1. Introduction
Vitamin C (VitC) or ascorbic acid is a molecule synthesized by all plants and a vast majority of vertebrates in which l-gulonolactone oxidase catalyzes the final step of its biosynthesis [
1]. Humans and other primates cannot synthesize VitC due to the mutation of the gene encoding for this enzyme [
2]. Intestinal absorption, entry into cells of various tissues and renal reabsorption of VitC depend on the expression of proteins belonging to the sodium-dependent vitamin C transporter (SVCT) family [
3]. Thus, the differential compartmentalization of vitamin C in numerous organs and systems is due to the expression of SVCT and its affinity for the substrate [
4]. Polymorphisms of genes responsible for SVCT protein synthesis and their possible activity variations are responsible for differences in plasma levels and/or possible permanent VitC deficiencies between individuals [
5]. Physiological plasma concentrations are achieved by oral ingestion and drug concentrations (millimolars), by parenteral administration [
6]. VitC acts on cellular metabolism as an electron donor playing an antioxidant role with consequent protective role in proteins, fats, and DNA structure/function [
6]. Thus, vitamin C is oxidized to ascorbyl radical and subsequently to dehydroascorbic acid which has a half-life of a few minutes and then is reconverted to vitamin C [
7]. This recycling process can be altered among smokers or during illness as diabetes, atherosclerosis, heart disease, stroke, macular degeneration [8-11].
The idea that VitC could help in cancer was born in the seventies [
12]. Since then, numerous studies have been performed with conflicting results, ranging from the total absence of the effect of VitC in cancer, to its possible protective effect, to its potential therapeutic effect when administered in high doses [13-15].
In the 1980s it was demonstrated that long-term administration of 3 g of VitC/day did not influence the prognosis of early breast cancer [
16]. In 2014 a meta-analysis study highlighted how the VitC supplement was associated with a reduced risk of breast cancer-specific mortality. Over the years numerous studies have shown that VitC slows the growth of breast cancer cells [
18]. Probably the difference in the results is linked on the one hand to the dosage of VitC and on the other to the heterogeneity of the disease due to the presence/absence of estrogen (ER) and progesterone (PgR) receptor expression and human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2)
in addition to the percentage of the proliferating index (Ki67). Gene expression profiling has allowed to identify molecular subtypes, namely luminal A (LumA), luminal B (LumB),
non-LumA and B, and triple-negative basal-like (TNBC) . LumA is ER+ and/or PgR+ and HER2-; LumB is further classified into LumB HER2- (ER+ and/or PgR+ and HER2-) and LumB HER2+ (ER +and/or PgR+ and HER2+). Non-LumA and B are hormone negative; TNBC is ER-, PgR-, and HER2- and has the worst prognosis of all subgroups [
19]
. Moreover, a triple negative claudin-low (ER-, PgR- and HER2-) subtype was described. With both genomic and transcriptomic analyses 10 breast cancer subtypes were identified based on integrated clusters (4 ER-negative, 6 triple-negative)[
19]
. Two-sample Mendelian randomization (MR) study aimed at analyzing the role of antioxidants including VitC in subcategories of breast cancer as ER+ breast cancer versus ER- breast cancer showed that VitC had no effect on the risk of developing the disease [
20].
Few studies have been performed
in vitro on the effect of VitC on experimental models reproducing breast cancer subtypes. The most studied cell lines are:
MCF7 as LumA model (ER+, PgR+/−, HER2-) and MDA-MB231 as triple-negative claudin-low (ER-, PgR-, HER2-) were used [
21]
. Subramani et al., 2014 demonstrated that
VitC supplementation to MCF7 cells reduced the cytotoxic effect of tamoxifen, indicating that the vitamin might reduce the therapeutic effect of the drug [
22]
. In the same cell type, VitC seems to potentiate the anti-proliferative effect of doxorubicin [
23]
. Ibrahim et al., 2022 demonstrated that concentrations of Vit.C above 82 μM induced a drastic reduction in the viability of MCF7 cells [
24].
Khazaei et al., 2022 demonstrated that VitC conferred different effect on radioresistance in dependence on its concentration and cell type, MCF7 and MDA-MB231 cells. Pharmacological concentrations of VitC were required after irradiation to reduce MCF7 cell viability and before irradiation to reduce MDA-MB231 cell viability [
25].
Recently the attention has focused on the role of sphingolipids (Sphs) in breast cancer both for their correlation with cell growth and as possible diagnostic and prognostic markers [
26]. The key molecule of SPH metabolism is the sphingomyelin (SM) that can be catabolized to or resynthesized by Ceramide (CER) by sphingomyelinase (SMase) or SM-synthase, respectively [
27]. CER is phosphorylated to CER-1-phosphate by CER kinase (CERK) or is degraded by ceramidase (CERase) to sphingosine (S) that can be converted to
sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P) by sphingosine kinase (SPHK). Moreover CER can be used to synthesize glucosylCER (GCER) or galactosylCER (GalCER). CER synthesis and turnover resulted altered in breast cancer [
28]. Kar et al., 2023 showed a difference between luminal and triple-negative subtypes by identifying only 5 differential SPHs [
29]. Specifically, the luminal types were characterized by a lower level of CER, GCER and S1P and a higher level of C1P and S than the triple-negative types. CERK resulted altered in
riple-negative and triple-positive breast cancer subtypes [
30]. Interestingly, CERK has been identified as a regulator of
tamoxifen resistance in ER+ breast cancer [
31]
. A correlation of CERK – SPHK1 with metastasis and/or drug resistance in breast cancer has been shown [
32]
. The possible mechanism of action of VitC in MCF7 and MDA-MB231 cells via membrane lipids has suggested
. It has been shown that
VitC, alone or in combination with somatostatin, decreased omega-6 linoleic acid and increased omega-3 fatty acids in MCF7 cells and decreased omega-6 linoleic, arachidonic acid and omega-3 in MDA-MB231 [
33]. It has been argued that VitC increases the production of sphingoid bases in keratinocytes [
34] but there is no data on the effect of VitC on SPH metabolism in breast cancer.
The present study tested the effects of low and pharmacological concentration of VitC on cell viability and hormone receptor expression in MCF7 and MDA-MB231 cells in order to be able to understand if its effect is limited to the reduction of cell growth or if it could influence the outcome of the therapeutic treatment. Moreover, SM metabolism as possible signaling mechanism was investigated.
The results clearly show that pharmacological doses of VitC reduce the MCF7 cell viability but also reduce ER expression and induce HER-2 expression. The results suggest that high dose of VitC, while limiting the growth of LumA breast cancer, makes it less responsive to hormone therapy. No effect of VitC was found in MDA-MB231 cells. The analysis of Sph metabolism highlights a specific enrichment in Cer content in MCF7 cells.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
MDA-MCF7 and MDA-MB231 cell lines were from Elabscience Biotechnology (Houston, Texas, USA). Cell culture medium (Dulbecco’s modified minimum essential medium, DMEM), fetal bovine serum (FBS), penicillin G, streptomycin, glutamine, and sodium pyruvate were from GIBCO Invitrogen (Carlsbad, CA, USA). Anti-neutral SMase (nSMase), anti-β-tubulin, anti-3-Hydroxy-3-Methylglutaryl-CoA Reductase (HMGCR) and horseradish peroxidase-conjugated goat anti-rabbit secondary antibodies were from Abcam (Cambridge, UK). 3-[4,5-dimethyl-2-thiazolyl]-2,5-diphenyl-2-tetrazoliumbromide (MTT) was from Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA). TaqMan SNP Genotyping Assay and Reverse Transcription kit were purchased from Applied Biosystems (Foster City, CA, USA). RNAqueous®-4PCR kit was from Ambion Inc. (Austin, TX, USA). SDS-PAGE molecular weight standards were purchased from Nzythech (Lisboa, Portugal). Chemiluminescence kit was purchased from Amersham (Rainham, Essex, UK).
