1. Introduction
Renewable energy technologies (such as solar energy, wind energy, hydropower, etc.) have developed rapidly in recent years [
1,
2,
3]. However, due to their inherent intermittency, volatility, and randomness, they face the challenge of large-scale grid connection. Using hydrogen energy as a bridge to achieve the separation of renewable energy generation and terminal electricity consumption in terms of time is one of the best solutions for the large-scale application of renewable energy [
4,
5,
6]. The primary approach is to use electricity generated from renewable energy to produce hydrogen and then continuously convert the chemical energy in hydrogen into electrical energy through proton exchange membrane fuel cells (PEMFCs) [
7,
8,
9,
10]. Unlike traditional thermal power generation, the hydrogen energy generation route using PEMFCs as carriers achieves zero emissions and has high energy conversion efficiency [
11].
For the electrochemical reactions in the cathode and anode of PEMFCs, the most efficient catalysts are precious metal platinum (Pt)-based catalysts [
12,
13,
14,
15]. However, due to the more complex cathodic oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) process and higher reaction energy barrier, it is necessary to use a large amount of Pt catalysts to achieve considerable performance. Therefore, developing high-performance Pt-based catalysts has always been a problem that continues to be solved to promote the large-scale commercialization of PEMFCs. Compared with Pt/C catalysts, using cheap transition metals (M) and Pt to construct alloy nanoparticles is currently widely considered the most promising method to solve the development problem of high-performance Pt-based catalysts [
16,
17,
18,
19,
20]. A series of research shows that introducing other transition metals in the Pt lattice can regulate Pt’s electronic structure and improve Pt atoms’ utilization through ligand and geometric effects respectively, thus effectively improving Pt’s mass activity [
21]. For example, Stamenkovic et al. first revealed that the specific activity of PtNi
3 (111) single crystal catalysts is 90 times that of commercial Pt/C [
22]. Shao-Horn’s research group developed PtNi alloy nanoparticles with a mass activity of ~0.6 A/mg
Pt at 0.9 V vs. RHE [
23].
At present, many Pt-alloy/C catalysts reported in the literature have achieved high activity. However, the loading density of Pt-alloy nanoparticles is much lower than Pt/C catalysts [
24,
25,26]. This results in an increase in the thickness of the membrane electrode catalytic layer during practical applications and a proportional increase in the mass transfer impedance of O
2, which limits the catalytic activity of the catalyst, especially when working at high current densities [27]. Generally, commercial fuel cell vehicle cathode catalysts require a Pt loading greater than 50% (mass fraction) [27]. In addition, Pt-alloy formation requires high temperatures of 500–700 °C [28,29]. It can be imagined that high-density Pt-alloy particles are extremely prone to sintering at such high temperatures. Therefore, it is of great challenge to prepare small-sized Pt-alloy/C catalysts with high loading of Pt as a practical catalyst for PEMFCs. The Pt-alloy/C catalysts prepared in such conditions generally present a large size and low electrochemical surface area (ECSA). Herein, we present a 40% Pt-weighted sub-3 nm PtCo/C alloy catalyst via a simple large-scaled incipient wetness impregnation method. By carefully optimizing the synthetic conditions such as Pt/Co ratios, calcination temperature and time, the size of supported PtCo nanoparticles is successfully controlled below 3 nm and a high electrochemical surface area (ECSA) achieves of 94 m
2/g is achieved, which is 2.8 times of commercial PtCo/C-TKK catalysts. Demonstrated by electrochemical oxygen reduction reaction, PtCo/C alloy catalysts present an enhanced mass activity of 0.45 A/mg at 0.9 V vs. RHE, which is 1.7 times that of the state-of-the-art commercial PtCo/C-TKK catalyst.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials’ preparation
Typically for preparing 40% Pt3Co2/C-8h catalysts, 0.84 g of 18.8% weighted H2PtCl6 solution and 0.32 mL of 1.27 mol/L Co(NO3)2·6H2O solution was added into 0.200 g of carbon black (Ketjenblack EC600JD). The mixture was dried in air at 200 °C for 2 hours with a heating rate of 2 °C/min. Subsequently, the dried mixture was reduced at 560 °C in a 10 vol% H2/Ar with a heating rate of 2 °C/min. When cooling to room temperature, the powder was carefully transferred from tube furnace.
The final Pt3Co2/C-8h alloy catalyst was obtained by etching the partial Co in 1.0 mol/L H2SO4 solution. After etching, the products was washed three times and finally dried in a vacuum oven at 60 °C.
The other materials were obtained with similar processes. The diffidence was the Pt/Co ratio, reduction temperature/time or the kinds of cheap metals.
2.2. Materials’ characterizations
The morphologies of samples were characterized by TEM (Technai G20 S-TWIN, FEI) with 200 kV accelerate voltage. The element distribution was studied by HAADF-STEM-EDX mapping. The phase of catalysts was analyzed by XRD (D8, Brook) with Cu Kα radiation (λ = 0.15418 nm).
2.3. Electrochemical measurements
Rotating disk electrode (RDE) measurements were performed in a three-electrode electrochemical cell. The cell temperature was controlled with a cycling water (25 °C). The reference electrode potentials were calibrated to the reversible hydrogen electrode (RHE) potentials. The working electrode was catalysts modified RDE (5.0 mm) with Pt loading of 15 µg cm−2. The catalysts were electrochemically activated by CV scanning between 0.05 and 1.05 V at 250 mV s−1 in N2-saturated 0.1 M HClO4 solution. Then the LSV curves were obtained from 0.05 V to 1.05 V at 10 mV s−1 in O2-saturated 0.1 M HClO4 with the rotating speed at 1600 rpm.
The mass related kinetic current density (Jk) of catalyst at 0.9 V vs. RHE was calculated according to: Jk = J × JL/((JL − J) × LPt), where J, JL, and LPt represent the current density at 0.9 V vs. RHE, the diffusion limited current density and Pt loading, respectively. The ohm resistance (R) was measured by electrochemical impedance spectroscopy from 0.1 Hz to 10,000 Hz with an amplitude of 5 mV at the initial potential of 0.05 V.
3. Results
3.1. Synthesis and Characterizations
The preparation process of PtCo/C alloy catalysts was described in the experimental section. Generally, a mixture solution containing H
2PtCl
6/Co(NO
3)
2 with a designed Pt/Co ratio was added in carbon black (Ketjenblack EC600JD). The loading of Pt was controlled to 40%. The dried H
2PtCl
6/Co(NO
3)
2/C mixture was subsequently reduced at 560 °C in 10% H
2/Ar with a 50 mL/min flow rate.
