Submitted:
08 June 2023
Posted:
08 June 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Nanotechnology in the fight against SARS-CoV-2
3. PPE with nanomaterials to fight the spread of the SARS-CoV-2 virus
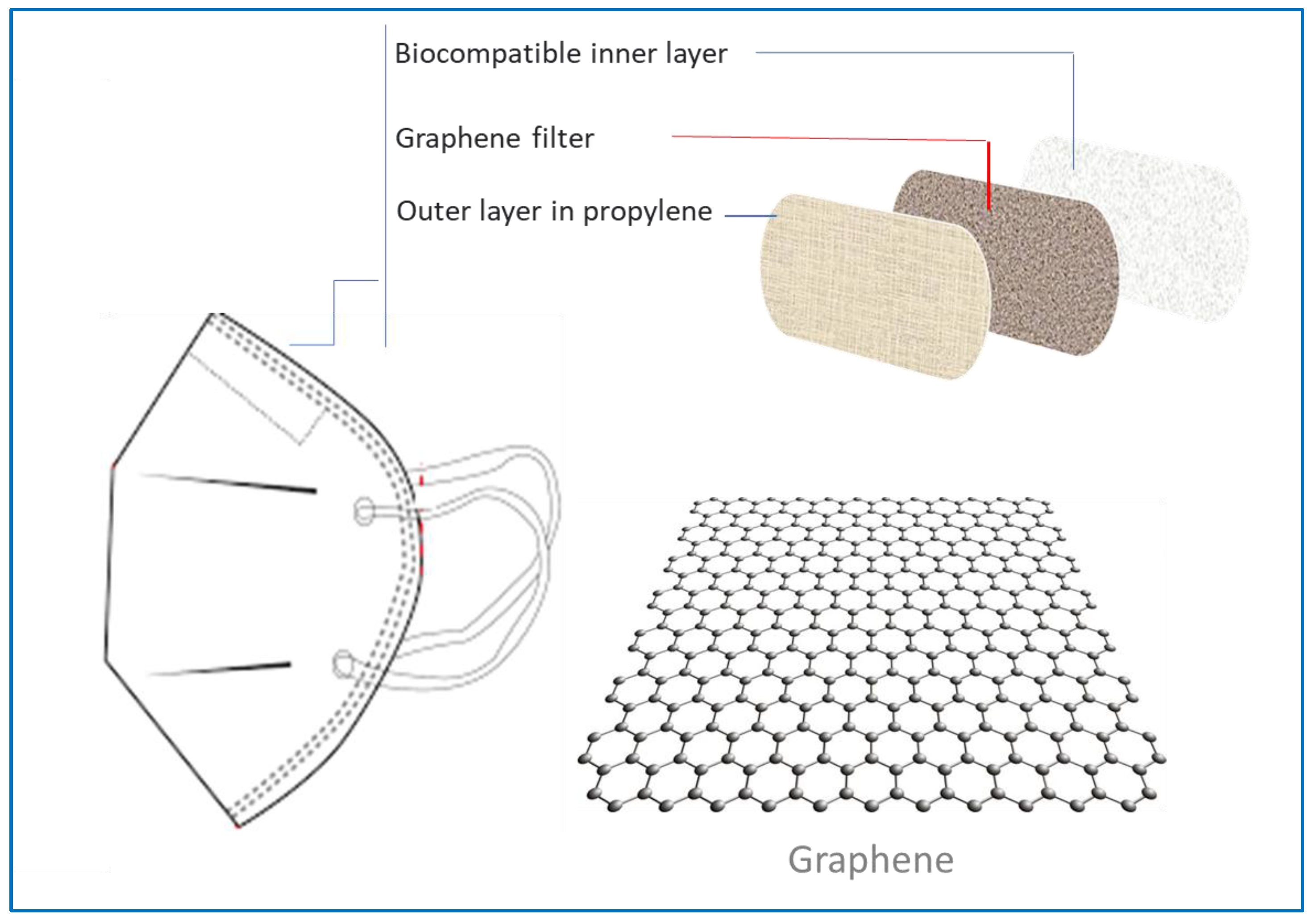
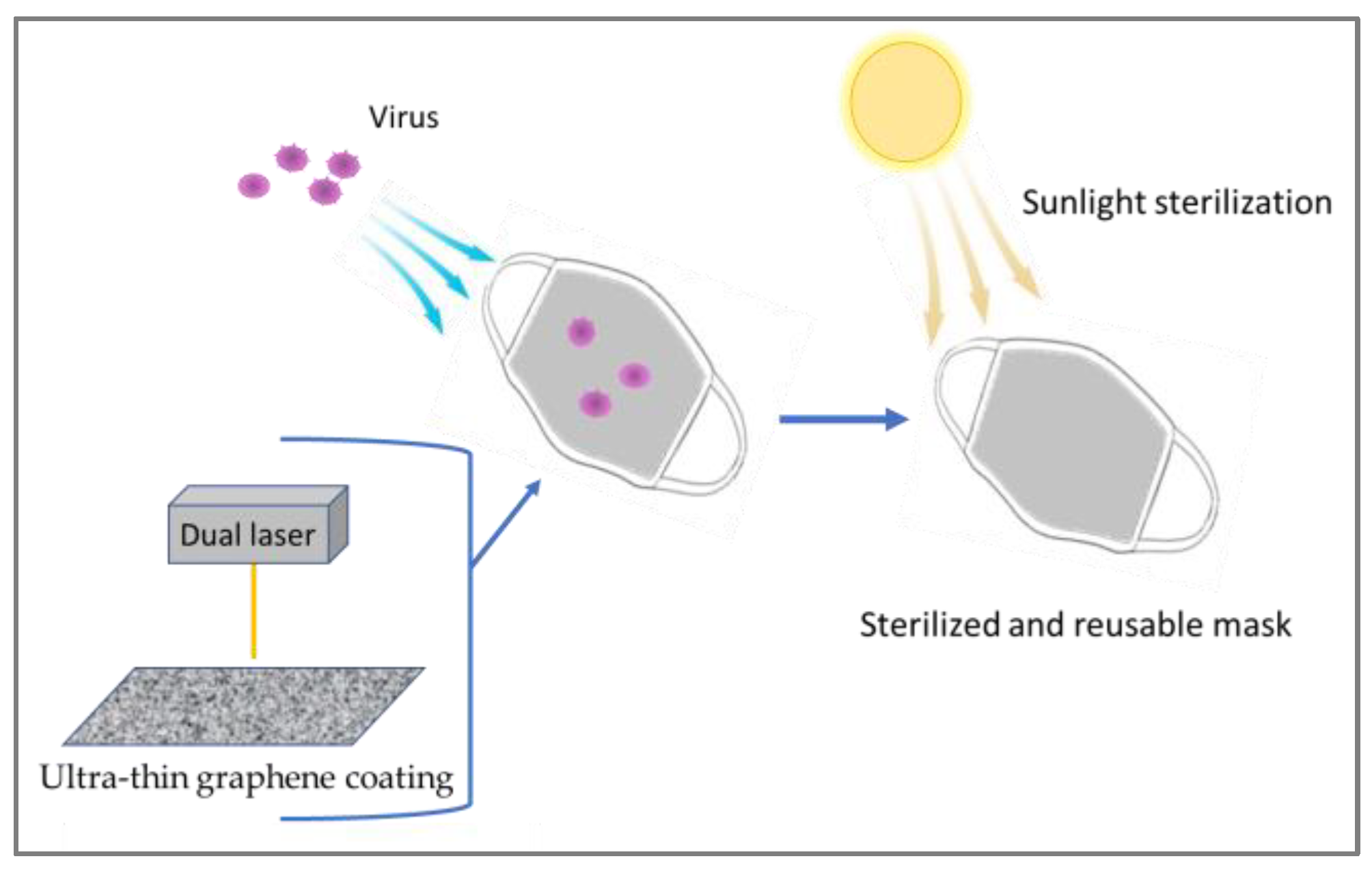
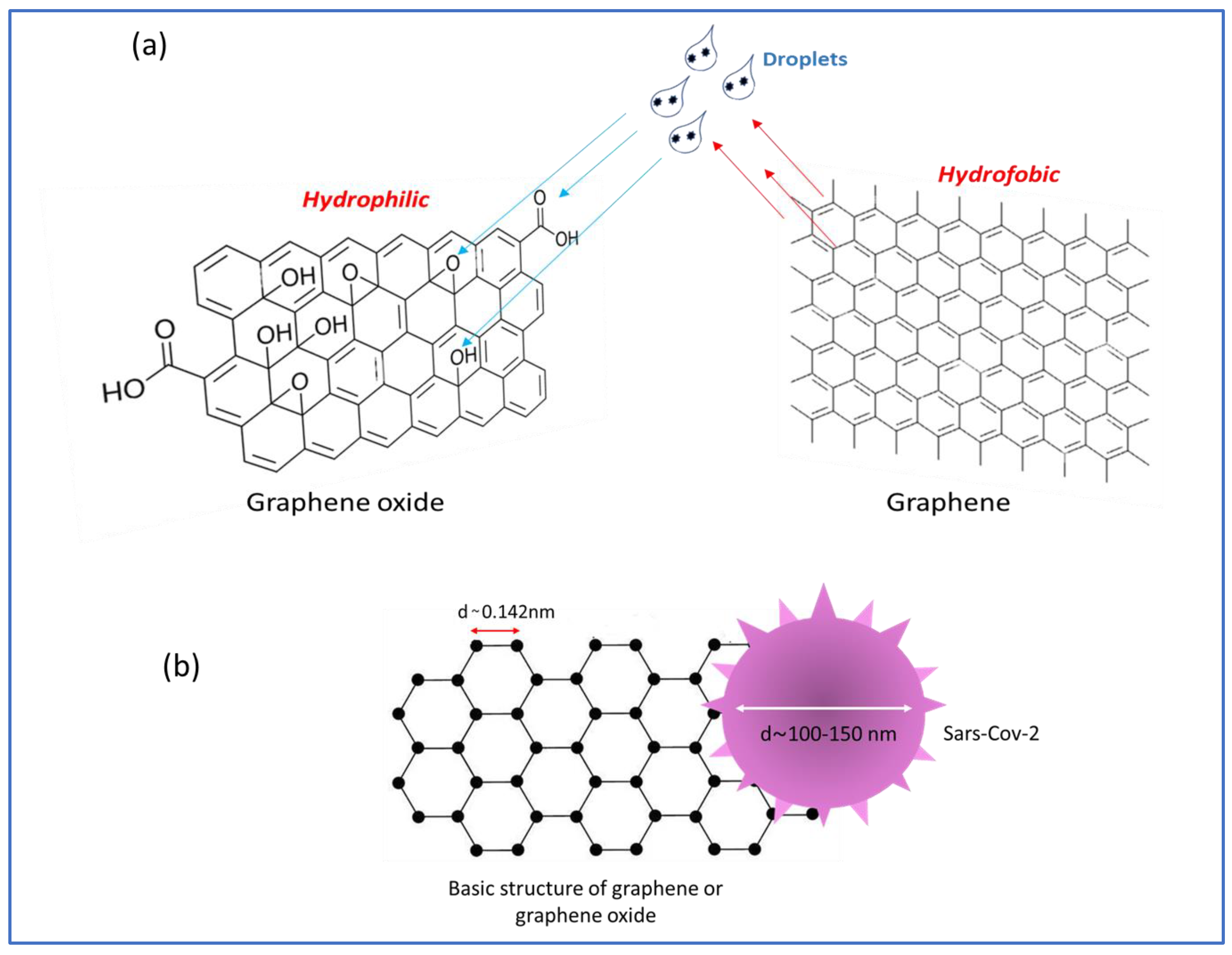
3.1. PPE with graphene
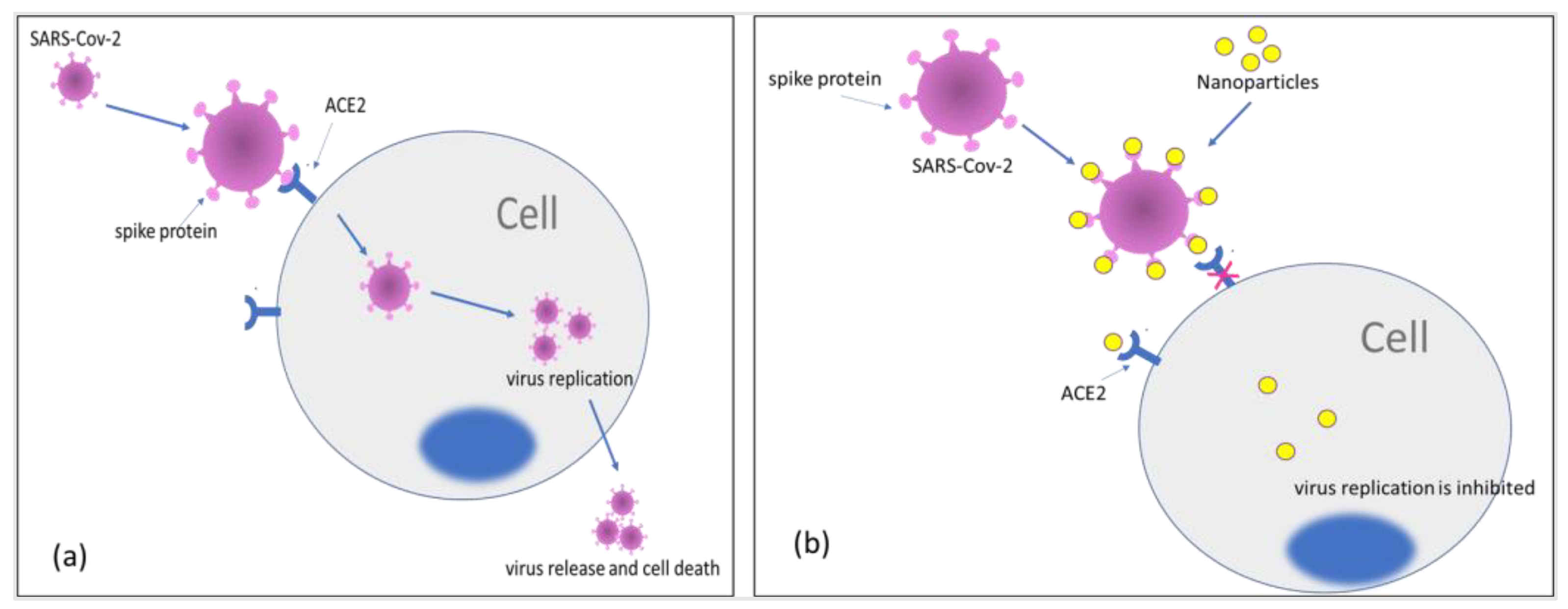
3.2. Nanoparticles against Sars-Cov-2
3.2.1. PPE with silver nanoparticles
3.2.2. PPE with copper nanoparticles
3.2.3. PPE with copper iodide nanoparticles
3.2.4. PPE containing copper oxide nanoparticles
3.2.5. PPE with zinc oxide
3.3. PPE with nanofibers
