Submitted:
15 May 2023
Posted:
16 May 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Mitochondria Move Along Microtubules and Actin Filaments
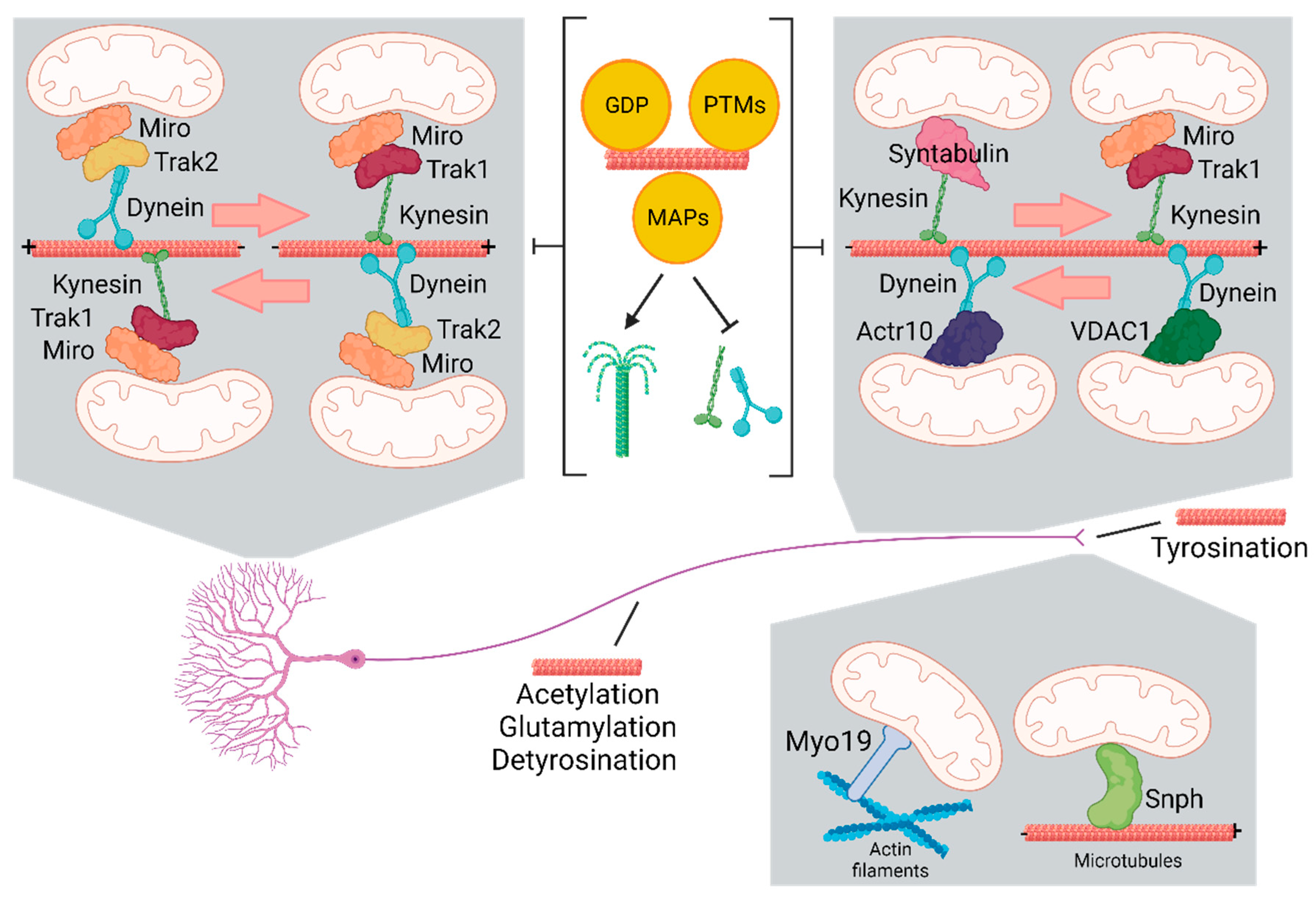
2.1. Microtubules
2.2. Actin
3. Molecular Motors Transport Mitochondria via Microtubules
4. Mitochondrial Docking and Anchoring Machineries in Neurons
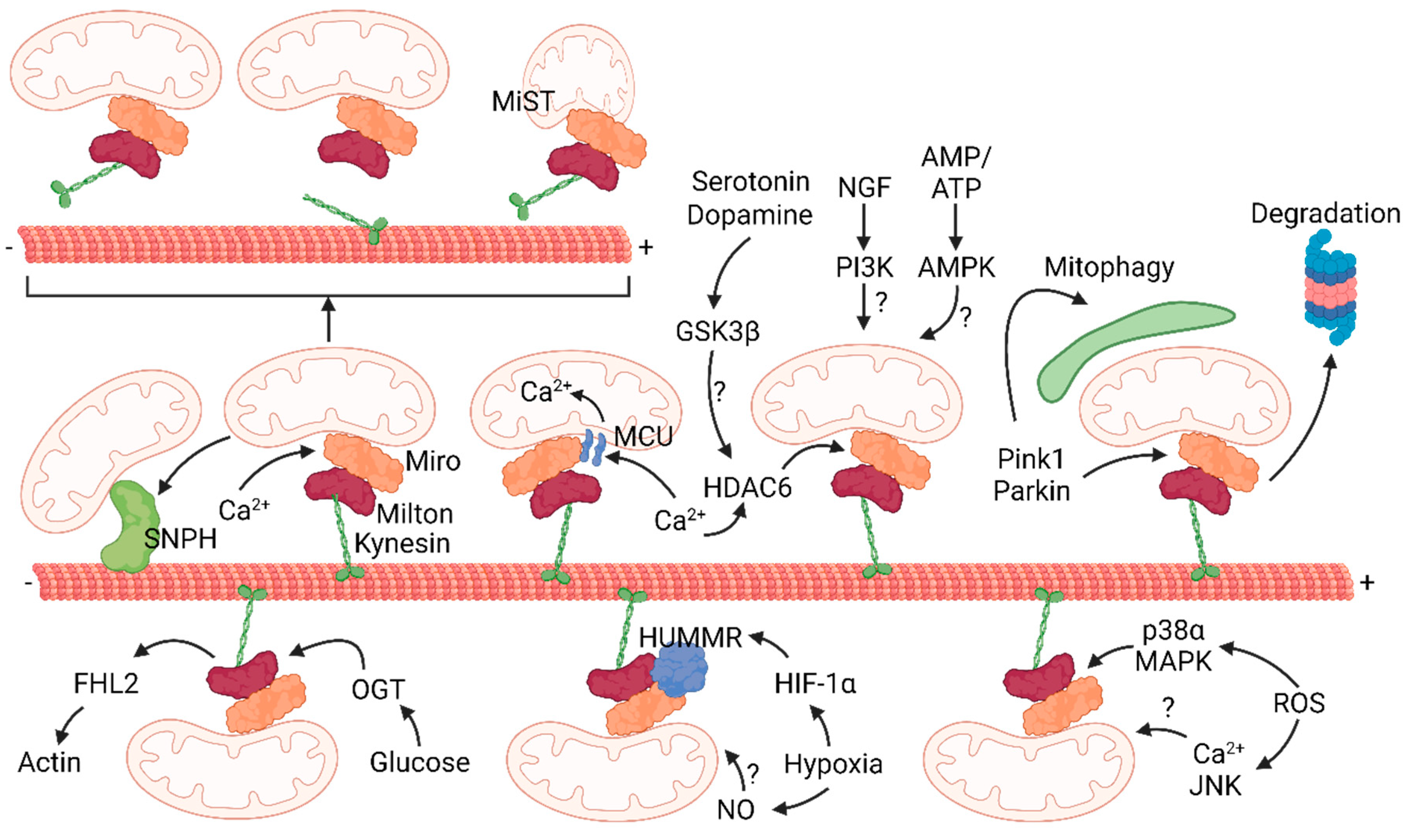
5. Metabolic Control of Mitochondrial Transport
5.1. Calcium
5.2. Glucose
5.3. ATP
5.4. Hypoxia
5.6. Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS)
5.7. Growth Factors and Neurotransmitters
6. Mitophagy
7. Specialized Cytoskeleton Structures Allow Mitochondria to Cross Cell Boundaries
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, Z.; Okamoto, K.; Hayashi, Y.; Sheng, M. The importance of dendritic mitochondria in the morphogenesis and plasticity of spines and synapses. Cell 2004, 119, 873–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farias, G.G.; Guardia, C.M.; Britt, D.J.; Guo, X.; Bonifacino, J.S. Sorting of Dendritic and Axonal Vesicles at the Pre-axonal Exclusion Zone. Cell Rep. 2015, 13, 1221–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misgeld, T.; Schwarz, T.L. Mitostasis in Neurons: Maintaining Mitochondria in an Extended Cellular Architecture. Neuron. 2017, 96, 651–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, R.L.; Hollenbeck, P.J. The regulation of bidirectional mitochondrial transport is coordinated with axonal outgrowth. J Cell Sci. 1993, 104 Pt 3, 917–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rustom, A.; Saffrich, R.; Markovic, I.; Walther, P.; Gerdes, H.-H. Nanotubular Highways for Intercellular Organelle Transport. Science 2004, 303, 1007–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Bukoreshtliev, N.V.; Gerdes, H.-H. Developing neurons form transient nanotubes facilitating electrical coupling and calcium signaling with distant astrocytes. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e47429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayakawa, K.; Esposito, E.; Wang, X.; Terasaki, Y.; Liu, Y.; Xing, C.; et al. Transfer of mitochondria from astrocytes to neurons after stroke. Nature 2016, 535, 551–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Nakamura, Y.; Lo, E.H.; Hayakawa, K. Astrocyte signaling in the neurovascular unit after central nervous system injury. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lippert, T.; Borlongan, C.V. Prophylactic treatment of hyperbaric oxygen treatment mitigates inflammatory response via mitochondria transfer. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2019, 25, 815–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocca, C.J.; Goodman, S.M.; Dulin, J.N.; Haquang, J.H.; Gertsman, I.; Blondelle, J.; et al. Transplantation of wild-type mouse hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells ameliorates deficits in a mouse model of Friedreich’s ataxia. Sci. Transl. Med. 2017, 9, eaaj2347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Guo, L.; Zhou, Z.; Pan, M.; Yan, C. Mesenchymal stem cells transfer mitochondria into cerebral microvasculature and promote recovery from ischemic stroke. Microvasc. Res. 2019, 123, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kevenaar, J.T.; Hoogenraad, C.C. The axonal cytoskeleton: From organization to function. Front Mol Neurosci. 2015, 8, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desai, A.; Mitchison, T.J. Microtubule polymerization dynamics. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 1997, 13, 83–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baas, P.W.; Black, M.M.; Banker, G.A. Changes in microtubule polarity orientation during the development of hippocampal neurons in culture. J. Cell Biol. 1989, 109, 3085–3094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimitrov, A.; Quesnoit, M.; Moutel, S.; Cantaloube, I.; Pous, C.; Perez, F. Detection of GTP-tubulin conformation in vivo reveals a role for GTP remnants in microtubule rescues. Science 2008, 322, 1353–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aumeier, C.; Schaedel, L.; Gaillard, J.; John, K.; Blanchoin, L.; Thery, M. Self-repair promotes microtubule rescue. Nat Cell Biol. 2016, 18, 1054–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakata, T.; Niwa, S.; Okada, Y.; Perez, F.; Hirokawa, N. Preferential binding of a kinesin-1 motor to GTP-tubulin-rich microtubules underlies polarized vesicle transport. J Cell Biol. 2011, 194, 245–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Steenbergen, V.; Lavoie-Cardinal, F.; Kazwiny, Y.; Decet, M.; Martens, T.; Verstreken, P.; et al. Nano-positioning and tubulin conformation contribute to axonal transport regulation of mitochondria along microtubules. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2203499119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tropini, C.; Roth, E.A.; Zanic, M.; Gardner, M.K.; Howard, J. Islands containing slowly hydrolyzable GTP analogs promote microtubule rescues. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e30103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vemu, A.; Szczesna, E.; Zehr, E.A.; Spector, J.O.; Grigorieff, N.; Deaconescu, A.M.; et al. Severing enzymes amplify microtubule arrays through lattice GTP-tubulin incorporation. Science 2018, 361, eaau1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guedes-Dias, P.; Nirschl, J.J.; Abreu, N.; Tokito, M.K.; Janke, C.; Magiera, M.M.; et al. Kinesin-3 Responds to Local Microtubule Dynamics to Target Synaptic Cargo Delivery to the Presynapse. Curr Biol. 2019, 29, 268–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shima, T.; Morikawa, M.; Kaneshiro, J.; Kambara, T.; Kamimura, S.; Yagi, T.; et al. Kinesin-binding-triggered conformation switching of microtubules contributes to polarized transport. J Cell Biol. 2018, 217, 4164–4183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Brady, S.T. Post-translational modifications of tubulin: Pathways to functional diversity of microtubules. Trends Cell Biol. 2015, 25, 125–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dent, E.W.; Gertler, F.B. Cytoskeletal dynamics and transport in growth cone motility and axon guidance. Neuron. 2003, 40, 209–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geraldo, S.; Gordon-Weeks, P.R. Cytoskeletal dynamics in growth-cone steering. J Cell Sci. 2009, 122 Pt 20, 3595–3604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammond, J.W.; Huang, C.F.; Kaech, S.; Jacobson, C.; Banker, G.; Verhey, K.J. Posttranslational modifications of tubulin and the polarized transport of kinesin-1 in neurons. Mol Biol Cell. 2010, 21, 572–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nirschl, J.J.; Magiera, M.M.; Lazarus, J.E.; Janke, C.; Holzbaur, E.L. alpha-Tubulin Tyrosination and CLIP-170 Phosphorylation Regulate the Initiation of Dynein-Driven Transport in Neurons. Cell Rep. 2016, 14, 2637–2652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez-Mateos, E.M.; Gonzalez-Billault, C.; Dawson, H.N.; Vitek, M.P.; Avila, J. Role of MAP1B in axonal retrograde transport of mitochondria. Biochem J. 2006, 397, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebneth, A.; Godemann, R.; Stamer, K.; Illenberger, S.; Trinczek, B.; Mandelkow, E. Overexpression of tau protein inhibits kinesin-dependent trafficking of vesicles, mitochondria, and endoplasmic reticulum: Implications for Alzheimer's disease. J Cell Biol. 1998, 143, 777–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahpasand, K.; Uemura, I.; Saito, T.; Asano, T.; Hata, K.; Shibata, K.; et al. Regulation of mitochondrial transport and inter-microtubule spacing by tau phosphorylation at the sites hyperphosphorylated in Alzheimer's disease. J Neurosci. 