Figure 1 shows a typical Pt
3Co
2/C-8h alloy catalysts obtained in a condition of Pt/Co ratio of 3/2 and reducing the time of 8h in 10% H
2/Ar. All the catalysts were treated in 0.5 M H
2SO
4 before characterizations and electrochemical measurements. According to the lower magnification transmission electron microscope (TEM) image (
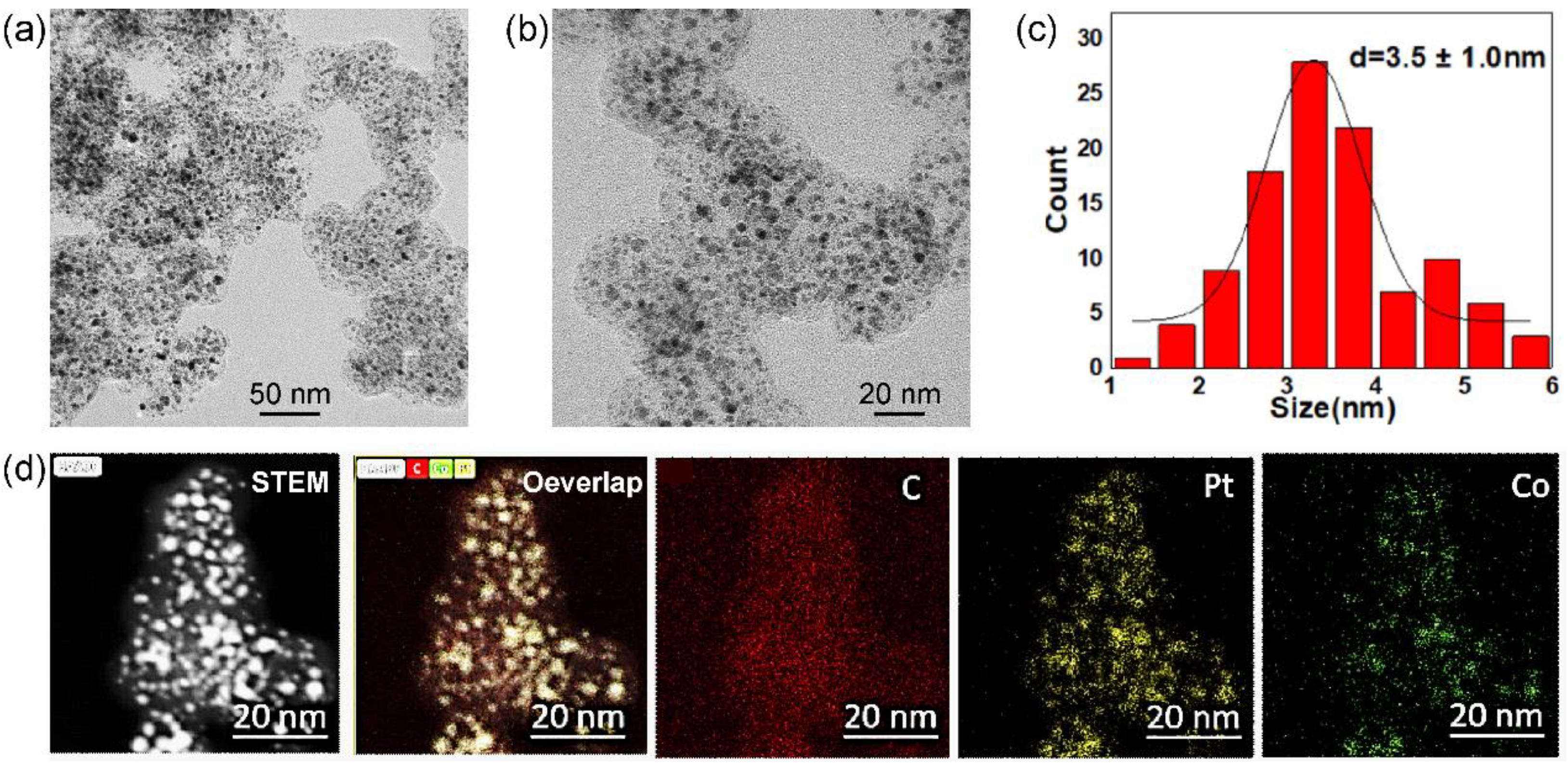
Figure 1a), PtCo alloy nanoparticles are uniformly dispersed on the carbon supports. It presents a small proportion of nanoparticles exceeding 6 nm. The higher magnification TEM image (
Figure 1b) further shows partial small nanoparticles with a size of less than 2 nm. Based on statistics of more than 200 random nanoparticles, the particle size of Pt
3Co
2/C-8h catalysts is 3.5 ± 1.0 nm. Furthermore, X-ray energy dispersive spectroscopy (EDS) mapping (
Figure 1c) equipped on high-angle annular dark field scanning transmission electron microscopy (HAADF-STEM) exhibits a good overlap of Pt and Co elements in individual nanoparticles, suggesting a high alloy degree of Pt/Co.
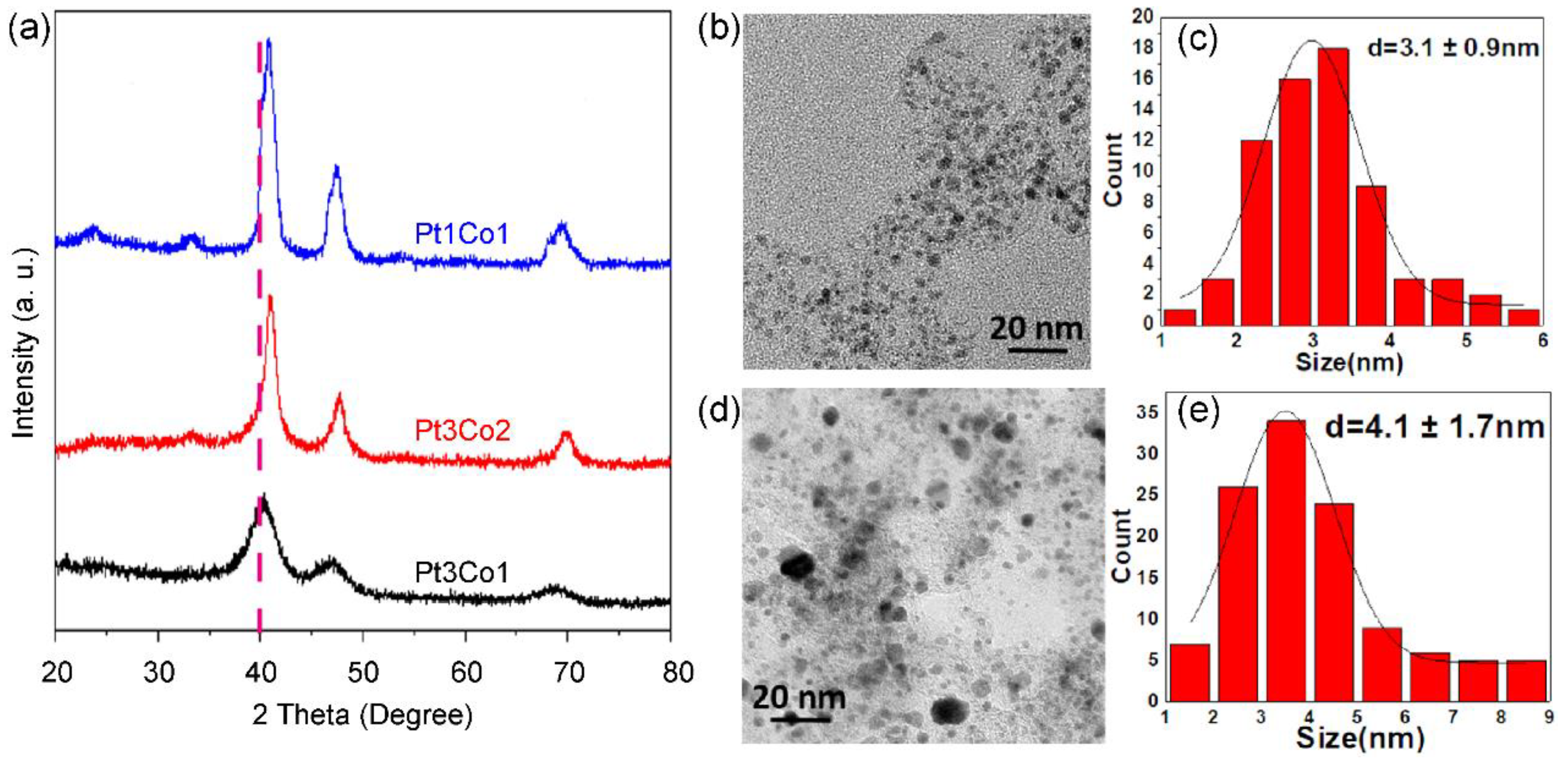
We further investigated the effect of Pt/Co ratio on the size and phase of alloyed nanoparticles. As shown in the X-ray powder diffraction (XRD) patterns (
