Introduction
Today, oil and gas are considered the most vital human need, and the process of producing and extracting optimal fluid from hydrocarbon reservoirs is one of the concerns of the current world in the field of fuel supply. However, considering the limitation of gas and oil resources in the vail and the limited ability of humans to explore, produce, exploitation of hydrocarbon resources, the need to develop new technologies in the direction of scientific development and extraction and production [
1]. Nanotechnology is increasingly influencing all sectors of industry. Nanotechnology can be used to increase the development of gas and oil resources. Nanotechnology is used to alter the function of drilling, and producing oil and gas, and also makes it simple to separate the oil and gas in the tank [
2]. Nanofluids have the capacity and potential to create transformative changes in various scopes of industries likewise exploration and extraction, drilling, production, and increased yield [
1,
2]. The realization of special and desirable structures of supramolecular nanofluids can be done with the help of precise changes in the macroscopic parameters of the system such as the composition of the system. Phase changes in the preparedness of nanofluids strongly modify the macroscopic virtues of the nanofluid mass [
1,
2]. nanofluids have thermophysical virtues in contrast to heat transfer factors [
3]. They improve established dissolution methods and completely remove foreign materials from reservoir surfaces and tubing surfaces instead of fixed dissolution methods alone that can transfer near-wellbore damage into the reservoir [
4].
The addition of specific nanoparticles (NPs) to injection solutions can significantly improve oil recovery (EOR), with benefits such as wettability periodicity, changes in fluid properties, improved mobility of trapped oil, increased sand integrity, and reduced interfacial tension (IFT) [
5]. Polymers enhance the viscosity of the injected liquid. Polyacrylamide and hydrolyzed polyacrylamide are among the polymers that are known as mobility improvers [
6]. They do not agree with vast temperatures and intense concentrations of salt environments. owing to hydrolysis and thermal decadence, their use is limited in such conditions [
6]. They move inside the pore network of the reservoir forth reducing the permeability [
6,
7,
8]. The amount of polymer absorption on the stone surface decreases in the presence of nanoparticles. Polymer nanocomposites show better thermal stability and salt tolerance than pure samples. So far, by using polymerization methods, various nanocomposites containing nanoparticles have been synthesized by linking a polymer chain to a polymer chain on the area of a nanoscale particle. Yi showed that water-soluble silica-polymer nanoparticle composites are thermally stable and have better transportability in porous media [9, 10].
Synthesis of Polymeric Nanofluid
There are two methods to synthesize polymer nanofluids in EOR. It is called the chemical bond of polymer on the area of PGN nanoparticles, and PNS is a hybrid that is formed by mixing nanoparticles and a polymer solution.
PGN synthesis is complex, and because of the kinds of polyelectrolytes availed, it shows more performance than PNS. Polyelectrolyte makes PGN nanoparticles not sensitive to the assault of cations in salts and creates freedom of movement in the macromolecular structure.
A Mechanism for Polymeric Nanofluid Applications in EOR
The energy industry faces many challenges and problems in its various sectors in the manufacturing of required materials and tools and the design of safe methods and operations. In recent years, nanotechnologies have possessed great notice in providing methods to solve such problems. The need for methods of increasing oil extraction from producing reservoirs is undeniable, which seems very vital to respond to the worldwide requisition for energy considering the decrease in the number of fields being discovered worldwide. Many of the fields are in the final stages of their production, and this is while about two-thirds of the oil is in the reservoirs with the help of normal methods. The product cannot be withdrawn [
1,
11]
Nanomaterials increase endurance and lower absorption. They change the wettability in the pores of the rock and improve the rheology of the polymer [
8,
12].
Polymeric Nanofluids
Nanotechnology is beneficial in various industries such as nanofluids, nanocatalysts, and nanoemulsions to enhance extraction, but in this article, as shown in
Figure 1, we will examine nanofluids in increasing extraction. Nanotechnology is a possible solution to solve most problems.
Polymeric nanofluids are used due to increase rheological stability and dynamic control, reducing polymer absorption, changing wettability.
