Submitted:
08 June 2023
Posted:
09 June 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Flavonoids
2.1. General Overview of Flavonoids
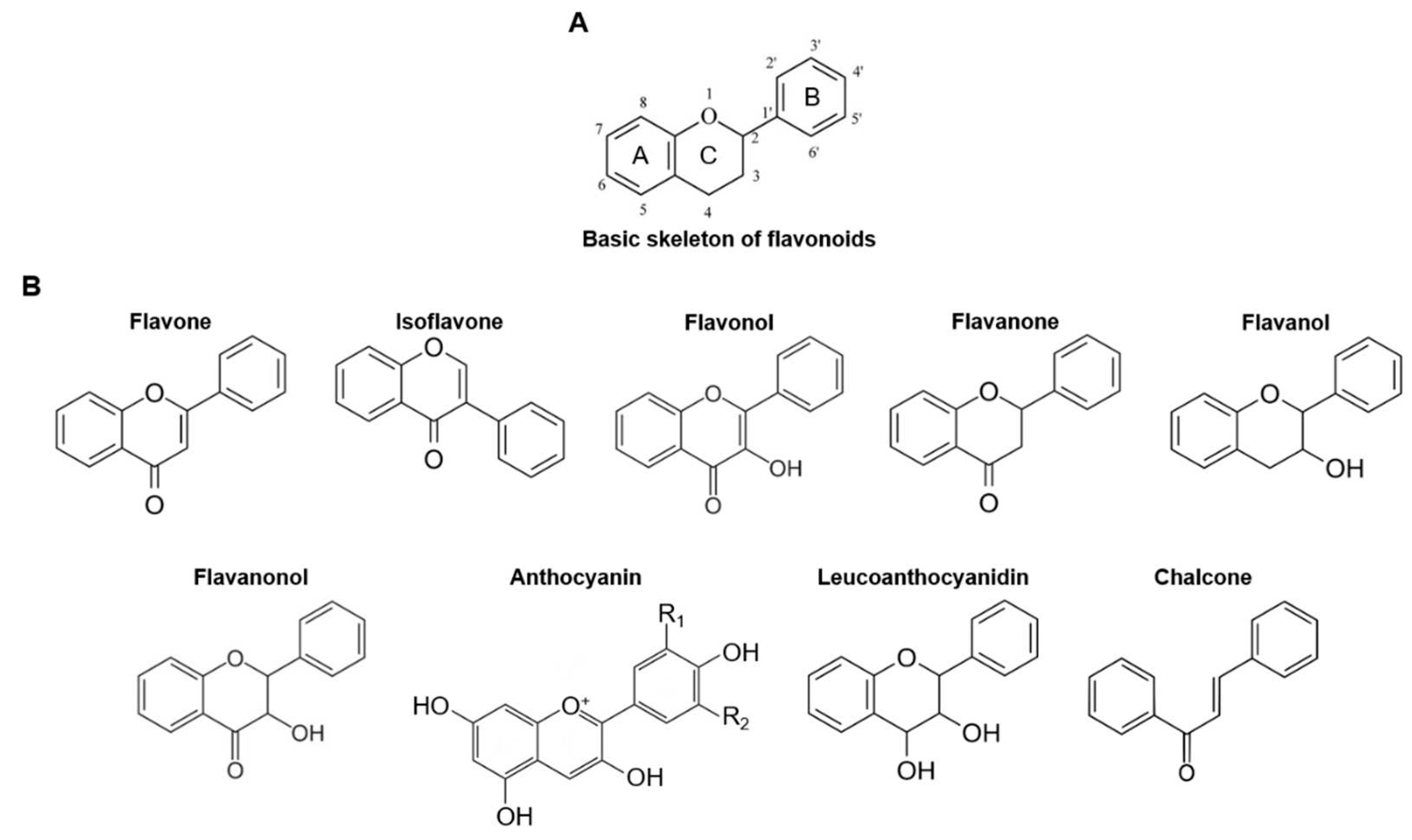
2.2. Structure and Classification of Flavonoids
3. Caspase-11 Non-Canonical Inflammasome
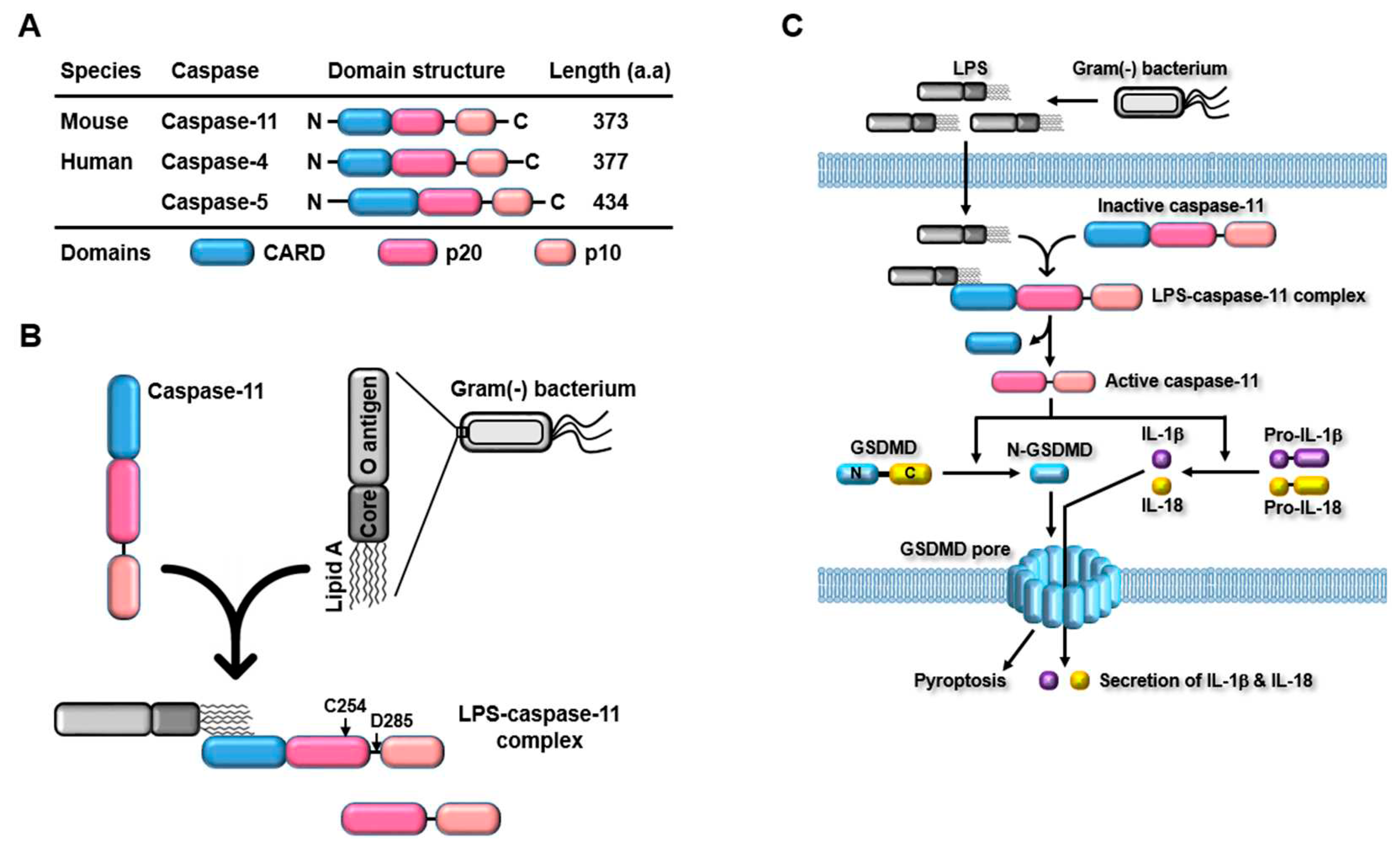
3.1. Discovery and Structure
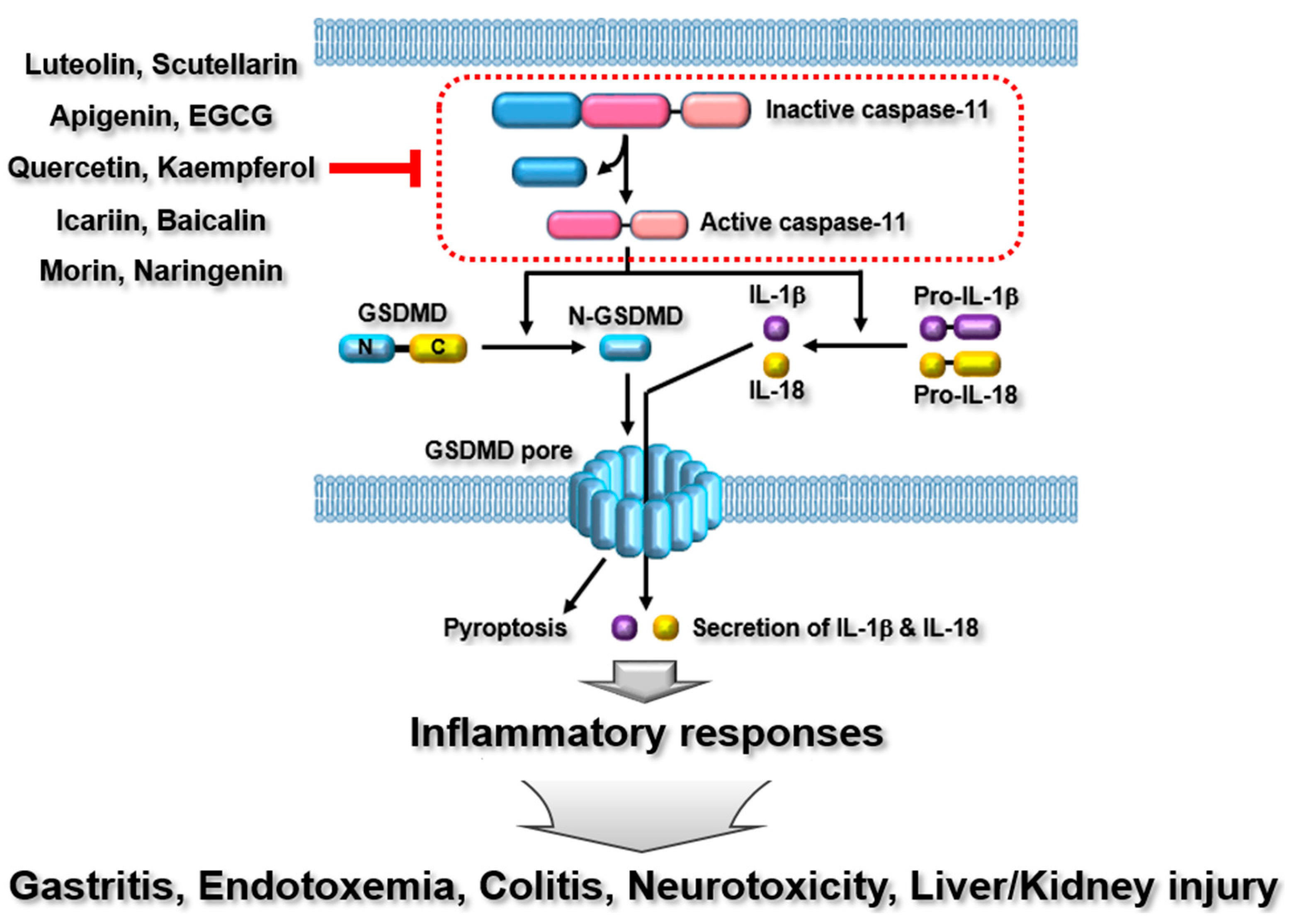
3.2. Caspase-11 Non-Canonical Inflammasome-Activated Inflammatory Signaling Pathways
4. Caspase-11 Non-Canonical Inflammasome
4.1. Luteolin
4.2. Scutellarin
4.3. Apigenin
4.4. Epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG)
4.5. Quercetin
4.6. Kaempferol
4.7. Icariin
4.8. Baicalin
4.9. Morin
4.10. Naringenin
5. Conclusions
Authors Contribution
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PRR | Pattern recognition receptor |
| PAMP | Pathogen-associated molecular pattern |
| DAMP | Danger-associated molecular pattern |
| NLR | NOD-like receptor |
| CARD | Caspase recruitment domain |
| AIM2 | Absent in melanoma 2 |
| LPS | Lipopolysaccharide |
| GSDMD | Gasdermin D |
| GBP | Guanylate-binding protein |
| ALI | Acute lung injury |
| IPF | Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis |
| EGCG | Epigallocatechin-3-gallate |
| I/R | Hypoxia/reoxygenation |
References
- Xue, Y.; Enosi Tuipulotu, D.; Tan, W.H.; Kay, C.; Man, S.M. Emerging Activators and Regulators of Inflammasomes and Pyroptosis. Trends Immunol 2019, 40, 1035–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, D.; Liwinski, T.; Elinav, E. Inflammasome activation and regulation: toward a better understanding of complex mechanisms. Cell Discov 2020, 6, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Huang, H.; Liu, B.; Zhang, Y.; Pan, X.; Yu, X.Y.; Shen, Z.; Song, Y.H. Inflammasomes as therapeutic targets in human diseases. Signal Transduct Target Ther 2021, 6, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boxberger, N.; Hecker, M.; Zettl, U.K. Dysregulation of Inflammasome Priming and Activation by MicroRNAs in Human Immune-Mediated Diseases. J Immunol 2019, 202, 2177–2187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, Y.S. Role of inflammasomes in inflammatory autoimmune rheumatic diseases. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol 2018, 22, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, H.; Callaway, J.B.; Ting, J.P. Inflammasomes: mechanism of action, role in disease, and therapeutics. Nat Med 2015, 21, 677–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, Y.S. Potential benefits of ginseng against COVID-19 by targeting inflammasomes. J Ginseng Res 2022. [CrossRef]
- Yi, Y.S. New mechanisms of ginseng saponin-mediated anti-inflammatory action via targeting canonical inflammasome signaling pathways. J Ethnopharmacol 2021, 278, 114292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kayagaki, N.; Warming, S.; Lamkanfi, M.; Vande Walle, L.; Louie, S.; Dong, J.; Newton, K.; Qu, Y.; Liu, J.; Heldens, S. , et al. Non-canonical inflammasome activation targets caspase-11. Nature 2011, 479, 117–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagar, J.A.; Powell, D.A.; Aachoui, Y.; Ernst, R.K.; Miao, E.A. Cytoplasmic LPS activates caspase-11: implications in TLR4-independent endotoxic shock. Science 2013, 341, 1250–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayagaki, N.; Wong, M.T.; Stowe, I.B.; Ramani, S.R.; Gonzalez, L.C.; Akashi-Takamura, S.; Miyake, K.; Zhang, J.; Lee, W.P.; Muszynski, A. , et al. Noncanonical inflammasome activation by intracellular LPS independent of TLR4. Science 2013, 341, 1246–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Gao, W.; Ding, J.; Li, P.; Hu, L.; Shao, F. Inflammatory caspases are innate immune receptors for intracellular LPS. Nature 2014, 514, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Shao, F. SnapShot: The Noncanonical Inflammasome. Cell 2017, 168, 544–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Y.S. Caspase-11 non-canonical inflammasome: a critical sensor of intracellular lipopolysaccharide in macrophage-mediated inflammatory responses. Immunology 2017, 152, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matikainen, S.; Nyman, T.A.; Cypryk, W. Function and Regulation of Noncanonical Caspase-4/5/11 Inflammasome. J Immunol 2020, 204, 3063–3069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Y.S. MicroRNA-mediated epigenetic regulation of inflammasomes in inflammatory responses and immunopathologies. Semin Cell Dev Biol 2022. [CrossRef]
- Yi, Y.S. Functional crosstalk between non-canonical caspase-11 and canonical NLRP3 inflammasomes during infection-mediated inflammation. Immunology 2020, 159, 142–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pellegrini, C.; Antonioli, L.; Lopez-Castejon, G.; Blandizzi, C.; Fornai, M. Canonical and Non-Canonical Activation of NLRP3 Inflammasome at the Crossroad between Immune Tolerance and Intestinal Inflammation. Front Immunol 2017, 8, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruhl, S.; Broz, P. Caspase-11 activates a canonical NLRP3 inflammasome by promoting K(+) efflux. Eur J Immunol 2015, 45, 2927–2936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Carvalho, R.V.H.; Andrade, W.A.; Lima-Junior, D.S.; Dilucca, M.; de Oliveira, C.V.; Wang, K.; Nogueira, P.M.; Rugani, J.N.; Soares, R.P.; Beverley, S.M. , et al. Leishmania Lipophosphoglycan Triggers Caspase-11 and the Non-canonical Activation of the NLRP3 Inflammasome. Cell Rep 2019, 26, 429–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, F.; Zheng, P.Q.; Zhao, L.Q.; Wang, Y.Z.; Miao, N.J.; Zhou, Z.L.; Cheng, Q.; Chen, P.P.; Xie, H.Y.; Li, J.Y. , et al. Caspase-11 promotes NLRP3 inflammasome activation via the cleavage of pannexin1 in acute kidney disease. Acta Pharmacol Sin 2022, 43, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, Y.S. Dual roles of the caspase-11 non-canonical inflammasome in inflammatory bowel disease. Int Immunopharmacol 2022, 108, 108739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, Y.S. Regulatory Roles of Caspase-11 Non-Canonical Inflammasome in Inflammatory Liver Diseases. Int J Mol Sci 2022, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, J.H.; Cho, H.J.; Yi, Y.S. A novel mechanism of Korean Red Ginseng-mediated anti-inflammatory action via targeting caspase-11 non-canonical inflammasome in macrophages. J Ginseng Res 2022, 46, 675–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Zhao, H.; Lu, J.; Lin, K.; Ni, J.; Wu, G.; Tang, H. Caspase-11-Mediated Hepatocytic Pyroptosis Promotes the Progression of Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol 2021, 12, 653–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, Y.S. Caspase-11 Noncanonical Inflammasome: A Novel Key Player in Murine Models of Neuroinflammation and Multiple Sclerosis. Neuroimmunomodulation 2021, 28, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, K.; Chen, Y.Q.; Chai, Y.S.; Lin, S.H.; Wang, C.J.; Xu, F. HMGB1 suppress the expression of IL-35 by regulating Naive CD4+ T cell differentiation and aggravating Caspase-11-dependent pyroptosis in acute lung injury. Int Immunopharmacol 2021, 91, 107295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Sun, J.; Meng, X. Pyroptosis by caspase-11 inflammasome-Gasdermin D pathway in autoimmune diseases. Pharmacol Res 2021, 165, 105408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, M.; Sun, X.; Liu, S.; Tang, Y.; Shi, Y.; Bai, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yang, Q.; Yang, Q.; Jiang, W. , et al. Caspase-11-Gasdermin D-Mediated Pyroptosis Is Involved in the Pathogenesis of Atherosclerosis. Front Pharmacol 2021, 12, 657486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colarusso, C.; Terlizzi, M.; Lamort, A.S.; Cerqua, I.; Roviezzo, F.; Stathopoulos, G.; Pinto, A.; Sorrentino, R. Caspase-11 and AIM2 inflammasome are involved in smoking-induced COPD and lung adenocarcinoma. Oncotarget 2021, 12, 1057–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agnew, A.; Nulty, C.; Creagh, E.M. Regulation, Activation and Function of Caspase-11 during Health and Disease. Int J Mol Sci 2021, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu Khweek, A.; Joldrichsen, M.R.; Kim, E.; Attia, Z.; Krause, K.; Daily, K.; Estfanous, S.; Hamilton, K.; Badr, A.; Anne, M.N.K. , et al. Caspase-11 regulates lung inflammation in response to house dust mites. Cell Immunol 2021, 370, 104425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Chen, Y.; Yu, S.; Jin, B.; Liu, W. Inhibition of C3a/C3aR Axis in Diverse Stages of Ulcerative Colitis Affected the Prognosis of UC by Modulating the Pyroptosis and Expression of Caspase-11. Inflammation 2020, 43, 2128–2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, Y.S. Caspase-11 Non-Canonical Inflammasome: Emerging Activator and Regulator of Infection-Mediated Inflammatory Responses. Int J Mol Sci 2020, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Meng, R.; Wang, X.; Xu, Y.; Tang, Y.; Wu, J.; Xue, Q.; Yu, S.; Duan, M.; Shan, D. , et al. Caspase-11 signaling enhances graft-versus-host disease. Nat Commun 2019, 10, 4044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caution, K.; Young, N.; Robledo-Avila, F.; Krause, K.; Abu Khweek, A.; Hamilton, K.; Badr, A.; Vaidya, A.; Daily, K.; Gosu, H. , et al. Caspase-11 Mediates Neutrophil Chemotaxis and Extracellular Trap Formation During Acute Gouty Arthritis Through Alteration of Cofilin Phosphorylation. Front Immunol 2019, 10, 2519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Y.S. Regulatory Roles of the Caspase-11 Non-Canonical Inflammasome in Inflammatory Diseases. Immune Netw 2018, 18, e41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, N.J.; Xie, H.Y.; Xu, D.; Yin, J.Y.; Wang, Y.Z.; Wang, B.; Yin, F.; Zhou, Z.L.; Cheng, Q.; Chen, P.P. , et al. Caspase-11 promotes renal fibrosis by stimulating IL-1beta maturation via activating caspase-1. Acta Pharmacol Sin 2019, 40, 790–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Fan, Z.; Yang, Z.; Huang, T.; Tong, Y.; Yang, D.; Mao, X.; Yang, M. Flavonoids-Natural Gifts to Promote Health and Longevity. Int J Mol Sci 2022, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamsudin, N.F.; Ahmed, Q.U.; Mahmood, S.; Ali Shah, S.A.; Khatib, A.; Mukhtar, S.; Alsharif, M.A.; Parveen, H.; Zakaria, Z.A. Antibacterial Effects of Flavonoids and Their Structure-Activity Relationship Study: A Comparative Interpretation. Molecules 2022, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciumarnean, L.; Milaciu, M.V.; Runcan, O.; Vesa, S.C.; Rachisan, A.L.; Negrean, V.; Perne, M.G.; Donca, V.I.; Alexescu, T.G.; Para, I. , et al. The Effects of Flavonoids in Cardiovascular Diseases. Molecules 2020, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, S.; Kumar, V.; Singh, S.K.; Dubey, A.K.; Kim, J.J. Flavonoids: Potential Candidates for the Treatment of Neurodegenerative Disorders. Biomedicines 2021, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santana, F.P.R.; Thevenard, F.; Gomes, K.S.; Taguchi, L.; Camara, N.O.S.; Stilhano, R.S.; Ureshino, R.P.; Prado, C.M.; Lago, J.H.G. New perspectives on natural flavonoids on COVID-19-induced lung injuries. Phytother Res 2021, 35, 4988–5006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafarinia, M.; Sadat Hosseini, M.; Kasiri, N.; Fazel, N.; Fathi, F.; Ganjalikhani Hakemi, M.; Eskandari, N. Quercetin with the potential effect on allergic diseases. Allergy Asthma Clin Immunol 2020, 16, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gouveia, H.; Urquiza-Martinez, M.V.; Manhaes-de-Castro, R.; Costa-de-Santana, B.J.R.; Villarreal, J.P.; Mercado-Camargo, R.; Torner, L.; de Souza Aquino, J.; Toscano, A.E.; Guzman-Quevedo, O. Effects of the Treatment with Flavonoids on Metabolic Syndrome Components in Humans: A Systematic Review Focusing on Mechanisms of Action. Int J Mol Sci 2022, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Shi, J.; Nice, E.C.; Huang, C.; Shi, Z. The Multifaceted Role of Flavonoids in Cancer Therapy: Leveraging Autophagy with a Double-Edged Sword. Antioxidants (Basel) 2021, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Khayri, J.M.; Sahana, G.R.; Nagella, P.; Joseph, B.V.; Alessa, F.M.; Al-Mssallem, M.Q. Flavonoids as Potential Anti-Inflammatory Molecules: A Review. Molecules 2022, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maleki, S.J.; Crespo, J.F.; Cabanillas, B. Anti-inflammatory effects of flavonoids. Food Chem 2019, 299, 125124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, H.; Heo, M.Y.; Kim, H.P. Flavonoids: Broad Spectrum Agents on Chronic Inflammation. Biomol Ther (Seoul) 2019, 27, 241–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choy, K.W.; Murugan, D.; Leong, X.F.; Abas, R.; Alias, A.; Mustafa, M.R. Flavonoids as Natural Anti-Inflammatory Agents Targeting Nuclear Factor-Kappa B (NFkappaB) Signaling in Cardiovascular Diseases: A Mini Review. Front Pharmacol 2019, 10, 1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, L.; Bai, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Huang, L.; Ma, R.; Wang, L.; Duan, H.; Wan, Q. Baicalin alleviates collageninduced arthritis and suppresses TLR2/MYD88/NFkappaB p65 signaling in rats and HFLSRAs. Mol Med Rep 2020, 22, 2833–2841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, H.; He, Y.; La, L.; Hou, C.; Song, L.; Yang, Q.; Wu, F.; Liu, W.; Hou, L.; Li, Y. , et al. The flavonoid-enriched extract from the root of Smilax china L. inhibits inflammatory responses via the TLR-4-mediated signaling pathway. J Ethnopharmacol 2020, 256, 112785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yahfoufi, N.; Alsadi, N.; Jambi, M.; Matar, C. The Immunomodulatory