Submitted:
19 May 2023
Posted:
22 May 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Leaves of Lawsonia inermis
2.2. Aqueous extract (AQ) obtention
2.3. Ointment formulation
2.4. Total phenolic compound content
2.5. Total Flavonoid Content
2.6. Total tannin content
2.7. Total saponin content
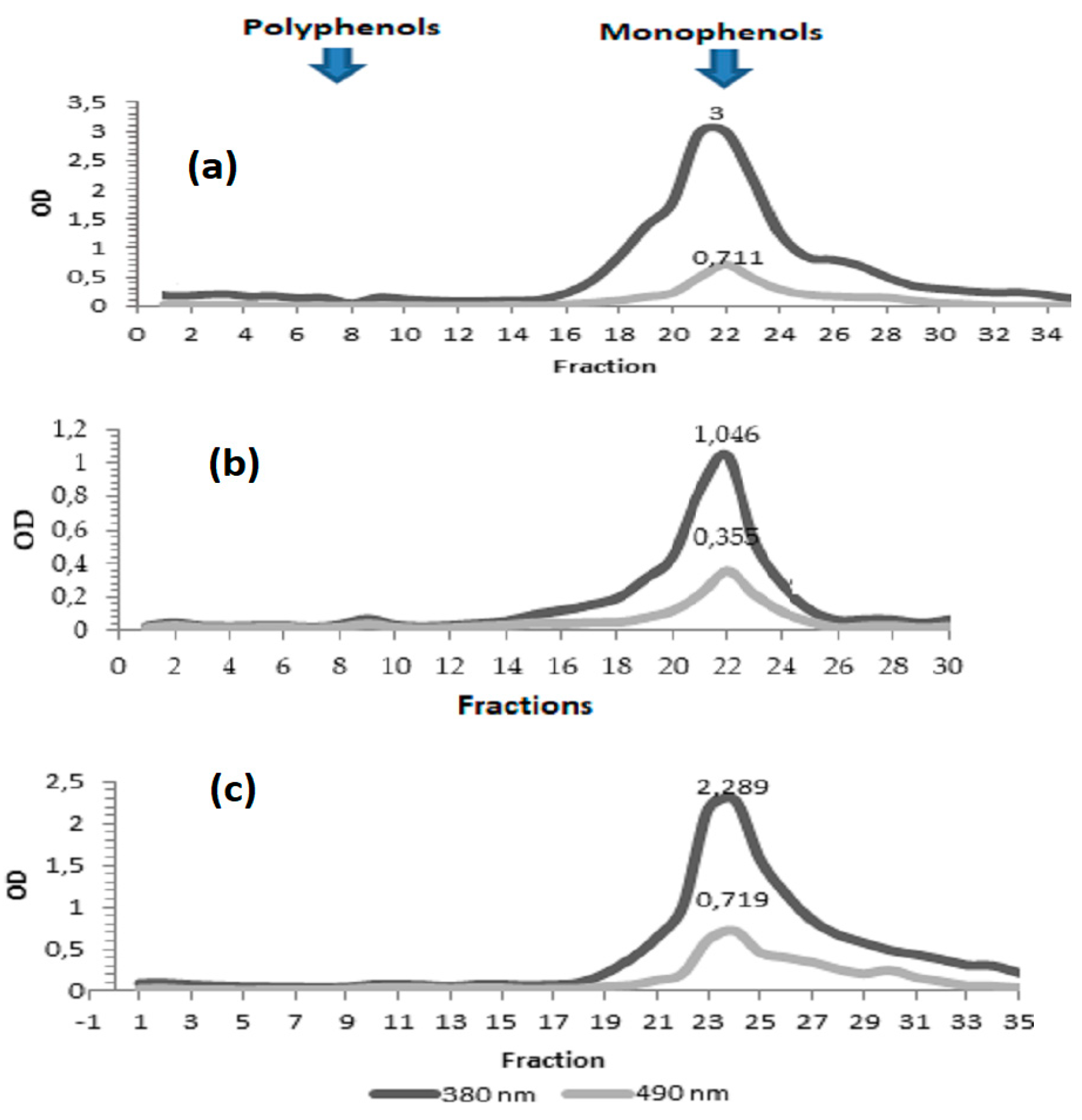
2.8. Gel filtration chromatography
