Submitted:
06 June 2023
Posted:
06 June 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
MSC: 05C90; 68R10
1. Introduction
2. Preliminaries
3. Main Results
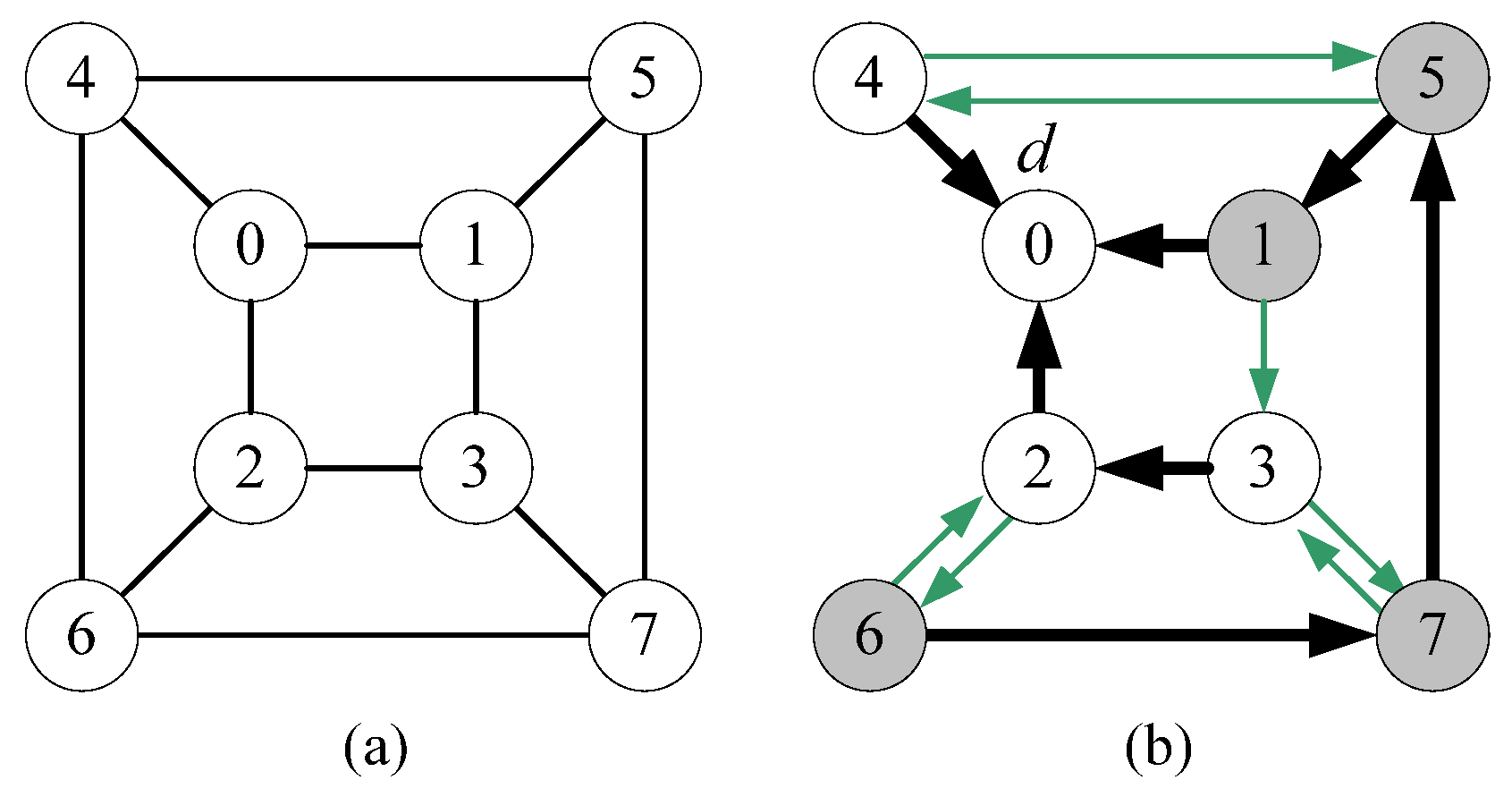
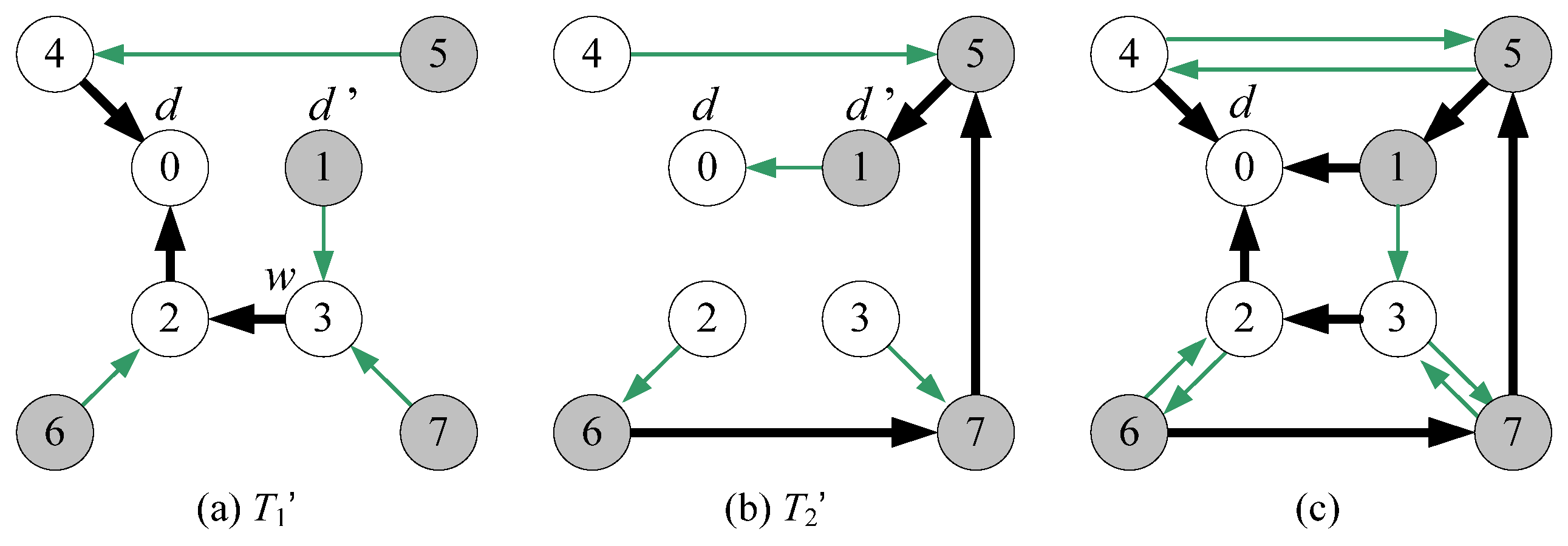
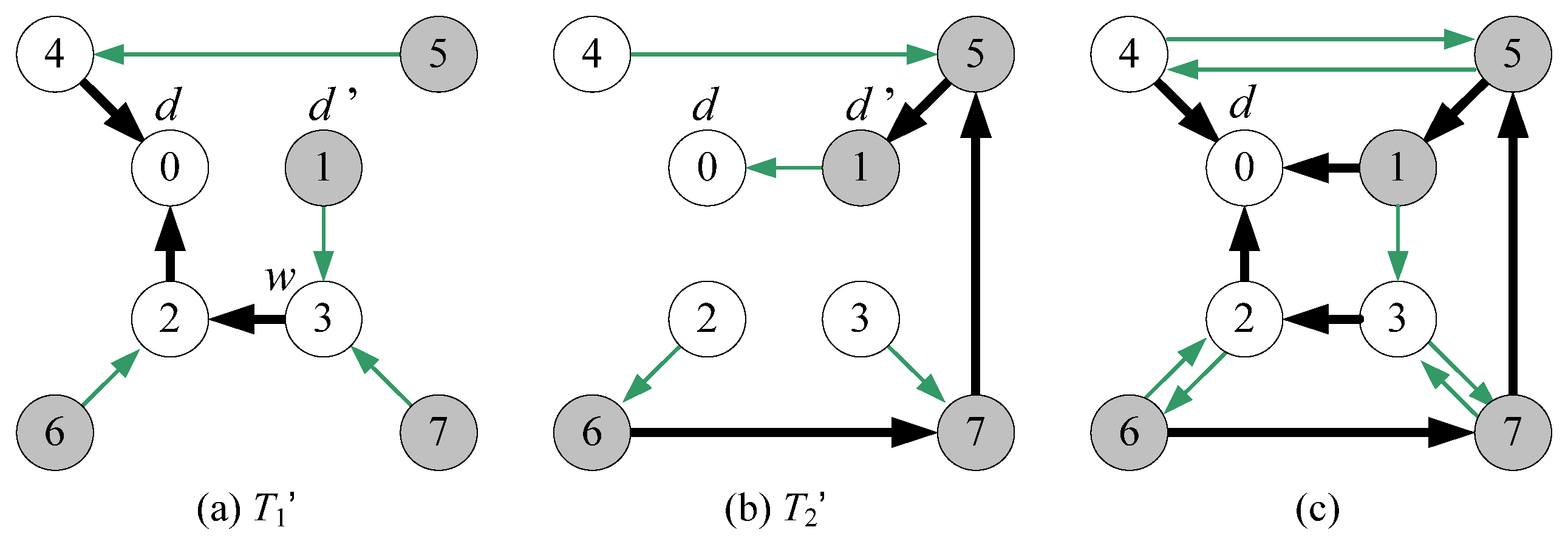
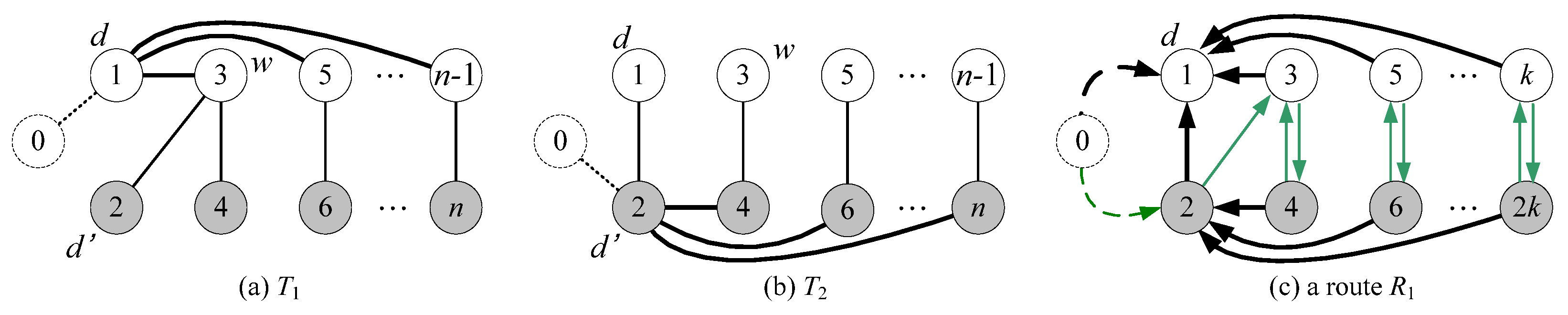
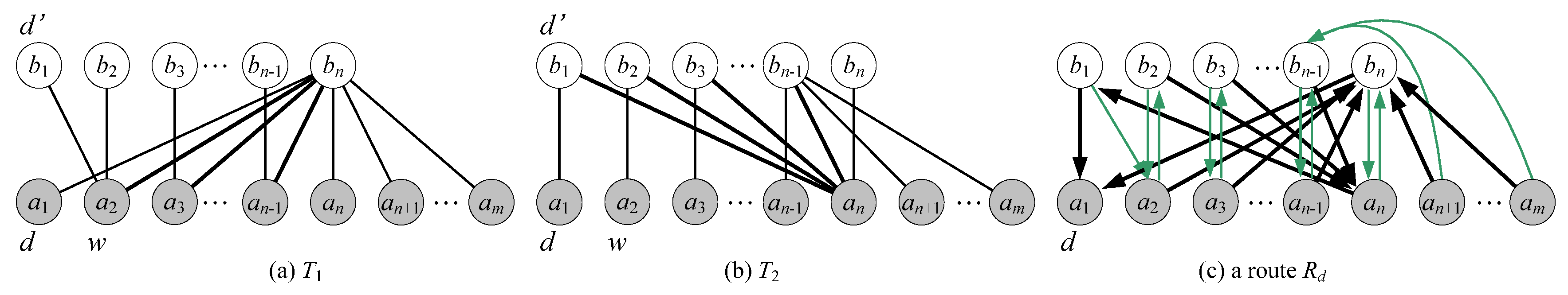
