Submitted:
30 May 2023
Posted:
30 May 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture
2.2. Treatments protocols and reagents
2.3. SIRT5 Activator
2.4. Generation of GLS1-silenced cells
2.5. Trypan blue assay
2.6. Flow Cytometry
2.7. Clonogenicity Assay
2.8. Proteins extraction and immunoblotting
2.9. Immunofluorescence
2.10. Measurements of Reactive Oxygen Species
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. MC3138 and lanthanum acetate effect on cancer cell lines
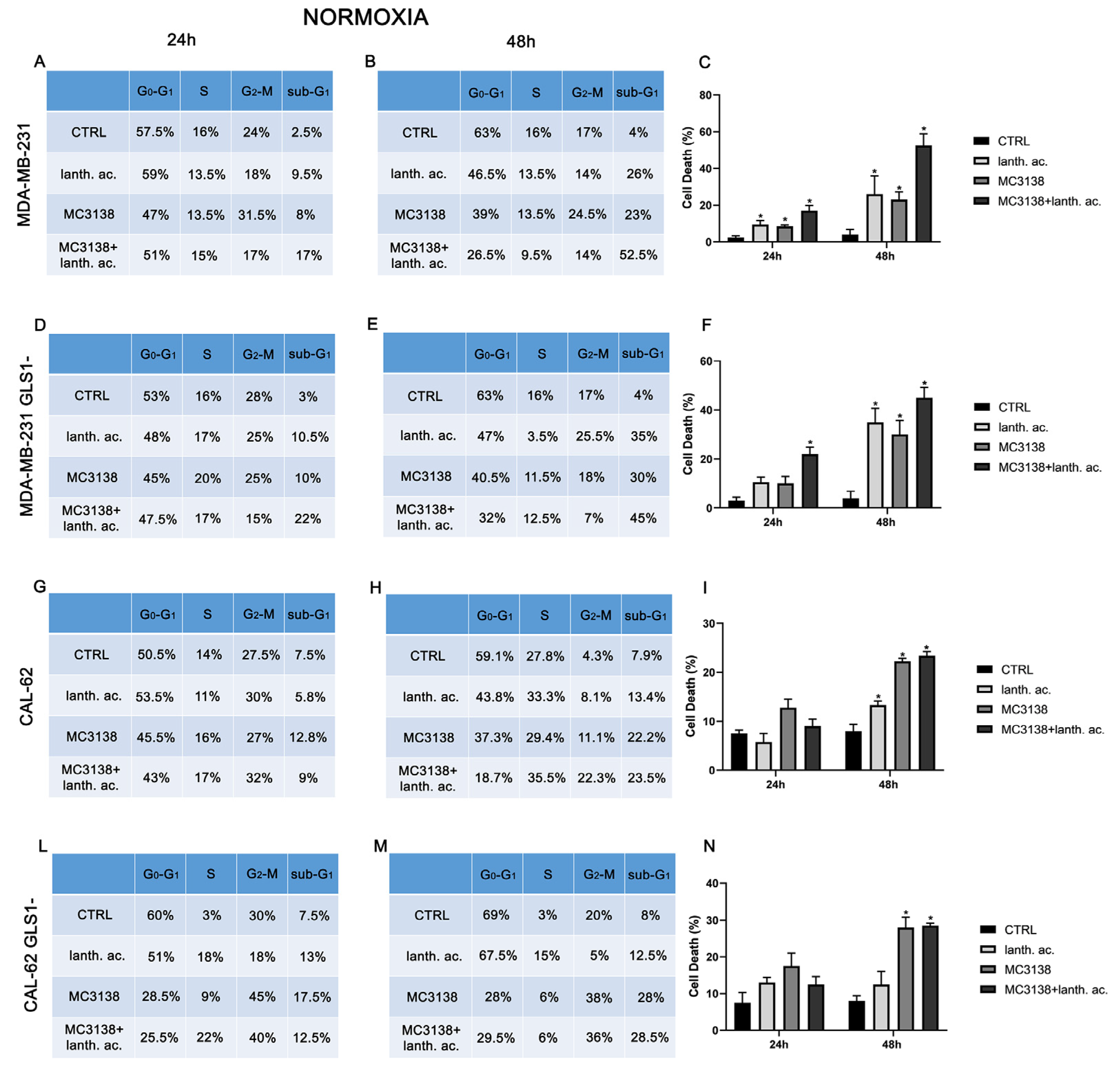
3.2. Cell cycle and cell death after MC3138 and lanthanum acetate treatment
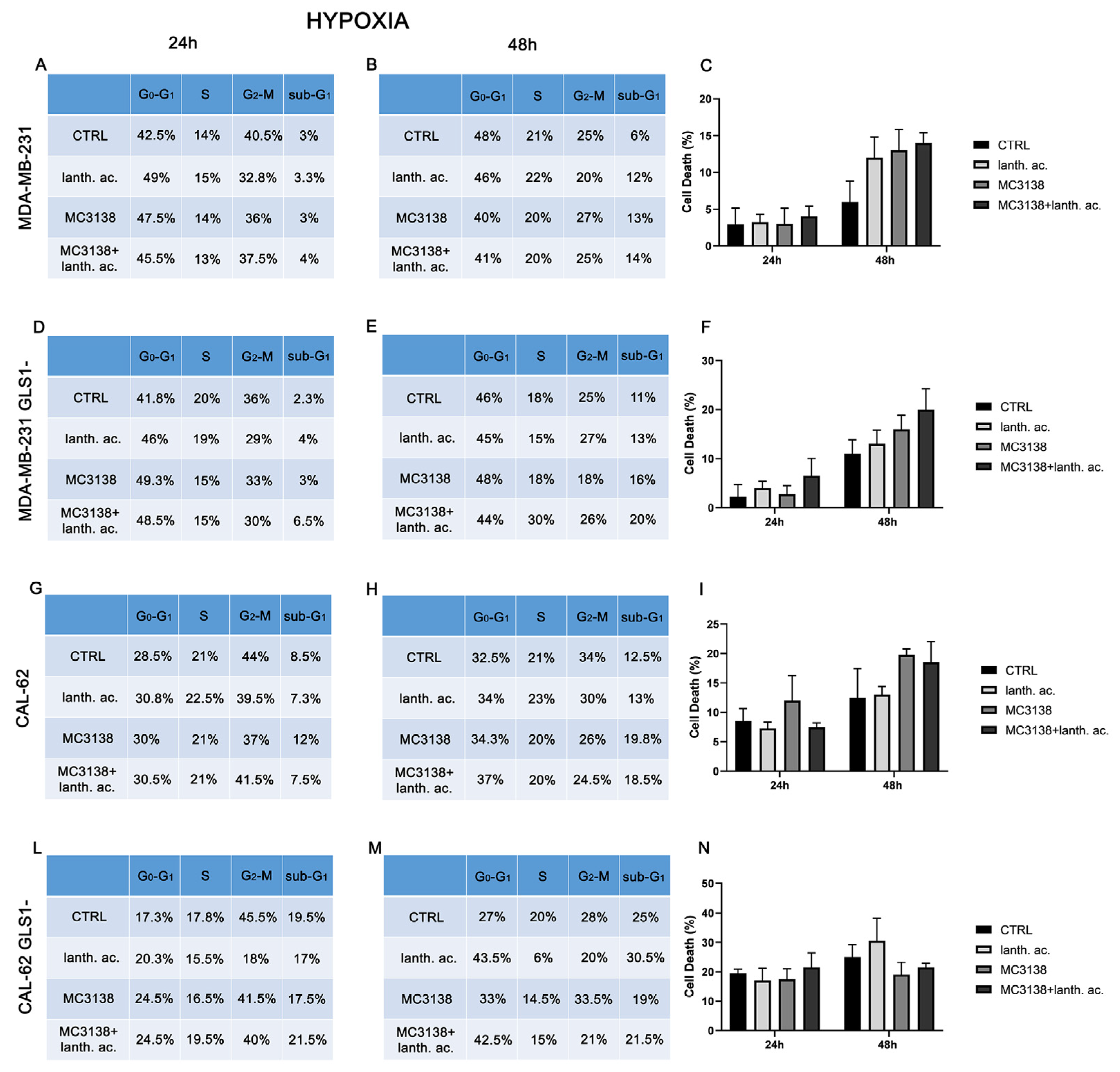
3.3. Cell cycle and cell death after MC3138 and lanthanum acetate treatment under hypoxia
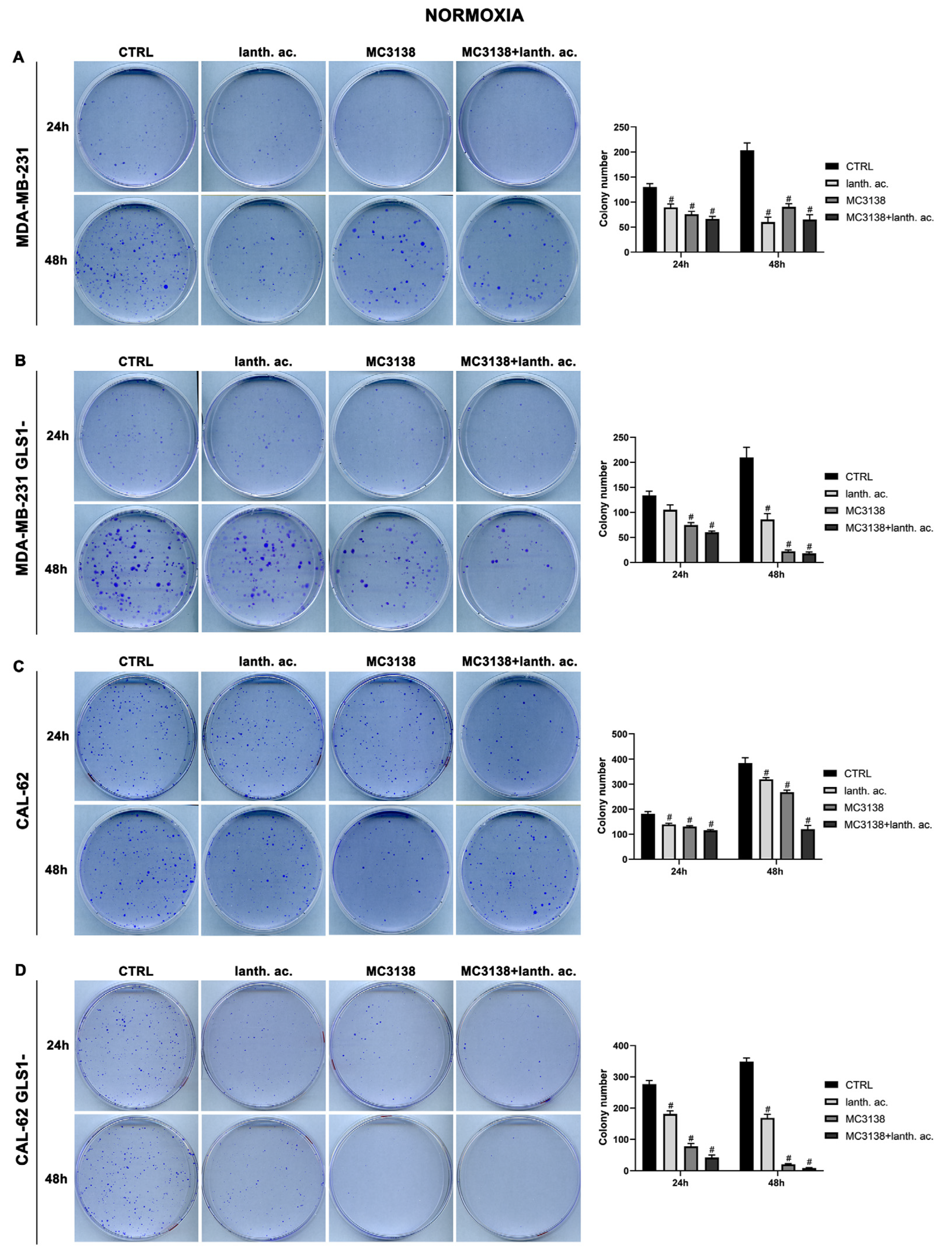
3.4. MC3138 and lanthanum acetate treatment reduces colonies formation.
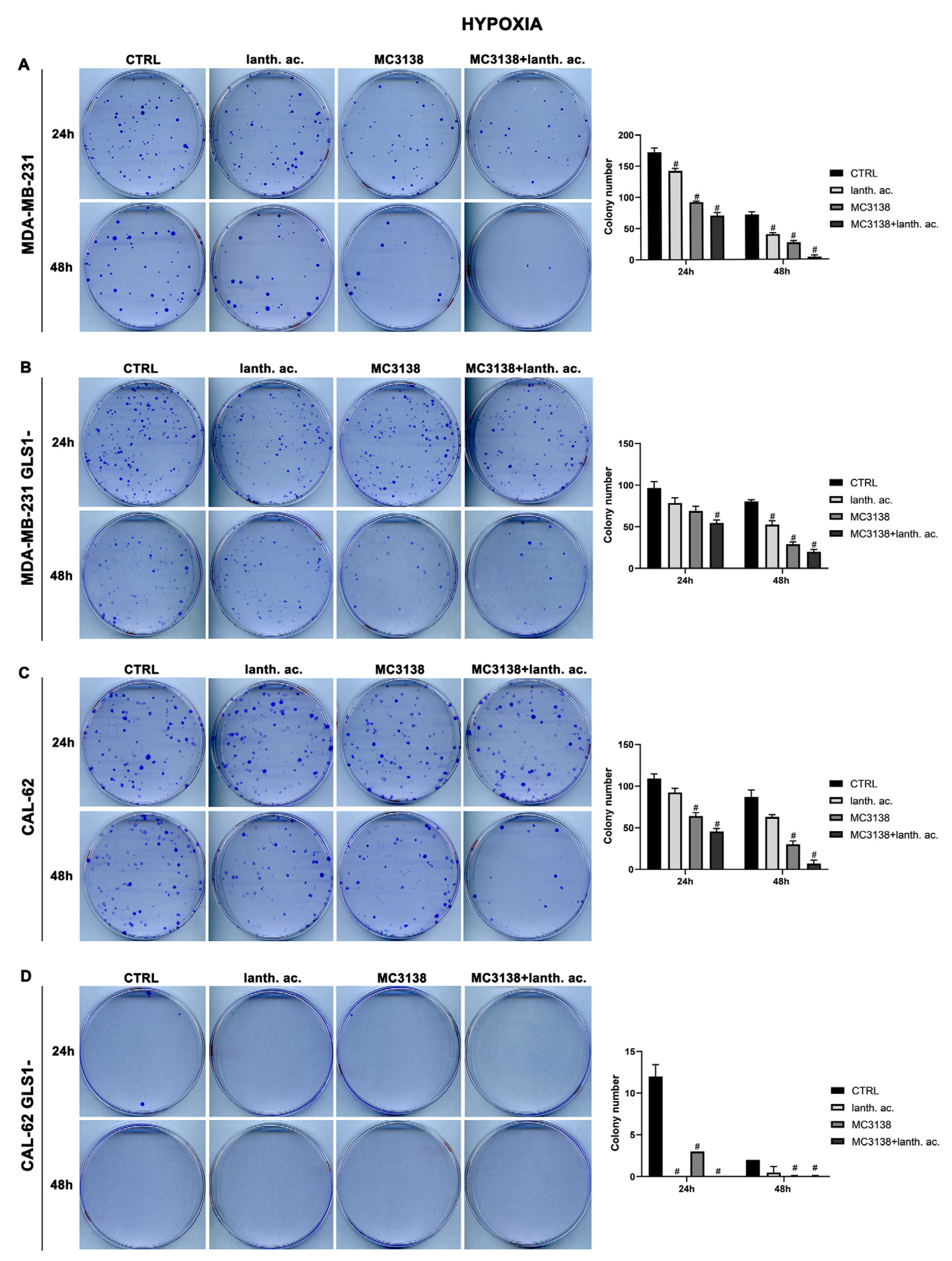
3.5. Colony formation after MC3138 and lanthanum acetate treatment under hypoxia
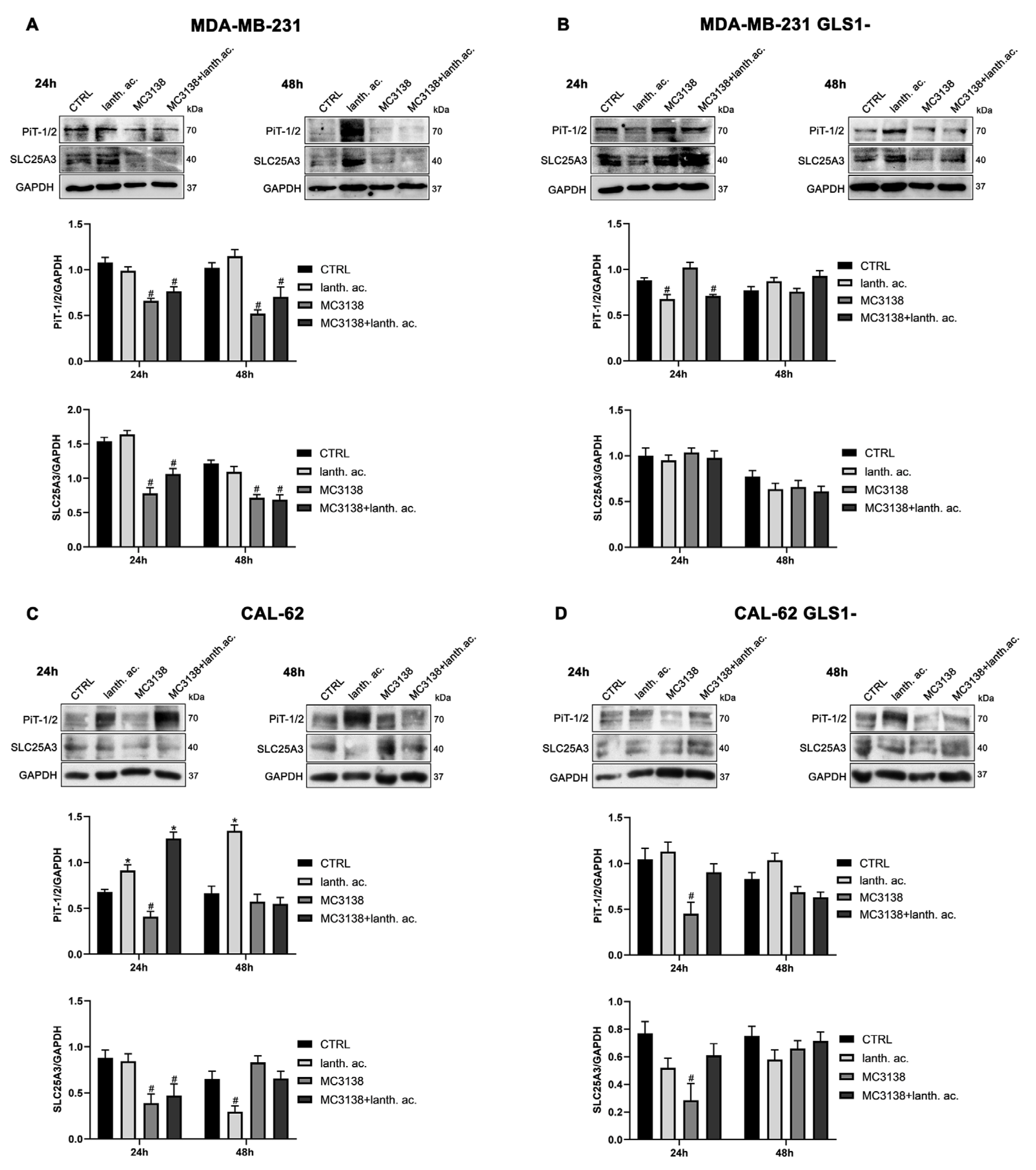
3.6. MC3138 reduces the expression of phosphate transporters.
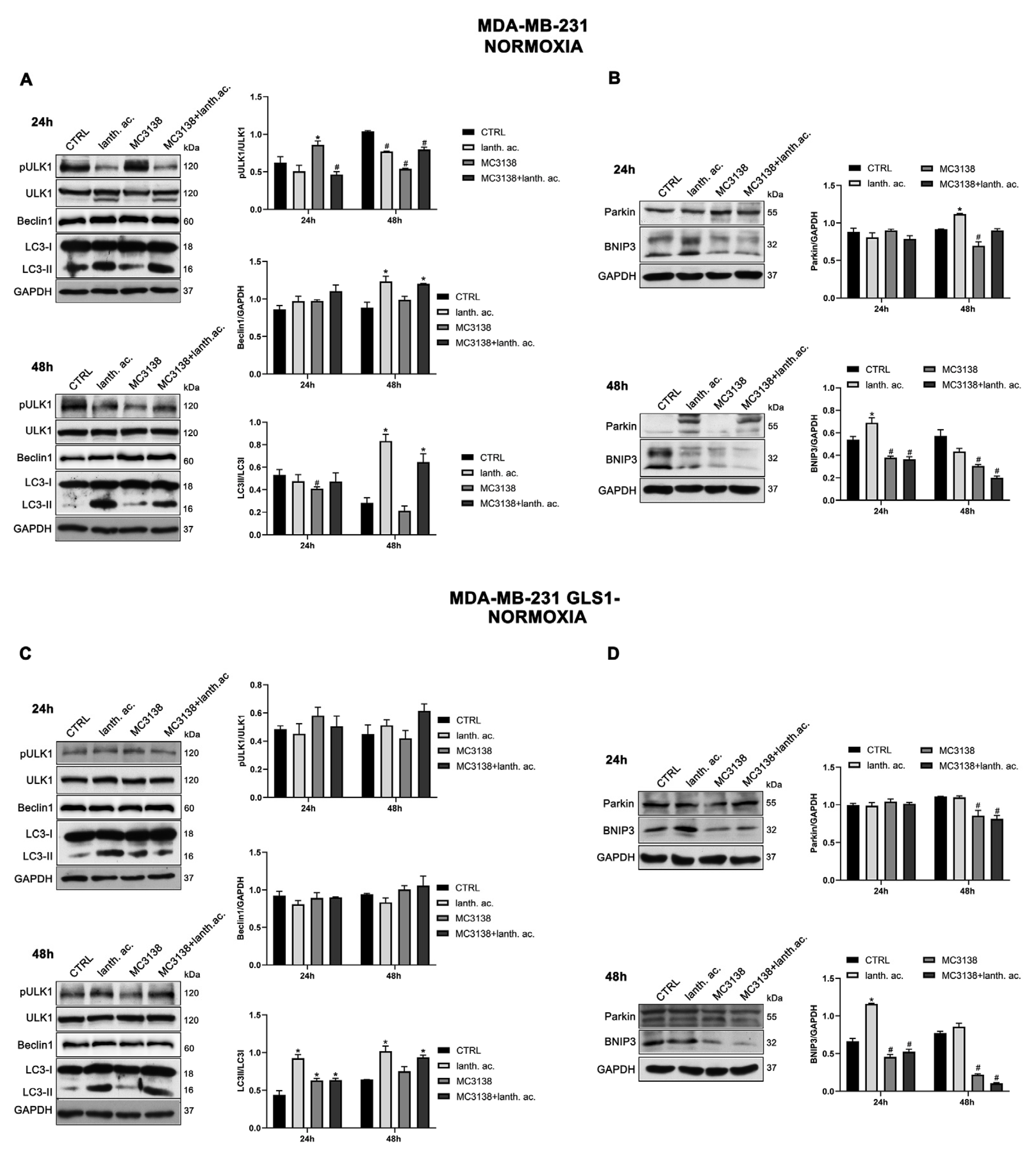
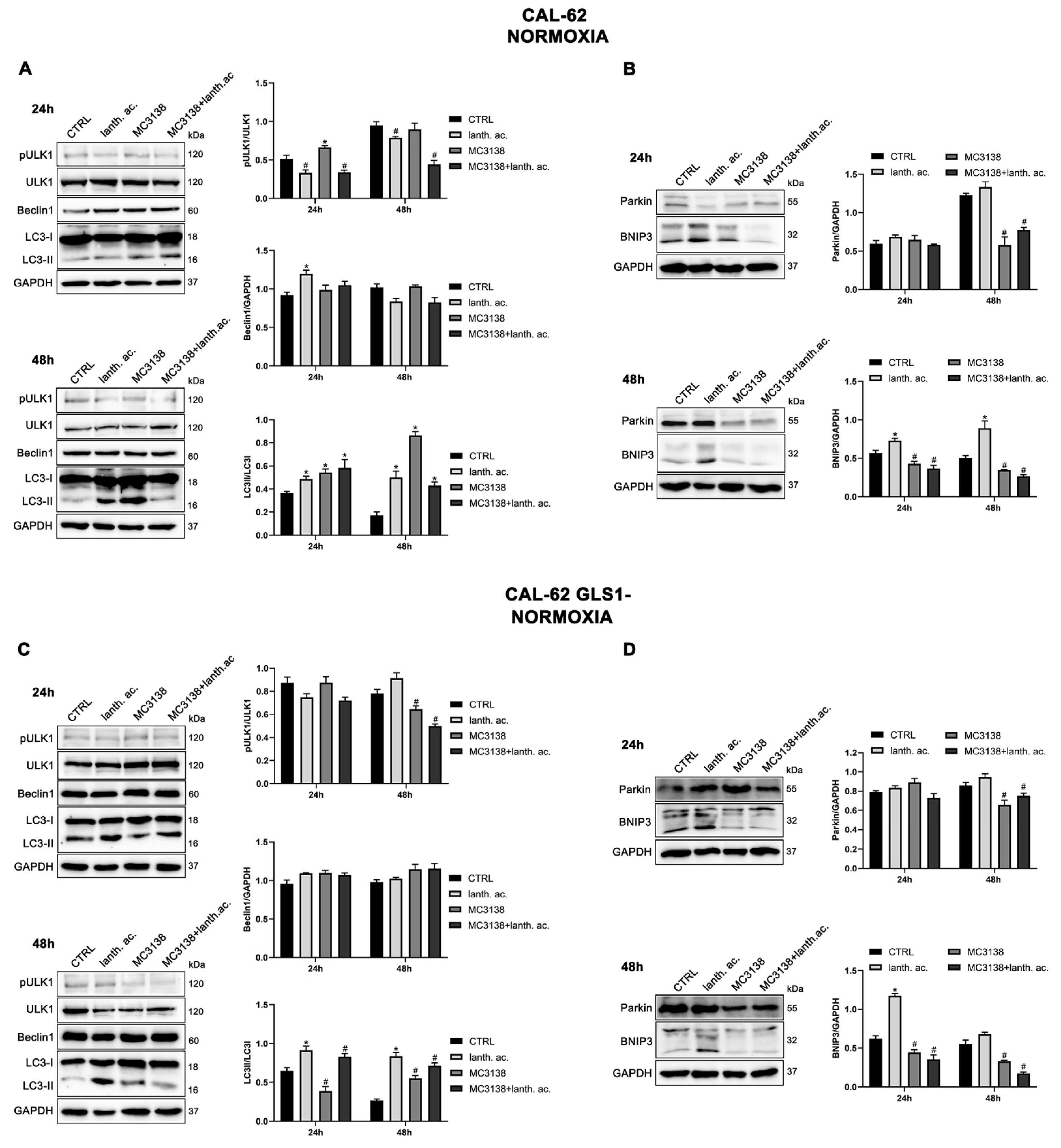
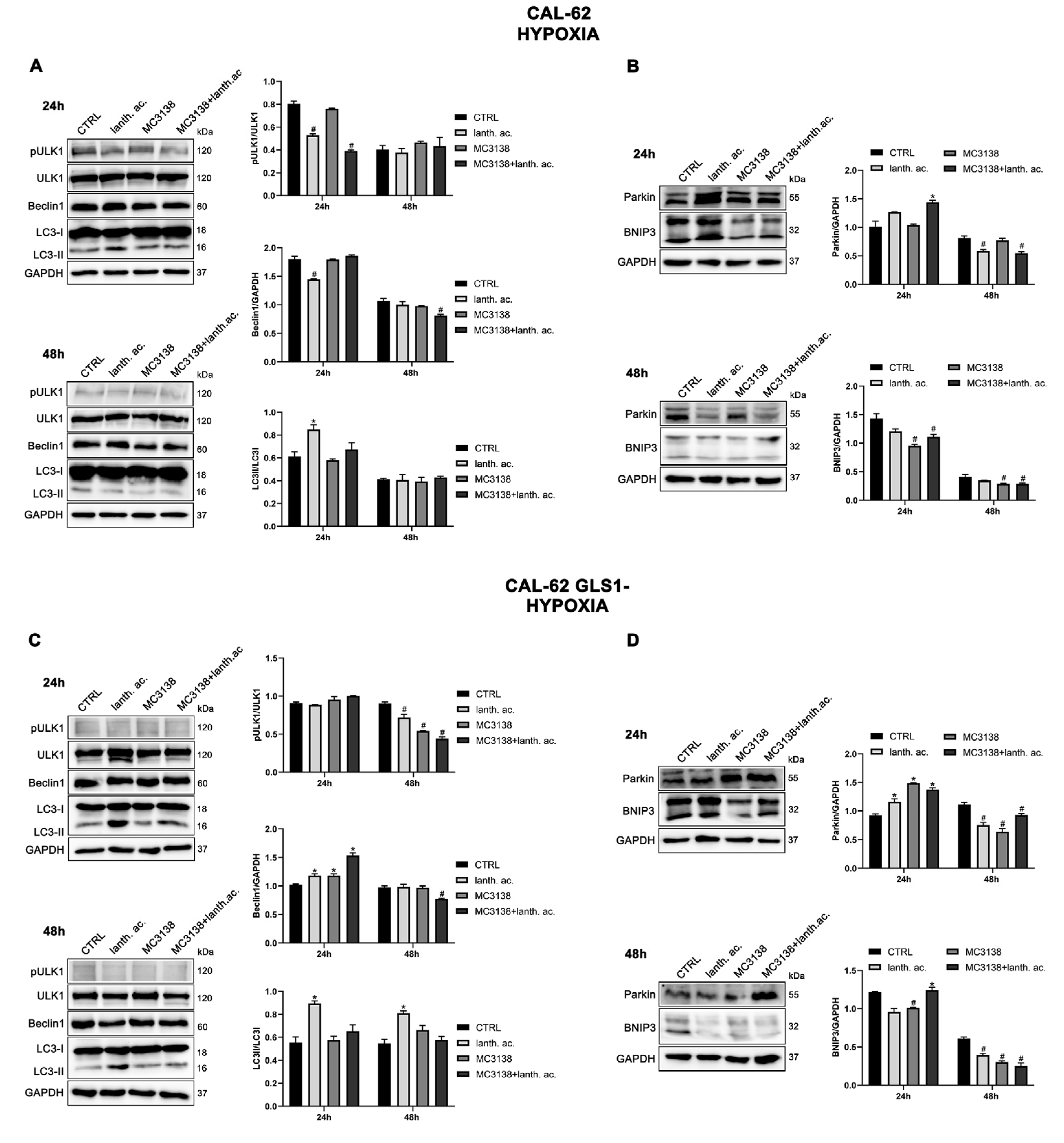
3.6. Autophagy and mitophagy are affected by treatment with MC3138 and lanthanum acetate.
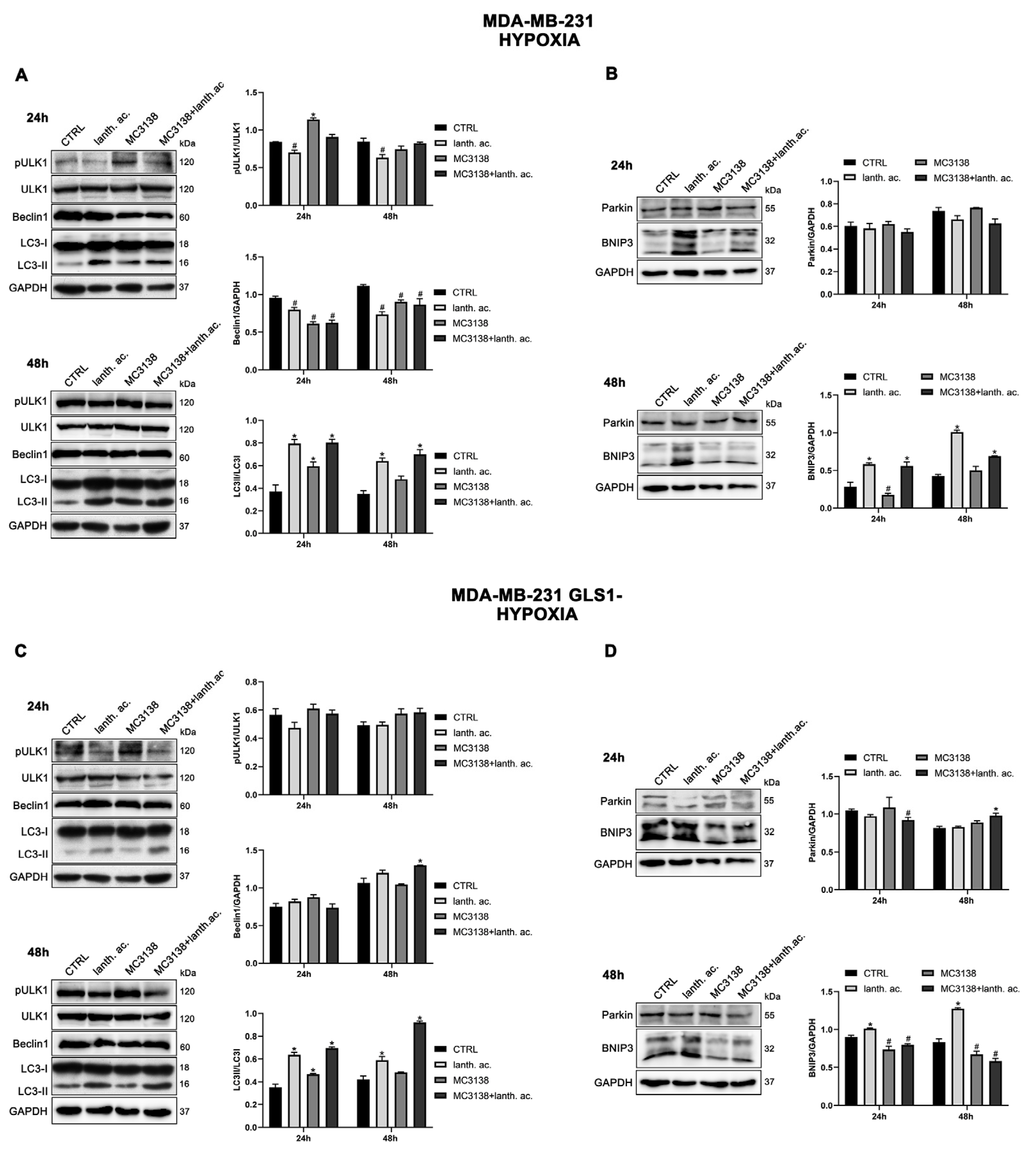
3.7. Autophagy and mitophagy with MC3138 and lanthanum acetate in the presence of hypoxia.
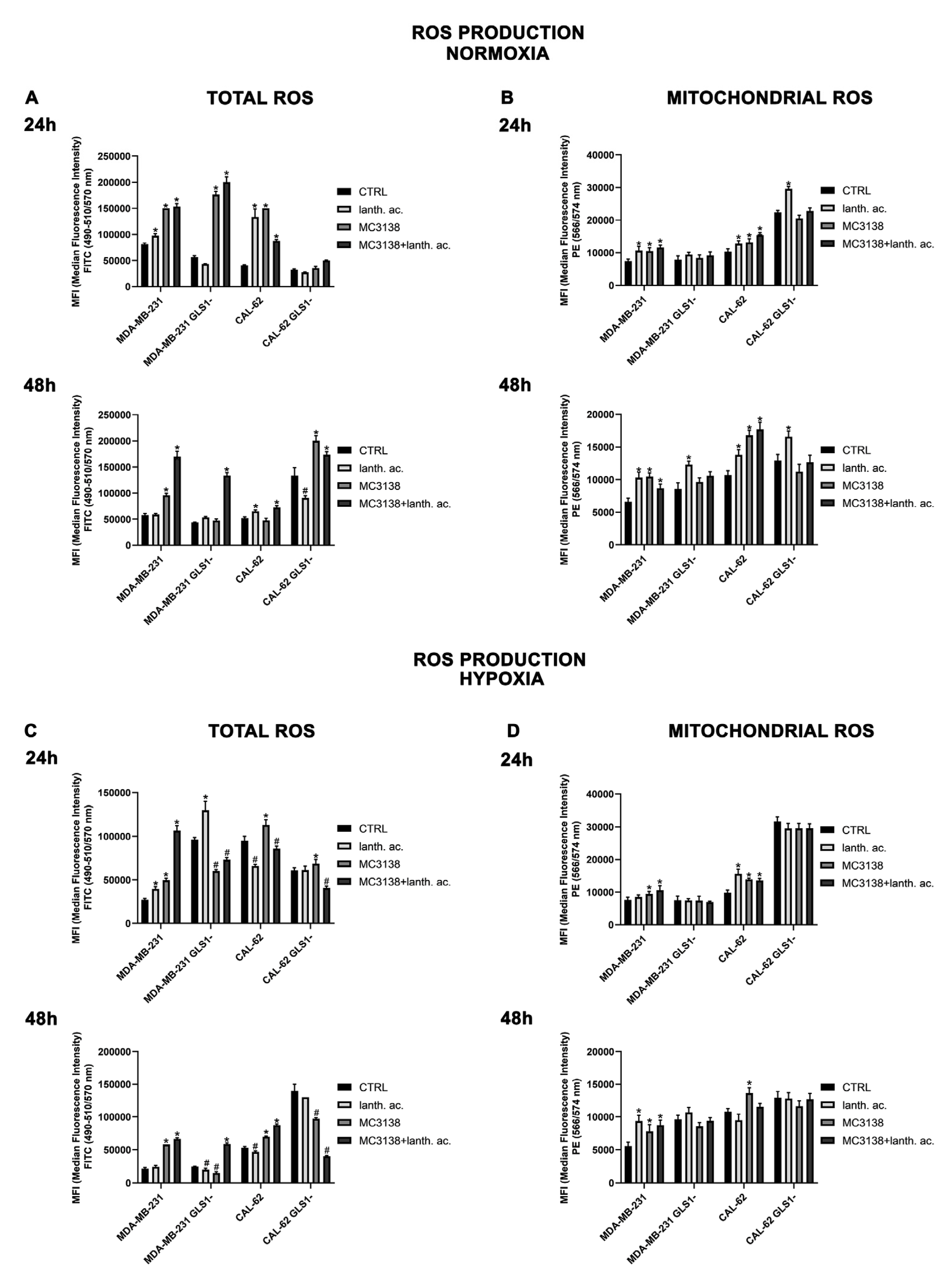
3.8. MC3138 and lanthanum acetate increase cytosolic and mitochondrial ROS under normoxia and hypoxia.
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Martínez-Reyes, I.; Chandel, N.S. Cancer metabolism: looking forward. Nat Rev Cancer. 