1. Introduction
In recent years, with the rapid development of Internet of Vehicles (IoV) technology, various full scene intelligent driving schemes supporting the integration of driving and parking, such as Navigate on Pilot (NOP) and Navigate on Autopilot (NOA), have begun to be deployed in mass-produced vehicles [
1]. Car-following behavior and lane-changing behavior are the two most fundamental driving behaviors for point-to-point driving [
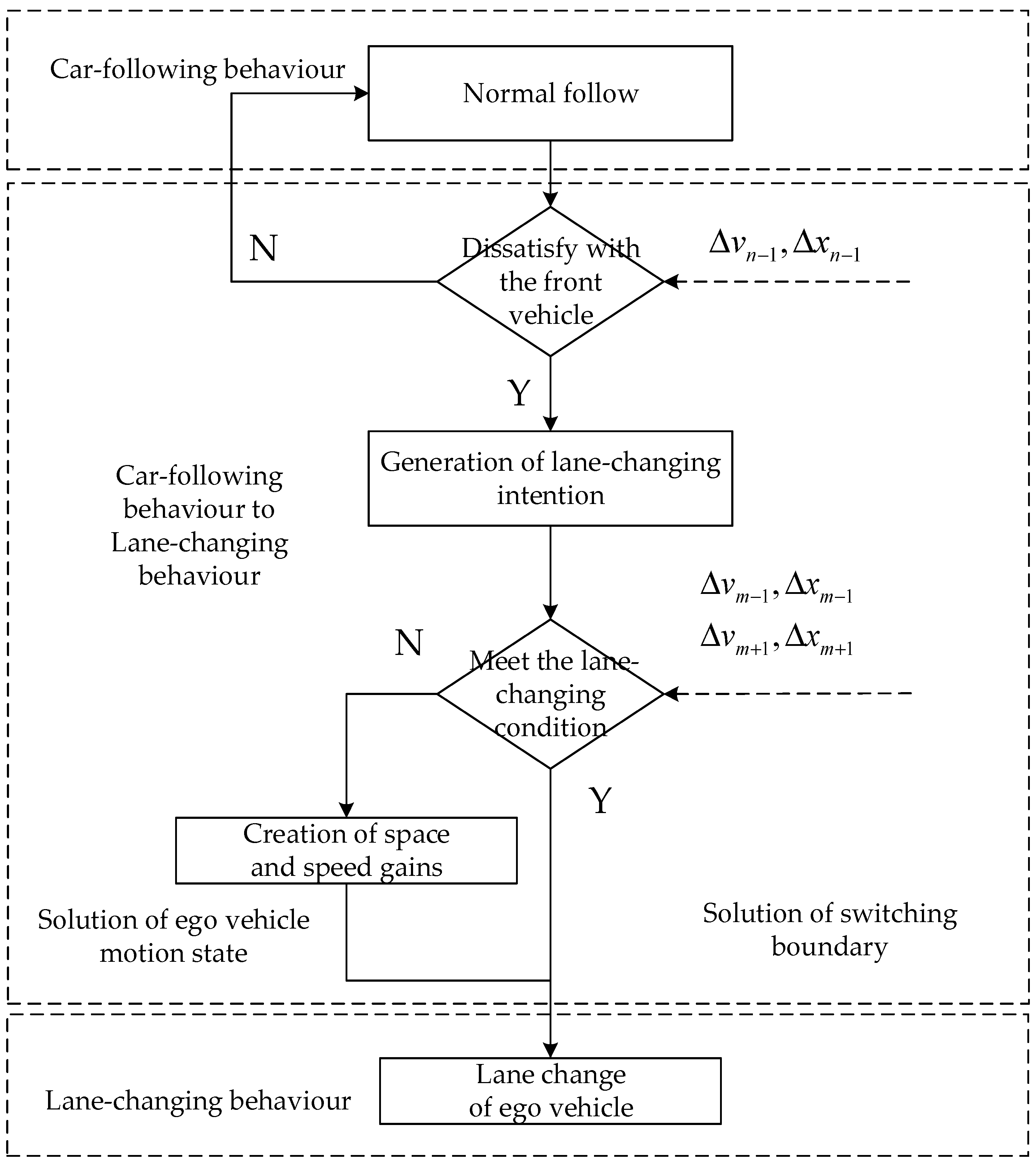
2]. In conjunction with the motion state of ego vehicle and surrounding interactive vehicles, it is necessary to frequently switch between the two categories of behavior. By studying the behavior switching mechanism from the driver's perspective, solving the switching boundary, and considering the vehicle constraints of the target lane for equivalent modelling, it is possible to achieve stepless switching between car-following behavior and lane-changing behavior, which has important theoretical significance and practical value for building point-to-point full scene intelligent driving.
The majority of car-following models are based on theory and rule-driven, and IDM is the most popular and most accurate prediction method [
3,
4]. In 2000, Treiber M et al. [
5] investigated the car-following behavior and proposed the IDM based on the influence of following distance and anticipated speed. Since then, specialists and academics have analyzed and optimized the IDM from a variety of perspectives. Qin P et al. [
6] optimized the applicable boundary of IDM based on road geometric conditions such as camber, superelevation, and slope. Yi Z et al. [
7] developed the Intelligent Back-looking Distance Driver Model (IBDM) with the influence of rear vehicles in the same lane. The Autonomous Vehicle-Intelligent Driver Model (AV-IDM) was created by Sharath M. and his team while taking into account circumferential environmental vehicles [
8]. Li Y et al. [
9] established a Long Short Term Memory-Intelligent Driver Model (LSTM-IDM) governed by data-rules capable of simulating extreme vehicle conditions such as static or extreme acceleration. Yang L. et al. [
10] added a cognitive risk coefficient to IDM based on driver behavior in ice and snow conditions and validated the model's efficacy and robustness. Jin P. et al. [
11] delved into the impact of data error accumulation on IDM precision and developed an error calibration function to reduce cumulative error. A hybrid flow simulation model, which merges IDM and Cooperative Adaptive Cruise Control (CACC), was developed by Chang X et al. [
12] in their study. The model's effectiveness was verified by its simulation in heterogeneous traffic flow. Hu X et al. [
13] established PS-IDM on the basis of IDM considering the change of driver's psychological state caused by the invasion of other vehicles, and demonstrated that PS-IDM can improve car-following performance effectively.
Lane-changing intention is caused by the driver's dissatisfaction with the current driving state causes, which compels the driver to generate space and speed gains prior to change lane through acceleration and deceleration in a specific time domain. Yuan W et al. [
14] defined eye movement parameters such as fixation time and saccade amplitude to effectively recognize a driver's lane-changing intention from the perspective of the driver's physiological characteristics. From the standpoint of the vehicle's motion state, there are currently two methodologies for lane-changing intention recognition of rule-driven and data-driven [
15]. In terms of rule-driven, Zhu N. et al. [
16] constructed dynamic and static risk fields based on the theory of artificial potential fields, and characterized the lane-changing risk by defining driver lane-changing planning and safety threshold. Chen H. et al. [
17] developed a dissatisfaction accumulation model based on the driver's anticipated speed in order to evaluate lane-changing decisions. Wang J. et al. [
18] introduced two quantitative indicators of lane-changing intensity and risk factor to devise and identify safe lane-changing conditions. Using the relative motion state of the ego vehicle and the surrounding vehicles, Ji X et al. [
19] established a data-driven LSTM model for recognizing driver's lane-changing intention. Guo Y. et al. [
20] developed a model for the recognition of lane-changing intentions based on the LSTM model of the attention mechanism. Zhao J. et al. [
21] proposed a recognition model of lane-changing intention that utilized a combination of convolutional neural network, gated recurrent neural network, and transformer model.
