Submitted:
15 May 2023
Posted:
16 May 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
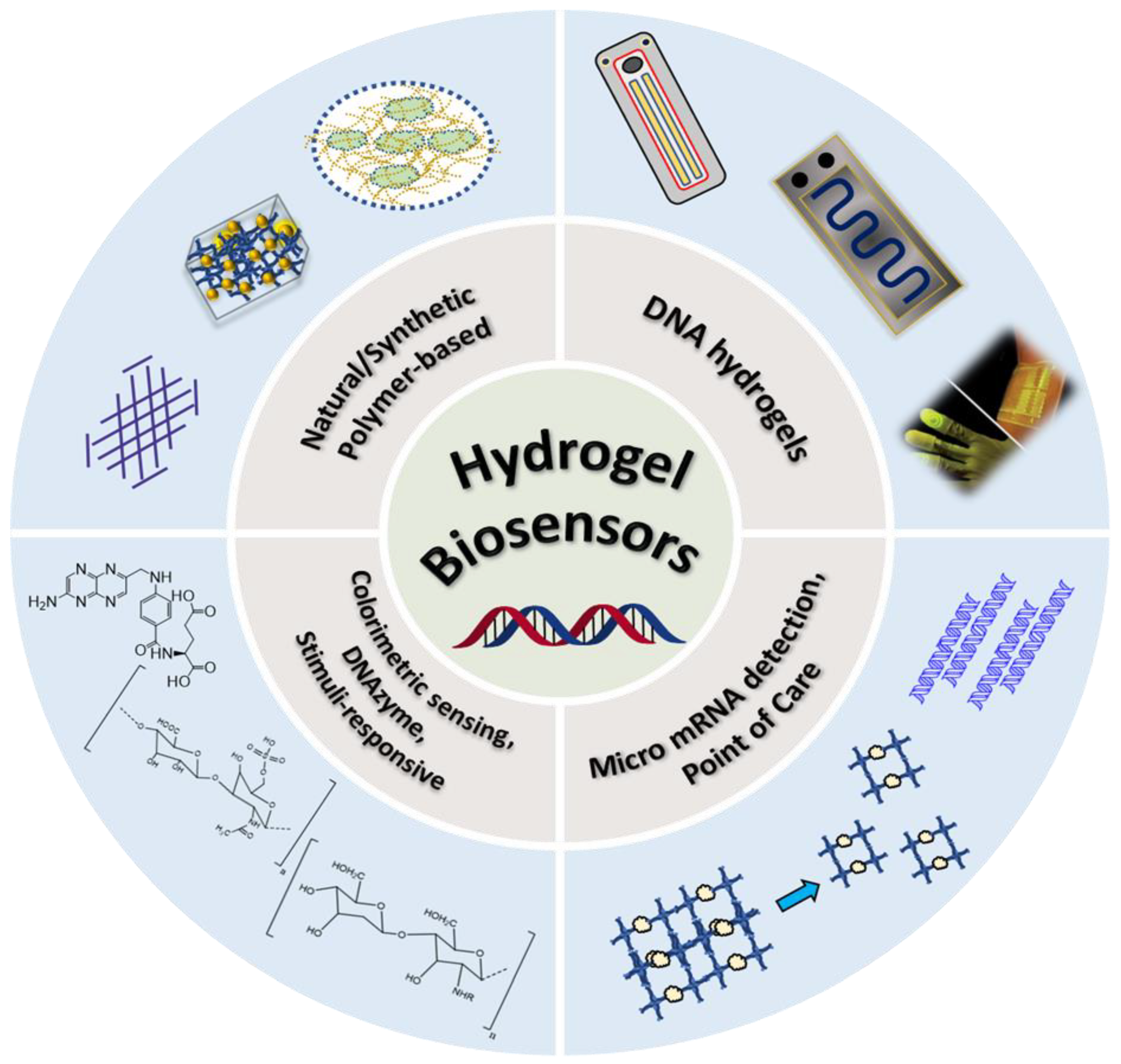
1. Introduction
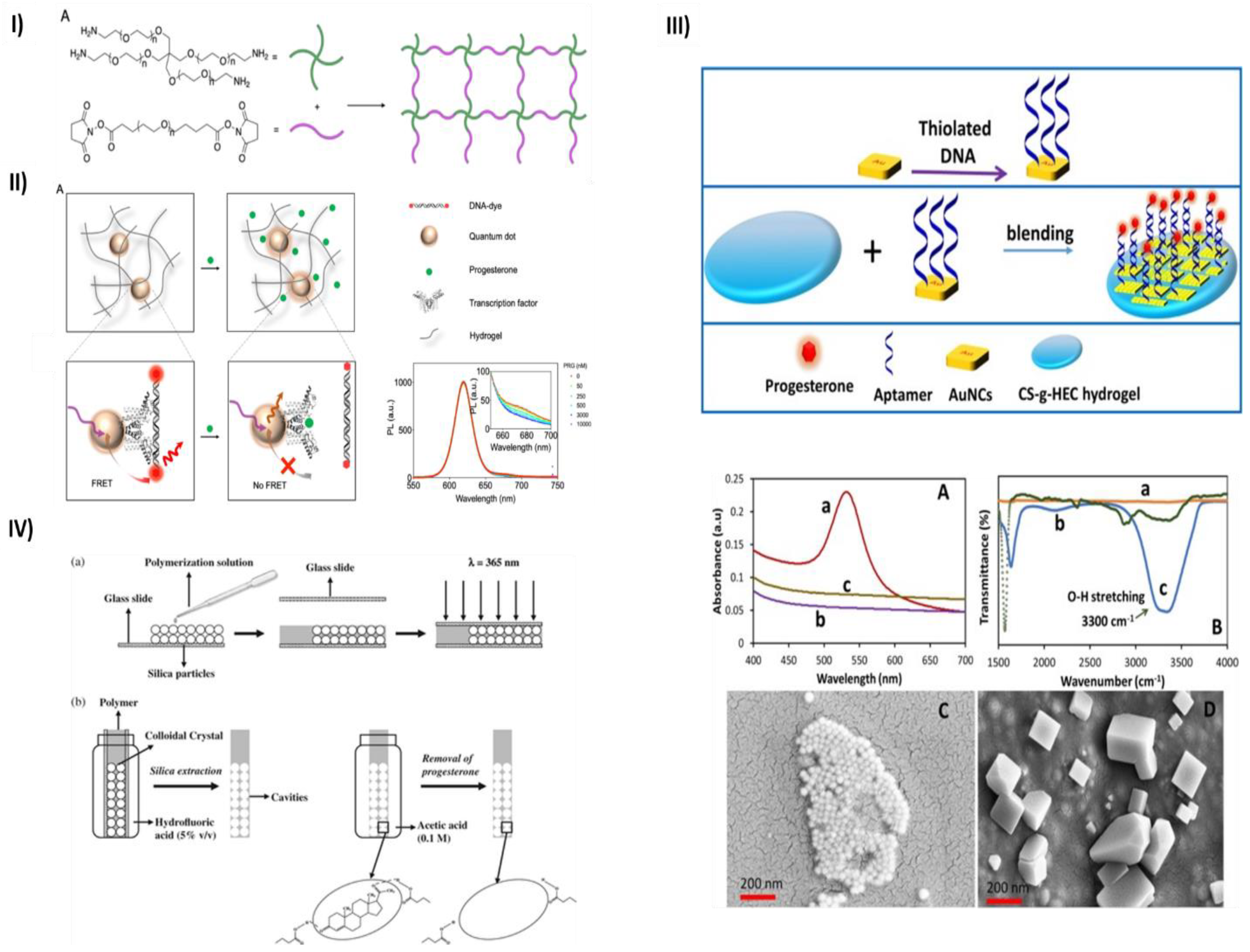
1.1. Hydrogels for progesterone detection
