welding area was observed by scanning electron microscope (SEM, FEI Company, Hillsboro, USA), and then X-ray diffraction (XRD, Rigaku Corporation, Tokyo, Japan) experiments were carried out. The bending strength of the welded samples was obtained by bending experiments.
4.2. Results and Discussion
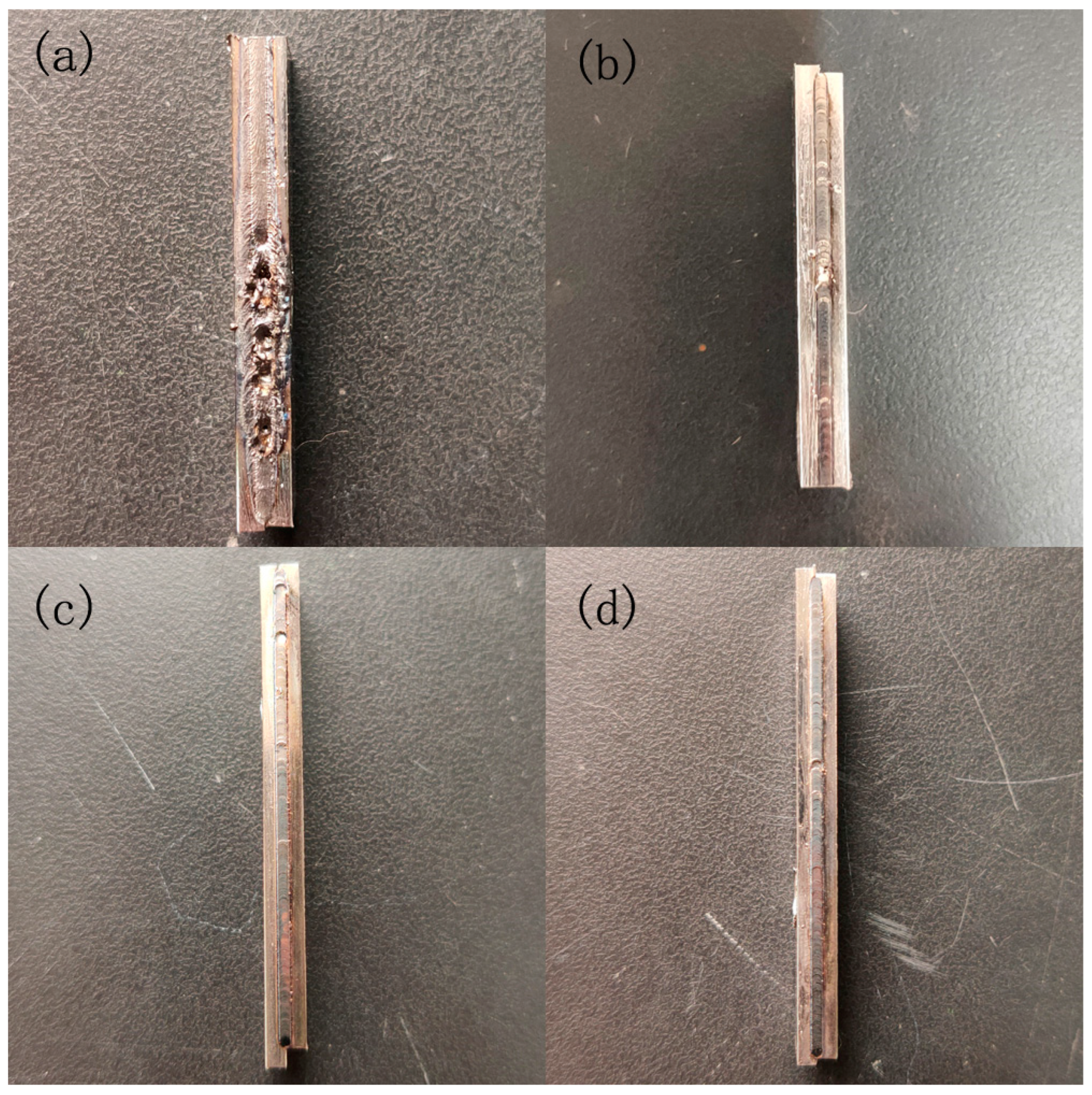
Laser welding results are shown in
Figure 11. Samples 1-4 were successfully welded together. Sample 1 was welded too slowly and the laser impacted the same welded part for too long, resulting in severe spattering at some weld locations and affecting the performance of the welded part. Samples 2-3 welded parts are good, only a small amount of spatter. Sample 1, has the slowest welding speed, so the temperature of the welding area in the four samples is the largest, and its heat-affected zone area is also the largest, with the increase in welding speed, the area of the heat-affected zone gradually reduced, until there is no heat-affected zone in Sample 4. Four samples have a varying number of porosity defects, of which Sample 1 is the most serious, which is due to the slow movement of the laser in Sample 1, the laser impact time on the same welding area is too long. With the increase in welding speed, the number of pores gradually decreased.
