1. Introduction and Background Information / Objectives of the Study
1.1. Background
In industrial societies, people have created unparalleled wealth and materials, which have not only provided us with advanced production tools, but also new challenges and problems, which have created contradictions and conflicts between man and nature. The continued emergence of unprecedented resource constraints, environmental degradation and ecological crises all suggest that replacing industrial civilisation with ecological civilisation is the only way for mankind to emerge from this crisis.
Since the 1960s, the importance attached to ecology and the environment has gradually penetrated into people's daily lives, and people have realised the importance they attach to the ecological environment and launched various ecological and environmental protection initiatives. In the country as a whole, environmental protection functions have been given attention and promotion by the government. In 1983, the concept of environmental protection was widely promoted as a long-term national policy. In 2007, the 17th National Congress of the Communist Party of China (CPC) further clarified that "an ecologically oriented value should be established in society as a whole.
Guangzhou is China's national core metropolis and a world-renowned seaport metropolis, leading the industrialisation and urbanisation of the Pearl River Delta. It is an important hub for the country's economy, finance, commerce and trade, shipping and convention, and is the region with the largest economic, economic and cultural radiation. Guangzhou achieved a GDP of $181 million (GDP) in 2016, with a per capita income of around US$20, 000, achieving an overall increase in GDP and realising a total citywide GDP of $134.91 billion, an increase of 8.5% year-on-year. The industrial structure was good, with 320 companies having set up their headquarters in Nansha and a new record of 1, 000 billion yuan in service sector output, with a ratio of 1.26:31.97:66.77 between the three industries.
In terms of investment in people's livelihood, the per capita disposable income of urban households reached RMB46, 600 and the per capita disposable income reached RMB19, 300. An additional 211.5400 urban jobs were created, greatly reducing the pressure on employment. The level of social security for urban residents increased by 89.41%, 166, 800 more affordable homes were built, and 1, 108, 000 more households used natural gas, giving effective protection to 56% of the population.
Across the country, the environment was effectively improved, with 312 days of atmospheric quality and an average PM2.5 concentration of 39 microns per square metre. The average PM2.5 concentration was 39 microns per square metre. The pollution control of water bodies has been stepped up continuously, with the Pearl River in Guangzhou still maintaining a Class IV status and the drinking water standard in urban areas reaching 100%. More than 3, 000 kilometres of green corridors have been built, and wetlands such as the Nansha Wetland, the Haizhu Wetland and the Huadu Lake have reached 42% forest coverage, realising green and low-carbon development.
Guangzhou ranks 5th in terms of overall strength, slightly behind Taipei City in Taiwan Province. Guangzhou has a resident population of 13.505 million, with 450.010 households and 2.74 persons per household per capita, of which 6.915.8 million (51.17%) are men, 6.582.9 million (48.76%) are women and 6.582.9 million (48.76%) are women, with a gender ratio of 105.08.
This year was also a year of accelerating urbanisation in China, with urbanisation levels reaching 71%, the highest in the country (Zhang Yuqin and Wu Xie, 2012). After the Asian Games, Guangzhou will accelerate its industrial restructuring, build a harmonious and stable society, promote "green ecology" and "low-carbon wisdom", and actively implement the urban development strategy of "southward expansion, northward optimization, eastward advancement and westward linkage". We will actively implement the urban development strategy of "expand in the south, optimize in the north, advance in the east and link up in the west", and integrate "landscape", "city", "field" and "seaside" into one, with natural, natural and natural resources. "It is a modern, natural and livable city.
