Submitted:
31 May 2023
Posted:
01 June 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
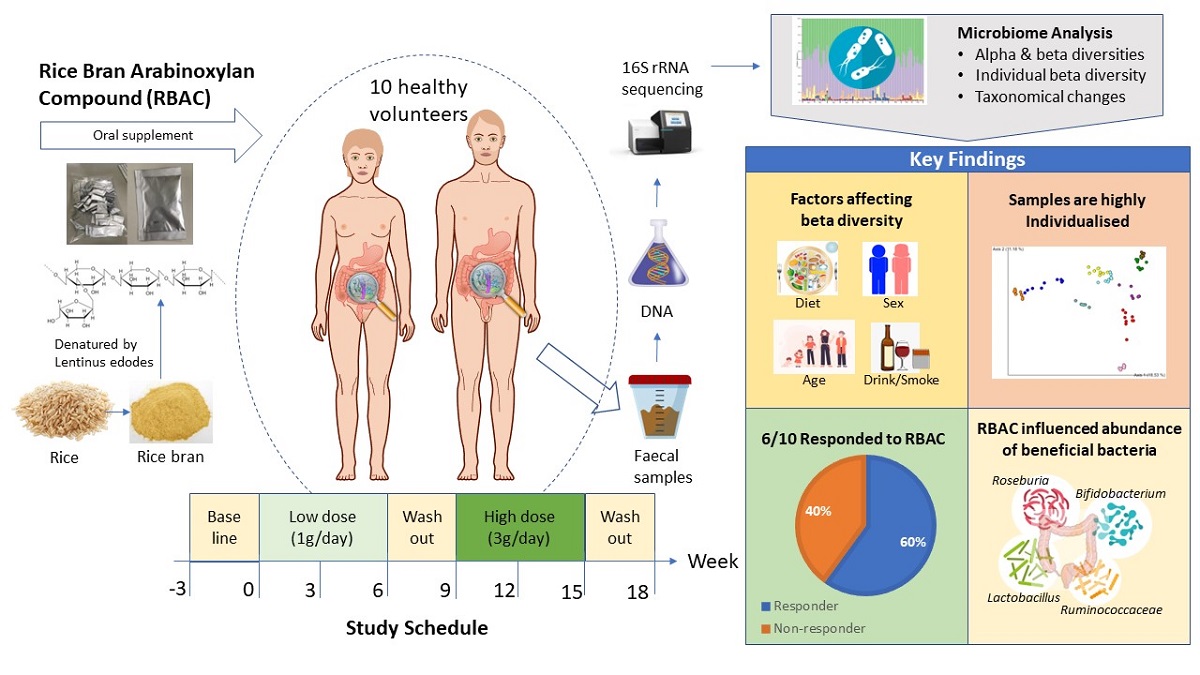
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Participant characteristics and dietary intake
2.2. DNA quality
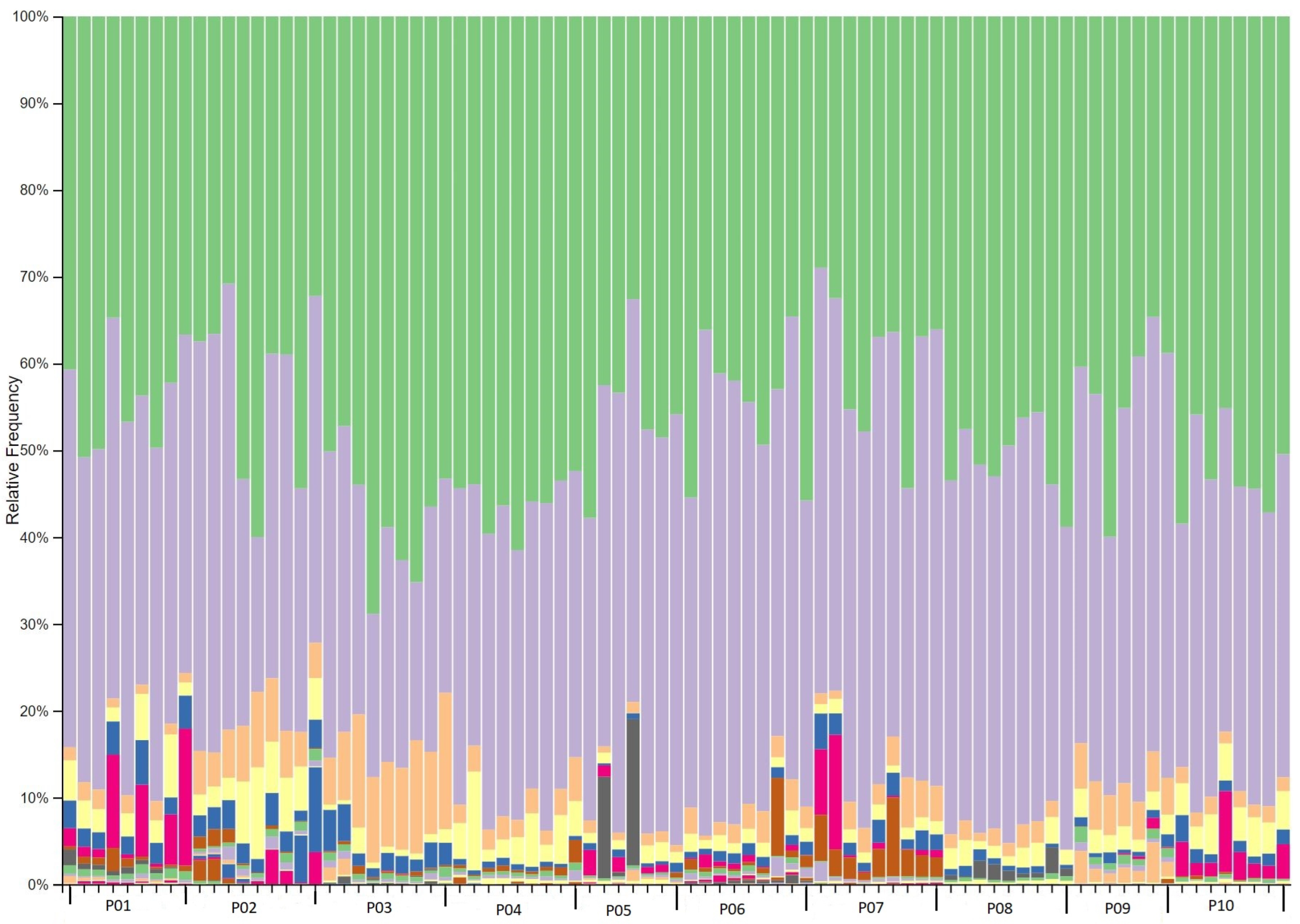
2.3. Phylogenetic taxonomy of the gut microbiota
2.4. Associations of alpha diversity of gut microbiota with explanatory factors
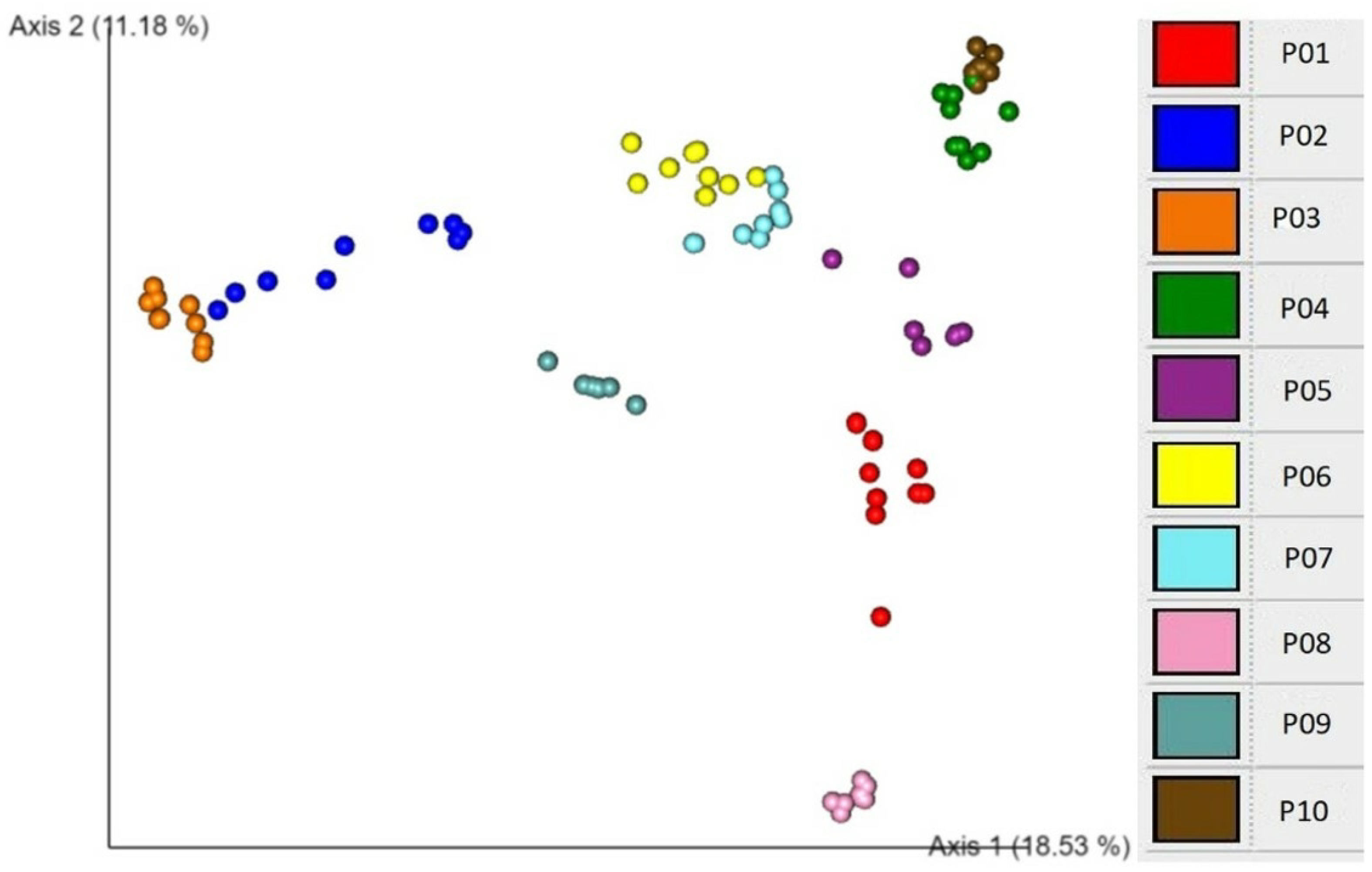
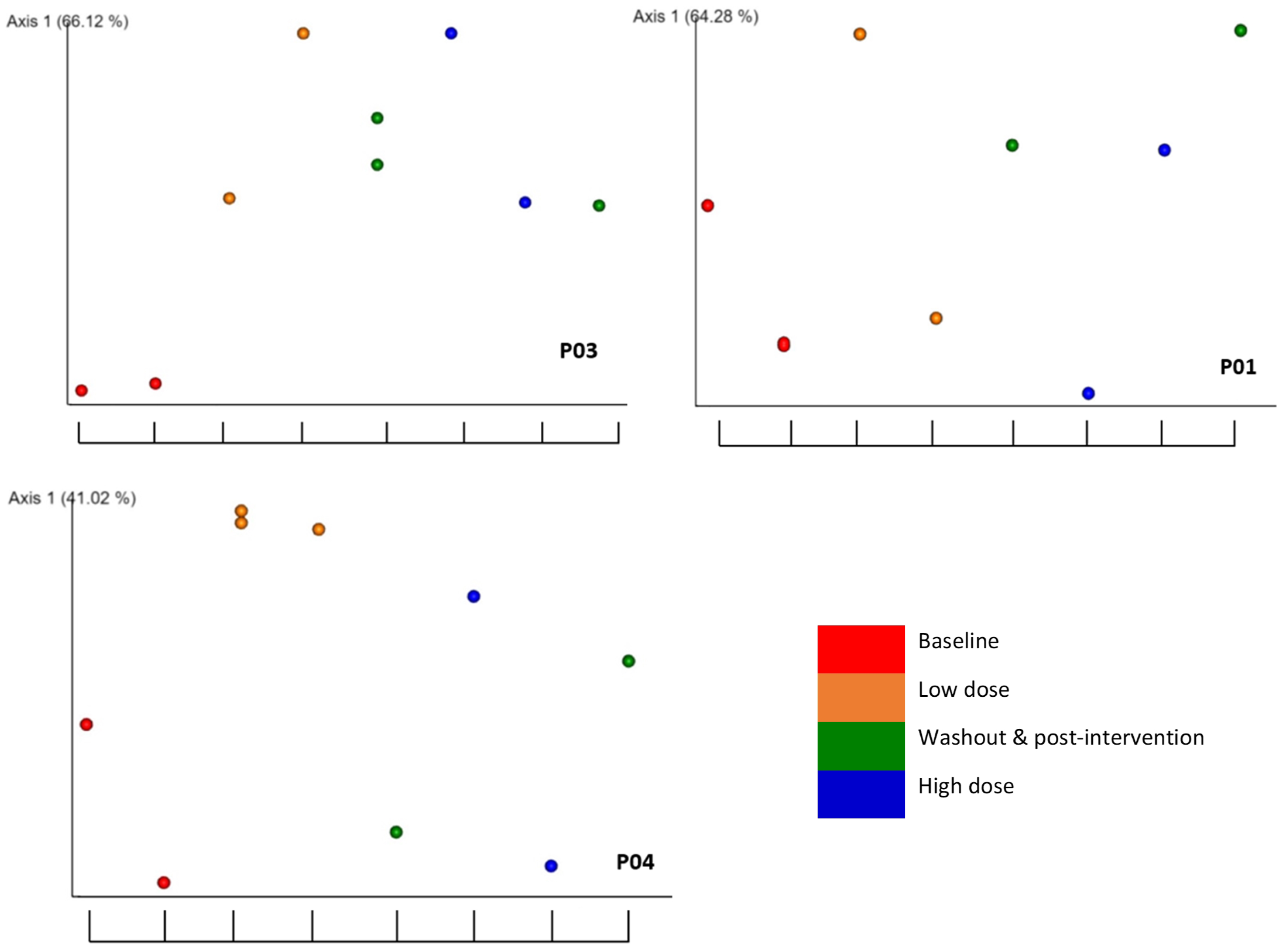
2.5. Associations of beta diversity of gut microbiota with explanatory factors
2.6. Detection of the association of microbial diversity with interactions of explanatory factors
2.7. Significant taxonomic changes from baseline to interventional period
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Participant recruitment and diet tracking
4.2. Design and intervention
4.3. Faecal sample collection, preservation, and DNA extraction
4.4. Amplification and sequencing of extracted microbial DNA
4.5. Microbiota profiling and statistical analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AES | Australian Eating Survey® |
| ARFS | Australian Recommended Food Score |
| DNA | Deoxyribonucleic acid |
| EMPeror | Earth Microbiome Project |
| PERMANOVA | Permutational multivariate analysis of variance |
| RBAC | Rice bran arabinoxylan compound |
| rRNA | Ribosomal ribonucleic acid |
| SCFAs | Short-chain fatty acids |
References
- Valdes, A.M.; Walter, J.; Segal, E.; Spector, T.D. Role of the gut microbiota in nutrition and health. BMJ 2018, 361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malard, F.; Dore, J.; Gaugler, B.; Mohty, M. Introduction to host microbiome symbiosis in health and disease. Mucosal Immunology 2021, 14, 547–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forbes, J.D.; Domselaar, G.V.; Bernstein, C.N. Microbiome survey of the inflamed and noninflamed gut at different compartments within the gastrointestinal tract of inflammatory bowel disease patients. Inflammatory Bowel Diseases 2016, 22, 817–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendis, M.; Leclerc, E.; Simsek, S. Arabinoxylans, gut microbiota and immunity. Carbohydrate Polymers 2016, 139, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, K.P.; Jean-Michel, A.; Midtvedt, T.; van Hemert, S. Manipulating the gut microbiota to maintain health and treat disease. Microbial Ecology in Health and Disease 2015, 26, 25877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rinninella, E.; Raoul, P.; Cintoni, M.; Franceschi, F.; Miggiano, G.A.; Gasbarrini, A.; Mele, M.C. What is the healthy gut microbiota composition? A changing ecosystem across age, environment, diet, and diseases. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, C.H.; Desai, H.; Sylvetsky, A.C.; LoTempio, J.; Ayanyan, S.; Carrie, J.; Crandall, K.A.; Fochtman, B.C.; Gasparyan, L.; Gulzar, N.; Howell, P.; Issa, N.; Krampis, K.; Mishra, L.; Morizono, H.; Pisegna, J.R.; Rao, S.; Ren, Y.; Simonyan, V.; Smith, K.; VedBrat, S.; Yao, M.D.; Mazumder, R. Baseline human gut microbiota profile in healthy people and standard reporting template. PLOS ONE 2019, 14, e0206484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ventura, M.; Turroni, F.; Lugli, G.A.; van Sinderen, D. Bifidobacteria and humans: our special friends, from ecological to genomics perspectives. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture 2014, 94, 163–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hald, S.; Schioldan, A.G.; Moore, M.E.; Dige, A.; Lærke, H.N.; Agnholt, J.; Knudsen, K.E.B.; Hermansen, K.; Marco, M.L.; Gregersen, S.; Dahlerup, J.F. Effects of arabinoxylan and resistant starch on intestinal microbiota and short-chain fatty acids in subjects with metabolic syndrome: a randomised crossover study. PLOS ONE 2016, 11, e0159223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Callaghan, A.; van Sinderen, D. Bifidobacteria and their role as members of the human gut microbiota. Frontiers in Microbiology 2016, 7, 925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, M.; Martínez-Martínez, D.; Amaretti, A.; Ulrici, A.; Raimondi, S.; Moya, A. Mining metagenomic whole genome sequences revealed subdominant but constant Lactobacillus population in the human gut microbiota. Environmental Microbiology Reports 2016, 8, 399–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mu, Q.; Tavella, V.J.; Luo, X.M. Role of Lactobacillus reuteri in human health and diseases. Frontiers in Microbiology 2018, 9, 757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamanai-Shacoori, Z.; Smida, I.; Bousarghin, L.; Loreal, O.; Meuric, V.; Fong, S.B.; Bonnaure-Mallet, M.; Jolivet-Gougeon, A. Roseburia spp.: a marker of health? Future Microbiology 2017, 12, 157–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.; Sim, J.X.Y.; Lee, W.L.; Cui, L.; Chan, Y.F.Z.; Chang, E.D.; Teh, Y.E.; Zhang, A.N.; Armas, F.; Chandra, F.; Chen, H.; Zhao, S.; Lee, Z.; Thompson, J.R.; Ooi, E.E.; Low, J.G.; Alm, E.J.; Kalimuddin, S. Low gut Ruminococcaceae levels are associated with occurrence of antibiotic-associated diarrhea. medRxiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neyrinck, A.M.; Possemiers, S.; Druart, C.; de Wiele, T.V.; Backer, F.D.; Cani, P.D.; Larondelle, Y.; Delzenne, N.M. Prebiotic effects of wheat arabinoxylan related to the increase in Bifidobacteria, Roseburia and Bacteroides/Prevotella in diet-induced obese mice. PLOS ONE 2011, 6, e20944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, W.W.; Wang, Z.; Levison, B.S.; Koeth, R.A.; Britt, E.B.; Fu, X.; Wu, Y.; Hazen, S.L. Intestinal Microbial Metabolism of Phosphatidylcholine and Cardiovascular Risk. New England Journal of Medicine 2013, 368, 