2.9. Wound healing activity assessment
- -
- Ethics statement
- -
- Animal preparation
- -
- Treatment application
- -
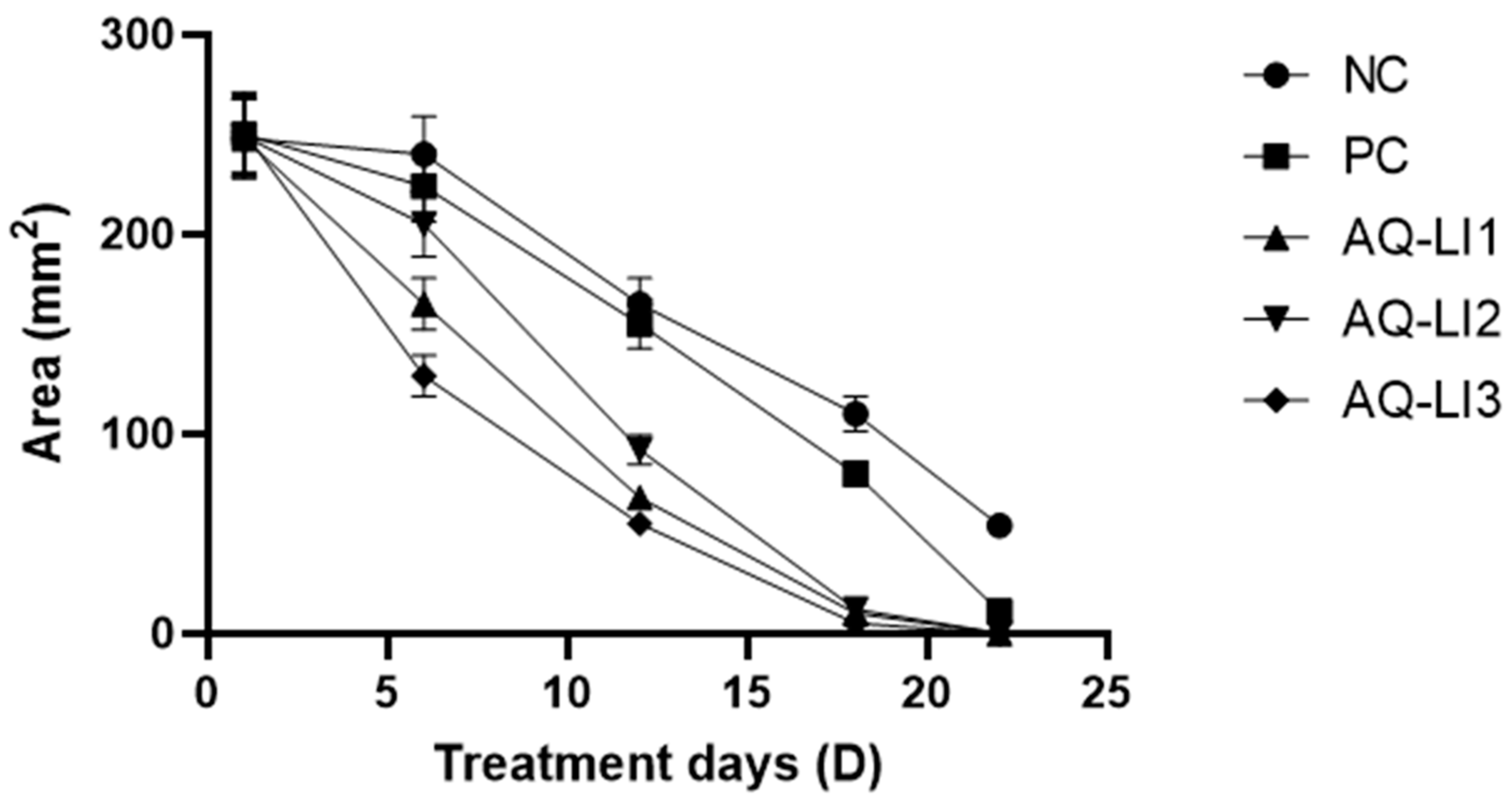
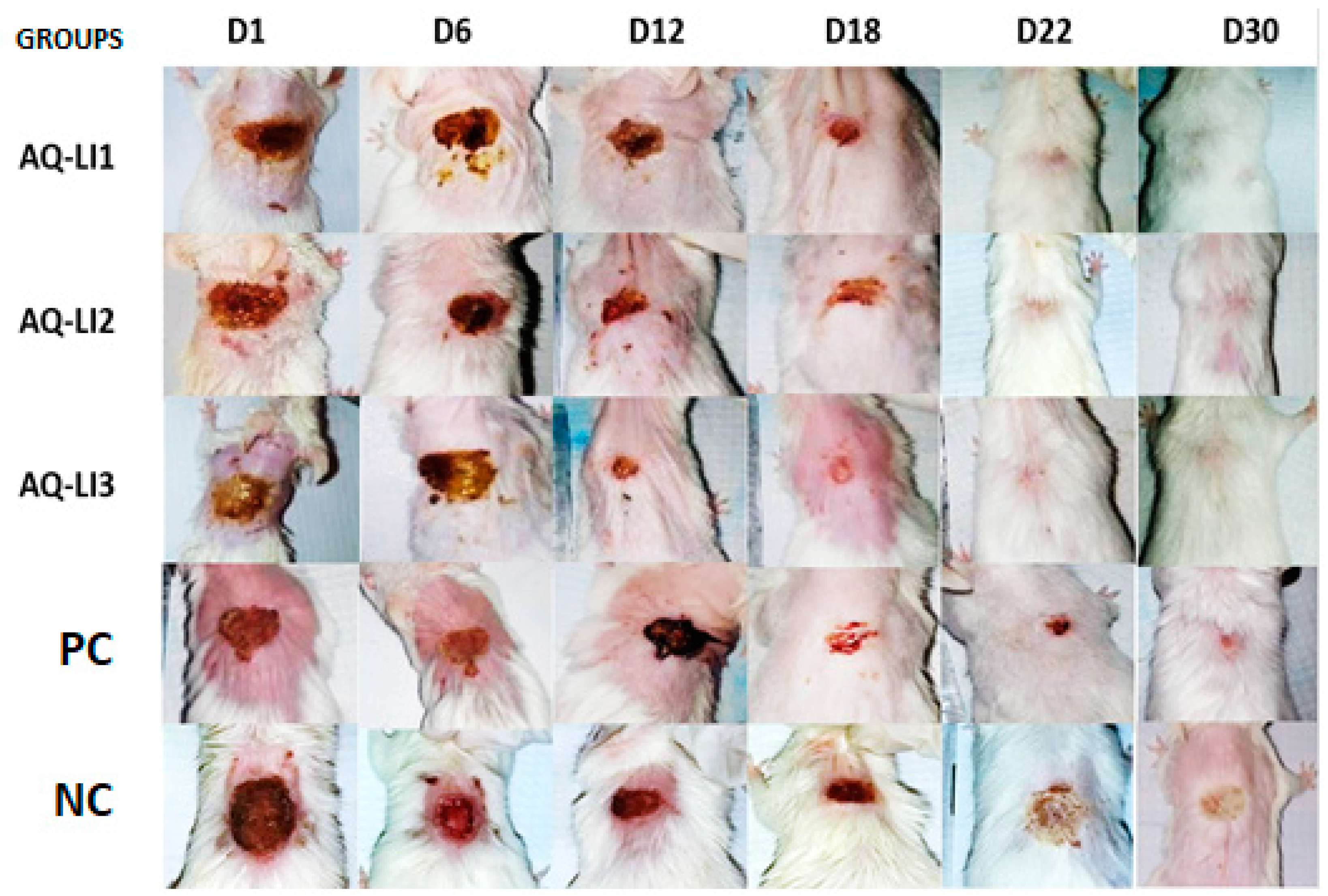