Materials
In this research, clay nanoplates, which are hydrophilic in nature, are used. These nanoplates are commercially prepared by Pishgaman Nano Materials Iranian Company.
Table 1 shows some of the specification of the mentioned nanosheets.. A type of acrylamide polymer made by a German company is also used to make polymer nanocomposites.
Table 2 displays the technological characteristics of the polymer.
Also, in this research, crude oil from the Kozhdami Formation of the Azadegan field was used, whose specifications are:
Temperature=25°C
Viscosity= 11 cP
Density= 0.780 gr/cc
A carbonate sample with an approximate length of 10 cm and a diameter of 3.5 cm was used as a porous sample in conducting core fluidization experiments. The considered sample has a porosity and permeability of about 20% and 300 millidarcys.
Preparation of Clay Nanofluid
The optimum concentration of 1000 ppm of ross nanoparticles was selected and applied. This optimal concentration has been provided by extensive research for various nanoparticles. To prepare the nanofluid of clay in the introduced dose, a certain amount of nano clay powder should be added to distilled water. Therefore, the mass of nanoparticles for the desired concentration is measured using a scale and a magnetic stirrer.
It was dispersed in distilled water at 200 rpm. The gathered nanofluid was exposed to ultrasound radiation with a frequency of 20 kHz for two hours. One hour was placed with an ultrasonic probe and one hour was placed inside an ultrasonic bath to completely disperse in the aqueous stage. A certain content of sodium chloride salt of 50000ppm was stepped up to the nanofluid and it was exposed to ultrasound radiation for another two hours. The reason for choosing such an amount of salt was to minimize the possible instability of nanoparticles.
Preparation of Polymer Solution and Nanocomposite of Polymer and Clay
Polymer solution (3000ppm) was accumulated by dissolving some polymer in salt water (50000ppm sodium chloride) with the help of a magnetic stirrer. After that, to prepare resin nanocomposite, resin nanofluid was added to the polymer solution and mixed slowly for 30 minutes.
Nano Clay on Wettability
There are two approaches to determining the conclusion of nano clay on rock wettability. First, after measuring the primary tangency angle, the rock sample is soggy in a nanofluid. By measuring a difference in contact angle of the sample before and after soaking, the effectiveness of nanoparticles on the change in wettability was characterized.
The second approach is the same as the first approach, except that the samples are after heterophilic.
In this study, the second approach was used to consider the result of nano clay on wettability. After preparing the core, they were placed in crude oil at 70°C for one week to become oleophilic. To determine the results of sludge particles on the wettability of carbonated sinks, oil-friendly blades are placed in closed containers for 24 hours. The system for determining the contact canton includes a camera with 200 magnification, a chamber for placing thin stone slices, an injection syringe, and a computer for image analysis.
Rheology Test of Polymer Solutions Containing Nano Clay
To check the effect of clay nano clay on polymer viscosity, viscosity measurement experiments are performed with the help of a rotary rheometer. In this section, a rotary rheometer manufactured by Anton Parr in Austria was used.
The action and reaction of the polymer with nano clay have a synergistic effect and a positive effect on rheological behavior, and the electrostatic stability of nanoparticles enhancement against absorption in the presence of salt water.
Core Flotation Test
The core fluidization machine has different parts, including the core holding chamber, two fluid-moving cylinders, applying external pressure around the core, pressure transducers, displays, and two high-pressure injection pumps.
