Submitted:
29 May 2023
Posted:
02 June 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
1.1. Motivation
1.2. Innovation and Contribution
- Evaluation of the application of the DOA in a photovoltaic MPPT as a function of conversion time and failure rate.
- Calculate the best swarm size to achieve the shortest time of convergence maintaining zero failure rate.
- Evaluating the performance of the MPPT with different initialization strategies.
- Using a novel strategy for avoiding the stagnation of search agents in LPs.
1.3. Paper Outlines
2. PV Array Modelling
3. Dandelion Optimization Algorithm
3.1. Rising Stage
3.2. Mutation Sowing
3.3. Selection Stage
3.4. Improved DOA for MPPT of PV Systems
4. Simulation Work
4.1. Optimal Design of the Boost Converter
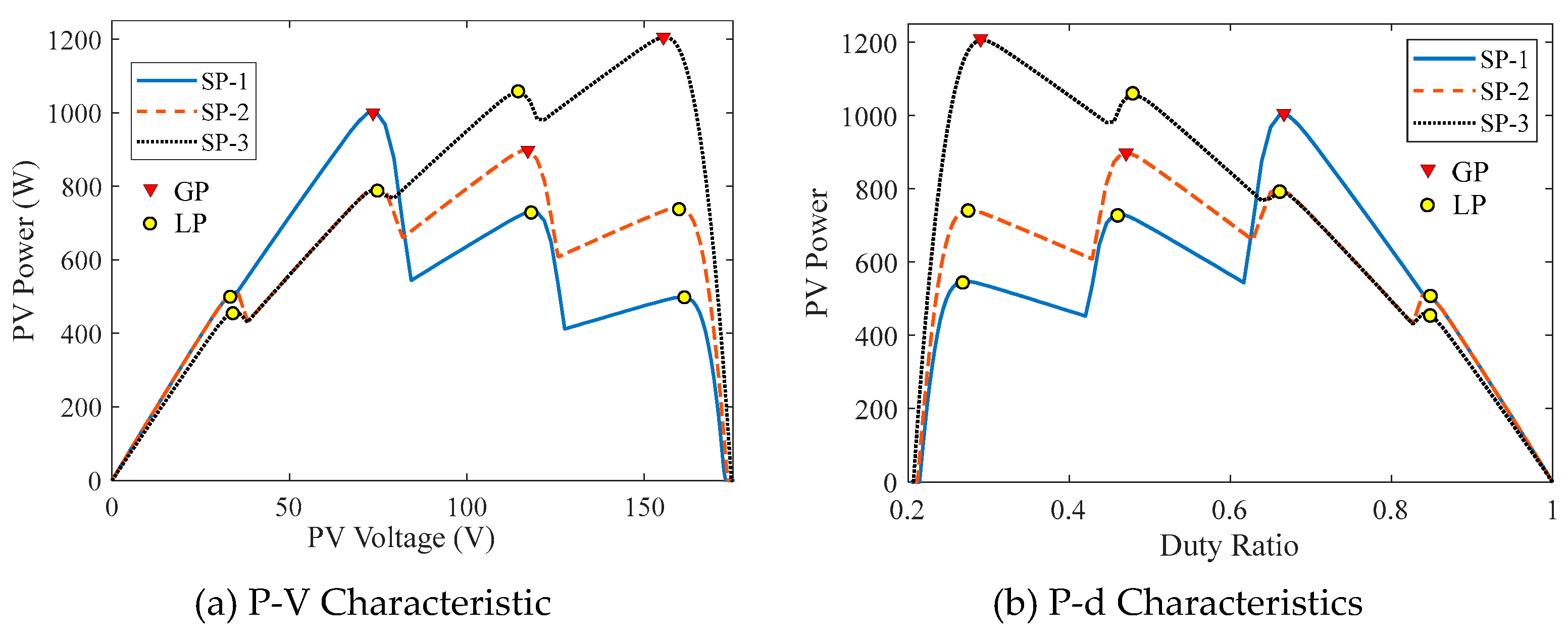
4.2. Optimal Initialization
4.3. Optimal Swarm Size
4.4. Real-Time Simulation Results
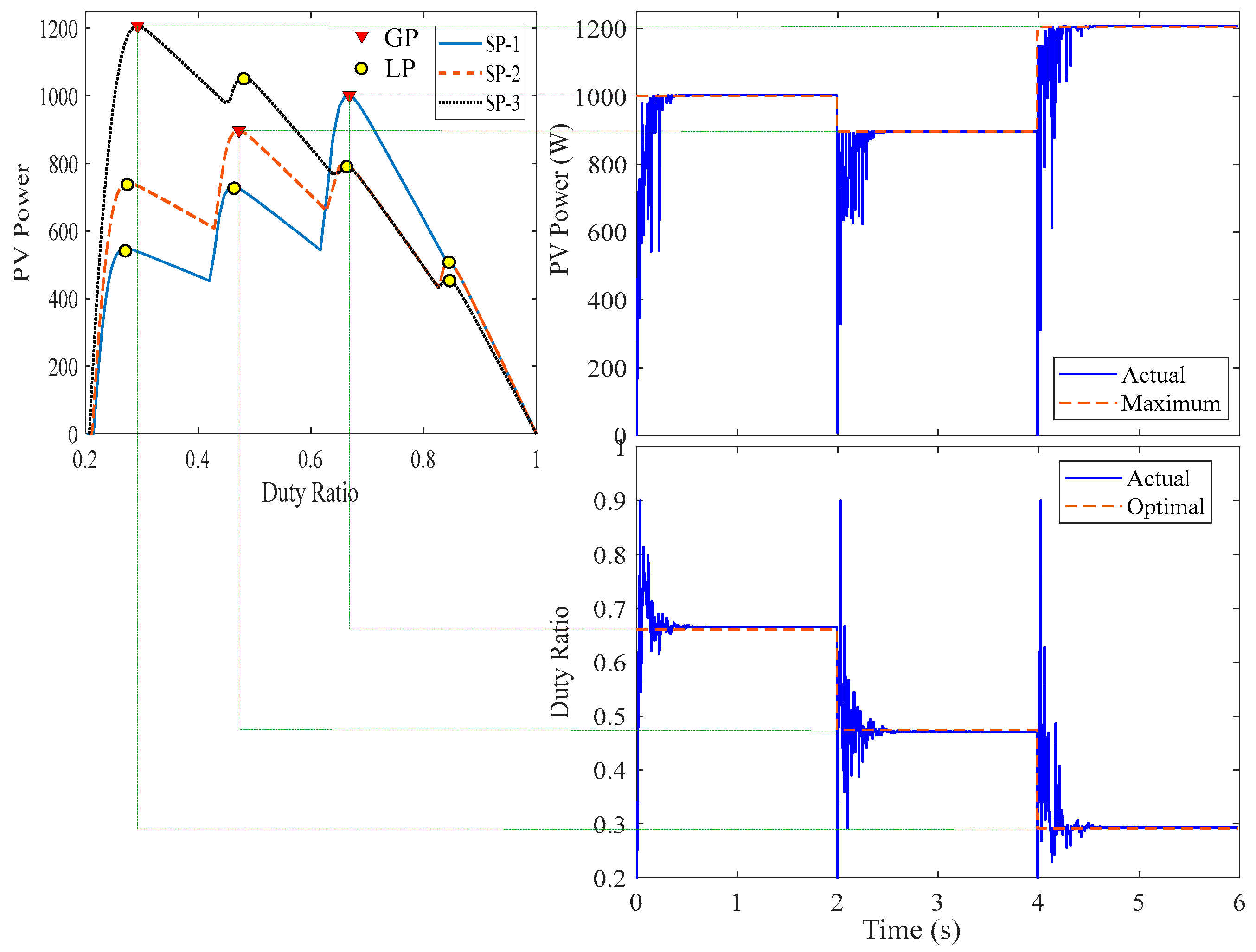
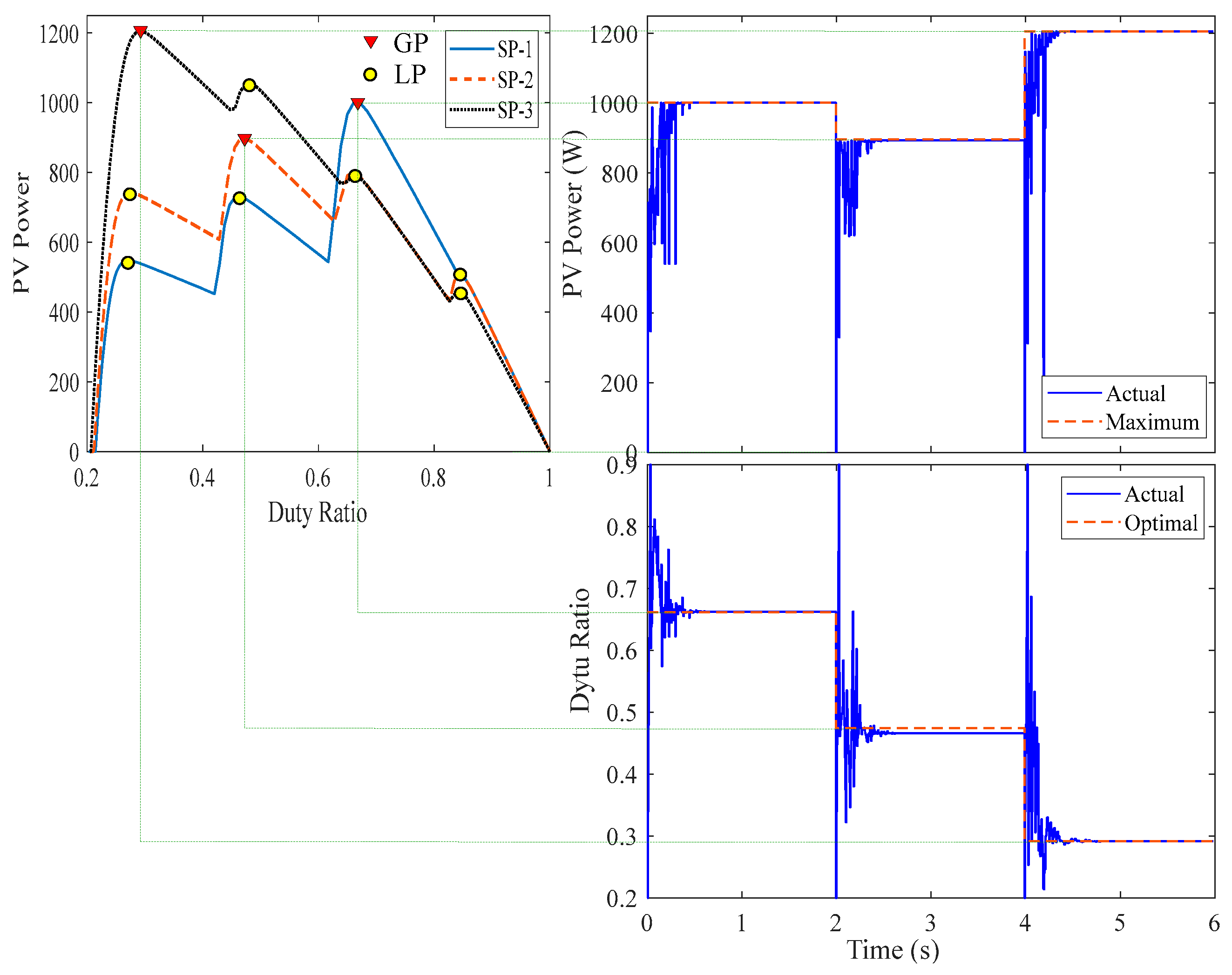
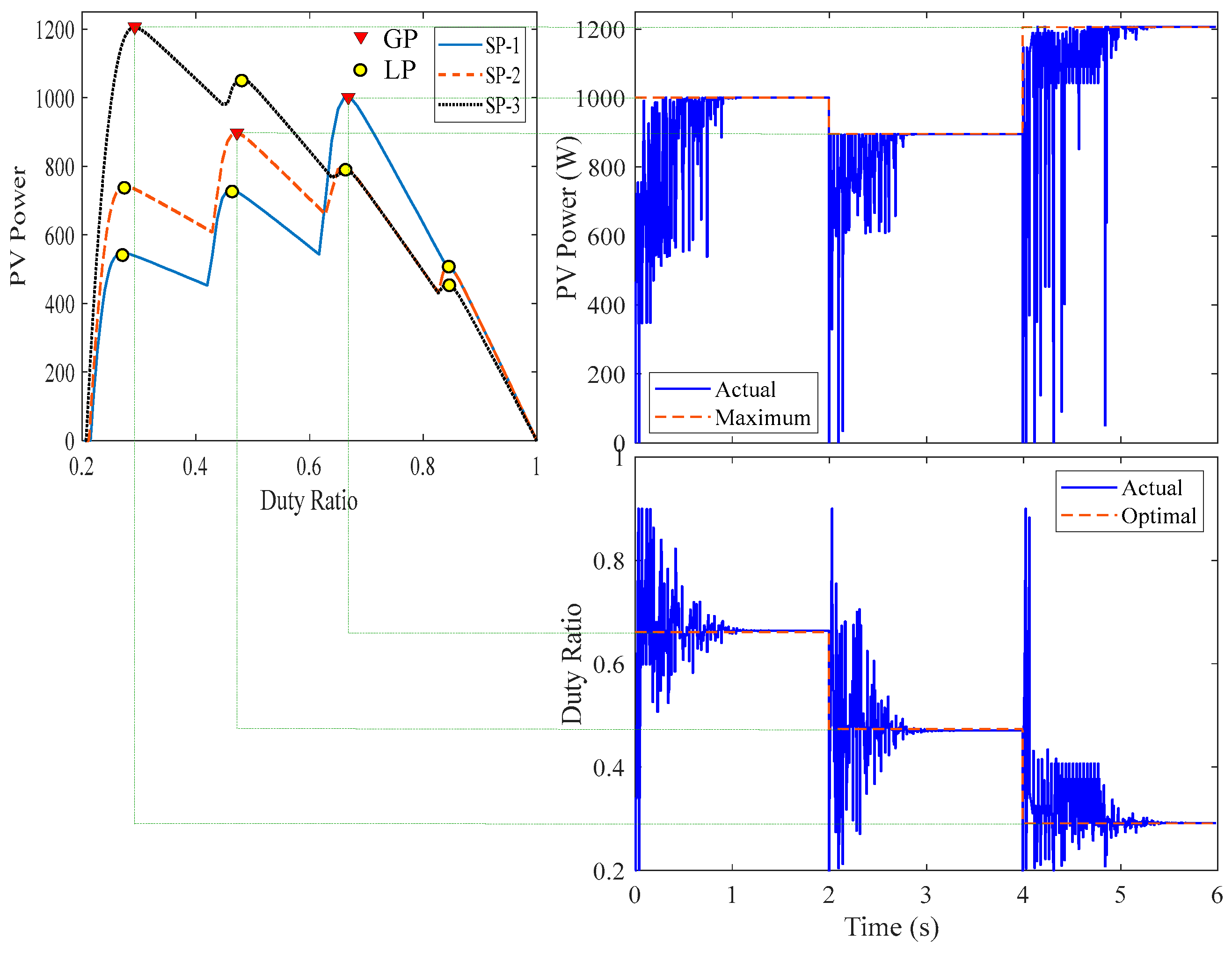
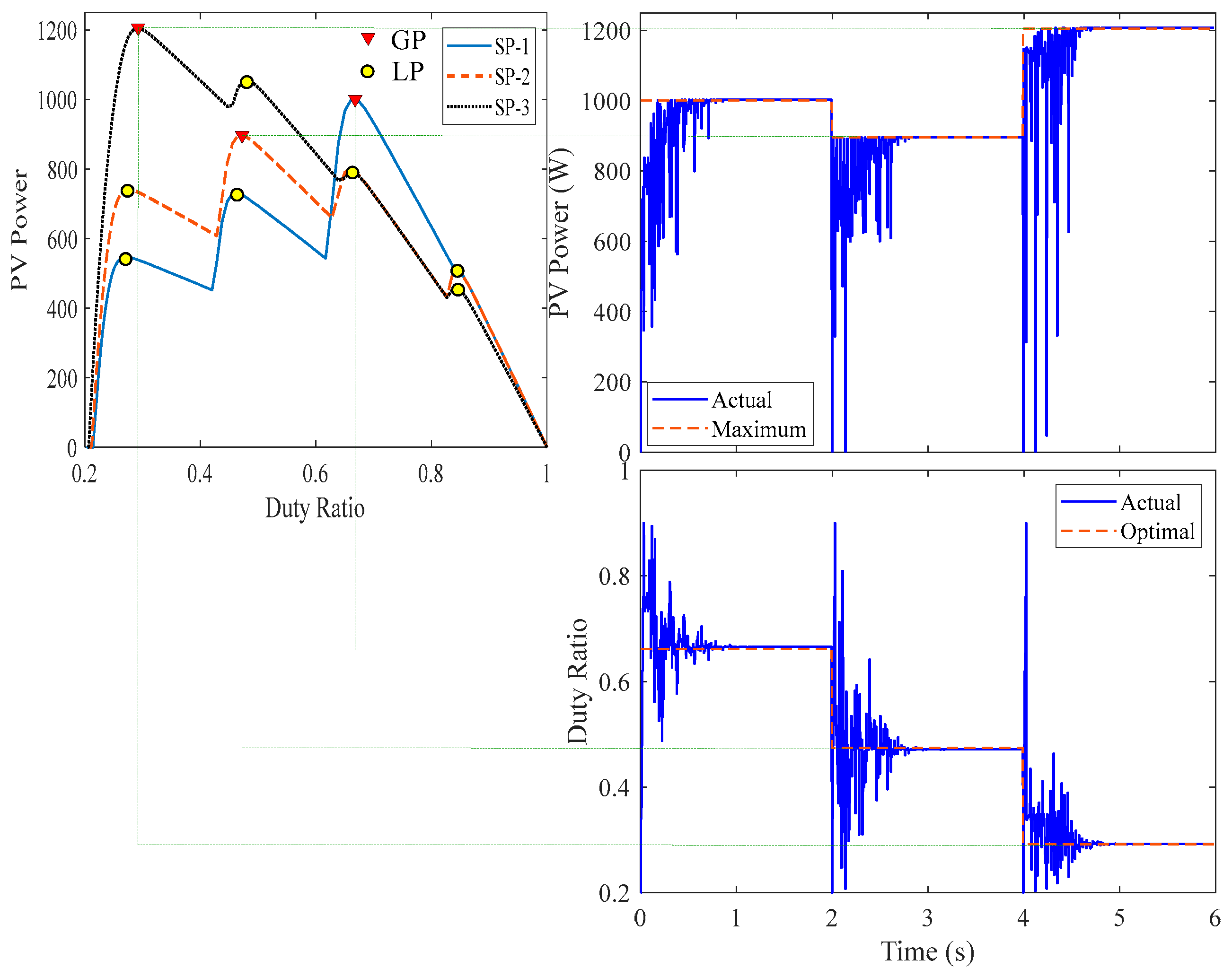
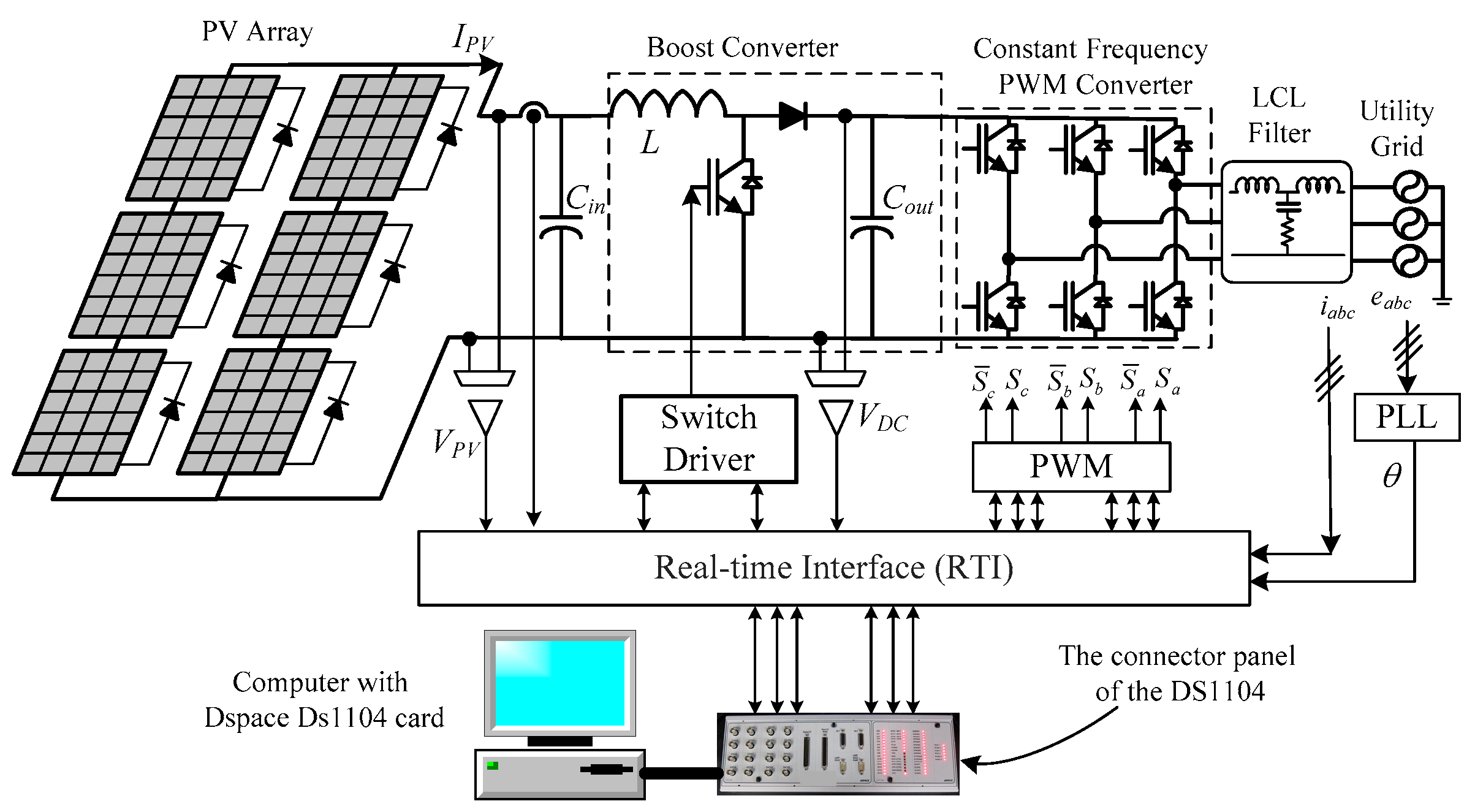
5. Experimental Work
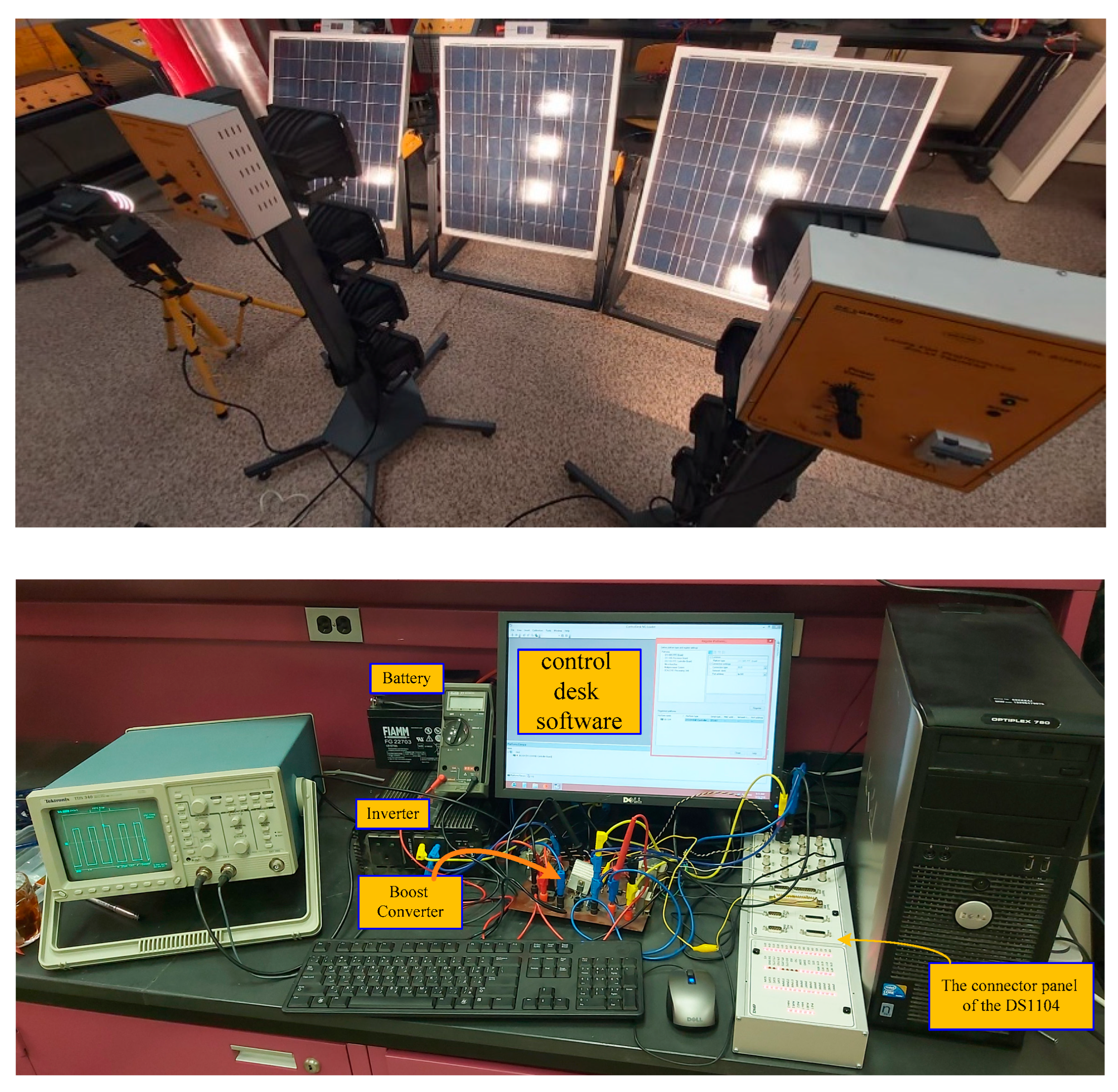

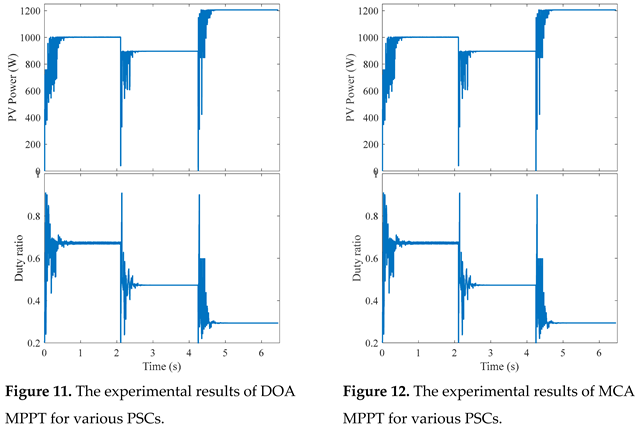
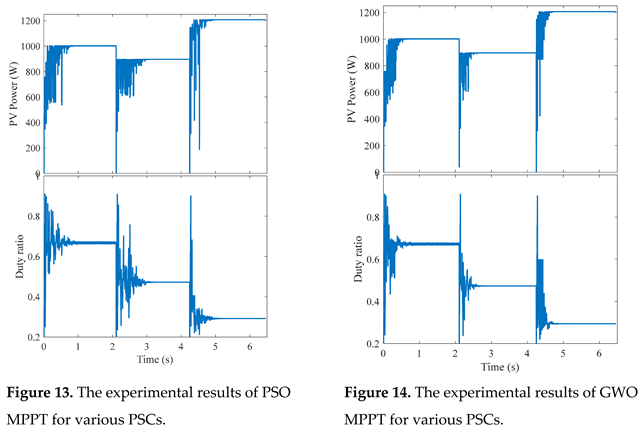
6. Conclusions
References