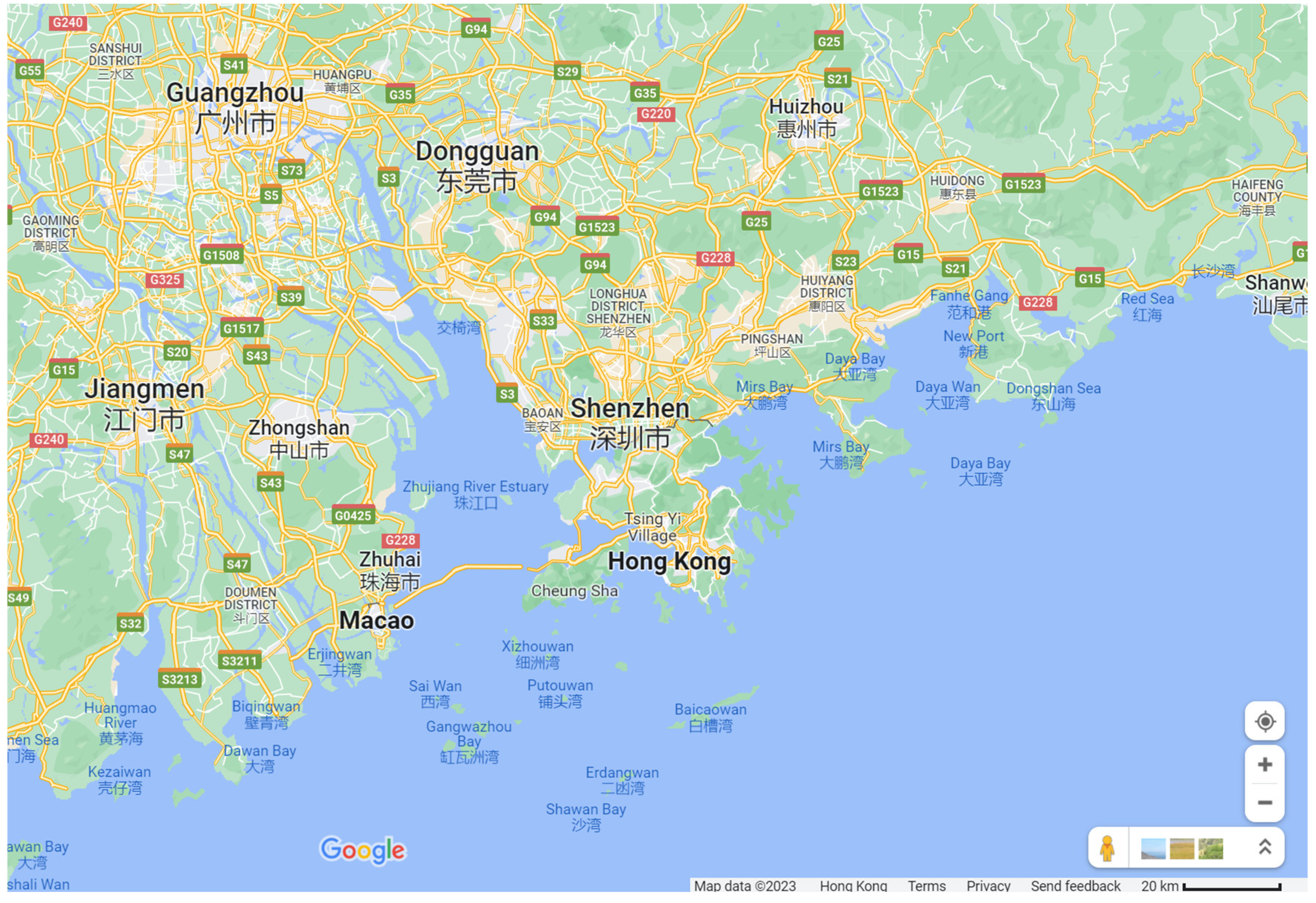
Nansha is located at the southernmost tip of Guangzhou, west of the Pearl River estuary, in the Pearl River Delta, 28 kilometres from Hong Kong and 41 kilometres from Macau. It is 28 kilometres from Hong Kong and 41 kilometres from Macau. If we draw a circle around Nansha, a radius of more than 100 kilometres, we will have a population of 40 million in Shenzhen, Zhuhai, Guangzhou, Foshan and Dongguan, making up a total of 14 cities. Nansha New District has a planned area of 803 square kilometres, and by the end of 2015, the total regional production value was 133.37 billion yuan, with a tax revenue of 33.41 billion yuan; a fixed asset investment of 62.05 billion yuan was realised; of which, the total production of agriculture, forestry and animal husbandry was 8.402 billion yuan, and the total industrial production was 292.773 billion yuan; of which, the port passed 200 million 87 million tonnes of cargo and 11, 852, 000 TEUs of cargo; the city's domestic trade turnover was RMB87.5 billion, of which RMB17.075 billion; there were 9.86 million visitors and RMB2.62 billion of tourism in the year; the average wage of the urban resident population was RMB3, 830 and the average wage of the rural population was RMB2, 800.