2. DNA-based hydrogels as biosensors
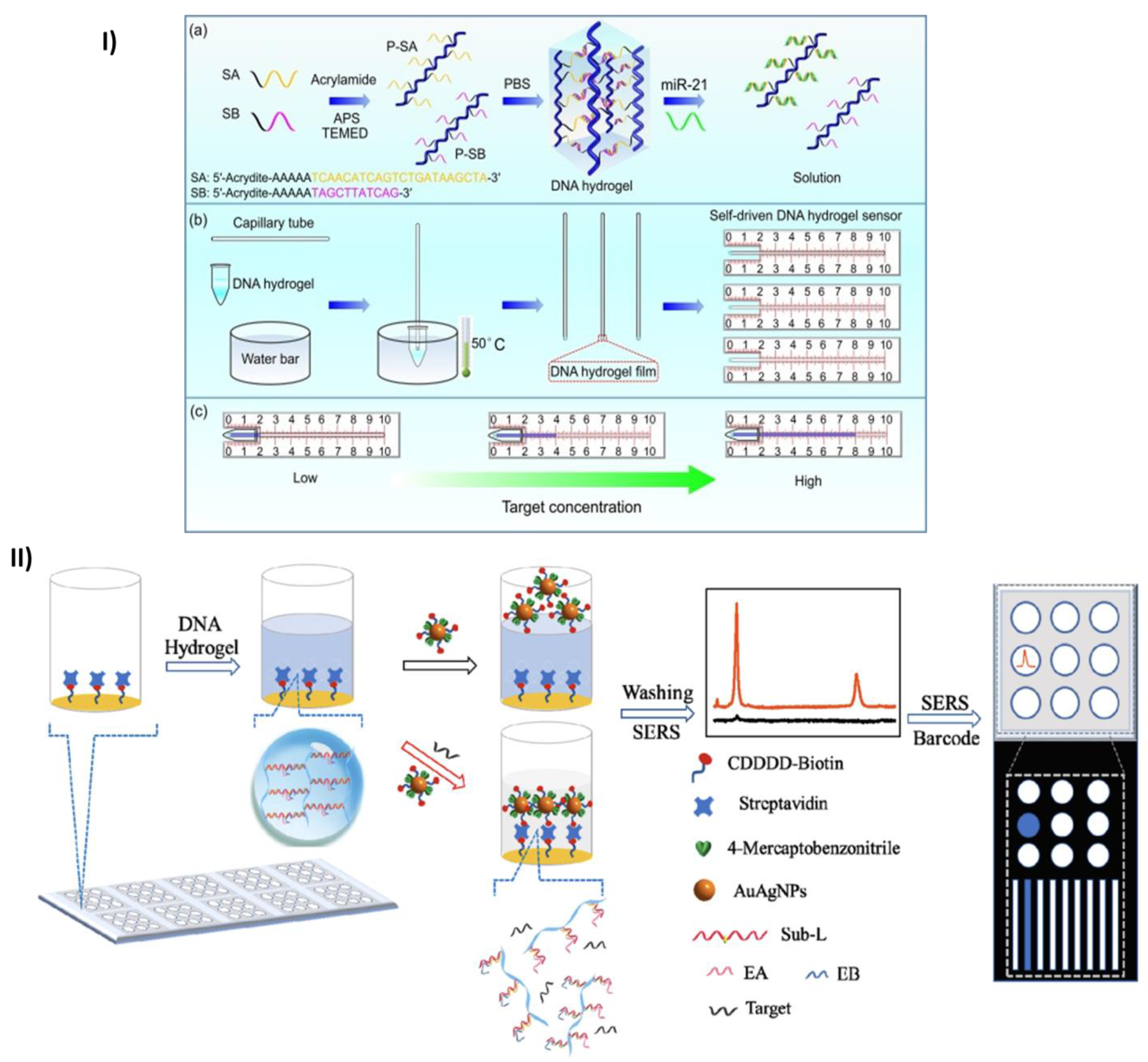
2.1. Micro RNA (miRNA) quantification and detection
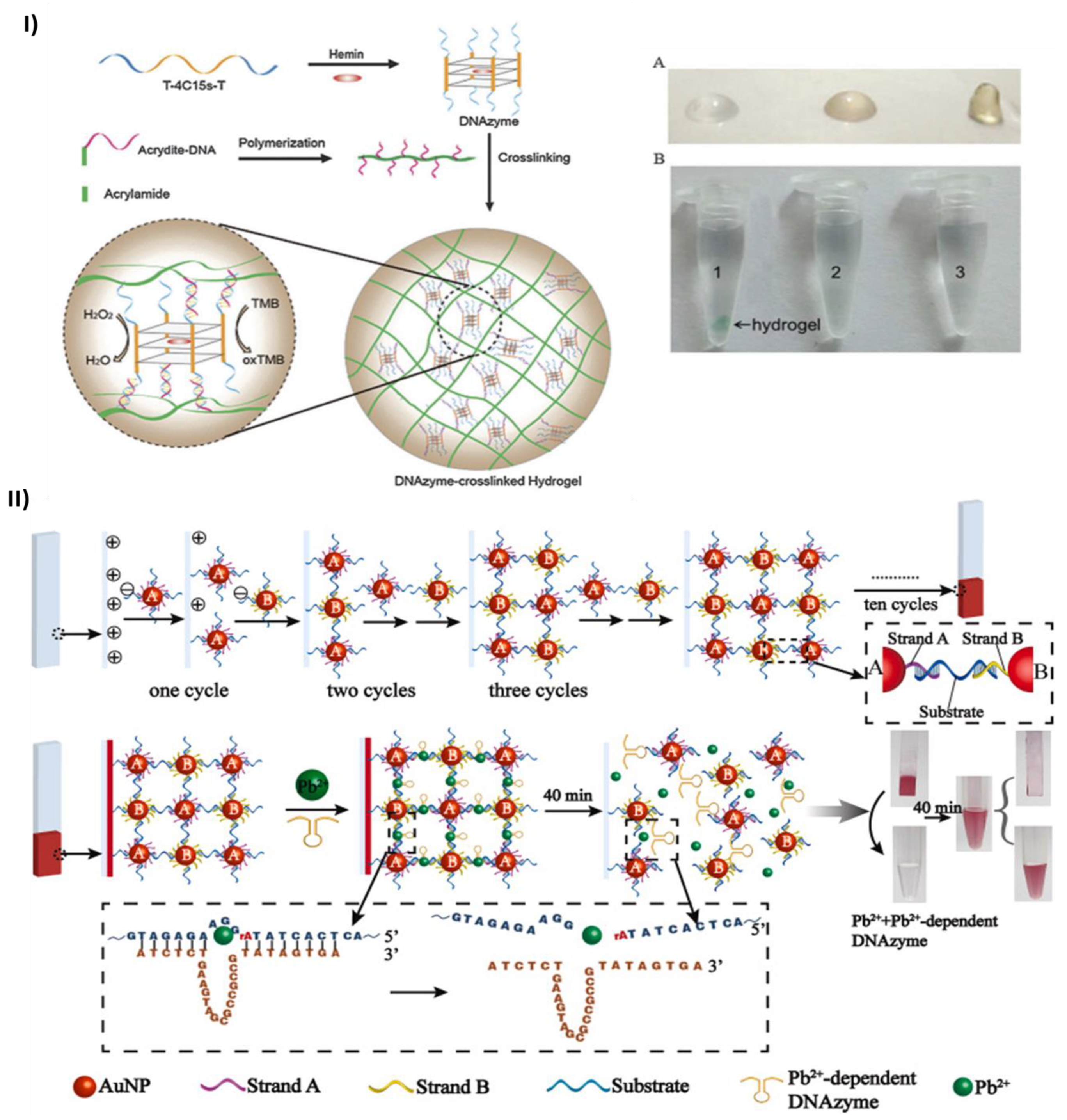
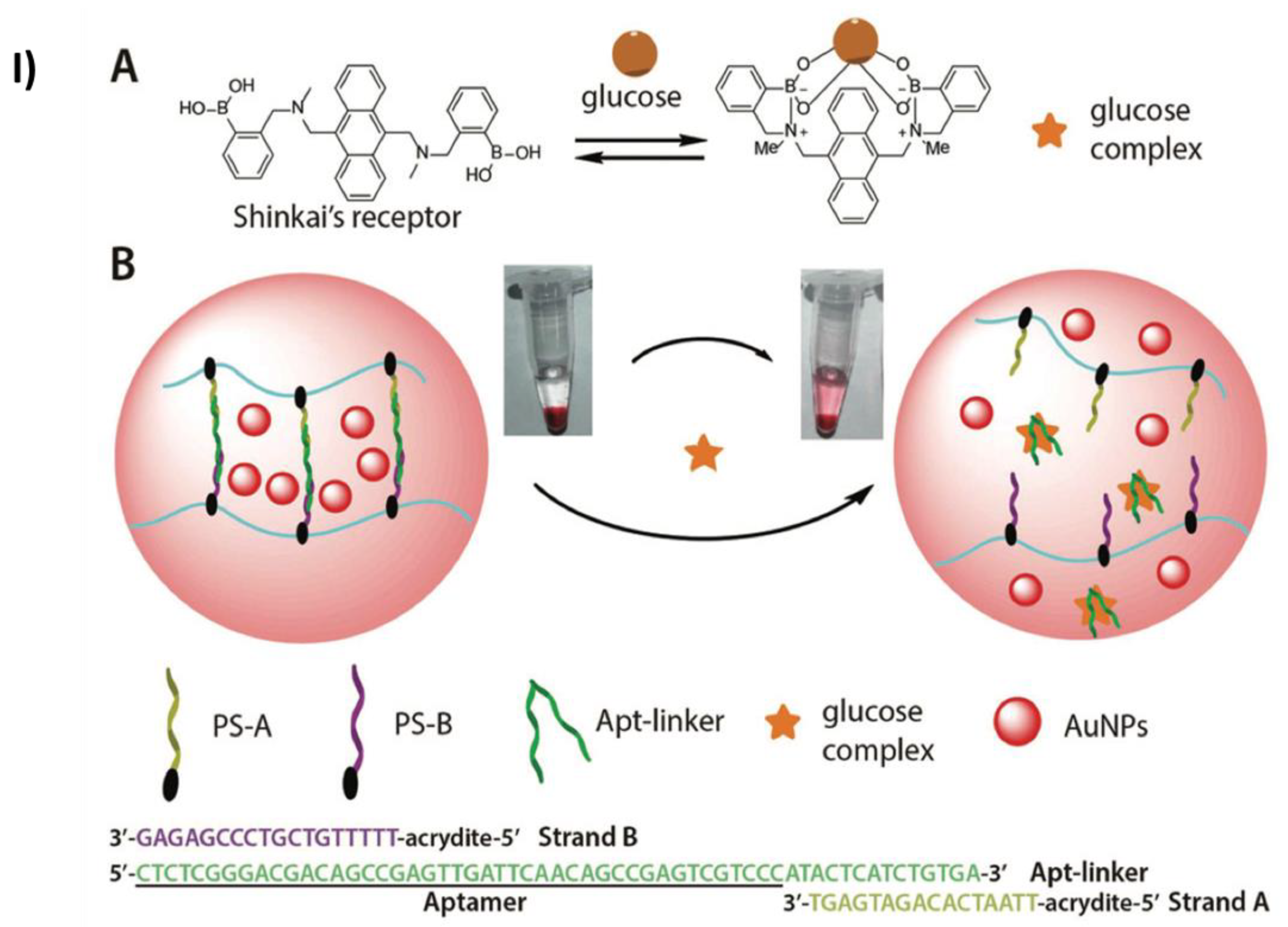
2.2. Colorimetric sensing
2.4. Point-of-care