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Poole, C.P.; Owens, F.J. Introduction to Nanotechnology; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2003.
- https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/IT/TXT/PDF/?uri=CELEX:32011H0696 (Accessed May 2023).
- Mohanraj, V.J.; Chen, Y. Nanoparticles-A review. Trop. J. Pharm. Res. 2006, 5, 1, pp. 561-573.
- Xu, L.; Liang H.W.; Yang Y.; Yu S.H. Stability and Reactivity: Positive and Negative Aspects for Nanoparticle Processing. Chem. Rev. 2018, 118, 7, 3209–3250.
- Lalitha A. Kolahalam; I.V. Kasi Viswanath; Bhagavathula S. Diwakar; B. Govindh; Venu Reddy; Y.L.N. Murthy. Review on nanomaterials: Synthesis and applications. Mater. Today: Proc. 2019, 18, 6, pp. 2182-2190.
- Mahmoud Nasrollahzadeh, S. Mohammad Sajadi, Mohaddeseh Sajjadi, Zahra Issaabadi. Chapter 1-An Introduction to Nanotechnology. Interface Sci. Technol. 2019, 28, pp.1-27. [CrossRef]
- Mishra, R.; Militky, J. Nanotechnology in Textiles Theory and Application; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; ISBN 978-0-08-102609-0.
- Ali, K.; Ye, T.; Hang, Q.; Amir, M.; Butt, H.; Mehmet, R.; Dokmeci, J.P.; Hinestroza, M.S.; Khademhosseini, A.; Yun, S.H. Nanotechnology in Textiles. ACS Nano 2016, 10, pp.3042–3068.
- López, O.V.; Castillo, L.A.; Garcia, M.A.; Villar, M.A.; Barbosa, S.E. Food packaging bags based on thermoplastic corn starch reinforced with talc nanoparticles. Food Hydrocoll. 2015, 43, pp.18–24.
- Singh, P. Nanotechnology in food preservation. Food Sci. 2018, 9, pp. 435–441.