1575–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Mello, V.D.; Paananen, J.; Lindström, J.; Lankinen, M.A.; Shi, L.; Kuusisto, J.; Pihlajamäki, J.; Auriola, S.; Lehtonen, M.; Rolandsson, O.; Bergdahl, I.A.; Nordin, E.; Ilanne-Parikka, P.; Keinänen-Kiukaanniemi, S.; Landberg, R.; Eriksson, J.G.; Tuomilehto, J.; Hanhineva, K.; Uusitupa, M. Indolepropionic acid and novel lipid metabolites are associated with a lower risk of type 2 diabetes in the Finnish diabetes prevention study. Scientific Reports 2017, 7, 46337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Influence of diet on the gut microbiome and implications for human health. Journal of Translational Medicine 2017, 15, 73. [CrossRef]
- Bowyer, R.C.E.; Jackson, M.A.; Roy, C.I.L.; Lochlainn, M.N.; Spector, T.D.; Dowd, J.B.; Steves, C.J. Socioeconomic status and the gut microbiome: a TwinsUK cohort study. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carson, T.L.; Wang, F.; Cui, X.; Jackson, B.E.; Pol, W.J.V.D.; Lefkowitz, E.J.; Morrow, C.; Baskin, M.L. Associations between race, perceived psychological stress, and the gut microbiota in a sample of generally healthy black and white women: a pilot study on the role of race and perceived psychological stress. Psychosomatic Medicine 2018, 80, 640–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagpal, R.; Mainali, R.; Ahmadi, S.; Wang, S.; Singh, R.; Kavanagh, K.; Kitzman, D.W.; Kushugulova, A.; Marotta, F.; Yadav, H. Gut microbiome and aging: Physiological and mechanistic insights. Nutrition and Healthy Aging 2018, 4, 267–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, J.; Li, R.; Raes, J.; Arumugam, M.; Burgdorf, K.S.; Manichanh, C.; Nielsen, T.; Pons, N.; Levenez, F.; Yamada, T.; Mende, D.R.; Li, J.; Xu, J.; Li, S.; Li, D.; Cao, J.; Wang, B.; Liang, H.; Zheng, H.; Xie, Y.; Tap, J.; Lepage, P.; Bertalan, M.; Batto, J.M.; Hansen, T.; Paslier, D.L.; Linneberg, A.; Nielsen, H.B.; Pelletier, E.; Renault, P.; Sicheritz-Ponten, T.; Turner, K.; Zhu, H.; Yu, C.; Li, S.; Jian, M.; Zhou, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, X.; Li, S.; Qin, N.; Yang, H.; Wang, J.; Brunak, S.; Doré, J.; Guarner, F.; Kristiansen, K.; Pedersen, O.; Parkhill, J.; Weissenbach, J.; Antolin, M.; Artiguenave, F.; Blottiere, H.; Borruel, N.; Bruls, T.; Casellas, F.; Chervaux, C.; Cultrone, A.; Delorme, C.; Denariaz, G.; Dervyn, R.; Forte, M.; Friss, C.; van de Guchte, M.; Guedon, E.; Haimet, F.; Jamet, A.; Juste, C.; Kaci, G.; Kleerebezem, M.; Knol, J.; Kristensen, M.; Layec, S.; Roux, K.L.; Leclerc, M.; Maguin, E.; Minardi, R.M.; Oozeer, R.; Rescigno, M.; Sanchez, N.; Tims, S.; Torrejon, T.; Varela, E.; de Vos, W.; Winogradsky, Y.; Zoetendal, E.; Bork, P.; Ehrlich, S.D.; Wang, J.; Consortium, M. A human gut microbial gene catalogue established by metagenomic sequencing. Nature 2010, 464, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Odamaki, T.; Kato, K.; Sugahara, H.; Hashikura, N.; Takahashi, S.; zhong Xiao, J.; Abe, F.; Osawa, R. Age-related