Submitted:
07 June 2023
Posted:
08 June 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Indicators of EC Performance According to Linear Non-Equilibrium Thermodynamics
2.1. Basic Provisions of Linear Non-Equilibrium Thermodynamics
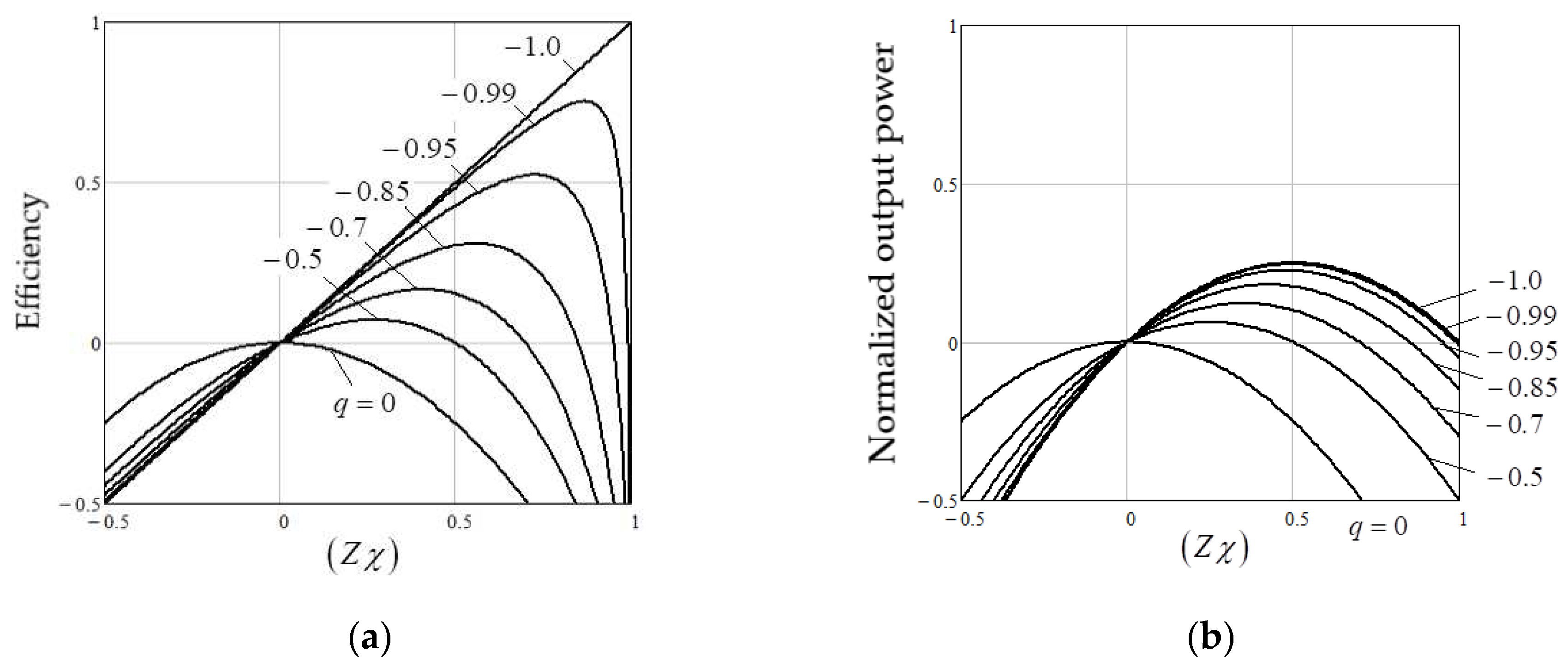
2.2. A Universal Method of Describing and Evaluating Performance Indicators of Linear ECs
2.3. Performance Indicators of Cascaded Linear ECs
2.4. The Energy Optimization Method of the Stady-State Operation Mode of the System