The pumps used in the device are reciprocating types that can inject the desired fluid with a constant flow rate. The injection accuracy of these pumps is equal to 0.004 cc/min and can reach a maximum injection pressure of 6000 pounds per square meter. For injection operation, the sample is placed inside a rubber chamber, which is generally subjected to a pressure of 500 pounds per square meter rather than the infusion pressure. The pressure is pragmatic by a hydraulic oil ram. A machine is used for brain cleaning. This method is the most common method of washing kernels with chemical detergents because the process of washing kernels can be seen in the sole. Therefore, when toluene, which is a washing agent, is perfect in terms of color
It became clear, the washing process comes to an end. To perform two-phase fluidization experiments, first, the cores are saturated with oil and placed in a pot with a temperature of 70 degrees Celsius for two weeks to become oil-loving. After they become oil-friendly, the kernels are washed with deionized water and organic solvents such as toluene or acetone. Next, they are injected with salt water under a constant flow rate
They are completely saturated with water. Crude oil is also injected after that until the kernels attain the primary water saturation. Saline water is injected to simulate the primary oil recovery process. To define the effect of polymer solution in recycling, a polymer solution containing salt is injected. Finally, the fluidization of polymer materials combined with clay nanoparticles is done and the results of oil recovery are compared.
Results and Discussion
The Viscosity of Nanofluid of Clay
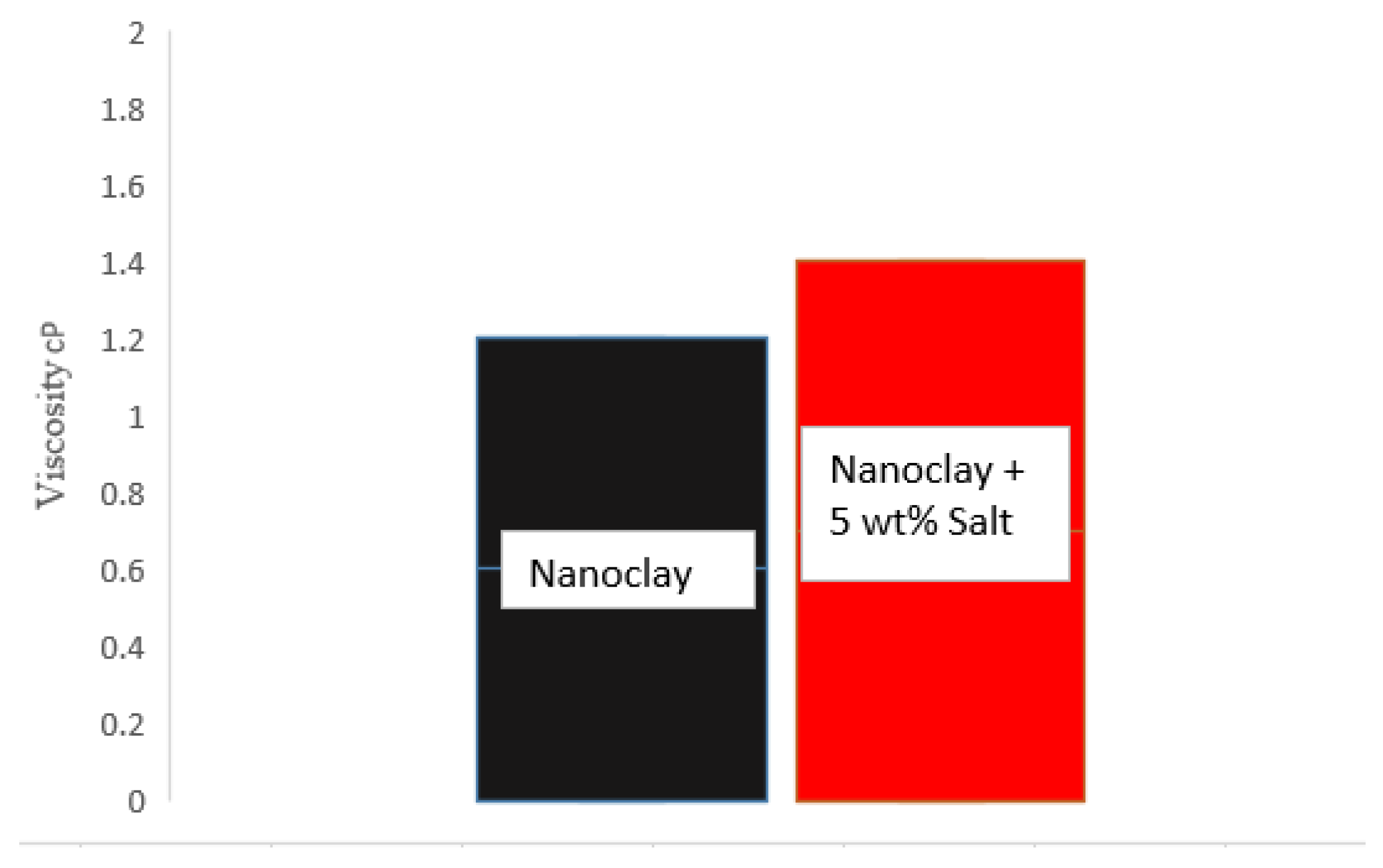
The effect of sodium chloride monovalent salt on the viscosity of nanofluid has been considered by viscosity measurement experiment.. For this purpose, first, the viscosity of a suspension containing 4000 ppm of clay nanoparticles was measured. After that, the amount of 5 mg/liter of salt was added to that suspension and the viscosity was determined again.