and Anti-Inflammatory Role of Polyphenols. Nutrients 2018, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Yoon, J.H.; Won, H.J.; Ji, H.S.; Yuk, H.J.; Park, K.H.; Park, H.Y.; Jeong, T.S. Isotrifoliol inhibits pro-inflammatory mediators by suppression of TLR/NF-kappaB and TLR/MAPK signaling in LPS-induced RAW264.7 cells. Int Immunopharmacol 2017, 45, 110–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owona, B.A.; Abia, W.A.; Moundipa, P.F. Natural compounds flavonoids as modulators of inflammasomes in chronic diseases. Int Immunopharmacol 2020, 84, 106498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, Y.S. Regulatory Roles of Flavonoids on Inflammasome Activation during Inflammatory Responses. Mol Nutr Food Res 2018, 62, e1800147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez, G.; Mijares, M.R.; De Sanctis, J.B. Effects of Flavonoids and Its Derivatives on Immune Cell Responses. Recent Pat Inflamm Allergy Drug Discov 2019, 13, 84–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Y.S. Flavonoids: Nutraceuticals for Rheumatic Diseases via Targeting of Inflammasome Activation. Int J Mol Sci 2021, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Peng, F.; Xing, Z.; Chen, J.; Peng, C.; Li, D. Beneficial effects of natural flavonoids on neuroinflammation. Front Immunol 2022, 13, 1006434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Speisky, H.; Shahidi, F.; Costa de Camargo, A.; Fuentes, J. Revisiting the Oxidation of Flavonoids: Loss, Conservation or Enhancement of Their Antioxidant Properties. Antioxidants (Basel) 2022, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huyut, Z.; Beydemir, S.; Gulcin, I. Antioxidant and Antiradical Properties of Selected Flavonoids and Phenolic Compounds. Biochem Res Int 2017, 2017, 7616791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopustinskiene, D.M.; Jakstas, V.; Savickas, A.; Bernatoniene, J. Flavonoids as Anticancer Agents. Nutrients 2020, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slika, H.; Mansour, H.; Wehbe, N.; Nasser, S.A.; Iratni, R.; Nasrallah, G.; Shaito, A.; Ghaddar, T.; Kobeissy, F.; Eid, A.H. Therapeutic potential of flavonoids in cancer: ROS-mediated mechanisms. Biomed Pharmacother 2022, 146, 112442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vitelli Storelli, F.; Molina, A.J.; Zamora-Ros, R.; Fernandez-Villa, T.; Roussou, V.; Romaguera, D.; Aragones, N.; Obon-Santacana, M.; Guevara, M.; Gomez-Acebo, I. , et al. Flavonoids and the Risk of Gastric Cancer: An Exploratory Case-Control Study in the MCC-Spain Study. Nutrients 2019, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Wei, Y.; Zhao, S.; Zhang, M.; Yan, X.; Gao, X.; Li, J.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, A.; Gao, Y. Antitumor and immunomodulatory activities of total flavonoids extract from persimmon leaves in H22 liver tumor-bearing mice. Sci Rep 2018, 8, 10523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, M.Y.; Kim, Y.; Ha, S.E.; Kim, H.H.; Bhosale, P.B.; Abusaliya, A.; Jeong, S.H.; Kim, G.S. Function and Application of Flavonoids in the Breast Cancer. Int J Mol Sci 2022, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, P.H.; Cheng, C.H.; Lin, C.Y.; Huang, Y.T.; Lee, L.T.; Kandaswami, C.C.; Lin, Y.C.; Lee, K.P.; Hung, C.C.; Hwang, J.J. , et al. Dietary Flavonoids Luteolin and Quercetin Suppressed Cancer Stem Cell Properties and Metastatic Potential of Isolated Prostate Cancer Cells. Anticancer Res 2016, 36, 6367–6380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, T.H.; Hsu, W.H.; Tsai, P.H.; Huang, Y.T.; Lin, C.W.; Chen, K.C.; Tsai, I.H.; Kandaswami, C.C.; Huang, C.J.; Chang, G.D. , et al. Dietary flavonoids, luteolin and quercetin, inhibit invasion of cervical cancer by reduction of UBE2S through epithelial-mesenchymal transition signaling. Food Funct 2017, 8, 1558–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, B.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, N.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, B. Rhoifolin from Plumula Nelumbinis exhibits anti-cancer effects in pancreatic cancer via AKT/JNK signaling pathways. Sci Rep 2022, 12, 5654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, X.; Jha, S.K.; Jha, N.K.; Dewanjee, S.; Dey, A.; Deka, R.; Pritam, P.; Ramgopal, K.; Liu, W.; Hou, K. Antioxidants in brain tumors: current therapeutic significance and future prospects. Mol Cancer 2022, 21, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saraei, R.; Marofi, F.; Naimi, A.; Talebi, M.; Ghaebi, M.; Javan, N.; Salimi, O.; Hassanzadeh, A. Leukemia therapy by flavonoids: Future and involved mechanisms. J Cell Physiol 2019, 234, 8203–8220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Ishaq, R.K.; Abotaleb, M.; Kubatka, P.; Kajo, K.; Busselberg, D. Flavonoids and Their Anti-Diabetic Effects: Cellular Mechanisms and Effects to Improve Blood Sugar Levels. Biomolecules 2019, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shamsudin, N.F.; Ahmed, Q.U.; Mahmood, S.; Shah, S.A.A.; Sarian, M.N.; Khattak, M.; Khatib, A.; Sabere, A.S.M.; Yusoff, Y.M.; Latip, J. Flavonoids as Antidiabetic and Anti-Inflammatory Agents: A Review on Structural Activity Relationship-Based Studies and Meta-Analysis. Int J Mol Sci 2022, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Barrado, M.J.; Iglesias-Osma, M.C.; Perez-Garcia, E.; Carrero, S.; Blanco, E.J.; Carretero-Hernandez, M.; Carretero, J. Role of Flavonoids in The Interactions among Obesity, Inflammation, and Autophagy. Pharmaceuticals (Basel) 2020, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rufino, A.T.; Costa, V.M.; Carvalho, F.; Fernandes, E. Flavonoids as antiobesity agents: A review. Med Res Rev 2021, 41, 556–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Zhang, S.L. The role of flavonoids in the prevention and management of cardiovascular complications: a narrative review. Ann Palliat Med 2021, 10, 8254–8263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Y.; Tu, Y.; Lao, S.; Wu, M.; Yin, H.; Wang, L.; Liao, W. The role and mechanism of citrus flavonoids in cardiovascular diseases prevention and treatment. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 2022, 62, 7591–7614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parmenter, B.H.; Croft, K.D.; Hodgson, J.M.; Dalgaard, F.; Bondonno, C.P.; Lewis, J.R.; Cassidy, A.; Scalbert, A.; Bondonno, N.P. An overview and update on the epidemiology of flavonoid intake and cardiovascular disease risk. Food Funct 2020, 11, 6777–6806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vauzour, D.; Vafeiadou, K.; Rodriguez-Mateos, A.; Rendeiro, C.; Spencer, J.P. The neuroprotective potential of flavonoids: a multiplicity of effects. Genes Nutr 2008, 3, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayaz, M.; Sadiq, A.; Junaid, M.; Ullah, F.; Ovais, M.; Ullah, I.; Ahmed, J.; Shahid, M. Flavonoids as Prospective Neuroprotectants and Their Therapeutic Propensity in Aging Associated Neurological Disorders. Front Aging Neurosci 2019, 11, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minocha, T.; Birla, H.; Obaid, A.A.; Rai, V.; Sushma, P.; Shivamallu, C.; Moustafa, M.; Al-Shehri, M.; Al-Emam, A.; Tikhonova, M.A. , et al. Flavonoids as Promising Neuroprotectants and Their Therapeutic Potential against Alzheimer’s Disease. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2022, 2022, 6038996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agati, G.; Azzarello, E.; Pollastri, S.; Tattini, M. Flavonoids as antioxidants in plants: location and functional significance. Plant Sci 2012, 196, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutha, R.E.; Tatiya, A.U.; Surana, S.J. Flavonoids as natural phenolic compounds and their role in therapeutics: an overview. Futur J Pharm Sci 2021, 7, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panche, A.N.; Diwan, A.D.; Chandra, S.R. Flavonoids: an overview. J Nutr Sci 2016, 5, e47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szkudelska, K.; Nogowski, L. Genistein--a dietary compound inducing hormonal and metabolic changes. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 2007, 105, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denaro, M.; Smeriglio, A.; Trombetta, D. Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Citrus Flavanones Mix and Its Stability after In Vitro Simulated Digestion. Antioxidants (Basel) 2021, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Funaguchi, N.; Ohno, Y.; La, B.L.; Asai, T.; Yuhgetsu, H.; Sawada, M.; Takemura, G.; Minatoguchi, S.; Fujiwara, T.; Fujiwara, H. Narirutin inhibits airway inflammation in an allergic mouse model. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 2007, 34, 766–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.J.; Park, E.J.; Lee, B.W.; Cho, H.M.; Pham, T.L.; Hoang, Q.H.; Pan, C.H.; Oh, W.K. Flavanonol Glycosides from the Stems of Myrsine seguinii and Their Neuroprotective Activities. Pharmaceuticals (Basel) 2021, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Xu, Q.; Li, J.X.; Chen, T. Structural revision of two flavanonol glycosides from Smilax glabra. Planta Med 2009, 75, 654–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heller, W.; Britsch, L.; Forkmann, G.; Grisebach, H. Leucoanthocyanidins as intermediates in anthocyanidin biosynthesis in flowers of Matthiola incana R. Br. Planta 1985, 163, 191–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casson, C.N.; Yu, J.; Reyes, V.M.; Taschuk, F.O.; Yadav, A.; Copenhaver, A.M.; Nguyen, H.T.; Collman, R.G.; Shin, S. Human caspase-4 mediates noncanonical inflammasome activation against gram-negative bacterial pathogens. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2015, 112, 6688–6693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meunier, E.; Dick, M.S.; Dreier, R.F.; Schurmann, N.; Kenzelmann Broz, D.; Warming, S.; Roose-Girma, M.; Bumann, D.; Kayagaki, N.; Takeda, K. , et al. Caspase-11 activation requires lysis of pathogen-containing vacuoles by IFN-induced GTPases. Nature 2014, 509, 366–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilla, D.M.; Hagar, J.A.; Haldar, A.K.; Mason, A.K.; Degrandi, D.; Pfeffer, K.; Ernst, R.K.; Yamamoto, M.; Miao, E.A.; Coers, J. Guanylate binding proteins promote caspase-11-dependent pyroptosis in response to cytoplasmic LPS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2014, 111, 6046–6051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, J.C.; Dick, M.S.; Lagrange, B.; Degrandi, D.; Pfeffer, K.; Yamamoto, M.; Meunier, E.; Pelczar, P.; Henry, T.; Broz, P. LPS targets host guanylate-binding proteins to the bacterial outer membrane for non-canonical inflammasome activation. EMBO J 2018, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, J.C.; Broz, P. Sensing of invading pathogens by GBPs: At the crossroads between cell-autonomous and innate immunity. J Leukoc Biol 2018, 104, 729–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Zhou, K.; Xu, Z.; Ma, H.; Cao, X.; Yin, X.; Zeng, W.; Zahid, A.; Fu, S.; Ni, K. , et al. Crystal structure of caspase-11 CARD provides insights into caspase-11 activation. Cell Discov 2020, 6, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.L.; Stowe, I.B.; Gupta, A.; Kornfeld, O.S.; Roose-Girma, M.; Anderson, K.; Warming, S.; Zhang, J.; Lee, W.P.; Kayagaki, N. Caspase-11 auto-proteolysis is crucial for noncanonical inflammasome activation. J Exp Med 2018, 215, 2279–2288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moretti, J.; Jia, B.; Hutchins, Z.; Roy, S.; Yip, H.; Wu, J.; Shan, M.; Jaffrey, S.R.; Coers, J.; Blander, J.M. Caspase-11 interaction with NLRP3 potentiates the noncanonical activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome. Nat Immunol 2022, 23, 705–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caporali, S.; De Stefano, A.; Calabrese, C.; Giovannelli, A.; Pieri, M.; Savini, I.; Tesauro, M.; Bernardini, S.; Minieri, M.; Terrinoni, A. Anti-Inflammatory and Active Biological Properties of the Plant-Derived Bioactive Compounds Luteolin and Luteolin 7-Glucoside. Nutrients 2022, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.N.; Lee, Y.; Wu, D.; Pae, M. Luteolin inhibits NLRP3 inflammasome activation via blocking ASC oligomerization. J Nutr Biochem 2021, 92, 108614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.C.; Li, Z.; Xu, W.; Xiang, C.H.; Ma, Y.F. Luteolin alleviates NLRP3 inflammasome activation and directs macrophage polarization in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated RAW264.7 cells. Am J Transl Res 2018, 10, 265–273. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hwang, S.H.; Lorz, L.R.; Yi, D.K.; Noh, J.K.; Yi, Y.S.; Cho, J.Y. Viburnum pichinchense methanol extract exerts anti-inflammatory effects via targeting the NF-kappaB and caspase-11 non-canonical inflammasome pathways in macrophages. J Ethnopharmacol 2019, 245, 112161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, L.; Liang, J.; Zhou, Y.; Huang, J.; Zhang, T.; Wang, X.; Yin, H. Switch Off “Parallel Circuit”: Insight of New Strategy of Simultaneously Suppressing Canonical and Noncanonical Inflammation Activation in Endotoxemic Mice. Adv Biosyst 2020, 4, e2000037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.T.; Zhang, D.Y.; Xie, K.; Wang, C.J.; Xu, F. Luteolin activates Tregs to promote IL-10 expression and alleviating caspase-11-dependent pyroptosis in sepsis-induced lung injury. Int Immunopharmacol 2021, 99, 107914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chledzik, S.; Strawa, J.; Matuszek, K.; Nazaruk, J. Pharmacological Effects of Scutellarin, An Active Component of Genus Scutellaria and Erigeron: A