- Study of scar evolution using digital planimetry
- -
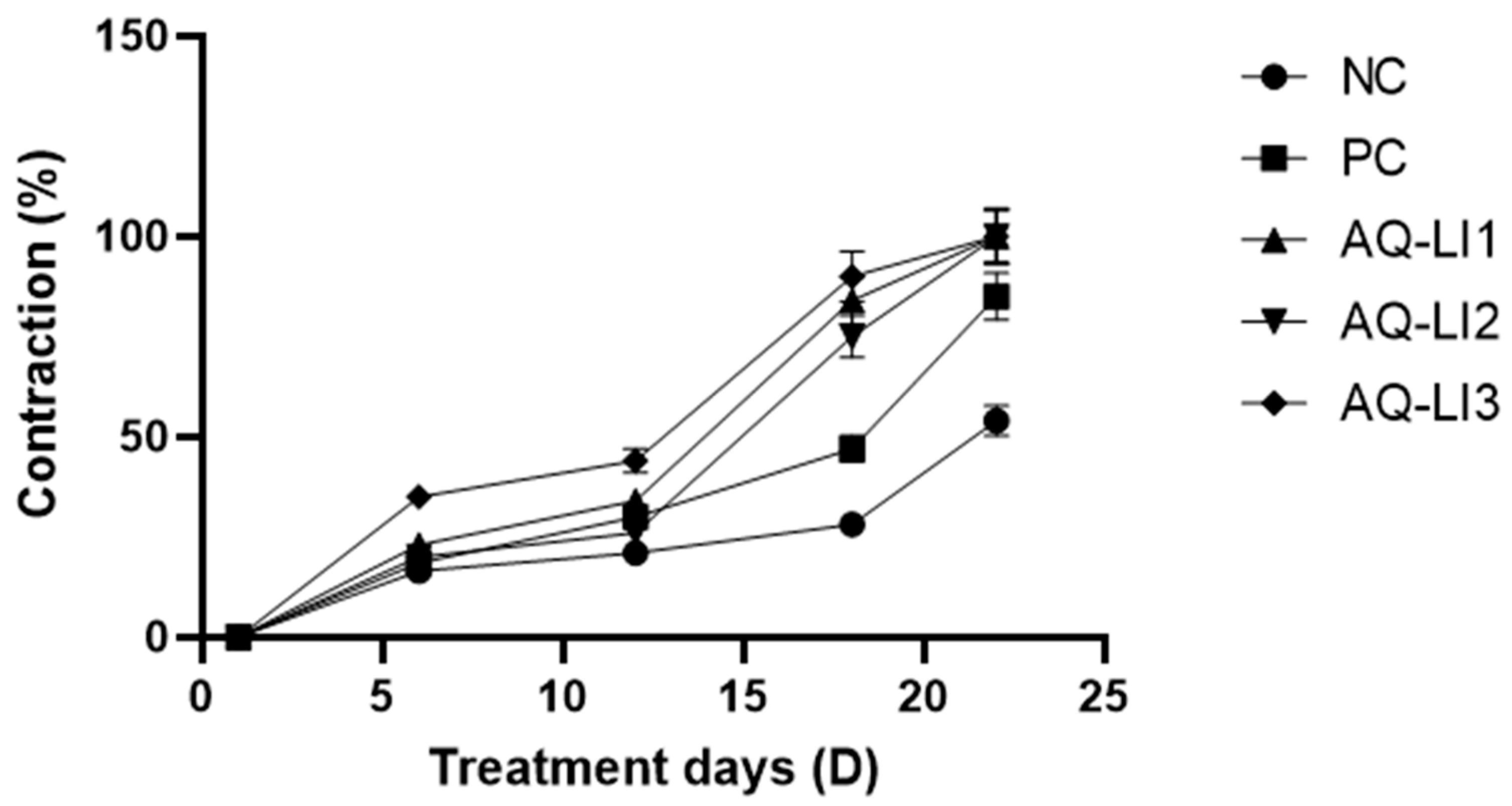
- Percentage of contraction
- -
- WCP: Wound contraction percentage;
- -
- D0: Day 0; and
- -
- Dn: Day n.
