1. Introduction
The tendency of growing life expectancy is observed all over the world. The numbers of age-related diseases and surgical operations have grown accordingly [
1]. Among them, there are osteoporosis [
2], injuries, and traumas of various types. The latter tend to increase in frequency in all age groups [
3]. Besides, osteosarcoma, which is the most prevalent primary bone tumor, mainly affecting children and young adults [
4], needs often surgical interventions . Currently, surgery is commonly accompanied by antibiotic therapy [
5] to reduce the risks of infections and inflammation. On the other hand, antibiotics may pose additional risks, related to growing prevalence of drug-resistant bacteria [
6] or other side effects [
7]. Hence, alternative strategies concerned with applications of antimicrobial materials, e.g., bone cements, are of great interest.
Bone cements were originally named “materials based on polymethyl methacrylate” and are currently used in clinical practice [
8]. Nevertheless, these materials have several disadvantages, such as an exothermic setting reaction (which can lead to damage to adjacent tissues) and the need for revision surgery [
9]. Therefore, a search for alternative materials is underway. In recent years, several resorbable calcium phosphate–based bone cements (CPCs) [
10], magnesium phosphate–based bone cements (MPCs) [
11], and magnesium calcium phosphate bone cements (MCPCs) were proposed [
12,
13,
14].
Antibacterial activity of such materials may be achieved in several ways. The first one is the impregnation of a cement matrix with antimicrobial agents. Although this solution is widespread and allows to implement the concept of local drug delivery [
15,
16,
17], several issues are still unresolved, such as the control of drug release kinetics and the above-mentioned growing antibiotic resistance of bacteria. Thus, an alternative approach devoid of these shortcomings and involving introduction of various ions into the cement matrix is attractive.
The most common ion introduced into cement materials to achieve antimicrobial activity is silver. It has been demonstrated that the presence of silver ions can eliminate chronic osteomyelitis [
18] and that the introduction of Ag
+ cations leads to greater mechanical strength and antibacterial effects against both gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria [
19]. Nonetheless, it should be noted that silver is not an element that is present in the body in appreciable amounts, and therefore there may be health risks associated with its toxicity [
20]. At present, this question is not fully clarified. An alternative—zinc—is present in various organs and tissues and is involved in various metabolic processes [
21]. The Zn
2+ ion plays a critical role in bone growth by promoting osteoblast differentiation and inhibiting osteoclast differentiation [
22]. Zinc in various compounds can exert antibacterial actions [
23,
24]. In addition, its presence can lead to further improvement of mechanical characteristics of a material [
25].
Newberyite-based MCPC described in our previous paper shows a neutral pH level (7–8), setting time of 10–13 min, mechanical strength up to 22 ± 3 MPa, cytocompatibility, and acceptable matrix surface properties [
13]. The improved mechanical properties as well as cytocompatibility and antibacterial activity have been achieved for newberyite–struvite-based bone cements that are doped with silver ions [
19]. On the other hand, regarding the controversial effects of silver, the development of Zn
2+-doped MCPCs is expected to improve antibacterial properties and osteogenic ability of MCPC because a release of Zn
2+ may enhance osteogenic differentiation of certain cells for accelerated bone regeneration.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Synthesis of Cement Materials
The synthesis of cement powders based on a (Ca + Mg)/P = 2.0 system with 40 mol.% Mg substitution was carried out by the method of precipitation from an aqueous solution of salts according to the following equation described in our previous paper [
13]:
Zn2+ ions were introduced into the synthesis mixture as solutions of a nitrate [Zn(NO3)2] in the amount of 0.5 and 1.0 wt.%. After solution mixing, the slurries were evaporated to maintain the predicted concentrations.
The cement powders were heat treated at 1150 °C followed by grinding in a planetary ball mill with zirconia balls in a dimethyl ketone medium for 20 min. Cement powders were obtained, and major phases that formed during the synthesis of magnesium-substituted calcium phosphate were MgO, Ca
3Mg
3(PO
4)
4, and Ca
2.589Mg
0.411(PO
4)
2, consistently with a CaO–P
2O
5–MgO phase diagram [
26].
Cement materials were prepared by mixing a cement powder with a cement liquid in a 2:1 ratio under sterile conditions on a glass slide using a spatula. The cement liquid was synthesized on the basis of ammonium phosphate (NH4)3PO4 and magnesium hydrogen phosphate MgHPO4 at controlled pH value: 4.6. Cement materials with the following names were obtained: MCPC, 0.5%Zn-MCPC and 1.0%Zn-MCPC.
2.2. Characterization of the Materials
Chemical composition was investigated by atomic emission spectrometry with inductively coupled plasma (AES-ICP, Vista Pro).
Granulometric composition of cement powders was examined by means of laser particle analyzer FRITSCH Analysis 22. Phase composition of the materials was determined by X-ray phase analysis (XRD) (on Shimadzu XRD-6000 using CuKα radiation, in the 2θ range from 10° to 70° with a step of 0.02°) using ICDD database, PDF2. The phases were matched with the following cards: magnesium oxide (MgO: ICDD 77-2364), a magnesium-substituted whitlockite phase [Ca2.589Mg0.411(PO4)2: ICDD 87-1582], stanfieldite [Mg3Ca3(PO4)4: ICDD 73-1182], newberyite (MgHPO4⋅3H2O: ICDD 75-1714), and struvite (MgNH4PO4⋅6H2O: ICDD 77-2303). Particle size of cement powders as well as the microstructure of set cement materials were investigated by scanning electron microscopy (SEM) (Tescan Vega II).
The pH value of the solutions and temperature during the mixing of the cement paste were measured with the help of a Testo pH meter (Testo, Germany).
The setting time of cement materials was determined by immersion of a 1.0 mm (400-g) Vicat needle in a sample according to ISO 9917 (2007). pH of the extracts of set cement samples was determined after 1, 7, and 28 days in model fluids—Kokubo Simulated Body Fluid (SBF) [
27] and Dulbecco’s phosphate-buffered saline without calcium and magnesium (DPBS) (Thermo Scientific)—at a ratio of 0.2 g/mL at room temperature.
2.3. Mechanical Testing
For this testing, samples were prepared in cylindrical form with a diameter of 0.8 mm; after setting, the samples were dried in a 100% humidity atmosphere for 24 h.
An Instron 5581 uniaxial testing machine was employed to measure compressive strength of cement samples at a cross-head speed of 1 mm/min according to ASTM D695-91. Five samples of each composition were analyzed to determine compressive strength, and the results are reported as mean ± standard deviation (SD).
2.4. Dissolution Assays
To understand degradation behavior and solubility of MCPC and 1.0%Zn-MCPC, samples in the form of 28-day-set disks (6 mm in diameter and 2 mm in height) were soaked in the model fluids SBF and DPBS at 37.0 °C at a w/v ratio of 0.2 g/mL and a surface area-to-volume ratio of 0.1 cm
−1 for various periods in a closed system [
28]. At predetermined time points (1, 3, 7, 14, 21, and 28 days), two samples were taken out of the solutions, frozen in a ULT Freezer MDF-60U50 down to −70 °C, and lyophilized in LS-1000 Prointeh-bio before weight loss calculations, and one sample was dried at 60 °C for studying the effect of holding time on phase composition and microstructure upon dissolution.
2.5. Testing of Antibacterial Properties
Antibacterial activities of MCPC, 0.5%Zn-MCPC, and 1.0%Zn-MCPC crystals were assessed against the gram-positive bacterium Staphylococcus aureus (strain ATCC 6538) and the gram-negative bacterium Escherichia coli (strain XL1-Blue) in accordance with ISO 20645. Tested cement samples were applied to the surface of agar. The results on antibacterial activity were recorded after 24 h. The size of a zone of growth inhibition of the microorganisms was determined by measuring the distance from the edge of a tested cement sample to the border of growth of a microorganism around the tested sample as well as by the absence or presence of bacterial growth in the zone of contact of the sample with the agar medium.