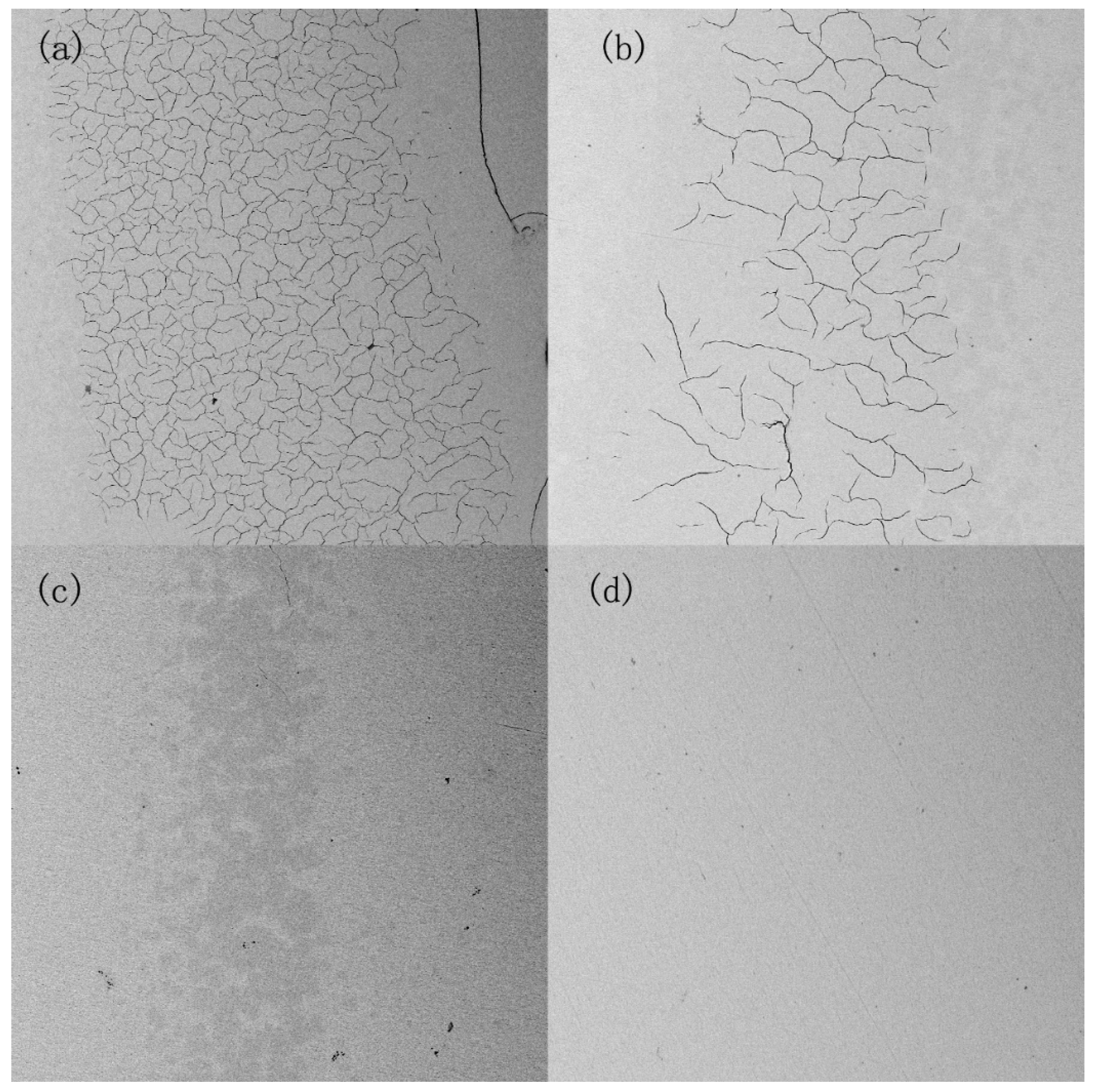
The heat-affected areas of the four samples were magnified to obtain
Figure 12. From the figure, it can be seen that a large number of cracks were produced in the heat-affected areas of Sample 1 and Sample 2 by the laser impact, and there were a large number of black spots in the heat-affected areas. Sample 1 crack range is wide and dense, which is due to excessive laser impact. With the increase in welding speed, the crack density decreased significantly, Sample 3 has been observed no obvious cracks. As the welding speed of Sample 3 is too small, no crack generation, but also can not observe the obvious heat-affected zone. So an appropriate increase in welding speed can reduce the generation of pores, cracks and other defects, increasing the mechanical properties of the welded area. However, when the welding speed is too large, there may be no weld penetration, reducing the performance of the welded area.