Figure 2a), all the diffraction peaks have shifted after doping of Co in comparison with pure Pt (36.8°). As the Co content increases, the degree of shift increases. The more shifted degree indicates a higher alloy degree of Pt/Co, which is consistent with the increased phase of intermetallic compounds [30]. However, the peak becomes sharper with the increase of Co content, indicating that the size of supported nanoparticles becomes larger, which is well agree with the TEM image and size distribution, Pt
3Co
1/C-8h (
Figure 2b,c) presents a uniform size distribution of 3.1 ±0.9 nm. However, many large nanoparticles exist in Pt
1Co
1/C-8h (
Figure 2d,e), suggesting that it is more difficult to control the size for highly alloyed catalysts.
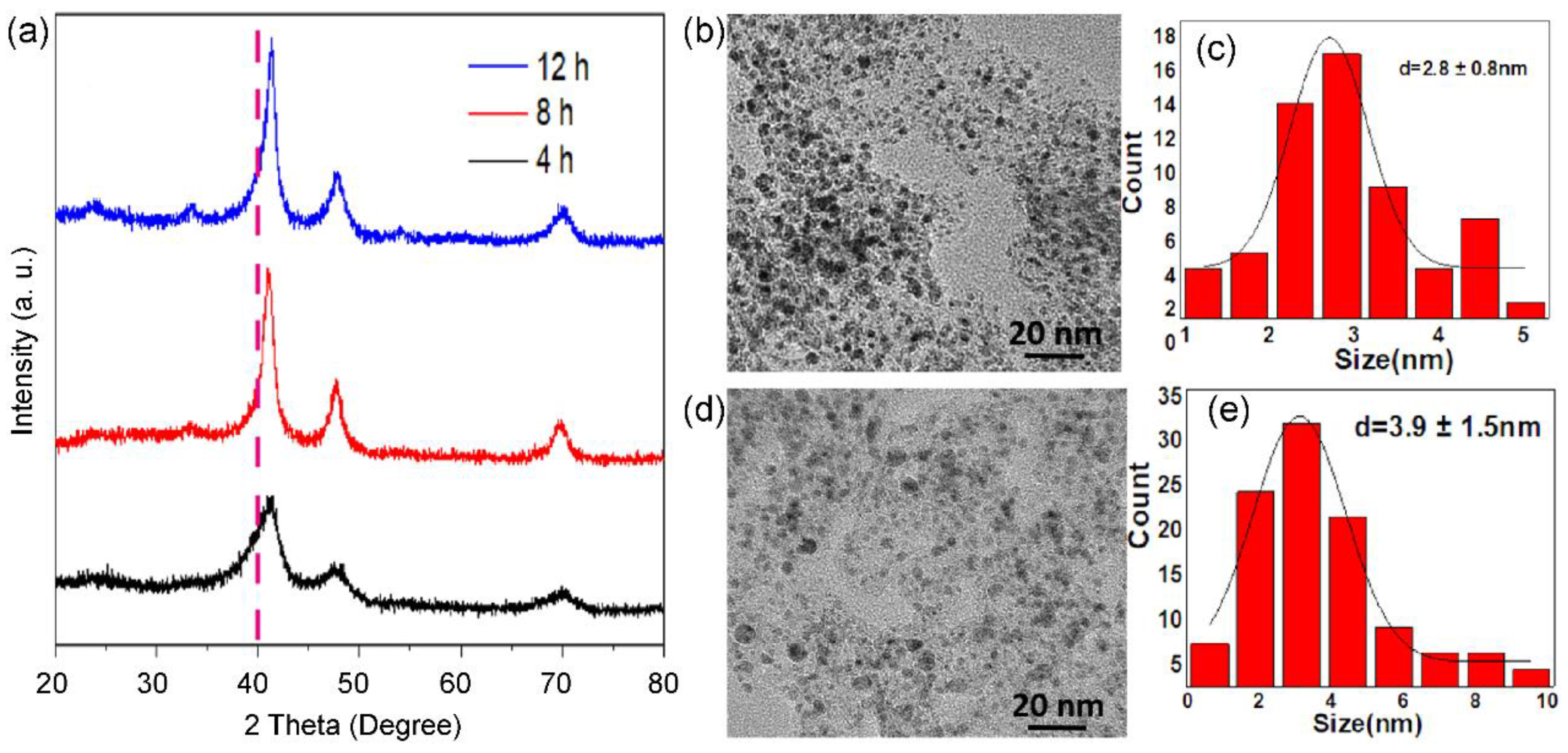
As displayed in
Figure 3, the calcination time in 10% H
2/Ar also affects the size and phase of alloyed nanoparticles. XRD patterns (
Figure 3a) show that the ordered intermetallic compounds appear within 4h. When the reduction time is prolonged to 12h, there presents a significant increase in size. Typically, Pt
3Co
2/C-4h (
Figure 3b,c) and Pt
3Co
2/C-12h (
Figure 3d,e) possess a size distribution of 2.8 ± 0.8 nm, and 3.9 ± 1.5 nm, respectively. In addition, we found that the diffraction peak of Pt
3Co
2/C-4h is asymmetric, indicating that there are partial PtCo nanoparticles with a low degree of alloying. Thus, the size and degree of alloying are a pair of constraints.