- -
- Epithelialization period
2.10. Statistical analyses
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Phenolic compounds analysis
3.2. Gel filtration chromatography
3.3. Evaluation of in vivo wound healing activity
- -
- Epithelialization period
- -
- Average surface and mean percentage of burn contraction
- -
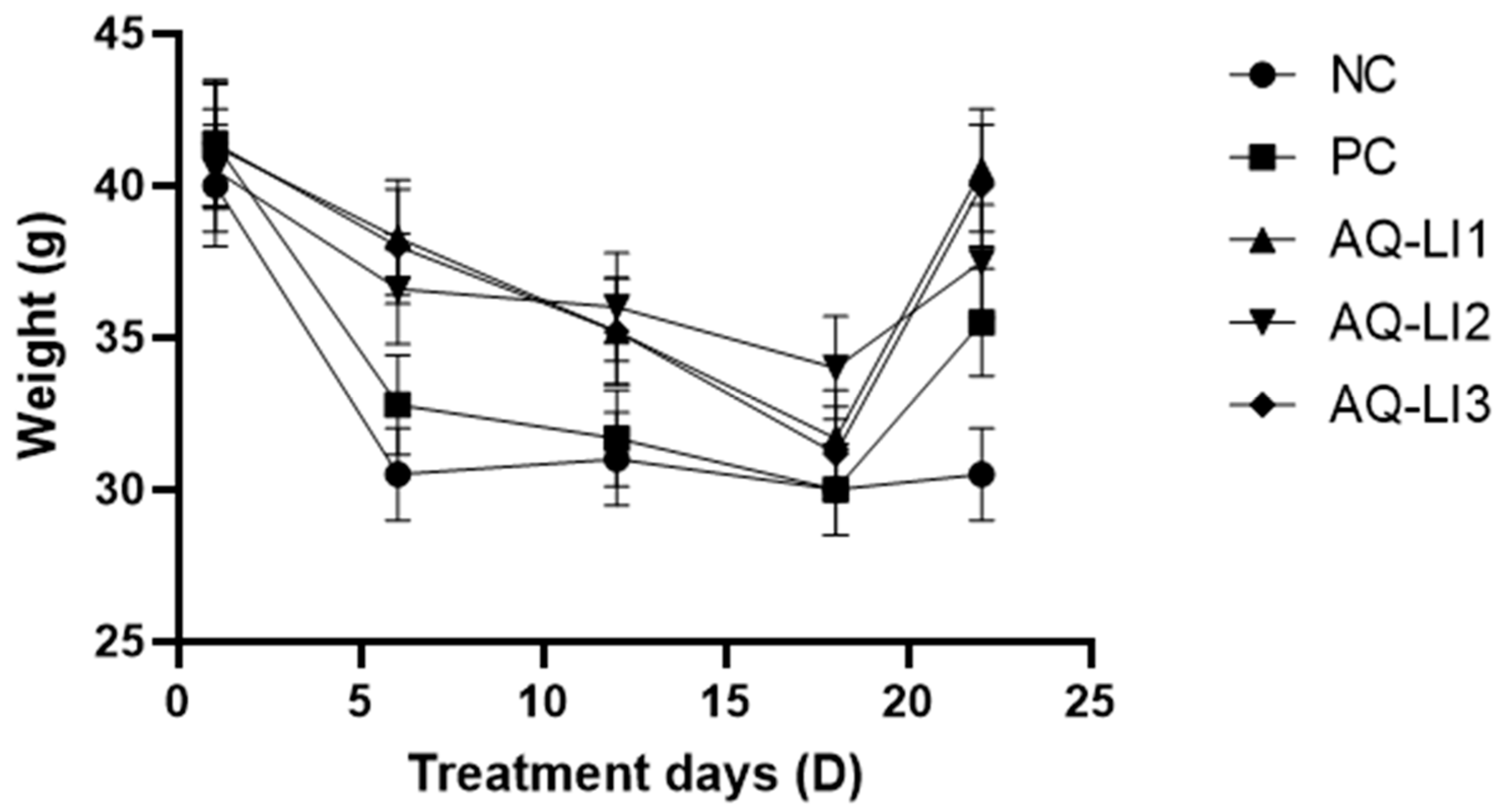
- Variation in weight of mice during treatment
4. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lydia, B. Y. Petite Histoire Du Maquillage. Stock, 1999.
- Hughes, K. , Ho, R., Butaud, J. F., Filaire, E., Ranouille, E., Berthon, J. Y., and Raharivelomanana, P. “A Selection of Eleven Plants Used as Traditional Polynesian Cosmetics and Their Development Potential as Anti-Aging Ingredients, Hair Growth Promoters and Whitening Products.” Journal of Ethnopharmacology, Vol. 245, 2019, p. 112159. [CrossRef]
- Walter, P. , Martinetto, P. , Tsoucaris, G., Bréniaux, R., Lefebvre, M. A., Richard, G., Talabot, J., and Dooryhee, E. “Making Make-up in Ancient Egypt.” Nature 1999 397:6719, Vol. 397, No. 6719, 1999, pp. 483–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, M. F. J. , and Bravo, D. L. “The Use of Plants in Skin-Care Products, Cosmetics and Fragrances: Past and Present.” Cosmetics 2018, Vol. 5, Page 50, Vol. 5, No. 3, 2018, p. 50. [CrossRef]
- Bouhlal, T. , Benkhnigue, O., Zidane, L., Sobh, M., and Fadli, M. “Vasculat Plants Used in Tradional Cosmetic by the Human Population in the Plain of the Gharb (Morocco) Full Paper.” Natural product an indian journal, Vol. 9, No. 8, 2013, pp. 326–330.