In the process of development, Nansha and Guangzhou are facing outstanding problems such as resource constraints, environmental pollution and ecological deterioration, and people's demands and requirements for ecological civilisation are becoming increasingly urgent. For this reason, it is necessary to follow the path of "green ecological" development in accordance with the concept of socialist ecological civilization and in line with the regional, municipal and provincial conditions.
1.2. Significance of the Study
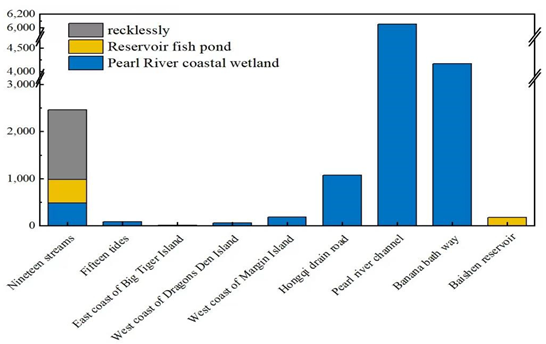
The Nansha New Area and Guangzhou as a whole must seriously implement the Central Government's policy of building a socialist ecological civilisation in accordance with its actual situation, and choose a "green" development path that is in line with its own regional, municipal and provincial conditions. The Nansha Coastal Wetland Scenic Area is located in the south of Guangzhou, covering an area of about 3, 400 hectares in Phase I and more than 6, 000 hectares in Phase II, and is one of the world's most famous tourist attractions. The wetlands are Guangzhou's rare "kidneys of the city", and together with the forest and the sea, they form the three largest ecosystems on earth, and are a resource on which human beings depend, both ecologically and economically.
What is the state of development and protection of the coastal wetlands in Nansha over the past few decades, and what should be the next step of development? On this basis, we will systematically analyse the main measures and achievements in the protection and development of Nansha coastal wetlands, identify the obvious problems and potential risks of Nansha coastal wetlands, analyse the causes of these risks, and provide a set of more targeted and operable strategies for strengthening the protection of Nansha coastal wetlands in the future, so as to maintain and promote the sustainable development of Nansha coastal wetlands. This will provide a scientific basis and technical support to maintain and promote the sustainable development of Nansha coastal wetlands, inspire the ecological civilisation of mankind, and guide the Nansha area and the entire Guangzhou city into a new stage of development.
The development of the new Nansha area in the south of Guangzhou, the upgrading of industries, the start of high-end industries on both sides of the Pearl River Delta, the rapid development of three major industries - Nansha port, emerging technologies and equipment manufacturing - as well as the construction of infrastructural support bases such as the automobile industry, shipyards, steel and petrochemicals, all need to be expedited. Under such circumstances, how to handle the relationship between the two is an issue that must be faced by the party committees and governments at all levels as well as the relevant functional departments.
The outcome of the project will provide scientific and rational policy recommendations for China's economic and social development, and provide a basis for decision-making on China's economic and social development.
Nansha New District has played a pivotal role in Guangzhou's "southern expansion", forming a "golden triangle" in the economic transformation of the Pearl River Delta, together with Qianhai in Shenzhen and Hengqin in Zhuhai. Located on the west bank of the Pearl River estuary, the Nansha coastal wetland is a shining pearl in the "Golden Triangle". If it can be further protected and utilised as a carrier, it will play a positive role in promoting the industrial and new urbanisation of the surrounding areas, bringing significant ecological effects as well as economic and social benefits. On this basis, a scientific and reasonable evaluation of the ecological system of our wetlands will be of great scientific value to the construction of our ecological environment.
1.3. Research Objectives
Based on the perspective of sustainable ecological values, we apply the theories of ecological economy, public goods, dissipative structure, sustainable development, etc., through a large number of international and domestic research on wetlands, and through comparison and generalisation, we obtain some useful experiences and inspirations to sort out the research status of coastal wetlands in Guangzhou, analyse the research results of coastal wetlands in Guangzhou, analyse the protection measures and effects of coastal wetlands in Guangzhou, and explore the research status of coastal wetlands in Nansha. The study also explores the potential problems and risks of Nansha coastal wetlands and their causes, and examines the conservation measures of Nansha coastal wetlands at both macro and micro levels, with a view to providing a scientific and credible basis and concrete practical guidance for the relevant departments of Guangzhou and Nansha New District to formulate sustainable development plans for Nansha coastal wetlands.