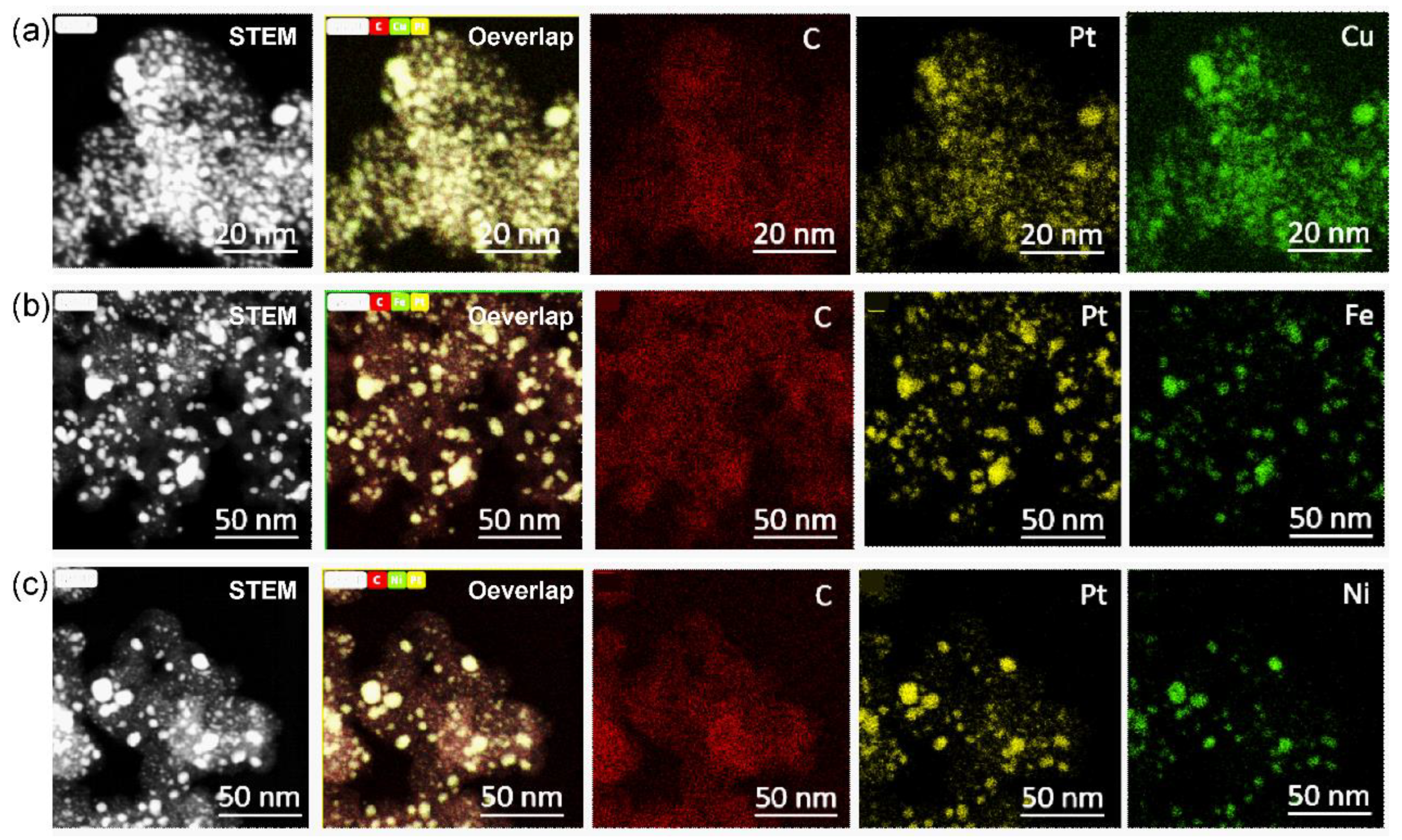
We further explored the carbon-supported 40% Pt-alloy catalysts with the cheaper Cu, Fe, and Ni metal. According to the HAADF-STEM-EDS-mappings, the signal of Pt are well overlapped with corresponding Cu (
Figure 4a), Fe (
Figure 4b) and Ni (
Figure 4d) elements, indicating the formation of highly alloyed nanoparticles. However, there were significant differences in size distribution. For Pt
3Cu
2/C, we can obtain a highly uniform size distribution of 3.1 ± 0.9 nm (
Figure S1). While the size control of PtFe/C (
Figure S2) and PtNi/C (
Figure S3) is still a big challenge.
3.2. Electrochemical evaluation for oxygen reduction reaction
The electrochemical surface area (ECSA) and mass activity at 0.9 V (
vs. RHE, and the same below) (MA
0.9) of 40% PtCo/C alloy catalysts were measured on a rotating disc electrode (RDE). To obtain the ECSAs, the cyclic voltammetry (CV) curves (
Figure 5a) were carried out in N
2-saturated 0.1 M HClO
4. The ECSAs were calculated according to the hydrogen adsorption/desorption current densities [31]. To obtain the MA
0.9 values, the linear cyclic voltammetry (LSV) curves (
Figure 5b) were performed in O
2-saturated 0.1 M HClO
4 and corrected with an ohmic resistance of 23 Ω determined by an electrochemical impedance testing.