Presently, the majority of car-following models and lane-changing intention recognition models are independent of each other. The switching between car-following behavior and lane-changing behavior is a stepped switching across models, which results in poor smoothness and stability of switching during simulations or real-vehicle verifications. This paper was combined with the entire process of behavior switching from the normal following, the generation of lane-changing intention, the creation of lane-changing space and speed gains, and the execution of lane change. Taking the scenario of changing lane after following a large vehicle for a distance as an example, the IDM was calibrated using natural driving data, and the switching boundary was determined. The target lane vehicle constraint components were added to construct SSIDM based on the switching boundary, and the balance coefficients of SSIDM were determined by actual data. On the basis of the test set, the model's predictive accuracy was validated. The results demonstrate that the model can realize the car-following behavior to lane-changing behavior stepless switching equivalent to the driver's coherent driving behavior, and that the model's accuracy is high, which is crucial for the realization of point-to-point full scene intelligent driving simulation.
2. Behavior switching scenario mining
2.1. Natural driving data collection
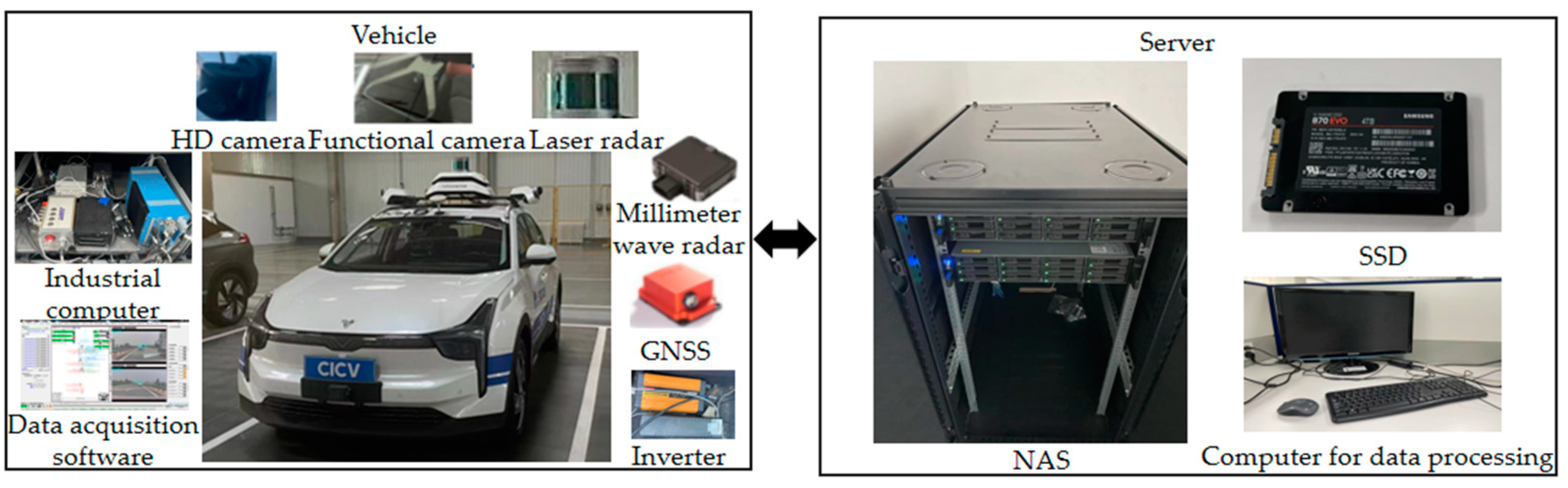
A data acquisition system was designed to collect information about the driver's natural driving behavior on open roads. As the test vehicle, an electric vehicle was equipped with functional camera, millimeter wave radar, laser lidar, GNSS and HD camera. The information of the circumferential targets was obtained by the target-level data fusion of the functional camera and the radar. The positioning, heading angle, road curvature and other information of the test vehicle were collected by GNSS. The high-performance industrial computer was connected with various sensors to obtain text and video data in real time. Concurrently, Network Attached Storage (NAS) equipment was deployed on the vehicle and office terminals to accomplish large-capacity storage, which communicated with industrial computers via high-speed network interfaces. 20 experienced drivers were recruited to execute driving tasks and the majority of the collection were structured roads, including highways and urban expressways. The entire system is shown in
Figure 1.
2.2. Behavior scenario mining
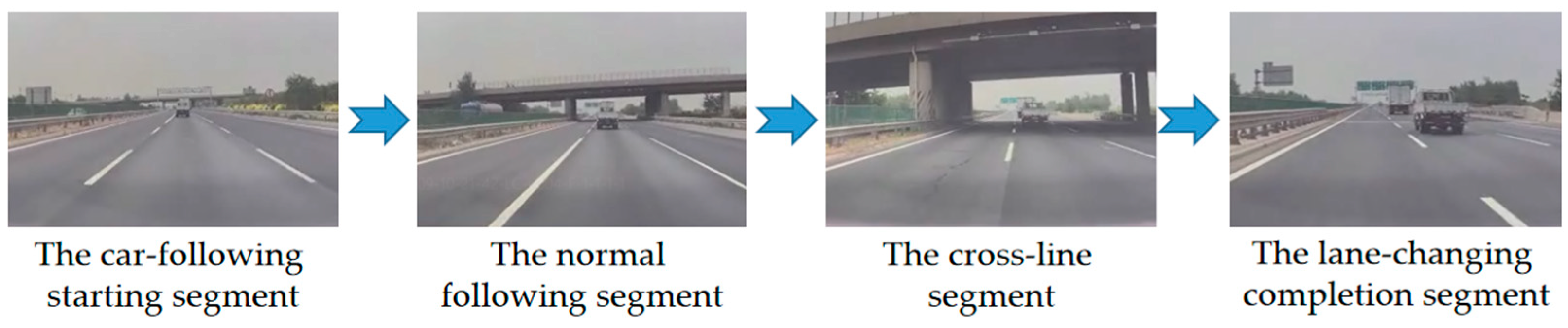
After cleaning multi-source heterogeneous original data, car-following behavior to lane-changing behavior scenario mining was performed. Initially, the switching behavior was defined, which included the car-following starting segment, the normal following segment, the cross-line segment, and the lane-changing completion segment. Among them, the starting segment of the car-following was defined as the constraints between the ego vehicle and the front vehicle in the ego lane, which including the distance constraint between the ego vehicle and the lane line, the speed constraint of the ego vehicle, the distance constraint between the front vehicle and the lane line, the distance constraint between the front vehicle and the ego vehicle, and the speed constraint of the front vehicle. The origin of the coordinates was defined as the center of the ego vehicle rear axle. The specific constraints are as follows.
where
Dn is the width of the ego vehicle,
W is lane width,
Ll and
Lr are the distance from the coordinate origin to the left and right lane lines,
vn is the ego vehicle speed,
Di is the width of each vehicle identified in the ego lane,
and
are the relative longitudinal and lateral distances between each vehicle identified in the ego lane and the ego vehicle,
is the relative longitudinal distance of the following target,
and
are the relative longitudinal distance thresholds between the ego vehicle and the following target,
is the following target speed.
The normal following segment was defined as the distance without mutation between the ego vehicle and the following target on the basis of satisfying the above conditions. All types of cut out and cut in scenarios were filtered out. The limitation is as follows.
where
is the distance mutation threshold.