2.2. Cell Culture and Treatments
MCF7 as luminal A model (ER+, PgR+/−, HER2) and MB231 as triple-negative model (ER-, PgR-, HER2-) were used [
21]. Cells were grown in DMEM supplemented with 10% heat-inactivated FBS, 100 IU/mL penicillin/streptomicyn, and 200 mM of L-glutammine. Cells were maintained at 37 °C in a saturating humidity atmosphere containing 95% air and 5% CO
2. For the experimental model VitC was added to the culture medium as reported below.
2.3. Cell Viability
MTT assay was used to test cell viability, as previously reported [
35]. MCF7 and MB231 treated with increasing concentration of VitC from 0.1mM to 20.0mM were seeded into 96-well plates at a density of 1 × 10
4 cells/well with DMEM complete culture medium. After 24 h, culture medium was replaced with new culture medium and the cells were incubated for 24 h. Samples with 1% or 2% DMSO were added as controls due to their cytotoxic effect [
36]. Then, MTT reagent was dissolved in PBS 1x and added to the culture at 0.5 mg/mL final concentration. After 3 h of incubation at 37 °C, the supernatant was carefully removed, and formazan salt crystals were dissolved in 200 µL DMSO that was added to each well. The absorbance (OD) values were measured spectrophotometrically at 540 nm using an automatic microplate reader (Eliza MAT 2000, DRG Instruments, GmbH, Marburg, Germany). Each experiment was performed two times in triplicate, and the results were expressed as a percentage relative to the control cells.
2.4. Immunocytochemistry
A cell block was obtained through the Hologic protocol relating to the Cellient®Automated Cell Block System (Hologic, Marlborough, MA, USA) [
https://www.hologic.com/sites/default/files/2020-07/MAN-06369-001_001_02.pdf]: in detail, the formalin-fixed cell cultures were previously centrifuged to 1727 RPM for 10 min. After the surnatant removing, the cell precipitate was put into a vial of Preservcyt® solution (buffered methanol -based solution) of the ThinPrep® system (Hologic, Marlborough, MA, USA) and processed through the Cellient® instrumentation for 45 min, concentrating the cells and distributed them in a thin layer into a paraffin cell block.
Subsequently, sections of 4 µm were performed and placed on positive charged slides, for the immunocytochemical staining through the BOND III fully automated immunohistochemistry stainer (Leica Biosystems, Nußloch, Germany): in detail, a heat-induced antigen retrieval was used with the ready to use citrate based pH 6 BondTM Epitope Retrieval Solution 1 (Leica Biosystems, Newcastle Upon Tyne, United Kingdom, Catalog No: AR9961) for 30 min, primary antibody incubation for 15 min with the ER (clone 6F11, RTU, Leica Biosystems, Newcastle Upon Tyne, United Kingdom, Catalog No: PA0151) and PgR (clone 16, RTU, Leica Biosystems, Newcastle Upon Tyne, United Kingdom, Catalog No: PA0312) and for 30 min with Ki-67 (MM1) della Leica Biosystems, RTU, Newcastle Upon Tyne, United Kingdom, Catalog No: PA0118; afterward, the ready to use BondTM Polymer Refine Detection System (Leica Biosystems, Newcastle Upon Tyne, United Kingdom, Catalog No: DS9800) was used to visualize the complex via a brown precipitate and the hematoxylin for nuclear counterstaining. The HER2 immunohistochemistry was performed using the RTU HercepTest™ (Glostrup, Denmark).
As regards the nuclear biomarkers (ER, PgR and Ki-67), 10 different areas of about 0.4 μ2 each were selected using the QuPath 0.2.0-m9 software (
https://github.com/qupath/qupath/releases?page=2), in order to automatically count the positive cells, whose accuracy was then checked manually. Afterwards, the average ± SD (standard deviation) of the percentage values as obtained was used to quantify the positivity of the staining.
Concerning the HER2 staining evaluation, a score from 0 to 3+ was applied, according to the current ASCO-CAP guidelines (J Clin Oncol 2018;36:2105-2122.
https://doi.org/10.1200/ JCO.2018.77.8738).
2.5. Reverse Transcription Quantitative PCR (RTqPCR)
Total RNA was extracted from MCF7 cells cultured for 24 h, as reported above, using RNAqueous-4PCR kit, as previously described [
37]. Samples were treated with RNase-free DNase to prevent amplification of genomic DNA possibly present. Samples were dissolved in RNase-free water, and total RNA amount was quantified by measuring the absorbance at 260 nm (A260). The purity of RNA was evaluated by using the A260/A280 ratio. A260/A230 ratio was also used to indicate chemical contaminants in nucleic acids. The extracted RNA was immediately frozen and maintained at −80 °C. Before cDNA synthesis, the integrity of RNA was evaluated by electrophoresis in TAE 1.2% agarose gel. cDNA was synthesized using 1μg total RNA for all samples by High-Capacity cDNA Reverse Transcription kit under the following conditions: 50 °C for 2 min, 95 °C for 10 min, 95 °C for 15 s and 60 °C for 1 min, for a total of 40 cycles. The following target genes were investigated: HMGCR (Hs00168352_m1), sphingomyelin phosphodiesterase 1 (SMPD, Hs03679347_g1), sphingomyelin phosphodiesterase 1 (SMPD4, Hs04187047_g1), Cyclin D1 (CCND1, HS00765553), Cyclin Dependent Kinase Inhibitor 1A (CDKN1A, Hs_00355782_m1), Growth Arrest And DNA Damage Inducible Alpha (GADD45A, Hs_00169255_m1), Glyceraldehyde-3-Phosphate Dehydrogenase
(GAPDH, Hs99999905_m1) and 18S rRNA (S18, Hs99999901_s1) were used as housekeeping genes. mRNA relative expression levels were calculated as 2−ΔΔCt, comparing the results of the treated samples with control sample [56].
2.6. Protein Concentration and Western Blotting
Protein concentration was measured as previously reported with modifications [
38]. Proteins (70 μg) were submitted to 10% SDS (sodium dodecyl sulfate)-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis at 180 V for 60 min. Briefly, proteins were transferred onto 0.45 μm cellulose nitrate strips membrane (Sartorius StedimBiotech S.A.) in transfer buffer for 75 min at 100 V at 4 °C . The membranes were blocked for 60 min with 5% no-fat dry milk in PBS (pH 7.4) and incubated overnight at 4 °C with HMGCR, aSMase or nSMase specific antibodies. Anti-βactin antibody was used to normalize the data. The blots were treated with HRP-conjugated secondary antibodies for 60 min. Band detection was performed using an enhanced chemilumiescence kit from Amersham Pharmacia Biotech (Rainham, Essex, UK). A densitometric analysis was performed by Chemidoc Imagequant LAS500–Ge Healthcare-Life Science (Milano, Italy).