1.4. Research Content
This paper first discusses the background of the project, the significance and purpose of the study, the research methodology and the technical approach, explains some basic concepts, summarises the basic theories of the project, and reviews and judges the research literature on wetland conservation and development by domestic and foreign scholars. It then analyses the important contents, basic practices and effects of the Nansha coastal wetland by describing the formation and development of the coastal wetland in Guangzhou, and based on this, the problems and hidden dangers of the Nansha coastal wetland and the causes of the "bright" and "dark" problems. A more comprehensive and insightful analysis is presented. Drawing on international experience and lessons on the conservation and utilisation of wetlands, the study also examines the "four major conservation relationships", "five major regulatory tools", "four major institutional reforms", "four major conservation techniques", and "four major conservation techniques", In the five aspects of "four major protection techniques" and "timely implementation of the four major protections", a series of policies to enhance the protection of coastal wetlands in China are proposed in the aspects of "45444" respectively. A series of policies and measures to enhance the protection of coastal wetlands were proposed in the aspects of "45444", and relevant research results were obtained.
1.5. Research Methodology
In the implementation of the project, the author will insist on combining theory and practice, norms and empirical evidence, field research and theory, and qualitative and quantitative research. Research Methodology: Based on theories related to ecological economy, public goods, dissipative structure and sustainable development, the author will conduct a comprehensive evaluation of the ecological environment of the Nansha coastal wetlands, identify the feasibility and necessity of enhancing the ecological environment of the Nansha coastal wetlands, and determine the research targets, research directions and methods.
Documentary Approach: Through checking and collating policy documents related to the construction of ecological civilisation in recent times and relevant literature on wetland conservation in China and overseas, we will conduct a comprehensive understanding of the formation and current state of Nansha coastal wetlands, carefully screen relevant research on Nansha coastal wetlands, sort out relevant theories and concepts, and identify clear research themes.
Comparative study: To understand the development history, conceptual evolution, classification, conservation methods, development history, successes and failures of typical coastal wetland conservation and utilisation in the international arena, and to extract useful extracts from them, so as to provide a basis for Guangzhou City and Nansha District to develop coastal wetland conservation.
On-site research: Through on-site research, we will conduct an in-depth investigation into the geographical location, natural ecology, landscape pattern, industrial structure, protected areas, the current state of conservation work, its effects, shortcomings and causes, and at the same time combine the characteristics of my work in Nansha Marsh to obtain more data, so as to lay a solid theoretical and practical foundation for further in-depth development.
Data analysis method: Taking Guangzhou City and Nansha District as examples, I used Internet terminal equipment, major bookstores and libraries to collate and analyse data related to Nansha coastal wetlands obtained from field research and questionnaire surveys, and applied them to the article, so that the research results of the article are more scientific and reliable.
Case study method: The analysis of representative cases in the development and protection of Nansha's coastal wetlands, the continuous collection and comparison, the threading of needles and the identification of the nature of the problem. By analysing the superficial phenomena, the core ideas will be extracted and some regularities will be found to match with the project designed in this topic, providing stronger opinions and evidence for Nansha New District to build a new coastal city under Guangzhou's "southward expansion" strategy and for the protection and utilisation of wetland resources in Nansha. The project will also provide stronger advice and evidence for the conservation and utilisation of wetland resources in Nansha.