2.6. Testing of Cytocompatibility
In vitro cytocompatibility of cement samples was evaluated by the MTT assay on a human osteosarcoma MG-63 cell line on the 1th an 3rd days of cells growth (Russian Collection of Cell Cultures, Institute of Cytology, Russian Academy of Sciences, St. Petersburg). Before the start of the
in vitro assays, cement samples were sterilized with γ-radiation at a dose of 18 kGy. Cement disk samples 5.0 mm in diameter and 3.0 mm high were placed into 96-well plates for cultivation (Corning Costar, USA) in triplicate at one 96-well plate per incubation period and were covered with a complete growth medium (CGM), which consisted of DMEM (PanEco, Russia), 10% of fetal bovine serum (PAA, Austria), 60 mg/mL glutamine (PanEco, Russia), 20 mM HEPES buffer (PanEco, Russia), and 50 μg/mL gentamycin (PanEco, Russia). Before that, in the 96-well plates, cell line MG-63 cells were seeded at a density of 15000 cells per well in 200 μL of the CGM. All the procedures were performed under sterile conditions at 37 °C in an atmosphere of humidified air that contained 5% of CO
2. Subsequently, optical density (OD) of the formazan solution (end product of the MTT reaction) was evaluated on a Multiscan FC spectrophotometer (Thermoscientific, USA) at a wavelength 540 nm. the calculation of the population of viable cells (PVC) in relation to the control (in %) was carried out according to formula :
where OD is the value of the optical density of the formazan solution.
A sample of cement was assumed to be cytocompatible at PVC ≥ 70%
The details of this method are described elsewhere [
29].
3. Results
3.1. Characterization of the Cement Powders
Based on AES-ICP results, Zn
2+ concentrations in the cement powders were close to the calculated ones (
Table 1).
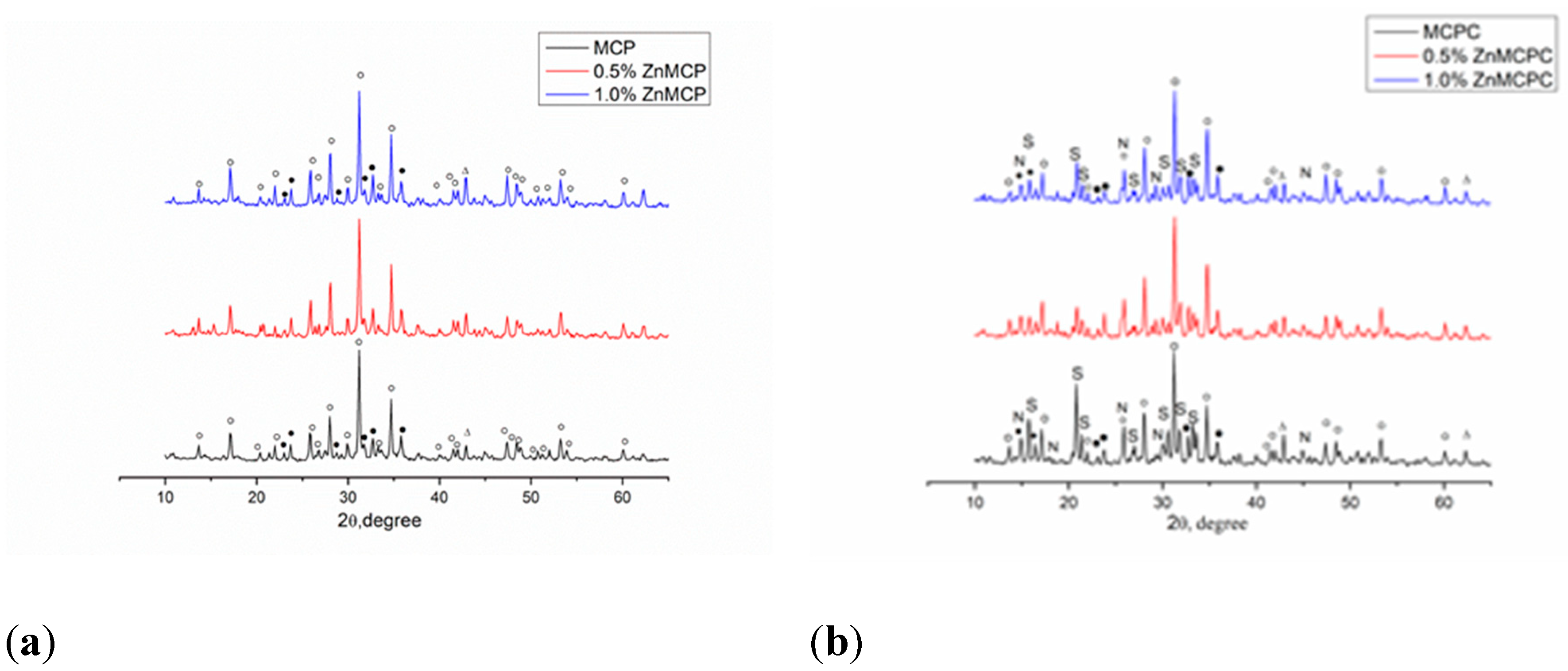
According to results of XRD analysis, the main phases of Zn-free magnesium calcium phosphate were magnesium-substituted whitlockite [Ca
2.589Mg
0.411(PO
4)
2] in the amount of 42 wt.% and stanfieldite at 29 wt.%; the rest of magnesium did not enter these phases and crystallized as MgO at 29 wt.% (
Table 1,
Figure 2). Subsequently, this cement powder (MCPC) was used as a control sample. The Zn
2+-substituted materials showed the formation of whitlockite and stanfieldite phases and magnesium oxide, just as in the undoped 40 mol.% Mg cement powder (
Figure 1a). With the increase in the Zn
2+ content of the cement, the quantity of the MgO phase noticeably increased.
The introduction of Zn
2+ into the material led to nonsignificant changes (an increase) in unit cell parameters of the stanfieldite phase (a = 22.82743 Å, b = 10.00122 Å, c = 17.08471 Å). We can hypothesize that substitution of Mg
2+ ions with Zn
2+ (ionic radius of Zn
2+ is 0.83 Å vs 0.65 Å in Mg
2+ [
30]) followed by a rise of the MgO amount in the materials.