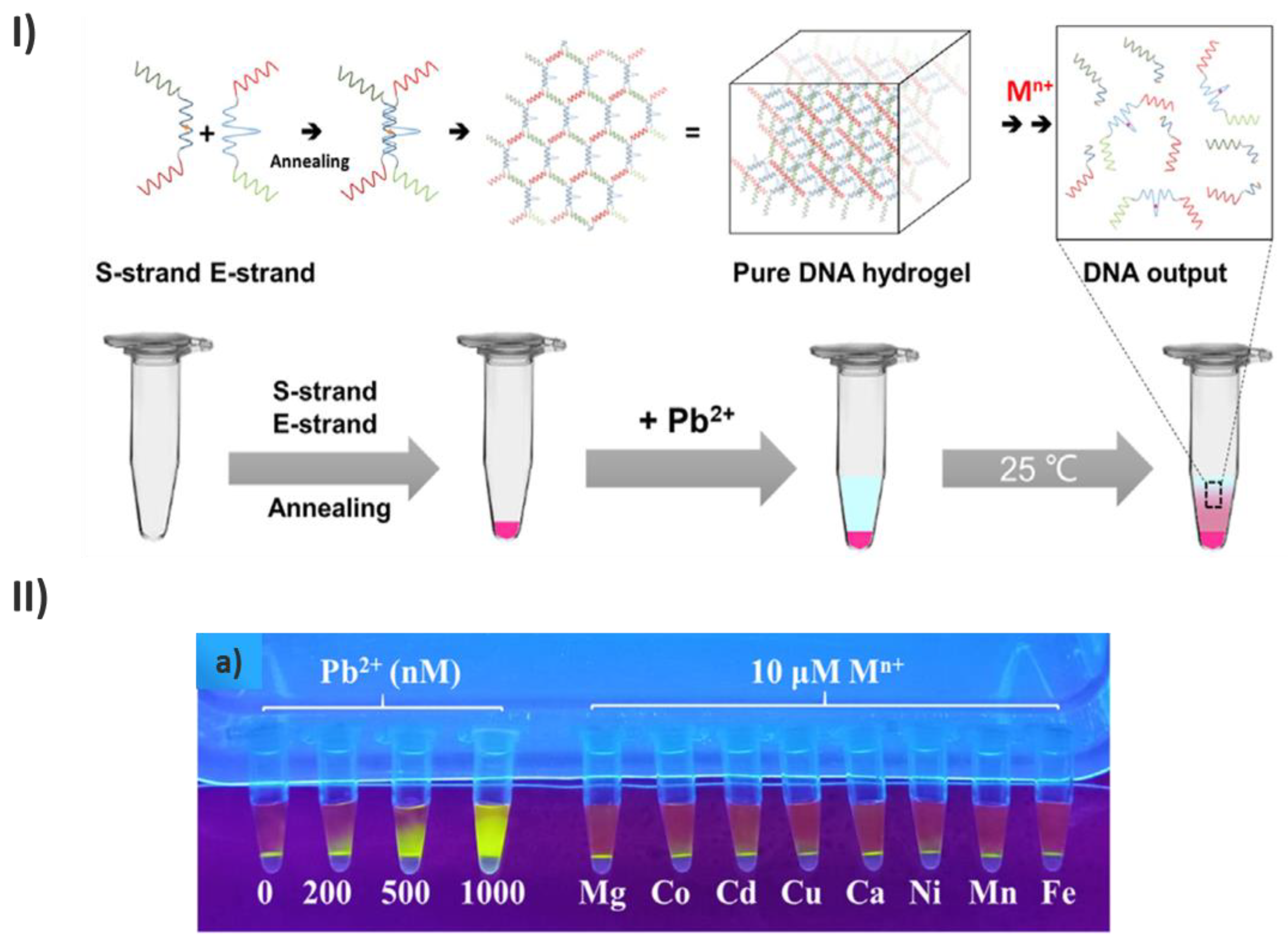
2.5. Label-free detection
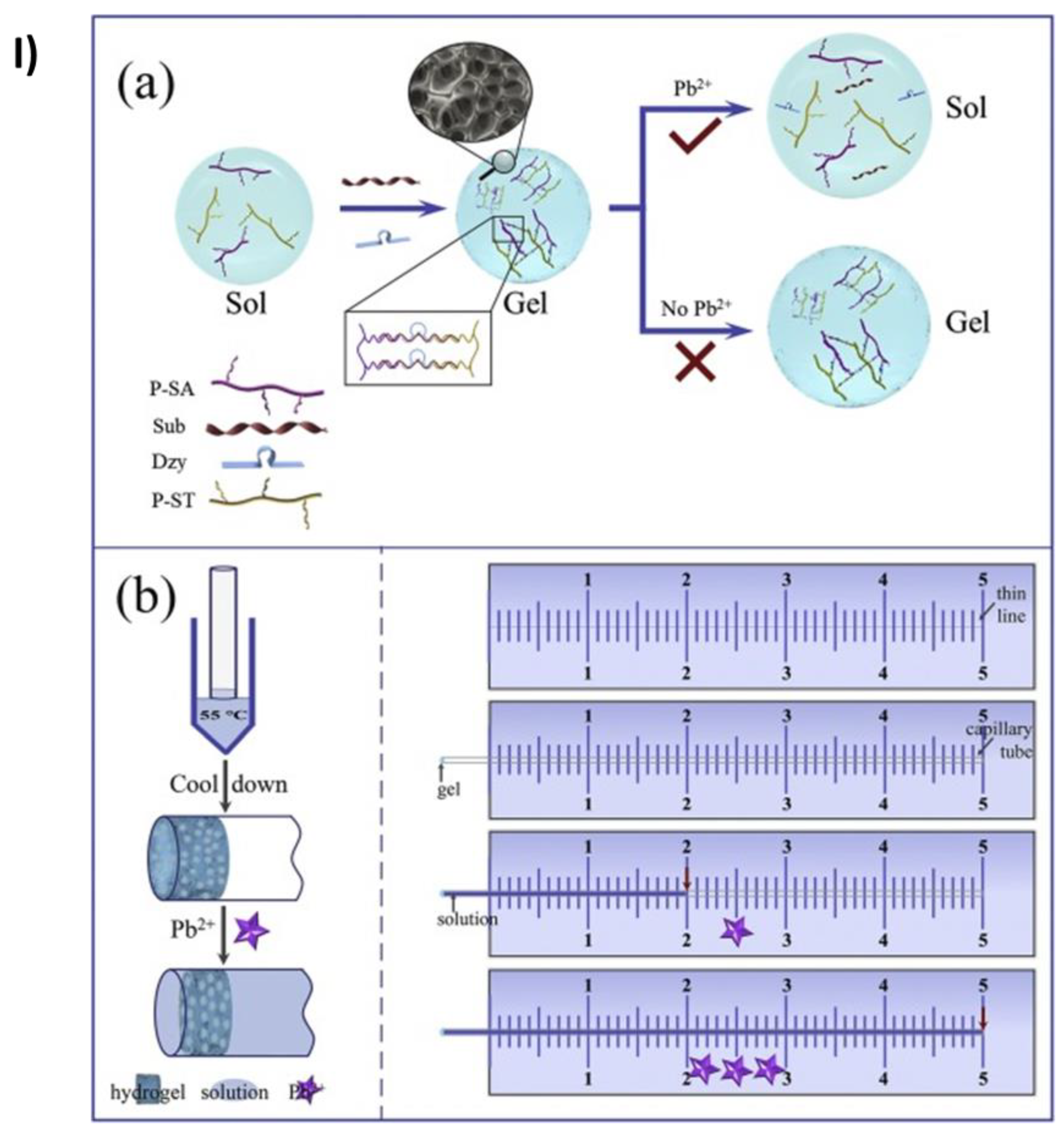
2.6. Target responsive
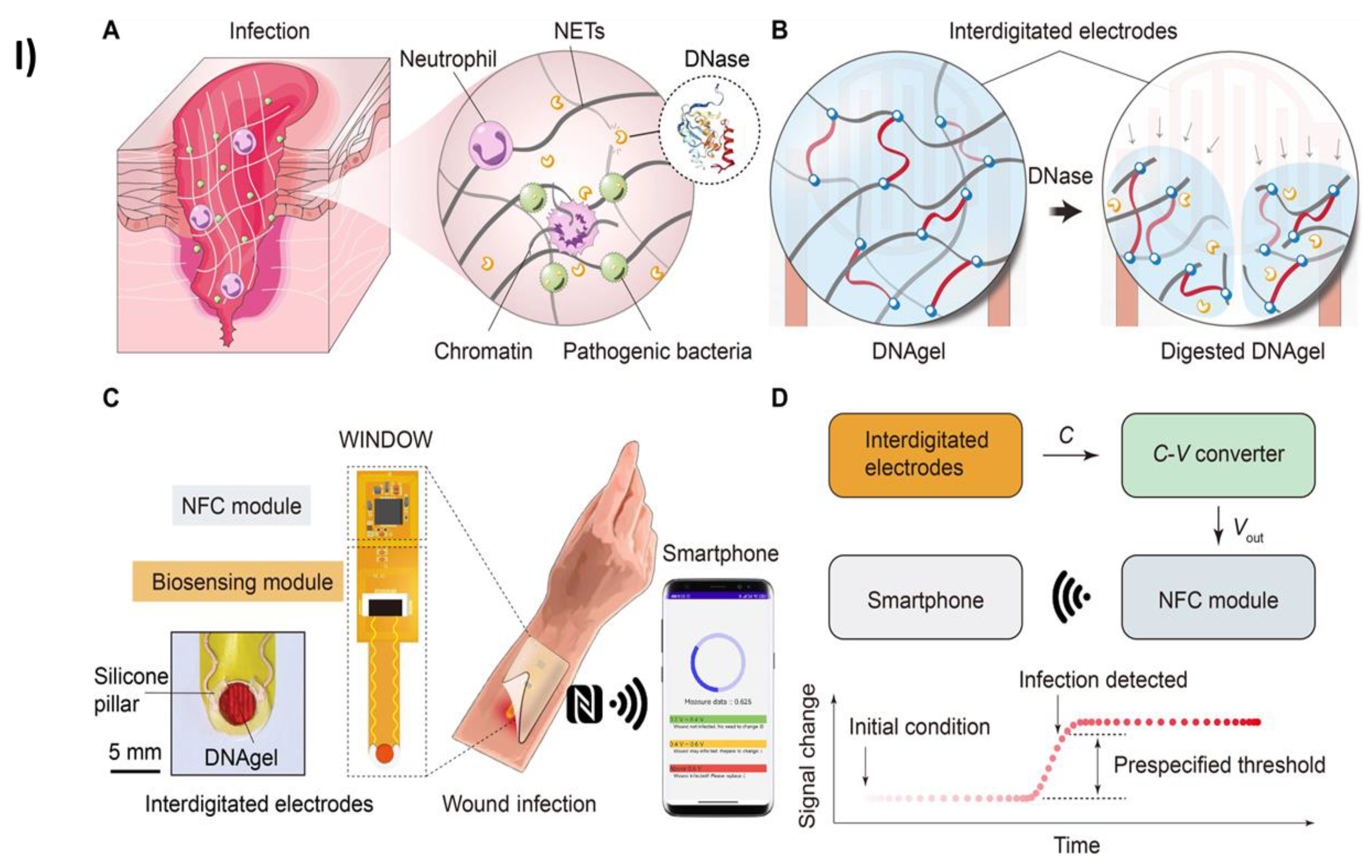
2.7. DNA Hydrogels induced miscellaneous application in sensing
3. Outlook and future directions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gavin, D.R.; Ross, H.E.; Skinner, H.A. Diagnostic Validity of the Drug Abuse Sereening Test in the Assessment of DSM-III Drug Disorders; 1989; Vol. 84.