Systematic Review. Am J Chin Med 2018, 46, 319–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Ma, Q. Clinical benefits and pharmacology of scutellarin: A comprehensive review. Pharmacol Ther 2018, 190, 105–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Jing, Y.Y.; Zeng, C.Y.; Li, C.G.; Xu, L.H.; Yan, L.; Bai, W.J.; Zha, Q.B.; Ouyang, D.Y.; He, X.H. Scutellarin Suppresses NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation in Macrophages and Protects Mice against Bacterial Sepsis. Front Pharmacol 2017, 8, 975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, L.; Wen, L.; Shi, Q.F.; Gao, F.; Huang, B.; Meng, J.; Hu, C.P.; Wang, C.M. Scutellarin ameliorates pulmonary fibrosis through inhibiting NF-kappaB/NLRP3-mediated epithelial-mesenchymal transition and inflammation. Cell Death Dis 2020, 11, 978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.J.; Chen, R.C.; Ma, X.Y.; Zhu, Y.; Sun, G.B.; Sun, X.B. Scutellarin protects against myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury by suppressing NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Phytomedicine 2020, 68, 153169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Guan, C.; Xu, L.; Wang, L.; Yang, C.; Zhao, L.; Zhou, B.; Luo, C.; Luan, H.; Jiang, W. , et al. Scutellarin Ameliorates Renal Injury via Increasing CCN1 Expression and Suppressing NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation in Hyperuricemic Mice. Front Pharmacol 2020, 11, 584942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Chen, R.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, Y.; Ma, X.; Sun, G.; Sun, X. Scutellarin protects against diabetic cardiomyopathy via inhibiting oxidative stress and inflammatory response in mice. Ann Palliat Med 2021, 10, 2481–2493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, P.; Zhao, Y.; Yu, F.; Wang, S.; Liu, K.; Cheng, X.; Shi, J.; He, Q.; Xia, Y. , et al. Scutellarin Protects Against Mitochondrial Reactive Oxygen Species-Dependent NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation to Attenuate Intervertebral Disc Degeneration. Front Bioeng Biotechnol 2022, 10, 883118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Zeng, B.; Zhong, M.; Li, H.; Xu, L.; Shu, J.; Wang, Y.; Yang, F.; Zhong, C.; Ye, X. , et al. Scutellarin inhibits caspase-11 activation and pyroptosis in macrophages via regulating PKA signaling. Acta Pharm Sin B 2021, 11, 112–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashyap, P.; Shikha, D.; Thakur, M.; Aneja, A. Functionality of apigenin as a potent antioxidant with emphasis on bioavailability, metabolism, action mechanism and in vitro and in vivo studies: A review. J Food Biochem 2022, 46, e13950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.L.; Yu, X.J.; Hu, H.B.; Yang, Q.W.; Liu, K.L.; Chen, Y.M.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, D.D.; Tian, H.; Zhu, G.Q. , et al. Apigenin Improves Hypertension and Cardiac Hypertrophy Through Modulating NADPH Oxidase-Dependent ROS Generation and Cytokines in Hypothalamic Paraventricular Nucleus. Cardiovasc Toxicol 2021, 21, 721–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Guo, T.; Deng, R.; Liu, L.; Yu, Y. Apigenin Ameliorates Insulin Resistance and Lipid Accumulation by Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and SREBP-1c/SREBP-2 Pathway in Palmitate-Induced HepG2 Cells and High-Fat Diet-Fed Mice. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 2021, 377, 146–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dourado, N.S.; Souza, C.D.S.; de Almeida, M.M.A.; Bispo da Silva, A.; Dos Santos, B.L.; Silva, V.D.A.; De Assis, A.M.; da Silva, J.S.; Souza, D.O.; Costa, M.F.D. , et al. Neuroimmunomodulatory and Neuroprotective Effects of the Flavonoid Apigenin in in vitro Models of Neuroinflammation Associated With Alzheimer’s Disease. Front Aging Neurosci 2020, 12, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmani, A.H.; Alsahli, M.A.; Almatroudi, A.; Almogbel, M.A.; Khan, A.A.; Anwar, S.; Almatroodi, S.A. The Potential Role of Apigenin in Cancer Prevention and Treatment. Molecules 2022, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.H.; Zhou, H.Y.; Cho, S.Y.; Kim, Y.S.; Lee, Y.S.; Jeong, C.S. Anti-inflammatory mechanisms of apigenin: inhibition of cyclooxygenase-2 expression, adhesion of monocytes to human umbilical vein endothelial cells, and expression of cellular adhesion molecules. Arch Pharm Res 2007, 30, 1318–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charalabopoulos, A.; Davakis, S.; Lambropoulou, M.; Papalois, A.; Simopoulos, C.; Tsaroucha, A. Apigenin Exerts Anti-inflammatory Effects in an Experimental Model of Acute Pancreatitis by Down-regulating TNF-alpha. In Vivo 2019, 33, 1133–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ginwala, R.; Bhavsar, R.; Chigbu, D.I.; Jain, P.; Khan, Z.K. Potential Role of Flavonoids in Treating Chronic Inflammatory Diseases with a Special Focus on the Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Apigenin. Antioxidants (Basel) 2019, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balez, R.; Steiner, N.; Engel, M.; Munoz, S.S.; Lum, J.S.; Wu, Y.; Wang, D.; Vallotton, P.; Sachdev, P.; O’Connor, M. , et al. Neuroprotective effects of apigenin against inflammation, neuronal excitability and apoptosis in an induced pluripotent stem cell model of Alzheimer’s disease. Sci Rep 2016, 6, 31450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.; Wang, X.; Qin, T.; Qu, R.; Ma, S. Apigenin ameliorates chronic mild stress-induced depressive behavior by inhibiting interleukin-1beta production and NLRP3 inflammasome activation in the rat brain. Behav Brain Res 2016, 296, 318–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marquez-Flores, Y.K.; Villegas, I.; Cardeno, A.; Rosillo, M.A.; Alarcon-de-la-Lastra, C. Apigenin supplementation protects the development of dextran sulfate sodium-induced murine experimental colitis by inhibiting canonical and non-canonical inflammasome signaling pathways. J Nutr Biochem 2016, 30, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Z.; Zhu, B.; Gao, M.; Wang, G.; Zhou, H.; Lu, J.; Guan, S. Apigenin alleviated PA-induced pyroptosis by activating autophagy in hepatocytes. Food Funct 2022, 13, 5559–5570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granja, A.; Frias, I.; Neves, A.R.; Pinheiro, M.; Reis, S. Therapeutic Potential of Epigallocatechin Gallate Nanodelivery Systems. Biomed Res Int 2017, 2017, 5813793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Li, X.; Hu, X.; Xu, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, H.; Diao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Li, L.; Yu, J. , et al. Epigallocatechin-3-gallate prevents inflammation and diabetes -Induced glucose tolerance through inhibition of NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Int Immunopharmacol 2021, 93, 107412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.E.; Yang, G.; Park, Y.B.; Kang, H.C.; Cho, Y.Y.; Lee, H.S.; Lee, J.Y. Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate Prevents Acute Gout by Suppressing NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation and Mitochondrial DNA Synthesis. Molecules 2019, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, X.; Liu, M.; Yao, W.; Du, K.; He, M.; Jin, X.; Jiao, L.; Ma, G.; Wei, B.; Wei, M. Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate Attenuates Microglial Inflammation and Neurotoxicity by Suppressing the Activation of Canonical and Noncanonical Inflammasome via TLR4/NF-kappaB Pathway. Mol Nutr Food Res 2019, 63, e1801230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, R.; Chen, J.; Jia, Q.; Yang, X.; Mehmood, S. Epigallocatechin-3-gallate ameliorates renal endoplasmic reticulum stress-mediated inflammation in type 2 diabetic rats. Exp Biol Med (Maywood) 2022, 247, 1410–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, D.; Hu, M.J.; Wang, Y.Q.; Cui, Y.L. Antioxidant Activities of Quercetin and Its Complexes for Medicinal Application. Molecules 2019, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bule, M.; Abdurahman, A.; Nikfar, S.; Abdollahi, M.; Amini, M. Antidiabetic effect of quercetin: A systematic review and meta-analysis of animal studies. Food Chem Toxicol 2019, 125, 494–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.L.A.; Bhattacharya, D. Antimicrobial Activity of Quercetin: An Approach to Its Mechanistic Principle. Molecules 2022, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gasmi, A.; Mujawdiya, P.K.; Lysiuk, R.; Shanaida, M.; Peana, M.; Gasmi Benahmed, A.; Beley, N.; Kovalska, N.; Bjorklund, G. Quercetin in the Prevention and Treatment of Coronavirus Infections: A Focus on SARS-CoV-2. Pharmaceuticals (Basel) 2022, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grewal, A.K.; Singh, T.G.; Sharma, D.; Sharma, V.; Singh, M.; Rahman, M.H.; Najda, A.; Walasek-Janusz, M.; Kamel, M.; Albadrani, G.M. , et al. Mechanistic insights and perspectives involved in neuroprotective action of quercetin. Biomed Pharmacother 2021, 140, 111729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, H.; Ullah, H.; Aschner, M.; Cheang, W.S.; Akkol, E.K. Neuroprotective Effects of Quercetin in Alzheimer’s Disease. Biomolecules 2019, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papakyriakopoulou, P.; Velidakis, N.; Khattab, E.; Valsami, G.; Korakianitis, I.; Kadoglou, N.P. Potential Pharmaceutical Applications of Quercetin in Cardiovascular Diseases. Pharmaceuticals (Basel) 2022, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.M.; Deng, X.T.; Zhou, J.; Li, Q.P.; Ge, X.X.; Miao, L. Pharmacological basis and new insights of quercetin action in respect to its anti-cancer effects. Biomed Pharmacother 2020, 121, 109604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yao, J.; Han, C.; Yang, J.; Chaudhry, M.T.; Wang, S.; Liu, H.; Yin, Y. Quercetin, Inflammation and Immunity. Nutrients 2016, 8, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, P.; Lin, W.; Deng, X.; Ba, X.; Han, L.; Chen, Z.; Qin, K.; Huang, Y.; Tu, S. Potential Implications of Quercetin in Autoimmune Diseases. Front Immunol 2021, 12, 689044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeedi-Boroujeni, A.; Mahmoudian-Sani, M.R. Anti-inflammatory potential of Quercetin in COVID-19 treatment. J Inflamm (Lond) 2021, 18, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byun, E.B.; Yang, M.S.; Choi, H.G.; Sung, N.Y.; Song, D.S.; Sin, S.J.; Byun, E.H. Quercetin negatively regulates TLR4 signaling induced by lipopolysaccharide through Tollip expression. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2013, 431, 698–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Chen, F.J.; Yang, W.L.; Qiao, H.Z.; Zhang, S.J. Quercetin improves cognitive disorder in aging mice by inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Food Funct 2021, 12, 717–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chanjitwiriya, K.; Roytrakul, S.; Kunthalert, D. Quercetin negatively regulates IL-1beta production in Pseudomonas aeruginosa-infected human macrophages through the inhibition of MAPK/NLRP3 inflammasome pathways. PLoS One 2020, 15, e0237752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.; Du, M.; Zhu, M.J. Quercetin suppresses NLRP3 inflammasome activation in epithelial cells triggered by Escherichia coli O157:H7. Free Radic Biol Med 2017, 108, 760–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Huang, Y.; Han, N.; He, F.; Li, M.; Bian, Z.; Liu, J.; Sun, T.; Zhu, L. Quercetin suppresses NLRP3 inflammasome activation and attenuates histopathology in a rat model of spinal cord injury. Spinal Cord 2016, 54, 592–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Periferakis, A.; Periferakis, K.; Badarau, I.A.; Petran, E.M.; Popa, D.C.; Caruntu, A.; Costache, R.S.; Scheau, C.; Caruntu, C.; Costache, D.O. Kaempferol: Antimicrobial Properties, Sources, Clinical, and Traditional Applications. Int J Mol Sci 2022, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.; Xiao, J.; El-Seedi, H.R.; Wozniak, K.S.; Daglia, M.; Little, P.J.; Weng, J.; Xu, S. Kaempferol and atherosclerosis: From mechanism to medicine. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 2022. [CrossRef]
- Ochiai, A.; Othman, M.B.; Sakamoto, K. Kaempferol ameliorates symptoms of metabolic syndrome by improving blood lipid profile and glucose tolerance. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 2021, 85, 2169–2176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva Dos Santos, J.; Goncalves Cirino, J.P.; de Oliveira Carvalho, P.; Ortega, M.M. The Pharmacological Action of Kaempferol in Central Nervous System Diseases: A Review. Front Pharmacol 2020, 11, 565700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imran, M.; Salehi, B.; Sharifi-Rad, J.; Aslam Gondal, T.; Saeed, F.; Imran, A.; Shahbaz, M.; Tsouh Fokou, P.V.; Umair Arshad, M.; Khan, H. , et al. Kaempferol: A Key Emphasis to Its Anticancer Potential. Molecules 2019, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, J.; Lu, Y.; Qian, Y.; Chen, B.; Wu, T.; Ji, G. Recent progress regarding kaempferol for the treatment of various diseases. Exp Ther Med 2019, 18, 2759–2776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, W.; Khan, H.; Shah, M.A.; Cauli, O.; Saso, L. Kaempferol as a Dietary Anti-Inflammatory Agent: Current Therapeutic Standing. Molecules 2020, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, K.P.; Malar, D.S.; Nabavi, S.F.; Sureda, A.; Xiao, J.; Nabavi, S.M.; Daglia, M. Kaempferol and inflammation: From chemistry to medicine. Pharmacol Res 2015, 99, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamalainen, M.; Nieminen, R.; Vuorela, P.; Heinonen, M.; Moilanen, E. Anti-inflammatory