changes in gut microbiota composition from newborn to centenarian: a cross-sectional study. BMC Microbiology 2016, 16, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagpal, R.; Tsuji, H.; Takahashi, T.; Kawashima, K.; Nagata, S.; Nomoto, K.; Yamashiro, Y. Sensitive quantitative analysis of the meconium bacterial microbiota in healthy term infants born vaginally or by cesarean section. Frontiers in Microbiology 2016, 7, 1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claesson, M.J.; Jeffery, I.B.; Conde, S.; Power, S.E.; O’Connor, E.M.; Cusack, S.; Harris, H.M.B.; Coakley, M.; Lakshminarayanan, B.; O’Sullivan, O.; Fitzgerald, G.F.; Deane, J.; O’Connor, M.; Harnedy, N.; O’Connor, K.; O’Mahony, D.; van Sinderen, D.; Wallace, M.; Brennan, L.; Stanton, C.; Marchesi, J.R.; Fitzgerald, A.P.; Shanahan, F.; Hill, C.; Ross, R.P.; O’Toole, P.W. Gut microbiota composition correlates with diet and health in the elderly. Nature 2012, 488, 178–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gavini, F.; Cayuela, C.; Antoine, J.M.; Lecoq, C.; Lefebvre, B.; Membré, J.M.; Neut, C. Differences in the distribution of bifidobacterial and enterobacterial species in human faecal microflora of three different (children, adults, elderly) age groups. Microbial Ecology in Health and Disease 2001, 13, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biedermann, L.; Zeitz, J.; Mwinyi, J.; Sutter-Minder, E.; Rehman, A.; Ott, S.J.; Steurer-Stey, C.; Frei, A.; Frei, P.; Scharl, M.; Loessner, M.J.; Vavricka, S.R.; Fried, M.; Schreiber, S.; Schuppler, M.; Rogler, G. Smoking Cessation Induces Profound Changes in the Composition of the Intestinal Microbiota in Humans. PLOS ONE 2013, 8, e59260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutlu, E.A.; Gillevet, P.M.; Rangwala, H.; Sikaroodi, M.; Naqvi, A.; Engen, P.A.; Kwasny, M.; Lau, C.K.; Keshavarzian, A. Colonic microbiome is altered in alcoholism. American Journal of Physiology-Gastrointestinal and Liver Physiology 2012, 302, G966–G978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leeming, E.R.; Johnson, A.J.; Spector, T.D.; Le Roy, C.I. Effect of Diet on the Gut Microbiota: Rethinking Intervention Duration. Nutrients 2019, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhurlova, O.D.; Kaprelyants, L.V. The current trends and future perspectives of arabinoxylans prebiotics research: A review. Grain Products and Mixed Fodder’s 2017, 17, 4–11, https://journals.ontu.edu.ua/index.php/gpmf/article/view/760/662. Accessed: 2022-10-28. [Google Scholar]