- Based on the analysis of the physical processes that take place in a specific EC, and based on the determined dissipative function, it is necessary to select pairs of input and output thermodynamic forces and flows.
- To justify the most appropriate energy optimization criterion and to formulate its mathematical expression.
- Substitute the values of q, Z and χ into the expression of the optimization criterion and investigate it to the maximum in turn according to the available parameters of the original mathematical model.
- Compare the obtained results and choose the best optimization option.
- In the case of two cascade-connected ECs, perform steps 1-5 for each EC separately. Find the value of the connection coefficient γ of the two initial ECs at the operating points or the function γ of the determining coordinate and compare the obtained values with the optimal value determined for the degrees of coupling of each of the constituent ECs obtained above. In the case of a significant difference between the real and optimal values of the connection coefficient, it is advisable to conduct additional studies aimed at finding ways to reduce this difference.
3. Thermodynamic Analysis of Energy Conversion Efficiency in WT
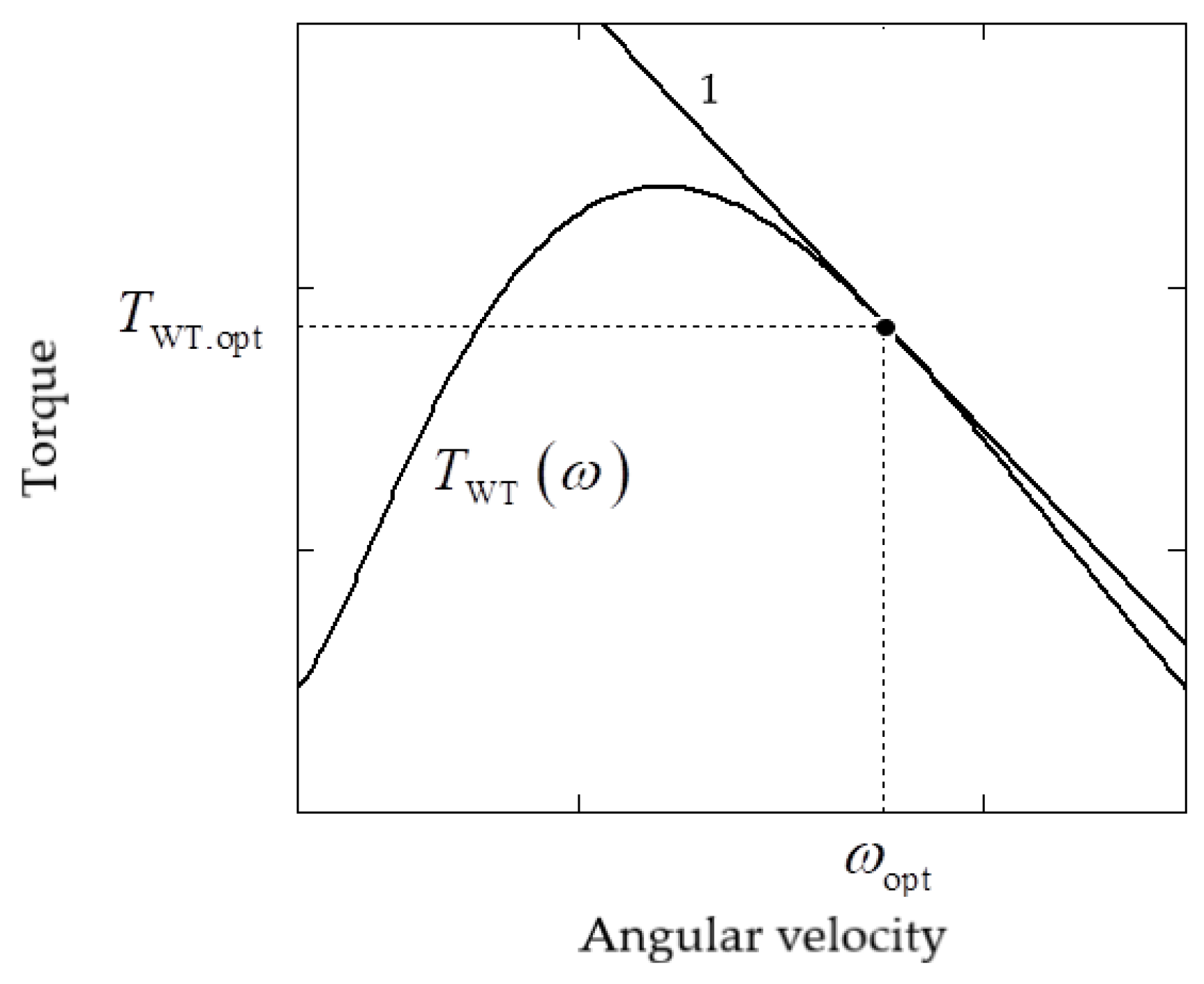
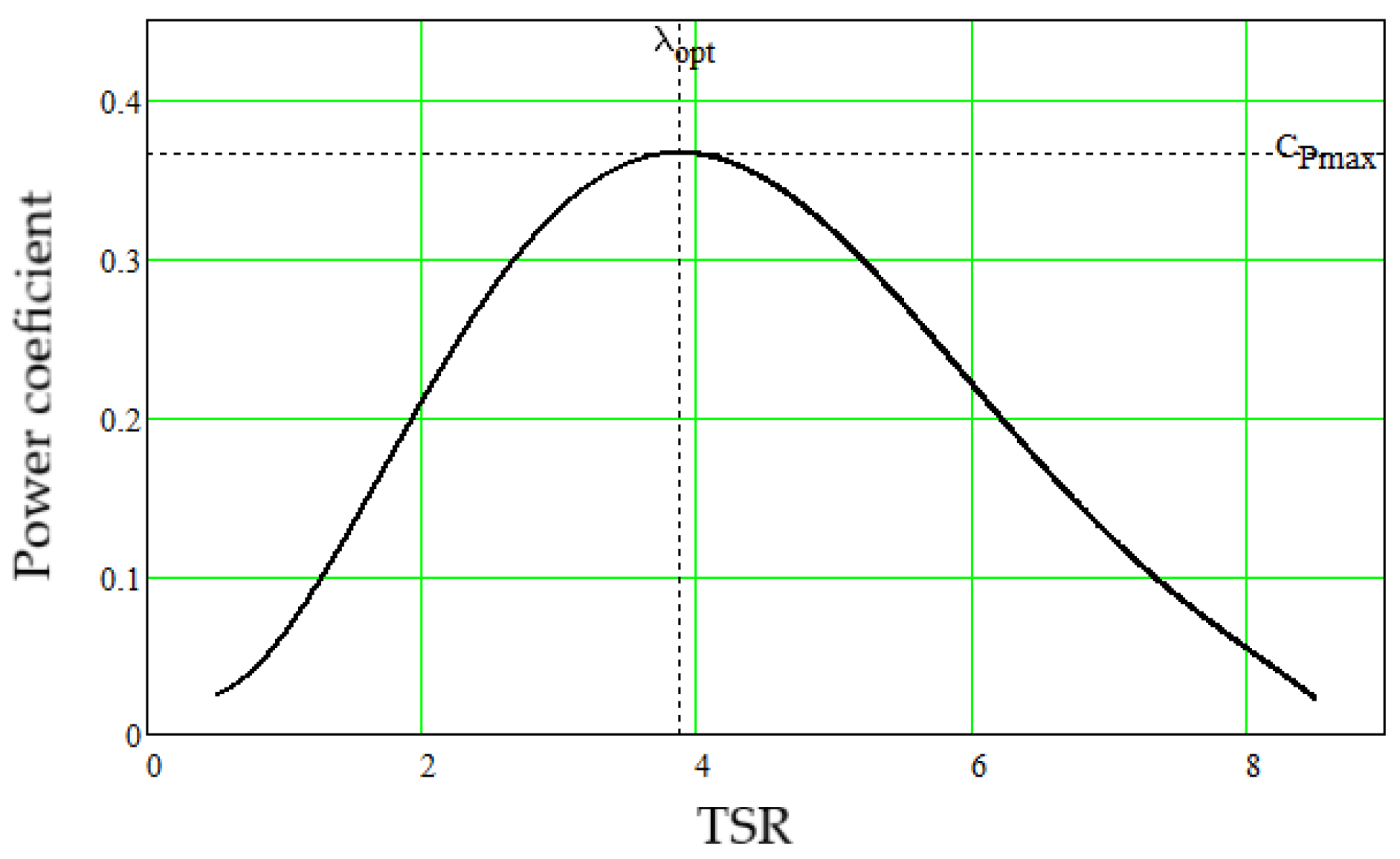
3.1. Mathematical Description of the Aeromechanical Regularities of WT Operation as a Linear EC
