Submitted:
12 June 2023
Posted:
13 June 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Project Summary
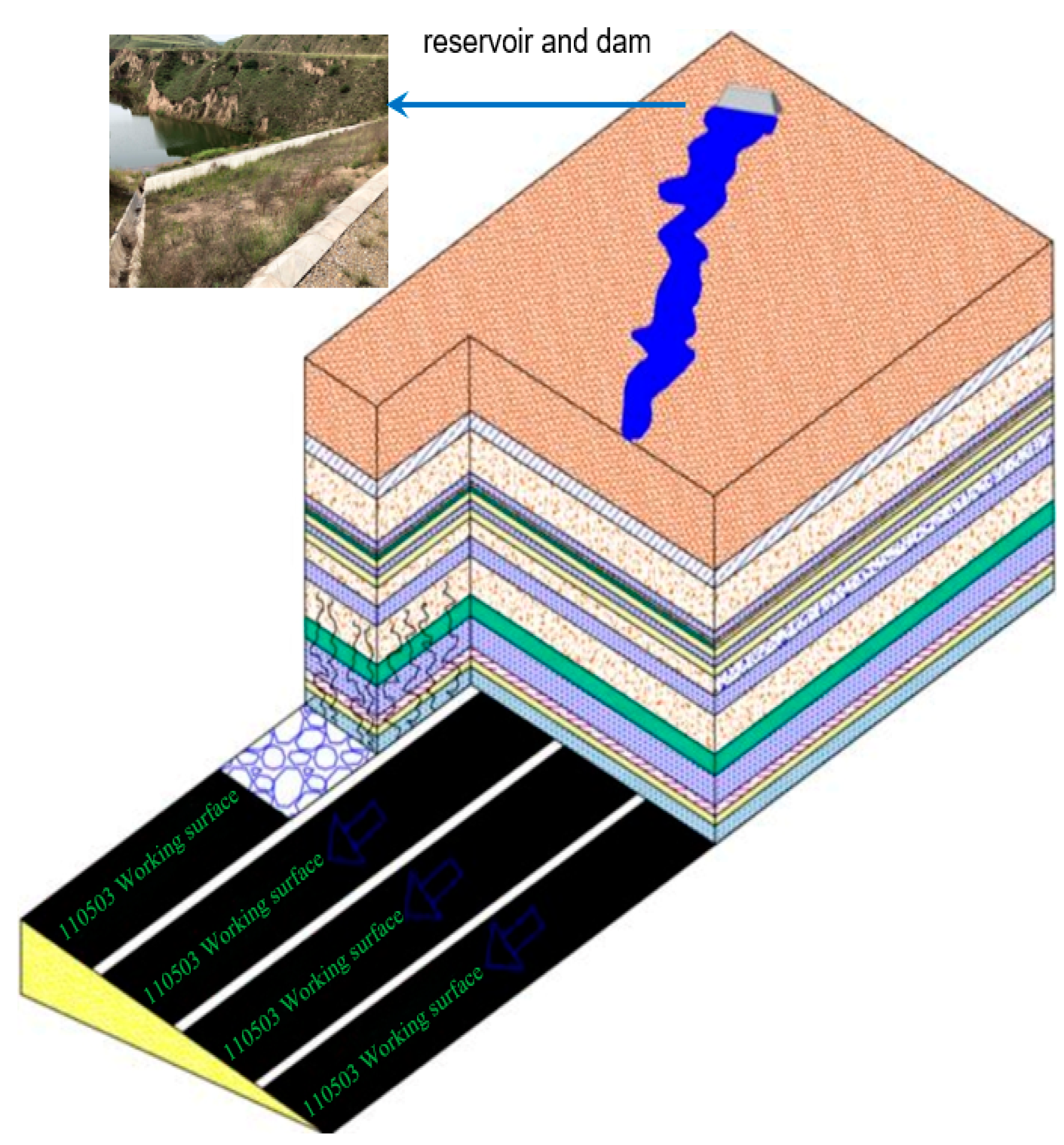
3. Analysis of fracture evolution of high-intensity mining overburden under reservoir dams
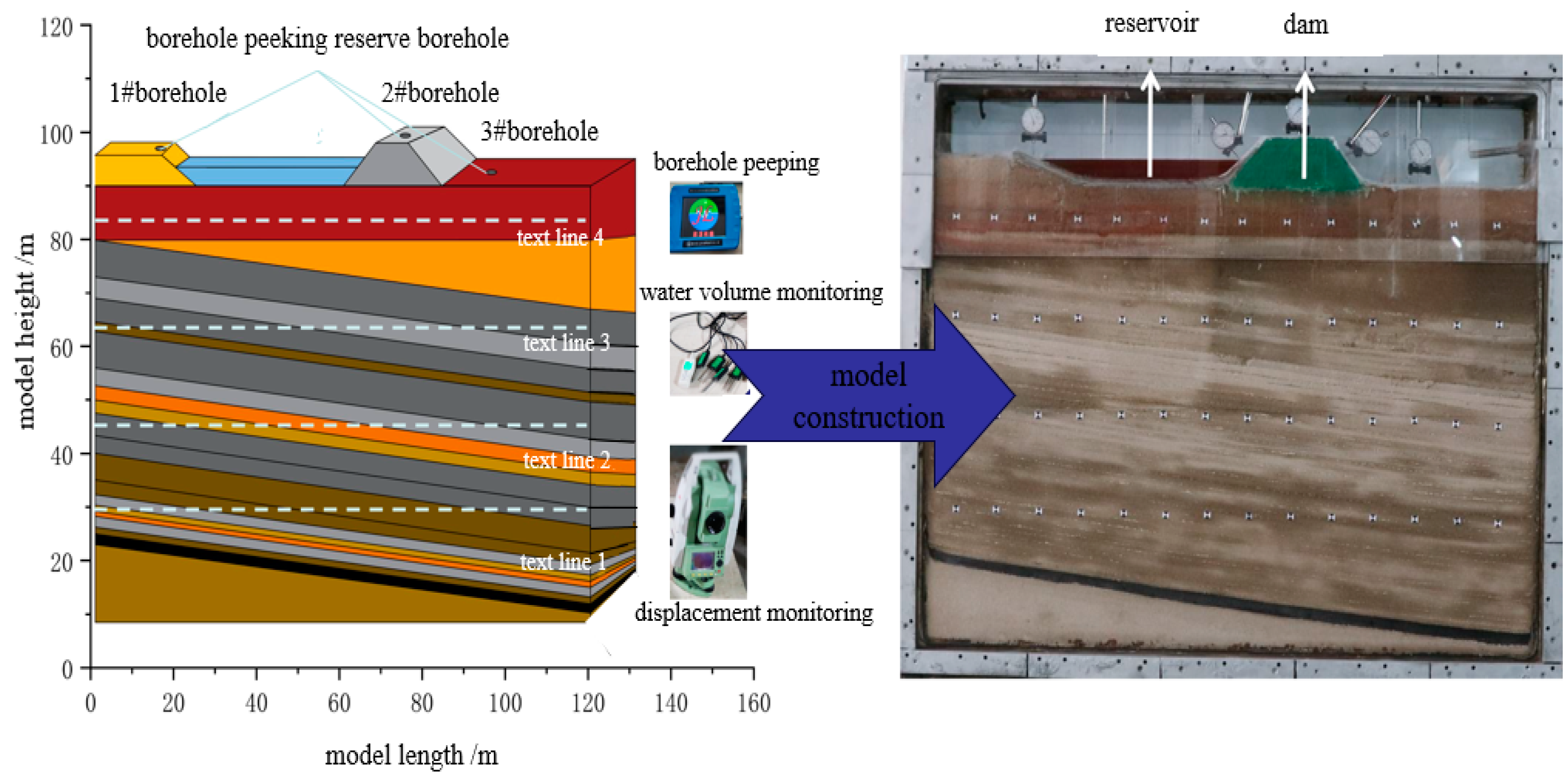
3.1. Experimental design of physical simulation
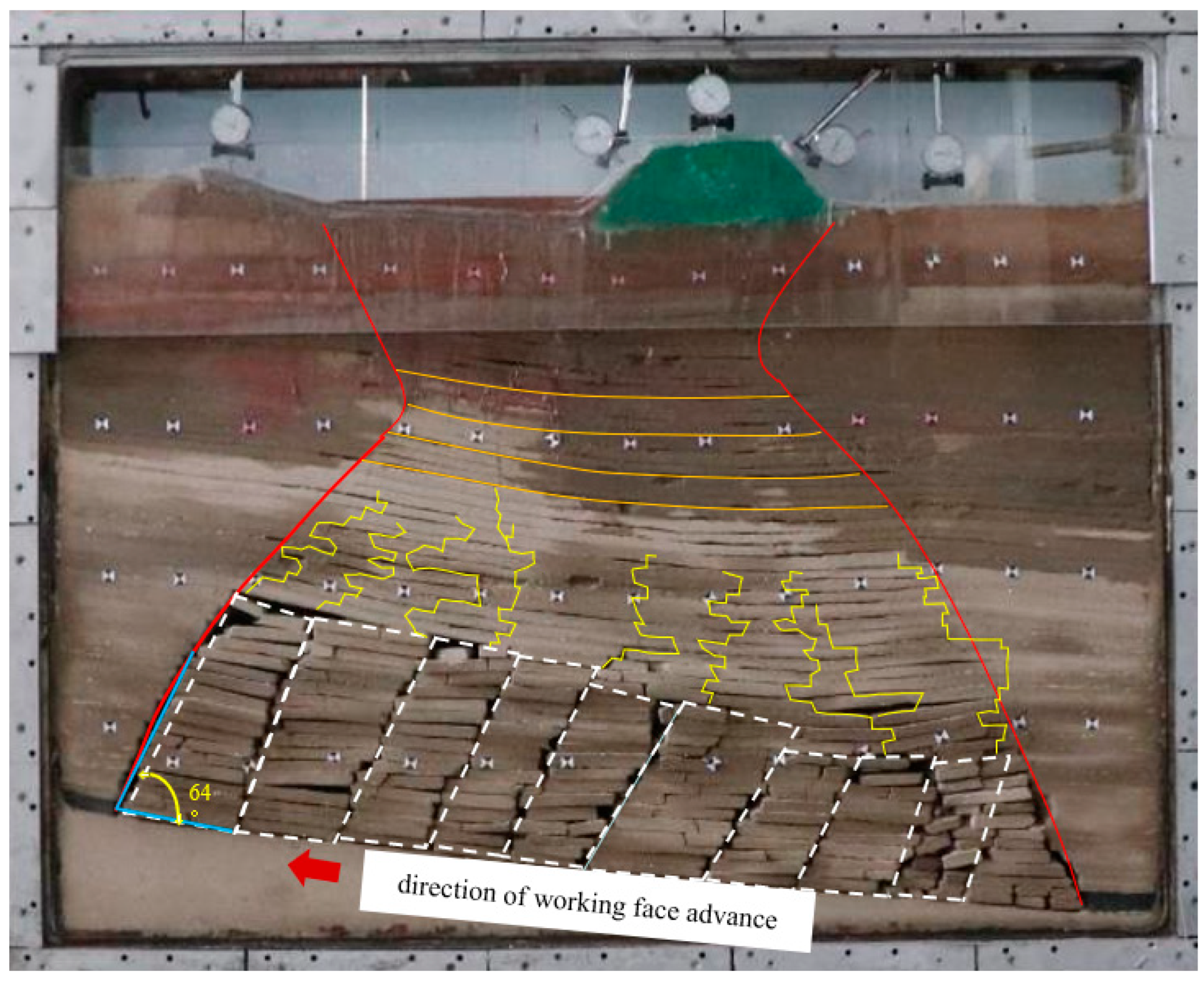
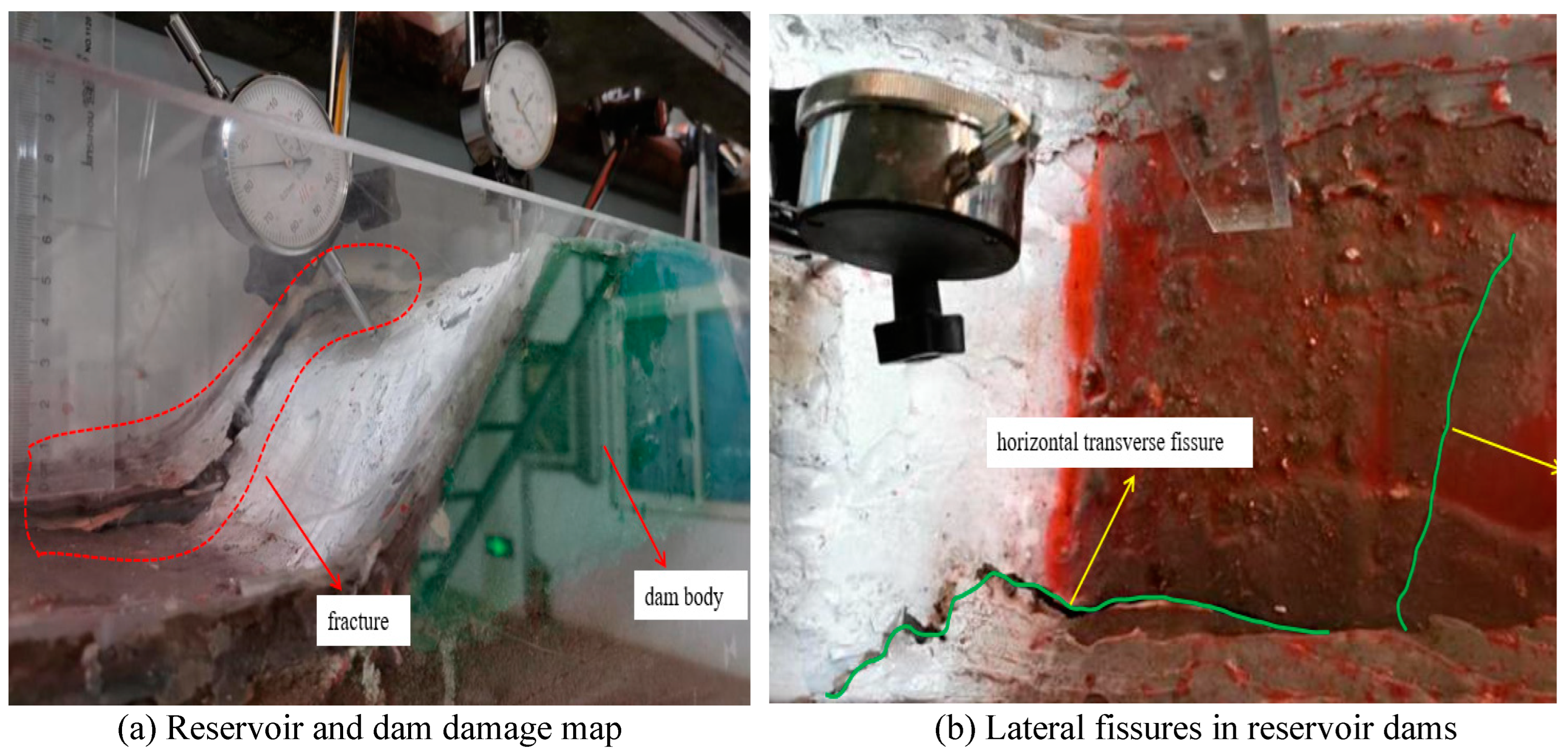
3.2. Overlying rock layers and dam body rock transport evolution pattern
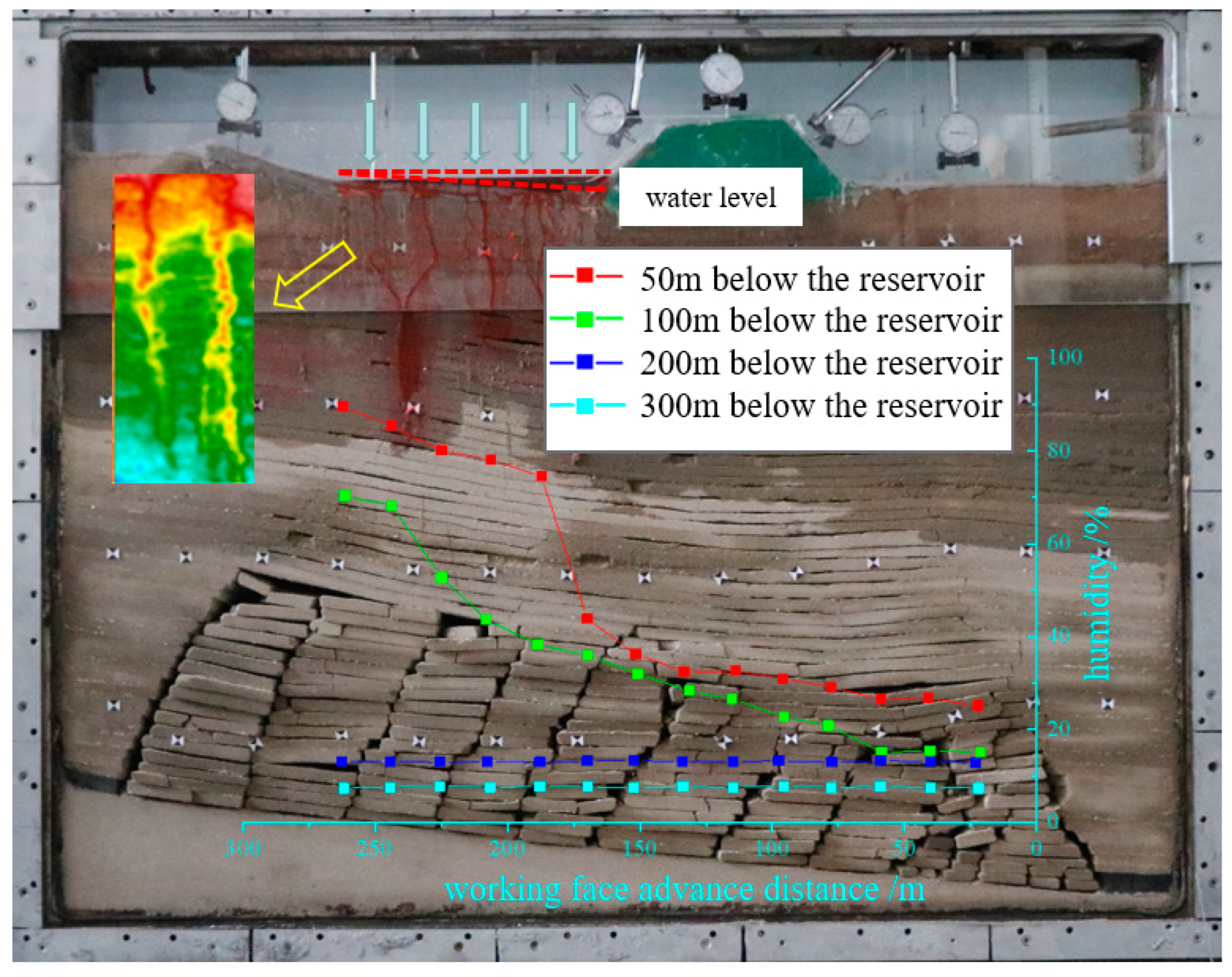
3.3. Reservoir water seepage pattern
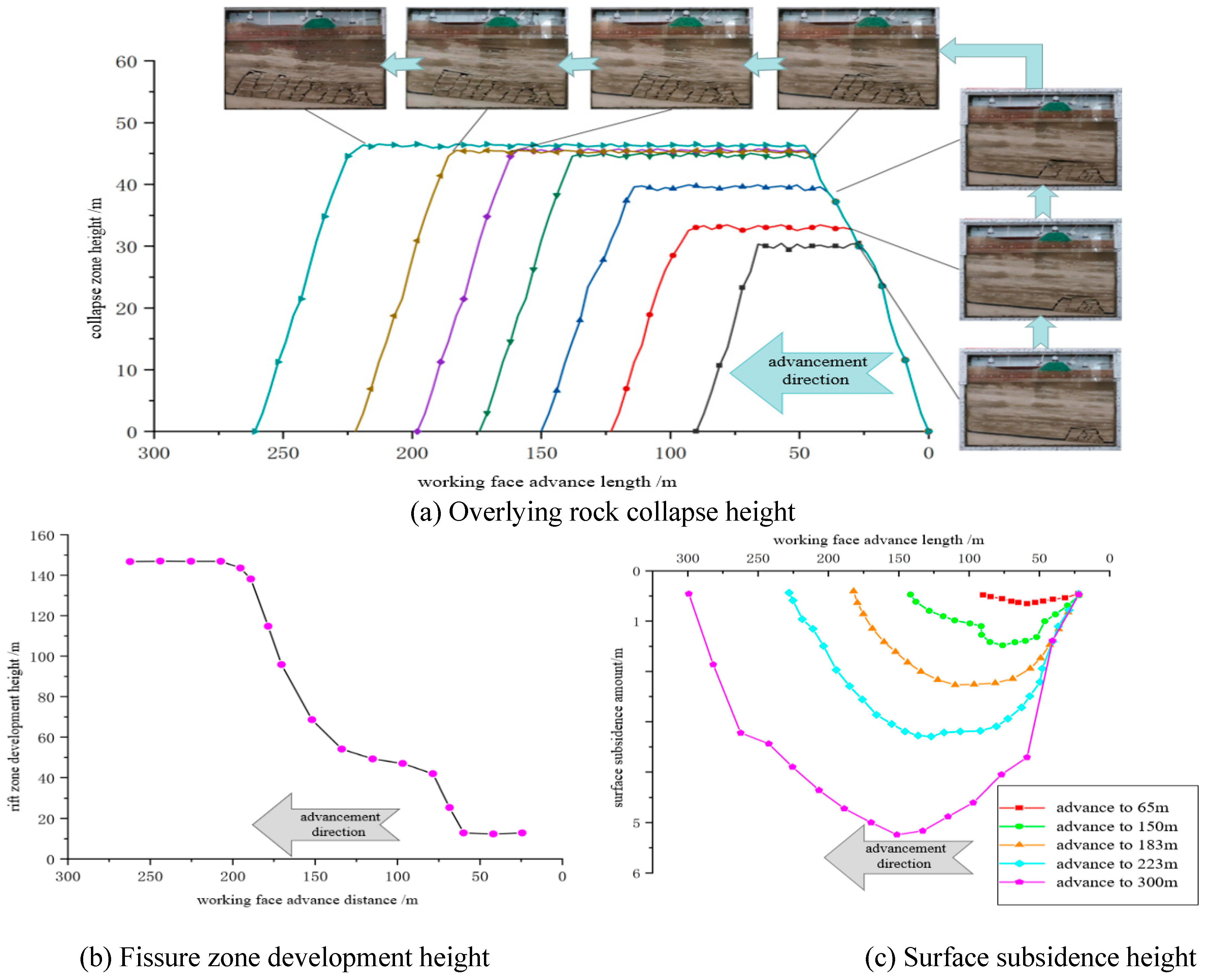
3.4. Overlying rock fracture development characteristics
4. Simulation analysis of overburden rock under different mining intensity of fracture
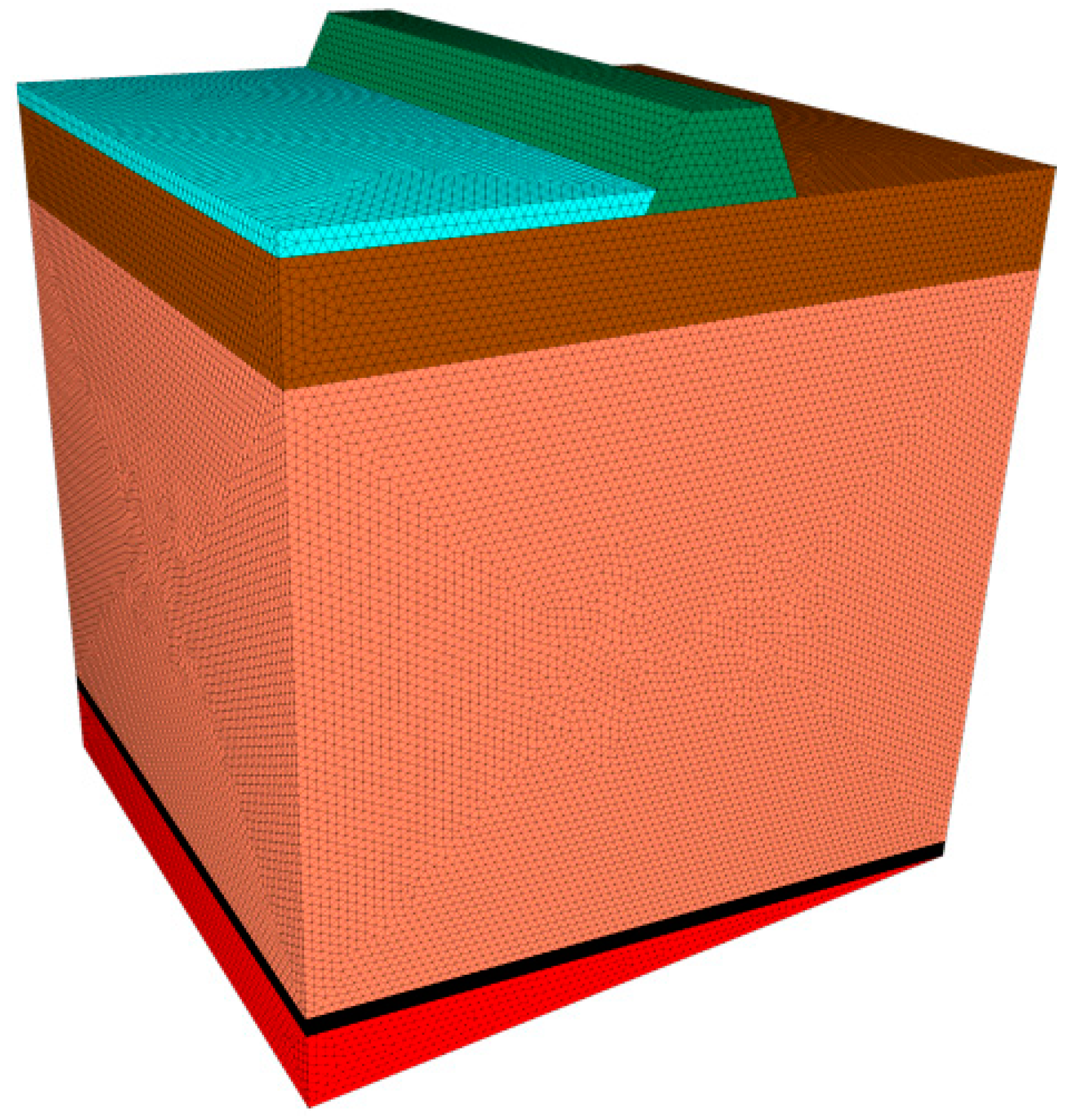
4.1. Numerical modeling of fluid-solid coupling
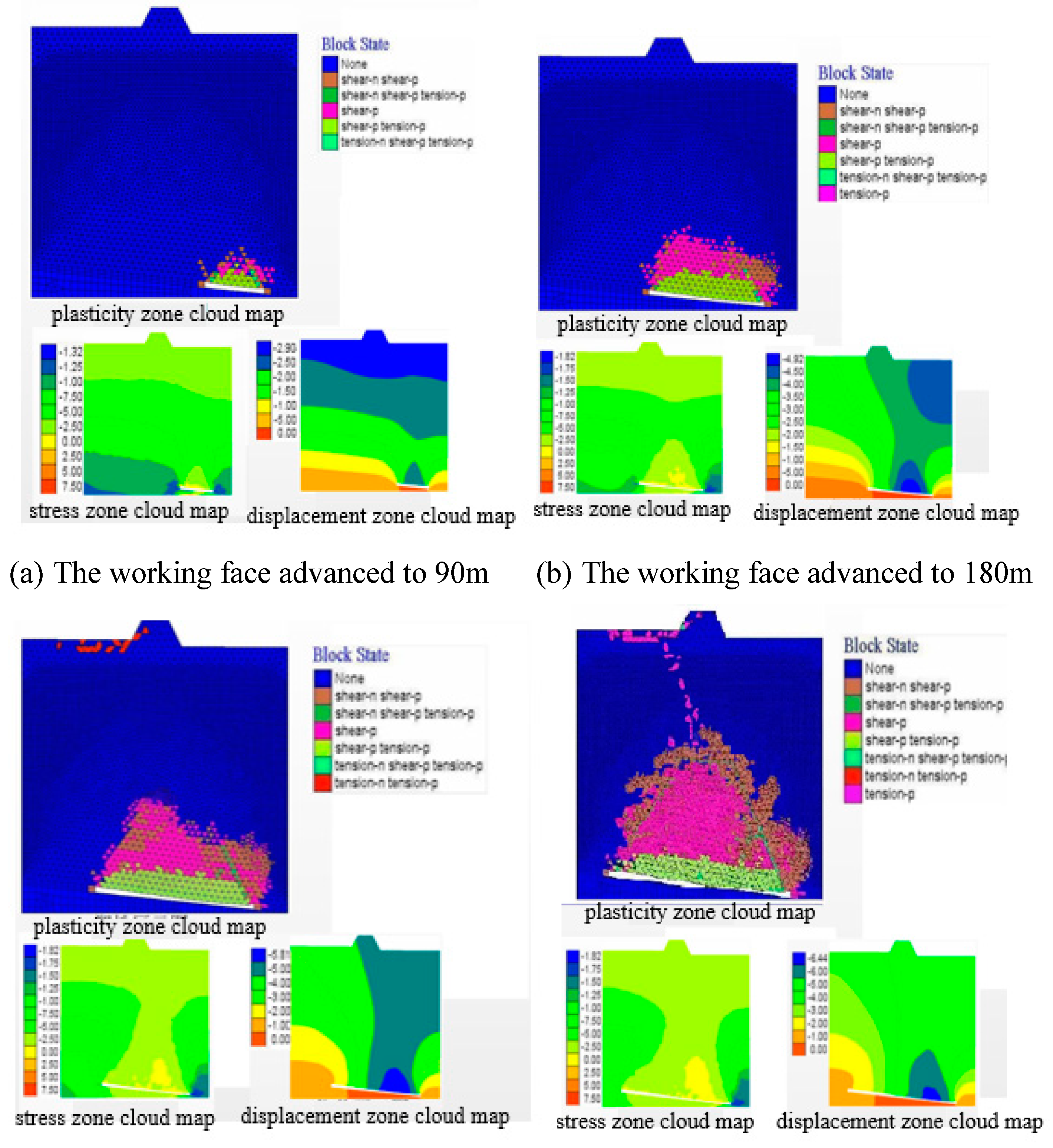
4.2. Simulation analysis of damage characteristics of overlying rock formations