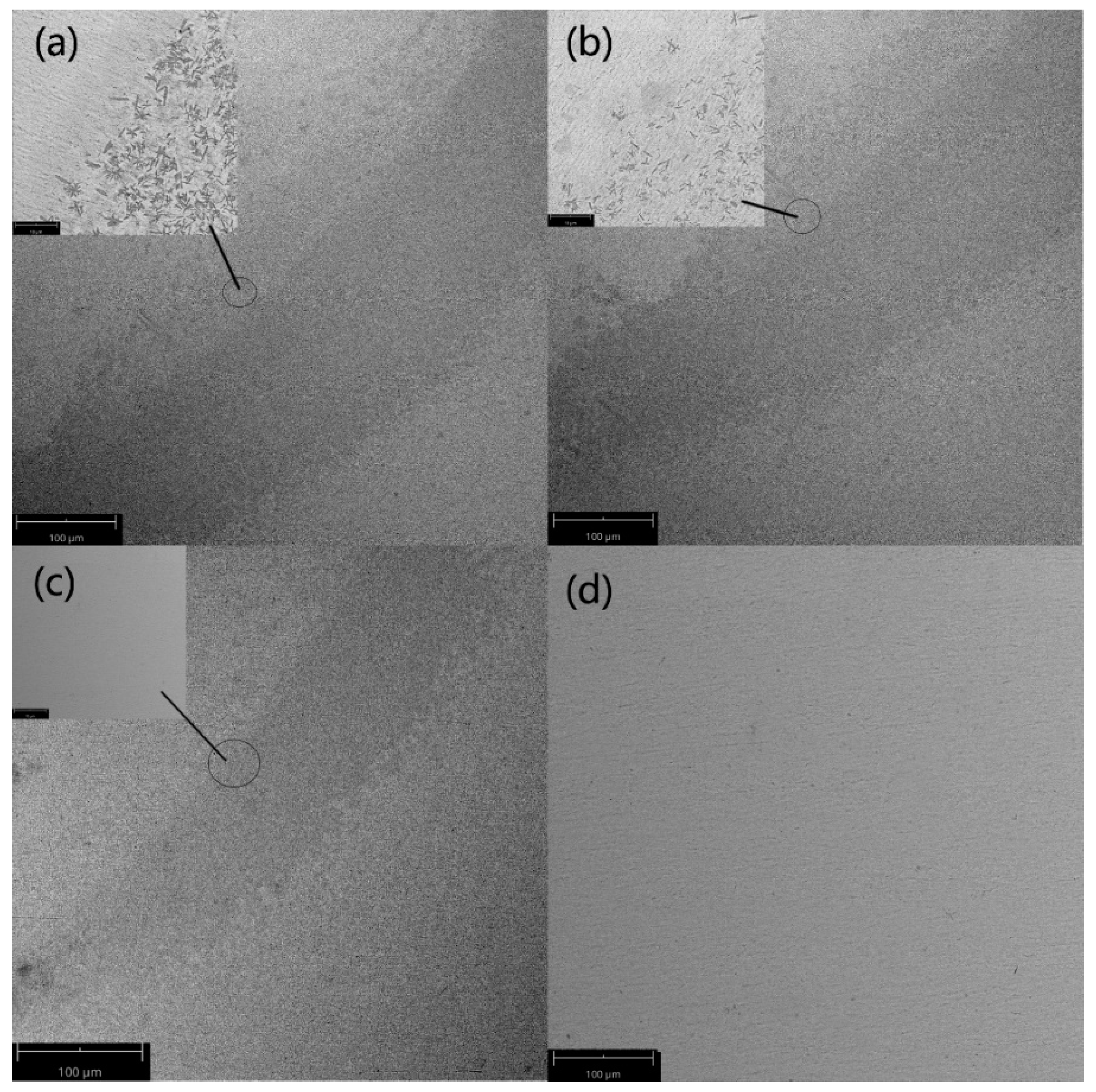
Figure 13 shows SEM images of the cross-section of four laser welding samples. It can be seen that different welding speed affects the microstructures of the welding area. Samples 1–3 have obvious welding fusion zones, heat-affected zones, and base metal zones. Sample 1 has the largest heat-affected zone, while Sample 4 has no obvious heat-affected zone. The reason may be that the change in welding speed affects the temperature of the welding area, changing the area of the heat-affected zone. For Sample 4, the weld fusion zone, heat-affected zone, and base metal zone cannot be distinguished by SEM because of the high speed of laser welding. It can be seen from
Figure 13, crystallization mainly occurs in the heat-affected zone, and there are no obvious crystals in the welding fusion zone. The results are consistent with the previous research [
28]. Grains appeared in the heat-affected zone of Sample 1 and Sample 2, and grains could not be observed by electron microscopy for Sample 3 and Sample 4, so it can be tentatively determined that crystallization occurred in Sample 1 and Sample 2, while no crystallization occurred in Sample 3 and Sample 4, which is consistent with the computer simulation results. To further determine the accuracy of the results, an XRD test was performed.