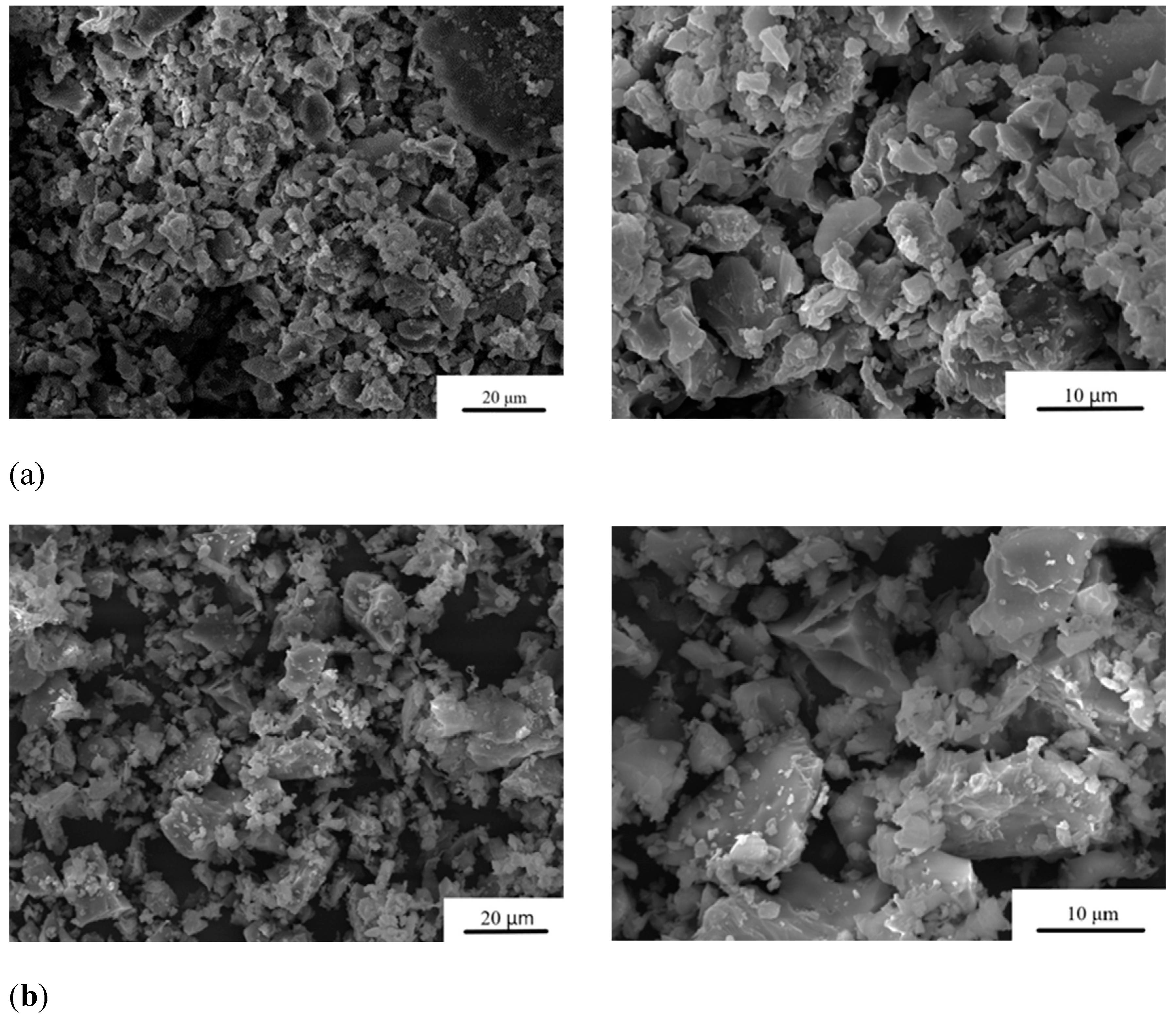
The particle size distribution after grinding of the cement powders is presented in
Table 1. The average particle size of MCPC is about 20 μm. It was found that under the same grinding conditions, the addition of Zn
2+ leads to an increase in particle size up to 36 μm at the 1.0 wt.% doping (
Figure 2).
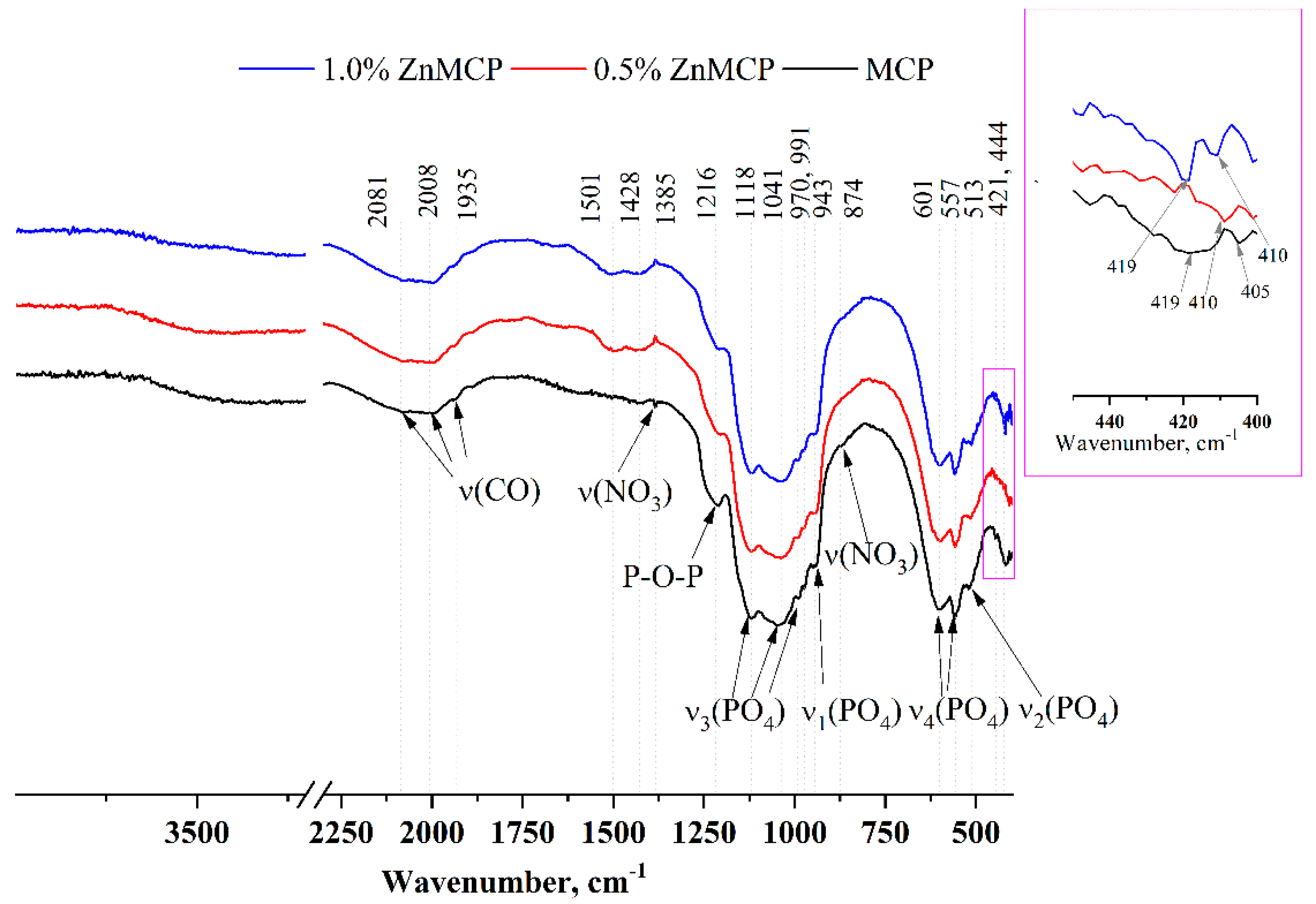
Infrared (IR) spectra of the obtained powders are given in
Figure 3. A broad phosphate band in the region 1200–900 cm
−1 and well-resolved bands of ν
3(PO
4) at 1118, 1034, 991, and 970 cm
−1 and of ν
1(PO
4) at 943 cm
−1 indicate that the structure of phosphate phases formed successfully. ν
4(PO
4) bands at 601 and 557 cm
−1 as well as ν
2(PO
4) at 513 cm
−1 are also clearly visible in all the materials. A broad peak formed by three bands at 1935, 2008, and 2081 cm
−1 is related to the C=O vibration from residual acetone after sample milling. In the absence of dopant ions, this region has a wide band at 419 cm
−1 and a low-intensity band at 405 cm
−1. In the presence of zinc, a narrower band is observed for the 0.5 wt.% substitution at 410 cm
−1, and for the 1.0 wt.% substitution, a doublet is seen at 419 and 410 cm
−1.