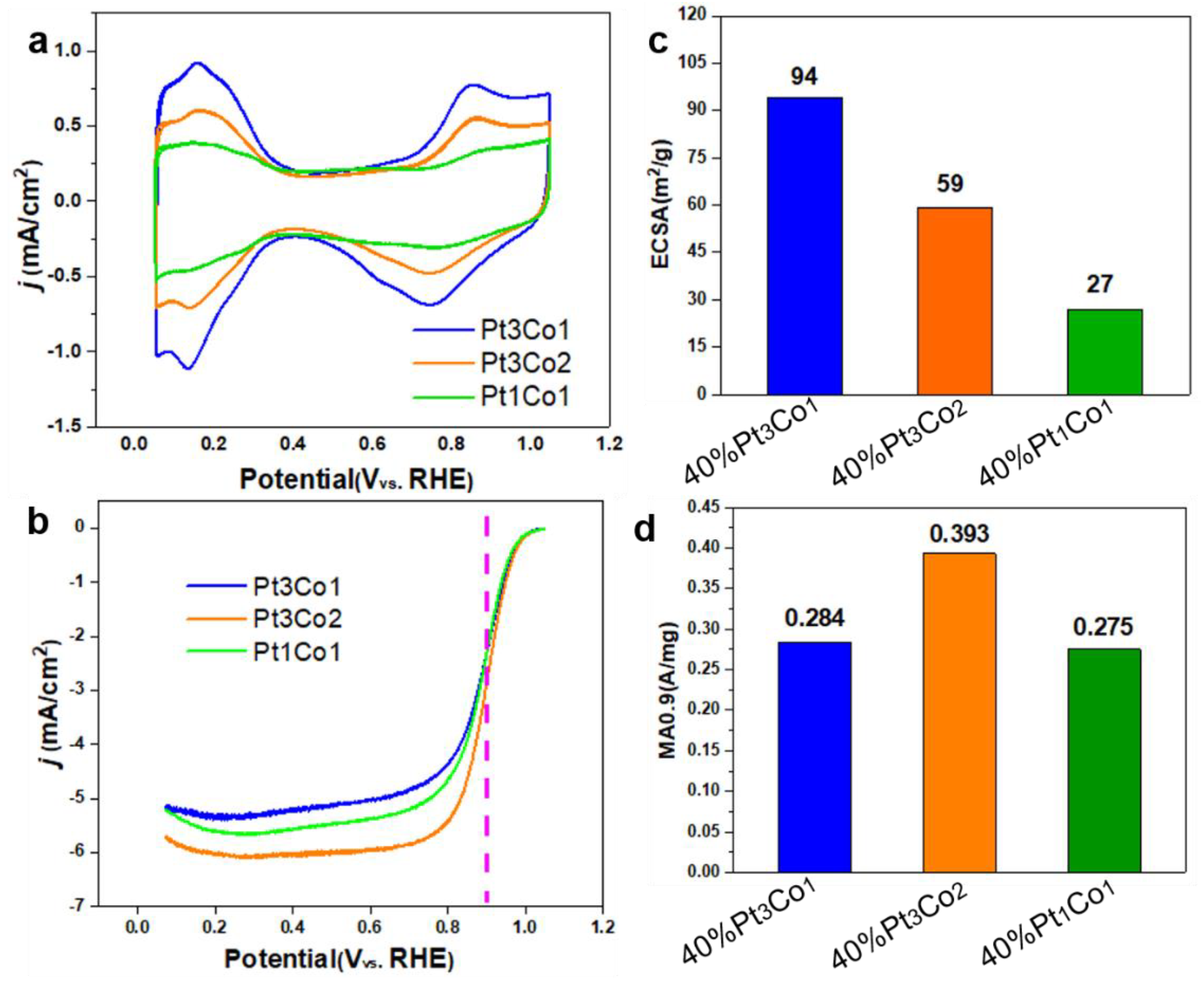
Figure 5c,d display the Pt/Co ratio-dependent ECSA and MA
0.9 values. The ECSAs of Pt
3Co
1/C-8h, Pt
3Co
2/C-8h, and Pt
1Co
1/C-8h are 94, 59, and 27 m
2/g, respectively. The MA
0.9 of Pt
3Co
1/C-8h, Pt
3Co
1/C-8h and Pt
1Co
1/C-8h are 0.0.284, 0.393 and 0.275 A mg
−1. Pt
3Co
1/C-8h present much lower MA
0.9 than Pt
3Co
2/C-8h although it possesses high ECSA, indicating the degree of alloy significantly affects the activity. In addition, Pt
1Co
1/C-8h with lower ECSA also exhibits low MA
0.9, although it has the highest degree of alloy. Thus, we must coordinate alloying degree and size to achieve optimal performance.
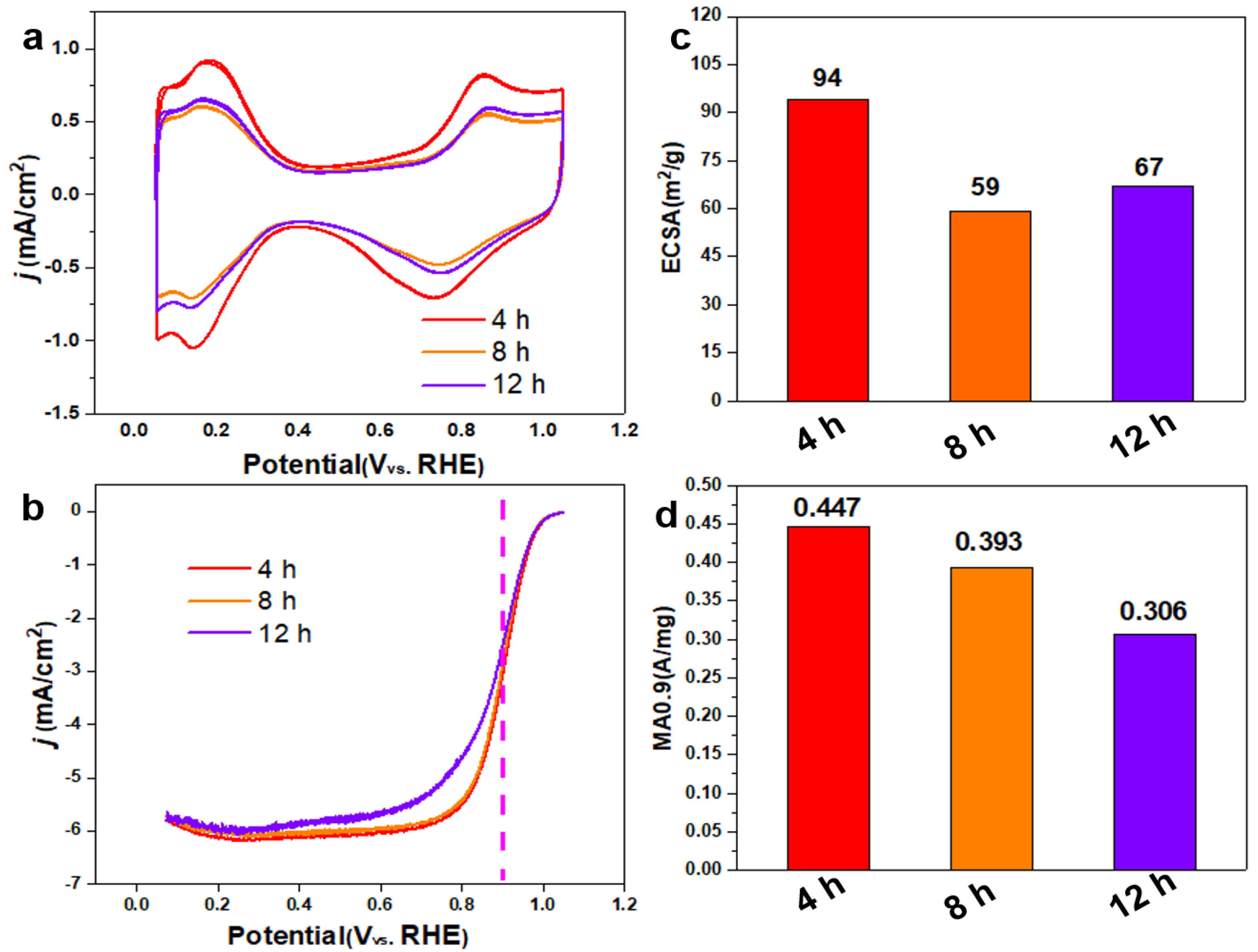
As shown in
Figure 6a, the CV curve shows that the hydrogen adsorption/desorption current density of the prepared 40% Pt
3Co
2/C-4h catalyst (red curve) is higher than that of both Pt
3Co
2/C-8h and Pt
3Co
2/C-12h catalysts, indicating that the ECSA is larger. In addition, according to
Figure 6b, the LSV curves of both Pt
3Co
2/C-4h and Pt
3Co
2/C-8h catalysts show a larger polarization current at 0.9 V than Pt
3Co
2/C-12h. As shown in
Figure 6c, the ECSA values for Pt
3Co
2/C-4h, Pt
3Co
2/C-8h and Pt
3Co
2/C-12h are 94, 59, and 67 m
2/g, respectively. The MA
0.9 values (
Figure 6d) for Pt
3Co
2/C-4h, Pt
3Co
2/C-8h and Pt
3Co
2/C-12h are 0.447, 0.393, and 306 A/mg, respectively. XRD patterns (
Figure 3a) have shown that the ordered intermetallic compounds appear within 4h. Pt
3Co
2/C-4h catalyst possesses an optimized alloying degree and size distribution, so it presents the highest MA
0.9 value.