2.7. Ultrafast Liquid Chromatography–Tandem Mass Spectrometry
Lipid extraction and analysis was performed as previously reported [
38]. The pellets of the cells were suspended in Tris 10 mM, pH 7.4, and diluted with 1 mL methanol. Three milliliters of ultra-pure water and 3 mL methyl tert-butyl ether (MTBE) were added. Each sample was vortexed for 1 min and centrifuged at 3000×
g for 5 min. The supernatant was recovered. The extraction with MTBE was repeated on the pellet and the supernatant was added to the first. The organic phase was dried under nitrogen flow and resuspended in 500 μL of methanol. The 12:0 SM, 16:0 SM, 18:1 SM, 24:0 SM, sphingosine-1-phosphate, C18:0 sphinganine, C6:0 Cer, C8:0 Cer, C16:0 Cer, C18:0 Cer, C20:0 Cer, C24:0 Cer. C12:0 dihydroCer, arachidonoylglycerol (2AG), C16:0 glucosylceramide (GluCer), 16-0 18-1 phosphatidylcholine (PC), 16-0 20-4 PC, 18-1 18-0 PC standards were dissolved in chloroform/methanol (9:1 vol/vol) at 10 μg/mL final concentration. The stock solutions were stored at −20 °C. Working calibrators were prepared by diluting stock solutions with methanol to 500:0, 250:0, 100:0, and 50:0 ng/mL final concentrations. Twenty microliters of external standards or lipids extracted from serum with 12:0 SM and 6:0 Cer as internal standards (500 ng/mL) were injected after purification with specific nylon filters (0.2 μm). The analyses were carried out by using the Ultra Performance Liquid Chromatography system tandem mass spectrometer (Applied Biosystems, Italy). The lipid species were separated, identified, and analyzed as previously reported [
38]. Liquid Chromatography system was Shimadzu Prominence UFLC, the pump was Shimadzu LC-20 AD, the detector was API 3200 linear triple quadrupole MS/MS, the injection valve was Valco valve, the autosampler was Schimadzu SR-20 AC HT, the column temperature stabilizer was Schimadzu CTO-20A. The samples were separated on a Phenomenex Kinetex phenyl-hexyl 100 A column (50 × 4.60-mm diameter, 2.6-μm particle diameter) with a precolumn security guard Phenomenex ULTRA phenyl-hexyl 4.6. Column temperature was set at 50 °C and the flow rate at 0.9 mL/min. Solvent A was 1% formic acid; solvent B was 100% isopropanol containing 0.1% formic acid. The run was performed for 3 min in 50% solvent B and then in a gradient to reach 100% solvent B in 5 min. The system needed to be reconditioned for 5 min with 50% solvent B before the next injection. The lipid species were identified by using positive turbo-ion spray (ESI) and modality multipole-reaction monitoring. Ion spray voltage was 5.4 kV, gas 1 was air, gas 2 was nitrogen, temperature was 650 °C, and the flow rate curtain gas was 40.5 L/h. The flow of the collision gas was maintained at 5.0 L/h. Data were acquired and processed using AnalystTM and Analyst 1.5 software in a Dell Precision T3400 personal computer with a Samsung ML-2851 MD graphical printer.
2.8. Immunofluorescence
Immunofluorescence of SM was performed as reported according to Albi et al. [
39]. The SM localization was studied by using the SM probe, enhanced green fluorescent protein-nontoxiclysenin (EGFP-NT-Lys). The probe was purified from E.coli strain BL21(DE3) harboring pET28/EGFP-NT-Lys according to Tomishige et al. [
40], with a little modification. In brief, after bacteria culture reaches OD600 = approx. 1, the expression of EGFP-NT-Lys was induced at 18 °C for two overnights in the presence of 125 µM IPTG (VWR life science). EGFP-NT-Lys was purified by Hitrap TALON crude column (Cytiva, Munzinger Str. 5, 79111 Freiburg im Breisgau, Germania) from bacteria lysate using its His-tag. Imidazole used in the elution of the protein from the column was removed by dialysis. The dialyzed protein was mixed with glycerol (VWR chemicals) at 50% (v/v) and stored at –20 °C. On the day of the experiment, the medium was removed, cells were washed with DMEM/5% lipid depleted serum (LPDS) and treated with 15 µg/mL EGFP-NT-Lys diluted in DMEM/5% LPDS for 45 min. Then, cells were fixed with 250 µL of 4% paraformaldehyde (PFA) at room temperature (RT) for 30 min. After washing, the residual PFA was neutralized by 0.1 M NH4Cl at RT for 15 min. Cells were washed three times with 500 µL of PBS and nuclei counterstained with DAPI. Coverslips were mounted and cells viewed in a DMRB Leica epimicroscope equipped with a digital camera.
2.9. Statistical Analysis
Three independent experiments performed in duplicate were carried out for each analysis. Data are expressed as mean ± SD; Student’s t-test was used for statistical analysis. To compare the effect of 0.1mM VitC versus CTR and/or 10mMVitC, ANOVA test was used.
4. Discussion
Overall, the results of this work suggest that high concentrations of VitC reduce the growth of luminal A breast cancer but not of triple negative breast cancer. The results of this work shed light on a mechanism triggered by high doses of VitC on Luminal A tumor cells that leads to the change of the phenotype characterized by a reduction of ER expression making the cells resistant to hormonal treatment and by an appearance of HER2 positivity. This may be relevant for cancer progression even if VitC treatment has led to a reduction in tumor burden. In fact, the choice of hormonal treatment is dictated by the histological type [