3.2. Characterization of the Cement Materials
During the mixing of the cement paste, no noticeable thermal reaction was detectable (
Figure 6b).
According to the XRD analysis (
Figure 1b), after the mixing of cement powders with the cement liquid, the formation of struvite (MgNH
4PO
4∙6H
2O) was observed, as was preservation of a minor amount of stanfieldite and magnesium-substituted whitlockite; MgO was detectable too (
Figure 4). In contrast, both cement materials doped with Zn
2+ manifested the formation of struvite and newberyite phases (MgHPO
4∙3H
2O) (
Table 2). It should be noted that the introduction of the zinc cation in the amount of 0.5 wt.% led to a slightly elevated proportion of the newberyite phase.
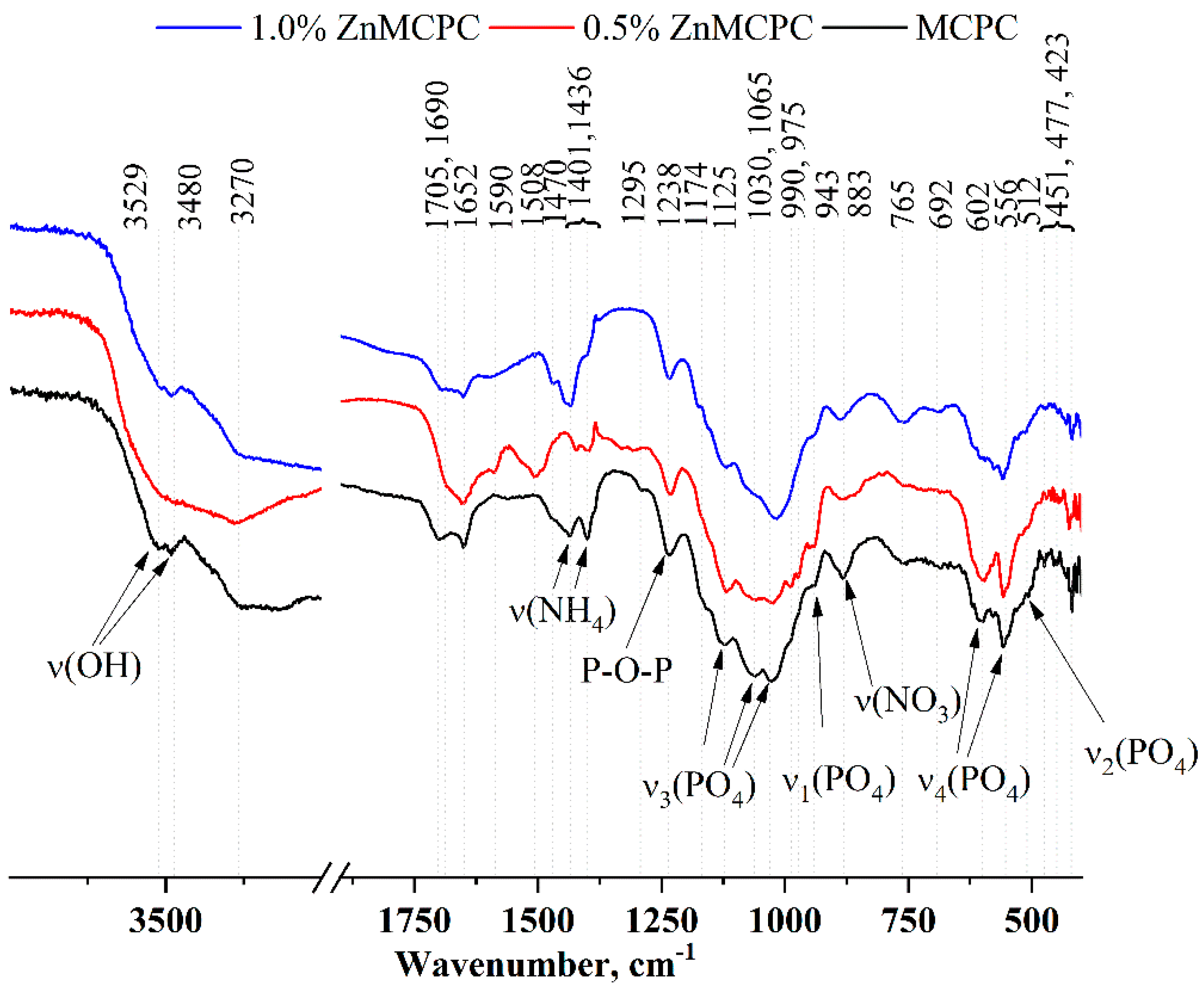
Furthermore, according to the XRD analysis, as a result of setting and hardening processes in the cement samples, crystals of phosphate phases are amorphized. The IR spectra (
Figure 4) contain bands related to PO
4 vibrations at 1125, 1030, 1065, 990, and 975 cm
−1 [ν
3(PO
4)], 943 cm
−1 [ν
1(PO
4)], 602 and 556 cm
−1 [ν
4(PO
4)], and 512 cm
−1 [ν
2(PO
4)]. It should be pointed out that with the increase in the amount of the dopant ion, the intensity and resolution of these bands noticeably diminished.
An ammonium salt was present in the setting cement liquid, which gave rise to a new phase: struvite (NH4MgPO4∙6H2O). Its presence was confirmed by the XRD analysis. The IR spectra also show reflections related to NH4 group vibrations in the region 1400–1710 cm−1 as well as in the region of 3600–3200 cm−1. To the latter, H-O-H vibrations of water contribute, which are present both in the newly formed crystal hydrates (struvite and brushite) and in free form.