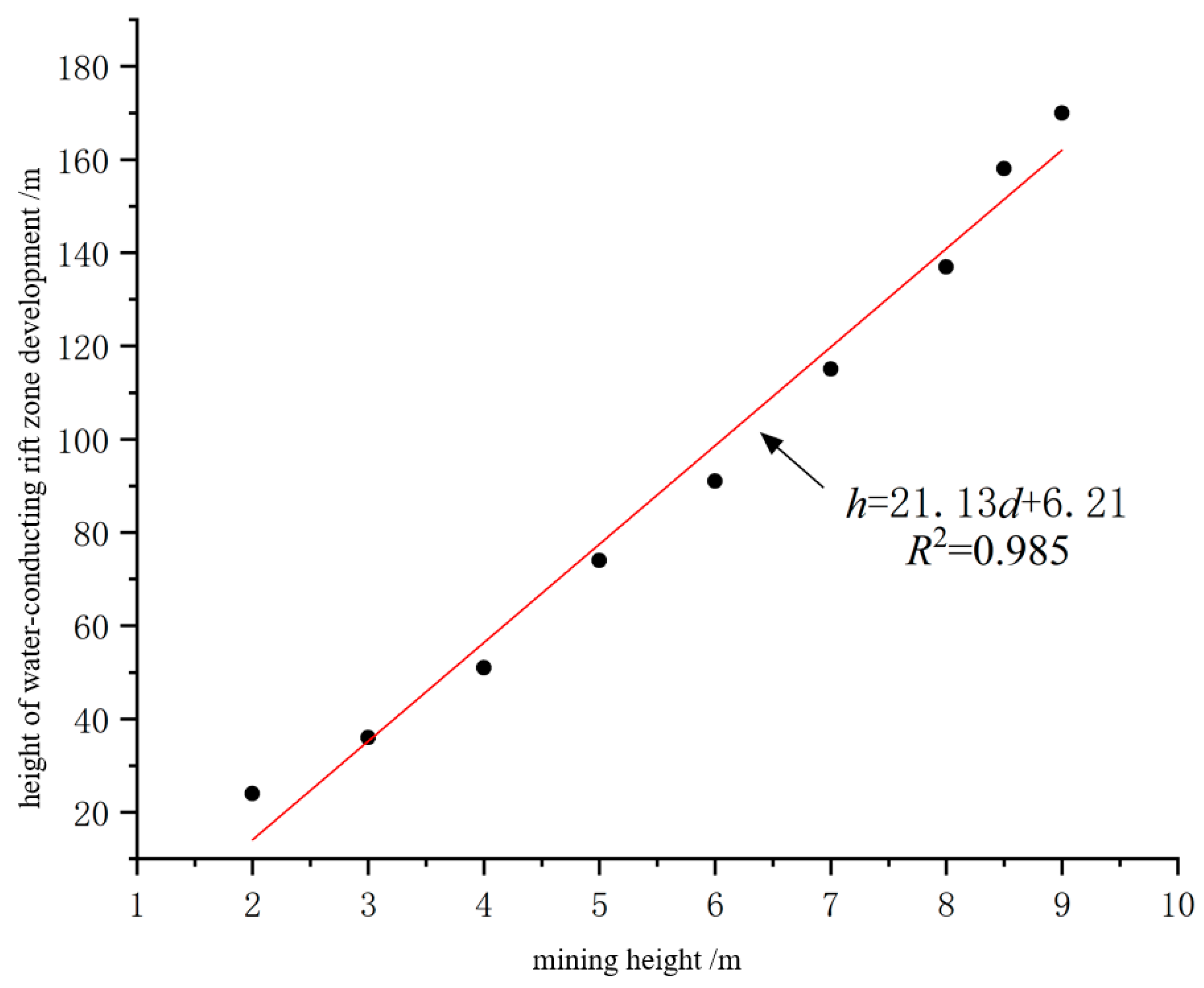
4.3. Development height of hydraulic fracture zone of overburden rock under different mining height
5. Field measurement of overburden damage height
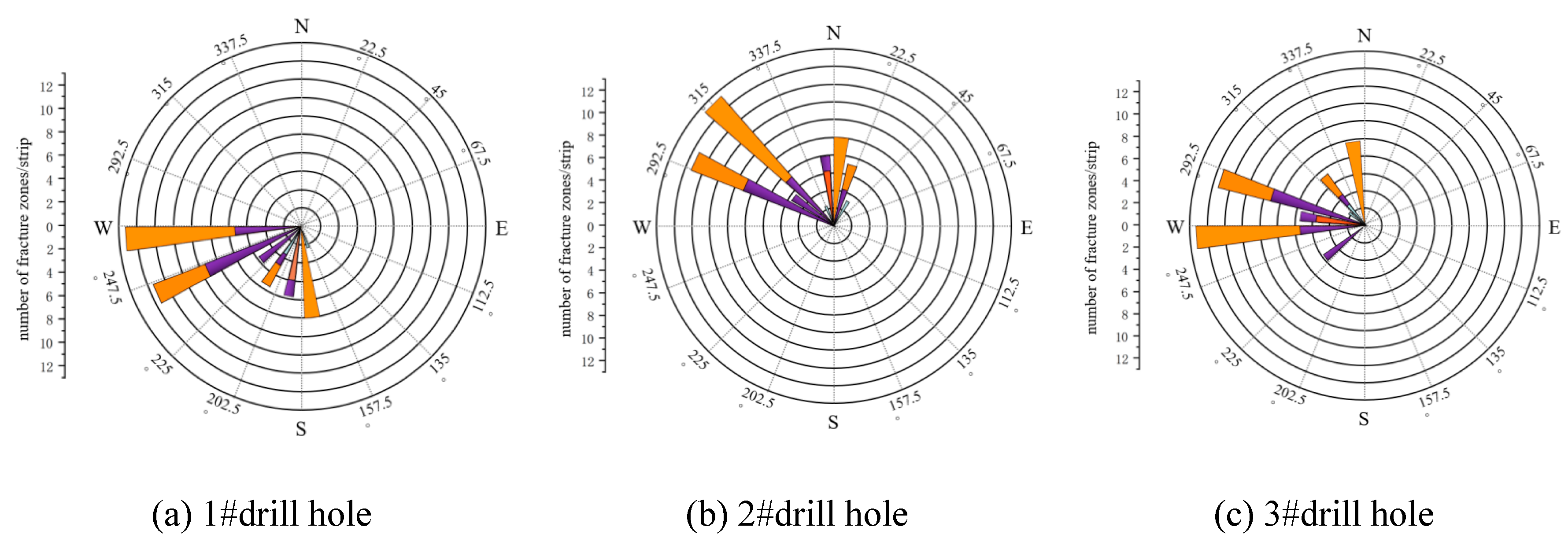
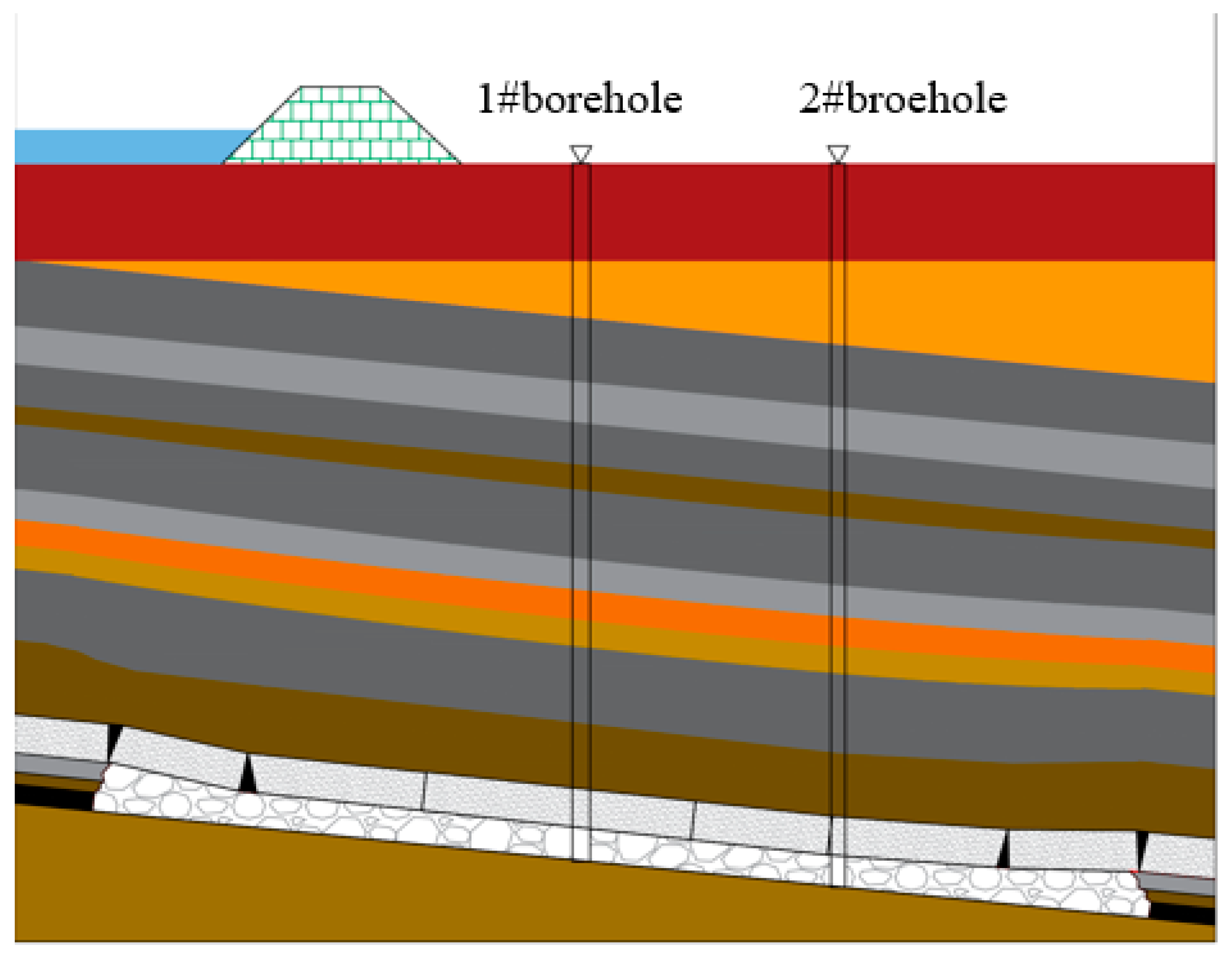
5.1. Drill hole location and program design
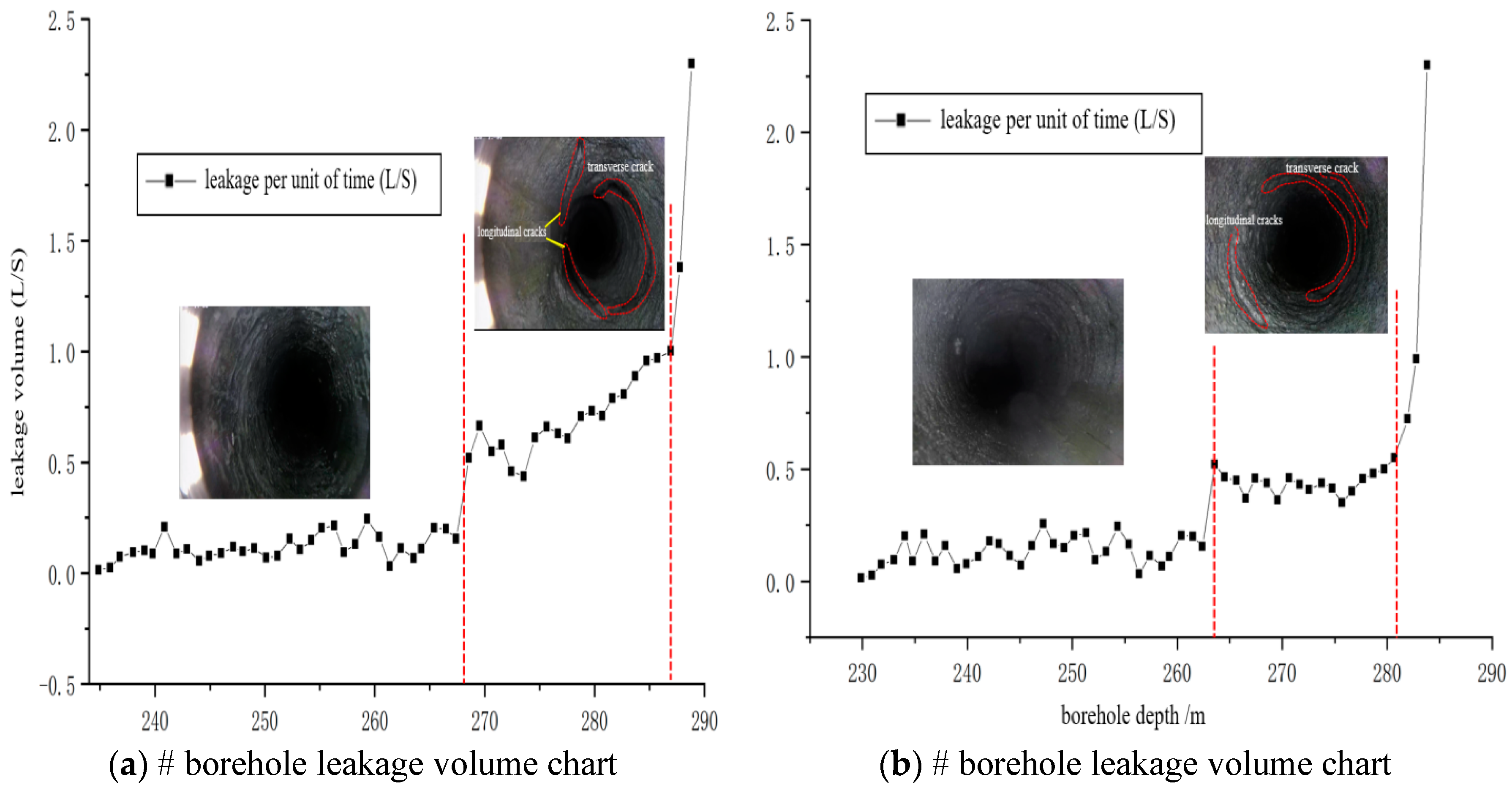
5.2. Detection results and analysis
5.3. Three-band height formula correction analysis
6. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- National Bureau of Statistics of the People's Republic of China. China Statistical Yearbook [M]. Beijing: China Statistics Press, 2020.
- Liu Gui, Wang Yilong, Gao Chao, etc. Feasibility analysis of multiple coal seams mining under reservoir and dam[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2020,48(10):185-191.
- Zeng Yifan, Wu Qiang, Zhao Suqi, et al. Characteristics, causes, and prevention measures of coal mine water hazard accidents in China[J/OL]. Coal Science and Technology,2023-0500.