- Zrira, S. “Some Important Aromatic and Medicinal Plants of Morocco.” 2017, pp. 91–125. [CrossRef]
- Saive, M. , Frederich, M., and Fauconnier, M.-L. “Plants Used in Traditional Medicine and Cosmetics in Mayotte Island (France): An Ethnobotanical Study.” Indian Journal of Traditional Knowledge, Vol. 17, No. 4, 2018, pp. 645–653.
- Badoni, S. , Semwal, D., Combrinck, S., Cartwright-Jones, C., and Viljoen, A. “Lawsonia Inermis L. (Henna): Ethnobotanical, Phytochemical and Pharmacological Aspects.” J Ethnopharmacol, Vol. 155, No. 1, 2014, pp. 80–103. [CrossRef]
- El Ghanjaoui Mohammed, Cervera, M. L., El Rhazi, M., and De La Guardia, M. “Assessment Of Trace Elements In Traditional Moroccan Cosmetics By Inductively Coupled Plasma Atomic Emission Spectroscopy.” Article in International Journal of Scientific & Technology Research, Vol. 3, No. 10, 2014, pp. 104–112.
- Fatahi, B. M. , Salary, S., Mirzaei, F., Mahmoodian, H., Meftahizade, H., and Zareshahi, R. “Antibacterial and Anti-Trichomunas Characteristics of Local Landraces of Lawsonia Inermis L.” BMC Complementary Medicine and Therapies, Vol. 22, No. 1, 2022, pp. 1–10. [CrossRef]
- Al-Snafi, A. E. “A Review on Lawsonia Inermis: A Potential Medicinal Plant.” International Journal of Current Pharmaceutical Research, Vol. 11, No. 5, 2019, pp. 1–13. [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y. , He, W., Yang, S., and Liu, L. “Stabilisation and Detoxification of Henna (Lawsonia Inermis L.) Extract for Hair Dye Cosmetics by Spray-Drying Encapsulation.” Coloration Technology, Vol. 135, No. 6, 2019, pp. 439–450. [CrossRef]
- Obat, R. , and Bosire, C. “Formulation and Evaluation of Herbal Lipstick Using Beta Vulgaris and Lawsonia Inermis as Natural Colorants.” Journal of Physical and Applied Sciences (JPAS), Vol. 1, No. 1, 2022, pp. 28–37. [CrossRef]
- Benzeid, H. , Gouaz, F. , Touré, A. H., Bouatia, M., Idrissi, M. O. B., and Draoui, M. “Inventory of Toxic Plants in Morocco: An Overview of the Botanical, Biogeography, and Phytochemistry Studies.” Journal of Toxicology, Vol. 2018, 2018, pp. 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singleton, V. L. , and Rossi, J. A. “Colorimetry of Total Phenolics with Phosphomolybdic-Phosphotungstic Acid Reagents.” American Journal of Enology and Viticulture, Vol. 16, No. 3, 1965.
- Zhishen, J. , Mengcheng, T., and Jianming, W. “The Determination of Flavonoid Contents in Mulberry and Their Scavenging Effects on Superoxide Radicals.” Food Chemistry, Vol. 64, No. 4, 1999, pp. 555–559. [CrossRef]
- Ba, K. , Tine, E., Destain, J., Cissé, N., and Thonart, P. “Étude Comparative Des Composés Phénoliques, Du Pouvoir Antioxydant De Différentes Variétés De Sorgho Sénégalais Et Des Enzymes Amylolytiques De Leur Malt.” Biotechnology, Agronomy and Society and Environment, Vol. 14, No. 1, 2010, pp. 131–139.