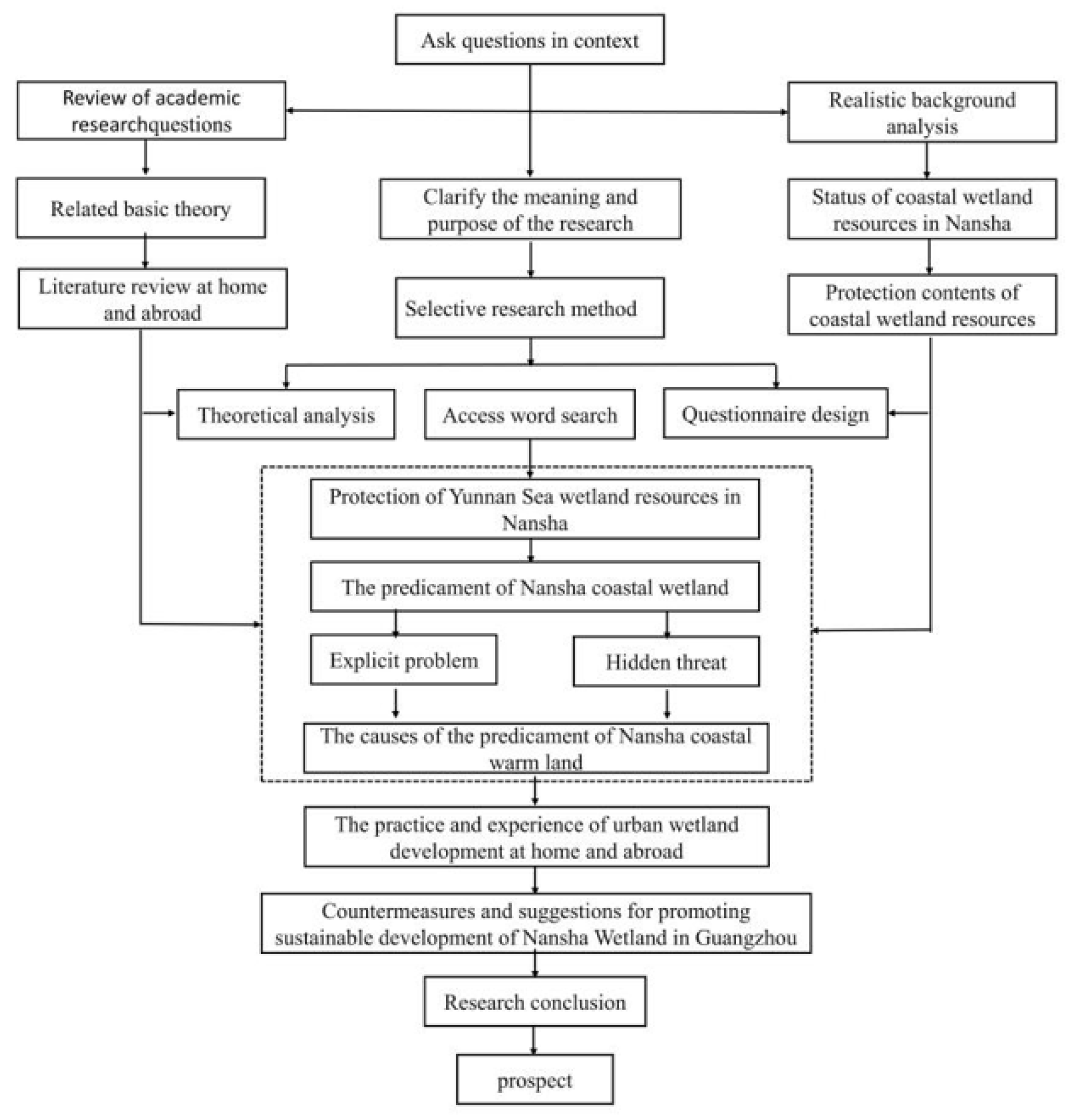
1.6. Technical Roadmap
Figure 1.1.
Technical Roadmap.
Figure 1.1.
Technical Roadmap.
7. Basic Conclusions and Prospects
7.1. Basic Conclusions
The Nansha area is located in the middle of the Pearl River Delta and is within one hour's reach of all major cities in the Pearl River Delta, thus Guangzhou has an important strategic position in the rational development and development of the Greater Nansha. In accordance with the strategic requirements of the Guangzhou government to "build a new Guangzhou", the rational development and construction of tourism should be a key component of the future development of the Nansha New Area, taking into account the rich tourism resources and the economic development of the Nansha New Area.