According to
Figure 2, the viscosity for salt-free nanofluid is about 1 centipoise, as a result of adding 5.wt% of salt, its viscosity increased and reached 1.4 cP. One of the reasons for affluence viscosity is regressive the degree of freedom and radius of gyration of nanoparticles have been proven that when Na + monovalent ions enter the aqueous phase containing nanoparticles, a strong connection is formed between them and the negative charges of nanoparticles, which causes the solid particles to join closer to each other and increases the viscosity of the aqueous form.
Effect of Nano Clay on Viscosity
The doping of 3000 ppm is specified for the tests. Then 3000 ppm of salt was added to the first sample and the test was repeated with the previous specifications. This test showed the negative effect of sodium chloride salt. Making the next sample, a concentration-000- of 1000 ppm of clay nanoparticles was added to the polymer solution containing salt, and the viscosity was measured again. The results of the tests can be viewed in
Figure 3.
The viscosity of the net polymer solution was about 70 poise cents at the beginning, but with the increase of the shear rate, it gradually decreased until the shear rate 1000sec-1 reached the minimum value of 40 cP. In the presence of salt, this procedure had a very sharp decrease because the viscosity of the polymer decreased from 70 to 35 poise cents and at the highest shear rate reached a negligible value of about 5 cP.
Nevertheless, when a small number of nanoparticles was added to the polymeric solution, its viscosity increased dramatically and reached 100 cent Poise at the lowest shear rate. When nanoparticles are added to the polymer solution, they prevent them from condensing in environments with high salt concentrations by placing them irregularly between the polymer chains. Therefore, the attendance of nano clay is very effective for improving the viscosity even in the presence of high salt concentrations.
The Effect of Nano Clay on Wettability
Clay nanoparticles cannot change the wettability much in the absence of salt. Therefore, we have prepared 2 samples to test the effect of clay nanoparticles and table salt on wettability. We placed an oily sample, two oil-loving carbonate thin plates in two nanofluids with the following details:
Sample 1: 1000 ppm salt-free clay (pH=1.4) and
Sample 2: 1000 ppm clay containing 50,000 ppm salt (pH = 3.4).
The contact angle of the blades in samples 1 and 2 were considered to be 87 degrees and 35 degrees, respectively.
Nanoparticle suspensions in nanofluids are acidic. If nano clay are absorbed on the same surface of the resin, the wettability of the resin changes from a completely oil-loving state to a neutral or hydrophilic state.