- National Development and Reform Commission, National Energy Administration. Development Plan of Mine Water Utilization [R]. Beijing: National Development and Reform Commission, 2013.
- Ministry of Environmental Protection. Water pollution prevention and control action plan: Chinese and English [M]. Beijing: People's Publishing House,2015.
- Wu Qiang, Shen Jianjun, Wang Yang. Mining techniques and engineering application for “Coal-Water” dual-resources mine[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2017,42(1):8-16.
- Cao Zhiguo, Ju Jinfeng, Xu Jialin. Distribution model of water-conducted fracture main channel and its flow characteristics[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2019,44(12):3719-3728.
- Cao Zhiguo, Li Quansheng, Dong Binqi. Water Resource Protection and Utilization Technology and Application of Coal Mining in Shendong Mining Area[J]. Coal engineering,2014,46(10):162-164+168.
- Wu Qiang, Li Duo. Research of "Coal-water" double-resources mine construction and development[J]. China Coal Geology.2009,21(3):32-35,62.
- Wang Shuangming, Huang Qingxiang, Fan Limin, etc. Study on overburden aquiclude and water protection mining regionalization in the ecological fragile mining area[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2010,35(01):7-14.
- Wang Shuangming. Thoughts about the main energy status of coal and green mining in China[J]. China Coal, 2020,46(02):11-16.
- Wang Shuangming, Shen Yanjun, Song Shijie, etc. Change of coal energy status and green and low-carbon development under the “dual carbon” goal[J/OL]. Journal of China Coal Society:1-17[2023-05-22].
- Fan Limin. Development of coal mining method with water protection in fragile ecological region[J]. Journal of Liaoning Technical University ( Natural Science Edition ), 2011,30 (5):667-671.