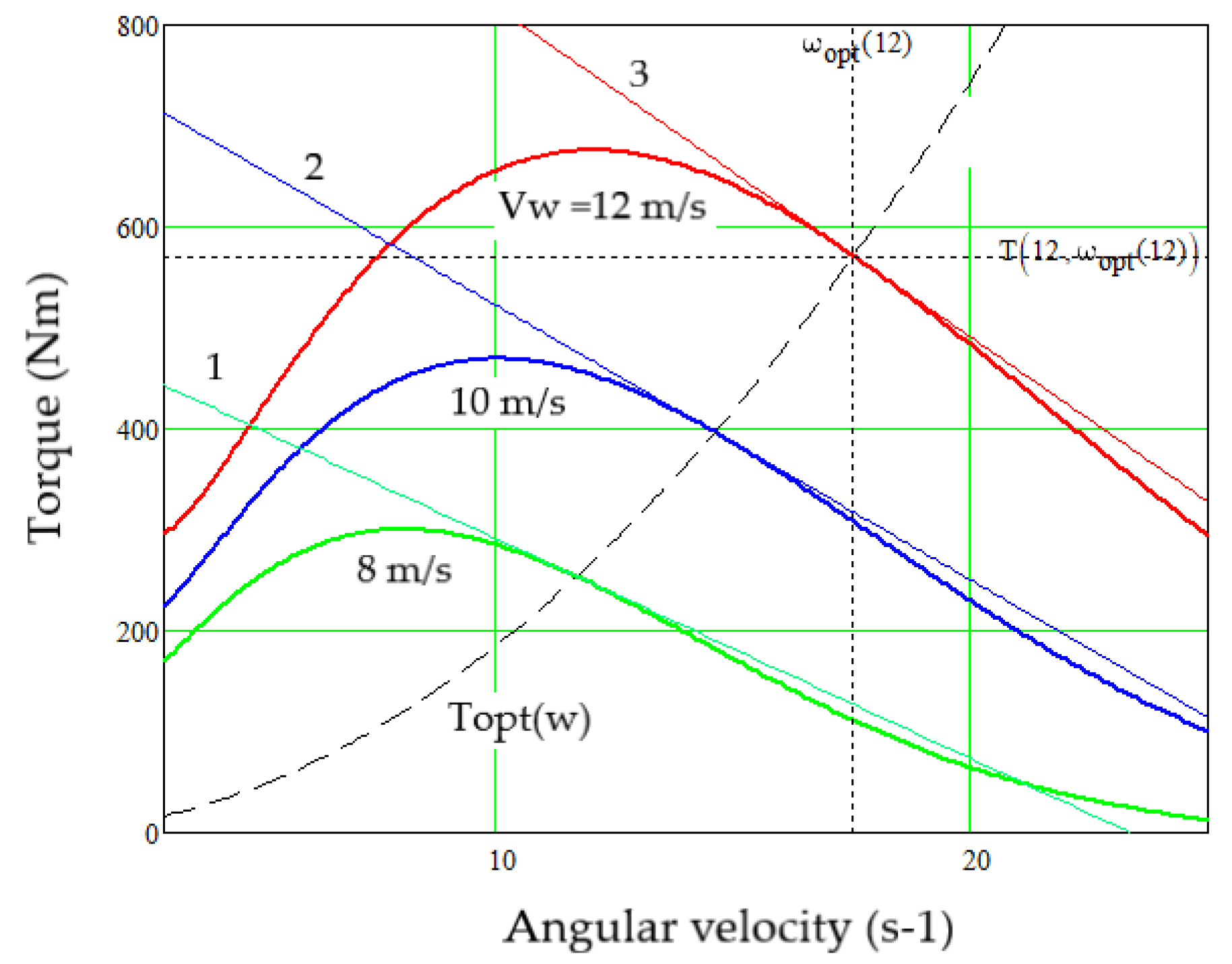
3.2. The Main Performance Indicators of the Experimental WT
4. Thermodynamic Analysis of PMSG Energy Conversion Efficiency
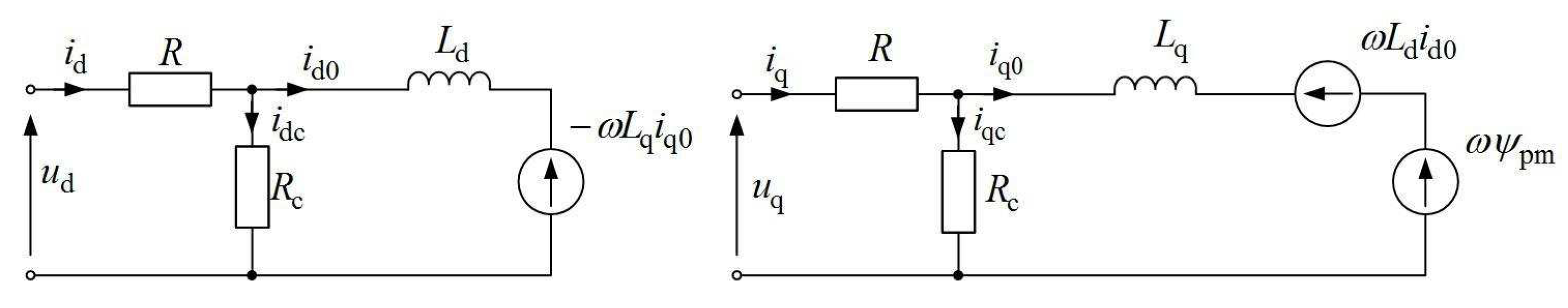
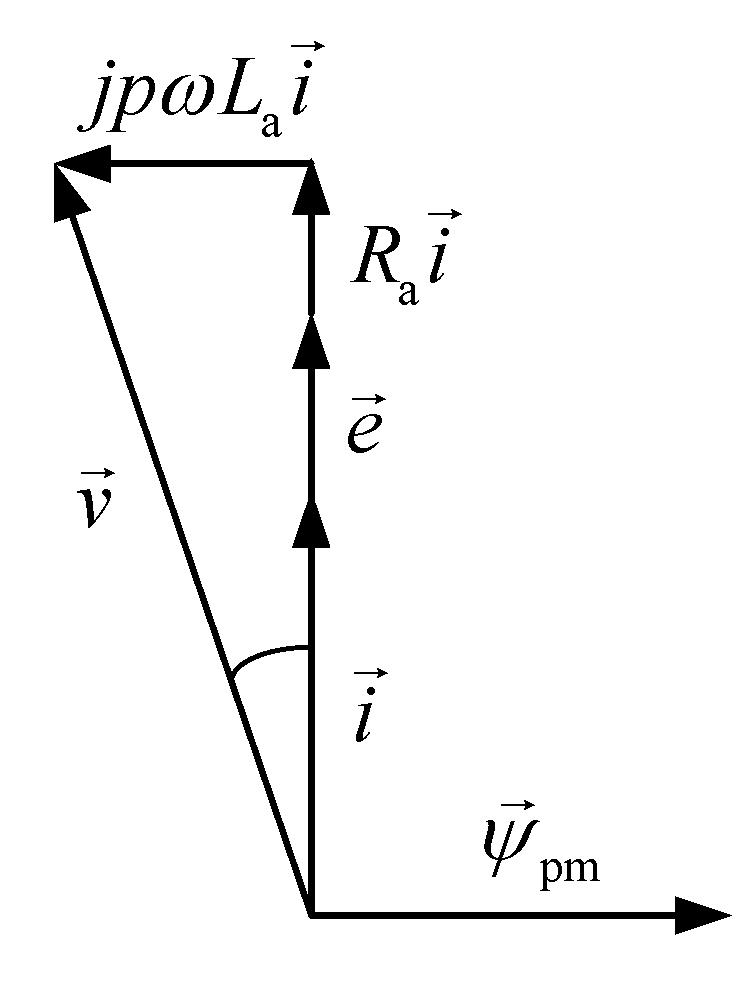
3.1. Mathematical Description of Mechano-Electrical Regularities of PMSG Operation as a Linear EC
4.2. Determination of the Parameters of the Studied PMSG