effects of flavonoids: genistein, kaempferol, quercetin, and daidzein inhibit STAT-1 and NF-kappaB activations, whereas flavone, isorhamnetin, naringenin, and pelargonidin inhibit only NF-kappaB activation along with their inhibitory effect on iNOS expression and NO production in activated macrophages. Mediators Inflamm 2007, 2007, 45673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.H.; Park, J.G.; Lee, J.; Yang, W.S.; Park, G.W.; Kim, H.G.; Yi, Y.S.; Baek, K.S.; Sung, N.Y.; Hossen, M.J. , et al. The dietary flavonoid Kaempferol mediates anti-inflammatory responses via the Src, Syk, IRAK1, and IRAK4 molecular targets. Mediators Inflamm 2015, 2015, 904142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, Y.; Dong, Y.; Sun, J.; Sun, M.; Hou, Q.; Lai, Y.; Zhang, B. Protective Effect of Kaempferol on LPS-Induced Inflammation and Barrier Dysfunction in a Coculture Model of Intestinal Epithelial Cells and Intestinal Microvascular Endothelial Cells. J Agric Food Chem 2020, 68, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spano, M.; Di Matteo, G.; Ingallina, C.; Ambroselli, D.; Carradori, S.; Gallorini, M.; Giusti, A.M.; Salvo, A.; Grosso, M.; Mannina, L. Modulatory Properties of Food and Nutraceutical Components Targeting NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation. Nutrients 2022, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Wu, F.; Zheng, T.; Wang, X.; Chen, Y.; Wu, X. Kaempferol attenuates retinal ganglion cell death by suppressing NLRP1/NLRP3 inflammasomes and caspase-8 via JNK and NF-kappaB pathways in acute glaucoma. Eye (Lond) 2019, 33, 777–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, H.; Min, D.S.; Park, H.; Kim, H.P. Flavonoids interfere with NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 2018, 355, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, J.; Hu, S.; Wang, J.; Zhang, X.; Yuan, D.; Zhang, C.; Liu, C.; Wang, T.; Zhou, Z. Icariin improves brain function decline in aging rats by enhancing neuronal autophagy through the AMPK/mTOR/ULK1 pathway. Pharm Biol 2021, 59, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, L.; Jin, X.; Shen, H.; Chen, X.; Chen, J.; Xu, B.; Xu, J. Icariin attenuates thioacetamide-induced bone loss via the RANKL-p38/ERK-NFAT signaling pathway. Mol Med Rep 2022, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaukat, A.; Shaukat, I.; Rajput, S.A.; Shukat, R.; Hanif, S.; Huang, S.; Aleem, M.T.; Li, K.; Li, Q.; Chen, C. , et al. Icariin Alleviates Escherichia coli Lipopolysaccharide-Mediated Endometritis in Mice by Inhibiting Inflammation and Oxidative Stress. Int J Mol Sci 2022, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, J.; Zhang, Y. Icariin, an Anti-atherosclerotic Drug from Chinese Medicinal Herb Horny Goat Weed. Front Pharmacol 2017, 8, 734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yang, H.; Xiong, J.; Zhao, J.; Guo, M.; Chen, J.; Zhao, X.; Chen, C.; He, Z.; Zhou, Y. , et al. Icariin as an emerging candidate drug for anticancer treatment: Current status and perspective. Biomed Pharmacother 2023, 157, 113991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhuo, S.; Song, D.; Wang, L.; Gu, J.; Ma, J.; Gu, Y.; Ji, M.; Chen, M.; Guo, Y. Icariin Inhibits Intestinal Inflammation of DSS-Induced Colitis Mice Through Modulating Intestinal Flora Abundance and Modulating p-p65/p65 Molecule. Turk J Gastroenterol 2021, 32, 382–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Meng, Q.; Wang, W.; Zhang, S.; Xiong, X.; Qin, S.; Zhang, J.; Li, A.; Liu, Z. Icariin inhibits the inflammation through down-regulating NF-kappaB/HIF-2alpha signal pathways in chondrocytes. Biosci Rep 2020, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.R.; Xu, X.Z.; Wang, Y.H.; Chen, J.W.; Xu, S.W.; Gu, L.Q.; Liu, P.Q. Icariin derivative inhibits inflammation through suppression of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase and nuclear factor-kappaB pathways. Biol Pharm Bull 2010, 33, 1307–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, Z.; Zhang, W.; Yan, X. Anti-inflammatory and immunoregulatory effects of icariin and icaritin. Biomed Pharmacother 2022, 151, 113180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, B.; Ye, H.; You, X.; Ni, H.; Chen, X.; Li, L. Icariin alleviates murine lupus nephritis via inhibiting NF-kappaB activation pathway and NLRP3 inflammasome. Life Sci 2018, 208, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zu, Y.; Mu, Y.; Li, Q.; Zhang, S.T.; Yan, H.J. Icariin alleviates osteoarthritis by inhibiting NLRP3-mediated pyroptosis. J Orthop Surg Res 2019, 14, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, W.; Ma, H.; Zhang, Z.; Jin, M.; Wang, J.; Xu, Y.; Wang, Z. The protective effect of icariin and phosphorylated icariin against LPS-induced intestinal goblet cell dysfunction. Innate Immun 2020, 26, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, K.; Liang, Y.; Cheng, A.; Wang, Q.; Li, Y.; Wei, H.; Zhou, C.; Wan, X. Antiviral Properties of Baicalin: a Concise Review. Rev Bras Farmacogn 2021, 31, 408–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, D.; Du, B.; Xu, J.; Xie, Q.; Lu, Z.; Kang, Y. Baicalin promotes antibacterial defenses by modulating mitochondrial function. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2022, 621, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Wu, F.; Shao, Q.; Chen, G.; Xu, L.; Lu, F. Baicalin Alleviates Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in Diabetic Nephropathy via Nrf2 and MAPK Signaling Pathway. Drug Des Devel Ther 2021, 15, 3207–3221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Snyder, S.A.; Smith, J.N.; Chen, Y.C. Anticancer properties of baicalein: a review. Med Chem Res 2016, 25, 1515–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, H.J.; Lee, J.Y.; Park, W. Baicalin Modulates Inflammatory Response of Macrophages Activated by LPS via Calcium-CHOP Pathway. Cells 2022, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, G.; Chen, L.; Wang, H.; Wu, S.; Li, S.; Wang, X. Baicalin inhibits LPS-induced inflammation in RAW264.7 cells through miR-181b/HMGB1/TRL4/NF-kappaB pathway. Am J Transl Res 2021, 13, 10127–10141. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ren, M.; Zhao, Y.; He, Z.; Lin, J.; Xu, C.; Liu, F.; Hu, R.; Deng, H.; Wang, Y. Baicalein inhibits inflammatory response and promotes osteogenic activity in periodontal ligament cells challenged with lipopolysaccharides. BMC Complement Med Ther 2021, 21, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, L.T.; Wang, S.Q.; Su, J.; Xu, L.X.; Ji, Z.Y.; Zhang, R.Y.; Zhao, Q.W.; Ma, Z.Q.; Deng, X.Y.; Ma, S.P. Baicalin ameliorates neuroinflammation-induced depressive-like behavior through inhibition of toll-like receptor 4 expression via the PI3K/AKT/FoxO1 pathway. J Neuroinflammation 2019, 16, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, S.; Liu, H.; Xu, L.; Qiu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wu, Z.; Ye, C.; Hou, Y.; Hu, C.A. Baicalin modulates NF-kappaB and NLRP3 inflammasome signaling in porcine aortic vascular endothelial cells Infected by Haemophilus parasuis Causing Glasser’s disease. Sci Rep 2018, 8, 807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Wang, Z.; Yuan, Z.; Lv, S.; Su, Q. Baicalin ameliorates atherosclerosis by inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice. Diab Vasc Dis Res 2020, 17, 1479164120977441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rui, W.; Li, S.; Xiao, H.; Xiao, M.; Shi, J. Baicalein Attenuates Neuroinflammation by Inhibiting NLRP3/caspase-1/GSDMD Pathway in MPTP Induced Mice Model of Parkinson’s Disease. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 2020, 23, 762–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Li, S.; Jiang, L.; Gao, X.; Liu, W.; Zhu, X.; Huang, W.; Zhao, H.; Wei, Z.; Wang, K. , et al. Baicalin protects against zearalenone-induced chicks liver and kidney injury by inhibiting expression of oxidative stress, inflammatory cytokines and caspase signaling pathway. Int Immunopharmacol 2021, 100, 108097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajput, S.A.; Wang, X.Q.; Yan, H.C. Morin hydrate: A comprehensive review on novel natural dietary bioactive compound with versatile biological and pharmacological potential. Biomed Pharmacother 2021, 138, 111511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, D.G.; Lee, S.; Kim, J.; Yang, S.; Lee, M.; Ahn, J.; Lee, H.; Chang, S.C.; Ha, N.C.; Lee, J. Anti-Inflammatory and Neuroprotective Effects of Morin in an MPTP-Induced Parkinson’s Disease Model. Int J Mol Sci 2022, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Y.; Wang, C.; Liu, N.; Gao, C.; Liu, F. Morin Exhibits Anti-Inflammatory Effects on IL-1beta-Stimulated Human Osteoarthritis Chondrocytes by Activating the Nrf2 Signaling Pathway. Cell Physiol Biochem 2018, 51, 1830–1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yao, Q.; Huang, J.; Jin, Q.; Xu, B.; Chen, F.; Tu, C. Morin Hydrate Inhibits TREM-1/TLR4-Mediated Inflammatory Response in Macrophages and Protects Against Carbon Tetrachloride-Induced Acute Liver Injury in Mice. Front Pharmacol 2019, 10, 1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinha, K.; Sadhukhan, P.; Saha, S.; Pal, P.B.; Sil, P.C. Morin protects gastric mucosa from nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug, indomethacin induced inflammatory damage and apoptosis by modulating NF-kappaB pathway. Biochim Biophys Acta 2015, 1850, 769–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, V.K.; Malik, S.; Narayanan, S.P.; Mutneja, E.; Sahu, A.K.; Bhatia, J.; Arya, D.S. Role of MAPK/NF-kappaB pathway in cardioprotective effect of Morin in isoproterenol induced myocardial injury in rats. Mol Biol Rep 2019, 46, 1139–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, X.; Xu, J.; Jiang, L.; Liu, W.; Hong, H.; Qian, Y.; Li, S.; Huang, W.; Zhao, H.; Yang, Z. , et al. Morin alleviates aflatoxin B1-induced liver and kidney injury by inhibiting heterophil extracellular traps release, oxidative stress and inflammatory responses in chicks. Poult Sci 2021, 100, 101513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salehi, B.; Fokou, P.V.T.; Sharifi-Rad, M.; Zucca, P.; Pezzani, R.; Martins, N.; Sharifi-Rad, J. The Therapeutic Potential of Naringenin: A Review of Clinical Trials. Pharmaceuticals (Basel) 2019, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Wei, Y.Z.; He, X.M.; Li, D.D.; Wang, G.Q.; Li, J.J.; Zhang, F. Naringenin Produces Neuroprotection Against LPS-Induced Dopamine Neurotoxicity via the Inhibition of Microglial NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation. Front Immunol 2019, 10, 936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, X.; Lin, T.; Zhu, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Song, Z.; Pan, X. Naringenin protects against acute pancreatitis-associated intestinal injury by inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome activation via AhR signaling. Front Pharmacol 2023, 14, 1090261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Ou, Y.; Hu, G.; Wen, C.; Yue, S.; Chen, C.; Xu, L.; Xie, J.; Dai, H.; Xiao, H. , et al. Naringenin attenuates non-alcoholic fatty liver disease by down-regulating the NLRP3/NF-kappaB pathway in mice. Br J Pharmacol 2020, 177, 1806–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Wan, S.; Liu, H.; Qiu, Q.; Chen, H.; Chen, Z.; Wang, L.; Liu, X. Naringenin Alleviates Renal Ischemia Reperfusion Injury by Suppressing ER Stress-Induced Pyroptosis and Apoptosis through Activating Nrf2/HO-1 Signaling Pathway. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2022, 2022, 5992436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abu Khweek, A.; Amer, A.O. Pyroptotic and non-pyroptotic effector functions of caspase-11. Immunol Rev 2020, 297, 39–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.M.; Kim, Y.M. HMGB1: LPS Delivery Vehicle for Caspase-11-Mediated Pyroptosis. Immunity 2018, 49, 582–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.B.; Cho, H.J.; Yi, Y.S. Anti-inflammatory role of Artemisia argyi methanol extract by targeting the caspase-11 non-canonical inflammasome in macrophages. J Ethnopharmacol 2023, 307, 116231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, H.J.; Kim, E.; Yi, Y.S. Korean Red Ginseng Saponins Play an Anti-Inflammatory Role by Targeting Caspase-11 Non-Canonical Inflammasome in Macrophages. Int J Mol Sci 2023, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Flavonoids | Diseases | Roles | Models | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Luteolin | Gastritis |
|
RAW264.7 cells HCl/EtOH-induced gastritis mice |
[102] |
| Sepsis |
|
RAW264.7, THP-1 cells LPS-induced sepsis mice |
[103] | |
| ALI |
|
CLP-induced ALI mice | [104] | |
| Scutellarin | Inflammatory response |
|
BMDMs, J774A.1, RAW264.7 cells | [113] |
| IPF |
|
Bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis mice | [108] | |
| Apigenin | Colitis |
|
DSS-induced colitis mice | [124] |
| EGCG | Inflammatory response |
|
BV-2, SH-SY5Y cells | [129] |
| Quercetin | Gastritis |
|
RAW264.7 cells HCl/EtOH-induced gastritis mice |
[102] |
| Kaempferol | Gastritis |
|
RAW264.7 cells HCl/EtOH-induced gastritis mice |
[102] |
| Icariin | Intestine injury |
|
LS174T cells | [172] |
| Baicalin | Liver & kidney injury |
|
ZEA-induced liver and kidney injury chicks | [184] |
| Morin | Liver & kidney injury |
|
AFB1-induced liver and kidney injury chicks | [191] |
| Naringenin | Renal I/R injury |
|
HK-2 cells I/R injury mice |
[196] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