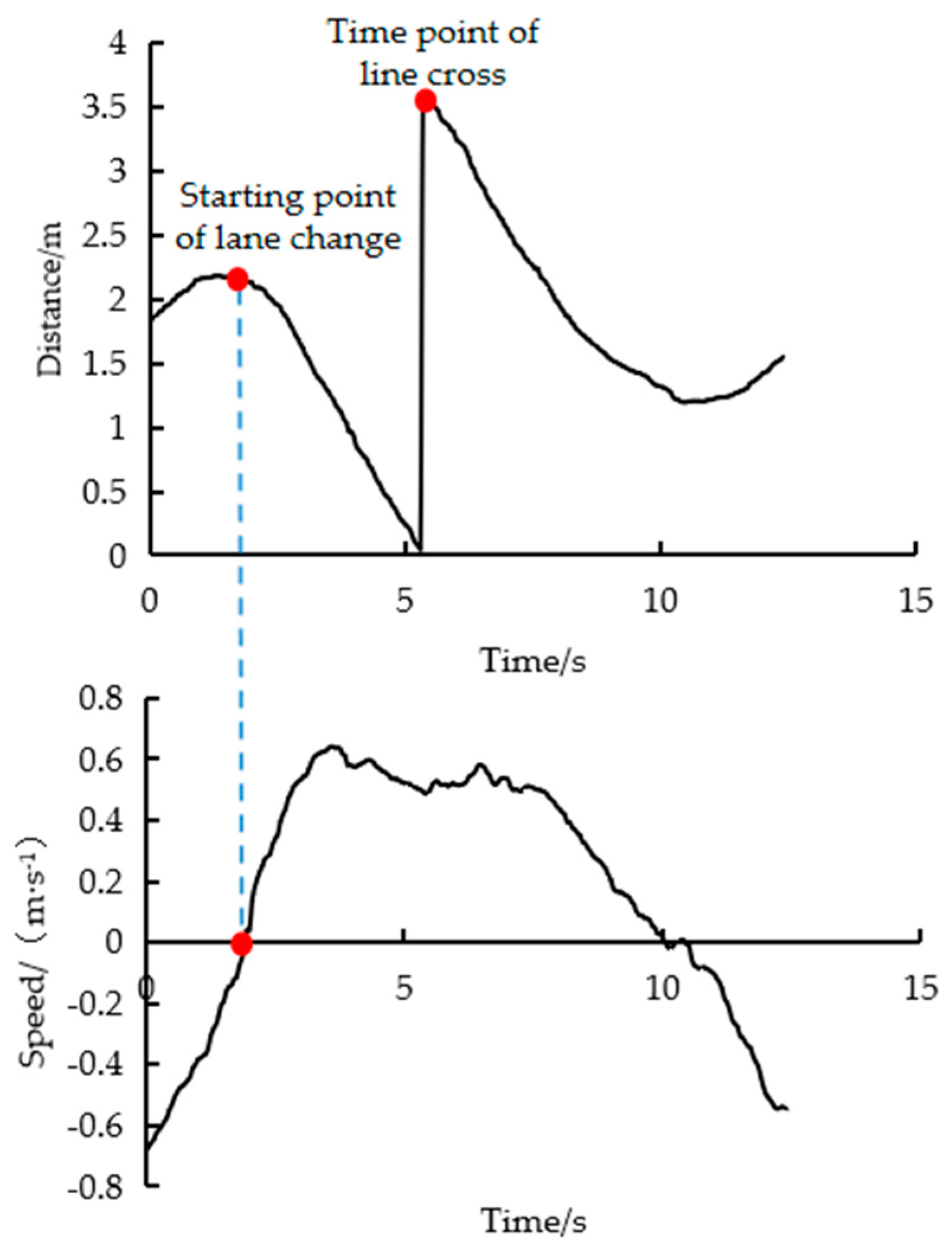
The cross-line segment was based on the lane line with the maximum level of confidence, which was defined as beginning to shift to the lane line on the lane-changing side until the distance changes abruptly. As shown in
Figure 2, the starting point of lane change was determined by the speed of the offset lane line, with the zero point of the offset speed change serving as the starting point.
Taking the steering wheel angle threshold and the distance threshold between the ego vehicle and the lane line as constraints, the constraints are as follows.
where
is the steering wheel angle,
and
are the lane line distance mutation threshold and the steering wheel angle threshold, respectively.
The lane-changing completion segment was defined by the vehicle stable driving in the target lane after crossing the line, and the comprehensive judgment was based on the yaw angle and steering wheel angle of the ego vehicle. When following large vehicles, drivers have a greater incentive to change lanes due to the safety principle. To eliminate the effect of the front vehicle type on the intention to change lanes, the variable was unified and the target type in front was restricted to large vehicle. Considering that the left lane is generally a fast lane, the left lane-changing scenario was finally selected.
Figure 3 depicts the mined scenario.
3. IDM parameter identification
3.1. IDM modeling mechanism
On the basis of the generalized force model, IDM for single lane car-following behavior was proposed. The research focused on alterations in traffic flow. It is capable of simulating the transition from free flow to congested flow, accounting for the acceleration trend in the free state of the vehicle and averting the deceleration trend of the front vehicle collision. It belongs to the expected measurement model and the specific expression is as follows.
where
is the driver's expected speed,
is the acceleration index,
is the maximum acceleration of the ego vehicle,
is the comfortable acceleration of the ego vehicle,
is the blocking interval,
is the expected headway,
is the relative speed of the ego vehicle and the front vehicle.
IDM can simulate the acceleration trend in a free flow. At this time, △
x(t) approaches infinity, and the IDM can be rewritten as follows.
In a congested flow state, the model can also be used to simulate the braking trend of the ego vehicle. At this time, the IDM can be simplified as follows.
3.2. Model parameter identification
Based on the Genetic Algorithm (GA) and actual data, IDM identification parameters were calibrated. As the objective function, the Root Mean Square Percentage Errors (RMSPE) were introduced. The predicted values and actual values of relative speed and relative distance were compared. The objective function is described as follows.
where
n is the total number of samples,
is the predicted relative distance between the two vehicles,
is the predicted ego vehicle speed.
The initial population was set to 100, and its population individuals were determined by a roulette wheel. The training set and test set were divided by 7:3 based on the typical car-following segment data. The parameter identification results are shown in
Table 1.