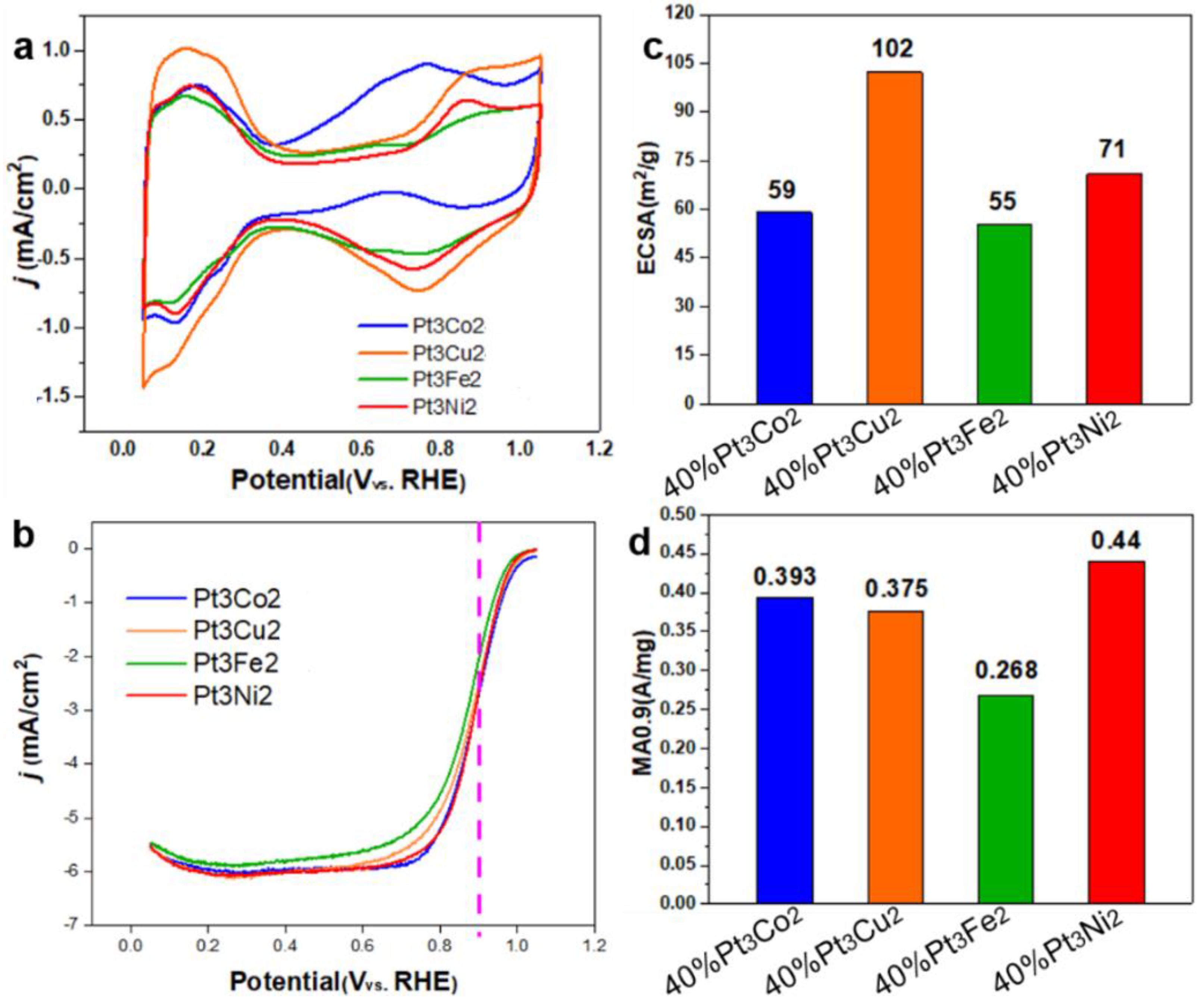
As a meaningful addition, we also studied the electrochemical performance of the obtained catalysts shown in
Figure 4. The CV curves (
Figure 7a) show that the hydrogen adsorption/desorption current density of Pt
3Cu
2/C (orange curve) is higher than that of Pt
3Co
2/C, Pt
3Fe
2/C and Pt
3Ni
2/C catalysts. While, the LSV curve of Pt
3Ni
2/C catalyst shows a largest polarization current at 0.9 V. The ECSA values (
Figure 7c) for Pt
3Cu
2/C, Pt
3Co
2/C, Pt
3Fe
2/C and Pt
3Ni
2/C catalysts are 59, 102, 55, and 71 m
2/g, respectively. The MA
0.9 values (
Figure 7d) for Pt
3Cu
2/C, Pt
3Co
2/C, Pt
3Fe
2/C and Pt
3Ni
2/C are 0.393, 0.375, 0.268, and 0.44 A/mg, respectively. It can be found that the size distribution and activity can be further adjusted by changing the doping metals.
4. Discussion
Above all, the optimized 40% weighted PtCo/C electrocatalyst is Pt
3Co
2/C-4h with ECSA and MA
0.9 value of 94 m
2/g and 0.45 A/mg, which is 2.8 and 1.7 times that of commercial PtCo/C catalysts (TANAKA TKK,
Figure S4). Pt
3Co
2/C-4h catalyst shows superior application potential for DMFCs. In addition, we also find that Pt
3Ni
2/C catalyst is a highly active catalyst with MA
0.9 value of 0.44. As a more potential catalysts, its MA
0.9 value would be further enhanced if the particles size could be well controlled. While, it is of more challenge to synthesize high-loading PtNi/C catalyst with size lower than 4 nm.
5. Conclusions
In summary, this work presents a 40% Pt-weighted sub-4 nm PtCo/C alloy catalysts via a simple incipient wetness impregnation method. The optimized PtCo/C alloy catalyst achieves a high electrochemical surface area achieves of 94 m2/g. Demonstrated by electrochemical oxygen reduction reaction, PtCo/C alloy catalysts present a mass activity of 0.45 A/mg at 0.9 V vs. RHE, which is 1.7 times of PtCo/C-TKK catalyst. The developed PtCo/C alloy catalysts is potential to be a highly practical catalysts for H2-air fuel cells.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on
Preprints.org. Figure S1: TEM image (left) and size distribution (right) of 40% Pt
3Cu
2/C catalyst; Figure S2: TEM image (left) and size distribution (right) of 40% Pt
3Fe
2/C catalyst; Figure S3: TEM image (left) and size distribution (right) of 40% Pt
3Ni
2/C catalyst; Figure S4: CV curve in N
2-saturated 0.1 M HClO
4 (a), iR-corrected LSV curve in O
2-saturated 0.1 M HClO
4 (b) of commercial PtCo/C catalysts (TANAKA TKK).