2012, 32, 2430–2441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamer, K.; Vogel, R.; Thies, E.; Mandelkow, E.; Mandelkow, E.M. Tau blocks traffic of organelles, neurofilaments, and APP vesicles in neurons and enhances oxidative stress. J Cell Biol. 2002, 156, 1051–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alonso, A.C.; Zaidi, T.; Grundke-Iqbal, I.; Iqbal, K. Role of abnormally phosphorylated tau in the breakdown of microtubules in Alzheimer disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1994, 91, 5562–5566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bodakuntla, S.; Magiera, M.M.; Janke, C. Measuring the Impact of Tubulin Posttranslational Modifications on Axonal Transport. Methods Mol Biol. 2020, 2101, 353–370. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ligon, L.A.; Steward, O. Role of microtubules and actin filaments in the movement of mitochondria in the axons and dendrites of cultured hippocampal neurons. J Comp Neurol. 2000, 427, 351–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, R.L.; Hollenbeck, P.J. Axonal transport of mitochondria along microtubules and F-actin in living vertebrate neurons. J Cell Biol. 1995, 131, 1315–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rangaraju, V.; Lauterbach, M.; Schuman, E.M. Spatially Stable Mitochondrial Compartments Fuel Local Translation during Plasticity. Cell. 2019, 176, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chada, S.R.; Hollenbeck, P.J. Nerve growth factor signaling regulates motility and docking of axonal mitochondria. Curr Biol. 2004, 14, 1272–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirokawa, N.; Noda, Y.; Tanaka, Y.; Niwa, S. Kinesin superfamily motor proteins and intracellular transport. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2009, 10, 682–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.-Y.; Sheng, Z.-H. Regulation of mitochondrial transport in neurons. Exp. Cell Res. 2015, 334, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nangaku, M.; Sato-Yoshitake, R.; Okada, Y.; Noda, Y.; Takemura, R.; Yamazaki, H.; et al. KIF1B, a novel microtubule plus end-directed monomeric motor protein for transport of mitochondria. Cell 1994, 79, 1209–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wozniak, M.J.; Melzer, M.; Dorner, C.; Haring, H.-U.; Lammers, R. The novel protein KBP regulates mitochondria localization by interaction with a kinesin-like protein. BMC Cell Biol. 2005, 6, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neuwald, A.F.; Aravind, L.; Spouge, J.L.; Koonin, E.V. AAA+: A class of chaperone-like ATPases associated with the assembly, operation, and disassembly of protein complexes. Genome Res. 1999, 9, 27–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canty, J.T.; Tan, R.; Kusakci, E.; Fernandes, J.; Yildiz, A. Structure and mechanics of dynein motors. Annu. Rev. Biophys. 2021, 50, 549–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKenney, R.J.; Huynh, W.; Tanenbaum, M.E.; Bhabha, G.; Vale, R.D. Activation of cytoplasmic dynein motility by dynactin-cargo adapter complexes. Science 2014, 345, 337–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drerup, C.M.; Herbert, A.L.; Monk, K.R.; Nechiporuk, A.V. Regulation of mitochondria-dynactin interaction and mitochondrial retrograde transport in axons. Elife, 2223. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, K.; Basu, H.; Izquierdo-Villalba, I.; Shurberg, E.; Schwarz, T.L. Miro GTPase domains regulate the assembly of the mitochondrial motor–adaptor complex. Life Sci. Alliance 2023, 6, e202201406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Spronsen, M.; Mikhaylova, M.; Lipka, J.; Schlager, M.A.; van den Heuvel, D.J.; Kuijpers, M.; et al. TRAK/Milton Motor-Adaptor Proteins Steer Mitochondrial Trafficking to Axons and Dendrites. Neuron. 