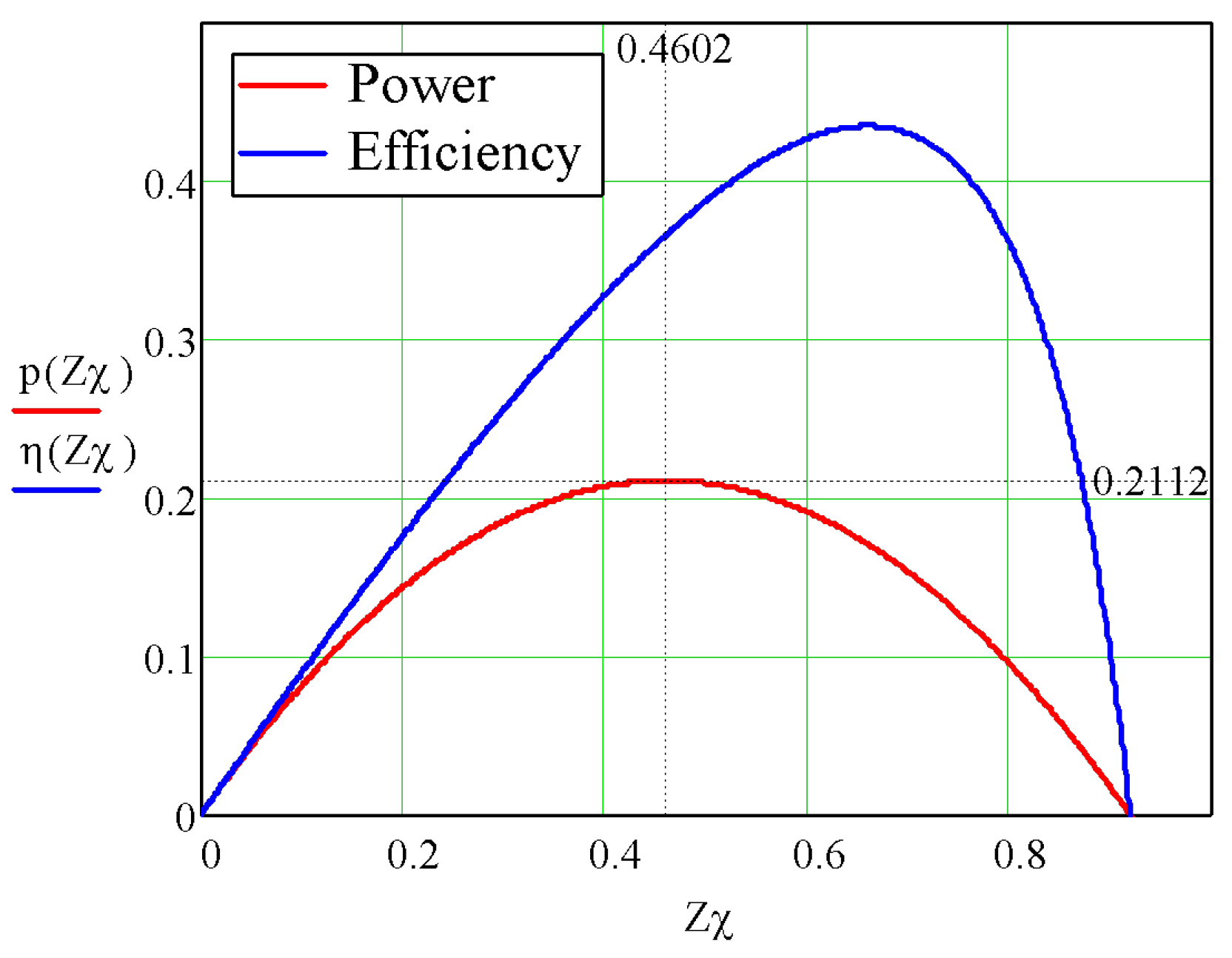
4.3. Thermodynamic Performance Indicators of the Studied PMSG
5. Thermodynamic Analysis of Energy Conversion Efficiency in the «VAWT – PMSG» Complex
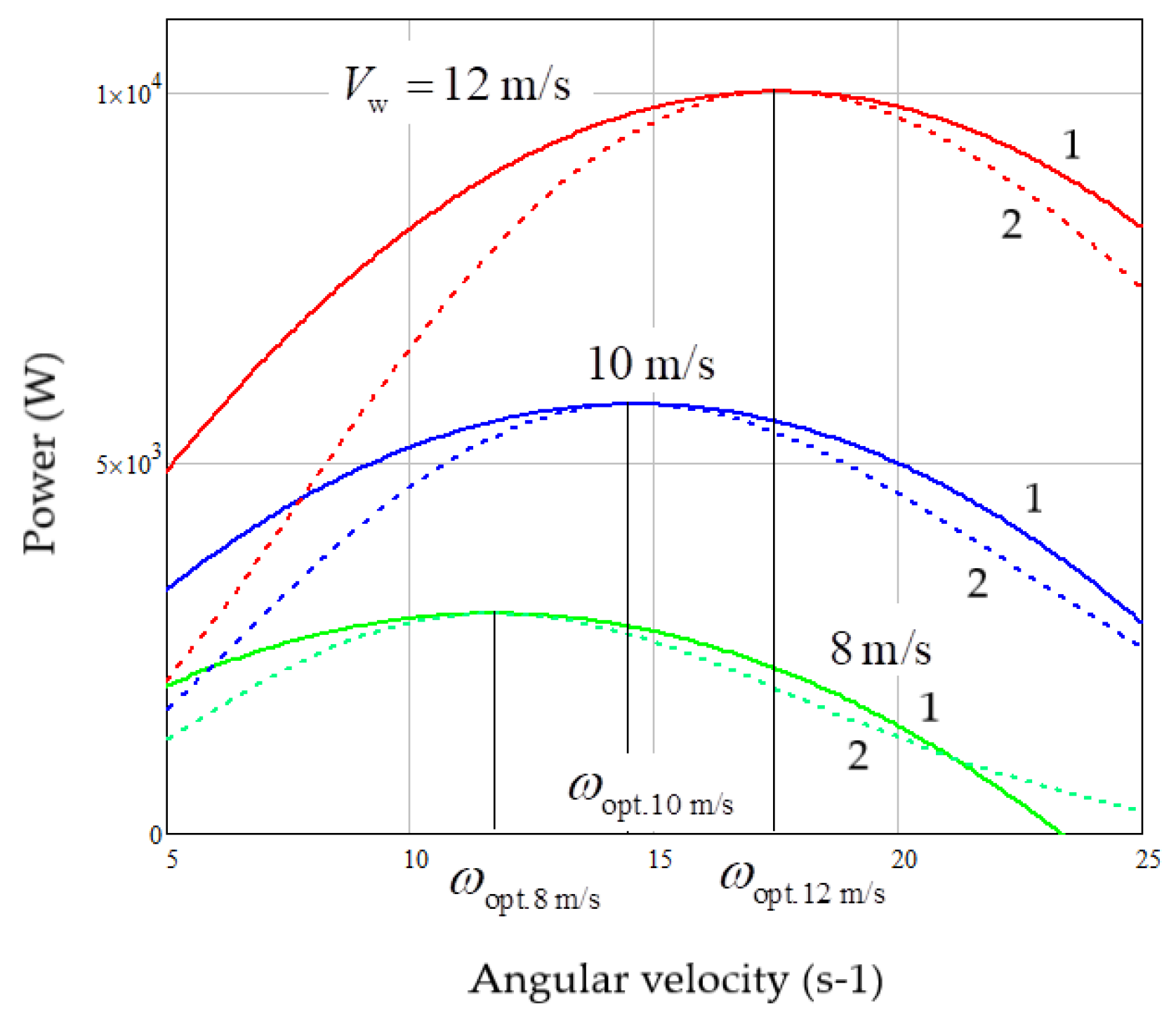
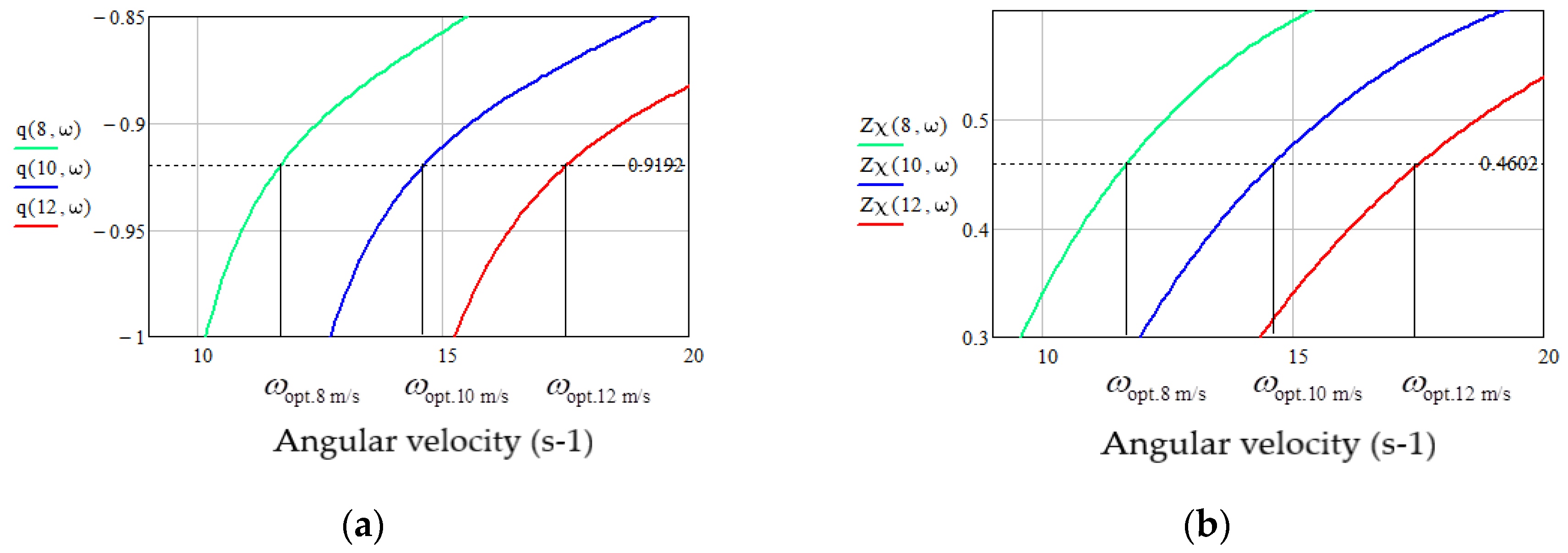
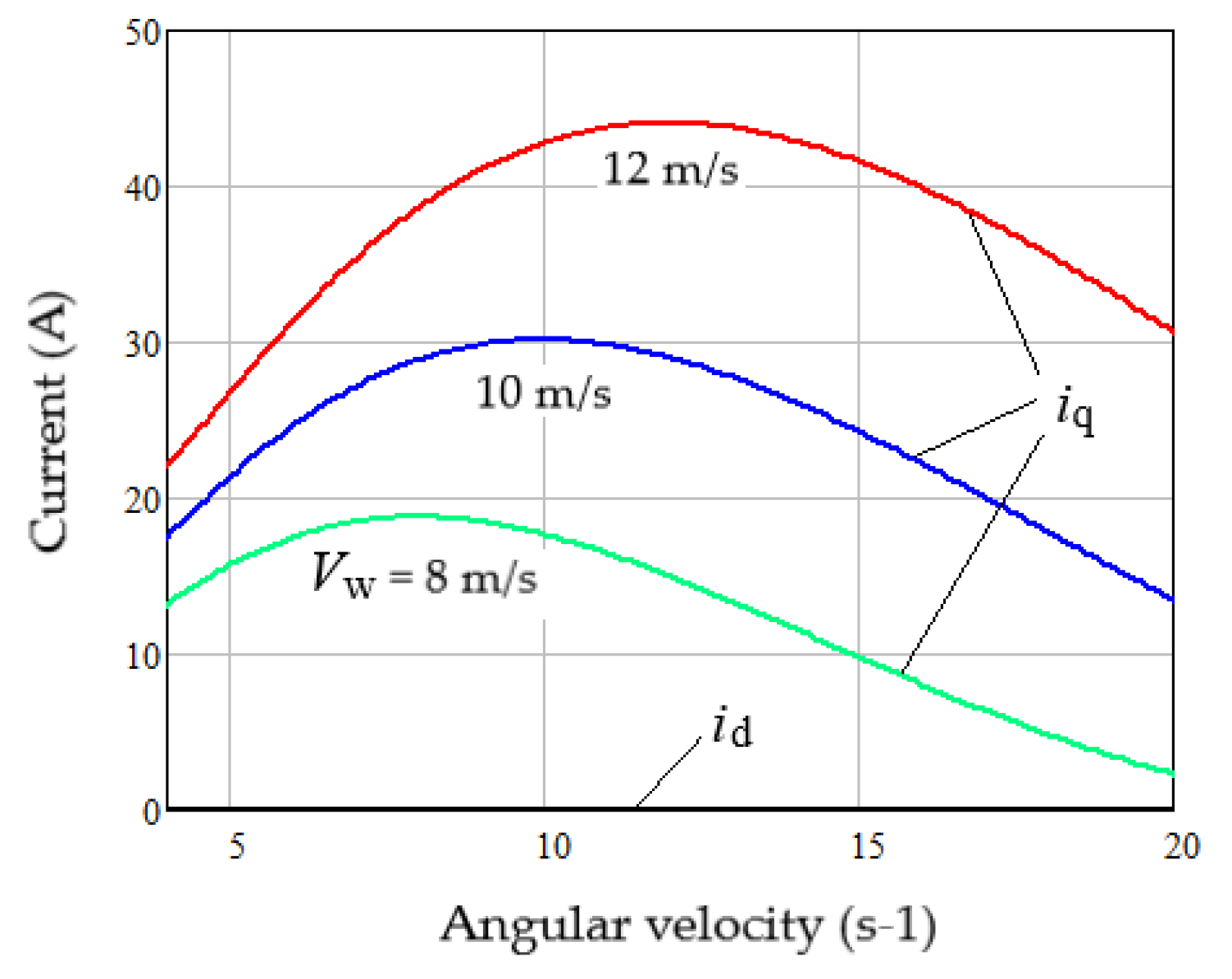
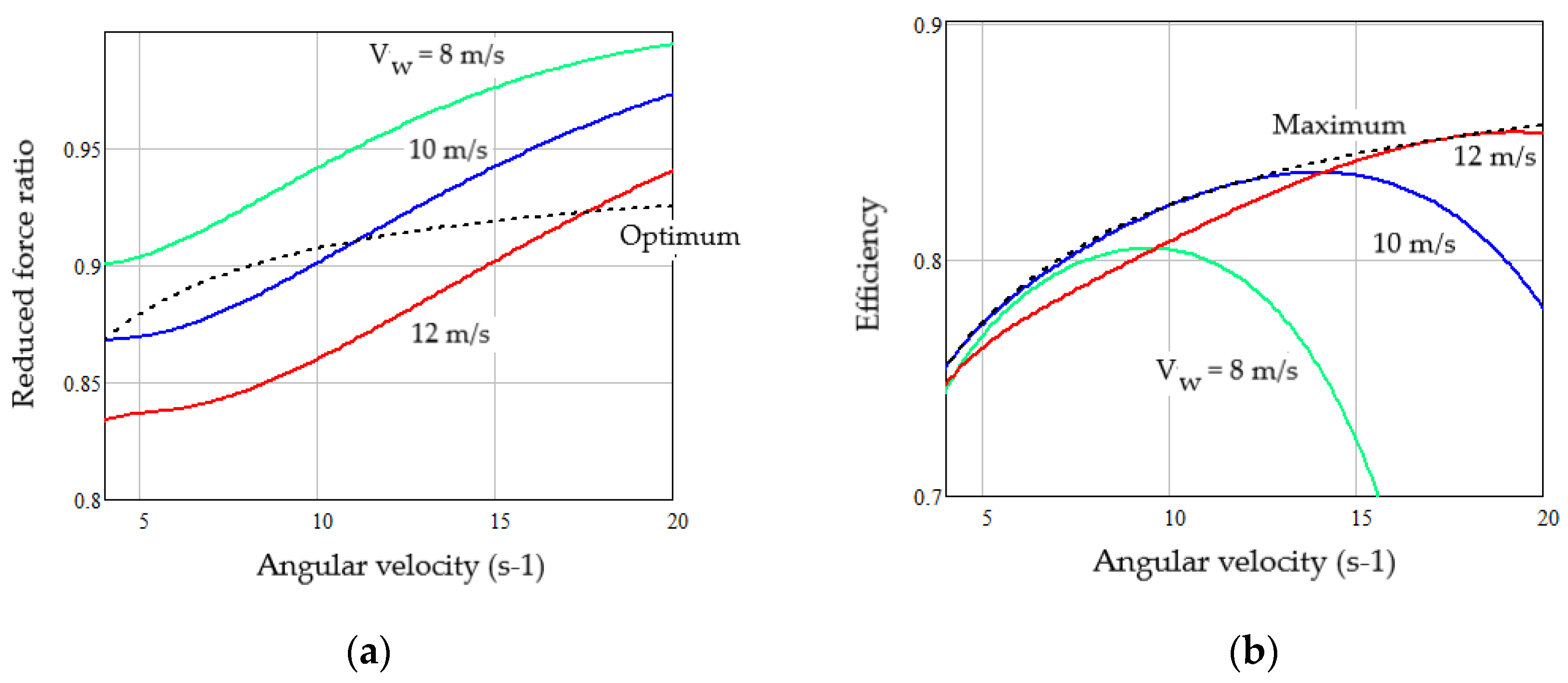
5.1. Thermodynamic Performance Indicators of the Studied PMSG Driven by the Studied VAWT
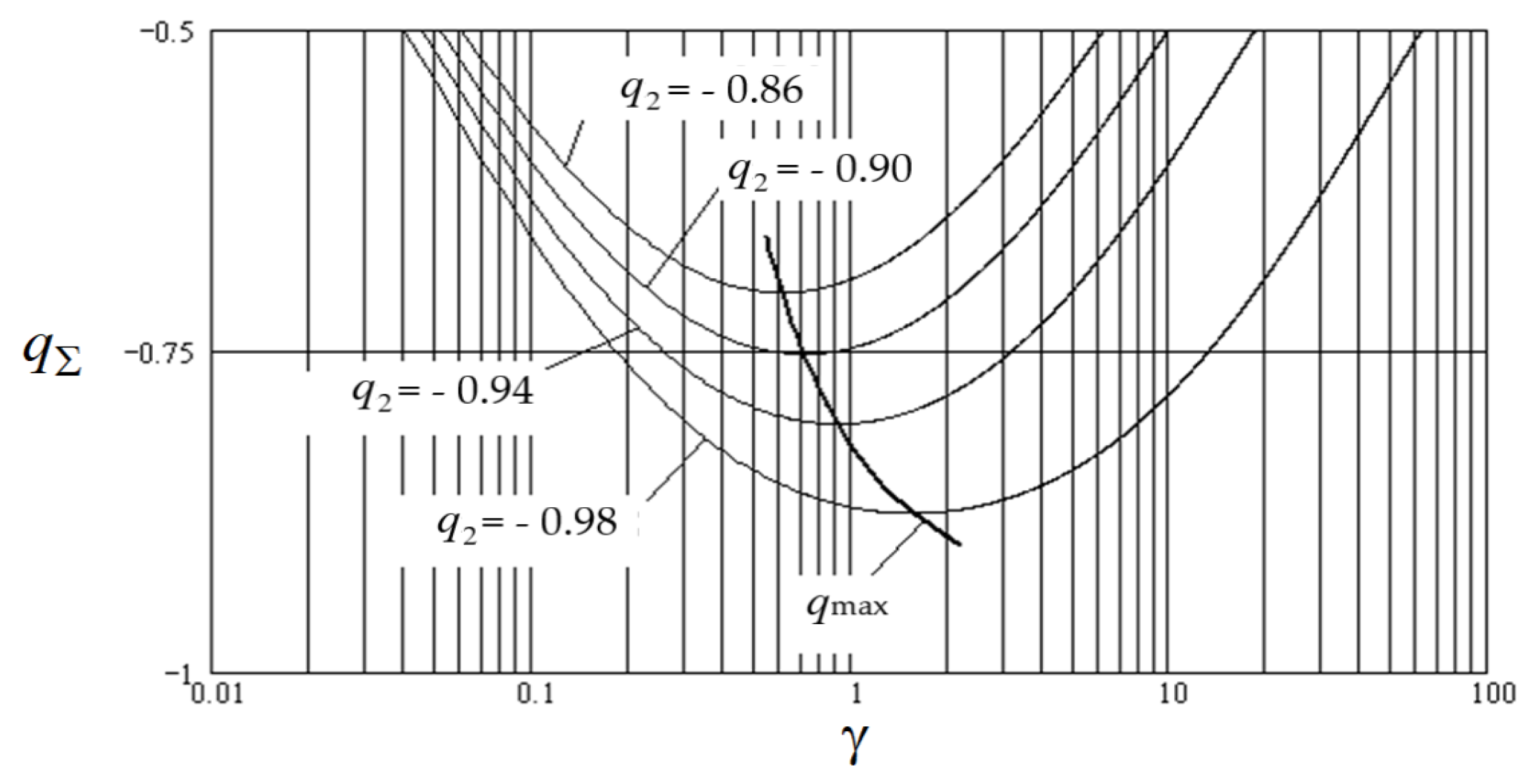