The preparation of a cement material is based on chemical reactions between compounds of the cement powder and cement liquid. When phosphate salts (NH
4)
3PO
4 and MgHPO
4 come into contact in the cement liquid, their molecules dissociate and, within a few seconds, the cement liquid is saturated with ions in accordance with reactions
Futher, MgO recrystallization into struvite occurs [
1], and dissolved ions interact with the original phases of the cement powder. Due to the presence of Ca
2+ at 60 mol.%, we assume the emergence of amorphous crystalline hydrate phase CaHPO
4∙2H
2O (brushite) via the following reaction:
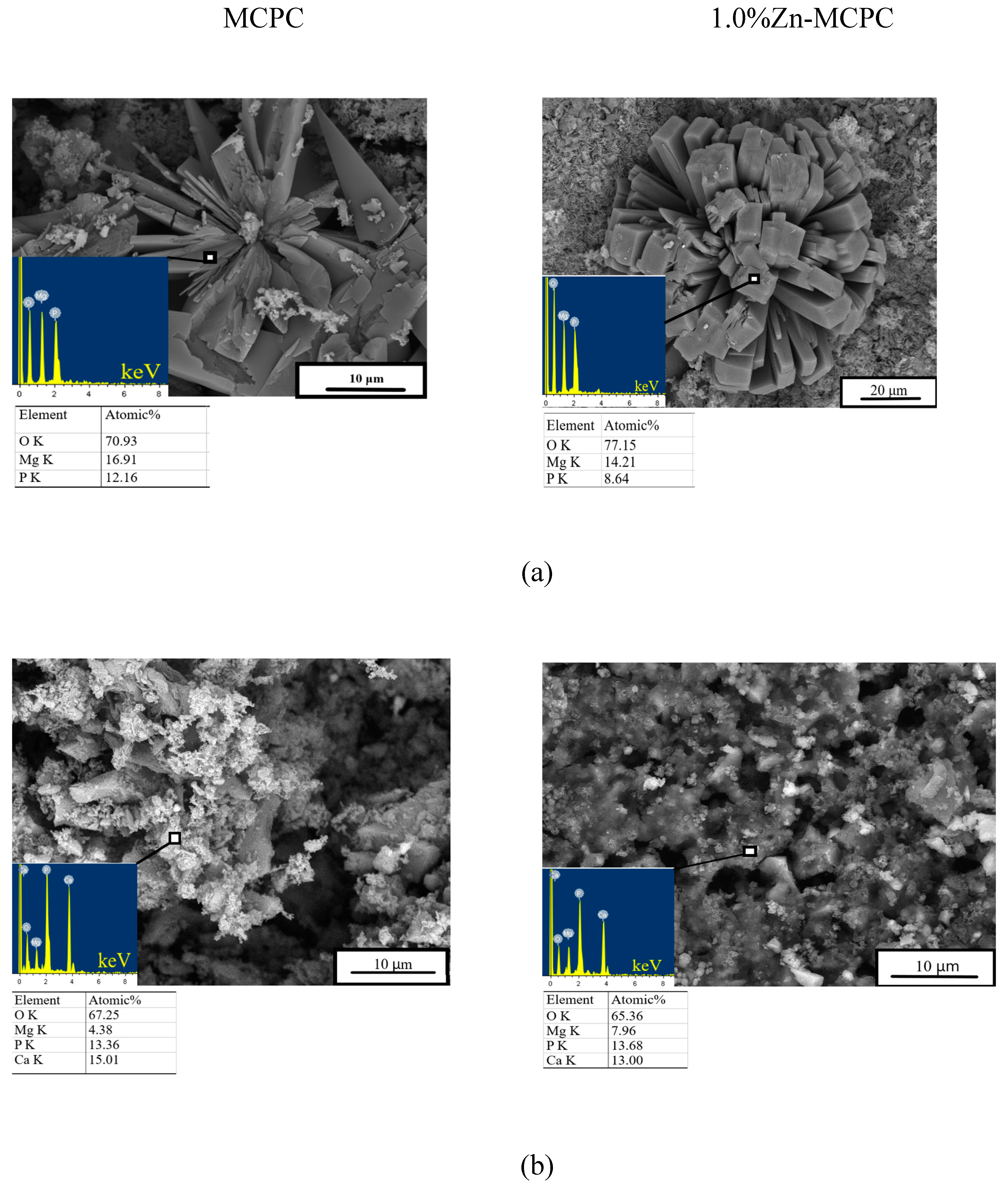
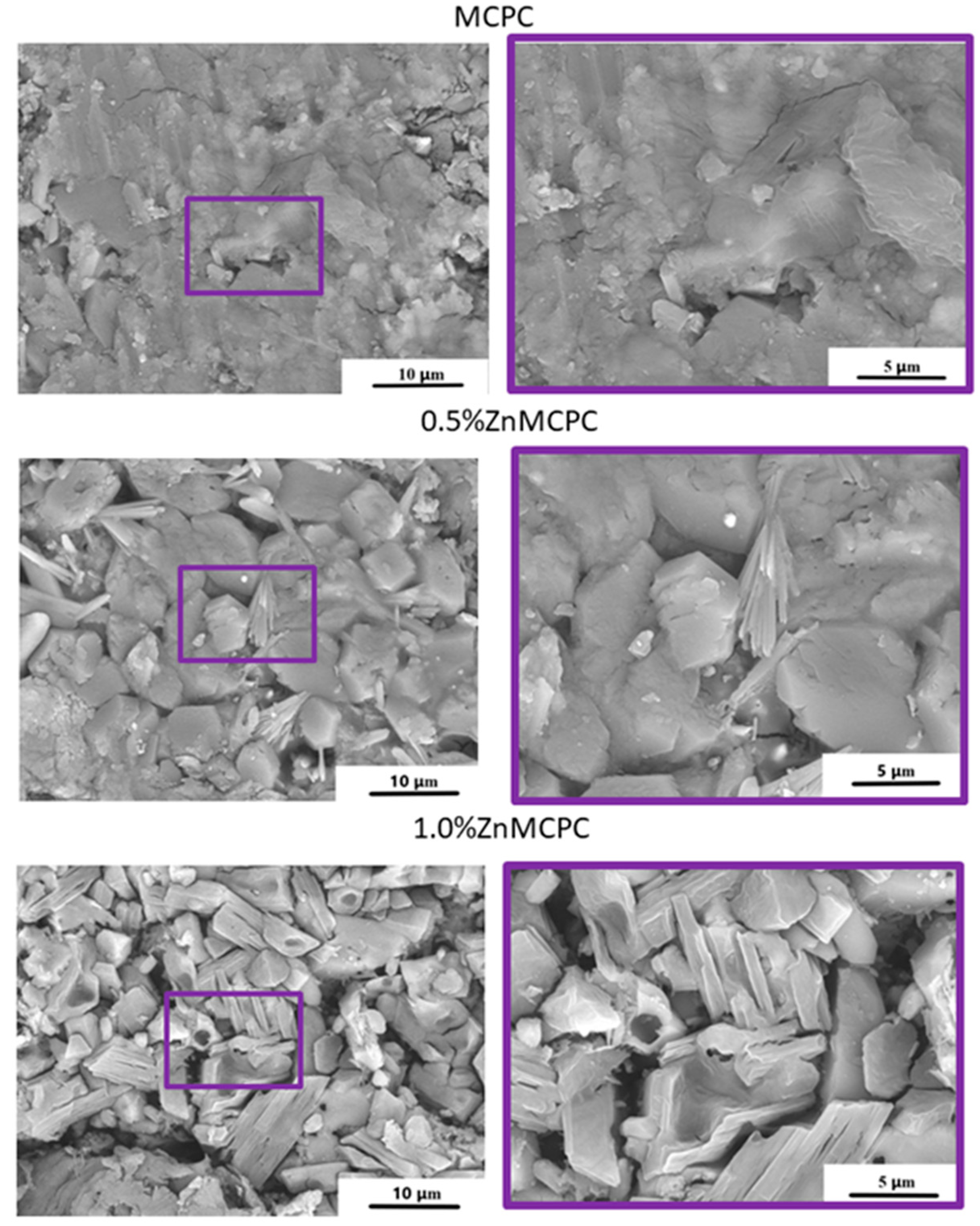
The microstructure of the set cement samples was investigated and indicated the formation of new cementing phases on the surface (
Figure 5). The MCPC sample is characterized by dense poreless structure of the struvite phase. On the surface of the Zn
2+-doped cement samples, the emergence of the new cementing crystalline hydrate phase newberyite was registered. The introduction of Zn
2+ ions led to a crystal shape modification. The crystalline phase has geometric features: a honeycomb appearance with the average crystalline size of approximately 5–8 μm for 0.5%Zn-MCPC. On the surface of the sample’s cracks, we noticed the newberyite phase in the BSE mode.