- Hiai, S. , Oura, H., and Nakajima, T. “Color Reaction of Some Sapogenins and Saponins with Vanillin and Sulfuric Acid.” Planta medica, Vol. 29, No. 2, 1976, pp. 116–122. [CrossRef]
- Mottaghipisheh, J. , Iriti, M., and Cacciola, F. “Molecules Sephadex ® LH-20, Isolation, and Purification of Flavonoids from Plant Species: A Comprehensive Review.” 2020. [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, B. S. , Uddin, N., Khan, A., Ali, M. I., Choudhary, M. I., Begum, S., and Marasini, B. P. “Bioassay-Guided Isolation of Urease and α-Chymotrypsin Inhibitory Constituents from the Stems of Lawsonia Alba Lam. (Henna).” Fitoterapia, Vol. 84, 2012, pp. 202–207. [CrossRef]
- Ettayebi, K. , Errachidi, F., Jamai, L., Tahri-Jouti, M. A., Sendide, K., and Ettayebi, M. “Biodegradation of Polyphenols with Immobilized Candida Tropicalis under Metabolic Induction.” FEMS Microbiology Letters, Vol. 223, No. 2, 2003, pp. 215–219. [CrossRef]
- Davidson, J. M. “Animal Models for Wound Repair.” Archives of Dermatological Research, Vol. 290, No. SUPPL. 1, 1998, pp. S1–S11. [CrossRef]
- Cai, E. Z. , Ang, C. H., Raju, A., Tan, K. B., Hing, E. C. H., Loo, Y., Wong, Y. C., Lee, H., Lim, J., Moochhala, S. M., Hauser, C. A., and Lim, T. C. “Creation of Consistent Burn Wounds: A Rat Model.” Archives of Plastic Surgery, Vol. 41, No. 4, 2014, p. 317. [CrossRef]
- Nunes, J. P. S. , and Dias, A. A. M. “ImageJ Macros for the User-Friendly Analysis of Soft-Agar and Wound-Healing Assays.” BioTechniques, Vol. 62, No. 4, 2017, pp. 175–179. [CrossRef]
- Abeje, B. A. , Bekele, T., Getahun, K. A., and Asrie, A. B. “Evaluation of Wound Healing Activity of 80% Hydromethanolic Crude Extract and Solvent Fractions of the Leaves of Urtica Simensis in Mice.” Journal of Experimental Pharmacology, Vol. 14, 2022, p. 221. [CrossRef]
- Shivananda Nayak, B. , Isitor, G., Davis, E. M., and Pillai, G. K. “WOUND HEALING ACTIVITY OF LAWSONIA INERMIS LINN. 827 The Evidence Based Wound Healing Activity of Lawsonia Inermis Linn.” Phytother. Res, Vol. 21, 2007, pp. 827–831. [CrossRef]
- Dev, S. K. , Choudhury, P. K., Srivastava, R., and Sharma, M. “Antimicrobial, Anti-Inflammatory and Wound Healing Activity of Polyherbal Formulation.” Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy, Vol. 111, 2019, pp. 555–567. [CrossRef]
- Rekik, D.M. Ben Khedir S. Daoud A. Ksouda Moalla K. Rebai T. Sahnoun Z. 2019. Wound Healing Effect of Lawsonia. Skin Pharmacology and Physiology, 2019;32:295–306µ. [CrossRef]
- Ibhim Mssillou, Meryem Bakour, Meryem Slighoua, Hassan Laaroussi, Hamza Saghrouchni, Fatima Ez-Zahra Amrati, Badiaa Lyoussi, Elhoussine Derwich 2022. Investigation on wound healing effect of Mediterranean medicinal plants and some related phenolic compounds: A review. Journal of Ethnopharmacology. 15 November 1156.
- Zhina Hadisi 1, Jhamak Nourmohammadi, Seyed Mahdi Nassiri 2018. The antibacterial and anti-inflammatory investigation of Lawsonia Inermis-gelatin-starch nano-fibrous dressing in burn wound. Int J Biol Macromol. 2018 Feb;107(Pt B):2008-2019. [CrossRef]
- Talab, A. T. , Alfuraiji, N., and Al-Snafi, A. E. “The Analgesic and Anti-Inflammatory Effect of Lawsone Isolated from Lawsonia Inermis.” ScienceRise: Pharmaceutical Science, Vol. 1, No. 35, 2022, pp. 77–84. [CrossRef]
- Goldenheim, P. D. “An Appraisal of Povidone-Iodine and Wound Healing - PubMed.” Postgrad Med J, Vol. 69, No. 3, 1993, pp. 97–105.