- K. Hansen, C. Breyer and H. Lund, "Status and perspectives on 100% renewable energy systems," Energy, 175, pp.471-480., 2019. [CrossRef]
- "Renewable Energy," PowerWeb, a Forecast International Inc, [Online]. Available: http://www.fi-powerweb.com/Renewable-Energy.html.
- A. Eltamaly, M. Alotaibi, A. Alolah and M. Ahmed, "A Novel Demand Response Strategy for Sizing of Hybrid Energy System with Smart Grid Concepts," IEEE Access, 2021.
- M. Alotaibi and A. Eltamaly, "A smart strategy for sizing of hybrid renewable energy system to supply remote loads in Saudi Arabia," Energies, 14(21), p.7069., 2021. [CrossRef]
- A. Eltamaly, "Performance of MPPT techniques of photovoltaic systems under normal and partial shading conditions," In Advances in renewable energies and power technologies (pp. 115-161). Elsevier., 2018.
- H. Rezk and A. M. Eltamaly, "A comprehensive comparison of different MPPT techniques for photovoltaic systems," Solar energy, 112, pp.1-11., 2015. [CrossRef]
- A. Eltamaly, "February. Modeling of fuzzy logic controller for photovoltaic maximum power point tracker," In Solar Future 2010 Conference, Istanbul, Turkey., 2010.
- S. Messalti, A. Harrag and A. Loukriz, "A new variable step size neural networks MPPT controller: Review, simulation and hardware implementation," Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 68, pp.221-233., 2017.