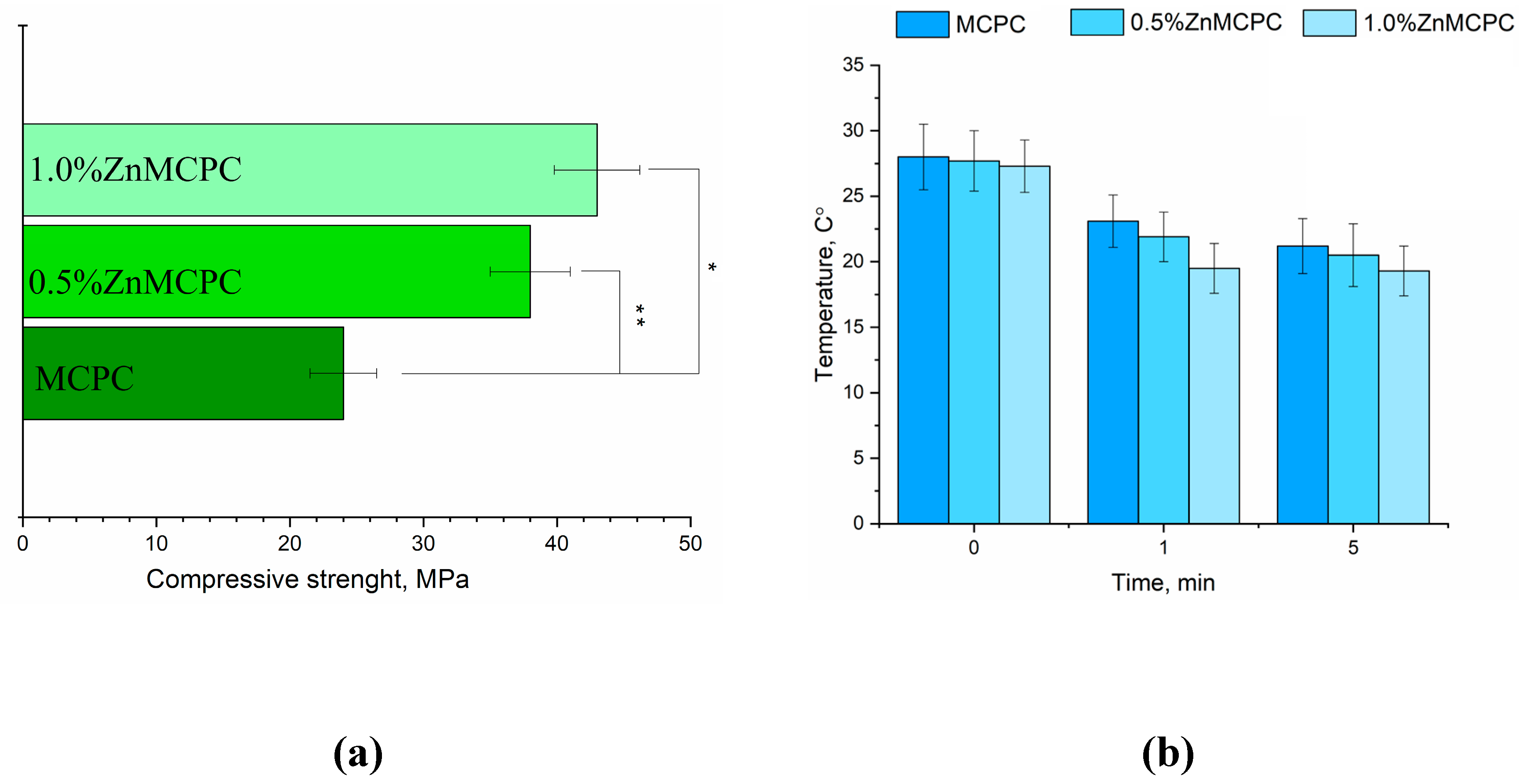
MCPC samples are characterized by a compressive strength of about 24 ± 3 MPa. It was found that the introduction of Zn
2+ cations enhances the strength. The greatest strength, 48 ± 5 MPa, was observed for 1.0%Zn-MCPC samples (
Figure 5(a)).
Measurement of pH value of solutions based on distilled water containing a cement material showed pH level close to neutral during exposure to the solution for more than 1 day. The pH value of samples with 40 mol.% of Mg after 24 days of holding in distilled water was 7.2.
Figure 6.
Results on the cement materials after mechanical testing for compressive strength (a); temperature measure during setting process of cement materials (b).
Figure 6.
Results on the cement materials after mechanical testing for compressive strength (a); temperature measure during setting process of cement materials (b).
The setting time for the cement materials was approximately 4–7 min regardless of composition. The setting time shorter than 15 min is adequate for surgery [
31]. Also, the inner temperature were measured during the setting process of cement material (
Figure 5(b)). It was shown, that maxima temperature value near 28 C° observed in the moment of mixing cement powder with cement liquid, next process of setting cements up to 5 minutes demonstrated tendency in decreasing temperature for all cements composition.
3.3. In Vitro Dissolution Assays
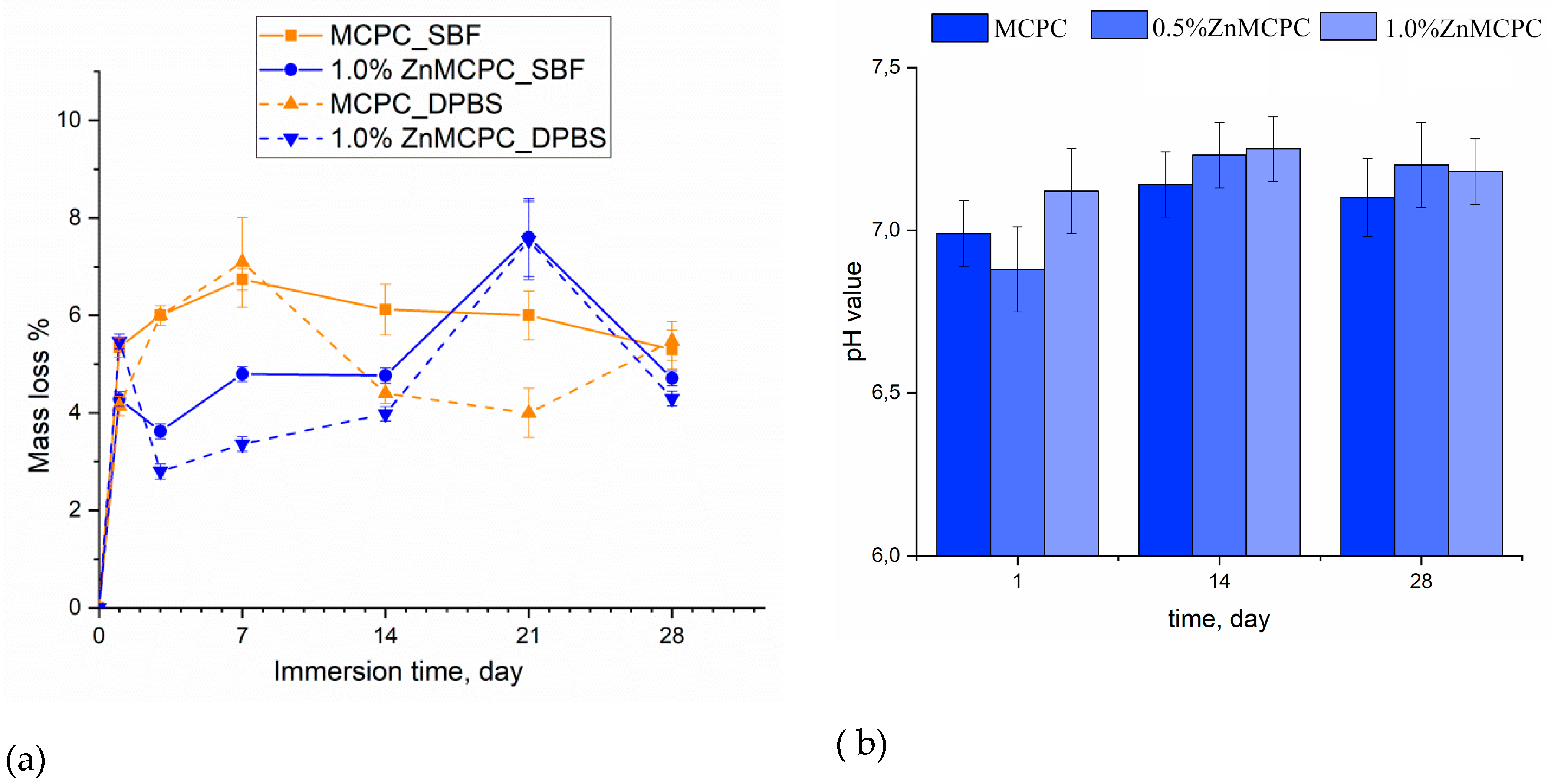
Degradation kinetics are determined by weight loss and pH value, and the profile is plotted as a function of time. The solubility assay of the cement materials revealed that on the first day of the experiment, the mass loss of the samples did not exceed 6%, regardless of the type of mortar. At the initial stage of the dissolution process, the unreacted cement liquid was removed, and subsequent features of the behavior of the cement materials in the model liquids were suggestive of processes taking place on the surface of the material, where interactions proceeded between the dissolved ions Ca2+, Mg2+, Na+, OH−, HPO42−, and PO43−. The greatest mass loss in the MCPC sample was 7% and happened on the 7th day of the experiment in the model liquids; on the 14th day, the solubility in DPBS was less than that in SBF; however, by the 28th day, the mass loss reached 5%. The introduction of zinc into MCPC affected the nature of the solubility of the samples, and mass losses in the model liquids diminished; however, by the 21st day, the loss reached 7%, and by the end of the experiment, the solubility of the samples declined.