- Fan Limin, Ma Xiongde, Ji Ruijun. Progress in engineering practice of water-preserved coal mining in the Western eco-environment frangible area[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2015,40(8):1711-1717.
- FAN Limin, WU Qunying, PENG Jie, et al. Thoughts and methods of geological environment monitoring for large coal bases in the middle reaches of the Yellow River[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2021,46(5):1417-1427.
- Huang Qingxiang. Impermeability Of Overburden Rock In Shallow Buried Coal Seam And Classification Of Water Conservation Mining[J]. Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2010,29(S2):3622-3627.
- Huang Qingxiang, Zhang Wenzhong, Hou Zhicheng. Study Of Simulation Materials Of Aquifuge For Solid-Liquid Coupling[J]. Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2010,29(S1):2813-2818.
- Huang Qingxiang. Progress and prospect of rock formation control for safe and green mining in large shallow-buried coalfields in the west[J]. Journal of Xi’an University of Science and Technology, 2021,41(3):382.
- Chi Mingbo. Evaluation of water resources carrying capacity and decision-making of scientific mining scale in the northwest mining area of China[D]. China University of Mining and Technology, 2019.
- Zhang Jie, Hou Zhongjie. Study on Three Strap in Water Resouces Preservation in Yu-shu-wan Shallow Seam Mining[J]. Journal of Hunan University of Science and Technology ( Natural Science Edition ), 2006(04):10-13.
- Lai Xingping, Cui Feng, Cao Jiantao, etc. Analysis on characteristics of overlying rock caving and fissure conductive water in top-coal caving working face at three soft coal seam[J]. Journal of Coal, 2017,42(01):148-154.
- State Administration of Safety Supervision, State Administration of Coal Mine Safety, National Energy Administration, et al. Specification for coal pillar retention and coal compression mining for buildings, water bodies, railroads and major shafts [M]. Beijing: Coal Industry Press,2017.
- Hu, B.N., Zhang, H.X., Shen, B.H. Guide to coal pillar retention and coal compression mining for buildings, water bodies, railroads and major shafts [M]. Beijing: Coal Industry Press,2017.
- Xue Shaobo, Wu Xiong, Xu Nengxiong. Pondering on Coal Mining under Large-sized Reservoir Research[J]. Coal geology of China,2008,20(S1):47-49.
- Zhang Jie, Yang Tao, Suo Yonglu, et al. Roof water-inrush disaster forecast based on the model of aquiclude instability[J]. Journal of Coal, 2017,42(10):2718-2724.
- LAI X,XU H,FAN J,et al. Study on the mechanism and control of rock burst of 2 coal pillar under complex conditions[J]. Geofluids, 2020.
- Hou Zhongjie, Zhang J. Experiment and analysis of diving protection solid-liquid two-phase coupling in mining area of northern Shaanxi Province[J]. Journal of Hunan University of Science and Technology (Natural Science Edition),2004,19(4):1-5.