- A. Eltamaly, "A novel particle swarm optimization optimal control parameter determination strategy for maximum power point trackers of partially shaded photovoltaic systems," Engineering Optimization, 54(4), pp.634-650., 2022. [CrossRef]
- A. Eltamaly, M. Al-Saud and A. Abokhalil, "A novel bat algorithm strategy for maximum power point tracker of photovoltaic energy systems under dynamic partial shading," IEEE Access, vol. 8, pp. 10048-10060, 2020. [CrossRef]
- S. Mohanty, B. Subudhi and P. Ray, "A new MPPT design using grey wolf optimization technique for photovoltaic system under partial shading conditions," IEEE Transactions on Sustainable Energy, 7(1), pp.181-188., 2015. [CrossRef]
- A. Eltamaly, "A novel musical chairs algorithm applied for MPPT of PV systems," Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 146, p.111135., 2021. [CrossRef]
- K. Ishaque and Z. Salam, "A deterministic particle swarm optimization maximum power point tracker for photovoltaic system under partial shading condition," IEEE transactions on industrial electronics, 60(8), pp.3195-3206., 2012. [CrossRef]
- T. Imtiaz, B. Khan and N. Khanam, "Fast and improved PSO (FIPSO)-based deterministic and adaptive MPPT technique under partial shading conditions," IET Renewable Power Generation, 14(16), pp.3164-3171., 2020. [CrossRef]