2013, 77, 485–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Doménech G, Covill-Cooke C, Ivankovic D; et al. Miro proteins coordinate microtubule-and actin-dependent mitochondrial transport and distribution. EMBO J. 2018, 37, 321–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Macleod, G.T.; Wellington, A.; Hu, F.; Panchumarthi, S.; Schoenfield, M.; et al. The GTPase dMiro is required for axonal transport of mitochondria to Drosophila synapses. Neuron. 2005, 47, 379–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Q.; Gerwin, C.; Sheng, Z.-H. Syntabulin-mediated anterograde transport of mitochondria along neuronal processes. J. Cell Biol. 2005, 170, 959–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho Ki Cai, Y.; Yi, H.; Yeh, A.; Aslanukov, A.; Ferreira, P.A. Association of the kinesin-binding domain of RanBP2 to KIF5B and KIF5C determines mitochondria localization and function. Traffic. 2007, 8, 1722–1735. [Google Scholar]
- Ikuta, J.; Maturana, A.; Fujita, T.; Okajima, T.; Tatematsu, K.; Tanizawa, K.; et al. Fasciculation and elongation protein zeta-1 (FEZ1) participates in the polarization of hippocampal neuron by controlling the mitochondrial motility. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2007, 353, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, G.-J.; Cheng, X.-T.; Sun, T.; Xie, Y.; Huang, N.; Li, S.; et al. Defects in syntabulin-mediated synaptic cargo transport associate with autism-like synaptic dysfunction and social behavioral traits. Mol. Psychiatry 2021, 26, 1472–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Fok, A.H.K.; Fan, R.; Kwan, P.-Y.; Chan, H.-L.; Lo, L.H.-Y.; et al. Specific depletion of the motor protein KIF5B leads to deficits in dendritic transport, synaptic plasticity and memory. eLife 2020, 9, e53456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misko, A.; Jiang, S.; Wegorzewska, I.; Milbrandt, J.; Baloh, R.H. Mitofusin 2 is necessary for transport of axonal mitochondria and interacts with the Miro/Milton complex. J. Neurosci. 2010, 30, 4232–4240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwarzer, C.; Barnikol-Watanabe, S.; Thinnes, F.P.; Hilschmann, N. Voltage-dependent anion-selective channel (VDAC) interacts with the dynein light chain Tctex1 and the heat-shock protein PBP74. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2002, 34, 1059–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, T.L. Mitochondrial trafficking in neurons. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2013, 5, a011304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilhelm, B.G.; Mandad, S.; Truckenbrodt, S.; Kröhnert, K.; Schäfer, C.; Rammner, B.; et al. Composition of isolated synaptic boutons reveals the amounts of vesicle trafficking proteins. Science 2014, 344, 1023–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.-S.; Tian, J.-H.; Pan, P.-Y.; Zald, P.; Li, C.; Deng, C.; et al. Docking of axonal mitochondria by syntaphilin controls their mobility and affects short-term facilitation. Cell 2008, 132, 137–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-M.; Gerwin, C.; Sheng, Z.-H. Dynein light chain LC8 regulates syntaphilin-mediated mitochondrial docking in axons. J. Neurosci 2009, 29, 9429–9438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Xiong, G.-J.; Huang, N.; Sheng, Z.-H. The cross-talk of energy sensing and mitochondrial anchoring sustains synaptic efficacy by maintaining presynaptic metabolism. Nat. Metab. 2020, 2, 1077–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacAskill, A.F.; Rinholm, J.E.; Twelvetrees, A.E.; Arancibia-Carcamo, I.L.; Muir, J.; Fransson, A.; et al. Miro1 is a calcium sensor for glutamate receptor-dependent localization of mitochondria at synapses. Neuron. 2009, 61, 541–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mironov, S.L. ADP regulates movements of mitochondria in neurons. Biophys. J. 2007, 92, 2944–2952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Schwarz, T.L. The mechanism of Ca2+-dependent regulation of kinesin-mediated mitochondrial motility. Cell. 2009, 136, 163–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niescier, R.F.; Hong, K.; Park, D.; Min, K.T. MCU Interacts with Miro1 to Modulate Mitochondrial Functions in Neurons. J Neurosci. 