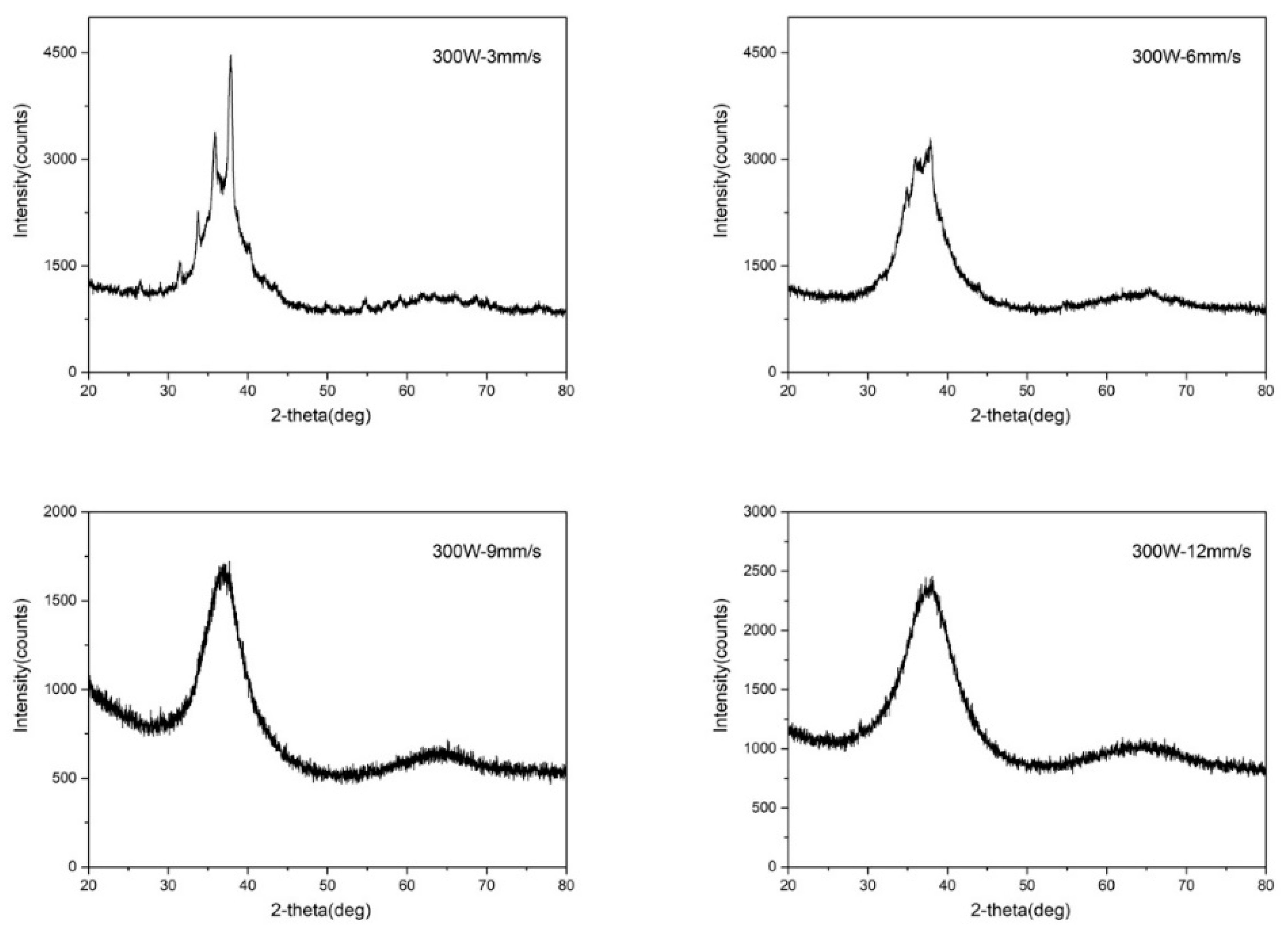
Figure 14 shows the XRD patterns of four welding samples. Sample 1 and sample 2 have obvious crystalline peaks, indicating that sample 1 and sample 2 have crystallized. Low welding speed increases the temperature of the welding area and decreases the temperature drop rate, so the crystallization degree of sample 1 is the most serious. Either Sample 3 or Sample 4 has only one classic amorphous peak, and no peak corresponding to a crystalline phase is observed, indicating that the structure is still amorphous. Both the SEM images and the XRD patterns prove that samples 1,2 crystallize and samples 3,4 keep amorphous, indicating VFT fitting can be used to predict the crystallization of Zr
41.2Ti
13.8Cu
12.5Ni
10Be
22.5 amorphous alloy better in laser welding.