- M. Merchaoui, A. Sakly and M. Mimouni, "March. Improved fast particle swarm optimization based PV MPPT," In 2018 9th international renewable energy congress (IREC) (pp. 1-7). IEEE., 2018.
- A. Jordehi, "Time varying acceleration coefficients particle swarm optimisation (TVACPSO): A new optimisation algorithm for estimating parameters of PV cells and modules," Energy Conversion and Management, 129, pp.262-274., 2016. [CrossRef]
- Y. Shi and R. Eberhart, "A modified particle swarm optimizer," In 1998 IEEE international conference on evolutionary computation proceedings, IEEE world congress on computational intelligence (Cat. No. 98TH8360) (pp. 69-73). IEEE., 1998.
- B. Jiao, Z. Lian and X. Gu, "A dynamic inertia weight particle swarm optimization algorithm," Chaos, Solitons & Fractals, 37(3), pp.698-705., 2008. [CrossRef]
- A. M. Eltamaly, H. M. Farh and A. G. Abokhalil, "A novel PSO strategy for improving dynamic change partial shading photovoltaic maximum power point tracker," Energy Sources, Part A: Recovery, Utilization, and Environmental Effects, pp. 1-15, 2020. [CrossRef]
- A. Eltamaly, M. Al-Saud, A. Abokhalil and H. Farh, "Photovoltaic maximum power point tracking under dynamic partial shading changes by novel adaptive particle swarm optimization strategy," Transactions of the Institute of Measurement and Control 42.1 (2020): 104-115., 2020. [CrossRef]
