1. Introduction
Demand for OTT service has increased as users spend longer staying at home since the COVID-19 pandemic. However, there has been a recent turning point in this trend; as the pandemic abates, the Korean government has begun to ease quarantine regulations. The promotion of ‘living with coronavirus’ and ‘going back to normal’ may bring various changes not only in our daily lives but also in the OTT content consumption environment. According to prior research [
1], even during the COVID-19 pandemic, when social distancing was enforced, people tended to consume OTT services more in non-residential areas such as workplaces, schools, transportation, and other indoor spaces during weekdays rather than on weekends. If the time people spend moving or staying outside continues to increase with the removal of social distancing mandates, OTT content consumption in non-residential areas would rise.
In Korea, most OTT subscribers have used mobile devices as their primary medium for watching OTT video content [
2]. In particular, as the number of OTT service subscribers has significantly increased since the outbreak of COVID-19, mobile network traffic has skyrocketed [
1,
3]. Currently, the mobile network traffic volume caused by online video streaming services has become a considerable burden for telecommunication operators [
3]; mobile traffic – mainly created by mobile video content streaming services such as Netflix and YouTube – grew at an average rate of 46% between 2017 and 2022 [
3,
4].
So far, users have experienced increasingly faster data transmission speed and better picture quality of online video content as mobile communication technology has developed. However, this uptrend is wavering as the existing mobile communication technology gradually reaches its limit in meeting the enormous demands of mobile network traffic [
3,
5]. Due to excessively high infrastructure costs and restricted resource, it becomes difficult to rely on deploying more base stations or expanding the network bandwidth as before [
6]. In addition to the infrastructure cost, a huge capital investment is required to operate cellular system [
7]. In a word, the cellular network system is expensive.
In April 2019, South Korea became the world’s first country to roll out commercial 5G networks [
8]. As of the end of March 2023, the number of 5G subscribers in Korea was 29.6 million. It is estimated that the number of 5G subscribers has exceeded 30 million as of the end of April [
9]. However, the growth rate is noticeably slowing down; the number of new subscribers halved in 2022 as a result of the negative perception of 5G service quality that has pervaded since the initial stages of commercialization [
10]. Combined with the limitations of wireless network technology and the increase in the use of mobile OTT services in non-residential areas, it is expected that mobile network traffic overloads would be severe.
Wireless D2D caching networks are considered one of the desirable alternatives to alleviate the overloads of mobile data traffic [
6]. Wireless D2D caching networks refer to a technology that pre-stores content repeatedly requested at a specific time and place in the mobile device storage space of a user, arriving there at that time [
3]. Then, the content is delivered to other nearby devices through a D2D link when requested [
3]. This technology has merits of reducing network-related overheads, saving related costs, and improving the quality of OTT service consumption [
3,
11].
Notably, wireless D2D caching networks attempt to solve the limitation of mobile network infrastructure with user engagement. Unlike conventional approach where users are passive customers, in the context of wireless D2D caching networks, the status of OTT service users is shifted from passive to entrepreneurial, as they adopt the role of a service provider. However, wireless D2D caching networks have pros and cons like any other technology. For instance, while wireless D2D caching technology improves the video quality, reduces the latency, and provides opportunities for mobile data plan cost incentivization, it also potentially compromises user privacy, occupies mobile device storage space, and consumes mobile device battery. Alongside these concerns, recognition of this new concept of user engagement-technology might differ among users.
Thus, the current study aims to examine the practical decision-making process of mobile OTT service users in response to the application of wireless D2D caching networks on their mobile devices. While there are numerous studies on OTT platforms and their relationships with users, limited studies focus on users’ perspectives and evaluations of accepting the new way of consuming mobile OTT services. For wireless D2D caching networks to be successfully commercialized, user acceptance and support must be prerequisite. Thus, to verify the criteria for mobile OTT service users to make decisions and their alternative choices based on the criteria, this study takes an AHP approach. This approach would enable us to scientifically measure and evaluate the different kinds of possible telecommunications alternatives for mobile OTT service consumption. As for mobile OTT service providers, the result from this AHP analysis can be used as a valuable groundwork for devising business strategies.
2. Literature Review
2.1. Overview of the Mobile OTT Services and Network Traffic in South Korea
OTT generally refers to the online video content delivery by an internet platform through internet protocol (IP) [12-14]. It is distinguished from a traditional broadcaster or an ISP/telecom operator in the sense that an OTT platform delivers content using internet broadband [
15]. However, this does not mean that the OTT platform is entirely distinct from these traditional gatekeepers: OTT services ride within an internet broadband provider’s network for content delivery and affiliates with broadcasters to provide popular TV series. As internet increasingly penetrates and smart connected devices become more prevalent in our daily lives, the global OTT market was valued at USD 101.42 billion in 2020 and it is expected to reach USD 223.07 billion by 2026 [
14,
16]. It means that its value registers a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 13.87% during the period of 2021–2026 [
16]. Moreover, according to this research, since the onset of COVID-19 pandemic, people have consumed more content at home via OTT devices. As the OTT market rapidly grows, internet bandwidth congestion caused by OTT video content streaming services has become a hot potato in many countries.