Core Flooding
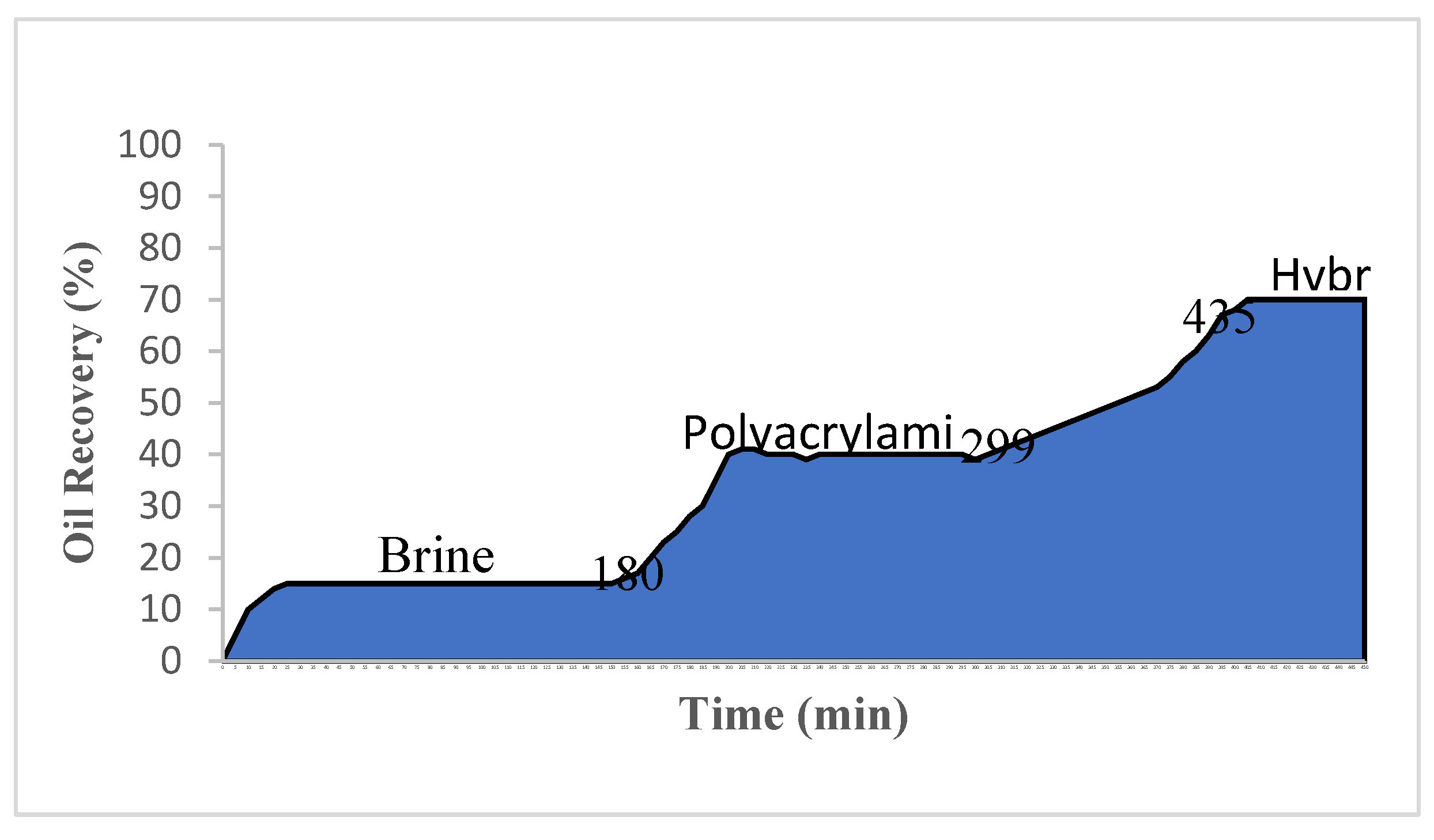
Result of this section for resin and polymer nano clay of recovered oil in three scenarios.
First, salt water with a salinity of 50,000 ppm was injected. In the next step, 3000 ppm of the sulfonated copolymer was prepared and injected. Finally, a combination of ross nanoparticles (1000 ppm) and sulfonated copolymer (3000 ppm) was injected into the nucleus. The amount of recovered oil was calculated for salt water, sulfonated copolymer, and a combination of copolymer and resin, 17, 25 and 29%, respectively. After all three injection scenarios, the amount of total yield of 70% was obtained (
Figure 4).