42]. The administration of VitC at high concentrations could be the cause of an unexpected lack of response to the hormonal treatment. The slowdown in the growth of hormonal mass could be misleading and there could be a late but rapid deterioration due to resistance to hormonal treatment.
In our very recent work, we described cholesterol and SM metabolism as a growth mediator of luminal A but not triple negative breast cancer ([
19]. Therefore, only Luminal A type is more easily influenced by VitC and lipids. Here, we report that high-dose VitC modulates the gene and protein expression of aSMase and nSMase by inhibiting the former and stimulating the latter in a near-equilibrium manner. As a result, a degradation of the SM accompanied by an increase of the Cer is not noticed, indicating the permanence of an equilibrium of the two molecules. Furthermore, both molecules are quantitatively reduced after treatment with VitC suggesting a possible reduction of synthesis rather than an activation of catabolism. It is known that Cer synthase is involved in cancer progression [
43] and induces chemoresistance [
44]. Therefore, the role of VitC in limiting the metastatic spread of triple negative cancer cannot be excluded. Future studies will be able to clarify this point. The effect of VitC on SM metabolism in Luminal A cells is different. There is a clear prevalence of nSMase1 increase over aSMase reduction with a stimulation of SM catabolism and production of high Cer levels. It is really difficult at the moment to establish whether the increase in Cer could be responsible for the reduction of ER expression and /or the appearance of HER2 positivity. A recent review reports that Sph metabolites, enzymes and transport proteins are deregulated in human breast cancer cells and/or tissues and Sph-driven mechanisms allow breast cancer cells to respond to or evade therapies [
45]. Ours is the first study showing a simultaneous change in the cell phenotype towards a form of cancer resistant to hormone therapy and a change in the metabolism of SM with production of Cer. It has been suggested that knowing the metabolism of Cer in Luminal breast cancer can be a valid aid for a new and correct therapeutic strategy [
46]. The results obtained open the door to future studies aimed at demonstrating that high doses of VitC modify the Luminal A cancer phenotype via SM metabolism, i.e. by inhibiting nSMase.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.C. and E.A; methodology, F.F., M.M., S.C., C.A, A.M., M.R.C., T.K., N.T.; software, F.F., S.C..; validation, M.C., T.B., A.S..; formal analysis, F.F..; investigation, M.M..; data curation, M.M., S.C., M.C., E.A..; writing—original draft preparation, E.A..; writing—review and editing, A.S., E.A..; All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
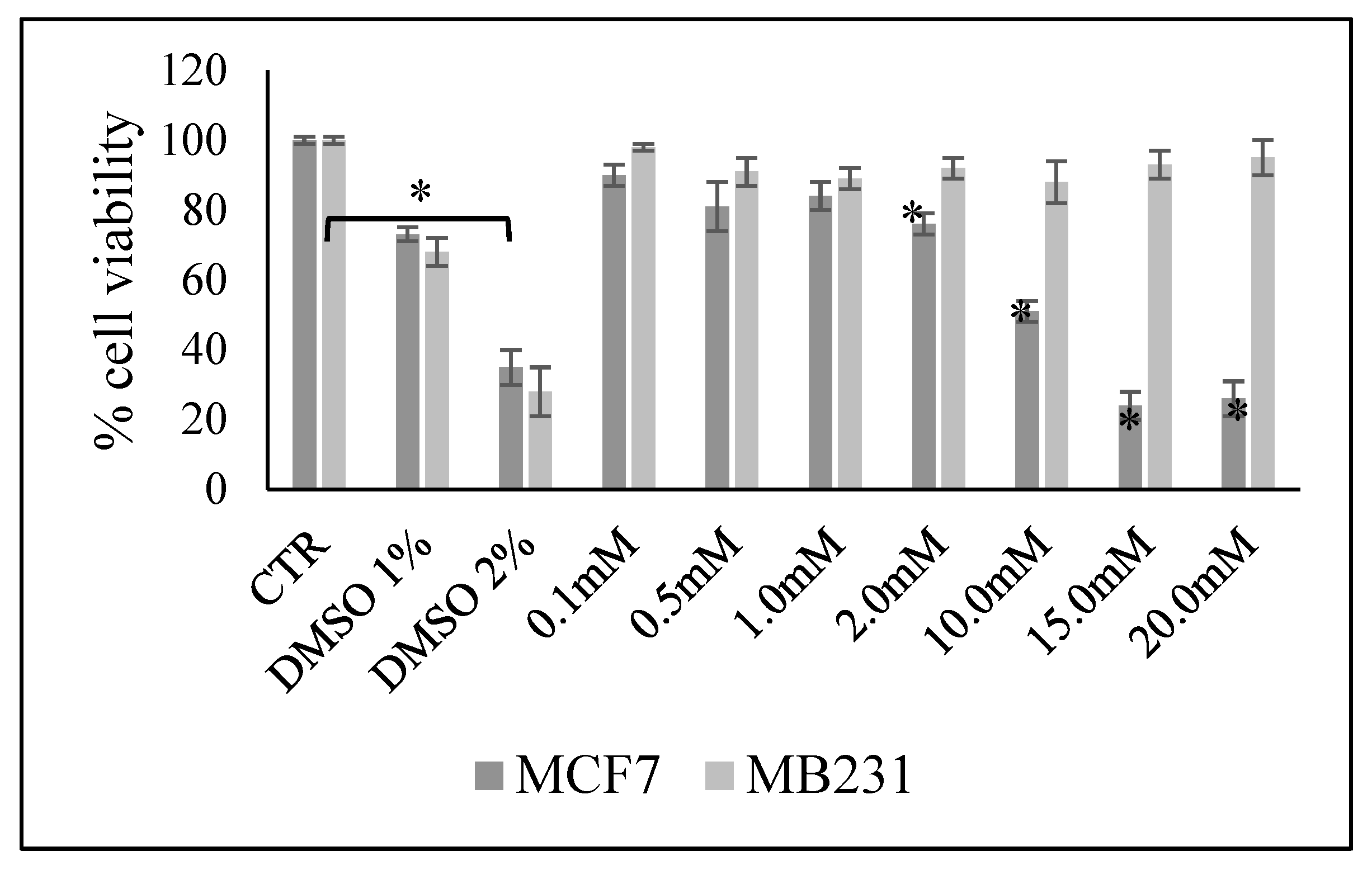
Figure 1.
Effect of increasing doses of vitamin C on MCF7 and MB231 cell viability. Data are expressed as percentage respect to control sample (CTR) and represent the mean+SD of 3 independent experiments performed in duplicate. DMSO treatment was used as positive CTR. *p<0.05 versus CTR.
Figure 1.
Effect of increasing doses of vitamin C on MCF7 and MB231 cell viability. Data are expressed as percentage respect to control sample (CTR) and represent the mean+SD of 3 independent experiments performed in duplicate. DMSO treatment was used as positive CTR. *p<0.05 versus CTR.
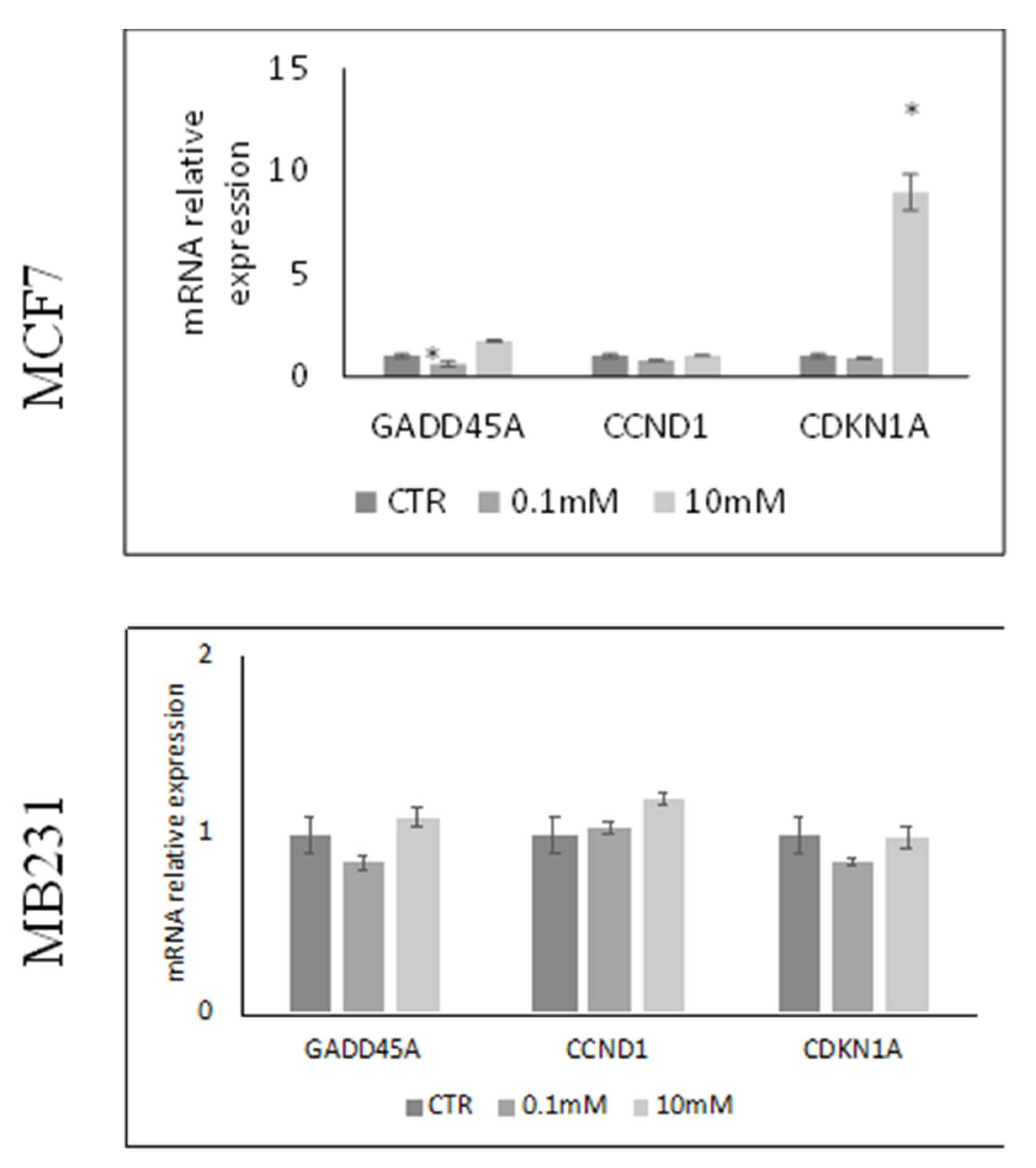
Figure 2.
Effect of 0.1mM and 10mM Vitamin C on gene expression of GADD45A coding growth arrest and DNA-damage-inducible alpha protein, CCND1 coding cyclin D1 protein and CDKN1A gene coding cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1A protein in MCF7 and MB231 cells. GAPDH and 18S rRNA were used as housekeeping genes. mRNA relative expression levels were calculated as 2−ΔΔCt, comparing the results of the treated samples with control sample (CTR) equal to 1, the origin of axes. Data are expressed as the mean ± SD of 3 independent experiments performed in duplicate. *p < 0.05 versus CTR.
Figure 2.
Effect of 0.1mM and 10mM Vitamin C on gene expression of GADD45A coding growth arrest and DNA-damage-inducible alpha protein, CCND1 coding cyclin D1 protein and CDKN1A gene coding cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1A protein in MCF7 and MB231 cells. GAPDH and 18S rRNA were used as housekeeping genes. mRNA relative expression levels were calculated as 2−ΔΔCt, comparing the results of the treated samples with control sample (CTR) equal to 1, the origin of axes. Data are expressed as the mean ± SD of 3 independent experiments performed in duplicate. *p < 0.05 versus CTR.