2021, 21, 669–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ward, P.S.; Thompson, C.B. Metabolic reprogramming: a cancer hallmark even Warburg did not anticipate. Cancer Cell. 2012, 21, 297–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weinberg, S.E.; Chandel, N.S. Targeting mitochondria metabolism for cancer therapy. Nat Chem Biol. 2015, 11, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hay, N. Reprogramming glucose metabolism in cancer: can it be exploited for cancer therapy? Nat Rev Cancer. 2016, 16, 635–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Copeland, C.; Le, A. Glutamine Metabolism in Cancer. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2021, 1311, 17–38. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Medina, M.A.; Sánchez-Jiménez, F.; Márquez, J.; Rodríguez Quesada, A.; Núñez de Castro, I. Relevance of glutamine metabolism to tumor cell growth. Mol Cell Biochem. 1992, 113, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasa, M.; Bode, B.P.; Abcouwer, S.F.; Collins, C.L.; Tanabe, K.K.; Souba, W.W. Glutamine as a regulator of DNA and protein biosynthesis in human solid tumor cell lines. Ann Surg. 1996, 224, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asantewaa, G.; Harris, I.S. Glutathione and its precursors in cancer. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2021, 68, 292–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaadige, M.R.; Looper, R.E.; Kamalanaadhan, S.; Ayer, D.E. Glutamine-dependent anapleurosis dictates glucose uptake and cell growth by regulating Mondo A transcriptional activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009, 106, 14878–14883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szeliga, M.; Obara-Michlewska, M. Glutamine in neoplastic cells: focus on the expression and roles of glutaminases. Neurochem Int. 2009, 55, 71–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Venneti, S.; Nagrath, D. Glutaminolysis: A Hallmark of Cancer Metabolism. Annu Rev Biomed Eng. 2017, 19, 163–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, M.M.; Adamoski, D.; Dos