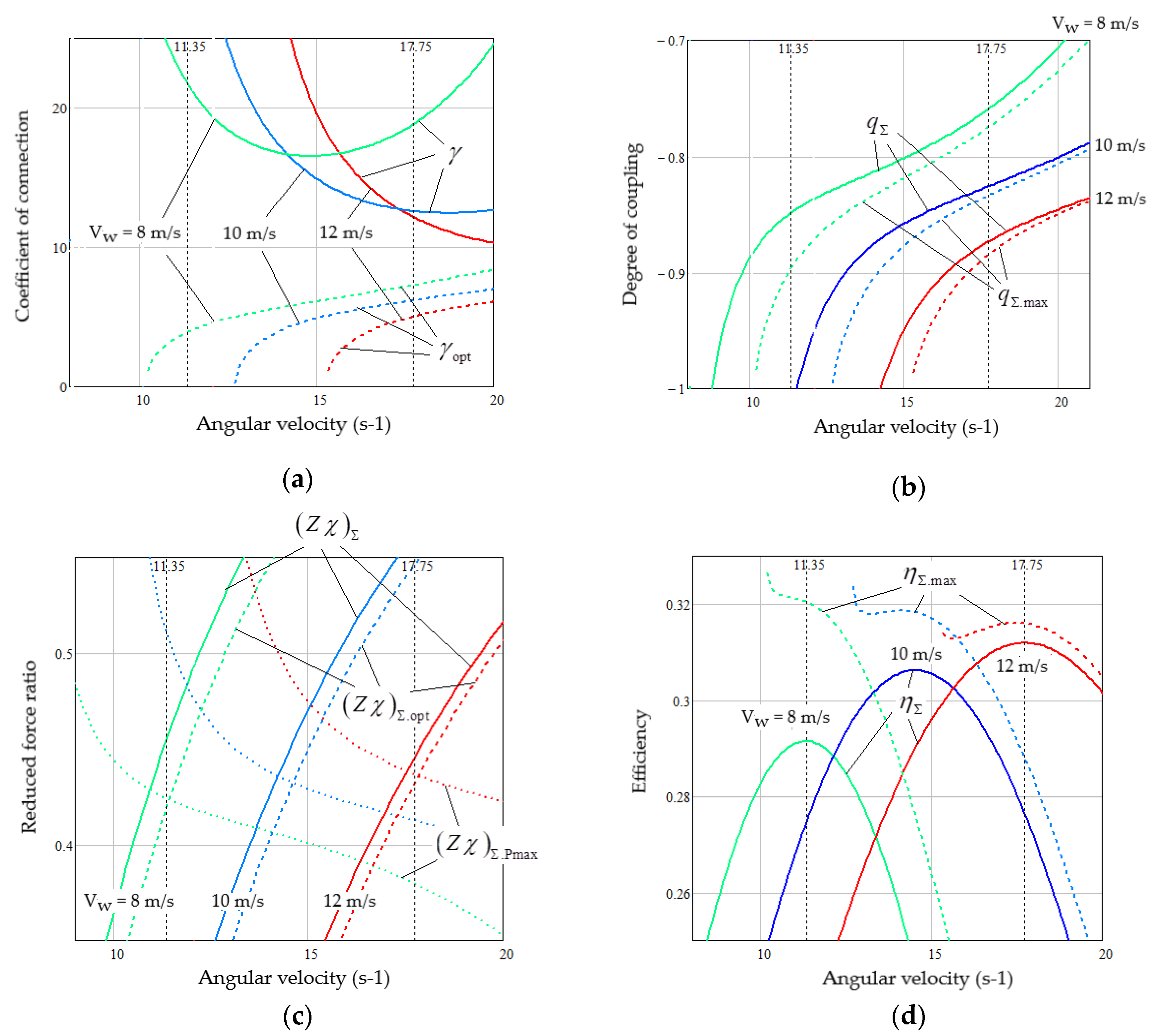
5.2. Thermodynamic Parameters of WECS as a Cascade EC
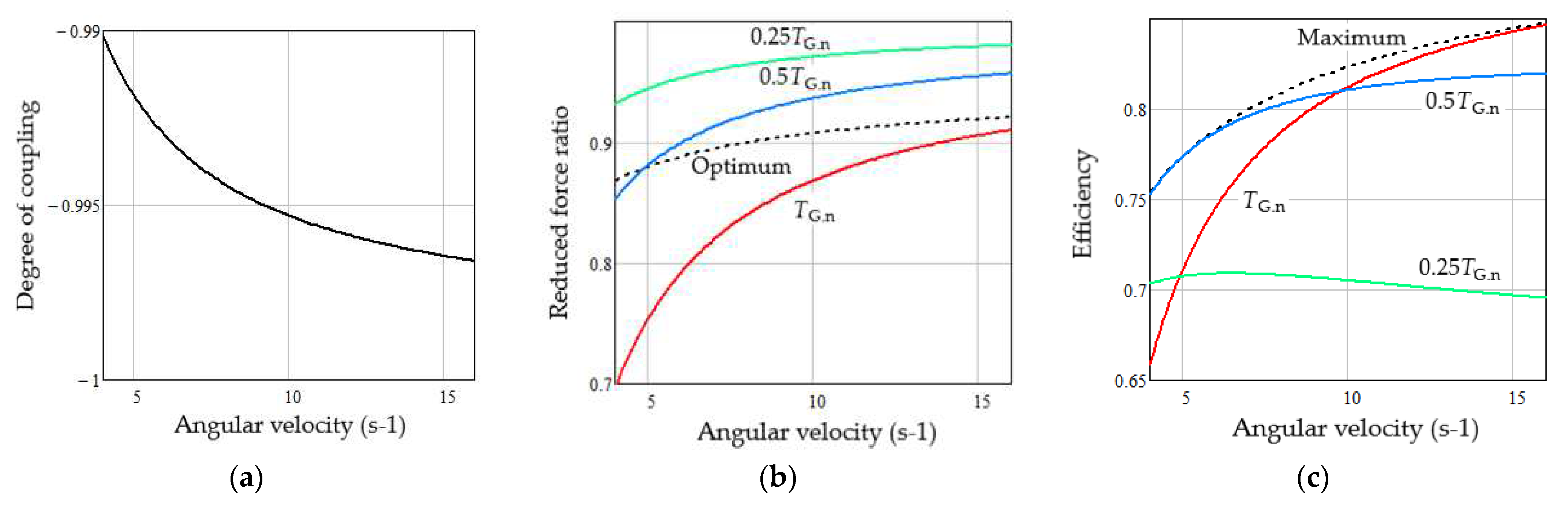
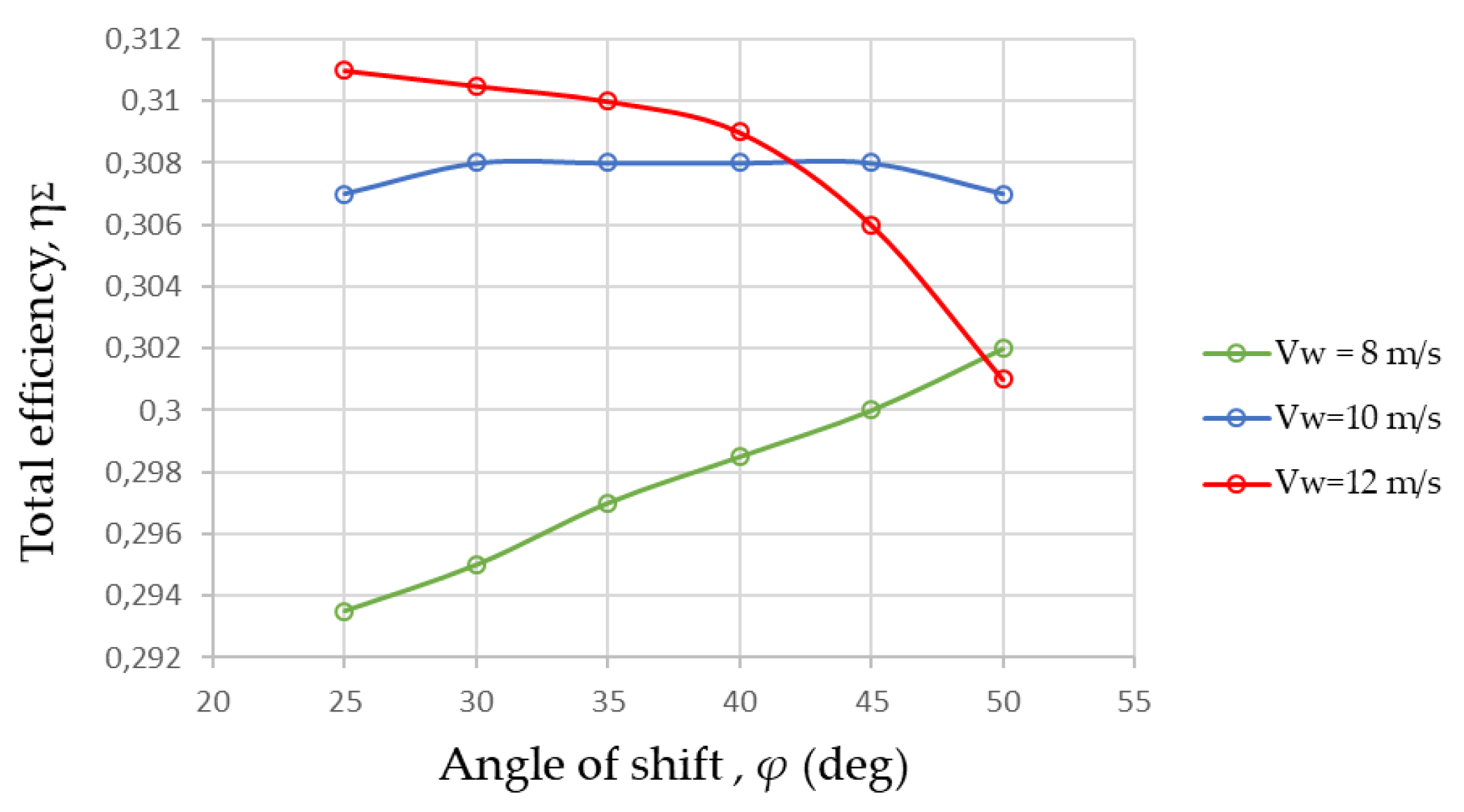
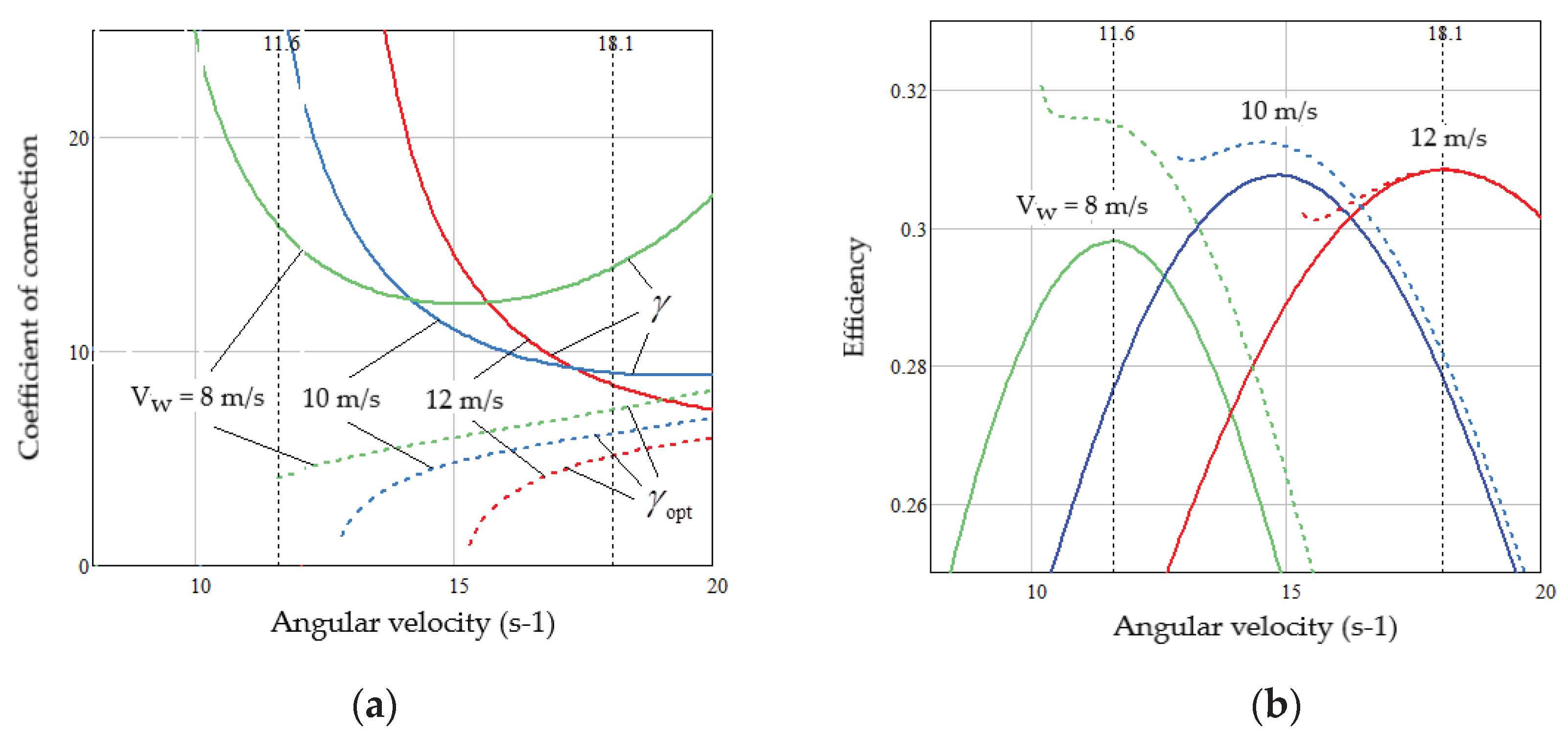
5.3. Research of the Ways to Improve the WECS Efficiency
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Turns, S.R.; Pauley, L.L. Thermodynamics: Concepts and Applications, 2nd ed., Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2020; 854 p.