- Mcnulty, C. , Rodgers, G. L., Mortensen, J. E., and Christopher’, S. “An Overview of the Topical Antimicrobial Agents Used in the Treatment of Burn Wounds.” Continuing Education Topics & Issues, 2004, pp. 74–78.
- Atiyeh, B. S. , Costagliola, M., Hayek, S. N., and Dibo, S. A. “Effect of Silver on Burn Wound Infection Control and Healing: Review of the Literature.” Burns : journal of the International Society for Burn Injuries, Vol. 33, No. 2, 2007, pp. 139–148. [CrossRef]
- Klasen, H. J. “A Historical Review of the Use of Silver in the Treatment of Burns. II. Renewed Interest for Silver.” Burns, Vol. 26, No. 2, 2000, pp. 131–138. [CrossRef]
- Seyed, J. H. , Ghasemali, K., Azadbakht, M., Peyman, Z., Ghasemi, M., and Amirhossein, A. “Effect of Aloe Cream versus Silver Sulfadiazine for Healing Burn Wounds in Rats - PubMed.” Acta Dermatovenerol Croat, Vol. 18, No. 1, 2010, pp. 2–7.
- Khorasani, G. , Hosseinimehr, S. J., Zamani, P., Ghasemi, M., and Ahmadi, A. “The Effect of Saffron (Crocus Sativus) Extract for Healing of Second-Degree Burn Wounds in Rats.” The Keio Journal of Medicine, Vol. 57, No. 4, 2008, pp. 190–195. [CrossRef]
- Bahramsoltani, R. , Farzaei, M. H., and Rahimi, R. “Medicinal Plants and Their Natural Components as Future Drugs for the Treatment of Burn Wounds: An Integrative Review.” Archives of Dermatological Research, Vol. 306, No. 7, 2014, pp. 601–617. [CrossRef]
- El Massoudi, S. , Benidir, M., Chabir, R., Benjelloun, M., El Ghadraoui, L., and Errachidi, F. “Morphological, Biochemical, and Climatological Analysis of Three Moroccan Henna Verities.” Scientific World Journal, Vol. 2019, 2019. [CrossRef]
- Manuja, A. , Rathore, N., Choudhary, S., and Kumar, B. “Phytochemical Screening, Cytotoxicity and Anti-Inflammatory Activities of the Leaf Extracts from Lawsonia Inermis of Indian Origin to Explore Their Potential for Medicinal Uses.” Medicinal Chemistry, Vol. 17, No. 6, 2020, pp. 576–586. [CrossRef]
- Ankita Raisagar, Chanchal Deep Kaur, Hemant A Sawarkar, Lokesh Kumar, Anita Raisagar, Arjun Karmakar, and Mahendra Sahu. “Comparative Study of Wound-Healing Effect of Bark Extracts of Ficus Religiosa & Ficus Benghalensis by Mice Model.” ~ 1815 ~ Journal of Pharmacognosy and Phytochemistry, Vol. 8, No. 2, 2019, pp. 1815–1821.
- Sahib, A. S. , Al-Jawad, F. H., and Alkaisy, A. A. “Effect of Antioxidants on the Incidence of Wound Infection in Burn Patients.” Annals of Burns and Fire Disasters, Vol. 23, No. 4, 2010, p. 199.
- Platon, J. F. “Lipids in Cosmetology.” Oleagineux Corps Gras Lipides (France), Vol. 4, No. 4, 1997, pp. 275–281.
| Extracts | AQ-LI 1 | AQ-LI 2 | AQ-LI 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aqueous extract (AQ) Yields (%) | 50.89±3.05 | 24.80±1.74 | 37.41±1.90 |
| Total phenolic compounds (g GAE) /100g DM) | 13.484±0.81 | 6.46±0.50 | 8.338±0.42 |
| Total flavonoids (g QE/100 g DM) | 9.246±0.55 | 4.425±0.40 | 5.539±0.28 |
| Total tannin (g TAE/100g DM) | 2.57±0.15 | 1.4284±0.15 | 0.3865 0.05 |
| Saponins (mg/100 g DM) | 291.67±17.50 | 83.38±5.84 | 321.5±16.10 |
| Ointment formulation | AQ-LI1 | AQ-LI2 | AQ-LI3 | PC | NC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Epithelialization period (day) | 20.33±4.65 | 21.67±5.1 | 19.33±0.05 | 30.67±3.63 | 42.33±24.54 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