- De Luca, P.; De Luca, P.; Candamano, S.; Macario, A.; Crea, F.; B.Nagy. J. Preparation and characterization of plasters with photodegradative action. Buildings. 2018, 8, 122. [CrossRef]
- Konsta-Gdoutos, M.S.; Metaxa, Z.S.; Shah, S.P. Highly dispersed carbon nanotube reinforced cement based materials. Cem. Concr. Res. 2010, 40, pp. 1052–1059.
- Kalam, K.; Otsus, M.; Kozlova, J.; Tarre, A.; Kasikov, A.; Rammula, R.; Link, J.; Stern, R.; Vinuesa, G.; Lendinez, J.M.; et al. Memory Effects in Nanolaminates of Hafnium and Iron Oxide Films Structured by Atomic Layer Deposition. Nanomater. 2022, 12, 2593.
- Hsu, C.S.; Chan, C.C.; Huang, H.T.; Peng, C.H.; Hsu, W.C. Electrochromic properties of nanocrystalline MoO3 thin films. Thin Solid Film. 2008,516, pp.4839–4844.
- Shang, Y.; Hasan, M.K.; Ahammed, G.J.; Li, M.; Yin, H.; Zhou, J. Applications of Nanotechnology in Plant Growth and Crop Protection: A Review. Molecules 2019, 24, 2558.
- Singh, H.; Sharma, A.; Bhardwaj, S.K.; Arya, S.K.; Bhardwaj, N.; Khatri, M. Recent advances in the applications of nano-agrochemicals for sustainable agricultural development. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2021, 23, pp. 213–239.
- De Luca, P., Macario, A., Siciliano, C., B.Nagy, J. Recovery of Biophenols from Olive Vegetation Waters by Carbon Nanotubes. Materials. 2022, 15, 8, 2893. [CrossRef]
- De Luca, P., Chiodo, A., Macario, A., Siciliano, C., B.Nagy, J. Semi-continuous adsorption processes with multi-walled carbon nanotubes for the treatment of water contaminated by an organic textile dye. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11,4, pp. 1–19, 1687. [CrossRef]
- Agrahari, P.A.J.R.A.; Bhatia, A.K.; Sexna, A.G.; Pant, G.; Singh, R.P.; Mishra, R.R.; Mishra, V.K. Advance Applications of Nanotechnology in Medicine. Int. J. Sci. Res. 2016, 7, pp. 1284–1315.
- Kargozar, S.; Mozafari, M. Nanotechnology and Nanomedicine: Start small, think big. Mater. Today Proc. 2018, 5, pp. 15492–15500.
- Hou, S.; Zhang, A.; Su, M. Nanomaterials for Biosensing Applications. Nanomater. 2016, 6, 4, 58. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Gu, F.X.; Chan, J.M.; Wang, A.Z.; Langer, R.S.; Farokhzad O.C. Nanoparticles in medicine: therapeutic applications and developments. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2008, 83, pp. 761–769.
- Davis, M.E.; Chen, Z.; Shin, D.M. Nanoparticle therapeutics: an emerging treatment modality for cancer. Nature Rev. Drug Discov. 2008, 7, pp. 771–782.
- Li, Z.; Shan, X.; Chen, Z.; Gao, N.; Zeng, W.; Zeng, X.; Mei, L. Applications of surface modification technologies in nanomedicine for deep tumor penetration. Adv. Sci. 2021,8, 2002589.
- Goldberg, M.; Langer, R.; Jia, X. Nanostructured materials for applications in drug delivery and tissue engineering. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. 2007, 18, pp. 241–268.
- Wang, J.L.; Chen, G.H.; Jiang, H.; Li, Z.Y.; Wang, X.M. Advances in Nano-Scaled Biosensors for Biomedical Applications. Analyst. 2013, 138, pp. 4427– 4435.
- Wu, Y.C., Chen, C.S.; Chan, Y.J. The outbreak of COVID-19: An overview. J. Chin. Med. Assoc. 2020, 83, 3, pp. 217-220.
- Singhal, T. A Review of Coronavirus Disease-2019 (COVID-19). Indian J Pediatr. 2020; 87,4, pp.281–286. [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Guo, H.; Zhou, P.; Shi, Z.L. Characteristics of SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2021, 19, pp.141–154.
- Deng, S.Q.;Peng, H.J. Characteristics of and public health responses to the coronavirus disease 2019 outbreak in China. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 575.
- Cui, J.; Li, F.; Shi, Z.L. Origin and evolution of pathogenic coronaviruses. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2019, 17, pp.181–192.
- Andersen, K.G.; Rambaut. A.; Lipkin, W.I.; Holmes, E.C.; Garry, R.F. The proximal origin of SARS-CoV-2. Nat. Med. 2020; 26:450–452.
- Zhu, H.; Wei, L.; Niu, P. The novel coronavirus outbreak in Wuhan, China. Glob health res policy. 2020, 5, 6. [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.J.; Shan, J. 2019 Novel coronavirus: where we are and what we know. Infection, 2020, 48, pp.155–163. [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Horby, P.W.; Hayden, F.G.; Gao, G.F. A novel coronavirus outbreak of global health concern. The Lancet. 2020, 395, 10223, pp. 470–473. [CrossRef]
- Campos, E.V.R.; Pereira, A.E.S.; de Oliveira, J.L.; Carvalho, L.B.; Guilger-Casagrande, M.; de Lima, R.; Fraceto, L.F. How can nanotechnology help to combat COVID-19? Opportunities and urgent need. J. Nanobiotechnology. 2020, 18, pp.125.
- Zhou, J.; Krishnan, N.; Jiang, Y.; Fang, R.H.; Zhang, L. Nanotechnology for virus treatment. Nano Today. 2021, 36, 101031.