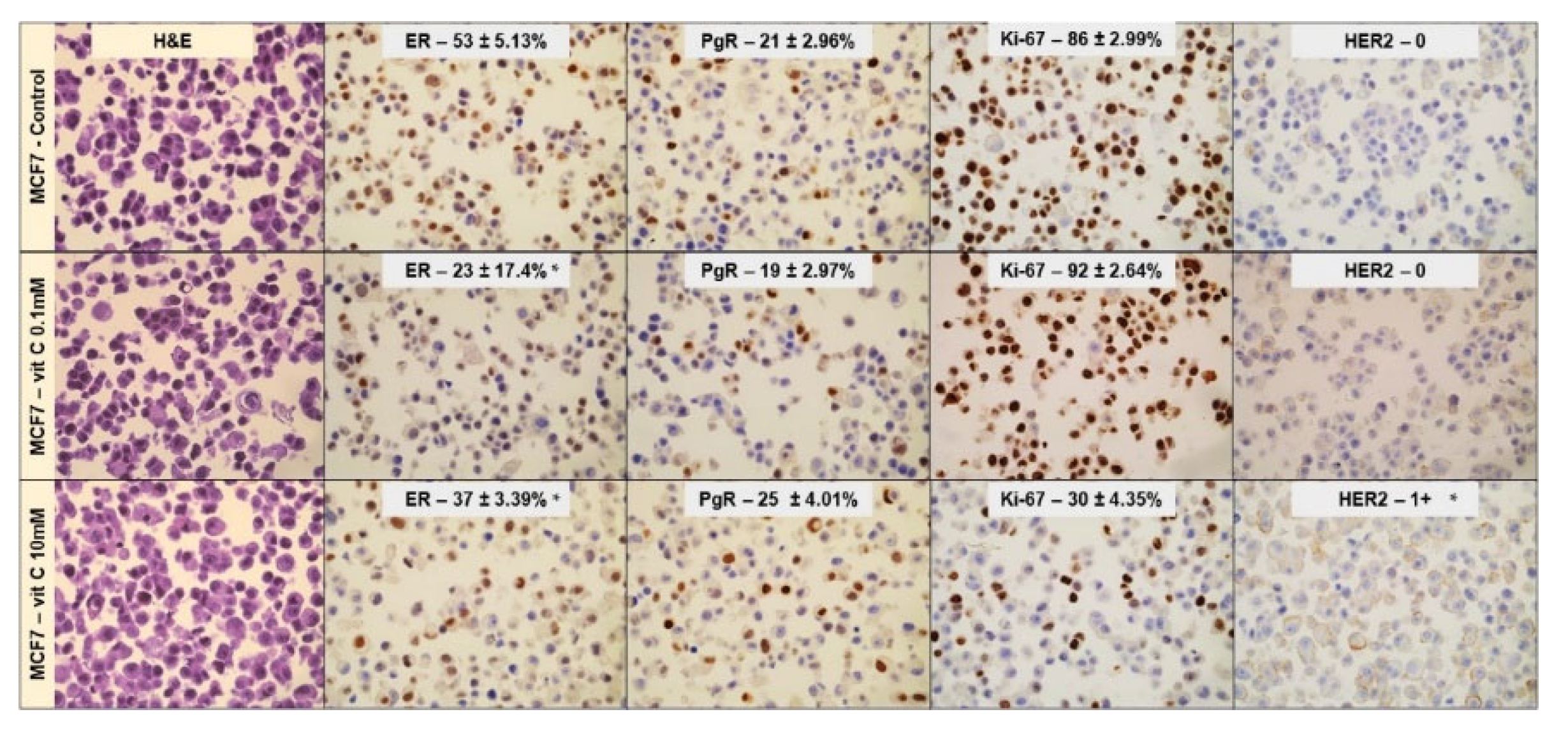
Figure 3.
Effect of 0.1mM and 10mM Vitamin C on MCF7 cells phenotype. Immunocytochemistry analysis of ER, PgR, Ki67, and HER2. Data represent the mean+SD of ten slide readings from 2 experiments performed in duplicate. *p < 0.05 versus control sample (CTR).
Figure 3.
Effect of 0.1mM and 10mM Vitamin C on MCF7 cells phenotype. Immunocytochemistry analysis of ER, PgR, Ki67, and HER2. Data represent the mean+SD of ten slide readings from 2 experiments performed in duplicate. *p < 0.05 versus control sample (CTR).
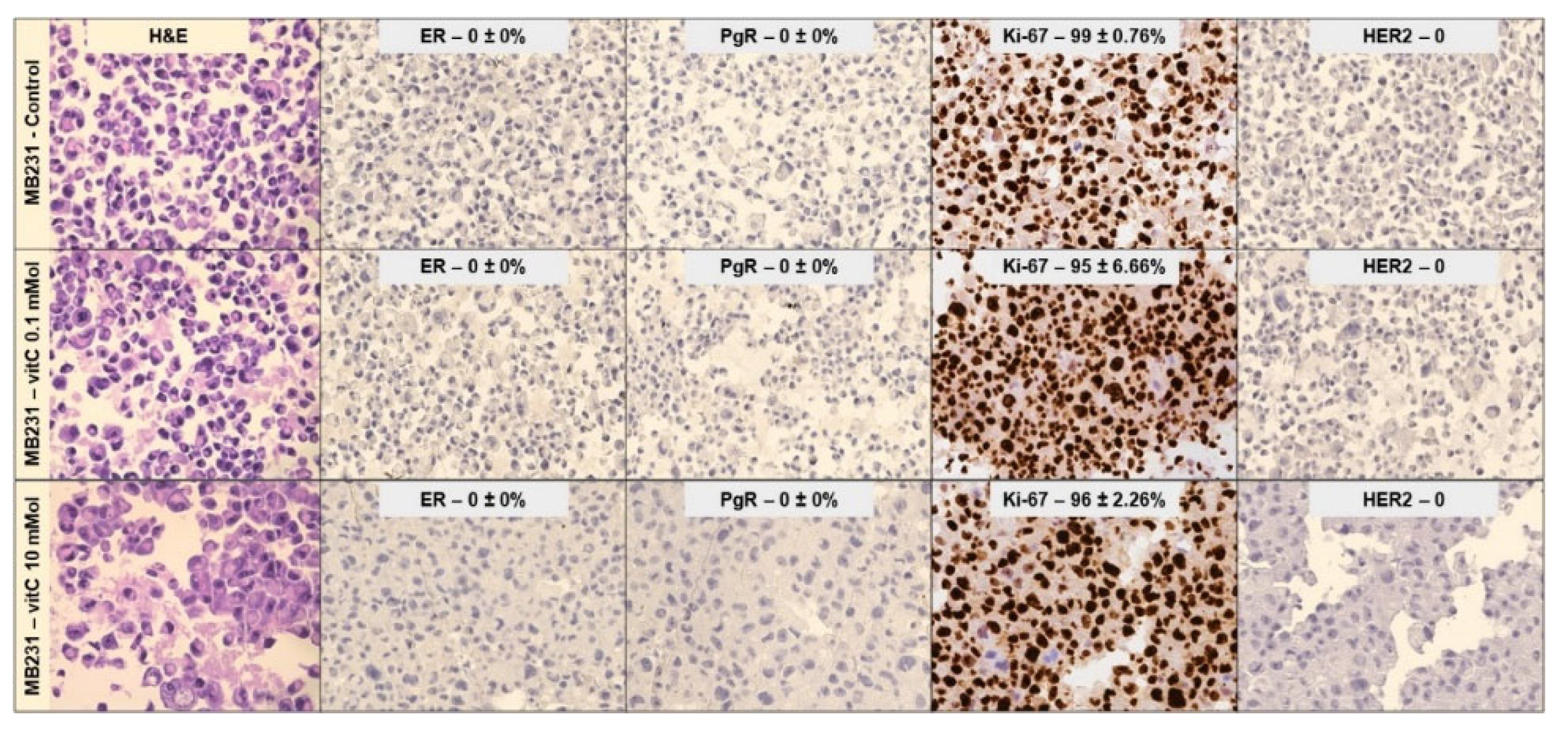
Figure 4.