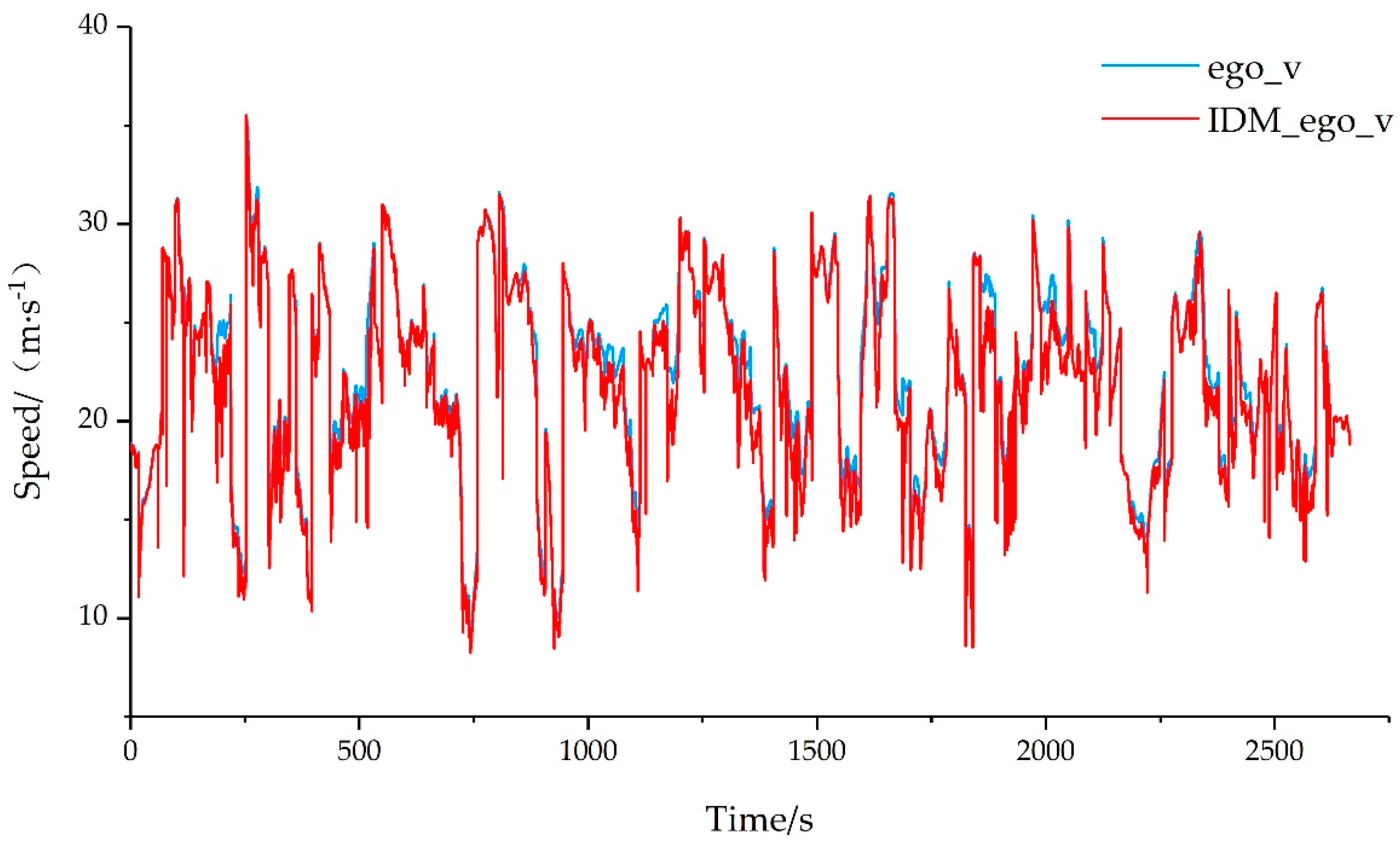
The identification results were verified based on the test set, and MSE was used to evaluate the speed prediction results of the ego vehicle. The comparison between the actual speed of the ego vehicle and the speed predicted by IDM is shown in
Figure 4.
The calculated MSE value for the test set was 0.749, representing an accurate identification result. For the behavior of following large vehicles, these identification results can be used to predict the motion state of the ego vehicle.
4. Construction of SSIDM
4.1. Modeling mechanism of SSIDM
IDM is proposed for car-following behavior in a single lane. In a broad sense, it is expressed that the vehicle will accelerate when it is far away from the front vehicle and decelerate when it is close to the front vehicle. However, in the actual car-following process, due to the dissatisfaction with the relative distance or speed of the front vehicle, the driver of ego vehicle will produce the intention of changing lane, and the decision is made through lane selection and whether to change lane. If the target lane has enough space and speed gains, the driver of ego vehicle will immediately change lanes, and the relative motion state between the ego vehicle and the front vehicle is defined as the switching boundary. If the target lane has front and rear vehicle constraints, the driver of ego vehicle will change motion state to create space and speed gains. This behavior still belongs to following, but the influence of the target lane vehicles needs to be considered on the basis of the single lane IDM. The relative distances between the vehicle and the front and rear vehicles of the target lane were defined as and , and the relative speeds between the vehicle and the front and rear vehicles of the target lane were defined as and . The SSIDM modeling mechanism for car-following behavior to lane-changing behavior switching is as follows.
Figure 5.
Modeling mechanism.
Figure 5.
Modeling mechanism.
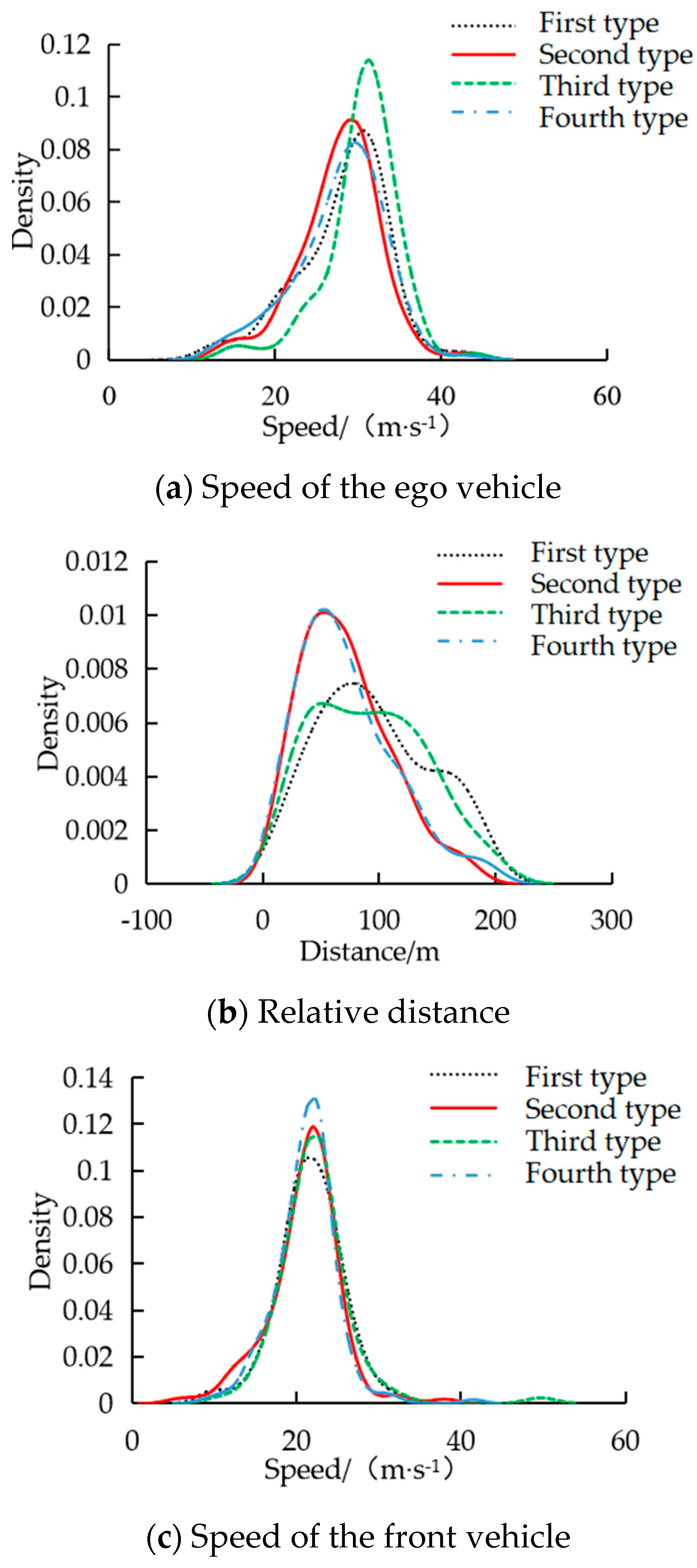
Based on whether the target lane has constrained vehicles, all segments were divided into four categories: only affected by the front vehicle of the ego lane, affected by the front vehicle of the ego lane and the front vehicle of the target lane, affected by the front vehicle of the ego lane and the rear vehicle of the target lane, affected by the front vehicle of the ego lane and the front and rear vehicles of the target lane. In order to characterize the differences of behavior switching boundary, four types of scenarios were analyzed, and the independence between variables was considered. Finally, the speed of the ego vehicle, the relative distance from the front vehicle and the speed of the front vehicle were taken as the characteristic parameters to obtain the statistics of the key parameters of the lane -changing starting point about each type of scenarios.
Table 2.
Statistical result.
Table 2.