- Quazi, M.Z.; Park, J.; Park, N. Phototherapy: A Conventional Approach to Overcome the Barriers in Oncology Therapeutics. Technol Cancer Res Treat 2023, 22, 153303382311709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De La Rica, R.; Stevens, M.M. Plasmonic ELISA for the Ultrasensitive Detection of Disease Biomarkers with the Naked Eye. Nat Nanotechnol 2012, 7, 821–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheller, F.W.; Schubert, F.; Neumann, B.; Pfeiffer, D.; Hintsche, R.; Dransfeld, I.; Wollenberger, U.; Renneberg, R.; Warsinke, A.; Johansson, G.; et al. Second Generation Biosensors; 1991; Vol. 6.
- ANKER, J.N.; HALL, W.P.; LYANDRES, O.; SHAH, N.C.; ZHAO, J.; VAN DUYNE, R.P. Biosensing with Plasmonic Nanosensors. In Nanoscience and Technology; Co-Published with Macmillan Publishers Ltd, UK, 2009; Vol. 7, pp. 308–319 ISBN 9789814287005.
- Jeong, Y.; Kook, Y.M.; Lee, K.; Koh, W.G. Metal Enhanced Fluorescence (MEF) for Biosensors: General Approaches and a Review of Recent Developments. Biosens Bioelectron 2018, 111, 102–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duverneuil, C.; Lorin De La Grandmaison, G.; De Mazancourt, P.; Alvarez, J.-C. A High-Performance Liquid Chromatography Method with Photodiode-Array UV Detection for Therapeutic Drug Monitoring of the Nontricyclic Antidepressant Drugs; 2003. 2003.
- Fricker, M.; Messelhäußer, U.; Busch, U.; Scherer, S.; Ehling-Schulz, M. Diagnostic Real-Time PCR Assays for the Detection of Emetic Bacillus Cereus Strains in Foods and Recent Food-Borne Outbreaks. Appl Environ Microbiol 2007, 73, 1892–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, C.C.; Link, N.; Fux, C.; Zisch, A.H.; Weber, W.; Fussenegger, M. Broad-Spectrum Protein Biosensors for Class-Specific Detection of Antibiotics. Biotechnol Bioeng 2005, 89, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourzac, K. Nanotechnology: Carrying Drugs. Nature 2012, 491, S58–S60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Tang, J.; Geng, J.; Luo, D.; Yang, D. Polymeric DNA Hydrogel: Design, Synthesis and Applications. Prog Polym Sci 2019, 98, 101163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathan, S.; Bose, S. Arsenic Removal Using “Green” Renewable Feedstock-Based Hydrogels: Current and Future Perspectives. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 5910–5917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alhaique, F.; Casadei, M.A.; Cencetti, C.; Coviello, T.; Di Meo, C.; Matricardi, P.; Montanari, E.; Pacelli, S.; Paolicelli, P. From Macro to Nano Polysaccharide Hydrogels: An Opportunity for the Delivery of Drugs. J Drug Deliv Sci Technol 2016, 32, 88–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.Y.; Mooney, D.J. Hydrogels for Tissue Engineering. Chem Rev 2001, 101, 1869–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermonden, T.; Censi, R.; Hennink, W.E. Hydrogels for Protein Delivery. Chem Rev 2012, 112, 2853–2888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaharwar, A.K.; Peppas, N.A.; Khademhosseini, A. Nanocomposite Hydrogels for Biomedical Applications. Biotechnol Bioeng 2014, 111, 441–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.Q.; Yang, W.; Zuo, H.; He, H.W.; Wang, Y.J. Recent Advances of DNA Hydrogels in Biomedical Applications. J Anal Test 2021, 5, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hydrophilic Gels for Biological Use.