- Demirel, Y. Nonequilibrium Thermodynamics: Transport and Rate Processes in Physical, Chemical and Biological Systems, 2nd ed., Elsevier Science & Technology Books: Amsterdam, Netherlands, 2007; 754p.
- Christen, T. Efficiency and Power in Energy Conversion and Storage: Basic Physical Concepts, CRC Press. Taylor & Francis Group: Boca Raton, USA, 2018; 178p. https://doi.org/10.1201/9780429454288. [CrossRef]
- Kleidon, A. Working at the limit: A review of thermodynamics and optimality of the Earth system. Preprint. Discussion started: 22 August 2022. https://doi.org/10.5194/esd-2022-38. [CrossRef]
- Perera, S.M.H.D.; Putrus, G.; Conlon, M.; Narayana, M.; Sunderland, K. Wind energy harvesting and conversion systems: A technical review. Energies 2022, 15, 9299. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15249299. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yang, K.; Li, X.; Xu, J. Thermodynamic analysis of energy conversion and transfer in hybrid system consisting of wind turbine and advanced adiabatic compressed air energy storage. Energy 2014, 77, 460-477. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2014.09.030. [CrossRef]
- Koschwitz, P.; Bellotti, D.; Sanz, M.C.; Alcaide-Moreno, A.; Liang, C.; Epple, B. Dynamic parameter simulations for a novel small-scale power-to-ammoniac. Processes 2023, 11, 680. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11030680. [CrossRef]
- Vosough, A.; Vosough, S. Different kind of renewable energy and exergy concept. Int. J. Multidisciplinary Sciences and Engineering 2011, 2(9), 1-7.
- Sahin, A.D.; Dincer, I.; Rosen, M.A. Thermodynamic analysis of wind energy. Int. J. Energy Res. 2006, 30, 553–566. https://doi.org/10.1002/er.1163. [CrossRef]
- Kocer, A.A.; Yuksel, Y.E.; Ozturk, M. Thermodynamic and environmental assessment of a wind turbine system. In Proceedings of the 5th International Symposium of Sustainable Development, Sarajevo, Bosnia and Herzegovina, 15-18 May, 2014; pp. 219-228.
- Hu, W.; Liu, Z.; Tan, J. Thermodynamic analysis of wind energy systems. In Wind Solar Hybrid Renewable Energy System; Kenneth, O.E.; Tahour, A.; Aissaou, A.G.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2019; pp. 1-19. http://doi.org/10.5772/intechopen.85067. [CrossRef]
- Westerhoff, H.V.; van Dam, K. Thermodynamics and Control of Biological Free-Energy Transduction. Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1987; 298 p. https://doi.org/10.15490/fairdomhub.1.datafile.4954.1. [CrossRef]
- Shchur, I.; Rusek, A.; Lis, M. Optimal frequency control of the induction electric drive based on the thermodynamics of irreversible processes. Electrotechnic and Computer Systems 2011, 3(79), 377-380. https://eltecs.op.edu.ua/index.php/journal/article/view/751.
- Kondepudi, D.; Prigogine, I. Modern Thermodynamics: From Heat Engines to Dissipative Structures, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: NY, USA, 2015; 560 p. https://doi.org/10.1002/9781118698723.fmatter. [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Zhao, S.; Feng, F.; Li, J.; Wang, N.; Bai, R. A review on aerodynamic characteristics of straight-bladed vertical axis wind turbine. Acta Aerodynamica Sinica 2017, 35(3), 368-382. https://doi.org/10.7638/kqdlxxb-2016.0189. [CrossRef]
- Krause, P.; Wasynczuk, O.; Sudhoff, S.; Pekarek, S. Analysis of Electric Machinery and Drive Systems, 3rd ed. Wiley: Hoboken NJ, USA, 2013; 688 p. https://doi.org/10.1002/9781118524336. [CrossRef]
- Majout, B.; El Alami, H.; Salime, H.; Zine Laabidine, N.; El Mourabit, Y.; Motahhir, S.; Bouderbala, M.; Karim, M.; Bossoufi, B. A review on popular control applications in wind energy conversion system based on permanent magnet generator PMSG. Energies 2022, 15, 6238. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15176238. [CrossRef]
- Shchur, I.; Rusek, A.; Biletskyi, Y. Energy-shaping optimal load control of PMSG in a stand-alone wind turbine as a port-controlled Hamiltonian system. Przegląd Elektrotechniczny (Electrical Review) 2014, 5, 50-55. http://dx.doi.org/10.12915/pe.2014.05.10. [CrossRef]
- Torki, W.; Grouz, F.; Sbita, L. Vector control of a PMSG direct-drive wind turbine. In Proceedings of 2017 International Conference on Green Energy Conversion Systems (GECS), Hammamet, Tunisia, 23-25 March 2017; pp. 1-6. https://doi.org/10.1109/GECS.2017.8066247. [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Bernal, F.; García-Cerrada, A.; Faure, R. Determination of parameters in interior permanent-magnet synchronous motors with iron losses without torque measurement. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2001, 37(5), 1265-1272. http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/28.952501. [CrossRef]
- Golovko, V.M.; Ostroverkhov, M.Y.; Kovalenko, M.A.; Kovalenko, I.Y.; Tsyplenkov, D.V. Mathematical simulation of autonomous wind electric installation with magnetoelectric generator. Naukovyi Visnyk Natsionalnoho Hirnychoho Universytetuthis 2022, 5, 74–79. https://doi.org/10.33271/nvngu/2022-5/074. [CrossRef]
| Parameters | Value |
|---|---|
| Rated power, PWT.n (kW) | 10 |
| Rated wind speed, Vw (m/s) | 12 |
| Maximum of power coefficient, Cp.max | 0.3661 |
| Optimum value of TSR, λopt | 3.873 |
| Rotor radius, R (m) | 2.65 |
| Rotor high, H (m) | 1.25 |
| Air density, ρ (kg/m3) | 4.78 |
| Parameters | Value |
|---|---|
| Rated power, PG.n (kW) | 10 |
| Rated angular velocity, ωG.n (s-1) | 17.54 |
| Rated torque, TG.n (Nm) | 570.2 |
| Number of pole pairs, p | 24 |
| PM flux linkage, ψpm (Wb) | 0.41 |
| Relative losses in copper, δCu | 0.07 |
| Relative losses in steel, δFe | 0.03 |
| Angle of shift between armature voltage and current, φ (deg) | 30 |
| Winding resistance, Ra (Ω) | 0.286 |
| Winding inductance, La (mH) | 6.1 |
| Rated equivalent iron loss resistance, Rc.n (Ω) | 84.4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