- Ooi, S.L.; Pak, S.C.; Micalos, P.S.; Schupfer, E.; Lockley, C.; Park, M.H.; Hwang, S.J. The health-promoting properties and clinical applications of rice bran arabinoxylan modified with shiitake mushroom enzyme-a narrative review. Molecules 2021, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schupfer, E.; Pak, S.C.; Wang, S.; Micalos, P.S.; Jeffries, T.; Ooi, S.L.; Golombick, T.; Harris, G.; El-Omar, E. The effects and benefits of arabinoxylans on human gut microbiota – A narrative review. Food Bioscience 2021, 43, 101267–101267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, Y.L.; Lin, T.L.; Chang, C.J.; Wu, T.R.; Lai, W.F.; Lu, C.C.; Lai, H.C. Probiotics, prebiotics and amelioration of diseases. Journal of Biomedical Science 2019, 26, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salden, B.N.; Troost, F.J.; Wilms, E.; Truchado, P.; Vilchez-Vargas, R.; Pieper, D.H.; Jáuregui, R.; Marzorati, M.; van de Wiele, T.; Possemiers, S.; Masclee, A.A. Reinforcement of intestinal epithelial barrier by arabinoxylans in overweight and obese subjects: A randomized controlled trial. Clinical Nutrition 2018, 37, 471–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- François, I.E.J.A.; Lescroart, O.; Veraverbeke, W.S.; Marzorati, M.; Possemiers, S.; Evenepoel, P.; Hamer, H.; Houben, E.; Windey, K.; Welling, G.W.; Delcour, J.A.; Courtin, C.M.; Verbeke, K.; Broekaert, W.F. Effects of a wheat bran extract containing arabinoxylan oligosaccharides on gastrointestinal health parameters in healthy adult human volunteers: a double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled, cross-over trial. British Journal of Nutrition 2012, 108, 2229–2242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kjølbæk, L.; Benítez-Páez, A.; del Pulgar, E.M.G.; Brahe, L.K.; Liebisch, G.; Matysik, S.; Rampelli, S.; Vermeiren, J.; Brigidi, P.; Larsen, L.H.; Astrup, A.; Sanz, Y. Arabinoxylan oligosaccharides and polyunsaturated fatty acid effects on gut microbiota and metabolic markers in overweight individuals with signs of metabolic syndrome: A randomized cross-over trial. Clinical Nutrition 2020, 39, 67–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chudan, S.; Ishibashi, R.; Nishikawa, M.; Tabuchi, Y.; Nagai, Y.; Ikushiro, S.; Furusawa, Y. Effect of Wheat-Derived Arabinoxylan on the Gut Microbiota Composition and Colonic Regulatory T Cells. Molecules 2023, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grootaert, C.; Delcour, J.A.; Courtin, C.M.; Broekaert, W.F.; Verstraete, W.; de Wiele, T.V. Microbial metabolism and prebiotic potency of arabinoxylan oligosaccharides in the human intestine. Trends in Food Science & Technology 2007, 18, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walton, G.E.; Lu, C.; Trogh, I.; Arnaut, F.; Gibson, G.R. A randomised, double-blind, placebo controlled cross-over study to determine the gastrointestinal effects of consumption of arabinoxylan-oligosaccharides enriched bread in healthy volunteers. Nutrition Journal 2012, 11, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daiwa Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. BioBran® Rice Bran Arabinoxylan Compound. https://www.biobran.org/uploads/downloads/BioBran_guide_new.pdf?v1.1.2, 2016. Accessed: 2022-10-28.