Measurement of the pH value in the SBF solution of the cement materials at various time points showed neutral level of about 6.8–7.3, which are typical for struvite-based MCPC [
32] (
Figure 7b).
After the 28 days of soaking, SEM data revealed the formation of a porous and loose surface with flower-like structures (radial-radiant aggregates) of the newly formed bobierrite phase [Mg
3(PO
4)
2∙8H
2O], confirmed by energy-dispersive X-ray (EDX) analysis as a magnesium phosphate phase in SBF (
Figure 8). Structure similar to the above-mentioned radial-radiant structure and composed of whisker-like particles is present in macroporous MPC obtained from amorphous magnesium phosphate cement powders after soaking in SBF for 7 days [
33].
The bobierrite phase was probably produced by reaction 6 (see below). MgO is not soluble in water in the absence of acidic components but can create a favorable basic environment for bobierrite synthesis via the reaction
According to XRD data, by the 14th day of the experiment, the newberyite that was registered in the Zn2+-doped materials fully dissolved in SBF. The emergence of the new bobierrite phase was detected on the surface of MCPC and of Zn2+-doped samples after 28 days of soaking.
Figure 8.
In vitro dissolution assays. Morphology (EDX data) of the cement materials’ surface after 28 days of soaking in (a) SBF or (b) DPBS.
Figure 8.
In vitro dissolution assays. Morphology (EDX data) of the cement materials’ surface after 28 days of soaking in (a) SBF or (b) DPBS.
3.4. Antibacterial Properties
The antibacterial assays were designed to assess possible antibacterial activities of the doped cements, namely, the ability to inhibit bacterial attachment to a sample’s surface and bacteriostatic action, i.e., the capacity to inhibit bacterial growth. The results are presented in
Table 4.
According to contact method results, the pure-MCPC sample exerted antibacterial activity toward
S. aureus because owing to its slow dissolution, this material is transformed into magnesium hydroxide, which releases hydroxyl ions when it dissociates [
34]. By contrast, the struvite-based MCPC does not inhibit the growth of another gram-positive bacterium:
S. sanguinis. In our test, the Zn
2+-doped samples produced inhibition zones for both bacteria:
S. aureus and
E. coli. As the amount of Zn
2+ increased, the inhibition areas enlarged, as reported earlier about CPC materials [
35].
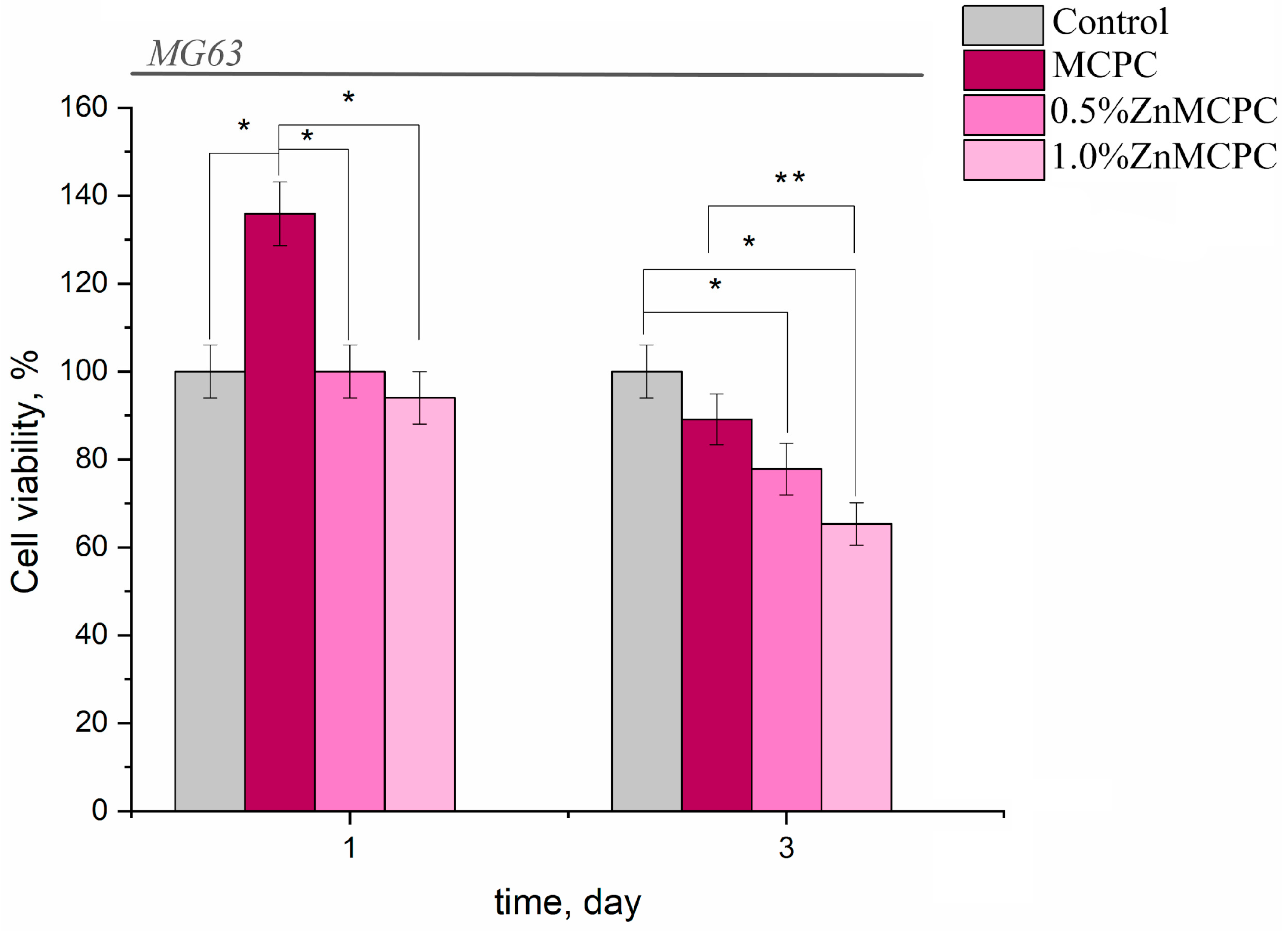
3.5. Cytocompatibility of the bone cements samples
Overall, the results of this assay indicated the absence of acute toxicity of the new bone cements to the cultured cells in question (Table 3). The findings made on the 3rd day were consistent with the cytocompatibility of the newly developed formulations having bactericidal properties, because in their presence, the value of fatty acids in the tested osteosarcoma cells was 77–87%, with the exception of the sample containing 1.0 wt.% of Zn (fatty acid value: 65.3%). The observed behavior may be attributed to the arising amorphous magnesium phosphate phases, which yielded rapid proliferation and differentiation of osteoblast-like cells in contrast to the crystalline phase.