In addition, bending experiments were carried out.
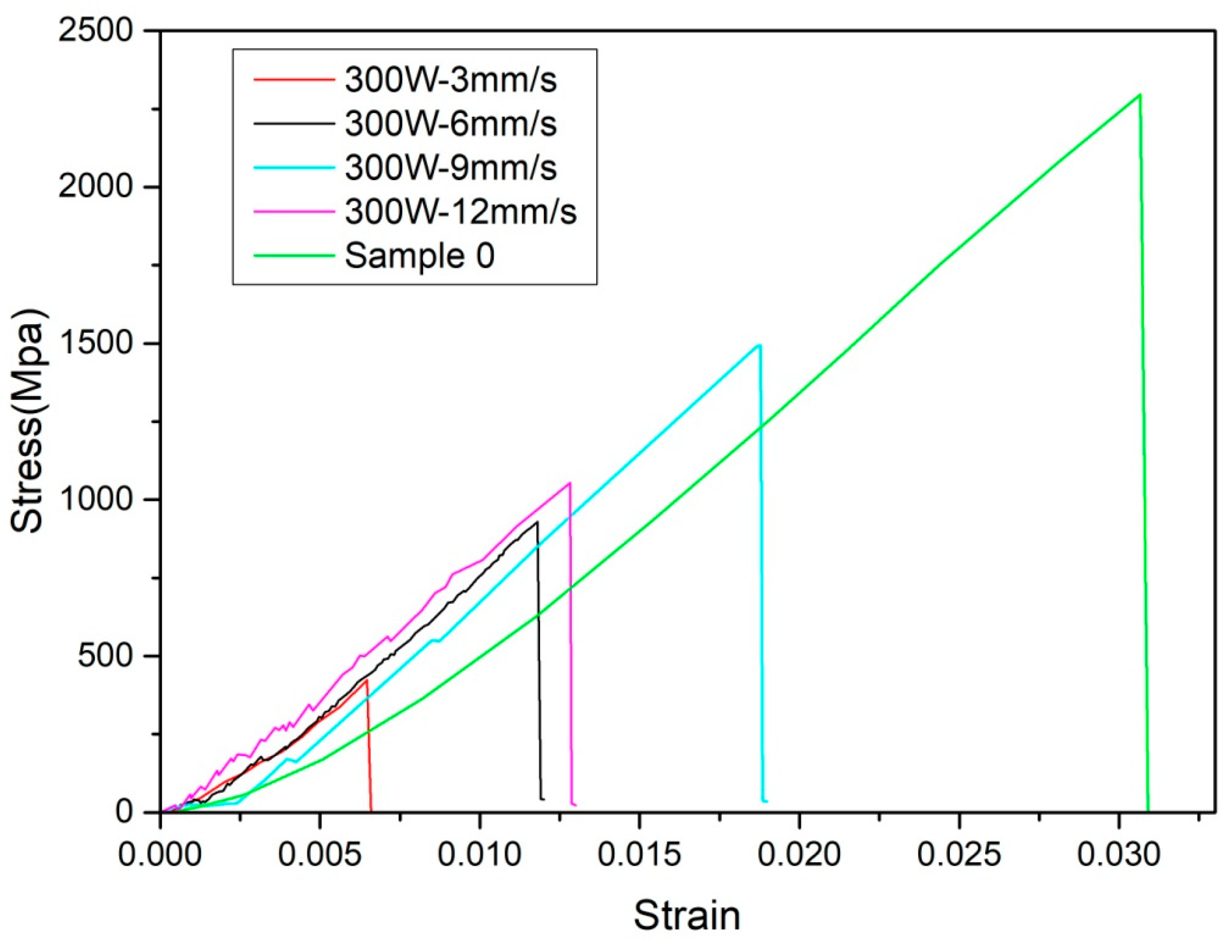
Figure 15 shows the stress-strain curves of the samples at different welding parameters. Sample 0 is an unwelded sample of size of 100 × 5 × 2 mm³. With the change in welding speed, the bending strength does not change monotonously. The bending strength at 300 W-3 mm/s is the lowest because the welding area has been seriously crystallized, which greatly reduces its strength. With the increase of welding speed, the crystallization gradually weakens and the bending strength begins to increase. After 300 W-9 mm/s, the bending strength decreases again, because the welding speed is too high and the sample is not fully welded. As can be seen from
Figure 15, the bending strength of sample 0 reaches 2256.25 Mpa, while the maximum bending strength of the welding samples is only 1502.1 Mpa. So laser welding can greatly reduce the bending strength of samples.