- Shannon, C.E. A mathematical theory of communication. Bell System Technical Journal 1948, 27, 379–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, B.D.; Grunwald, G.K.; Zerbe, G.O.; Mikulich-Gilbertson, S.K.; Robertson, C.E.; Zemanick, E.T.; Harris, J.K. On the use of diversity measures in longitudinal sequencing studies of microbial communities. Frontiers in Microbiology 2018, 9, 1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodrich, J.; Davenport, E.; Beaumont, M.; Jackson, M.; Knight, R.; Ober, C.; Spector, T.; Bell, J.; Clark, A.; Ley, R. Genetic determinants of the gut microbiome in UK twins. Cell Host & Microbe 2016, 19, 731–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, H.; Hakim, J.A.; Crossman, D.K.; Lefkowitz, E.J.; Morrow, C.D. Sharing of gut microbial strains between selected individual sets of twins cohabitating for decades. PLOS ONE 2019, 14, e0226111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, L.A.; Materna, A.C.; Friedman, J.; Campos-Baptista, M.I.; Blackburn, M.C.; Perrotta, A.; Erdman, S.E.; Alm, E.J. Host lifestyle affects human microbiota on daily timescales. Genome Biology 2014, 15, R89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capurso, G.; Lahner, E. The interaction between smoking, alcohol and the gut microbiome. Best Practice & Research Clinical Gastroenterology 2017, 31, 579–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Yun, Y.; Kim, S.J.; Lee, E.J.; Chang, Y.; Ryu, S.; Shin, H.; Kim, H.L.; Kim, H.N.; Lee, J.H. Association between cigarette smoking status and composition of gut microbiota: population-based cross-sectional study. Journal of Clinical Medicine 2018, 7, 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aslam, H.; Collier, F.; Davis, J.A.; Quinn, T.P.; O’Hely, M.; Pasco, J.A.; Jacka, F.N.; Loughman, A. Gut microbiome diversity and composition are associated with habitual dairy intakes: a cross-sectional study in men. The Journal of Nutrition 2021, 151, 3400–3412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senghor, B.; Sokhna, C.; Ruimy, R.; Lagier, J.C. Gut microbiota diversity according to dietary habits and geographical provenance. Human Microbiome Journal 2018, 7-8, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, T.; Vila, A.V.; Garmaeva, S.; Jankipersadsing, S.A.; Imhann, F.; Collij, V.; Bonder, M.J.; Jiang, X.; Gurry, T.; Alm, E.J.; D’Amato, M.; Weersma, R.K.; Scherjon, S.; Wijmenga, C.; Fu, J.; Kurilshikov, A.; Zhernakova, A. Analysis of 1135 gut metagenomes identifies sex-specific resistome profiles. Gut Microbes 2019, 10, 358–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominianni, C.; Sinha, R.; Goedert, J.J.; Pei, Z.; Yang, L.; Hayes, R.B.; Ahn, J. Sex, body mass index, and dietary fiber intake influence the human gut microbiome. PLOS ONE 2015, 10, e0124599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valeri, F.; Endres, K. How biological sex of the host shapes its gut microbiota. Frontiers in Neuroendocrinology 2021, 61, 100912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, X.; Zhang, M.; Xue, J.; Huang, J.; Zhuang, R.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, H.; Fu, Q.; Hao, Y. Body mass index differences in the gut microbiota are gender specific. Frontiers in Microbiology 2018, 9, 1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heiman, M.L.; Greenway, F.L. A healthy gastrointestinal microbiome is dependent on dietary diversity. Molecular Metabolism 2016, 5, 317–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LaButti, K.; Pukall, R.; Steenblock, K.; Rio, T.G.D.; Tice, H.; Copeland, A.; Cheng, J.F.; Lucas, S.; Chen, F.; Nolan, M.; Bruce, D.; Goodwin, L.; Pitluck, S.; Ivanova, N.; Mavromatis, K.; Ovchinnikova, G.; Pati, A.; Chen, A.; Palaniappan, K.; Land, M.; Hauser, L.; Chang, Y.J.; Jeffries, C.D.; Chain, P.; Saunders, E.; Brettin, T.; Detter, J.C.; Han, C.; Göker, M.; Bristow, J.; Eisen, J.A.; Markowitz, V.; Hugenholtz, P.; Kyrpides, N.C.; Klenk, H.P.; Lapidus, A. Complete genome sequence of Anaerococcus prevotii type strain (PC1T). Standards in Genomic Sciences 2009, 1, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernard, K. The genus Corynebacterium and other medically relevant Coryneform-like bacteria. Journal of Clinical Microbiology 2012, 50, 3152–3158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smits, S.A.; Marcobal, A.; Higginbottom, S.; Sonnenburg, J.L.; Kashyap, P.C. Individualized responses of gut microbiota to dietary intervention modeled in humanized mice. mSystems 2016, 1, e00098–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Ni, Y.; Cheung, C.K.; Lam, K.S.; Wang, Y.; Xia, Z.; Ye, D.; Guo, J.; Tse, M.A.; Panagiotou, G.; Xu, A. Gut microbiome fermentation determines the efficacy of exercise for diabetes prevention. Cell Metabolism 2020, 31, 77–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sims, T.T.; Alam, M.B.E.; Karpinets, T.V.; Dorta-Estremera, S.; Hegde, V.L.; Nookala, S.; Yoshida-Court, K.; Wu, X.; Biegert, G.W.G.; Medrano, A.Y.D.; Solley, T.; Ahmed-Kaddar, M.; Chapman, B.V.; Sastry, K.J.; Mezzari, M.P.; Petrosino, J.F.; Lin, L.L.; Ramondetta, L.; Jhingran, A.; Schmeler, K.M.; Ajami, N.J.; Wargo, J.; Colbert, L.E.; Klopp, A.H. Gut microbiome diversity is an independent predictor of survival in cervical cancer patients receiving chemoradiation. Communications Biology 2021, 4, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bovis, F.; Carmisciano, L.; Signori, A.; Pardini, M.; Steinerman, J.R.; Li, T.; Tansy, A.P.; Sormani, M.P. Defining responders to therapies by a statistical modeling approach applied to randomized clinical trial data. BMC Medicine 2019, 17, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, C.; Burrows, T.; Rollo, M.; Boggess, M.; Watson, J.; Guest, M.; Duncanson, K.; Pezdirc, K.; Hutchesson, M. The Comparative Validity and Reproducibility of a Diet Quality Index for Adults: The Australian Recommended Food Score. Nutrients 2015, 7, 785–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norgen Biotek Corp. Stool/faecal nucleic acid preservative safety data sheet. https://norgenbiotek.com/sites/default/files/resources/45630_45660_SDS.pdf, 2015. Accessed: 2022-10-28.