Figure 9.
Viability of MG-63 cells during the cultivation on bone cement samples or on control samples (polystyrene).
Figure 9.
Viability of MG-63 cells during the cultivation on bone cement samples or on control samples (polystyrene).
From the results of the in vitro assays, it can be concluded that the proposed bone cements are nontoxic and cytocompatible.
4. Discussion
The aim of the present study was to determine effects of Zn2+ ions introduced into MCPCs. According to the XRD analysis, it was revealed that initial powders are characterized by the presence of whitlockite, stanfieldite, and MgO phases. The greater amount of introduced Zn2+ raised the concentration of MgO because of a large quantity of Mg2+ displaced by Zn2+ ions in the stanfieldite lattice. After mixing of the initial cement powder with a cement liquid, the main cementing phase (struvite) crystallized. One of the key findings in this study was that during the cementing, the thermal reaction did not proceed at all the tested compositions of cements.
It is well known that MgO is one of the main phases in MPC, which reacts by recrystallizing during its interaction with a cement liquid [
36]. Several factors affect the rate of the struvite formation during the mixing of magnesium calcium phosphate with a cement liquid based on (NH
4)
2HPO
4 [
37]. The hydration of MPC is basically an exothermal acid–base neutralization reaction. On the one hand, there is the reactivity of the initial MgO because its specific surface plays a key part in the kinetics of the reaction. On the other hand, the type of phosphate acid applied and its concentration determine the solution’s initial pH, which evolves in the course of the chemical reactions. There is a hypothesis that the successive dissolution of MgO rapidly increases the pH value of the system [
38]. When the pH value is greater than 7, NH
4MgPO
4·6H
2O starts to form needle-like crystals and generates a network. The solubility product constant K
sp of struvite is 2.5 × 10
−13 at 25 °C, whereas K
sp of other products is far higher than this; therefore, struvite is the main hydration product of MPC.
It was noteworthy here that the main difference between Zn
2+-doped and Zn
2+-free MCPC is the appearance of the newberyite phase during the interaction with the cement liquid, according to XRD data. Boistelle et al. [
39] have noted that pH value and the degree of supersaturation of a substance in solution play a key role in phase crystallization. They investigated the reaction between MgSO
4 and NH
4H
2PO
4 in equimolar amounts and demonstrated that struvite is metastable at specific pH levels (pH < 6.2) and supersaturation. Struvite precipitates first and then dissolves generating newberyite (MgHPO
4·3H
2O), which is stable at low pH value.
As shown in our work, the introduction of Zn
2+ into MCPC cements increases mechanical strength by almost twofold. In ref. [
40], researchers demonstrated the effect of introduction of ZnO nanoparticles at up to 0.2 wt.% on mechanical strength of Portland cement (PO 42.5). It was found that with an increase in the concentration of zinc oxide from 0 to 0.2 wt.%, the strength went up and amounted to ~62 and 78 MPa, respectively, by the end of the experiment. By contrast, on the 7th day of the experiment, the strength of zinc-doped cement was ~50 MPa. The same tendency of increasing strength with the introduction of Zn ions into the matrix was documented in ref. [
41], where the strength of cement not doped with zinc was ~15.4 MPa on day 7, whereas for cement doped with zinc (1.4 wt.% of Zn), it was 17.5 MPa. In the present work, the synthesized MCPC doped with 1 wt.% of Zn
2+ had strength 48 ± 5 MPa, which is comparable to structural Portland cement and almost 2 times stronger than CPC. Such high strength of MCPC may be due to the nascent newberyite phase [
42]. A similar effect—strengthening of magnesium phosphate cements by doping with 1 wt.% of ZnO resulting in a mechanical strength of 49.2 MPa—the authors of ref. [
43] explain as follows: the incorporated ZnO not only acted as stress concentration points absorbing a large amount of energy and promoting shear strain of the MPC matrix under the influence of external stress but also served as an effective barrier to dislocation movement and efficiently impeded crack extension.
As already mentioned in the introduction, the present authors have evaluated MCPC doped with silver ions [
19], but, given the high cost of silver as a metal, the present authors decided to try an alternative: a study on doping with zinc. Zinc is known to have an antibacterial effect. Ref. [
41] suggests that the addition of 1.4 wt.% of Zn
2+ into brushite cements gives antibacterial properties against
E. coli,
E. faecium, and
P. aeruginosa. In the work, the inhibition zone of
E. coli for MCPC was 14 mm, whereas for MCPC doped with 1.0 wt.% of Zn
2+, it was 2 mm. This phenomenon is most likely due to the fact that the solubility of calcium phosphate cements is higher, and consequently the release of zinc ions is more intense. It should be emphasized that gram-negative bacteria are more susceptible to zinc ions than gram-positive ones owing to the thicker cell wall. No antibacterial effect against
E. coli was observed in the case of MCPC, but for both Zn
2+-doped materials under study, a sufficient antibacterial activity was achieved. Thus, the doping with Zn
2+ contributed to the antibacterial properties of the newly developed MCPCs. In ref. [
35], the average release of zinc ions from CPC at 0.6 wt.% of Zn was 0.3070.01 mg/L, and at 1.2 wt.% of Zn, it was 0.1070.01 mg/L. On the other hand, the results of antibacterial assays showed an inhibitory effect against pathogenic
E. coli only for CPC containing 0.6 wt.% of Zn
2+. In our work, we demonstrated a high antibacterial activity against the bacterium
S. aureus ATCC 6538 at a lower yield of zinc ions, less than 0.1 mg/L. In ref. [
44], researchers were unable to detect any bactericidal effect of CPC doped with zinc against gram-positive bacterium
S. aureus ATCC 25923, whereas in our work, a strong inhibitory effect was registered for all compositions of the cements.
It is known that Zn
2+ is a biocompatible ion and is present in many tissues of the human body [
21,
45]. For instance, the introduction of zinc into brushite cement at 1.4 wt.% improves the viability of NCTC L929 cells by approximately 10% relative to pure cement; this finding can be explained by the positive influence of Zn
2+ ions on the proliferation of fibroblasts. A probable reason is the fact that zinc plays an important role in various biological processes and participates in a number of metabolic functions necessary for cell growth and development [
41]. Introduction of 5 wt.% of zinc into apatite cement is reported to result in significantly higher proliferation rates of human osteoblasts as compared to pure apatite [
46], and it is proved that the release of zinc does not have toxic effects on the environment. In our work, all MCPCs were found to be nontoxic to the MG-63 cell line. The observed slight decrease in cell viability can be ascribed to the formation of amorphous phases in the cement and higher solubility on the 1st day of the experiment (6% mass losses). In ref. [
47], it is demonstrated that in biphasic mixtures of amorphous β-tricalcium magnesium phosphate, the viability of human mesenchymal stem cells decreases on the 7th day of the experiment. Those authors explain this outcome by rapid proliferation and confluence of cells, i.e., the fastest cell proliferation at the beginning of the experiment. Further proliferation is slower.
Therefore, the developed cement materials are potentially useful in reconstructive surgery. Additionally, according to our analysis of the literature, there is no information on the doping of MCPCs with zinc cations; therefore, this study is novel in the field of cement materials. Here, in a CaO–P2O5–MgO system at (Ca + Mg)/P = 2.0 and 40 mol.% Mg substitution, we created MCPCs that possess improved physicochemical, mechanical, and biological properties because of a combination of different concentrations of Zn.