In the first scenario, saltwater injection, due to the high displacement ratio of the injected phase and the strong fingering phenomenon, the output oil amount was not a significant number. But in the second scenario, i.e. polymer fluidization, higher viscosity caused better control of the mobility ratio and more recovered oil compare to saltwater salt in the water injection scenario. Meanwhile, in the third scenario, i.e., a combination of resin nanoparticles and sulfonated copolymer, the amount of oil recovery was slightly higher than in the previous two stages. Among the possible mechanisms for this scenario, we can mention an increase in viscosity and a change in wettability.
Conclusions
Adding a little salt to the clay nanofluid improved the viscosity of this suspension to 0.18. Also, when the same content of salt was augmented to the polymer dilution, the viscosity decreased sharply and reached from 70 cent poise to 35 cent poise. Nevertheless, when a little clay nanoparticle was added to the polymer solution containing salt, the viscosity reached an approximate value of 100 poise cents, which shows the positive effect of clay nanoparticles in improving the viscosity of the polymer dilution even at numerous salt concentrations. Nano clay has a better potential to change the wettability from a more oil-like state to a more water-like one, because in the attendance of salt, they change the tangency angle of the oil-loving carbonate blade from a highly oil-loving state (150 degrees) to a water-like state. They changed the extreme affinity (35 degrees). In core fluidization experiments, the highest efficiency was obtained in the third scenario, i.e., a combination of resin nanoparticles and sulfonated copolymer. Because in this case, the polymer solution had the highest viscosity and nanoparticles was also present in it.
References
- R. Khoramian, A. Ramazani S. A, M. Hekmatzadeh, R. Kharrat, E. Asadian. Graphene Oxide Nanosheets for Oil Recovery, ACS Applied Nano Materials. (2019). [CrossRef]
- J. Fadi EL-Masry, K. Fahmi. Bou- Hamdan, A. Hashim Abbas, Dmitriy A. Martyushev. A Comprehensive Review on Utilizing Nanomaterials in Enhanced Oil Recovery Applications. Energies 16 (2) (2023). 691. [CrossRef]
- N. K. Maurya, P. Kushwaha, A. Mandal, Studies on interfacial and rheological properties of water- soluble polymer grafted nanoparticle for application in enhanced oil recovery, Journal of the Taiwan Institute of Chemical Engineers. (2017) . [CrossRef]
- M. Iravani, Z. Khalilnezhad, A. Khalilnezhad, A review on application of nanoparticles for EOR purposes: history and current challenges, Journal of Petroleum Exploration and Production Technology. (2023). [CrossRef]
- Afeez, Gbadamosi, R. Junin, A. Muhammad, Manan, N. Yekeen, A. Augustine, Hybrid suspension of polymer and nanoparticles for enhanced oil recovery, Polymer Bulletin. (2019).
- A.O. Gbadamosi, R. Junin, M.A.Manan,N. Yekeen, A. Agi, J.O. Oseh, Recent Advances and Prospects in Polymeric Nanofluids Application for Enhanced Oil Recovery, Journal of Industrial and engineering chemistry, Graphene Oxide Nanosheets for Oil Recovery. (2018). 1-62. [CrossRef]
- Sircar, K. Rayavarapu, N. Bist,K. Yadav, S. Singh, Applications of nanoparticles in enhanced oil recovery, Petroleum Research. 38 (2021) 1-14. [CrossRef]
- R. Moshfeghi, D. Toghraie, An analytical and statistical review of selected researches in the field of estimation of rheological behavior of nanofluids, Powder Technology. (2021). [CrossRef]
- Abolfazl Dehghan Monfared, Mohammad Hossein Ghazanfari, Mohammad Jamialahmadi, Abbas Helalizadeh. "Potential Application of Silica Nanoparticles for Wettability Alteration of Oil–Wet Calcite: A Mechanistic Study", Energy & Fuels, 2016 . [CrossRef]
- G. Cheraghian,S. Rostami,M. Afrand, Nanotechnology in Enhanced Oil Recovery, MDPI.(2020)1-17. [CrossRef]
- K.Li, D.wang, sh. Jiang, Review on enhanced oil recovery by nanofluids, Oil & Gas Science and Technology - Rev. IFP Energies nouvelles.73(4) (2018) 37.