2018, 38, 4666–4677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, K.T.; Niescier, R.F.; Min, K.T. Mitochondrial matrix Ca2+ as an intrinsic signal regulating mitochondrial motility in axons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2011, 108, 15456–15461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, L.; Sharma, K.; Dodi, L.D.; Rieder, L.S.; Fallier-Becker, P.; Casadei, N.; et al. Miro1 R272Q disrupts mitochondrial calcium handling and neurotransmitter uptake in dopaminergic neurons. Front Mol Neurosci. 2022, 15, 966209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinsmaier, K.E. Mitochondrial Miro GTPases coordinate mitochondrial and peroxisomal dynamics. Small GTPases. 2021, 12, 372–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemani, N.; Carvalho, E.; Tomar, D.; Dong, Z.; Ketschek, A.; Breves, S.L.; et al. MIRO-1 Determines Mitochondrial Shape Transition upon GPCR Activation and Ca(2+) Stress. Cell Rep. 2018, 23, 1005–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalinski, A.L.; Kar, A.N.; Craver, J.; Tosolini, A.P.; Sleigh, J.N.; Lee, S.J.; et al. Deacetylation of Miro1 by HDAC6 blocks mitochondrial transport and mediates axon growth inhibition. J Cell Biol. 2019, 218, 1871–1890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaman, M.; Shutt, T.E. The Role of Impaired Mitochondrial Dynamics in MFN2-Mediated Pathology. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022, 10, 858286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.S.; Tian, J.H.; Pan, P.Y.; Zald, P.; Li, C.; Deng, C.; et al. Docking of axonal mitochondria by syntaphilin controls their mobility and affects short-term facilitation. Cell. 2008, 132, 137–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Sheng, Z.H. Kinesin-1-syntaphilin coupling mediates activity-dependent regulation of axonal mitochondrial transport. J Cell Biol. 2013, 202, 351–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, J.M.; Burnett, A.L.; Rameau, G.A. Activity-dependent regulation of surface glucose transporter-3. J Neurosci. 2011, 31, 1991–1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weisova, P.; Concannon, C.G.; Devocelle, M.; Prehn, J.H.; Ward, M.W. Regulation of glucose transporter 3 surface expression by the AMP-activated protein kinase mediates tolerance to glutamate excitation in neurons. J Neurosci. 2009, 29, 2997–3008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashrafi, G.; Wu, Z.; Farrell, R.J.; Ryan, T.A. GLUT4 Mobilization Supports Energetic Demands of Active Synapses. Neuron. 2017, 93, 606–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pekkurnaz, G.; Trinidad, J.C.; Wang, X.; Kong, D.; Schwarz, T.L. Glucose regulates mitochondrial motility via Milton modification by O-GlcNAc transferase. Cell. 2014, 158, 54–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagerlof, O.; Hart, G.W.; Huganir, R.L. O-GlcNAc transferase regulates excitatory synapse maturity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017, 114, 1684–1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.R.; Song, S.; Hwang, H.; Jung, J.H.; Kim, S.J.; Yoon, S.; et al. Memory and synaptic plasticity are impaired by dysregulated hippocampal O-GlcNAcylation. Sci Rep. 2017, 7, 44921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, H.; Pekkurnaz, G.; Falk, J.; Wei, W.; Chin, M.; Steen, J.; et al. FHL2 anchors mitochondria to actin and adapts mitochondrial dynamics to glucose supply. J Cell Biol. 2021, 220, e201912077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, K.; Matsuki, N.; Koyama, R. AMP-activated protein kinase mediates activity-dependent axon branching by recruiting mitochondria to axon. Dev Neurobiol. 2014, 74, 557–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watters, O.; Connolly, N.M.C.; Konig, H.G.; Dussmann, H.; Prehn, J.H.M. AMPK Preferentially Depresses Retrograde Transport of Axonal Mitochondria during Localized Nutrient Deprivation. J Neurosci. 