- Klindworth, A.; Pruesse, E.; Schweer, T.; Peplies, J.; Quast, C.; Horn, M.; Glöckner, F.O. Evaluation of general 16S ribosomal RNA gene PCR primers for classical and next-generation sequencing-based diversity studies. Nucleic Acids Research 2013, 41, e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolyen, E.; Rideout, J.R.; Dillon, M.R.; Bokulich, N.A.; Abnet, C.C.; Al-Ghalith, G.A.; Alexander, H.; Alm, E.J.; Arumugam, M.; Asnicar, F.; Bai, Y.; Bisanz, J.E.; Bittinger, K.; Brejnrod, A.; Brislawn, C.J.; Brown, C.T.; Callahan, B.J.; Caraballo-Rodríguez, A.M.; Chase, J.; Cope, E.K.; Silva, R.D.; Diener, C.; Dorrestein, P.C.; Douglas, G.M.; Durall, D.M.; Duvallet, C.; Edwardson, C.F.; Ernst, M.; Estaki, M.; Fouquier, J.; Gauglitz, J.M.; Gibbons, S.M.; Gibson, D.L.; Gonzalez, A.; Gorlick, K.; Guo, J.; Hillmann, B.; Holmes, S.; Holste, H.; Huttenhower, C.; Huttley, G.A.; Janssen, S.; Jarmusch, A.K.; Jiang, L.; Kaehler, B.D.; Kang, K.B.; Keefe, C.R.; Keim, P.; Kelley, S.T.; Knights, D.; Koester, I.; Kosciolek, T.; Kreps, J.; Langille, M.G.I.; Lee, J.; Ley, R.; Liu, Y.X.; Loftfield, E.; Lozupone, C.; Maher, M.; Marotz, C.; Martin, B.D.; McDonald, D.; McIver, L.J.; Melnik, A.V.; Metcalf, J.L.; Morgan, S.C.; Morton, J.T.; Naimey, A.T.; Navas-Molina, J.A.; Nothias, L.F.; Orchanian, S.B.; Pearson, T.; Peoples, S.L.; Petras, D.; Preuss, M.L.; Pruesse, E.; Rasmussen, L.B.; Rivers, A.; Robeson, M.S.; Rosenthal, P.; Segata, N.; Shaffer, M.; Shiffer, A.; Sinha, R.; Song, S.J.; Spear, J.R.; Swafford, A.D.; Thompson, L.R.; Torres, P.J.; Trinh, P.; Tripathi, A.; Turnbaugh, P.J.; Ul-Hasan, S.; van der Hooft, J.J.J.; Vargas, F.; Vázquez-Baeza, Y.; Vogtmann, E.; von Hippel, M.; Walters, W.; Wan, Y.; Wang, M.; Warren, J.; Weber, K.C.; Williamson, C.H.D.; Willis, A.D.; Xu, Z.Z.; Zaneveld, J.R.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, Q.; Knight, R.; Caporaso, J.G. Reproducible, interactive, scalable and extensible microbiome data science using QIIME 2. Nature Biotechnology 2019, 37, 852–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.A.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nature Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rognes, T.; Flouri, T.; Nichols, B.; Quince, C.; Mahé, F. VSEARCH: a versatile open source tool for metagenomics. PeerJ 2016, 4, e2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Peddada, S.D. Analysis of compositions of microbiomes with bias correction. Nature Communications 2020, 11, 3514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oksanen, J.; Simpson, G.; Blanchet, F.G.; Kindt, R.; Legendre, P.; Minchin, P.R.; O’Hara, R.B.; Solymos, P.; Stevens, H.H.; Szoecs, E.; Wagner, H.; Barbour, M.; Bedward, M.; Bolker, B.; Borcard, D.; Carvalho, G.; Chirico, M.; Caceres, M.D.; Durand, S.; Evangelista, H.B.A.; FitzJohn, R.; Friendly, M.; Furneaux, B.; Hannigan, G.; Hill, M.O.; Lahti, L.; McGlinn, D.; Ouellette, M.H.; Cunha, E.R.; Smith, T.; Stier, A.; Braak, C.J.T.; Weedon, J. vegan: Community Ecology Package. https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/vegan/index.html, 2022. Accessed: 2022-10-28.
| Participant | Sex | Age | Age group | Cigarette smoking |
Alcohol consumption |
Diet | ARFS average |
ARFS group1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P01 | F | 26 | ≤ 30 | No | No | Omnivore | 16 | Very low |
| P02 | M | 29 | ≤ 30 | No | Yes | Omnivore | 31.5 | Medium |
| P03 | M | 25 | ≤ 30 | No | No | Vegan | 42.5 | High |
| P04 | F | 26 | ≤ 30 | No | Yes | Omnivore | 29 | Low |
| P05 | F | 27 | ≤ 30 | No | Yes | Pescatarian | 28 | Low |
| P06 | M | 22 | ≤ 30 | No | Yes | Omnivore | 25.5 | Low |
| P07 | F | 56 | > 30 | Yes | No | Omnivore | 32 | Medium |
| P08 | M | 37 | > 30 | No | Yes | Omnivore | 34 | High |
| P09 | F | 28 | ≤ 30 | No | No | Omnivore | 16.5 | Very low |
| P10 | M | 30 | ≤ 30 | No | Yes | Omnivore | 22 | Very low |
| Explanatory factor | Shannon’s evenness | Faith’s PD |
|---|---|---|
| Participant | 9.66e-8 | 0.002 |
| Alcohol consumption | 7.92-6 | 0.389 |
| Cigarette smoking | 0.008 | 0.113 |
| Sex | 0.003 | 0.165 |
| ARFS group | 0.032 | 0.494 |
| Age group | 0.390 | 0.149 |
| Interventional period1 | 0.394 | 0.602 |
| RBAC dosage2 | 0.592 | 0.442 |
| Experimental phase3 | 0.756 | 0.442 |
| Time point4 | 0.875 | 0.527 |
| Explanatory factor | Unweighted unifrac | Weighted unifrac | Bray Curtis | Jaccard |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Participant | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 |
| Sex | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 |
| Alcohol consumption | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 |