- Xia, L.W.; Xie, R.; Ju, X.J.; Wang, W.; Chen, Q.; Chu, L.Y. Nano-Structured Smart Hydrogels with Rapid Response and High Elasticity. Nat Commun 2013, 4, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziai, Y.; Rinoldi, C.; Nakielski, P.; De Sio, L.; Pierini, F. Smart Plasmonic Hydrogels Based on Gold and Silver Nanoparticles for Biosensing Application. Curr Opin Biomed Eng 2022, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawamura, A. Design of Nano- and Micro-Structured Molecule-Responsive Hydrogels. Polym J 2017, 49, 751–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vundavalli, R.; Vundavalli, S.; Nakka, M.; Rao, D.S. Biodegradable Nano-Hydrogels in Agricultural Farming - Alternative Source For Water Resources. Procedia Materials Science 2015, 10, 548–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Völlmecke, K.; Afroz, R.; Bierbach, S.; Brenker, L.J.; Frücht, S.; Glass, A.; Giebelhaus, R.; Hoppe, A.; Kanemaru, K.; Lazarek, M.; et al. Hydrogel-Based Biosensors. Gels 2022, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Um, S.H.; Lee, J.B.; Park, N.; Kwon, S.Y.; Umbach, C.C.; Luo, D. Enzyme-Catalysed Assembly of DNA Hydrogel. Nat Mater 2006, 5, 797–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Zhang, G.; Liu, S. Enzyme-Responsive Polymeric Assemblies, Nanoparticles and Hydrogels. Chem Soc Rev 2012, 41, 5933–5949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, F.; Othman, M.B.H.; Javed, F.; Ahmad, Z.; Akil, H.M. Classification, Processing and Application of Hydrogels: A Review. Materials Science and Engineering C 2015, 57, 414–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quazi, M.Z.; Park, N. Nanohydrogels: Advanced Polymeric Nanomaterials in the Era of Nanotechnology for Robust Functionalization and Cumulative Applications. Int J Mol Sci 2022, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.B.; Peng, S.; Yang, D.; Roh, Y.H.; Funabashi, H.; Park, N.; Rice, E.J.; Chen, L.; Long, R.; Wu, M.; et al. A Mechanical Metamaterial Made from a DNA Hydrogel. Nat Nanotechnol 2012, 7, 816–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vandermeulen, G.W.M.; Klok, H.A. Peptide/Protein Hybrid Materials: Enhanced Control of Structure and Improved Performance through Conjugation of Biological and Synthetic Polymers. Macromol Biosci 2004, 4, 383–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.; Lee, J.; Shin, M.E.; Been, S.; Lee, D.H.; Khang, G. Eggshell Membrane/Gellan Gum Composite Hydrogels with Increased Degradability, Biocompatibility, and Anti-Swelling Properties for Effective Regeneration of Retinal Pigment Epithelium. Polymers (Basel) 2020, 12, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Ouyang, J.; Chen, Q.; Deng, C.; Meng, F.; Zhang, J.; Cheng, R.; Lan, Q.; Zhong, Z. EGFR and CD44 Dual-Targeted Multifunctional Hyaluronic Acid Nanogels Boost Protein Delivery to Ovarian and Breast Cancers in Vitro and in Vivo. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 2017, 9, 24140–24147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topuz, F.; Okay, O. Rheological Behavior of Responsive DNA Hydrogels. Macromolecules 2008, 41, 8847–8854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyata, T. Preparation of Smart Soft Materials Using Molecular Complexes. Polym J 2010, 42, 277–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quazi, M.Z.; Kim, T.; Yang, J.; Park, N. Tuning Plasmonic Properties of Gold Nanoparticles by Employing Nanoscale DNA Hydrogel Scaffolds. Biosensors (Basel) 2023, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Yang, R.; Yang, S.; Guan, J.; Zhang, D.; Ma, Y.; Liu, H. Research Progress of Self-Assembled Nanogel and Hybrid Hydrogel Systems Based on Pullulan Derivatives. Drug Deliv 2018, 25, 278–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Gou, S.; Bi, Y.; Gao, Q.; Sun, J.; Hu, S.; Guo, W. Smart DNA-Gold Nanoparticle Hybrid Hydrogel Film Based Portable, Cost-Effective and Storable Biosensing System for the Colorimetric Detection of Lead (II) and Uranyl Ions. Biosens Bioelectron 2022, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Gou, S.; Bi, Y.; Gao, Q.; Sun, J.; Hu, S.; Guo, W. Smart DNA-Gold Nanoparticle Hybrid Hydrogel Film Based Portable, Cost-Effective and Storable Biosensing System for the Colorimetric Detection of Lead (II) and Uranyl Ions. Biosens Bioelectron 2022, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bidram, E.; Esmaeili, Y.; Amini, A.; Sartorius, R.; Tay, F.R.; Shariati, L.; Makvandi, P. Nanobased Platforms for Diagnosis and Treatment of COVID-19: From Benchtop to Bedside. ACS Biomater Sci Eng 2021, 7, 2150–2176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spychalska, K.; Zajac, D.; Baluta, S.; Halicka, K.; Cabaj, J. Functional Polymers Structures for (Bio)Sensing Application-a Review. Polymers (Basel) 2020, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tavakoli, J.; Tang, Y. Hydrogel Based Sensors for Biomedical Applications: An Updated Review. Polymers (Basel) 2017, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinelli, F.; Nespoli, T.; Fiorati, A.; Farè, S.; Magagnin, L.; Rossi, F. Graphene Nanoplatelets Can Improve the Performances of Graphene Oxide – Polyaniline Composite Gas Sensing Aerogels. Carbon Trends 2021, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Zhai, J.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, N.; Xie, X. Hydrogel-Based Optical Ion Sensors: Principles and Challenges for Point-of-Care Testing and Environmental Monitoring. ACS Sens 2021, 6, 1990–2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khajouei, S.; Ravan, H.; Ebrahimi, A. DNA Hydrogel-Empowered Biosensing. Adv Colloid Interface Sci 2020, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Xu, T.; Zhang, X. Multifunctional Conductive Hydrogel-Based Flexible Wearable Sensors. TrAC - Trends in Analytical Chemistry 2021, 134.
- Shi, J.; Shi, Z.; Dong, Y.; Wu, F.; Liu, D. Responsive DNA-Based Supramolecular Hydrogels. ACS Appl Bio Mater 2020, 3, 2827–2837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrmann, A.; Haag, R.; Schedler, U. Hydrogels and Their Role in Biosensing Applications. Adv Healthc Mater 2021, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gačanin, J.; Synatschke, C.V.; Weil, T. Biomedical Applications of DNA-Based Hydrogels. Adv Funct Mater 2020, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posthuma-Trumpie, G.A.; van Amerongen, A.; Korf, J.; van Berkel, W.J.H. Perspectives for On-Site Monitoring of Progesterone. Trends Biotechnol 2009, 27, 652–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Grazon, C.; Sensharma, P.; Nguyen, T.T.; Feng, Y.; Chern, M.; Baer, R.C.; Varongchayakul, N.; Cook, K.; Lecommandoux, S.; et al. Hydrogel-Embedded Quantum Dot−transcription Factor Sensors for Quantitative Progesterone Detection. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 2020, 12, 43513–43521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velayudham, J.; Magudeeswaran, V.; Paramasivam, S.S.; Karruppaya, G.; Manickam, P. Hydrogel-Aptamer Nanocomposite Based Electrochemical Sensor for the Detection of Progesterone. Mater Lett 2021, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casis, N.; Busatto, C.; Fidalgo de Cortalezzi, M.M.; Ravaine, S.; Estenoz, D.A. Molecularly Imprinted Hydrogels from Colloidal Crystals for the Detection of Progesterone. Polym Int 2015, 64, 773–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quazi, M.Z.; Park, N. DNA Hydrogel-Based Nanocomplexes with Cancer-Targeted Delivery and Light-Triggered Peptide Drug Release for Cancer-Specific Therapeutics. Biomacromolecules 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Light-Responsible DNA Hydrogel–Gold Nanoparticle.Pdf.
- He, Y.; Yang, X.; Yuan, R.; Chai, Y. A Novel Ratiometric SERS Biosensor with One Raman Probe for Ultrasensitive MicroRNA Detection Based on DNA Hydrogel Amplification. J Mater Chem B 2019, 7, 2643–2647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, N.; Um, S.H.; Funabashi, H.; Xu, J.; Luo, D. A Cell-Free Protein-Producing Gel. Nat Mater 2009, 8, 432–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Y.; Cheng, E.; Yang, Y.; Chen, P.; Zhang, T.; Sun, Y.; Yang, Z.; Liu, D. Self-Assembled DNA Hydrogels with Designable Thermal and Enzymatic Responsiveness. Advanced Materials 2011, 23, 1117–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.X.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.X.; Du, Y.C.; Huang, Y.; Tang, A.N.; Cui, Y.X.; Kong, D.M. DNA Nanostructure-Based Nucleic Acid Probes: Construction and Biological Applications. Chem Sci 2021, 12, 7602–7622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nöll, T.; Schönherr, H.; Wesner, D.; Schopferer, M.; Paululat, T.; Nöll, G. Construction of Three-Dimensional DNA Hydrogels from Linear Building Blocks. Angewandte Chemie - International Edition 2014, 53, 8328–8332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Im, K.; Hwang, S.; Hur, J.; Nam, J.; Ahn, G.O.; Hwang, S.; Kim, S.; Park, N. DNA Hydrogel Delivery Vehicle for Light-Triggered and Synergistic Cancer Therapy. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 9433–9437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seeman, N.C. Nucleic Acid Junctions and Lattices; 1982; Vol. 99.