Statistical result.
| Statistic |
Mean Value |
Standard Deviation |
| First type |
/(m·s-1) |
28.108 |
5.491 |
|
/m |
95.569 |
48.412 |
|
/(m·s-1) |
21.602 |
3.915 |
| Second type |
/(m·s-1) |
27.788 |
4.879 |
|
/m |
71.472 |
38.233 |
|
/(m·s-1) |
20.998 |
3.697 |
| Third type |
/(m·s-1) |
30.424 |
4.426 |
|
/m |
91.829 |
47.457 |
|
/(m·s-1) |
21.209 |
3.581 |
| Fourth type |
/(m·s-1) |
27.811 |
5.393 |
|
/m |
72.232 |
41.618 |
|
/(m·s-1) |
21.178 |
3.763 |
In order to analyze the characteristics of the parameters, the kernel density estimation of these three types of parameters was carried out. The kernel density curves corresponding to the speed of the ego vehicle, the relative distance from the front vehicle and the speed of the front vehicle are shown in
Figure 6.
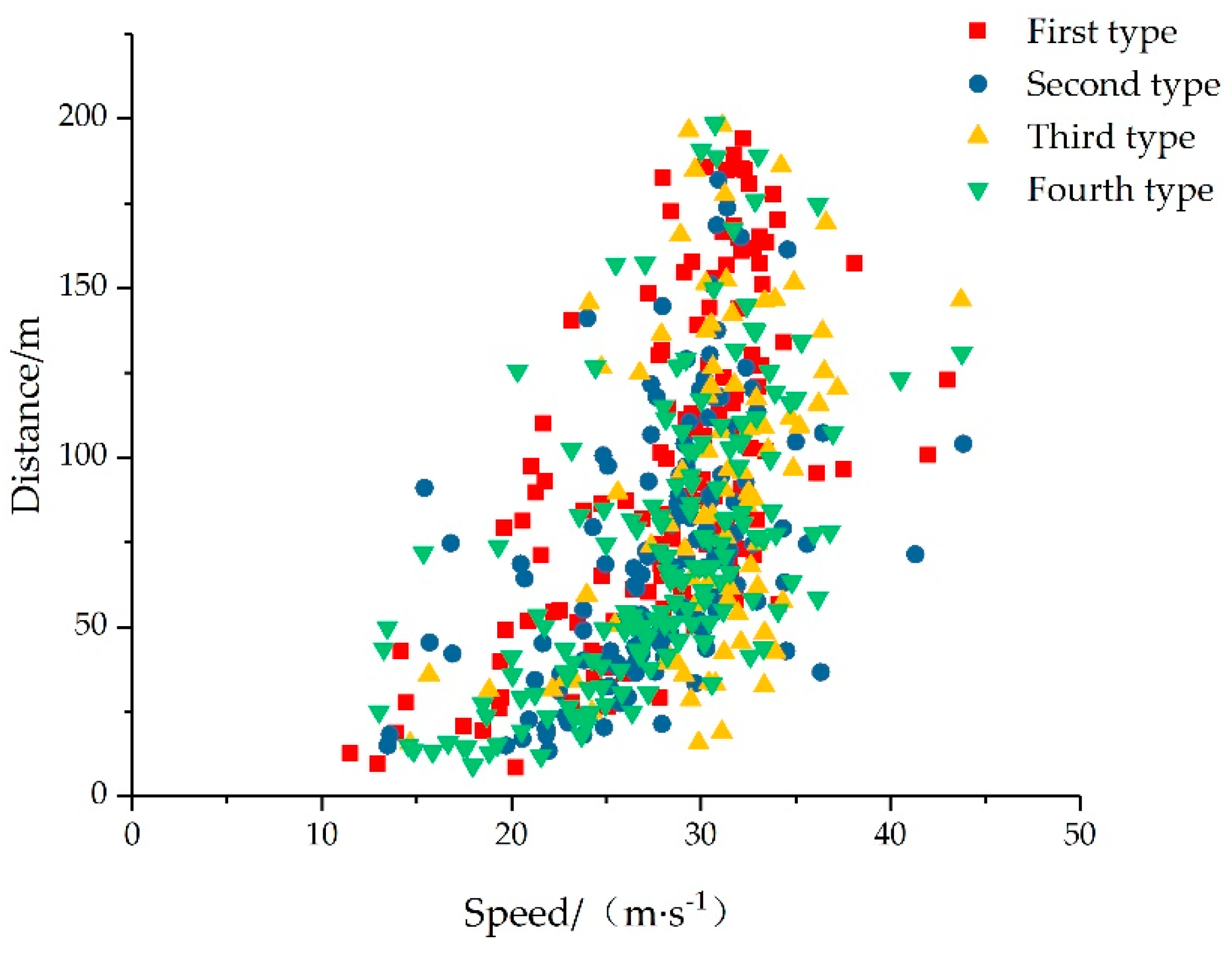
Through the analysis of the statistical table and the kernel density estimation curves, it can be concluded that for the second and fourth types of scenarios, the relative distance between the ego vehicle and the following front vehicle is the closest. Due to the influence of the front vehicle on the target line, it is necessary to have enough space benefit of lane change. For the third type of scenario, the ego vehicle speed is the largest. Because the target lane in the third type of scenario has a rear vehicle, the ego vehicle needs to accelerate to exceed the vehicle of the target lane to create lane-changing space. The speed of the following vehicle in the four scenarios is basically consistent and concentrated. The ego vehicle speed was defined as the input independent variable, it can be judged that the ego vehicle speed at the initial point of lane change is mainly affected by the relative distance from the front vehicle in these four scenarios. The relationship between the ego vehicle speed and the relative distance of the front vehicle in four scenarios is shown in
Figure 7.
4.2. Solution of switching boundary conditions
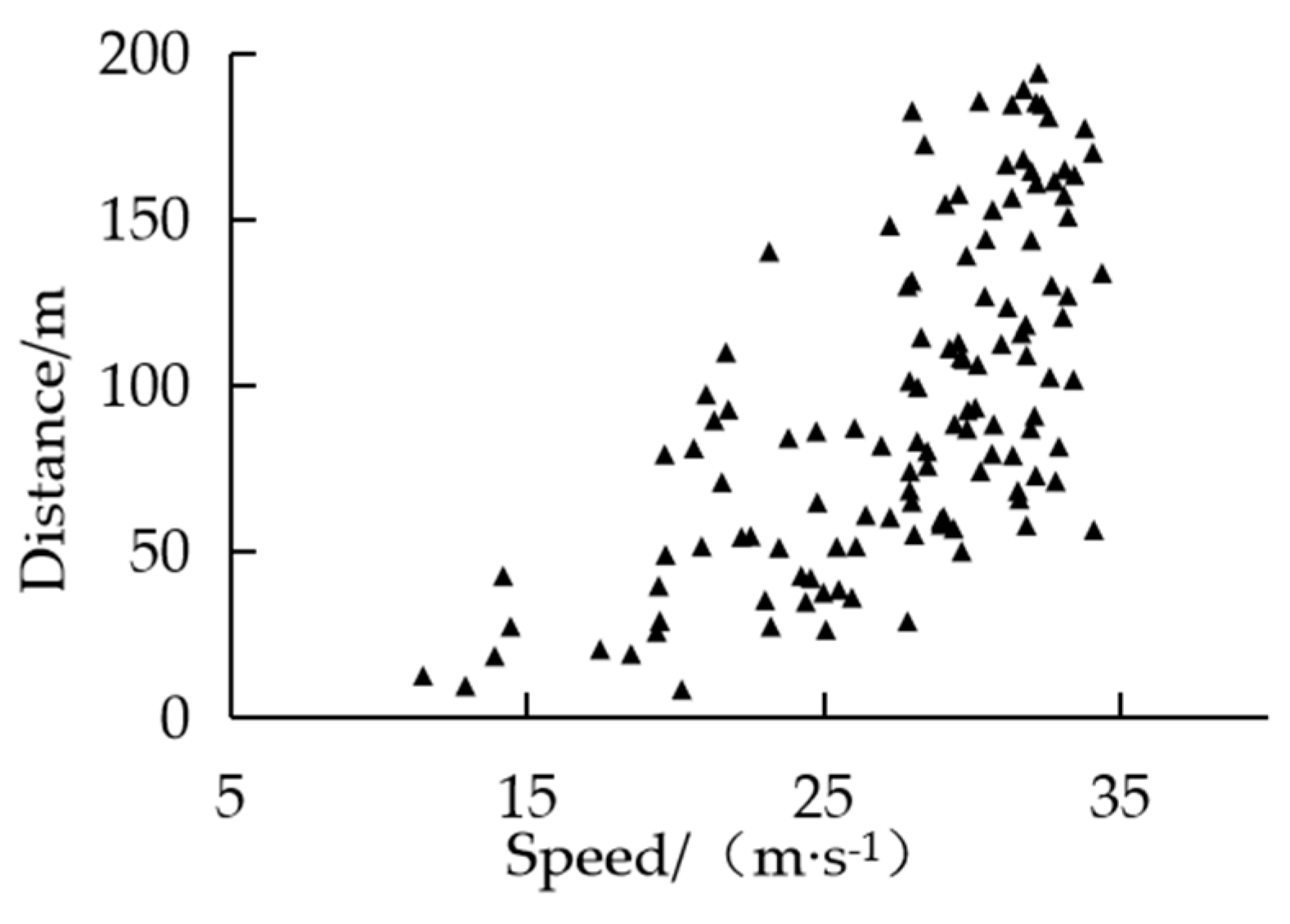
Considering that the drivers' response time is short, if the target lane has no front and rear vehicle constraints, the lane change will be carried out immediately when the tolerance boundary is reached. So the initial point of lane change in the first type of scenario can be directly defined as the drivers' tolerance boundary. The scatter distribution of the relative distance between the ego vehicle and the target vehicle in the first type of scenario is shown in
Figure 8.