- A. Chatterjee and P. Siarry, "Nonlinear inertia weight variation for dynamic adaptation in particle swarm optimization," Computers & operations research, 33(3), pp.859-871., 2006. [CrossRef]
- M. Abdulkadir, A. H. M. Yatim and S. T. Yusuf, "An improved PSO-based MPPT control strategy for photovoltaic systems," International Journal of Photoenergy 2014 (2014)., 2014. [CrossRef]
- K. Sundareswaran, S. Peddapati and S. Palani, "MPPT of PV systems under partial shaded conditions through a colony of flashing fireflies," IEEE transactions on energy conversion 29, no. 2 (2014): 463-472., 2014. [CrossRef]
- A. Eltamaly, "Optimal control parameters for bat algorithm in maximum power point tracker of photovoltaic energy systems," International Transactions on Electrical Energy Systems, 31(4), p.e12839., 2021. [CrossRef]
- Y. Liu, S. Huang, J. Huang and W. Liang, "A particle swarm optimization-based maximum power point tracking algorithm for PV systems operating under partially shaded conditions," IEEE transactions on energy conversion, 27(4), pp.1027-1035., 2012. [CrossRef]
- H. Chaieb and A. Sakly, "Comparison between P&O and PSO methods based MPPT algorithm for photovoltaic systems," In 2015 16th International Conference on Sciences and Techniques of Automatic Control and Computer Engineering (STA) (pp. 694-6, 2015.