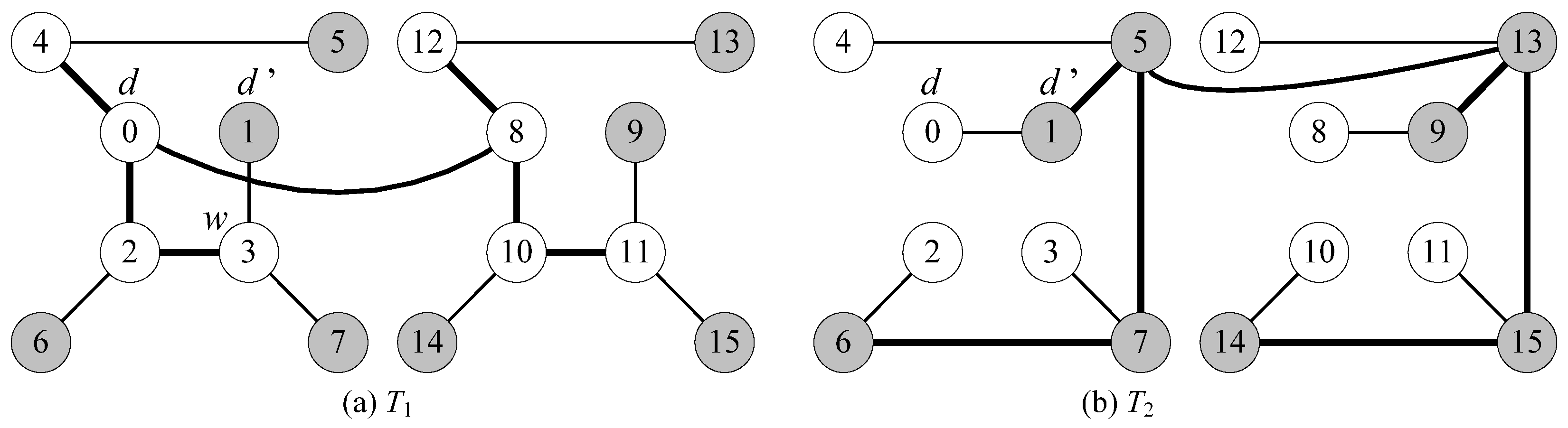
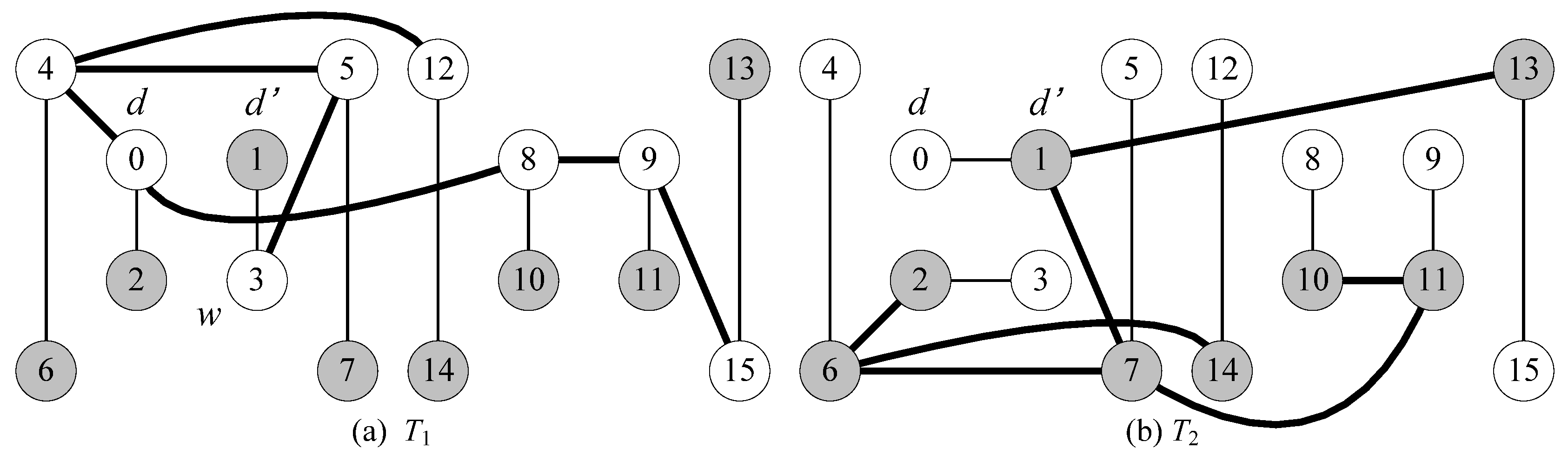
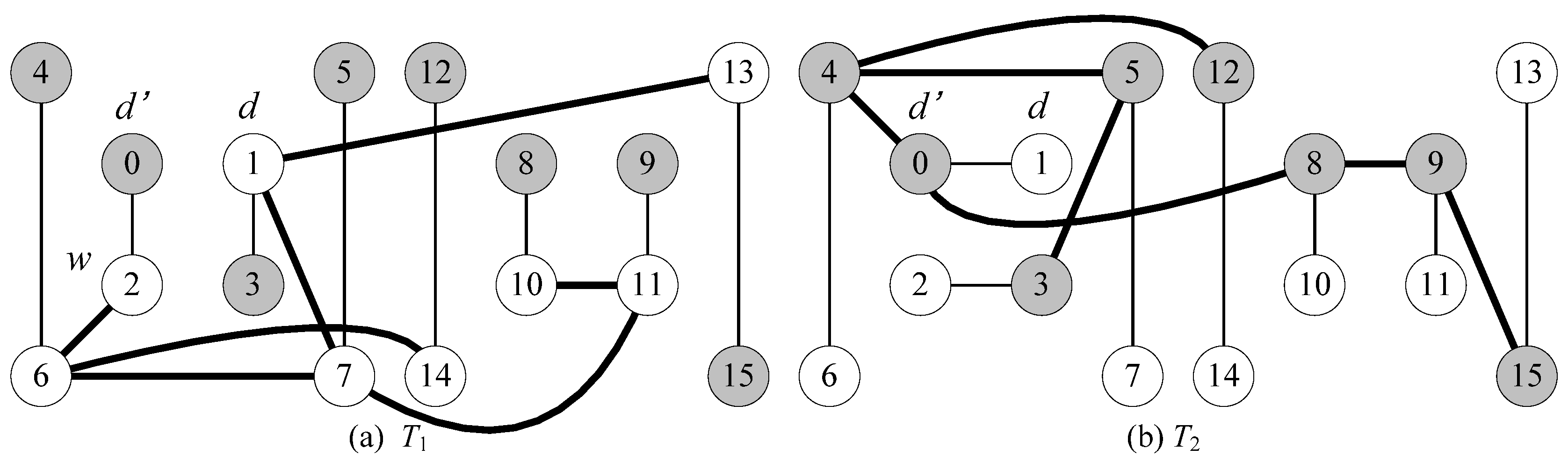
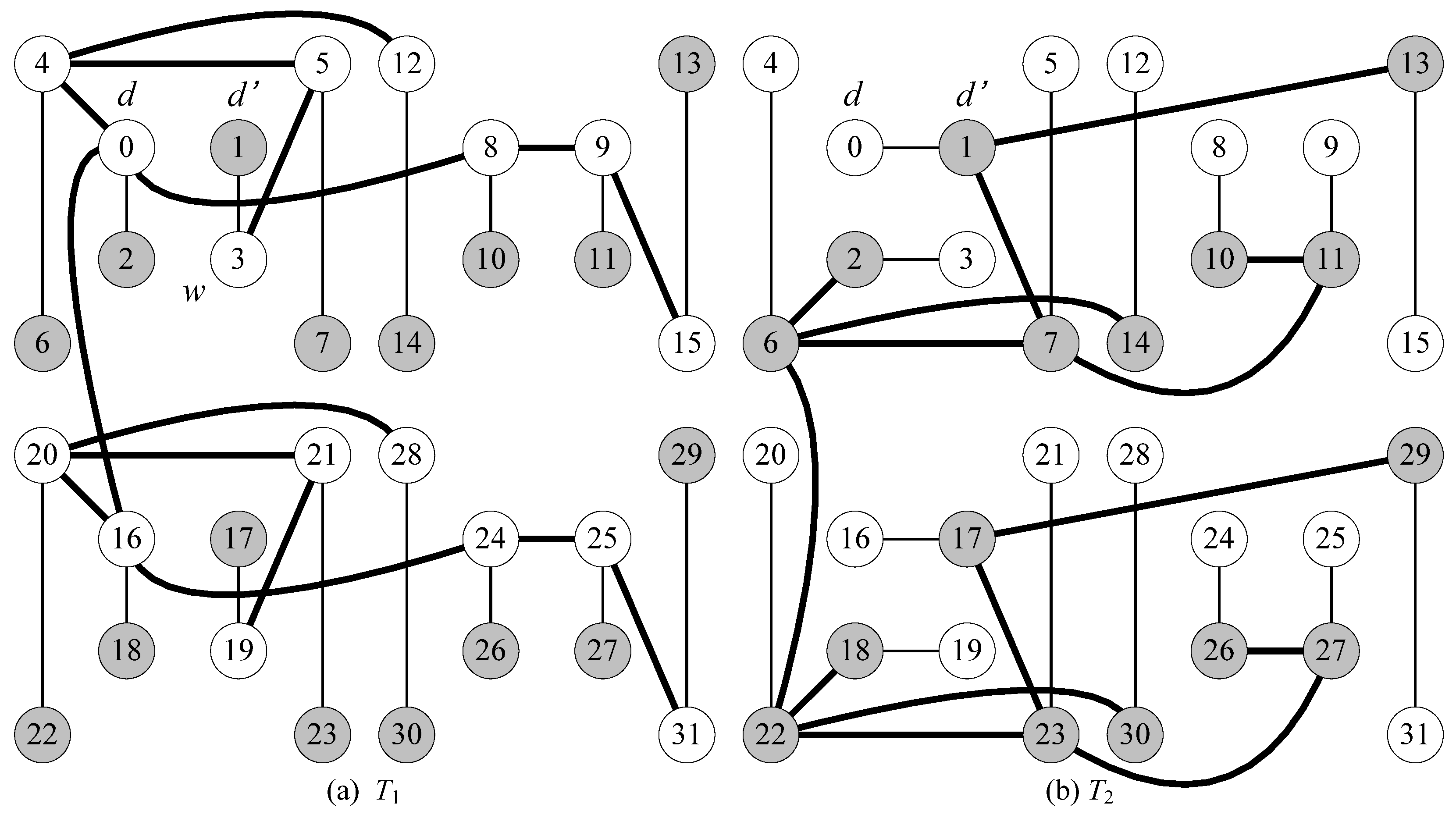
- Without loss of generality, we assume that node d is an inner vertex in T1. There exists an inner node d’ in T2 such that (d, d’) is a leaf edge in T2 and d’ is adjacent to another inner node w (≠ d) in T1.