Effect of 0.1mM and 10mM Vitamin C on Mb231 cells phenotype. Immunocytochemistry analysis of ER, PgR, Ki67, and HER2. Data represent the mean+SD of ten slide readings from 2 experiments performed in duplicate. *p < 0.05 versus control sample (CTR).
Figure 4.
Effect of 0.1mM and 10mM Vitamin C on Mb231 cells phenotype. Immunocytochemistry analysis of ER, PgR, Ki67, and HER2. Data represent the mean+SD of ten slide readings from 2 experiments performed in duplicate. *p < 0.05 versus control sample (CTR).
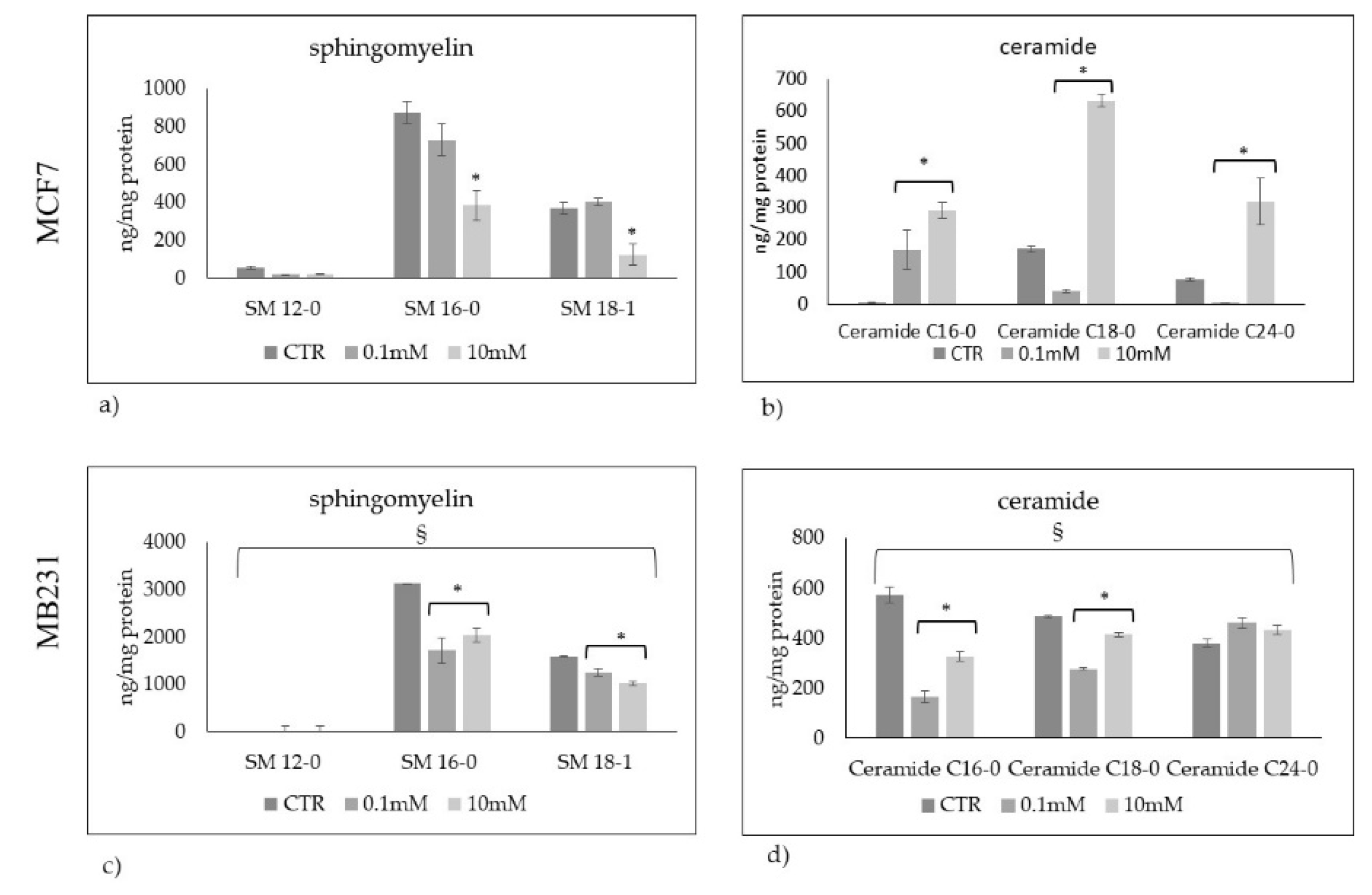
Figure 5.
Sphingomyelin and ceramide species in MCF7 (a,b) and Mb231 (c,d) cells treated with 0.1mM and 10mM Vitamin C. Data are expressed as the mean ± SD of 3 independent experiments performed in duplicate. *p < 0.05 versus control sample (CTR). § p < 0.05 versus MCF7 cells.
Figure 5.
Sphingomyelin and ceramide species in MCF7 (a,b) and Mb231 (c,d) cells treated with 0.1mM and 10mM Vitamin C. Data are expressed as the mean ± SD of 3 independent experiments performed in duplicate. *p < 0.05 versus control sample (CTR). § p < 0.05 versus MCF7 cells.
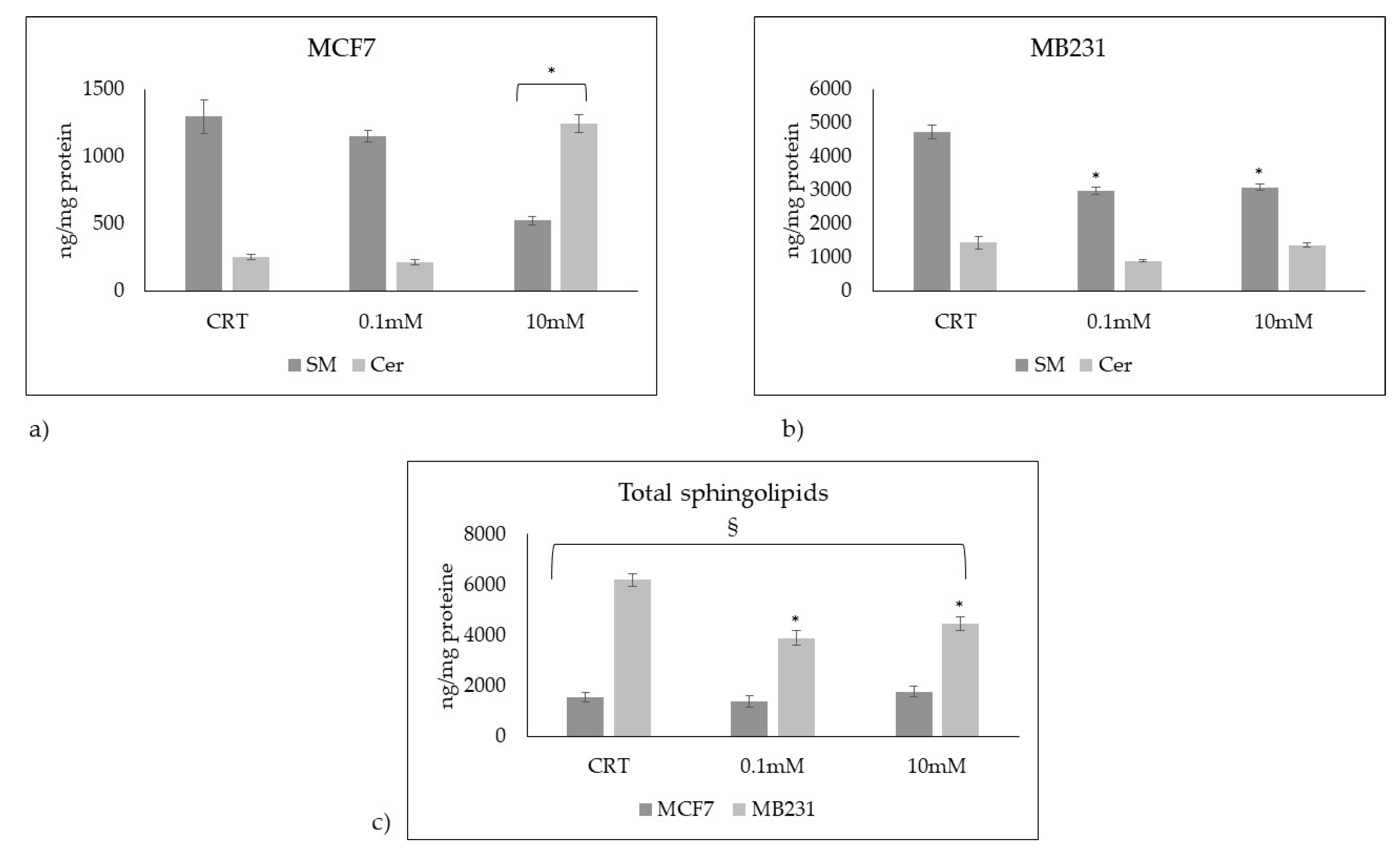
Figure 6.