- K. Sundareswaran and S. Palani, "Application of a combined particle swarm optimization and perturb and observe method for MPPT in PV systems under partial shading conditions," Renewable Energy, 75, pp.308-317., 2015. [CrossRef]
- A. Eltamaly, "An Improved Cuckoo Search Algorithm for Maximum Power Point Tracking of Photovoltaic Systems under Partial Shading Conditions," Energies, vol. 14, no. 4, p. 953, 2021. [CrossRef]
- M. da Rocha, L. Sampaio and S. da Silva, "Comparative analysis of MPPT algorithms based on Bat algorithm for PV systems under partial shading condition," Sustainable Energy Technologies and Assessments, 2020.
- S. Mohanty, B. Subudhi and R. PK., "A grey wolf-assisted perturb & observe MPPT algorithm for a PV system," IEEE Trans Energy Convers. 2017;32(1):340-347., 2017.
- C.C. Ahmed, M. Cherkaoui and M. Mokhlis, "PSO-SMC Controller Based GMPPT Technique for Photovoltaic Panel Under Partial Shading Effect," International Journal of Intelligent Engineering and Systems 13.2 (2020): 307-316., 2020. [CrossRef]
- N. Kamal, A. Azar, G. Elbasuony, K. Almustafa and Almakhles, "PSO-based adaptive perturb and observe MPPT technique for photovoltaic systems." International Conference on Advanced Intelligent Systems and Informatics," Springer, Cham, 2019., 2019.
- A. M. Eltamaly and H. M. Farh., "Dynamic global maximum power point tracking of the PV systems under variant partial shading using hybrid GWO-FLC," Solar Energy 177 (2019): 306-316., 2019. [CrossRef]
- F. Davoodkhani, S. Arabi Nowdeh, A. Abdelaziz, S. Mansoori, S. Nasri and M. Alijani, "A new hybrid method based on gray wolf optimizer-crow search algorithm for maximum power point tracking of photovoltaic energy system," Modern Maximum Power Point Tracking Techniques for Photovoltaic Energy Systems. Springer,, 2020.
- M. Seyedmahmoudian, R. Rahmani, S. O. A. Mekhilef, A. Stojcevski, T. Soon and A. Ghandhari, "Simulation and hardware implementation of new maximum power point tracking technique for partially shaded PV system using hybrid DEPSO method," IEEE transactions on sustainable energy 6.3 (2015): 850-862. [CrossRef]
- A. Eltamaly, "Photovoltaic Maximum Power Point Trackers: An Overview," Advanced Technologies for Solar Photovoltaics Energy Systems, pp.117-200., 2021.
- A. M. S. Furtado, F. Bradaschia, M. C. Cavalcanti and L. R. Limongi, "A Reduced Voltage Range Global Maximum Power Point Tracking Algorithm for Photovoltaic Systems Under Partial Shading Conditions," IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, vol. 65,, 2018. [CrossRef]
- S. Xu, Y. Gao, G. Zhou and G. Mao, "A Global Maximum Power Point Tracking Algorithm for Photovoltaic Systems Under Partially Shaded Conditions Using Modified Maximum Power Trapezium Method," IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, pp. 1-1, 2020. [CrossRef]
- M. Kermadi, Z. Salam, J. Ahmed and E. M. Berkouk, "A High-Performance Global Maximum Power Point Tracker of PV System for Rapidly Changing Partial Shading Condition," IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, pp. 1-1, 2020., 2020. [CrossRef]
- M. Boztepe, F. Guinjoan, G. Velasco-Quesada, S. Silvestre, A. Chouder and E. Karatepe, "Global MPPT Scheme for Photovoltaic String Inverters Based on Restricted Voltage Window Search Algorithm," IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, vol. 61, no. 7. [CrossRef]
- M. Kermadi, Z. Salam, J. Ahmed and E. M. Berkouk, "An Effective Hybrid Maximum Power Point Tracker of Photovoltaic Arrays for Complex Partial Shading Conditions," IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, vol. 66, no. 9, pp. 6990-7000, 2019., 2019. [CrossRef]