After the above analysis found that the welding parameters of 300W-9mm / s and 300W-12mm / s amorphous alloys do not crystallize, followed by a flexural test at Vit1 in 300W-9mm / s welding parameters of the maximum flexural strength is greater, so we choose to go to 300W-9mm / s welding parameters to weld the gripper. The welding results are shown in
Figure 16. The top view shows that the gripper is not welded through, and due to the high temperature, the weld around the gripper part of the damage, which is mainly due to improper selection of the laser angle during the welding process, as well as the welding speed is too slow. As can be seen from the side view, the weld appears larger molten metal, changing the original shape of the gripper, which will increase the workload of subsequent processing, which is not conducive to actual production. From the above analysis, it can be seen that although the amorphous alloy did not crystallize under 300W-9mm/s, and the maximum bending strength is larger, due to the small size of the gripper can not withstand the higher temperature generated by this parameter, resulting in damage around the gripper welding line, the morphology of a large change. So in the actual welding process to change the welding parameters, continue to reduce the welding temperature to achieve the desired effect.
5. Conclusions
In this paper, the CHT curves of Vit1 amorphous alloy are fitted by the Kissinger equation and the VFT equation respectively, and the temperature field curves are obtained by computer simulation, predicting the crystallization of amorphous alloy during laser welding. Although the VFT fitting and the Kissinger fitting almost coincide in large time intervals, they are far apart in small time intervals. Because the welding speed is fast which leads to a small time interval, two kinds of CHT curves are fitted to verify their ability of predicting crystallization in laser welding.
To investigate whether the CHT curve can be used to predict the crystallization of Vit1 amorphous alloy in laser welding, experiments are carried out. It can be seen from SEM images that 300 W-3 mm/s causes serious crystallization and produce large crystals. With the increase of welding speed, the size of the crystals decreases. XRD results show that the samples at 300 W-3 mm/s and 300 W-6 mm/s crystallize, while the samples under 300 W-9 mm/s and 300 W-12 mm/s keep amorphous, which is consistent with the predicted results of CHT curved fitted by VFT equation. The results show that the CHT curves fitted by the VFT equation can be used to accurately predict the crystallization of Vit1 amorphous alloy in laser welding.
In addition to exploring the crystallization prediction, we can also see from the electron microscope picture that the area of the various parts of the weld area will also change with the change in welding speed, when the welding speed becomes slower, the temperature of the weld area will also rise, which leads to a larger heat-affected zone area. Changes in welding parameters will also change the bending strength of the welded parts, with the increase in welding speed, the maximum bending strength of the specimen shows a trend of first increasing and then decreasing. Overall, however, laser welding will greatly reduce the bending strength of the welded parts. Therefore, laser welding has a large impact on all aspects of the specimen, and to obtain a better performance of the joint, it is necessary to consider not only the crystallization problem but also the bending strength and other issues.
The results of this study can be used for providing technical support for the production of various amorphous alloy products, especially for the processing and manufacturing of various medical devices. This will facilitate the optimization of relevant process flow and the improvement of product performance.
Author Contributions
S.Y., C.S. and C.W. conceived this project. L.H. and L.H. carried out finite element simulation, performed experiments and collected the relevant data and analyzed them. All the authors contributed to the writing of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No.: 51735003) and the National Key R&D Program of the Ministry of Science and Technology - digital medical equipment R&D (Grant No.: 2019YFC0120402).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Terekhov, S.V. Single- and Multistage Crystallization of Amorphous Alloys. Physics of Metals and Metallography 2020, 121, 664–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuvandikov, O.K.; Subkhankulov, I.; Amonov, B.U.; Imamnazarov, D.H. Physical Properties of High-Cobalt Amorphous Alloys. Metallofizika i Noveishie Tekhnologii 2021, 43, 1601–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meagher, P.; O'Cearbhaill, E.D.; Byrne, J.H.; Browne, D.J. Bulk Metallic Glasses for Implantable Medical Devices and Surgical Tools. Advanced Materials 2016, 28, 5755–5762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loye, A.M.; Kwon, H.K.; Dellal, D.; Ojeda, R.; Lee, S.; Davis, R.; Nagle, N.; Doukas, P.G.; Schroers, J.; Lee, F.Y.; et al. Biocompatibility of platinum-based bulk metallic glass in orthopedic applications. Biomedical Materials 2021, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajan, S.T.; Arockiarajan, A. Thin film metallic glasses for bioimplants and surgical tools: A review. Journal of Alloys and Compounds 2021, 876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, N.; Das, P.; Gollapudi, S. Can an amorphous alloy crystallize into a high entropy alloy? Modelling and Simulation in Materials Science and Engineering 2022, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasannaeimi, V.; Wang, X.; Salloom, R.; Xia, Z.; Schroers, J.; Mukherjee, S. Nanomanufacturing of Non-Noble Amorphous Alloys for Electrocatalysis. ACS Applied Energy Materials 2020, 3, 12099–12107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerstl, S.S.A.; Schaublin, R.; Loffler, J. Nanoscale Clusters and Heterogeneities