Reis, L.M.; Ascenção, C.F.R.; de Oliveira, K.R.S.; Mafra, A.C.P.; da Silva Bastos, A.C.; Quintero, M.; de G Cassago, C.; Ferreira, I.M.; Fidelis, C.H.V.; Rocco, S.A.; Bajgelman, M.C.; Stine, Z.; Berindan-Neagoe, I.; Calin, G.A.; Ambrosio, A.L.B.; Dias, S.M.G. GLS2 is protumorigenic in breast cancers. Oncogene. 2020, 39, 690–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seltzer, M.J.; Bennett, B.D.; Joshi, A.D.; Gao, P.; Thomas, A.G.; Ferraris, D.V.; Tsukamoto, T.; Rojas, C.J.; Slusher, B.S.; Rabinowitz, J.D.; Dang, C.V.; Riggins, G.J. Inhibition of glutaminase preferentially slows growth of glioma cells with mutant IDH1. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 8981–8987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van den Heuvel, A.P.; Jing, J.; Wooster, R.F.; Bachman, K.E. Analysis of glutamine dependency in non-small cell lung cancer: GLS1 splice variant GAC is essential for cancer cell growth. Cancer Biol Ther. 2012, 13, 1185–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Timmerman, L.A.; Holton, T.; Yuneva, M.; Louie, R.J.; Padró, M.; Daemen, A.; Hu, M.; Chan, D.A.; Ethier, S.P.; van 't Veer, L.J.; Polyak, K.; McCormick, F.; Gray, J.W. Glutamine sensitivity analysis identifies the xCT antiporter as a common triple-negative breast tumor therapeutic target. Cancer Cell. 2013, 24, 450–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dias, M.M.; Adamoski, D.; Dos Reis, L.M.; Ascenção, C.F.R.; de Oliveira, K.R.S.; Mafra, A.C.P.; da Silva Bastos, A.C.; Quintero, M.; de G Cassago, C.; Ferreira, I.M.; Fidelis, C.H.V.; Rocco, S.A.; Bajgelman, M.C.; Stine, Z.; Berindan-Neagoe, I.; Calin, G.A.; Ambrosio, A.L.B.; Dias, S.M.G. GLS2 is protumorigenic in breast cancers. Oncogene. 