- Zhang Jie, Yu Xueyi, Cheng Lianhua. Failure mechanism of soil layer in longwall face intermission advance in shallow seam mining [J]. Journal of Liaoning Technical University (Natural Science Edition), 2008,27(6):801-804.
- Zhang Jie, Yang Tao, Suo Yonglu, et al. Forecast model for roof water inrush in Anshan coal mine based on coupling evaluation[J]. Xi’ an: Xi’ an University of Science and Technology,2018,38(04):569-576.
- Lai Xingping, Sun Huan, Shan Pengfei, etc. Acoustic emission and temperature variation in failure process of hard rock pillars sandwiched between thick coal seams of extremely steep[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2015,34(11):2285-2292.
- Zhang Yin, Tang Jianxin, Wang Yanlei, et al. A model for predicting mining subsidence in bedding rock slopes[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2017,36(12):3012–3020.
- Lai Xingping, Zhang Xudong, Shan Pengfei, etc. Study on development law of water-conducting fractures in overlying strata of three soft coal seam mining under thick loose layers[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2021,40(09):1739-1750.
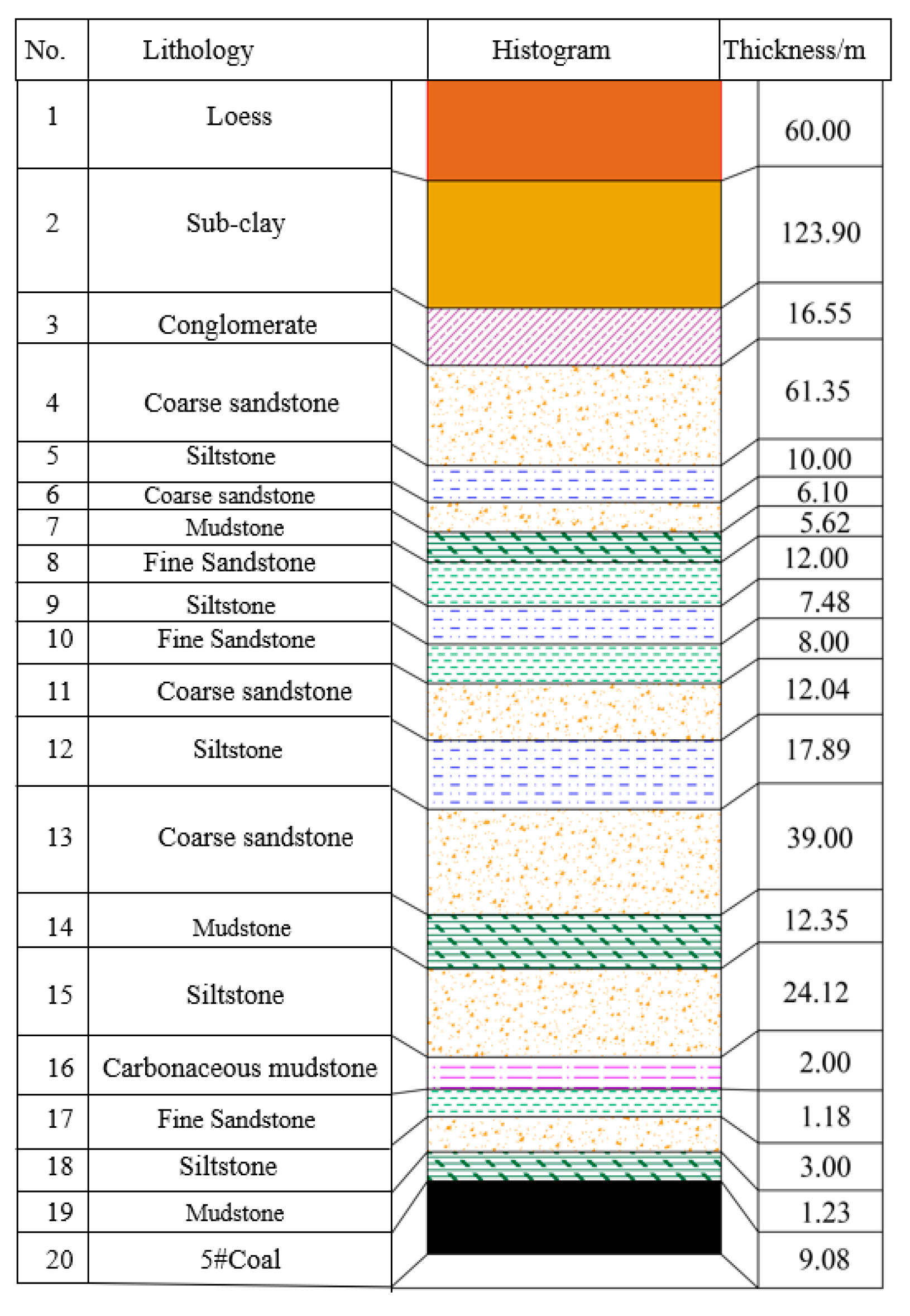

| Number | Lithology | Rock thickness /m | Model thickness Degree /cm |
Proportion |
| 1 | Dams | 15 | 3 | 100:5:3:1 (river: sand: cement: macadam: starch) |
| 2 | Loess | 50 | 10 | 25:25:1:1 (river: sand: loess: petroleum jelly: solid grease) |
| 3 | Laterite | 50 | 10 | 25:25:1:1 (river: sand: laterite: petroleum: jelly: solid: grease) |
| 4 | Coarse sandstone | 60 | 12 | 100:5:3:2:1 (river: sand: cement: macadam: liquid: paraffin: starch) |
| 5 | Mudstone | 40 | 8 | 100:5:3:2:4 (river: sand: cement: white: powder: liquid: paraffin: starch) |
| 6 | Coarse sandstone | 20 | 4 | 100:5:3:2:1(river: sand: cement: white: powder: liquid: paraffin: starch) |
| 7 | Siltstone | 75 | 15 | 100:6:3:4:3 (river: sand: cement: white: powder: liquid: paraffin: starch) |
| 8 | Coarse sandstone | 23 | 4.6 | 100:5:3:2:1 (river: sand: cement: white: powder: liquid: paraffin: starch) |
| 9 | Mudstone | 75 | 15 | 100:5:3:2:4 (river: sand: cement: white: powder: liquid: paraffin: starch) |
| 10 | Siltstone | 50 | 25 | 100:6:3:4:3 (river: sand: cement: white: powder: liquid: paraffin: starch) |
| 11 | 5# Coal | 9.08 | 4.5 | 20:20:1:5 (river: sand: cement: white: powder: liquid: paraffin: starch) |
| 12 | Siltstone | 4 | 2 | 100:8:3:2:3 (river: sand: cement: white: powder: liquid: paraffin: starch) |
| Method classification | Overburden damage height /m | Error /% | ||
| collapse zone | Water-conducting fissure zone | collapse zone | Water-conducting fissure zone | |
| Physical Simulation | 52.4 | 162 | +9.72 | -5.13 |
| Numerical Simulation | 48.11 | 164 | +0.73 | -3.96 |
| Empirical formulas | 42.42 | 120.57 | -11.18 | -29.39 |
| Field measurements | 47.76 | 170.76 | 0 | 0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