| Algorithm 1: Configuring a protection routing via dual-PRTds |
| Input: Dual-PRTds T1, T2 of a network G where d is the destination node. |
| Output: A protection routing Rd = (V(G), PL, AL) where PL is the primary links set and AL is the alternative links set |
| Step 1 T1’ ← T1 which takes all links directed to root d; Step 2 T2’ ← T2 which takes all links directed to root d; Step 3 PL ← all stems in T1’ ∪ all stems in T2’ ∪ {<d’, d>}; Step 4 AL ← all leaf edges in T1’ ∪ all leaf edges in T2’ except <d’, d>; Step 5 If a vertex is a leaf in both T1 and T2, then add its T1 leaf edge to PL and add its T2 leaf edge to AL; Step 6 Return Rd = (V(G), PL, AL) |
3.1. Dual-PRTds on complete graphs
3.2. Dual-PRTds on Complete bipartite graphs
3.3. Dual-PRTds on hypercubes
3.4. Dual-PRTds on LTQs
- (1)
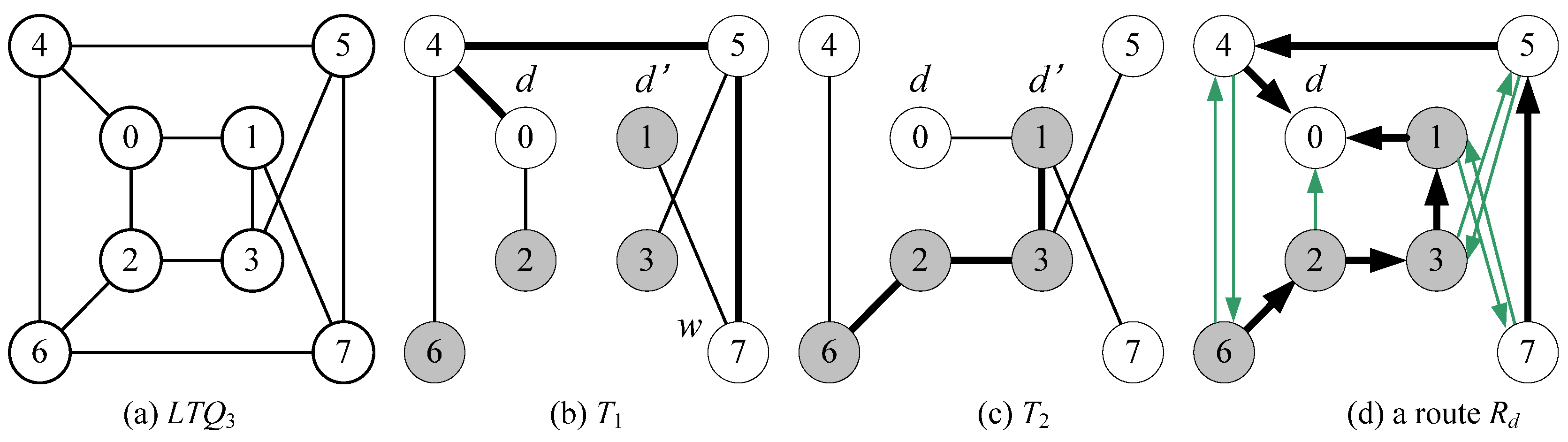
- LTQ1 is the complete graph on two vertices labeled by 0 and 1. LTQ2 is a graph consisting of four vertices with labels 00, 01, 10, 11 together with four edges (00, 01), (00, 10), (01, 11), and (10, 11).