- Molecular Structure of Nucleic Acids A Structure for Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid.
- Lee, J.B.; Shai, A.S.; Campolongo, M.J.; Park, N.; Luo, D. Three-Dimensional Structure and Thermal Stability Studies of DNA Nanostructures by Energy Transfer Spectroscopy. ChemPhysChem 2010, 11, 2081–2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Chen, S.; An, B.; Huang, K.; Bai, T.; Xu, M.; Bellot, G.; Ke, Y.; Xiang, Y.; Wei, B. Complex Wireframe DNA Nanostructures from Simple Building Blocks. Nat Commun 2019, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Condrat, C.E.; Thompson, D.C.; Barbu, M.G.; Bugnar, O.L.; Boboc, A.; Cretoiu, D.; Suciu, N.; Cretoiu, S.M.; Voinea, S.C. MiRNAs as Biomarkers in Disease: Latest Findings Regarding Their Role in Diagnosis and Prognosis. Cells 2020, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Zhang, J.; Wang, C.; Liu, C.; Wang, H.; Li, Z. Highly Sensitive and Specific Multiplexed MicroRNA Quantification Using Size-Coded Ligation Chain Reaction (LCR); 2013.
- Cheng, Y.; Zhang, X.; Li, Z.; Jiao, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y. Highly Sensitive Determination of MicroRNA Using Target-Primed and Branched Rolling-Circle Amplification. Angewandte Chemie 2009, 121, 3318–3322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, R.; Tang, L.; Tian, Q.; Wang, Y.; Lin, L.; Li, J. Toehold-Initiated Rolling Circle Amplification for Visualizing Individual MicroRNAs in Situ in Single Cells. Angewandte Chemie - International Edition 2014, 53, 2389–2393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Ridzon, D.A.; Broomer, A.J.; Zhou, Z.; Lee, D.H.; Nguyen, J.T.; Barbisin, M.; Xu, N.L.; Mahuvakar, V.R.; Andersen, M.R.; et al. Real-Time Quantification of MicroRNAs by Stem-Loop RT-PCR. Nucleic Acids Res 2005, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Gregory, R.I. MicroRNA Biogenesis Pathways in Cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 2015, 15, 321–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bracken, C.P.; Scott, H.S.; Goodall, G.J. A Network-Biology Perspective of MicroRNA Function and Dysfunction in Cancer. Nat Rev Genet 2016, 17, 719–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavazoie, S.F.; Alarcón, C.; Oskarsson, T.; Padua, D.; Wang, Q.; Bos, P.D.; Gerald, W.L.; Massagué, J. Endogenous Human MicroRNAs That Suppress Breast Cancer Metastasis. Nature 2008, 451, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esteller, M. Non-Coding RNAs in Human Disease. Nat Rev Genet 2011, 12, 861–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Wang, H.; Li, Y.; Jiang, C.; Chen, D.; Wen, Y.; Li, Z. Capillarity Self-Driven DNA Hydrogel Sensor for Visual Quantification of MicroRNA. Sens Actuators B Chem 2020, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quazi, M.Z.; Lee, U.; Park, S.; Shin, S.; Sim, E.; Son, H.; Park, N. Cancer Cell-Specific Enhanced Raman Imaging and Photothermal Therapeutic Effect Based on Reversibly PH-Responsive Gold Nanoparticles. ACS Appl Bio Mater 2021, 4, 8377–8385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Li, H.; Ge, J.; Jie, G. Versatile Fluorescence Detection of MicroRNA Based on Novel DNA Hydrogel-Amplified Signal Probes Coupled with DNA Walker Amplification. Chemical Communications 2019, 55, 3919–3922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, Y.; Xu, L.; Wang, N.; Zheng, J.; Yang, R.; Li, J. Target MicroRNA-Responsive DNA Hydrogel-Based Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering Sensor Arrays for MicroRNA-Marked Cancer Screening. Anal Chem 2020, 92, 2649–2655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elghanian, R.; Storhoff, J.J.; Mucic, R.C.; Letsinger, R.L.; Mirkin, C.A. Selective Colorimetric Detection of Polynucleotides Based on the Distance-Dependent Optical Properties of Gold Nanoparticles. Science (1979) 1997, 277, 1078–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baeissa, A.; Dave, N.; Smith, B.D.; Liu, J. DNA-Functionalized Monolithic Hydrogels and Gold Nanoparticles for Colorimetric DNA Detection. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 2010, 2, 3594–3600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, R.A.; Mirkin, C.A.; Letsinger, R.L. Homogeneous, Nanoparticle-Based Quantitative Colorimetric Detection of Oligonucleotides [13]. J Am Chem Soc 2000, 122, 3795–3796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storhoff, J.J.; Elghanian, R.; Mucic, R.C.; Mirkin, C.A.; Letsinger, R.L. One-Pot Colorimetric Differentiation of Polynucleotides with Single Base Imperfections Using Gold Nanoparticle Probes; 1998.