2020, 40, 4798–4812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Lim, S.; Hoffman, D.; Aspenstrom, P.; Federoff, H.J.; Rempe, D.A. HUMMR, a hypoxia- and HIF-1alpha-inducible protein, alters mitochondrial distribution and transport. J Cell Biol. 2009, 185, 1065–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanelli, S.A.; Trimmer, P.A.; Solenski, N.J. Nitric oxide impairs mitochondrial movement in cortical neurons during hypoxia. J Neurochem. 2006, 97, 724–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rintoul, G.L.; Bennett, V.J.; Papaconstandinou, N.A.; Reynolds, I.J. Nitric oxide inhibits mitochondrial movement in forebrain neurons associated with disruption of mitochondrial membrane potential. J Neurochem. 2006, 97, 800–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, P.C.; Tandarich, L.C.; Hollenbeck, P.J. ROS regulation of axonal mitochondrial transport is mediated by Ca2+ and JNK in Drosophila. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0178105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, C.; Bourdette, D.; Banker, G. Oxidative stress inhibits axonal transport: Implications for neurodegenerative diseases. Mol Neurodegener. 2012, 7, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debattisti, V.; Gerencser, A.A.; Saotome, M.; Das, S.; Hajnoczky, G. ROS Control Mitochondrial Motility through p38 and the Motor Adaptor Miro/Trak. Cell Rep. 2017, 21, 1667–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chada, S.R.; Hollenbeck, P.J. Mitochondrial movement and positioning in axons: The role of growth factor signaling. J Exp Biol. 2003, 206 Pt 12, 1985–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Owens, G.C.; Crossin, K.L.; Edelman, D.B. Serotonin stimulates mitochondrial transport in hippocampal neurons. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2007, 36, 472–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Owens, G.C.; Edelman, D.B. Dopamine inhibits mitochondrial motility in hippocampal neurons. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e2804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Owens, G.C.; Makarenkova, H.; Edelman, D.B. HDAC6 regulates mitochondrial transport in hippocampal neurons. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e10848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Winter, D.; Ashrafi, G.; Schlehe, J.; Wong, Y.L.; Selkoe, D.; et al. PINK1 and Parkin target Miro for phosphorylation and degradation to arrest mitochondrial motility. Cell 2011, 147, 893–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weihofen, A.; Thomas, K.J.; Ostaszewski, B.L.; Cookson, M.R.; Selkoe, D.J. Pink1 forms a multiprotein complex with Miro and Milton, linking Pink1 function to mitochondrial trafficking. Biochemistry 2009, 48, 2045–2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, Q.; Zakaria, H.M.; Simone, A.; Sheng, Z.H. Spatial parkin translocation and degradation of damaged mitochondria via mitophagy in live cortical neurons. Curr Biol. 2012, 22, 545–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maday, S.; Wallace, K.E.; Holzbaur, E.L. Autophagosomes initiate distally and mature during transport toward the cell soma in primary neurons. J Cell Biol. 2012, 196, 407–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wu, X.; Jiang, L.; Ahsan, A.; Ma, S.; et al. Somatic autophagy of axonal mitochondria in ischemic neurons. J Cell Biol. 2019, 218, 1891–1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trigo, D.; Avelar, C.; Fernandes, M.; Sa, J.; da Cruz, E.S.O. Mitochondria, energy, and metabolism in neuronal health and disease. FEBS Lett. 2022, 596, 1095–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Cui, J.; Sun, X.; Zhang, Y. Tunneling-nanotube development in astrocytes depends on p53 activation. Cell Death Differ. 