- Kirtane, A.R.; Verma, M.; Karandikar, P. et al. Nanotechnology approaches for global infectious diseases. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2021, 16, 369–384. [CrossRef]
- Solanki, R.; Shankar, A.; Modi, U.; Patel, S. New insights from nanotechnology in SARS-CoV-2 detection, treatment strategy, and prevention. Mater Today Chem. 2023, 29,101478. [CrossRef]
- Hasanzadeh, A.; Alamdaran, M.; Ahmadi, S.; Nourizadeh, H.; Bagherzadeh, M.A.; Mofazzal, J.M.; Simon, P.; Karim,i M.; Hamblin, M.R.Nanotechnology against COVID-19: Immunization, diagnostic and therapeutic studies. J Control Release. 2021, 336, pp. 355-365.
- Abdelhamid, H.N.; Badr, G. Nanobiotechnology as a Platform for the Diagnosis of COVID-19: A Review.Nanotechnol. Environ. Eng. 2021, 6, 19. [CrossRef]
- Al-Hindawi, A.; AlDallal, U.; Waly, Y.M.; Hussain, M.H.; Shelig, M.; Saleh ElMitwalli ,O.S.M.M.; Deen, G.R.; Henari, F.Z.. An Exploration of Nanoparticle-Based Diagnostic Approaches for Coronaviruses: SARS-CoV-2, SARS-CoV and MERS-CoV. Nanomat. 2022, 11;12,20, 3550. [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, S.; Dusane, A.; Morajkar, R.; Venkat, A.; Vernekar, A.A. Deciphering the role of nanostructured materials in the point-of-care diagnostics for COVID-19: A comprehensive review. J. Mater. Chem. B. 2021; 9, pp. 5967–5981. [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.R. Development of Point-of-Care Biosensors for COVID-19. Front. Chem. 2020, 8. [CrossRef]
- Shan, B.; Broza, Y.Y.; Li, W.; Wang, Y.; Wu, S.; Liu, Z.; Wang, J.; Gui, S.; Wang, L.; Zhang Z., et al. Multiplexed nanomaterial-based sensor array for detection of COVID-19 in exhaled breath. ACS Nano.2020, 14, pp.12125–12132. [CrossRef]
- Bhalla, N.; Pan, Y.; Yang, Z.; Payam, A.F. Opportunities and Challenges for Biosensors and Nanoscale Analytical Tools for Pandemics: COVID-19. ACS Nano 2020, 14, pp. 7783–7807.
- Chakravarty, M.; Vora, A. Nanotechnology-based antiviral therapeutics. Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2021, 11, 3, pp. 748-787. [CrossRef]
- Weiss, C.; Carriere, M.; Fusco, L.; Capua, I.; Regla-Nava, J.A.; Pasquali, M.; Scott, J.A.; Vitale, F.; Unal, M.A.; Mattevi, C.; Bedognetti, D.; Merkoçi, A.; Tasciotti, E.; Yilmazer, A.; Gogotsi, Y.; Stellacci, F.; Delogu, L.G. Toward Nanotechnology-Enabled Approaches against the COVID-19 Pandemic. ACS Nano. 2020, 23, 14, 6, pp. 6383-6406. [CrossRef]
- Bwalya, A. W.; Pedzisai, A.M.; Larry, LM.; Pascal,V.N.; Melissa, T.R.C.; Scott K.M.; Chiluba, M.; Steward, M.; Jonathan K.; Roderick, B.W. Nano-Biomimetic Drug Delivery Vehicles: Potential Approaches for COVID-19 Treatment. Molecules. 2020,16, 25, 24, pp. 5952. [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Shu, Y.; Guo, M.; Zhang, H.; Tao, W. Insights from Nanotechnology in COVID-19 Treatment. Nano Today 2021, 36, 101019. [Google Scholar]
- Nanomedicine and the COVID-19 vaccines. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2020, 15, 963. [CrossRef]
- Krammer, F. SARS-CoV-2 vaccines in development. Nature. 2020, 586, 7830, pp.516–527.
- Chauhan, G.; Madou, M.J., Kalra, S.; Chopra, V.; Ghosh, D.; Martinez-Chapa, S.O. Nanotechnology for COVID-19: therapeutics and vaccine research. ACS Nano 2020, 17, 7760–7782. [CrossRef]
- Meo, S.A.; Bukhari, I.A.; Akram, J.; Meo, A.S.; Klonoff, D.C. COVID-19 vaccines: comparison of biological, pharmacological characteristics and adverse effects of Pfizer/BioNTech and Moderna vaccines. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2021, 25, 3, pp.1663–1669.
- Khurana, A.; Allawadhi, P.; Khurana, I.; Allwadhi, S.; Weiskirchen, R.; Banothu, A.K.; Chhabra, D.; Joshi, K.; Bharani, K.K. Role of nanotechnology behind the success of mRNA vaccines for COVID-19. Nano Today. 2021, 38, 101142. [CrossRef]
- Holland, M.; Zaloga, D.J.; Friderici, C.S. COVID-19 Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) for the emergency physician.Vis. J. Emerg. Med. 2020, 19, 100740.
- Lee, S.A.; Hwang, D.C.; Li, H.Y; Tsai, C.F.; Chen, C.W.; Chen, J.K. Particle Size-Selective Assessment of Protection of European Standard FFP Respirators and Surgical Masks against Particles-Tested with Human Subjects. J Healthc Eng. 2016; 2016, 8572493. [CrossRef]
- McCarthy, R.; Gino, B.; d'Entremont ,P.; Barari, A.; Renouf, T.S. The Importance of Personal Protective Equipment Design and Donning and Doffing Technique in Mitigating Infectious Disease Spread: A Technical Report. Cureus. 2020, 12, 2, e12084. [CrossRef]
- Abbasinia, M.; Karimie, S.; Haghighat, M.; Mohammadfam, I. Application of Nanomaterials in Personal Respiratory Protection Equipment: A Literature Review. Safety 2018, 4, 4, 47. [CrossRef]
- Nasir, S.; Hussein, M.Z.; Zainal, Z.; Yusof, N.A. Carbon-Based Nanomaterials/Allotropes: A Glimpse of Their Synthesis, Properties and Some Applications. Materials. 2018. 11, pp. 2-16.