- (2)
- For n ≥ 3, LTQn is composed of two subcubes LTQ0n−1 and LTQ1n−1 such that each vertex x = 0bn-1bn-2···b1 ∈ V(LTQ0n−1) is connected with the vertex 1(bn-1⊕b1)bn-2···b1 ∈ V(LTQ1n−1) by an edge where ⊕ represents exclusive or.
- Case 1. Destination node d is any even vertex in LTQn while n ≥ 5.
- Case 2. Destination node d is any even odd in LTQn while n ≥ 5.
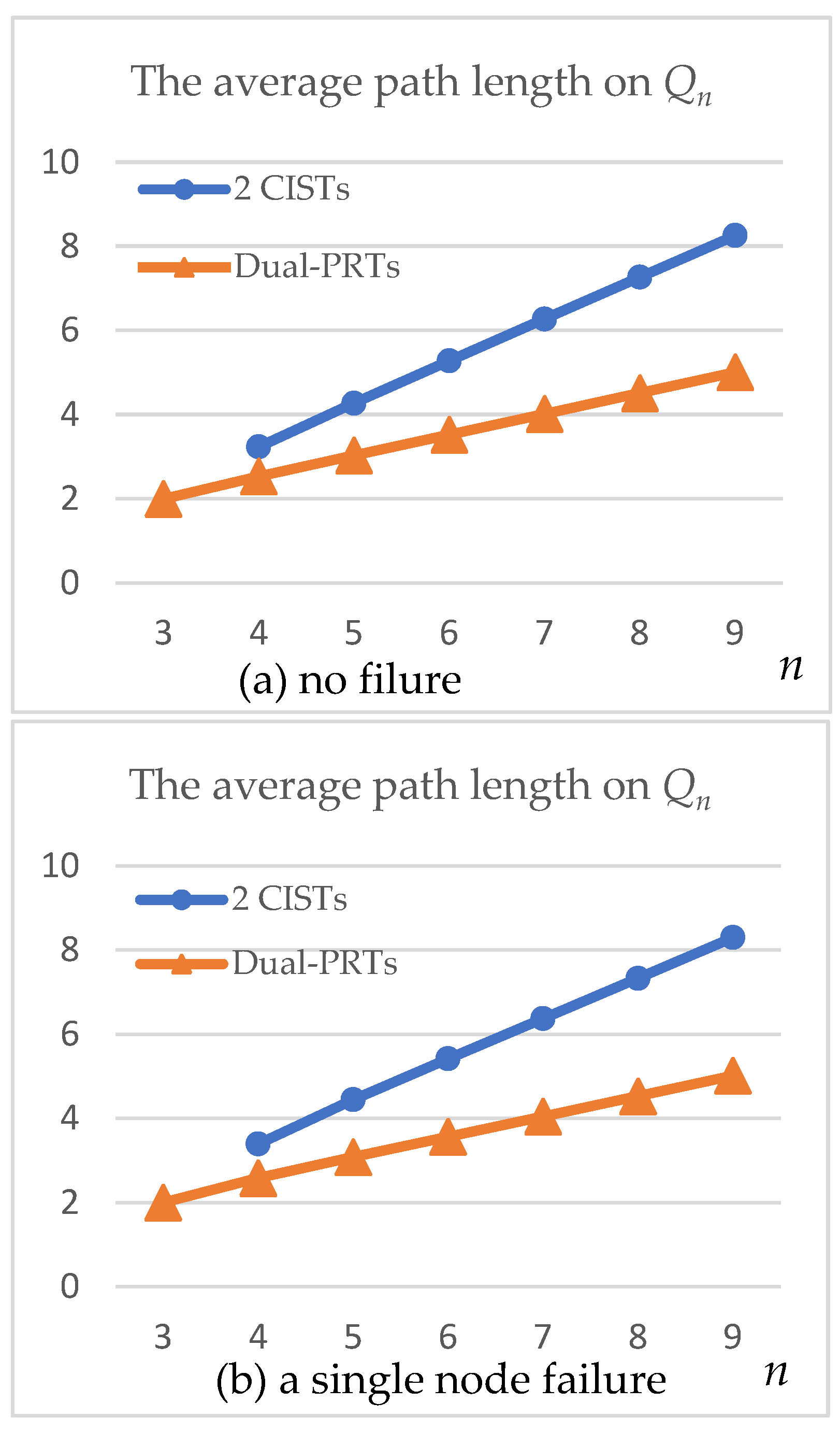
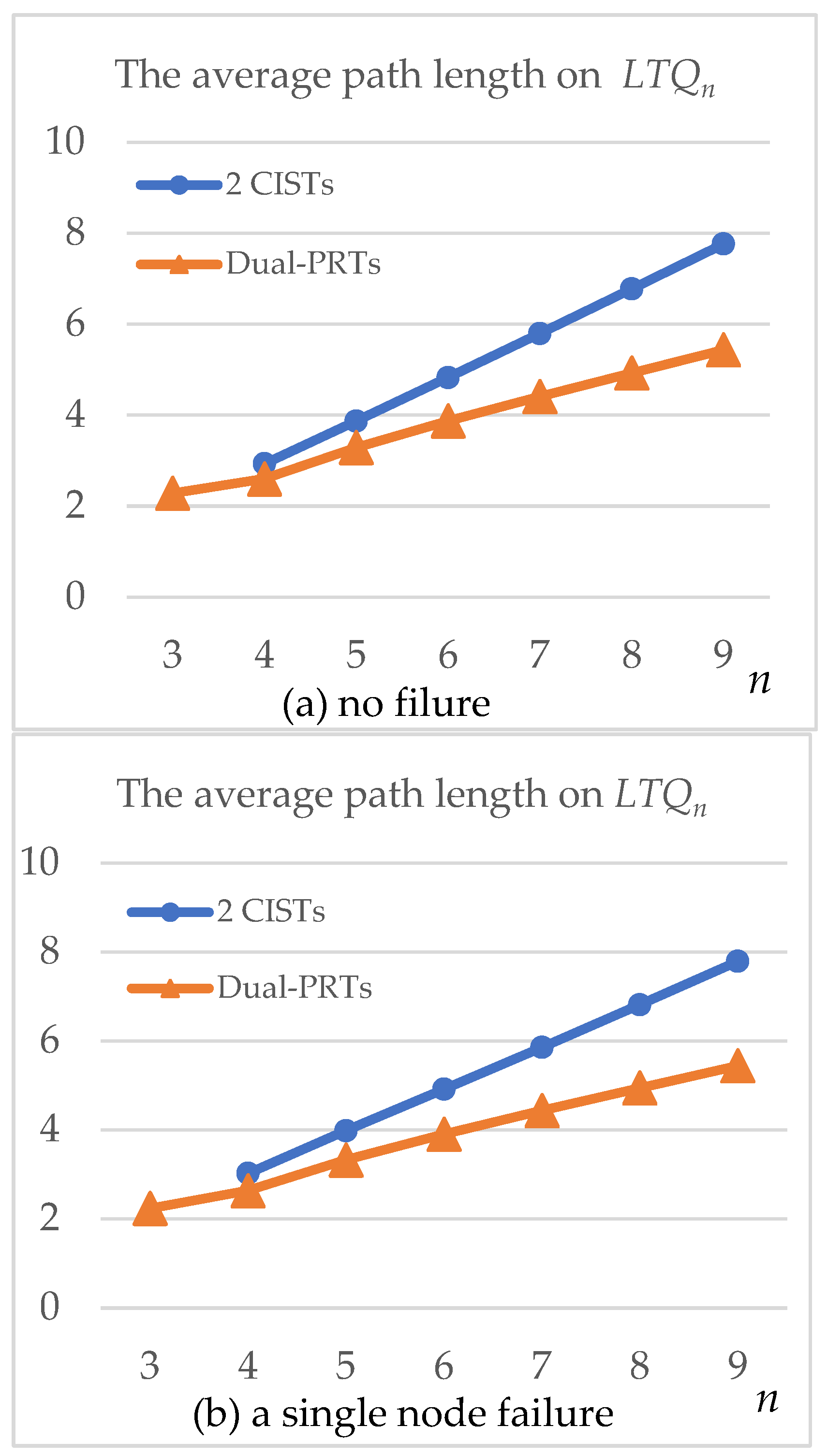
4. Performance Evaluation
5. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kwong, K.-W.; Gao, L.; Guérin, R.; Zhang, Z.-L. On the feasibility and efficacy of protection routing in IP networks. IEEE/ACM Trans. Netw. 2011, 19, 1543–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasunuma, T. Completely independent spanning trees in the underlying graph of a line digraph. Discrete Math. 2001, 234, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapolcai, J. Sufficient conditions for protection routing in IP networks. Optim. Lett. 2013, 7, 723–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasunuma, T. Completely independent spanning trees in maximal planar graphs. In: Goos, G., Hartmanis, J., van Leeuwen, J., Kuˇcera, L. (eds.) WG 2002. LNCS, Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, 2002, 2573, pp. 235–245.
- Hasunuma, T.; Morisaka, C. Completely independent spanning trees in torus networks. Networks 2012, 60, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, B.; Wang, D.; Fan, J. Constructing completely independent spanning trees in crossed cubes. Discrete Appl. Math. 2017, 219, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darties, B.; Gastineau, N.; Togni, O. Completely independent spanning trees in some regular graphs. Discrete Appl. Math. 2017, 217, 163–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pai, K.-J.; Tang, S.-M.; Chang, J.-M.; Yang, J.-S. Completely independent spanning trees on complete graphs, complete bipartite graphs and complete tripartite graphs. Adv Intelligent Syst. Appl. vol 1, Smart Innovation, Systems and Technologies, Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg 2013, 20, pp. 107–113.