Total sphingomyelin and ceramide species in a) MCF7 and b) Mb231 cells treated with 0.1mM and 10mM Vitamin C. c) total sphingolipids (sphingomyelin + ceramide species) in MCF7 and MB231 cells. Data are expressed as the mean ± SD of 3 independent experiments performed in duplicate. *p < 0.05 versus control sample (CTR). § p < 0.05 MB231 cells versus MCF7 cells.
Figure 6.
Total sphingomyelin and ceramide species in a) MCF7 and b) Mb231 cells treated with 0.1mM and 10mM Vitamin C. c) total sphingolipids (sphingomyelin + ceramide species) in MCF7 and MB231 cells. Data are expressed as the mean ± SD of 3 independent experiments performed in duplicate. *p < 0.05 versus control sample (CTR). § p < 0.05 MB231 cells versus MCF7 cells.
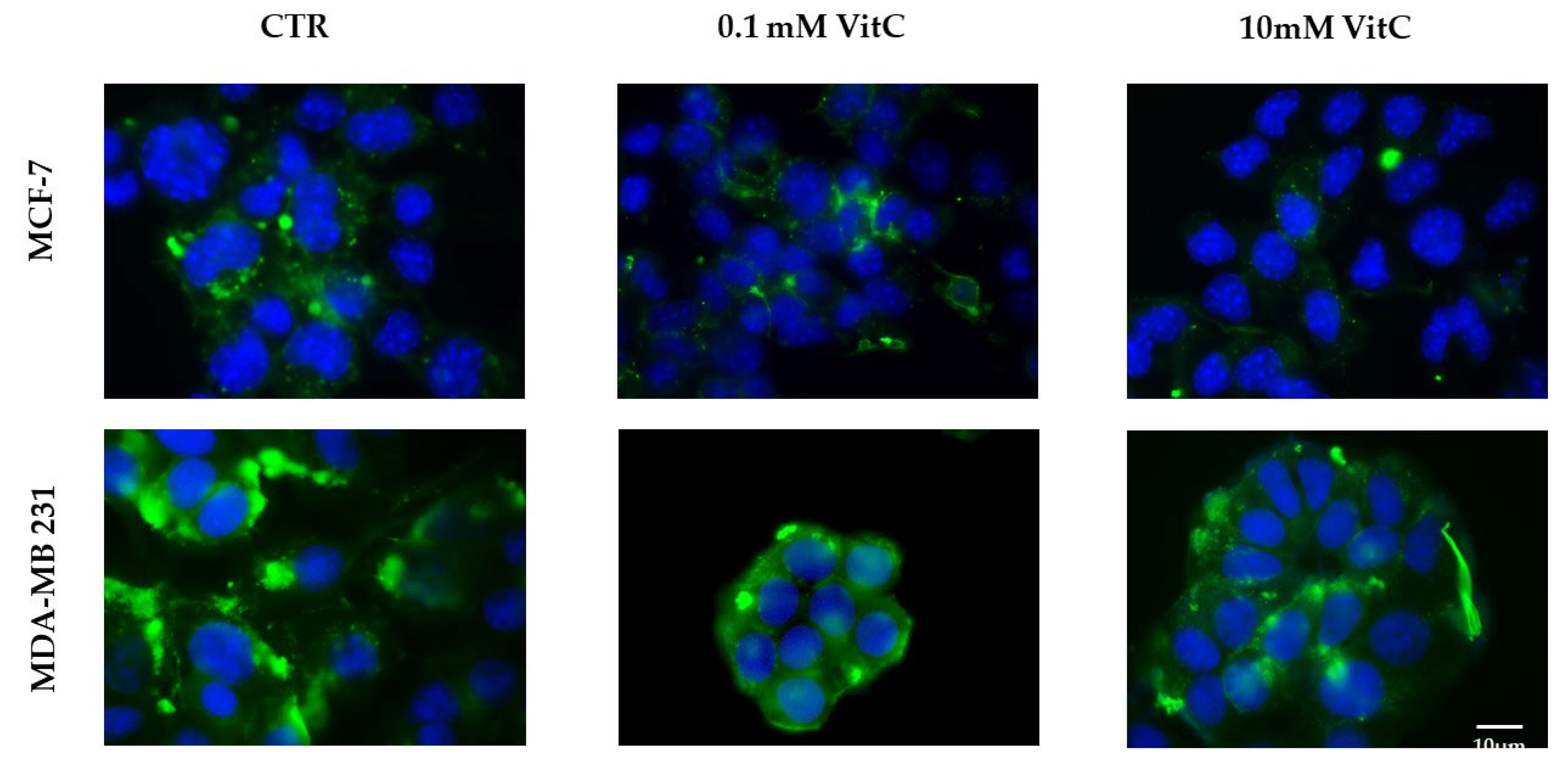
Figure 7.
Presence of sphingomyelin in control (CTR), 0.1mM and 10mM treated MCF7 and Mb231 cells with fluorescent probe EGFP-NT-Lys.
Figure 7.
Presence of sphingomyelin in control (CTR), 0.1mM and 10mM treated MCF7 and Mb231 cells with fluorescent probe EGFP-NT-Lys.