- M. Kermadi, Z. Salam, A. Eltamaly, J. Ahmed, S. Mekhilef, C. Larbes and E. Berkouk, "Recent Developments of MPPT Techniques for PV Systems under Partial Shading Conditions: A Critical Review and Performance Evaluation," IET Renewable Power Generation, 2020. [CrossRef]
- A. M. Eltamaly, M. S. Al-Saud and A. G. Abokhalil, "A novel scanning bat algorithm strategy for maximum power point tracker of partially shaded photovoltaic energy systems," Ain Shams Engineering Journal (2020)., 2020. [CrossRef]
- J. Ahmed and Z. Salam, "A Maximum Power Point Tracking (MPPT) for PV system using Cuckoo Search with partial shading capability," Applied Energy 119 (2014): 118-130., 2014. [CrossRef]
- A.M. Eltamaly, H. M. Farh and M. S. A. Saud, "Impact of PSO reinitialization on the accuracy of dynamic global maximum power detection of variant partially shaded PV systems," Sustainability, vol. 11, no. 7, p. 2091, 2019. [CrossRef]
- A.M. Eltamaly, M. S. Al-Saud and A. G. Abokhalil, "A novel scanning bat algorithm strategy for maximum power point tracker of partially shaded photovoltaic energy systems," Ain Shams Engineering Journal, 2020. [CrossRef]
- A.M. Eltamaly, M. S. Al-Saud and A. G. Abo-Khalil, "Performance Improvement of PV Systems’ Maximum Power Point Tracker Based on a Scanning PSO Particle Strategy," Sustainability, vol. 12, no. 3, p. 1185, 2020. [CrossRef]
- R. Celikel, M. Yilmaz and A. Gundogdu, "A voltage scanning-based MPPT method for PV power systems under complex partial shading conditions," Renewable Energy, 184, pp.361-373., 2022. [CrossRef]
- X. Li, S. Han, L. Zhao, C. Gong and X. Liu, "New dandelion algorithm optimizes extreme learning machine for biomedical classification problems," Computational intelligence and neuroscience, 2017. [CrossRef]
- A.M. Eltamaly, "Performance of smart maximum power point tracker under partial shading conditions of photovoltaic systems," Journal of Renewable and Sustainable Energy, vol. 7, no. 4, p. 043141, 2015. [CrossRef]
- D. Cotfas, P. Cotfas and S. Kaplanis, "Methods to determine the dc parameters of solar cells: a critical review," Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews 28 (2013): 588-596., 2013. [CrossRef]
- V. Khanna, B. Das, D. Bisht and P. Singh, "A three diode model for industrial solar cells and estimation of solar cell parameters using PSO algorithm," Renewable Energy, 78, pp.105-113., 2015. [CrossRef]
- A. Eltamaly, "Musical chairs algorithm for parameters estimation of PV cells," Solar Energy, 241, pp.601-620., 2022. [CrossRef]
- C. Gong, S. Han, X. Li, L. Zhao and X. Liu, "A new dandelion algorithm and optimization for extreme learning machine," Journal of ExpErimEntal & thEorEtical artificial intElligEncE, 30(1), pp.39-52., 2018. [CrossRef]
- X. Liu and X. Qin, "A probability-based core dandelion guided dandelion algorithm and application to traffic flow prediction," Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, 96, p.103922., 2020. [CrossRef]
- R. Abbassi, S. Saidi, A. Abbassi, H. Jerbi, M. Kchaou and B. Alhasnawi, "Accurate Key Parameters Estimation of PEMFCs’ Models Based on Dandelion Optimization Algorithm," Mathematics, 11(6), p.1298., 2023. [CrossRef]
- S. Zhao, T. Zhang, S. Ma and M. Chen, "Dandelion Optimizer: A nature-inspired metaheuristic algorithm for engineering applications," Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, 114, p.105075., 2022. [CrossRef]
- M. Alharbi, M. Ragab, K. AboRas, H. Kotb, M. Dashtdar, M. Shouran and E. Elgamli, "Innovative AVR-LFC design for a multi-area power system using hybrid fractional-order PI and PIDD2 controllers based on dandelion optimizer," Mathematics, 11(6), p.1387., 2023. [CrossRef]