- Pai, K.-J.; Yang, J.-S.; Yao, S.-C.; Tang, S.-M.; Chang, J.-M. Completely independent spanning trees on some interconnection networks. IEICE Trans. Inform. Syst. 2014, E97–D(9), 2514–2517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pai, K.-J.; Chang, J.-M. Constructing two completely independent spanning trees in hypercube-variant networks. Theor. Comput. Sci. 2016, 652, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pai, K.-J.; Chang, J.-M. Improving the diameters of completely independent spanning trees in locally twisted cubes. Inf. Process. Lett. 2019, 141, 22–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pai, K.-J.; Chang, R.-S.; Chang, J.-M. A protection routing with secure mechanism in Möbius cubes. J. Parallel Distrib. Comput. 2020, 140, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pai, K.-J.; Chang, R.-S.; Wu, R.-Y.; Chang, J.-M. Three completely independent spanning trees of crossed cubes with application to secure-protection routing. Inf. Sci. 2020, 541, 516–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.-W.; Hao, R.-X.; Chang, J.-M. Constructing dual-CISTs of DCell data center networks. Appl. Math. Comput. 2019, 362, 124546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.-Y.; Lin, W.; Guo, W.; Chang, J.-M. A secure data transmission scheme based on multi-protection routing in datacenter networks. J. Parallel Distributed Comput. 2022, 167, 222–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.-Y.; Lin, W.; Liu, X.; Lin, C.-K.; Pai, K.-J.; Chang, J.-M. Completely Independent Spanning Trees on BCCC Data Center Networks With an Application to Fault-Tolerant Routing. IEEE Trans. Parallel Distributed Syst. 2022, 33, 1939–1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.-Y.; Lin, W.; Liu, X.; Chang, J.-M.; Jia, X. Transmission Failure Analysis of Multi-Protection Routing in Data Center Networks With Heterogeneous Edge-Core Servers. IEEE/ACM Trans. Netw. 2022, 30, 1689–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pai, K.-J.; Chang, J.-M. Dual-CISTs: configuring a protection routing on some Cayley networks. IEEE/ACM Trans. Netw. 2019, 27, 1112–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pai, K.-J.; Chang, R.-S.; Chang, J.-M. Constructing Dual-CISTs of Pancake Graphs and Performance Assessment of Protection Routing on Some Cayley Networks. J. Supercomput. 2021, 77, 990–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pai, K.-J.; Yang, J.-S.; Chen, G.-Y.; Chang, J.-M. Configuring Protection Routing via Completely Independent Spanning Trees in Dense Gaussian On-Chip Networks. IEEE Trans. Netw. Sci. Eng. 2022, 9, 932–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leighton, F.T. Introduction to Parallel Algorithms and Architectures: Arrays, Trees, Hypercubes, Morgan Kaufmann, San Mateo, CA, 1992.
- Yang, X.; Evans, D.J.; Megson, G.M. The locally twisted cubes. Int. J. Comput. Math. 2005, 82, 401–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, X.; Ma, J.; Yang, D.-W. Symmetric property and reliability of locally twisted cubes. Discrete Appl. Math. 2021, 288, 257–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simulation results for evaluating the performance of the protection routings on Qn and LTQn. Available online: http://210.240.238.53/dprt1 (accessed on 1st June 2023).
| Component failure | Second Next-Hop |
| <1, 0> | SNH(1) = 3 |
| <2, 0> | SNH(2) = 6 |
| <4, 0> | SNH(4) = 5 |
| <3, 2> or 2 <5, 1> or 1 <6, 7> or 7 <7, 5> or 5 |
SNH(3) = 7 SNH(5) = 4 SNH(6) = 2 SNH(7) = 3 |
| no failure | a single node failure | |||
| n | 2 CISTs | Dual-PRTds | 2 CISTs | Dual-PRTds |
| 3 | 2.000 | 2.000 (* 16.69%) | ||
| 4 | 3.233 | 2.533 | 3.394 (* 15.94%) | 2.580 (* 10.98%) |
| 5 | 4.272 | 3.031 | 4.445 (* 10.92%) | 3.081 (* 6.77%) |
| 6 | 5.278 | 3.523 | 5.417 (* 6.91%) | 3.562 (* 4.08%) |
| 7 | 6.271 | 4.016 | 6.369 (* 4.17%) | 4.042 (* 2.40%) |
| 8 | 7.264 | 4.510 | 7.327 (* 2.46%) | 4.527 (* 1.37%) |
| 9 | 8.257 | 5.008 | 8.296 (* 1.42%) | 5.018 (* 0.77%) |
| no failure | a single node failure | |||
| n | 2 CISTs | Dual-PRTds | 2 CISTs | Dual-PRTds |
| 3 | 2.285 | 2.237 (* 21.41%) | ||
| 4 | 2.932 | 2.600 | 3.027 (* 13.83%) | 2.637 (* 11.44%) |
| 5 | 3.869 | 3.290 | 3.983 (* 9.53%) | 3.325 (* 7.64%) |
| 6 | 4.826 | 3.870 | 4.914 (* 6.16%) | 3.902 (* 4.59%) |
| 7 | 5.794 | 4.411 | 5.853 (* 3.78%) | 4.434 (* 2.67%) |
| 8 | 6.774 | 4.926 | 6.811 (* 2.26%) | 4.941 (* 1.55%) |
| 9 | 7.766 | 5.432 | 7.788 (* 1.34%) | 5.442 (* 0.85%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