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Long Kuai; Data curation, Linlin Xiang and Yanyan Zhao; Formal analysis, Yunqin Hu; Funding acquisition, Long Kuai; Methodology, Linlin Xiang and Yunqin Hu; Project administration, Long Kuai; Supervision, Long Kuai; Validation, Sufeng Cao; Writing—original draft, Linlin Xiang; Writing—review & editing, Yanyan Zhao, Sufeng Cao and Long Kuai. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Science and Technology Program of Wuhu (2022yf60), the University Synergy Innovation Program of Anhui Province (GXXT-2022-007), and the foundation from Anhui Polytechnic University (Youth Talent Training Program (2021)) and Anhui Provincial Education Department (gxgnfx2021132).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Nazir, H.; Louis, C.; Jose, S.; Prakash, J.; Muthuswamy, N.; Buan, M.E.M.; Floxf, C.; Chavan, S.; Shi, X.; Kauranen, P.; Kallio, T.; Maia, G.; Tammeveski, K.; Lymperopoulos, N.; Carcadea, E.; Veziroglu, E.; Iranzo, A.; Kannan, A.M. Is the H2 economy realizable in the foreseeable future? Part I: H2 production methods. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2020, 45, 13777–13788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, N.; Song, J.J.; Tao, Q.M.; Kan, E.J.; Kuai, L. High-loading single-atom Pt/TiO2 mesoporous catalysts for superior photocatalytic oxidation of benzyl alcohol. Micropor. Mesopor. Mater. 2022, 337, 111949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amjith, L.R.; Bavanish, B. A review on biomass and wind as renewable energy for sustainable environment. Chemosphere 2022, 293, 133579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, K.; Xuan, J.; Du, Q.; Bao, Z.M.; Xie, B.; Wang, B.W.; Zhao, Y.; Fan, L.H.; Wang, H.Z.; Hou, Z.J.; Huo, S.; Brandon, N.P.; Yin, Y. Designing the Next Generation of Proton-exchange Membrane Fuel Cells. Nature 2021, 595, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Ruiz Diaz, D.F.; Chen, K.S.; Wang, Z.; Adroher, X.C. Materials, Technological Status, and Fundamentals of PEM Fuel Cells-A Review. Mater. Today 2020, 32, 178–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ioroi, T.; Siroma, Z.; Yamazaki, S.I.; Yasuda, K. Electrocatalysts for PEM Fuel Cells. Adv. Energy Mater. 2018, 9, 1801284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.W.; Bukas, V.J.; Park, H.; Park, S.; Diederichsen, K.M.; Lim, J.; Cho, Y.H.; Kim, J.; Kim, W.; Han, T.H.; Voss, J.; Luntz, A.C.; McCloskey, B.D. Mechanisms of Two-Electron and Four-Electron Electrochemical Oxygen Reduction Reactions at Nitrogen-Doped Reduced Graphene Oxide. ACS Catal. 2019, 10, 852–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, F.; Wang, Y.C.; Wu, Z.P.; Chen, G.; Yang, F.; Zhu, S.; Siddharth, K.; Kong, Z.; Lu, A.; Li, J.C.; Zhong, C.J.; Zhou, Z.Y.; Shao, M. Recent Advances in Electrocatalysts for Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells and Alkaline Membrane Fuel Cells. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, e2006292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryoo, R.; Kim, J.; Jo, C.; Han, S.W.; Kim, J.C.; Park, H.; Han, J.; Shin, H.S.; Shin, J.W. Rare-earth-platinum Alloy Nanoparticles in Mesoporous Zeolite for Catalysis. Nature 2020, 585, 221–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.M.; Zhang, D.F.; Guo, L. Structure Design Reveals the Role of Au for ORR Catalytic Performance Optimization in PtCo-Based Catalysts. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 2001575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Li, M.; Gao, M.; Jin, J.; van Spronsen, M.A.; Salmeron, M.B.; Yang, P. High-Performance Pt-Co Nanoframes for Fuel-Cell Electrocatalysis. Nano letter. 2020, 20, 1974–1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, X.; Wang, Y.; Lu, Y.; Zheng, L.; Sun, S.; Li, H.; Chen, G.; Zhang, J. Single-atom Alloy with Pt-Co Dual Sites as an Efficient Electrocatalyst for Oxygen Reduction Reaction. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 2022, 306, 121112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, P.; Pu, M.; Chen, Q.; Zhu, H. Pt-Based Intermetallic Nanocrystals in Cathode Catalysts for Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells: From Precise Synthesis to Oxygen Reduction Reaction Strategy. Catalysts 2021, 11, 1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Z.; Wang, C.; Li, C.; Zeng, Y.; Hwang, S.; Li, B.; Karakalos, S.; Park, J.; Kropf, A.J.; Wegener, E.C.; Gong, Q.; Xu, H.; Wang, G.; Myers, D.J.; Xie, J.; Spendelow, J.S.; Wu, G. Atomically Dispersed Single Iron Sites for Promoting Pt and Pt3Co Fuel Cell Catalysts: Performance and Durability Improvements. Energ. Environ. Sci. 2021, 14, 4948–4960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamenkovic, V.R.; Mun, B.S.; Arenz, M.; Mayrhofer, K.J.J.; Lucas, C.A.; Wang, G.F.; Ross, P.N.; Marković, N.M. Trends in electrocatalysis on extended and nanoscale Pt-bimetallic alloy surfaces. Nat. Mater. 2007, 6, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamenkovic, V.R.; Fowler, B.; Mun, B.S.; Wang, G.F.; Ross, P.N.; Lucas, C.A.; Marković, N.M. Improved Oxygen Reduction Activity on Pt3Ni(111) via Increased Surface Site Availability. Science 2007, 315, 493–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, W.T.; Risch, M.; Stoerzinger, K.A.; Grimaud, A.; Suntivich, J.; Shao-Horn, Y. Toward the rational design of non-precious transition metal oxides for oxygen electrocatalysis. Energy Environ. Sci. 2015, 8, 258–266. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, H.; Gui, R.; Yu, H.; Wang, C.; Liu, S.; Liu, H.F.; Zhou, T.P.; Zhang, N.; Zheng, X.S.; Chu, W.S.; Lin, Y.; Wu, H.A.; Wu, C.Z.; Xie, Y. Subsize Pt-based Intermetallic Compound Enables Long-term Cyclic Mass Activity for Fuel-cell Oxygen Reduction. PNAS 2021, 118, e2104026118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, L.; Wen, J.G.; Kubal, J.; Sen, F.G.; Zou, J.X.; Greeley, J.; Chan, M.; Barkholtz, H.; Ding, W.J.; Liu, D.-J. Ultralow-loading Platinum-cobalt fuel Cell Catalysts Derived Fromimidazolate Frameworks. Science 2018, 362, 1276–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Xin, H.L.; Hovden, R.; Wang, H.; Yu, Y.; Muller, D.A.; DiSalvo, F.J.; Abruna, H.D. Structurally Ordered Intermetallic Platinum-cobalt Core-shell Nanoparticles with Enhanced Activity and Stability as Oxygen Reduction Electrocatalysts. Nat. Mater. 2013, 12, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Ma, M.; Tu, F. Recent advances in high-loading catalysts for low-temperature fuel cells: From nanoparticle to single atom. SusMat 2021, 1, 569–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Xi, Z.; Pan, Y.T.; Spendelow, J.S.; Duchesne, P.N.; Su, D.; Li, Q.; Yu, C.; Yin, Z.; Shen, B.; Kim, Y.S.; Zhang, P.; Sun, S. Fe Stabilization by Intermetallic L10-FePt and Pt Catalysis Enhancement in L10-FePt/Pt Nanoparticles for Efficient Oxygen Reduction Reaction in Fuel Cells. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 2926–2932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.-L.; Wang, L.-N.; Yin, P.; Liu, J.Y.; Chen, M.-X.; Yan, Q.-Q.; Wang, Z.-S.; Xu, S.-L.; Chu, S.-Q.; Cui, C.H.; Ju, H.X.; Zhu, J.F.; Lin, Y.; Shui, J.L.; Liang, H.-W. Sulfur-anchoring Synthesis of Platinum Intermetallic Nanoparticle Catalysts for Fuel Cells. Science 2021, 374, 459–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Sharma, S.; Liu, X.; Pan, Y.-T.; Spendelow, J.S.; Chi, M.; Jia, Y.; Zhang, P.; Cullen, D.A.; Xi, Z.; Lin, H.; Yin, Z.; Shen, B.; Muzzio, M.; Yu, C.; Kim, Y.S.; Peterson, A.A.; More, K.L.; Zhu, H.; Sun, S. Hard-Magnet L10-CoPt Nanoparticles Advance Fuel Cell Catalysis. Joule 2019, 3, 124–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.; Wang, P.; Su, C.J.; Liu, H.F.; Tai, X.L.; Zhang, N.; Lv, H.F.; Lin, Y.; Chu, W.S.; Wu, X.J.; Wu, C.Z.; Xie, Y. Epitaxial growth of ultrathin highly crystalline Pt-Ni nanostructure on a metal carbide template for efficient oxygen reduction reaction. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, 2109188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Figure 1.
Lower (a) and higher (b) magnification TEM images, size distributions of supported nanoparticles (c) and HAADF-STEM-EDS-mappings of Pt3Co2/C-8h catalysts with Pt loading of 40%.
Figure 1.
Lower (a) and higher (b) magnification TEM images, size distributions of supported nanoparticles (c) and HAADF-STEM-EDS-mappings of Pt3Co2/C-8h catalysts with Pt loading of 40%.
Figure 2.
XRD patterns (a) of Pt3Co1/C-8h (black curve), Pt3Co2/C-8h (red curve) and Pt1Co1/C-8h (blue curve) catalysts. TEM images (b,d), size distributions (c,e) of supported nanoparticles of Pt3Co1/C-8h (b,c) and Pt1Co1/C-8h (d,e) catalysts.
Figure 2.
XRD patterns (a) of Pt3Co1/C-8h (black curve), Pt3Co2/C-8h (red curve) and Pt1Co1/C-8h (blue curve) catalysts. TEM images (b,d), size distributions (c,e) of supported nanoparticles of Pt3Co1/C-8h (b,c) and Pt1Co1/C-8h (d,e) catalysts.
Figure 3.
XRD patterns (a) of Pt3Co2/C-4h (black curve), Pt3Co2/C-8h (red curve) and Pt3Co2/C-12h (blue curve) catalysts. TEM images (b,d), size distributions (c,e) of supported nanoparticles of Pt3Co2/C-4h (b,c) and Pt3Co2/C-12h (d,e) catalysts.
Figure 3.
XRD patterns (a) of Pt3Co2/C-4h (black curve), Pt3Co2/C-8h (red curve) and Pt3Co2/C-12h (blue curve) catalysts. TEM images (b,d), size distributions (c,e) of supported nanoparticles of Pt3Co2/C-4h (b,c) and Pt3Co2/C-12h (d,e) catalysts.
Figure 4.
HAADF-STEM-EDS-mappings of Pt3Cu2/C (a), Pt3Fe2/C (b) and Pt3Ni2/C (c) catalysts with Pt loading of 40%.
Figure 4.
HAADF-STEM-EDS-mappings of Pt3Cu2/C (a), Pt3Fe2/C (b) and Pt3Ni2/C (c) catalysts with Pt loading of 40%.
Figure 5.
CV curves in N2-saturated 0.1 M HClO4 (a), iR-corrected LSV curves in O2-saturated 0.1 M HClO4 (b), ECSA (c) and MA values (d) of Pt3Co1/C-8h, Pt3Co2/C-8h and Pt1Co1/C-8h. The measurements were performed on a RDE with rotating speed of 1600 rpm at room temperature.
Figure 5.
CV curves in N2-saturated 0.1 M HClO4 (a), iR-corrected LSV curves in O2-saturated 0.1 M HClO4 (b), ECSA (c) and MA values (d) of Pt3Co1/C-8h, Pt3Co2/C-8h and Pt1Co1/C-8h. The measurements were performed on a RDE with rotating speed of 1600 rpm at room temperature.
Figure 6.
CV curves in N2-saturated 0.1 M HClO4 (a), iR-corrected LSV curves in O2-saturated 0.1 M HClO4 (b), ECSA (c) and MA values (d) of Pt3Co2/C-4h, Pt3Co2/C-8h and Pt3Co2/C-12h. The measurements were performed on a RDE with rotating speed of 1600 rpm at room temperature.
Figure 6.
CV curves in N2-saturated 0.1 M HClO4 (a), iR-corrected LSV curves in O2-saturated 0.1 M HClO4 (b), ECSA (c) and MA values (d) of Pt3Co2/C-4h, Pt3Co2/C-8h and Pt3Co2/C-12h. The measurements were performed on a RDE with rotating speed of 1600 rpm at room temperature.
Figure 7.
CV curves in N2-saturated 0.1 M HClO4 (a), iR-corrected LSV curves in O2-saturated 0.1 M HClO4 (b), ECSA (c) and MA values (d) of Pt3Co1/C-8h, Pt3Co2/C-8h and Pt1Co1/C-8h. The measurements were performed on a RDE with rotating speed of 1600 rpm at room temperature.
Figure 7.
CV curves in N2-saturated 0.1 M HClO4 (a), iR-corrected LSV curves in O2-saturated 0.1 M HClO4 (b), ECSA (c) and MA values (d) of Pt3Co1/C-8h, Pt3Co2/C-8h and Pt1Co1/C-8h. The measurements were performed on a RDE with rotating speed of 1600 rpm at room temperature.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).