in Engineering and Amorphous Alloys. Microscopy and Microanalysis 2022, 28, 712–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karna, S.; Cheepu, M.; Venkateswarulu, D.; Srikanth, V. Recent Developments and Research Progress on Friction Stir Welding of Titanium Alloys: An Overview. IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering 2018, 330, 012068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanjeevi, C.; Arputhabalan, J.J.; Dutta, R.; Pradeep. Investigation on the Effect of Friction Welding Parameters on Impact Strength in Dissimilar Joints. IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering 2017, 197, 012069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.Q.; Huang, B.M.; Jiang, Z.J.; Lu, C.; Dai, L.H. Joining of bulk metallic glass to brass by thick-walled cylinder explosion. Scripta Materialia 2015, 97, 17–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Chen, P.; An, E.; Feng, J. Experimental Study on the Explosive Welding of Thin Al/Cu Composite Plates. Materials Science Forum 2018, 910, 52–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tariq, N.H.; Shakil, M.; Hasan, B.A.; Akhter, J.I.; Haq, M.A.; Awan, N.A. Electron beam brazing of Zr62Al13Ni7Cu18 bulk metallic glass with Ti metal. Vacuum 2014, 101, 98–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, J.; Yu, P.; Wu, Y.; Chen, T.; Du, Y.; Yang, J. A Compact Review of Laser Welding Technologies for Amorphous Alloys. Metals 2020, 10, 1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Tang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, Y.; Wu, D. Development of Laser Fabrication Technology for Amorphous Alloys. Chinese Journal of Lasers-Zhongguo Jiguang 2021, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caiazzo, F.; Caggiano, A. Investigation of Laser Welding of Ti Alloys for Cognitive Process Parameters Selection. Materials 2018, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, R.; Zhao, Y.X.; Liu, H.B.; Oliveira, J.P.; Tan, C.W.; Xia, H.B.; Yang, J. Dissimilar laser spot welding of aluminum alloy to steel in keyhole mode. Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids 2022, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J. Mechanical manufacturing technology and precision machining technology. Proc. SPIE (USA) 2022, 12339, 123390M (123397 pp.)-123390M (123397 pp.). [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.F.; Li, Y. Bulk metallic glass formation near intermetallic composition through liquid quenching. Applied Physics Letters 2009, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhao, D.Q.; Pan, M.X.; Wang, W.H. Glass forming properties of Zr-based bulk metallic alloys. Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids 2003, 315, 206–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.R.; Zhang, S.; Shi, Z.L.; Wang, F.L.; Wei, C.; Ma, M.Z.; Liu, R.P. Corrosion behavior and mechanical properties of Vit1 metallic glasses prepared at different cooling rates. Journal of Alloys and Compounds 2023, 934, 167848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.M.; Guo, C.; Wu, S.S.; Li, Y.; Ying, M.; Kang, T.Y. Influence of Laser Pulse Welding Power on Welding Joints of Zr-Based Amorphous Alloys. Crystal Research and Technology 2022, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, P.S.; Sen, A.; Chattopadhyaya, S.; Sharma, S.; Singh, J.; Dwivedi, S.P.; Saxena, A.; Khan, A.M.; Pimenov, D.Y.; Giasin, K. Prediction of Transient Temperature Distributions for Laser Welding of Dissimilar Metals. Applied Sciences-Basel 2021, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Shi, T.; Li, M.; Wen, C.; Liao, G. Crystallization of Zr55Cu30Al10Ni5 Bulk Metallic Glass in Laser Welding: Simulation and Experiment. Advanced Engineering Materials 2015, 17, 483–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, L.; Ding, D.; Shan, S.T.; Dong, Y.D. Evaluation of the thermal stability of Nd60Al20Co20 bulk metallic glass. Applied Physics Letters 2007, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Wang, X.; Han, F.; Xie, H.; Wen, C.E. Thermal stability of the Al70Ni10Ti10Zr5Ta5 amorphous alloy powder fabricated by mechanical alloying. Journal of Alloys and Compounds 2010, 496, 313–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Zhang, Y.; Xia, L.; Yu, P. Kinetics and thermal stability of the Ni62Nb38–xTax(x=5, 10, 15, 20 and 25) bulk metallic glasses. Science China Physics, Mechanics & Astronomy 2017, 60, 076111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Cui, C.; Zhao, L.; Ding, J.; Cui, S.; Liu, S.; Sun, Y. Thermodynamic calculation and thermal stability of Al-Y-Ce-Ni metallic glass. Materials Research Express 2018, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Liang, W. Effect of room temperature ageing on structure and thermal stability of as-cast and deformed Pd40Ni40P20 metallic glass. International Journal of Modern Physics B 2018, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Wen, P.; Pan, M.X.; Zhao, D.; Wang, W.; Wang, W.L. A highly glass-forming alloy with low glass transition temperature. Applied Physics Letters 2003, 82, 4699–4701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, D.; Xia, L.; Shan, S.-T.; Dong, Y.-D. Long-term thermal stability of binary Cu50.3Zr49.7 bulk metallic glass. Chinese Physics Letters 2008, 25, 306–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.; Wang, C.; Ma, M.; Shan, D.; Guo, B. Non-isothermal crystallization kinetics of Zr41.2Ti13.8Cu12.5Ni10Be22.5 amorphous alloy. Thermochimic A Acta 2014, 587, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamasaki, M.; Kagao, S.; Kawamura, Y.; Yoshimura, K. Thermal diffusivity and conductivity of supercooled liquid in Zr41Ti14Cu12Ni10Be23 metallic glass. Applied Physics Letters 2004, 84, 4653–4655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Shi, T.L.; Li, M.; Yang, F.; Yan, F.; Liao, G.L. Laser welding of annealed Zr55Cu30Ni5Al10 bulk metallic glass. Intermetallics 2014, 46, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Figure 1.