| ARFS group | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 |
| Age group | 0.001 | 0.013 | 0.001 | 0.001 |
| Cigarette smoking | 0.001 | 0.100 | 0.001 | 0.001 |
| Interventional Period1 | 0.826 | 0.275 | 0.866 | 0.928 |
| RBAC dosage2 | 0.936 | 0.644 | 0.997 | 0.999 |
| Experimental phase3 | 0.992 | 0.730 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| Time point4 | 1.000 | 0.998 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| Weighted unifrac | Bray Curtis | |||||
| Participant | RBAC dosage1 |
Experimental phase2 |
Interventional Period3 |
RBAC dosage1 |
Experimental phase2 |
Interventional Period3 |
| P01 | 0.200 | 0.413 | 0.471 | 0.141 | 0.258 | 0.168 |
| P02 | 0.095 | 0.060 | 0.010 | 0.064 | 0.067 | 0.012 |
| P03 | 0.520 | 0.034 | 0.052 | 0.129 | 0.002 | 0.028 |
| P04 | 0.035 | 0.146 | 0.894 | 0.018 | 0.044 | 0.114 |
| P05 | 0.269 | 0.162 | 0.316 | 0.082 | 0.060 | 0.174 |
| P06 | 0.948 | 0.763 | 0.924 | 0.775 | 0.631 | 0.787 |
| P07 | 0.086 | 0.102 | 0.062 | 0.068 | 0.025 | 0.025 |
| P08 | 0.046 | 0.094 | 0.569 | 0.039 | 0.001 | 0.025 |
| P09 | 0.015 | 0.008 | 0.945 | 0.039 | 0.021 | 0.271 |
| P10 | 0.961 | 0.926 | 0.174 | 0.832 | 0.087 | 0.165 |
| Participant | Bacteria (phylum, class, order, family, genus, and species) | W | Associated Change |
|---|---|---|---|
| P01 | Firmicutes; Clostridia; Lachnospirales; Lachnospiraceae; Hungatella | 40 | increase |
| Proteobacteria; Gammaproteobacteria; Enterobacterales; Enterobacteriaceae; Citrobacter | 12 | increase (washout) | |
| Firmicutes; Bacilli; Erysipelotrichales; Erysipelatoclostridiaceae; Erysipelatoclostridium | 8 | increase (washout) | |
| Firmicutes; Clostridia; Lachnospirales; Lachnospiraceae; unknown | 6 | decrease | |
| P02 | Firmicutes; Clostridia; Peptostreptococcales-Tissierellales; Peptostreptococcales-Tissierellales; Anaerococcus | 64 | decrease |
| Actinobacteriota; Actinobacteria; Corynebacteriales; Corynebacteriaceae; Corynebacterium; unknown | 63 | decrease | |
| Actinobacteriota; Actinobacteria; Corynebacteriales; Corynebacteriaceae; Corynebacterium; unknown | 50 | decrease | |
| Firmicutes; Clostridia; Peptostreptococcales-Tissierellales; Peptostreptococcales-Tissierellales; Finegoldia | 48 | decrease | |
| P03 | Negativicutes; Veillonellales-Selenomonadales; Veillonellaceae; Dialister | 94 | decrease |
| Cyanobacteria; Vampirivibrionia; Gastranaerophilales; Gastranaerophilales; Gastranaerophilales | 86 | decrease | |
| P07 | Firmicutes; Bacilli; Erysipelotrichales; Erysipelatoclostridiaceae | 102 | decrease |
| P08 | Firmicutes; Clostridia; Oscillospirales; Ruminococcaceae; Eubacterium siraeum group | 35 | decrease |
| Firmicutes; Clostridia; Lachnospirales; Lachnospiraceae; Eisenbergiella | 9 | decrease | |
| Firmicutes; Clostridia; Lachnospirales; Lachnospiraceae; Lachnospiraceae ND3007 group | 7 | increase | |
| Proteobacteria; Gammaproteobacteria; Enterobacterales;Enterobacteriaceae; Escherichia-Shigella | 6 | increase (low dose) | |
| Firmicutes; Clostridia; Lachnospirales; Lachnospiraceae; Frisingicoccus | 5 | increase | |
| P09 | Firmicutes; Clostridia; Oscillospirales; Ruminococcaceae; Eubacterium siraeum group | 38 | increase |
| Firmicutes; Clostridia; Peptostreptococcales-Tissierellales; Peptostreptococcales-Tissierellales; Anaerococcus | 8 | increase (low dose) | |
| Firmicutes; Clostridia; Oscillospirales;Ruminococcaceae; Ruminococcus | 8 | increase (high dose) | |
| Firmicutes; Negativicutes; Veillonellales-Selenomonadales; Veillonellaceae; Megasphaera | 8 | increase (low dose) | |
| Firmicutes; Bacilli; Erysipelotrichales; Erysipelotrichaceae; Solobacterium | 7 | increase (low dose) | |
| Firmicutes; Clostridia; Lachnospirales; Lachnospiraceae; Eubacterium hallii group | 5 | increase | |
| Firmicutes; Bacilli; Erysipelotrichales; Erysipelotrichaceae; Turicibacter | 5 | increase (high dose) | |
| Firmicutes; Clostridia; Lachnospirales; Lachnospiraceae; Stomatobaculum | 5 | increase | |
| P10 | Bacteroidota; Bacteroidia; Bacteroidales; Prevotellaceae; Prevotella | 20 | decrease |
| Firmicutes; Clostridia; Oscillospirales; Butyricicoccaceae; Butyricicoccus | 8 | increase | |
| Firmicutes; Bacilli; Lactobacillales; Carnobacteriaceae; Granulicatella | 5 | increase |
| Time point | RBAC dose | Faecal sample | Experimental |
|---|---|---|---|
| (week) | (g/day) | number | phase |
| -3 | 0 | 1 | Baseline |
| 0 | 0 | 2 | Baseline |
| 3 | 1 | 3 | Low dose |
| 6 | 1 | 4 | Low dose |
| 9 | 0 | 5 | Washout |
| 12 | 3 | 6 | High dose |
| 15 | 3 | 7 | High dose |
| 18 | 0 | 8 | Post-intervention |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