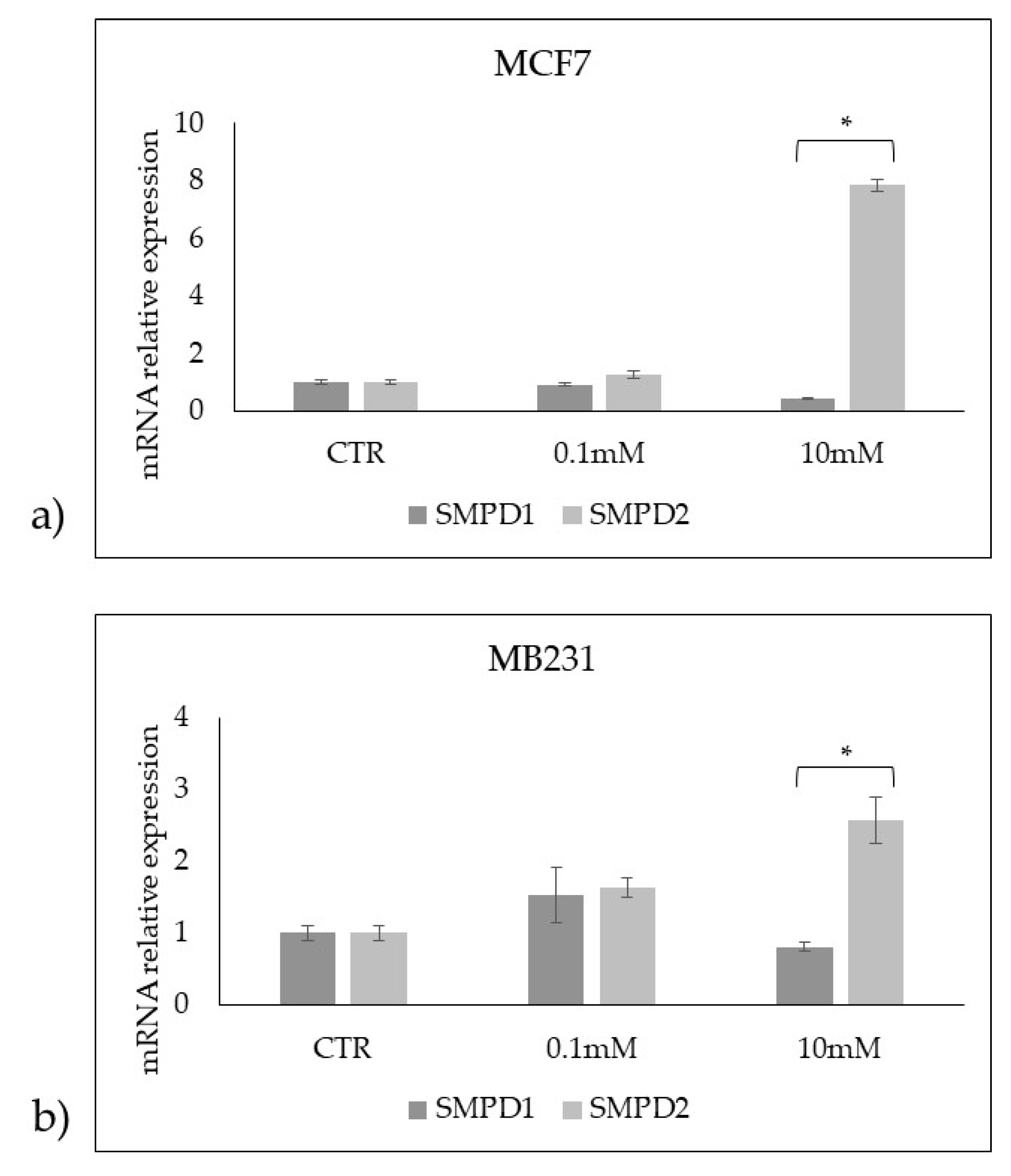
Figure 8.
Effect of 0.1mM and 10mM Vitamin C on gene expression of SMPD1 coding acid sphingomyelinase and SMPD2 coding neutral sphingomyelinase 1 in a) MCF7 and b) MB231 cells. GAPDH and 18S rRNA were used as housekeeping genes. mRNA relative expression levels were calculated as 2−ΔΔCt, comparing the results of the treated samples with control sample (CTR) equal to 1, the origin of axes. Data are expressed as the mean ± SD of 3 independent experiments performed in duplicate. *p < 0.05 versus CTR.
Figure 8.
Effect of 0.1mM and 10mM Vitamin C on gene expression of SMPD1 coding acid sphingomyelinase and SMPD2 coding neutral sphingomyelinase 1 in a) MCF7 and b) MB231 cells. GAPDH and 18S rRNA were used as housekeeping genes. mRNA relative expression levels were calculated as 2−ΔΔCt, comparing the results of the treated samples with control sample (CTR) equal to 1, the origin of axes. Data are expressed as the mean ± SD of 3 independent experiments performed in duplicate. *p < 0.05 versus CTR.
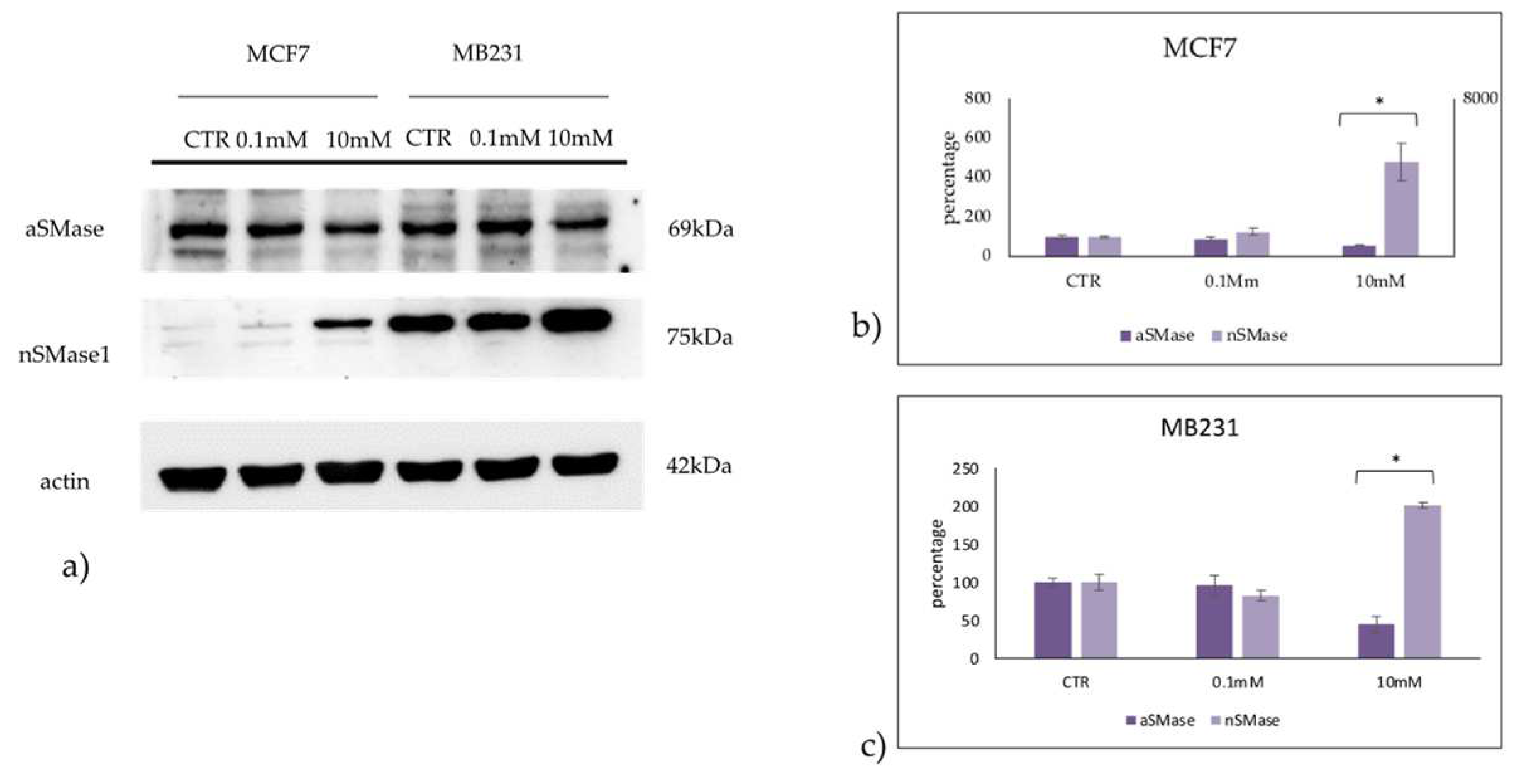
Figure 9.
Effect of 0.1mM and 10mM Vitamin C on acid sphingomyelinase (aSMase) and neutral sphingomyelinase1 (nSMase) in MCF7 and MB231 cells. a) western blotting panel of aSMase and nSMase1 and actin as reference; b) densitometric analysis, the values were normalized with actin and were expressed as percentage of control sample (CTR). Data are expressed as expressed as the mean+SD of 3 independent experiments performed in duplicate. *p<0.05 versus CTR.
Figure 9.
Effect of 0.1mM and 10mM Vitamin C on acid sphingomyelinase (aSMase) and neutral sphingomyelinase1 (nSMase) in MCF7 and MB231 cells. a) western blotting panel of aSMase and nSMase1 and actin as reference; b) densitometric analysis, the values were normalized with actin and were expressed as percentage of control sample (CTR). Data are expressed as expressed as the mean+SD of 3 independent experiments performed in duplicate. *p<0.05 versus CTR.