- T. Sharma, S. Iglauer, J.S. Sangwai, Silica Nanofluids in an Oilfield Polymer Polyacrylamide: Interfacial Properties, Wettability Alteration and Applications for Chemical Enhanced Oil Recovery, I&EC Industrial& Engineering Chemistry Research. (2016)1-42. [CrossRef]
- Wenyue Tang, Changjun Zou, Hao Liang, Chang Da, Zhengguo Zhao. "The comparison of interface properties on crude oil-water and rheological behavior of four polymeric nanofluids (nano-SiO2, nano-CaO, GO and CNT) in carbonates for enhanced oil recovery", Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering. (2022).
- Seyed Shahram Khalilinezhad, Amir H. Mohammadi, Abdolnabi Hashemi, Mojtaba Ghasemi. "Rheological characteristics and flow dynamics of polymer nanohybrids in enhancing oil recovery from low permeable carbonate oil reservoirs", Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering. (2020). [CrossRef]
- Zhongliang Hu, Maje Haruna, Hui Gao, Ehsan Nourafkan, Dongsheng Wen. "Rheological Properties of Partially Hydrolyzed Polyacrylamide Seeded by Nanoparticles", Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research. (2017). [CrossRef]
- Reza Songolzadeh, Jamshid Moghadasi. "Stabilizing silica nanoparticles in high saline water by using ionic surfactants for wettability alteration application", Colloid and Polymer Science. (2016). [CrossRef]
- F. Farahbod, Investigation of gas sweetening by nanofluid in the isothermal tower with consideration of thermodynamic equilibrium; experimentally and theoretically, Separation and Purification Technology.211(2019)799-808. [CrossRef]
- S.H. Esmaeili.Faraj, M. Nasr Esfahany, M.H, Karimi Darvanjooghi, Application of water-based nanofluids in bio scrubber for improvement of biogas sweetening in a pilot scale, Chemical Engineering and Processing. (2019).
- W. Lee, R. Xu, S. Kim, J. Ha Park, Y. Tae Kang, Nanofluid and nanoemulsion absorbents for the enhancement of CO2 absorption performance, 291 (2021). [CrossRef]
- Safaei, A.Hossein Nezhad, A. Rashidi. High temperature nanofluids based on therminol 66 for improving the heat exchangers power in gas refineries, Applied Thermal Engineering. 170 (2020).
- Hamed Farhangian, Seyyed Milad Abrishamifar, Masih Palizian, Milad Janghorban Lariche, Alireza Baghban. "The application of nanofluids for recovery of asphaltenic oil", Petroleum Science and Technology. (2018). [CrossRef]
- F. Ozar Asl, GH. Zargar, A. Khaksar Manshad, M. Arif, Stefan Iglauer, A. Keshavarz, Impact of PAM-ZnO nanocomposite on oil recovery, Fuel Journal. (2023).
- Bakalem, B. Farouk, O. Kitous, M. Drouiche, N. Mameri. Performance of a new electrochemical process using a three-dimensional microelectrode reactor", International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology.18 (2) (2021).1-8. [CrossRef]
- Anurag Pandey, Himanshu Kesarwani, Chetna Tewari, Amit Saxena, Shivanjali Sharma, Nanda Gopal Sahoo. "Waste plastic derived reduced graphene oxide as a potential additive for the surfactant polymer flooding: A sustainable solution", Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering.(2023). [CrossRef]
- Eugene N. Ngouangna, Mohd Zaidi Jaafar, MNAM Norddin, Augustine Agi, Jeffrey O. Oseh, Stanley Mamah. "Surface modification of nanoparticles to improve oil recovery Mechanisms: A critical review of the methods, influencing Parameters, advances and prospects", Journal of Molecular Liquids. (2022).
- B.T. Kelley, J.A. Valencia, P.S. Northrop, C.J. Mart, Controlled Freeze ZoneTM for developing sour gas reserves, Elsevier Energy Procedia. 4 (2011) 824-829.