2020, 39, 690–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cassago, A.; Ferreira, A.P.; Ferreira, I.M.; Fornezari, C.; Gomes, E.R.; Greene, K.S.; Pereira, H.M.; Garratt, R.C.; Dias, S.M.; Ambrosio, A.L. Mitochondrial localization and structure-based phosphate activation mechanism of Glutaminase C with implications for cancer metabolism. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012, 109, 1092–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.T.; Ramachandran, S.; Hill, M.J.; Cerione, R.A. High-resolution structures of mitochondrial glutaminase C tetramers indicate conformational changes upon phosphate binding. J Biol Chem. 2022, 298, 101564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papaloucas, C.D.; Papaloucas, M.D.; Kouloulias, V.; Neanidis, K.; Pistevou-Gompaki, K.; Kouvaris, J.; Zygogianni, A.; Mystakidou, K.; Papaloucas, A.C. Measurement of blood phosphorus: a quick and inexpensive method for detection of the existence of cancer in the body. Too good to be true, or forgotten knowledge of the past? Med Hypotheses. 2014, 82, 24–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobko, A.A.; Eubank, T.D.; Driesschaert, B.; Dhimitruka, I.; Evans, J.; Mohammad, R.; Tchekneva, E.E.; Dikov, M.M.; Khramtsov, V.V. Interstitial Inorganic Phosphate as a Tumor Microenvironment Marker for Tumor Progression. Sci Rep. 2017, 7, 41233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frye, R.A. Phylogenetic classification of prokaryotic and eukaryotic Sir2-like proteins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2000, 273, 793–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, B.C.; Denu, J.M. Sir2 protein deacetylases: evidence for chemical intermediates and functions of a conserved histidine. Biochemistry. 2006, 45, 272–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houtkooper, R.H.; Pirinen, E.; Auwerx, J. Sirtuins as regulators of metabolism and healthspan. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2012, 13, 225–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Lombard, D.B. Mitochondrial sirtuins and their relationships with metabolic disease and cancer. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2015, 22, 1060–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osborne, B.; Bentley, N.L.; Montgomery, M.K.; Turner, N. The role of mitochondrial sirtuins in health and disease. Free Radic Biol Med. 2016, 100, 164–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karaca, M.; Frigerio, F.; Maechler, P. From pancreatic islets to central nervous system, the importance of glutamate dehydrogenase for the control of energy homeostasis. Neurochem Int. 2011, 59, 510–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polletta, L.; Vernucci, E.; Carnevale, I.; Arcangeli, T.; Rotili, D.; Palmerio, S.; Steegborn, C.; Nowak, T.; Schutkowski, M.; Pellegrini, L.; Sansone, L.; Villanova, L.; Runci, A.; Pucci, B.; Morgante, E.; Fini, M.; Mai, A.; Russo, M.A.; Tafani, M. SIRT5 regulation of ammonia-induced autophagy and mitophagy. Autophagy. 2015, 11, 253–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greene, K.S.; Lukey, M.J.; Wang, X.; Blank, B.; Druso, J.E.; Lin, M.J.; Stalnecker, C.A.; Zhang, C.; Negrón Abril, Y.; Erickson, J.W.; Wilson, K.F.; Lin, H.; Weiss, R.S.; Cerione, R.A. SIRT5 stabilizes mitochondrial glutaminase and supports breast cancer tumorigenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019, 116, 26625–26632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, T.; Shukla, S.K.; Vernucci, E.; He, C.; Wang, D.; King, R.J.; Jha, K.; Siddhanta, K.; Mullen, N.J.; Attri, K.S.; Murthy, D.; Chaika, N.V.; Thakur, R.; Mulder, S.E.; Pacheco, C.G.; Fu, X.; High, R.R.; Yu, F.; Lazenby, A.; Steegborn, C.; Lan, P.; Mehla, K.; Rotili, D.; Chaudhary, S.; Valente, S.; Tafani, M.; Mai, A.; Auwerx, J.; Verdin, E.; Tuveson, D.; Singh, P.K. Metabolic Rewiring by Loss of Sirt5 Promotes Kras-Induced Pancr,eatic Cancer Progression. Gastroenterology. 