- Urade, A.R., Lahiri, I. & Suresh, K.S. Graphene Properties, Synthesis and Applications: A Review. JOM. 2023, 75, 614–630. [CrossRef]
- C&S ITALY S.R.L. https://avmaskpro.it/ (Accessed April 2023).
- Hygraner Srl https://www.hygraner.it/ (Accessed April 2023).
- Pal, K.J.; Kyzas, G.Z.; Kralj, S.; Gomes de Souza, F. Sunlight sterilized, recyclable and super hydrophobic anti-COVID laser-induced graphene mask formulation for indelible usability. J. Mol. Struct. 2021, 1233, pp. 1-6.
- Zhong, H.; Zhu, Z.; Lin, J.; Cheung, C.F.; Lu, V.L.; Yan, F.; Chan, C.Y.; Li, G. Reusable and Recyclable Graphene Masks with Outstanding Superhydrophobic and Photothermal Performances. ACS Nano 2020 26, 14, 5, pp. 6213-6221. [CrossRef]
- Fukuda, M.; Islam, M.S.; Shimizu, R.; Nasser, H.; Rabin, N.N.; Takahashi, Y.; Sekine, Y.; Lindoy, L.F.; Fukuda, T.; Ikeda, T.; Hayami, S. Lethal Interactions of SARS-CoV-2 with Graphene Oxide: Implications for COVID-19 Treatment. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2021, 4, 11, 11881–11887.
- Rhazouani ,A.; Aziz, K.; Gamrani, H.; Gebrati, L.; Uddin, M.S.; Faissal, A. Can the application of graphene oxide contribute to the fight against COVID-19? Antiviral activity, diagnosis and prevention. Curr Res Pharmacol Drug Discov. 2021; 2, 100062. [CrossRef]
- Palmieri, V.;Papi, M. Can graphene take part in the fight against COVID-19?. Nano Today, 2020, 33, p. 1-3. [CrossRef]
- De Maio, F., et al. Graphene nanoplatelet and graphene oxide functionalization of face mask materials inhibits infectivity of trapped SARS-CoV-2. iScience. 2021, 24, 7. [CrossRef]
- Mbayachi, V.B.; Ndayiragije, E.; Sammani, T.; Taj, S;. Mbuta, E.R.; khan, A. Graphene synthesis, characterization and its applications: A review. Results in Chemistry. 2021, 3,100163. [CrossRef]
- Laue, M.; Kauter, A.; Hoffmann, T. et al. Morphometry of SARS-CoV and SARS-CoV-2 particles in ultrathin plastic sections of infected Vero cell cultures. Sci Rep. 2021, 11, 3515. [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Liu, J.; Gan, L.; Long, M. Surface-modified graphene oxide-based cotton fabric by ion implantation for enhancing antibacterial activity. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 8, pp. 7686–7692. [CrossRef]
- Lysenko, V.; Lozovski, V.; Lokshyn, M.; Gomeniuk, Y.V.; Dorovskih, A.; Rusinchuk, N.; Pankivska, Y.; Povnitsa, O.; Zagorodnya, S.; Tertykh, V.; et al. Nanoparticles as antiviral agents against adenoviruses. Adv. Nat. Sci. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 025021.
- Rai, M.; Yadav, A.; Gade, A. Silver nanoparticles as a new generation of antimicrobials. Biotechnology Advances, 2009, 27, pp. 76-80.
- Khoshnevisan, K.; Maleki, H.; Baharifar, H. Nanobiocide Based-Silver Nanomaterials Upon Coronaviruses: Approaches for Preventing Viral Infections. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2021, 16, pp. 1-6.
- Fung, M.C.; Bowen, D.L. Silver products for medical indications: risk-benefit assessment. J. Toxicol. Clin. Toxicol, 1996, 34, pp. 119-124.
- New Silver-Copper Nanolayer-based Antimicrobial Mask Inactivates SARS-CoV-2. Industry News. Edited Special chem. 2021. https://omnexus.specialchem.com/news/industry-news/silver-copper-mask-000225616 (Accessed May 2023).
- Bello-Lopez, M.; Silva-Bermudez, P.; Prado, G.; Martínez, A.; Ibáñez-Cervantes, G.; Cureño-Díaz, M.A.; Rocha-Zavaleta, L.; Manzo-Merino, J.; Almaguer-Flores, A.; Ramos-Vilchis, C.; Rodil, S.E. Biocide effect against SARS-CoV-2 and ESKAPE pathogens of a noncytotoxic silver–copper nanofilm. Biomed. Mater. 2021. 17, 1, 015002.
- Kolzer Srl https://www.kolzer.com/it/kolzer/news/418-nanoparticelle-argento-mascherine-coronavirus (Accessed May 2023).
- São Paulo-based company develops fabric that eliminates novel coronavirus by contact. https://agencia.fapesp.br/sao-paulo-based-company-develops-fabric-that-eliminates-novel-coronavirus-by-contact/33568/ (Accessed May 2023).
- Grass,G.; Rensing, C.; Solioz, M. Metallic copper as an antimicrobial surface. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, pp. 1541-1545.
- Govind, V.; Bharadwaj, S.; Sai Ganesh, M.R. et al. Antiviral properties of copper and its alloys to inactivate covid-19 virus: a review. Biometals 2021, 34, pp. 1217–1235. [CrossRef]
- Italtex S.P.A. https://virkill.it/ (Accessed may 2023).
- Archana, K.M.; Rajagopal, R.; Krishnaswamy, V.G.; Aishwarya, S. Application of green synthesised copper iodide particles on cotton fabric-protective face mask material against COVID-19 pandemic. J. Mater. Res. and Technol., 202115, p.p. 2102-2113.