It can be seen from
Figure 8 that the shape of the scatter distribution is approximately to the convex function, so various commonly convex functions were used for fitting. Based on GA, the fitting parameters were optimized and evaluated by goodness of fitting. The identification evaluation results are shown in
Table 3.
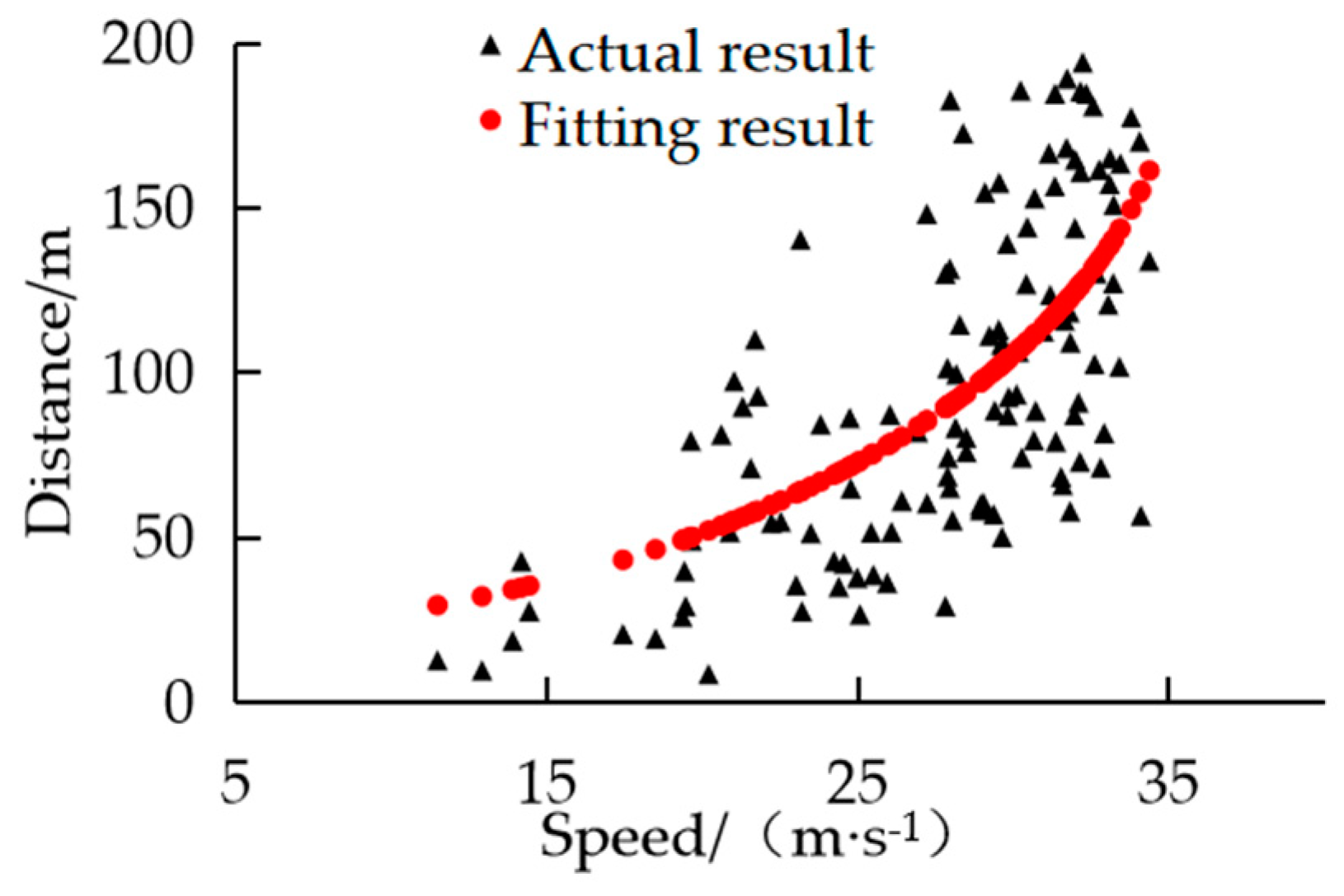
By analyzing
Table 3, the elliptic curve has the highest goodness of fitting, so the elliptic equation was finally selected to characterize the tolerance boundary conditions. The fitting results are shown in
Figure 9.
This switching boundary can constrain the car-following behavior of large vehicles in front of the ego vehicle. When there are no interacting vehicles in the target lane, the relative distance from the front vehicle of ego lane reaches this switching boundary, the ego vehicle changes lanes and the IDM fails.
4.3. Model Unified Expression
In the second, third and fourth types of scenarios, if the switching boundary is reached but there is no lane-changing space or speed gains, the driver will change the motion state of the ego vehicle to generate lane change gains. Referring to the statistical distribution and kernel density estimation of the characteristic parameters of the four types of scenarios, a deceleration component was defined for the front vehicle of the target lane to ensure that the vehicle has sufficient lane change gains.
For the rear vehicle of the target lane, an acceleration component was defined to ensure that the vehicle has enough lane-changing space.
On the basis of IDM, the front and rear vehicle constraint components of the target lane were added. Considering the influence degree of the target lane vehicles on the ego vehicle, the dimensionless balance coefficients were added before the two components, and the vehicle acceleration can be obtain as follows.
where
and
are the balance coefficients of the front and rear vehicle components of the target lane respectively.
When there is a certain lane-changing space and speed gains, the driver of ego vehicle begins to change the lane. It is defined that there is enough lane changing space when the front and rear vehicles of the target lane meet the safety distance and the distance between the front vehicle of the target lane and the ego vehicle is greater than the distance between the front vehicle of the ego line and the ego vehicle, and there is enough speed gains when the speed of the front vehicle of the target lane is greater than the speed of the front vehicle of the ego lane. This termination condition is used as the initial point of lane change in the second, third and fourth types of scenarios.
where
is the safety distance threshold between the interactive vehicles in the target lane and the ego vehicle.