The article concludes the following:
(1) In the process of Guangzhou's "southern expansion", it is necessary to rationalise the thinking and correctly grasp the common interests of "Nansha New Area", "coastal wetland" and "Nansha coastal wetland". "(2) The common interests of Nansha
(2) The idea of tourism development in Nansha is to adopt an ecology-based approach, carry out ecological planning and theoretical analysis of the city and its landscape, focus on the creation of a tourism culture and the culture of Sha Tin and the water village, and use sustainable development as a guiding principle to co-ordinate urban and rural areas and strengthen economic and tourism exchanges with neighbouring cities.
(3) In the future, Nansha New Town will become a world-renowned waterfront resort and a focus of global attention. The tourism industry in Nansha should follow the concept of integrating ecological and urban development, and on the basis of sustainable development, maintain the original natural scenery and construct a greening system in the process of developing and maintaining scenic spots, so as to both maintain its own ecology and enhance its own tourism industry in the process of promoting the development of tourism in Nansha New Town.
7.2. Prospects
Since China officially signed the Convention on Wetlands, studies on wetland conservation and development have been conducted throughout the country, and the general public has been mobilised to work together in this area. At a conference on the 20th anniversary of China's signing of the Convention on Wetlands, Hui Liangyu proposed a policy of "focusing on energy conservation, ecological protection and restoration, and promoting ecological protection and ecological conservation at the same time", incorporating it into the scope of ecological protection and making it closely linked to China's ecological protection so that Our country's ecological environment and economy have reached a new level.
The Standing Committee of Guangzhou City has endorsed the Strategic Plan for the Construction of Guangzhou Nansha Smart Island, which clearly defines the overall development goals up to 2020. This indicates that Nansha will remain at the centre of the "southern expansion of Guangzhou" and will continue to play a central role in the next one to two decades. The Strategic Plan specifies the objective of building a "smart island", with Guangdong, Hong Kong and Macao as the base, and "Guangdong", "Hong Kong" and "Macao" as the basis. Nansha will become a "Smart City" and a "Smart City" based on "Guangdong", "Hong Kong" and "Macao", and supported by "smart" technologies. The "City of Wisdom".Nansha New District is the frontline of Guangzhou's "development to the south", and is also the key to Guangzhou's integration with the international community and the promotion of "early and pilot implementation" in Hong Kong and Macao. The study intends to formulate a pragmatic plan, clarify the functions of various departments, strengthen public participation, and actively seek support from national, provincial and municipal policies, so as to build a sound "Nansha Smart Island" as the core, with Hong Kong and Macao as the backing, and the "Free Trade Zone" as the backing, and provide quality professional and technical personnel to the Nansha New Area and introduce them into the "green" field. We will also introduce them to the field of "green environmental protection" and develop the concept of "green low-carbon and green environmental protection".
The author believes that in the future, Nansha New District will continue to improve the information system and network of the tourism industry, and combine modern information technology and technology such as mobile internet, big data and social networking to meet the increasing needs of people for internet and make it easier for people to experience the changes brought about by mobile business. Based on the characteristics and resource advantages of Nansha's tourism industry and drawing on the successful experience of international smart tourism, it will be developed into a new growth point for tourism development, allowing people to have better access to information about Nansha when they are out and about, allowing the Nansha government to make better use of this information, and better provide resources for Nansha's This will enable the Nansha government to make better use of this information and provide technical assurance for the development of Nansha's resources and ecological protection, so that it can be more accurately positioned, better planned, more rationally developed, more harmoniously developed, and more consistently developed, so that Nansha New District, the sub-centre of Guangzhou, can truly become a new coastal city suitable for living and life in the context of the "southern expansion" of Guangzhou.
7.3. Issues to Be Explored
In collecting important information and data on the Nansha Wetland Scenic Area, especially in the in-depth study and sorting out the conflicting issues between wetland development and conservation, the author has identified a number of issues that need further study in the future:
- (1)
The quantitative linkage between the conservation of the Nansha Marsh Scenic Area and the local social and economic development of the Nansha District is illustrated.
- (2)
The general and specific aspects of the development of "Territorial Tourism" and "Ecotourism" in Nansha District.
- (3)
The variable relationship between the direction of urban development in Guangzhou and the direction of urban development in Nansha, and the linkage between the direction of urban development and the direction of urban development.