- Hasan R. Production of antimicrobial textiles by using copper oxide nanoparticles. IJCRR 2018, 9, p.p. 20195-20200.
- Pasquet, J.; Chevalier, Y.; Pelletier, J.; Couval, E.; Bouvier, D.; Bolzinger, M.A. The contribution of zinc ions to the antimicrobial activity of zinc oxide. Colloids Surf. A, 2014, 457, p.p. 263-274. [CrossRef]
- Moezzi, A.; McDonagh, A. M.; Cortie, M. B. Zinc oxide particles: Synthesis, properties and applications. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 185–186, p.p. 1–22.
- Read, S.A.; Obeid, S.; Ahlenstiel, C.; Ahlenstiel, G. The role of zinc in antiviral immunity. Adv. Nutr.2019, 10, p.p. 696–710.
- Gonzalez, A.; Aboubakr, H.A.; Brockgreitens, J.; Hao,W.; Wang, Y.; Goyal, S.M.; Abbas A. Durable nanocomposite face masks with high particulate filtration and rapid inactivation of coronaviruses. Sci Rep. 2021, 11, 24318. [CrossRef]
- Essa, W.K.; Yasin, S.A.; Saeed, I.A; Ali, G.A.M. Nanofiber-Based Face Masks and Respirators as COVID-19 Protection: A Review. Membranes 2021, 11,4, 250. [CrossRef]