Finally, the complete SSIDM expression considering the front and rear vehicle constraints of the target lane can be obtained.
- (1)
When the target lane has no front and rear vehicle constraints.
- (2)
When the target lane has front or rear vehicle constraints.
5. Model validation
5.1. SSIDM identification
Combining the switching boundary fitted by the first type of scenario, the switching boundary conditions in the second, third and fourth types of scenarios were taken as the starting point, and the corresponding fragments were intercepted at the starting point of lane change. According to the 7:3 ratio, the intercepted fragments were assigned to the training set and the test set. In SSIDM, the two component balance coefficients were identified and calibrated using the GA method and training set. The final identification results are shown in
Table 4.
5.2. Comparison of results
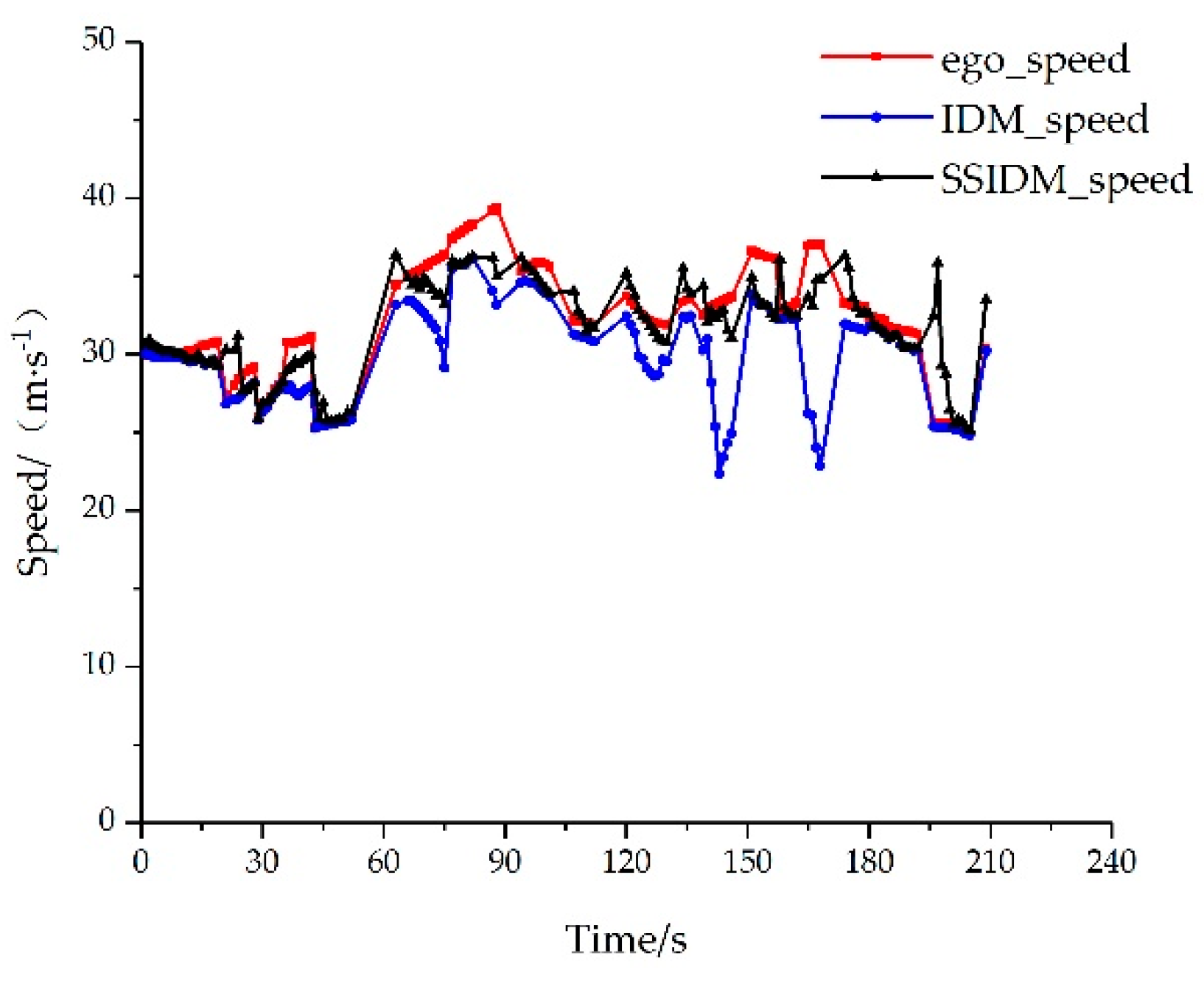
For the second type of scenario, the test set was input into IDM and SSIDM respectively. The comparison between the prediction results of the two types of models and the actual speed is shown in
Figure 10.
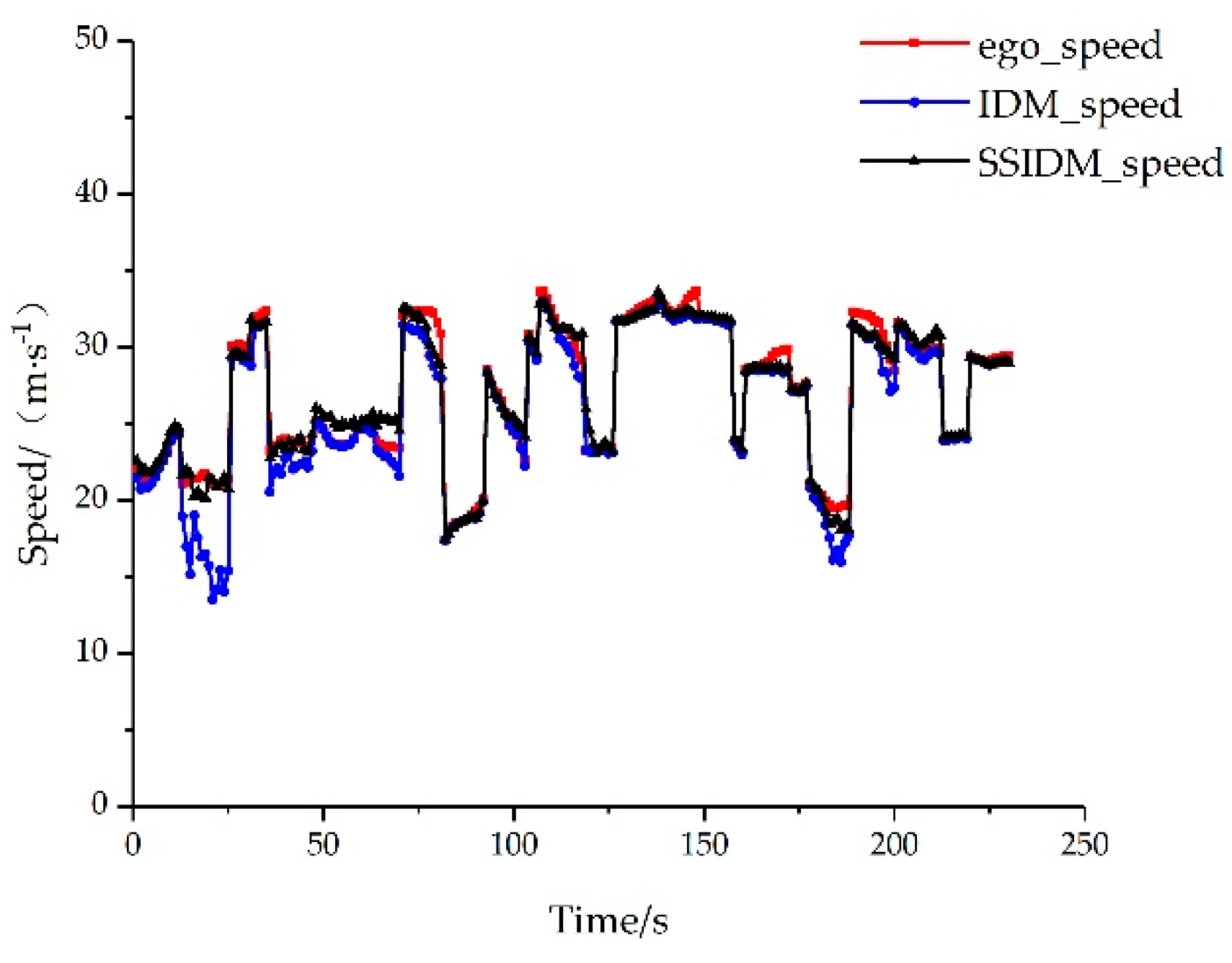
For the third type of scenario, the test set was input into IDM and SSIDM respectively, and the comparison between the prediction results and the actual speed is shown in
Figure 11.