2011, 18, 732–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, C.-h.O.; Kim, K.-Y.; Bushong, E.A.; Mills, E.A.; Boassa, D.; Shih, T.; et al. Transcellular degradation of axonal mitochondria. Proc. Natl. Acad. Scis. SA 2014, 111, 9633–9638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boukelmoune, N.; Chiu, G.S.; Kavelaars, A.; Heijnen, C.J. Mitochondrial transfer from mesenchymal stem cells to neural stem cells protects against the neurotoxic effects of cisplatin. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2018, 6, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caicedo, A.; Fritz, V.; Brondello, J.-M.; Ayala, M.; Dennemont, I.; Abdellaoui, N.; et al. MitoCeption as a new tool to assess the effects of mesenchymal stem/stromal cell mitochondria on cancer cell metabolism and function. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 9073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babenko, V.A.; Silachev, D.N.; Popkov, V.A.; Zorova, L.D.; Pevzner, I.B.; Plotnikov, E.Y.; et al. Miro1 enhances mitochondria transfer from multipotent mesenchymal stem cells (MMSC) to neural cells and improves the efficacy of cell recovery. Molecules. 2018, 23, 687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maeda, H.; Kami, D.; Maeda, R.; Murata, Y.; Jo Ji Kitani, T.; et al. TAT-dextran–mediated mitochondrial transfer enhances recovery from models of reperfusion injury in cultured cardiomyocytes. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2020, 24, 5007–5020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahrouf-Yorgov, M.; Augeul, L.; Da Silva, C.C.; Jourdan, M.; Rigolet, M.; Manin, S.; et al. Mesenchymal stem cells sense mitochondria released from damaged cells as danger signals to activate their rescue properties. Cell Death Differ. 2017, 24, 1224–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Gao, Y.; Liu, J.; Huang, Y.; Yin, J.; Feng, Y.; et al. Intercellular mitochondrial transfer as a means of tissue revitalization. Signal Transduct. Target. Therapy 2021, 6, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, T.; Mukherjee, S.; Pattnaik, B.; Kumar, M.; Singh, S.; Kumar, M.; et al. Miro1 regulates intercellular mitochondrial transport & enhances mesenchymal stem cell rescue efficacy. EMBO J. 2014, 33, 994–1010. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gao, L.; Zhang, Z.; Lu, J.; Pei, G. Mitochondria are dynamically transferring between human neural cells and alexander disease-associated GFAP mutations impair the astrocytic transfer. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Ji, K.; Guo, L.; Wu, W.; Lu, H.; Shan, P.; et al. Mesenchymal stem cells rescue injured endothelial cells in an in vitro ischemia-reperfusion model via tunneling nanotube like structure-mediated mitochondrial transfer. Microvasc Res. 2014, 92, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.C.; Wu, S.L.; Liu, K.H.; Chen, Y.H.; Chuang, C.S.; Cheng, F.C.; et al. Allogeneic/xenogeneic transplantation of peptide-labeled mitochondria in Parkinson's disease: Restoration of mitochondria functions and attenuation of 6-hydroxydopamine-induced neurotoxicity. Transl Res. 2016, 170, 40–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Zhao, M.; Fu, C.; Fu, A. Intravenous administration of mitochondria for treating experimental Parkinson's disease. Mitochondrion 2017, 34, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robicsek, O.; Ene, H.M.; Karry, R.; Ytzhaki, O.; Asor, E.; McPhie, D.; et al. Isolated Mitochondria Transfer Improves Neuronal Differentiation of Schizophrenia-Derived Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells and Rescues Deficits in a Rat Model of the Disorder. Schizophr Bull. 2018, 44, 432–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Ma, Z.; Yan, C.; Pu, K.; Wu, M.; Bai, J.; et al. Muscle-derived autologous mitochondrial transplantation: A novel strategy for treating cerebral ischemic injury. Behav Brain Res. 2019, 356, 322–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babenko, V.A.; Silachev, D.N.; Zorova, L.D.; Pevzner, I.B.; Khutornenko, A.A.; Plotnikov, E.Y.; et al. Improving the Post-Stroke Therapeutic Potency of Mesenchymal Multipotent Stromal Cells by Cocultivation With Cortical Neurons: The Role of Crosstalk Between Cells. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2015, 4, 1011–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, P.-J.; Kuo, C.-C.; Lee, H.-C.; Shen, C.-I.; Cheng, F.-C.; Wu, S.-F.; et al. Transferring Xenogenic Mitochondria Provides Neural Protection against Ischemic Stress in Ischemic Rat Brains. Cell Transp. 2016, 25, 913–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pourmohammadi-Bejarpasi, Z.; Roushandeh, A.M.; Saberi, A.; Rostami, M.K.; Toosi, S.M.R.; Jahanian-Najafabadi, A.; et al. Mesenchymal stem cells-derived mitochondria transplantation mitigates I/R-induced injury, abolishes I/R-induced apoptosis, and restores motor function in acute ischemia stroke rat model. Brain Res. Bull. 2020, 165, 70–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gollihue, J.L.; Patel, S.P.; Eldahan, K.C.; Cox, D.H.; Donahue, R.R.; Taylor, B.K.; et al. Effects of mitochondrial transplantation on bioenergetics, cellular incorporation, and functional recovery after spinal cord injury. J. Neurotraum. 2018, 35, 1800–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bamshad, C.; Habibi Roudkenar, M.; Abedinzade, M.; Yousefzadeh Chabok, S.; Pourmohammadi-Bejarpasi, Z.; Najafi-Ghalehlou, N.; et al. Human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells-harvested mitochondrial transplantation improved motor function in TBI models through rescuing neuronal cells from apoptosis and alleviating astrogliosis and microglia activation. Int Immunopharmacol. 2023, 118, 110106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, C.C.; Su, H.L.; Chang, T.L.; Chiang, C.Y.; Sheu, M.L.; Cheng, F.C.; et al. Prevention of Axonal Degeneration by Perineurium Injection of Mitochondria in a Sciatic Nerve Crush Injury Model. Neurosurgery 2017, 80, 475–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Disease | Treatment | Clinical Outcome | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rat model of Parkinson Disease (PD) | Mitochondria | Restored mitochondrial functions and reduced oxitative damage in dopaminergic neurons | (110) |
| Mouse model of PD | Mitochondria | Increased electron transport chain activity, reduced ROS level and prevented apoptosis and necrosis. | (111) |
| Rat model of schizophrenia (SZ) | Mitochondria | Prevented mitochondrial dysfunction in intra-prefrontal cortex neurons and emergence of attention deficit | (112) |
| Middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) in rats | Mitochondria | Decreased brain infarct volume and reversed neurological deficits | (113) |
| MCAO in rats | Mesenchymal multipotent stromal cells | Reduced infarct volume in the brain and partial restoration of neurological status*. | (114) |
| Ischemic Stress in rats | Mitochondria | Restored motor performance; attenuated brain infarct area and neuronal cell death | (115) |
| MCAO in rats | MSCs-derived mitochondria | Declined blood creatine phosphokinase level, abolished apoptosis, decreased astroglyosis and microglia activation, reduced infarct size, and improved motor function | (116) |
| Ischemia-reperfusion stroke injury | MSCs | Rescued damaged cerebrovascular system in stroke | (109) |
| Spinal cord injury (SCI) in rats | Mitochondria | Maintenance of normal bioenergetics without recovery of motor and sensory functions | (117) |
| Traumatic brain injury (TBI) in rats | MSCs-derived mitochondria | Improved sensorimotor functions | (118) |
| Nerve crush injury in rats | Mitochondria | Improved neurobehaviors, electrophysiology of nerve conduction, and muscle activities | (119)Kuo |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