- Rasmi, Y.; Saloua, K.S.; Nemati, M.; Choi, J.R. Recent Progress in Nanotechnology for COVID-19 Prevention, Diagnostics and Treatment. Nanomater., 2021, 11, p.p. 1-4.
- https://www.inveniosolutions.it/electrospinning/nanofibre (Accessed may 2023).
- Hemmer, C.J.; Hufert, F.; Siewert, S.; Reisinger, E. Protection From COVID-19–The Efficacy of Face Masks. Dtsch Arztebl Int.2021, 118, p.p. 59-65.
- Leung, W.W.F.; Sun, Q. Charged PVDF multilayer nanofiber filter in filtering simulated airborne novel coronavirus (COVID-19) using ambient nano-aerosols. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 245, 116887. [CrossRef]

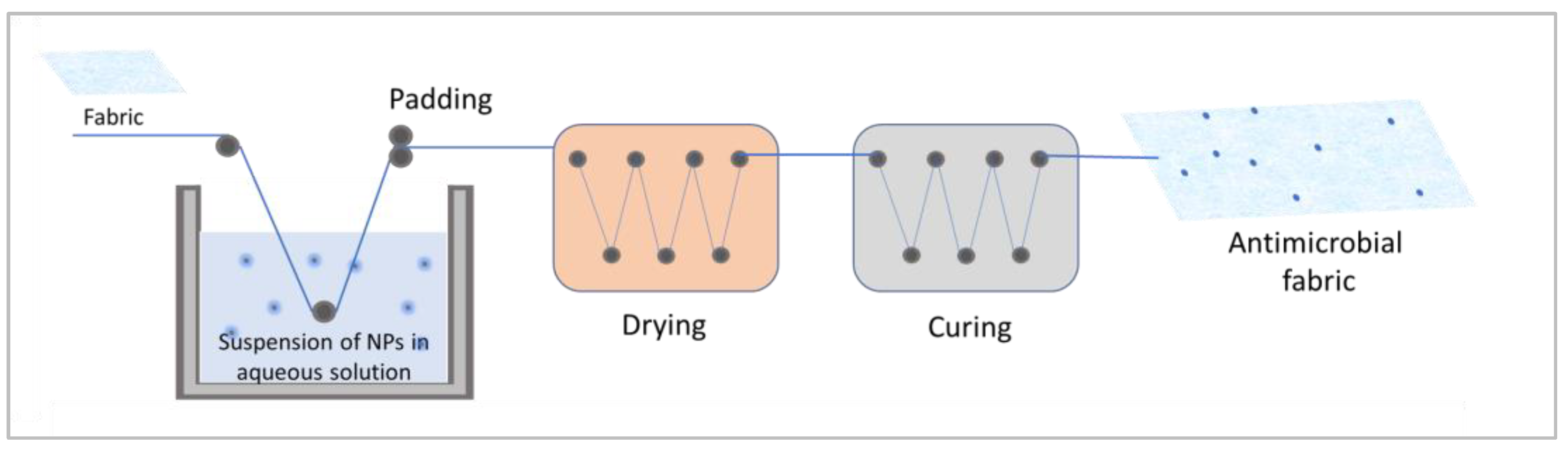
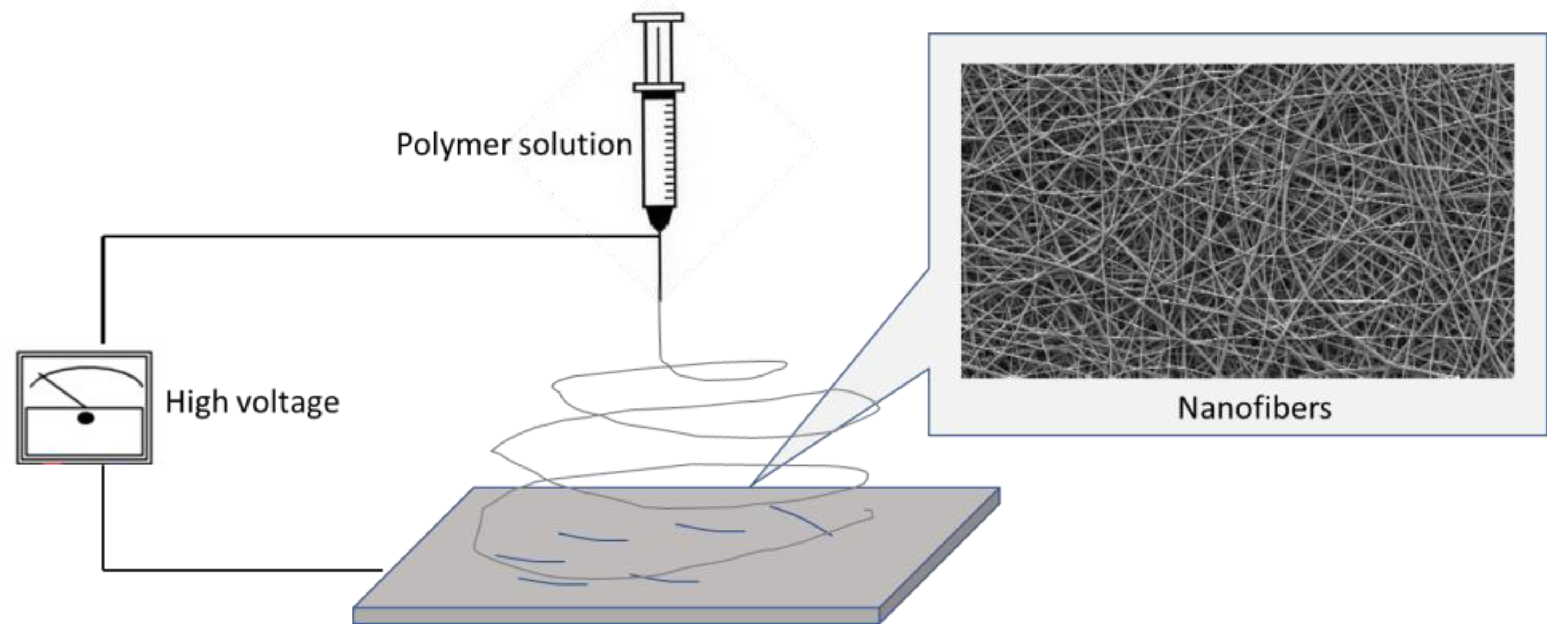
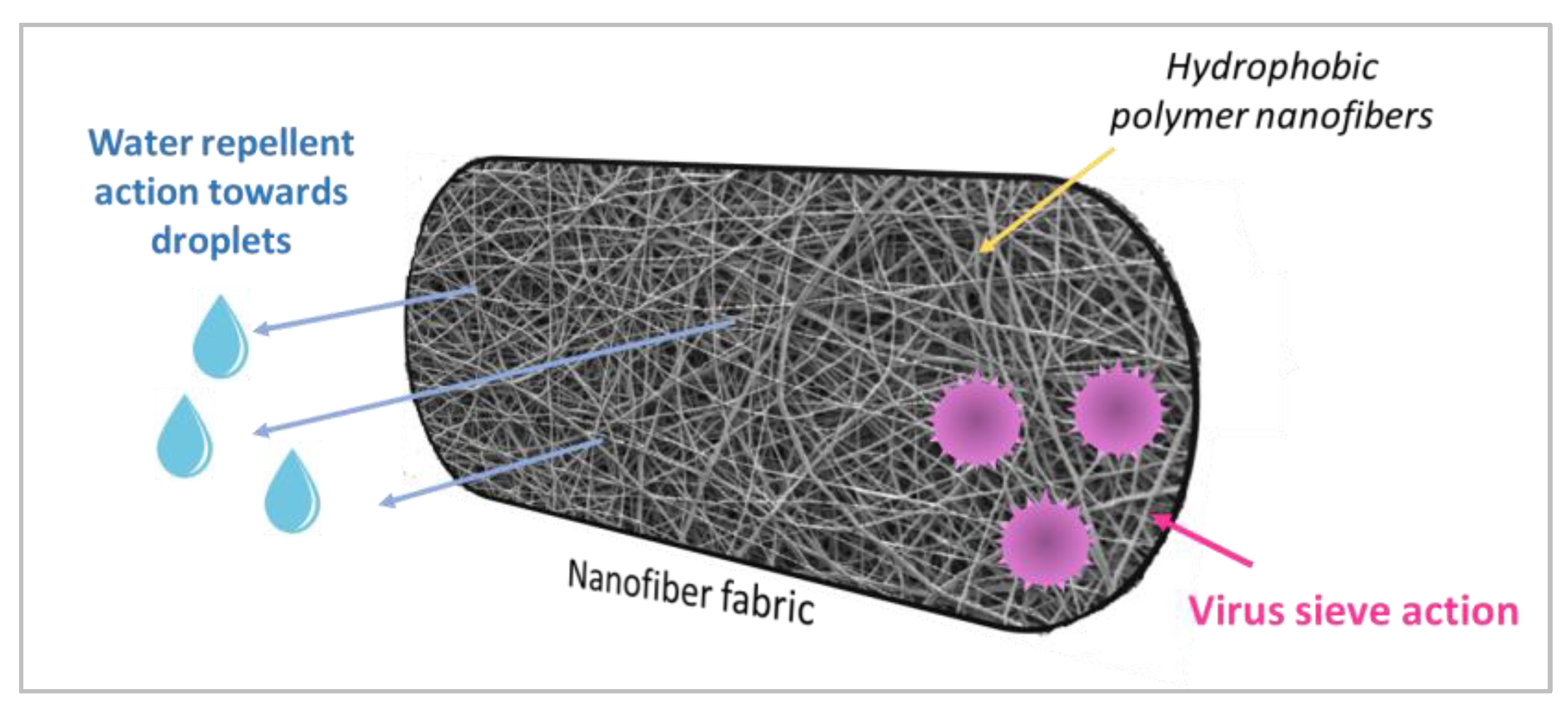
| Fiber | Diameter [µm] |
|---|---|
| Wool | 30-120 |
| Silk | 20 |
| Microfiber | 2-5 |
| Nanofiber | 0.05-1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