- M. Taheri, A. Mohebbi, H. Hashemipour, A.M. Rashidi, Simultaneous absorption of carbon dioxide (CO2) and hydrogen sulfide (H2S) from CO2–H2S–CH4 gas mixture using amine-based nanofluids in a wetted wall column, Journal of Natural Gas Science and engineering. (2015)1-15. [CrossRef]
- Ababneh, H, AlNouss, A, & Karimi, I. A,. Muhtaseb,SH.A, Natural Gas Sweetening Using an Energy-Efficient, State-of-the-Art, Solid–Vapor Separation Process.energies..(2022). 15,5286.
- Farshad, F, Investigation of gas sweetening by nanofluid in the isothermal tower with consideration of thermodynamic equilibrium; experimentally and theoretically. International. Journal Elsevier. Separation and Purification Technology. (2019)..211,799-808.
- Saidur R. Leong, K.Y. Mohammad, H.A, A review of applications and challenges of nanofluids. International. Journal Elsevier. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews..(2011).15,1646-1668.
- Jagar, K. Kolo, A. Khaksar Manshad, A. H. Mohammadi, Recent advances in application of nanotechnology in chemical enhanced oil recovery: Effects of nanoparticles on wettability alteration, interfacial tension reduction, and flooding, Egyptian Journal of Petroleum. (2018). [CrossRef]
- V. Irani, A. Maleki. A, Tavasoli, CO2 Absorption Enhancement in Graphene-Oxide/MDEA Nanofluid. International. Journal of Environment Chemical Engineering. 7(1) (2019).
- G. Huminic, A. Huminic, C. Teodor Fleaca, M. Ion, Experimental study on viscosity of water- based Fe–Si hybrid nanofluids, Journal of Molecular Liquids. 321 (2021). [CrossRef]
- M. Niu, H. Yang, X. Zhang, Y. Wang, A. Tang, Amine-impregnated mesoporous silica nanotube as an emerging nanocomposite for CO2 capture. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 8 (27) (2016). [CrossRef]
- Xuan. Y,. Li, Q, Heat transfer enhancement of nanofluids. International. Journal Elsevier. Journal of Heat and Fluid Flow.(2000). 21,58-64.
- Trisaksri, V, Wongwises,S, Critical review of heat transfer characteristics of nanofluids. International. Journal Elsevier. (2007). 11,512-523. [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.T, Lin,Yu,sh,.& Yin,Yan.Sh, A novel one-step chemical method for preparation of copper nanofluids. International. Journal Elsevier. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science. (2004). 277,100–103.
- Liu, G, Zhu,L,.& Cao,W,.Liu,H,.He,Y.(2021). New Technique Integrating Hydrate-Based Gas Separation and Chemical Absorption for the Sweetening of Natural Gas with High H2 S and CO 2 Contents.AcsOMEGA.6,26180,26190.
- Bonab, P.J,. Esrafili, M.D,.& Ebrahimzadeh, A.R,. Sardroodi,J.J, Are choline chloride-based deep eutectic solvents better than methyl diethanolamine solvents for natural gas Sweetening? Theoretical insights from molecular dynamics simulations. International. Journal Elsevier. Journal of Molecular Liquids. (2021). 338,116716.
- Abdulrahman,R.K,. Sebastine, I.M. Natural gas sweetening process simulation and optimization: a case study of the Khurmala field in Iraqi Kurdistan. Petroleum and Mineral Resources. (2012).37-46.
- Kelley, B. T, Valencia, J.A, Northrop, P.S, Mart.C.J. Controlled Freeze ZoneTM for developing sour gas reserves. International. Journal Elsevier. Energy Procedia (2011). 4, 824–829.
- L.M. Corredor, M. M. Husein, B.B. Maini, Impact of PAM-Grafted Nanoparticles on the Performance of Hydrolyzed Polyacrylamide Solutions for Heavy Oil Recovery at Different Salinities, Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research. 58 (23) ( 2019). [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).