- Zhao, H.; Jiang, G.; Weng, J.; Ma, Q.; Zhang, H.; Ito, Y.; Liu, M. A Signal-Accumulating DNAzyme-Crosslinked Hydrogel for Colorimetric Sensing of Hydrogen Peroxide. J Mater Chem B 2016, 4, 4648–4651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brolo, A.G. Plasmonics for Future Biosensors. Nat Photonics 2012, 6, 709–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, S.J.; Campolongo, M.J.; Luo, D.; Cheng, W. Building Plasmonic Nanostructures with DNA. Nat Nanotechnol 2011, 6, 268–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, L.; Luan, J.; Liu, K.-K.; Jiang, Q.; Tadepalli, S.; Gupta, M.K.; Naik, R.R.; Singamaneni, S. Plasmonic Biofoam: A Versatile Optically Active Material. Nano Lett 2016, 16, 609–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; Chen, J.; Li, Z.Y.; Au, L.; Hartland, G.V.; Li, X.; Marquez, M.; Xia, Y. Gold Nanostructures: Engineering Their Plasmonic Properties for Biomedical Applications. Chem Soc Rev 2006, 35, 1084–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Li, Y.; Wang, H.; Chen, D.; Wen, Y. A Portable Visual Capillary Sensor Based on Functional DNA Crosslinked Hydrogel for Point-of-Care Detection of Lead Ion. Sens Actuators B Chem 2020, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Zhu, Z.; Zou, Y.; Huang, Y.; Liu, D.; Jia, S.; Xu, D.; Wu, M.; Zhou, Y.; Zhou, S.; et al. Target-Responsive “Sweet” Hydrogel with Glucometer Readout for Portable and Quantitative Detection of Non-Glucose Targets. J Am Chem Soc 2013, 135, 3748–3751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Guan, Z.; Jia, S.; Lei, Z.; Lin, S.; Zhang, H.; Ma, Y.; Tian, Z.Q.; Yang, C.J. Au@pt Nanoparticle Encapsulated Target-Responsive Hydrogel with Volumetric Bar-Chart Chip Readout for Quantitative Point-of-Care Testing. Angewandte Chemie - International Edition 2014, 53, 12503–12507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Liu, Y.; Huang, J.; Liu, W.; Huang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Fu, W. Label-Free Techniques for Laboratory Medicine Applications. Frontiers in Laboratory Medicine 2017, 1, 82–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collin, M.S.; Venkatraman, S.K.; Vijayakumar, N.; Kanimozhi, V.; Arbaaz, S.M.; Stacey, R.G.S.; Anusha, J.; Choudhary, R.; Lvov, V.; Tovar, G.I.; et al. Bioaccumulation of Lead (Pb) and Its Effects on Human: A Review. Journal of Hazardous Materials Advances 2022, 7, 100094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, S.; Chakraborty, A.J.; Tareq, A.M.; Emran, T. Bin; Nainu, F.; Khusro, A.; Idris, A.M.; Khandaker, M.U.; Osman, H.; Alhumaydhi, F.A.; et al. Impact of Heavy Metals on the Environment and Human Health: Novel Therapeutic Insights to Counter the Toxicity. J King Saud Univ Sci 2022, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aschner, M.; Jiang, G.C.T. Toxicity Studies on Depleted Uranium in Primary Rat Cortical Neurons and in Caenorhabditis Elegans: What Have We Learned? J Toxicol Environ Health B Crit Rev 2009, 12, 525–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Needleman, H. Lead Poisoning. Annu Rev Med 2004, 55, 209–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, J.; Chen, C.; Li, X.; Yu, L.; Li, W.; Cheng, M.; Tang, W.; Xiong, Z. A Responsive Pure DNA Hydrogel for Label-Free Detection of Lead Ion. Anal Chim Acta 2021, 1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.H.; Park, J.; Kang, S.; Kim, M. Surface Plasmon Resonance: A Versatile Technique for Biosensor Applications. Sensors (Switzerland) 2015, 15, 10481–10510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, B.; Wen, B.; Cheng, W.; Zhou, X.; Duan, X.; Zhao, M.; Xia, Q.; Ding, S. An Enzyme-Free and Label-Free Surface Plasmon Resonance Biosensor for Ultrasensitive Detection of Fusion Gene Based on DNA Self-Assembly Hydrogel with Streptavidin Encapsulation. Biosens Bioelectron 2018, 112, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, B.; Zhao, H.; Du, L.; Gan, X.; Quan, X. A Versatile Fluorescent Biosensor Based on Target-Responsive Graphene Oxide Hydrogel for Antibiotic Detection. Biosens Bioelectron 2016, 83, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Mao, Y.; An, Y.; Tian, T.; Zhang, H.; Yan, J.; Zhu, Z.; Yang, C.J. Target-Responsive DNA Hydrogel for Non-Enzymatic and Visual Detection of Glucose. Analyst 2018, 143, 1679–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Wang, X.; Sun, Y.; Dai, Y.; Sun, W.; Zhu, X.; Liu, H.; Han, R.; Gao, D.; Luo, C. A Chemiluminescent Biosensor for Ultrasensitive Detection of Adenosine Based on Target-Responsive DNA Hydrogel with Au@HKUST-1 Encapsulation. Sens Actuators B Chem 2019, 289, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Fang, L.; Zhu, Z.; Ma, Y.; Zhou, L.; Chen, X.; Xu, D.; Yang, C. Design and Synthesis of Target-Responsive Hydrogel for Portable Visual Quantitative Detection of Uranium with a Microfluidic Distance-Based Readout Device. Biosens Bioelectron 2016, 85, 496–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Ma, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wu, X.; Fang, L.; Zhu, Z.; Yang, C.J. Target-Responsive DNAzyme Cross-Linked Hydrogel for Visual Quantitative Detection of Lead. Anal Chem 2014, 86, 11434–11439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Z.; Guan, Z.; Jia, S.; Lei, Z.; Lin, S.; Zhang, H.; Ma, Y.; Tian, Z.Q.; Yang, C.J. Au@pt Nanoparticle Encapsulated Target-Responsive Hydrogel with Volumetric Bar-Chart Chip Readout for Quantitative Point-of-Care Testing. Angewandte Chemie - International Edition 2014, 53, 12503–12507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ullah, F.; Othman, M.B.H.; Javed, F.; Ahmad, Z.; Akil, H.M. Classification, Processing and Application of Hydrogels: A Review. Materials Science and Engineering C 2015, 57, 414–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morya, V.; Walia, S.; Mandal, B.B.; Ghoroi, C.; Bhatia, D. Functional DNA Based Hydrogels: Development, Properties and Biological Applications. ACS Biomater Sci Eng 2020, 6, 6021–6035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Duan, J.; Liu, J.; Yi, H.; Zhang, Z.; Song, H.; Li, Y.; Zhang, K. Stimuli-Responsive Self-Degradable DNA Hydrogels: Design, Synthesis, and Applications. Adv Healthc Mater 2023. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Lyu, D.; Liu, S.; Guo, W. DNA Hydrogels and Microgels for Biosensing and Biomedical Applications. Advanced Materials 2020, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrmann, A.; Haag, R.; Schedler, U. Hydrogels and Their Role in Biosensing Applications. Adv Healthc Mater 2021, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Peng, Y.; Li, S.; Han, D.; Ren, S.; Qin, K.; Li, S.; Gao, Z. Stimuli-Responsive DNA-Based Hydrogels for Biosensing Applications. J Nanobiotechnology 2022, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, S.; Matsuhisa, N.; Beker, L.; Li, J.; Wang, S.; Wang, J.; Jiang, Y.; Yan, X.; Yun, Y.; Burnett, W.; et al. A Wireless Body Area Sensor Network Based on Stretchable Passive Tags. Nat Electron 2019, 2, 361–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhvapathy, S.R.; Wang, H.; Kong, J.; Zhang, M.; Yoon Lee, J.; Bin Park, J.; Jang, H.; Xie, Z.; Cao, J.; Avila, R.; et al. A P P L I E D S C I E N C E S A N D E N G I N E E R I N G Reliable, Low-Cost, Fully Integrated Hydration Sensors for Monitoring and Diagnosis of Inflammatory Skin Diseases in Any Environment; 2020; Vol. 6.
- Lin, R.; Kim, H.J.; Achavananthadith, S.; Kurt, S.A.; Tan, S.C.C.; Yao, H.; Tee, B.C.K.; Lee, J.K.W.; Ho, J.S. Wireless Battery-Free Body Sensor Networks Using near-Field-Enabled Clothing. Nat Commun 2020, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuart, T.; Cai, L.; Burton, A.; Gutruf, P. Wireless and Battery-Free Platforms for Collection of Biosignals. Biosens Bioelectron 2021, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Min, J.; Yu, Y.; Wang, H.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Gao, W. A P P L I E D S C I E N C E S A N D E N G I N E E R I N G Wireless Battery-Free Wearable Sweat Sensor Powered by Human Motion; 2020; Vol. 6.
- Xiong, Z.; Achavananthadith, S.; Lian, S.; Edward Madden, L.; Xin Ong, Z.; Chua, W.; Kalidasan, V.; Li, Z.; Liu, Z.; Singh, P.; et al. E N G I N E E R I N G A Wireless and Battery-Free Wound Infection Sensor Based on DNA Hydrogel; 2021; Vol. 7.
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