For the fourth type of scenario, the test set was input into IDM and SSIDM respectively, and the speed prediction results of the ego vehicle were compared with the actual speed, as shown in
Figure 12.
Using MSE as the error comparison index, the comparison error of IDM and SSIDM on the ego vehicle speed prediction for the second, third, and fourth types of scenarios can be calculated as follows.
By adding the constraint components of the front and rear vehicles of the target lane, SSIDM can effectively simulate the acceleration and deceleration of the ego vehicle after reaching the tolerance boundary, according to the analysis of
Table 5. The vehicle speed prediction accuracy is greater than that of the traditional single-line IDM, and the mean value of MSE is 57.98% less than that of IDM.
6. Conclusions
(1) Through the classification statistics and kernel density estimation of the switching scenario key features, it can be obtained that the driver will generate the lane-changing intention and execute the lane-changing behavior during the car-following process. However, due to the influence of the target lane interaction vehicles, there are some differences in the speed of the ego vehicle and the relative distance from the front vehicle at the beginning of lane change in the four categories of scenarios. At this time, the single-lane IDM cannot simulate the vehicle's motion state.
(2) The mechanism of switching between the car-following behavior and lane-changing behavior was analyzed. Combined with the first type of scenario, the tolerance boundary was fitted based on the elliptic equation, and the goodness of fitting is 0.572. Based on this boundary, the target lane vehicle constraint components were added to construct SSIDM. The model consistently expressed the coherent driving behavior that can encompass normal following, generate lane-changing intention and create lane-changing space and speed gains.
(3) The prediction results of IDM and SSIDM for the second, third, and fourth scenarios were validated through a comparison with the actual collected data. The average MSE for SSIDM is 2.172, which is 57.98% less than IDM. Therefore, The SSIDM considering the tolerance boundary and adding the vehicle constraints of the target lane can simulate the acceleration and deceleration to create lane-changing space and speed gains to equivalent driver behavior. The SSIDM can also achieve the car-following behavior to lane-changing behavior stepless switching, which accuracy is higher than that of IDM for single lane.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, R.F.; validation, R.F.; formal analysis, R.F.; investigation, R.F.; data processing, R.F.; writing—original draft preparation, R.F.; writing—review and editing, R.F. Author has read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Beijing Science and Technology Plan Project under grant number Z211100004221016.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Miao, L.; Wang, F. Review on Research and Applications of V2X Key Technologies. Chin. J. Automot. Eng. 2020, 10, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, X. Motion Control and Decision Planning for Car Following and Lane Changing of Autonomous Vehicle. Jilin University, Changchun, China, 2022.
- Zhu, M.; Wang, X.; Tarko, A.; Fang, S. Modeling car-following behavior on urban expressways in Shanghai:A naturalistic driving study. Transp. Res. Part. C. Emerg. Technol. 2018, 93, 425–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Sun, P.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, K. Calibrating Car-following Models on Freeway Based on Naturalistic Driving Data. China J. Highw. Transp. 2020, 33, 132–142. [Google Scholar]
- Treiber, M.; Hennecke, A.; Helbing, D. Congested traffic states in empirical observations and microscopic simulations. Phys. Rev. E: Stat. Phys., Plasmas, Fluids, Relat. Interdiscip. Top. 2000, 62, 1805–1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, P.; Pei, S.; Yang, C.; Meng, Q.; Wan, Q. Influence of Road Geometrics on Car-following of the Intelligent Driver Model. J. Transp. Syst. Eng. Inf. Technol. 2017, 17, 77–84. [Google Scholar]
- Yi, Z.; Lu, W.; Xu, L.; Qu, X.; Ran, B. Intelligent back-looking distance driver model and stability analysis for connected and automated vehicles. J. Cent. South Univ. (Sci. Technol.). 2020, 27, 3499–3512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharath, M.; Velaga, N. Enhanced intelligent driver model for two-dimensional motion planning in mixed traffic. Transp. Res. Part. C. Emerg. Technol. 2020, 120, 102780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Lu, X.; Ren, C.; Zhao, H. Fusion Modeling Method of Car-Following Characteristics. IEEE Access, 2019, 7, 162778–162785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Zhang, C.; Qiu, X.; Wu, Y.; Li, S.; Wang, H. Car-following Behavior and Model of Chinese Drivers under Snow and Ice Conditions. J. Transp. Syst. Eng. Inf. Technol. 2020, 20, 145–155. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, P.; Yang, D.; Ran, B. Reducing the Error Accumulation in Car-Following Models Calibrated With Vehicle Trajectory Data. IEEE. Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2014, 15, 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, X.; Li, H.; Rong, J.; Qin, L.; Yang, Y. Analysis on fundamental diagram model for mixed traffic flow with connected vehicle platoons. J. Southeast Univ., Nat. Sci. Ed. 2020, 50, 782–788. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, X.; Zheng, M.; Zhao, J.; Long, B.; Dai, G. Stability Analysis of Mixed Traffic Flow Considering Personal Space under the Connected and Automated Environment. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 3231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, W.; Fu, R.; Guo, Y.; Peng, J.; Ma, Y. Drivers Lane Changing Intention Identification Based on Visual Characteristics. China J. Highw. Transp. 2013, 26, 132–138. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, R.; Zhang, H.; Liu, W.; Zhang, H. Review on driver intention recognition. J. Chang'an Univ., Nat. Sci. Ed. 2022, 42, 33–60. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, N.; Gao, Z.; Hu, H.; Lu, Y.; Zhao, W. Research on Personalized Lane Change Triggering Based on Traffic Risk Assessment. Automot. Eng. 2021, 43, 1314–1321. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Wang, J. A Decision-making Method for Lane Changes of Automated Vehicles on Freeways Based on Drivers Dissatisfaction. China J. Highw. Transp. 2019, 32, 1–9+45. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Gao, C.; Zhu, Z.; Yan, X. Multi-lane Changing Model with Coupling Driving Intention and Inclination[J]. PROMET-ZAGREB, 2017, 29, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, X.; Fei, C.; He, X.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y. Intention Recognition and Trajectory Prediction for Vehicles Using LSTM Network. China J. Highw. Transp. 2019, 32, 34–42. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wang, C.; Sun, Q.; Li, W. Driver Lane Change Intention Recognition in the Connected Environment. Phys. A (Amsterdam, Neth.). 2021, 575, 126057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Zhao, Z.; Qu, Y.; Xie, D.; Sun, H. Vehicle Lane Change Intention Recognition Driven by Trajectory Data. J. Transp. Syst. Eng. Inf. Technol. 2022, 22, 63–71. [Google Scholar]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).