2021, 161, 1584–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.Q.; Wang, H.L.; Xu, J.; Tan, J.; Fu, L.N.; Wang, J.L.; Zou, T.H.; Sun, D.F.; Gao, Q.Y.; Chen, Y.X.; Fang, J.Y. Sirtuin5 contributes to colorectal carcinogenesis by enhancing glutaminolysis in a deglutarylation-dependent manner. Nat Commun. 2018, 9, 545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suenkel, B.; Valente, S.; Zwergel, C.; Weiss, S.; Di Bello, E.; Fioravanti, R.; Aventaggiato, M.; Amorim, J.A.; Garg, N.; Kumar, S.; Lombard, D.B.; Hu, T.; Singh, P.K.; Tafani, M.; Palmeira, C.M.; Sinclair, D.; Mai, A.; Steegborn, C. Potent and Specific Activators for Mitochondrial Sirtuins Sirt3 and Sirt5. J Med Chem. 2022, 65, 14015–14031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; He, S.; Ma, B. Autophagy and autophagy-related proteins in cancer. Mol Cancer. 2020, 19, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorman, M.W.; He, M.X.; Hall, C.S.; Sparks, H.V. Inorganic phosphate as regulator of adenosine formation in isolated guinea pig hearts. Am J Physiol. 1997, 272 (2 Pt 2), H913–H920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- K-Laflamme, A.; Oster, L.; Cardinal, R.; de Champlain, J. Effects of renin-angiotensin blockade on sympathetic reactivity and beta-adrenergic pathway in the spontaneously hypertensive rat. Hypertension. 1997, 30 (2 Pt 1), 278–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inden, M.; Iriyama, M.; Zennami, M.; Sekine, S.I.; Hara, A.; Yamada, M.; Hozumi, I. The type III transporters (PiT-1 and PiT-2) are the major sodium-dependent phosphate transporters in the mice and human brains. Brain Res. 2016, 1637, 128–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peoples, J.N.; Ghazal, N.; Duong, D.M.; Hardin, K.R.; Manning, J.R.; Seyfried, N.T.; Faundez, V.; Kwong, J.Q. Loss of the mitochondrial phosphate carrier SLC25A3 induces remodeling of the cardiac mitochondrial protein acylome. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2021, 321, C519–C534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aventaggiato, M.; Vernucci, E.; Barreca, F.; Russo, M.A.; Tafani, M. Sirtuins' control of autophagy and mitophagy in cancer. Pharmacol Ther. 2021, 221, 107748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naumann, C.; Müller, J.; Sakhonwasee, S.; Wieghaus, A.; Hause, G.; Heisters, M.; Bürstenbinder, K.; Abel, S. The Local Phosphate Deficiency Response Activates Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress-Dependent Autophagy [published correction appears in Plant Physiol. 2020 Dec;184(4):2240-2241]. Plant Physiol. 2019, 179, 460–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Kundu, M.; Viollet, B.; Guan, K.L. AMPK and mTOR regulate autophagy through direct phosphorylation of Ulk1. Nat Cell Biol. 2011, 13, 132–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poole, L.P.; Macleod, K.F. Mitophagy in tumorigenesis and metastasis. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021, 78, 3817–3851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moloney, J.N.; Cotter, T.G. ROS signalling in the biology of cancer. Semin Cell Dev Biol 2018, 80, 50–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mak, T.W.; Grusdat, M.; Duncan, G.S.; Dostert, C.; Nonnenmacher, Y.; Cox, M.; Binsfeld, C.; Hao, Z.; Brüstle, A.; Itsumi, M.; Jäger, C.; Chen, Y.; Pinkenburg, O.; Camara, B.; Ollert, M.; Bindslev-Jensen, C.; Vasiliou, V.; Gorrini, C.; Lang, P.A.; Lohoff, M.; Harris, I.S.; Hiller, K.; Brenner, D. Glutathione Primes T Cell Metabolism for Inflammation [published correction appears in Immunity. 2017 Jun 20;46(6):1089-1090]. Immunity. 2017, 46, 675–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ueno, T.; Komatsu, M. Autophagy in the liver: functions in health and disease. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017, 14, 170–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bi, Q.C.; Luo, R.G.; Li, Y.S.; Zhao, J.; Fu, X.; Chen, H.; Lv, Y.F.; Liu, Z.X.; Liang, Q.R.; Tang, Q. Low Inorganic Phosphate Stress Inhibits Liver Cancer Progression: from In Vivo to In Vitro. Advanced Therapeutics. 2021, 5, 2100224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houtkooper, R.H.; Pirinen, E.; Auwerx, J. Sirtuins as regulators of metabolism and healthspan. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2012, 13, 225–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, M.; Li, S.; Chen, Y.; Wang, M.; Wu, Z.; Sun, X.; Yao, L.; Dong, H.; Song, Y.; Xu, Y. HIF-1-induced mitochondrial ribosome protein L52: a mechanism for breast cancer cellular adaptation and metastatic initiation in response to hypoxia. Theranostics. 2021, 11, 7337–7359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mak, T.W.; Grusdat, M.; Duncan, G.S.; Dostert, C.; Nonnenmacher, Y.; Cox, M.; Binsfeld, C.; Hao, Z.; Brüstle, A.; Itsumi, M.; Jäger, C.; Chen, Y.; Pinkenburg, O.; Camara, B.; Ollert, M.; Bindslev-Jensen, C.; Vasiliou, V.; Gorrini, C.; Lang, P.A.; Lohoff, M. Glutathione Primes T Cell Metabolism for Inflammation [published correction appears in Immunity. 2017 Jun 20;46(6):1089-1090]. Immunity. 2017, 46, 675–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maldonado, E.; Morales-Pison, S.; Urbina, F.; Solari, A. Aging Hallmarks and the Role of Oxidative Stress. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023, 12, 651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, C.K.; Chhabra, G.; Ndiaye, M.A.; Garcia-Peterson, L.M.; Mack, N.J.; Ahmad, N. The Role of Sirtuins in Antioxidant and Redox Signaling. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2018, 28, 643–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