Experimental amorphous alloy sample strips.
Figure 1.
Experimental amorphous alloy sample strips.
Figure 2.
Block to be observed.
Figure 2.
Block to be observed.
Figure 3.
Kissinger plot of ln(/α)vs. 1000/T for Vit1.
Figure 3.
Kissinger plot of ln(/α)vs. 1000/T for Vit1.
Figure 4.
VFT plot of ln(α) vs. T for Vit1.
Figure 4.
VFT plot of ln(α) vs. T for Vit1.
Figure 5.
Plots of VFT fitting and Kissinger fitting.
Figure 5.
Plots of VFT fitting and Kissinger fitting.
Figure 6.
VFT fitting and Kissinger fitting at a short time interval.
Figure 6.
VFT fitting and Kissinger fitting at a short time interval.
Figure 7.
Simulation model for laser welding.
Figure 7.
Simulation model for laser welding.
Figure 8.
The temperature field curve along the weld line at 300 W-12 mm/s.
Figure 8.
The temperature field curve along the weld line at 300 W-12 mm/s.
Figure 9.
The temperature field curve is normal to point Cat 300 W-12 mm/s.
Figure 9.
The temperature field curve is normal to point Cat 300 W-12 mm/s.
Figure 10.
The CHT curves and the temperature field curves.
Figure 10.
The CHT curves and the temperature field curves.
Figure 11.
Laser welding results, (a)-(d) corresponding to samples 1-4.
Figure 11.
Laser welding results, (a)-(d) corresponding to samples 1-4.
Figure 12.
Electron microscopy images of the heat-affected zone, (a)-(d) corresponding to samples 1-4.
Figure 12.
Electron microscopy images of the heat-affected zone, (a)-(d) corresponding to samples 1-4.
Figure 13.
SEM images of the welded zone, (a)–(d) correspond to samples 1–4.
Figure 13.
SEM images of the welded zone, (a)–(d) correspond to samples 1–4.
Figure 14.
XRD patterns of 4 samples.
Figure 14.
XRD patterns of 4 samples.
Figure 15.
The stress-strain curves from three-point bend tests.
Figure 15.
The stress-strain curves from three-point bend tests.
Figure 16.
Gripper laser welding results.
Figure 16.
Gripper laser welding results.
Table 1.
The characteristic temperature of Vit1.
Table 1.
The characteristic temperature of Vit1.
Heating
Rate (K/min) |
Tg (K) |
Tx (K) |
Tp1 (K) |
Tp2 (K) |
Tp3 (K) |
| 5 |
623 |
682 |
- |
726 |
- |
| 10 |
627 |
697 |
- |
735 |
- |
| 20 |
630 |
712 |
726 |
746 |
802 |
| 30 |
633 |
724 |
736 |
754 |
808 |
| 40 |
636 |
732 |
744 |
759 |
815 |
Table 2.
Parameters required in the simulation.
Table 2.
Parameters required in the simulation.
| Temperature (K) |
Specific Heat
(J·g−1·K−1) |
Thermal Conductivity
(W·m−1·K−1) |
Density
(×10−6 (kg·mm−3) |
| 300 |
0.382 |
4.5 |
6.12 |
| 440 |
0.411 |
6.5 |
6.12 |
| 580 |
0.523 |
10.8 |
6.12 |
| 650 |
0.724 |
14.6 |
6.13 |
| 700 |
0.543 |
17.0 |
6.19 |
Table 3.
Parameters used in laser welding.
Table 3.
Parameters used in laser welding.
| Sample Number |
Power (W) |
Speed (mm/s) |
| 1 |
300 |
3 |
| 2 |
300 |
6 |
| 3 |
300 |
9 |
| 4 |
300 |
12 |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).