- M. Ali, A. Soliman and A. Adel, "Optimization of Reactive Power Dispatch Considering DG Units Uncertainty By Dandelion Optimizer Algorithm," International Journal of Renewable Energy Research (IJRER), 12(4), pp.1805-1818., 2022. [CrossRef]
- H. Zhu, G. Liu, M. Zhou, Y. Xie, A. Abusorrah and Q. Kang, "Optimizing weighted extreme learning machines for imbalanced classification and application to credit card fraud detection," Neurocomputing, 407, pp.50-62., 2020. [CrossRef]
- A. Zamuda, J. Brest and E. Mezura-Montes, "Structured population size reduction differential evolution with multiple mutation strategies on CEC 2013 real parameter optimization," In 2013 IEEE congress on evolutionary computation (pp. 1925-1931). IEEE., 2013. [CrossRef]
- A.M. Eltamaly and A. Hamdy, "Novel musical chairs," IEEE, vol. 3, no. 5, pp. 20-27, 2020.
- J. Brest and M. Sepesy Maučec, "Population size reduction for the differential evolution algorithm," Applied Intelligence, 29, pp.228-247., 2008. [CrossRef]
- N. Noman and H. Iba, "Accelerating differential evolution using an adaptive local search," IEEE Transactions on evolutionary Computation, 12(1), pp.107-125., 2008. [CrossRef]
- F. Neri and V. Tirronen, "Scale factor local search in differential evolution," Memetic Computing, 1, pp.153-171., 2009. [CrossRef]
- F. Neri, G. Iacca and E. Mininno, "Disturbed exploitation compact differential evolution for limited memory optimization problems," Information Sciences, 181(12), pp.2469-2487., 2011. [CrossRef]
- F. Caraffini, G. Iacca, F. Neri, L. Picinali and E. Mininno, "A CMA-ES super-fit scheme for the re-sampled inheritance search," In 2013 IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation (pp. 1123-1130). IEEE., 2013.
- A. Eltamaly, "Performance of MPPT techniques of photovoltaic systems under normal and partial shading conditions," In Advances in renewable energies and power technologies (pp. 115-161). Elsevier., 2018.
- A. M. Eltamaly and H. M. Farh, "Dynamic global maximum power point tracking of the PV systems under variant partial shading using hybrid GWO-FLC," Solar Energy 177 (2019): 306-316., 2019. [CrossRef]
- M. Abdulkadir, A. Yatim and S. Yusuf, "An improved PSO-based MPPT control strategy for photovoltaic systems," International Journal of Photoenergy, 2014. [CrossRef]
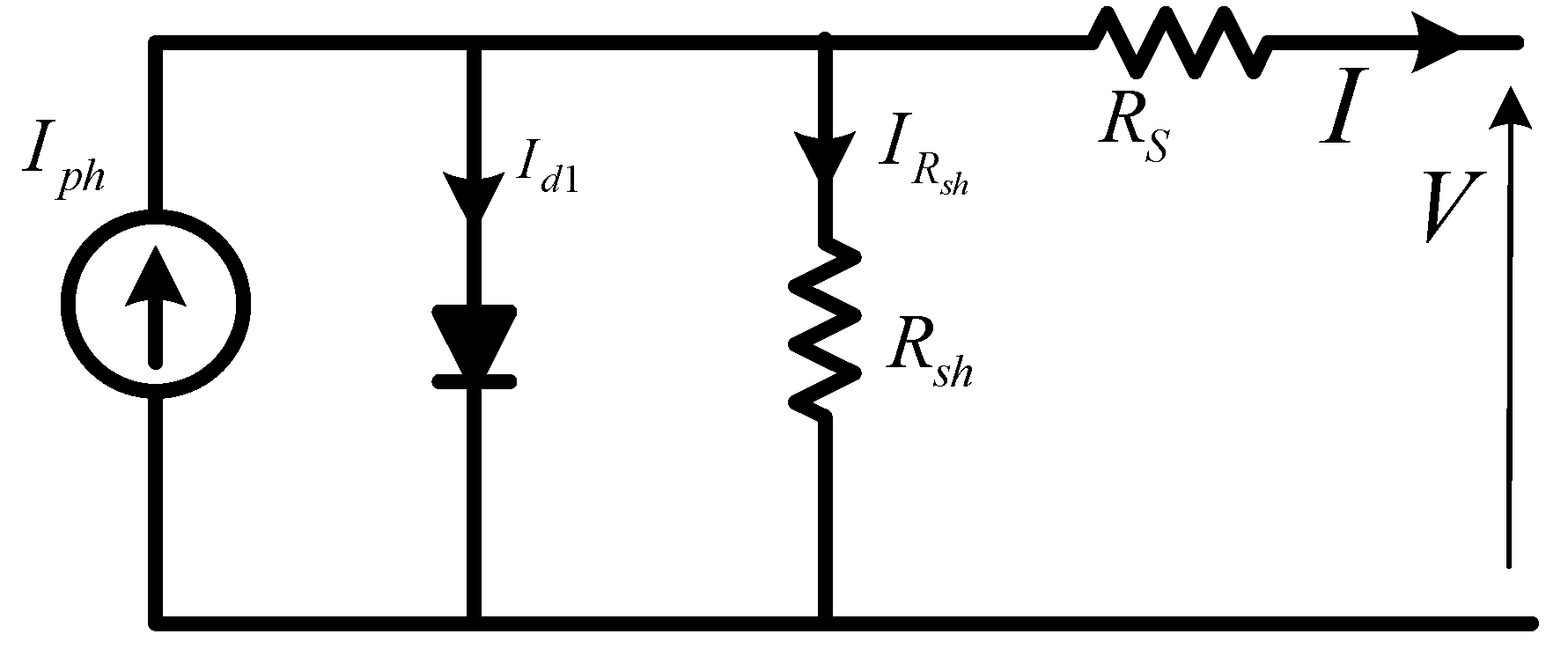
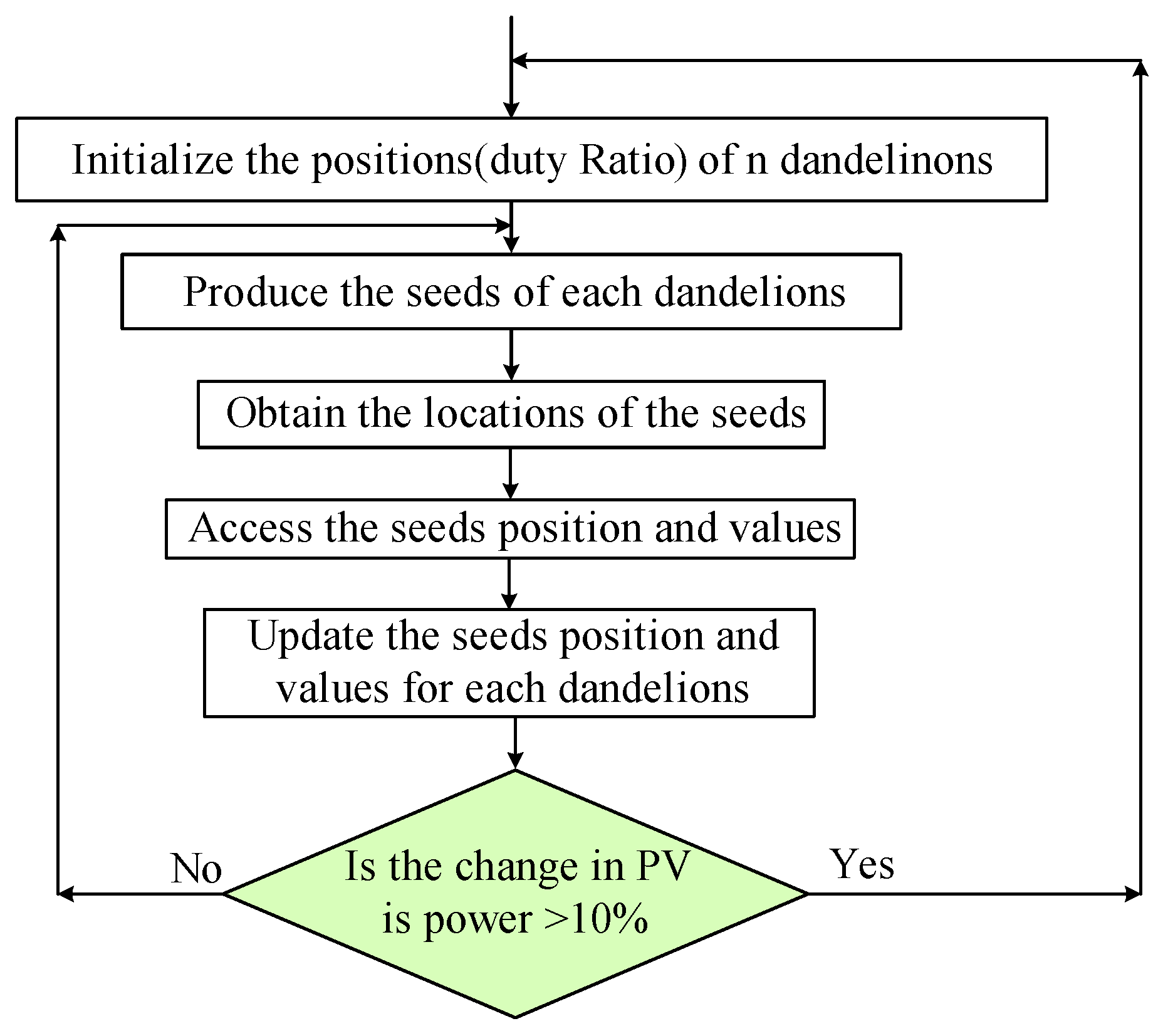

| Name | Solar Irradiances (W/m2) | GP Parameters | |||||
| G1 | G2 | G3 | G4 | d | V (V) | P (W) | |
| SP-1 | 1000 | 900 | 400 | 200 | 0.6613 | 74.51140 | 1001.4 |
| SP-2 | 1000 | 700 | 500 | 300 | 0.4740 | 115.7296 | 897.32 |
| SP-3 | 900 | 700 | 600 | 500 | 0.2912 | 155.9261 | 1205.8 |
| Initialization Strategy | Convergence Time (s) | Failure Rate (%) |
| Random Duty Ratio | 0.49 | 2 |
| Equal Distance | 0.41 | 0 |
| Anticipated Position of Peaks | 0.40 | 0 |
| Swarm size | Convergence Time (s) | Failure Rate (%) | ||||||
| DOA | MCA | PSO | GWO | DOA | MCA | PSO | GWO | |
| 3 | 0.35 | 0.38 | 0.68 | 0.49 | 6.5 | 8.1 | 11.7 | 8.8 |
| 4 | 0.39 | 0.40 | 0.82 | 0.61 | 3.3 | 4.5 | 5.8 | 4.5 |
| 5 | 0.40 | 0.41 | 1.07 | 0.78 | 1.1 | 2.1 | 3.5 | 2.2 |
| 6 | 0.41 | 0.43 | 1.25 | 0.92 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 7 | 0.48 | 0.51 | 1.36 | 1.06 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 8 | 0.57 | 0.57 | 1.44 | 1.15 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 9 | 0.62 | 0.61 | 1.52 | 1.21 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 10 | 0.65 | 0.62 | 1.58 | 1.29 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