As it did in many other countries, OTT service attracted a lot of subscribers in South Korea and increased their share in the broadcasting and movie market [
17]. Global OTT services, including Netflix, Apple TV+, and Disney+, as well as Korean local platforms, including Wavve, Tving, and Watcha, compete to increase their market share. Indeed, as the Korean media industry expands its influence in the global OTT service market, the Korean OTT service market is evaluated as the most competitive in Asia [
18]. Notably, as Korean telecommunication operators launch mobile data plans including subscription to mobile OTT services, taking advantage of the feature that OTT platforms provide streaming services using telecommunication operators’ broadband connections, Korean OTT service users mostly use their smartphones for watching OTT video content [
1]. According to KCC’s research [
1], about 66% of Korean people subscribe to paid OTT services such as Netflix, Tving, and Wavve. Moreover, demand for OTT service has significantly increased as users spend more time staying at home after the lockdown. Of course, people also enjoy the OTT content in various places other than their homes, such as schools, workplaces, restaurants, transportation, etc. [
1].
In line with this tendency, mobile network traffic generated by mobile video content streaming is continuously increasing [
3]. For example, Cisco [
4] announced that mobile data traffic would grow at a CAGR of 46% between 2017 and 2022, and their demand is mainly from online video streaming applications such as Netflix and YouTube [
3]. Regarding this, SK broadband, a Korean internet service provider, filed a lawsuit against Netflix claiming the cost of using the network. Multiple South Korean lawmakers have also spoken out against content providers who do not pay for network usage despite producing explosive network traffic [
19]. In June 2021, a Seoul court ruled that it is reasonable for Netflix to give some compensation in return for the mobile carriers’ network usage [
20]. However, Netflix has appealed against the claim with net neutrality logic, and the two companies’ fights in court are still ongoing.
Historically, users’ desire for improved quality and seamless media experience has been realized with the development of mobile communication technology and the diversification of OTT services. Many prior studies have investigated users’ desires for the technology related to OTT service consumption. For example, users significantly preferred high-quality video content when they have a choice [
6,
21,
22]. This preference has been more strongly shown by Asian OTT service users [
13]. Additionally, OTT service users prefer to have both live streaming and downloading options to fully enjoy the OTT service wherever and whenever they want. So far, mobile communication technology has been advancing to meet the needs of users who want to watch online video content with higher speed and clearer picture quality. However, with existing mobile communication technology, it is becoming increasingly difficult to support this trend [
3,
5].
With the commercialization of 5G services for the first time in the world in April 2019, telecommunication operators claimed that 5G networks are more widely available and speedier in Korea than anywhere in the world [
8,
23]. Currently, approximately 38% of mobile data plan subscribers are using 5G networks in South Korea [
9]. However, the growth rate of 5G subscriptions is noticeably slowing down. This is a result of the negative perception of 5G quality that has continued since 5G technology’s initial stages of commercialization [
24]. Moreover, deploying more base stations or expanding the network bandwidth becomes difficult because of excessively high infrastructure costs, restricted resources, and government regulations [
3]. Consequently, technological alternatives are being sought to break through the exploding OTT consumption and mobile data demand.
2.2. The Development of Wireless and Mobile Communication Technology
Wireless and mobile communication technologies have been advancing quickly in the communications industry. As the development of wireless and mobile communication technology engrossed the media and the public, small handheld devices such as smartphones have become critical tools in our everyday lives. Currently, wireless and mobile communication technology has supplemented and replaced wired networks in many use cases [
25]. Mobile communication technology enabling information exchange between people and devices is the frontier of communications and keeps going from strength to strength. So far, mobile communication technology has evolved from precellular technology (0G) to 5G cellular networks. Notably, as wireless and mobile communication technology has been realized, multiple alternative technologies have been proposed to fill the gap in cellular networks. For instance, ad hoc networks have long attracted attention as a reliable technological alternative. Ad hoc networks refer to a collection of communications devices (nodes) that desire to communicate but without fixed infrastructures and pre-determined organization of available links [
26]. Multihop communication is another representative alternative technology. Multihop communication allows the establishment of wireless networks and the exchange of information among devices in areas where the coverage of traditional network infrastructure is limited or nonexistent [
27]. These alternative network technologies have many technological and practical advantages. However, they each hold inherent weaknesses that cannot be ignored, and thus, they have failed to be fully and widely commercialized. In the meantime, the technological alternatives for mobile communication, which improved from the previous ones, have continuously developed and steadily improved to solve the saturation of the current mobile network. Among them, wireless D2D caching networks have recently emerged as the rising technological alternative. Unlike previous alternative technologies, for wireless D2D caching networks to succeed in commercialization, it is important to understand their strengths and weaknesses, identify which of these factors are most critical to users, and devise an appropriate strategy. Thus, this study tried to verify the important criteria for mobile OTT service users to adopt wireless D2D caching networks and to provide the basis for a successful commercialization strategy.
2.3. Wireless D2D Caching Networks
As the mobile network traffic generated from online video content streaming increases rapidly, wireless D2D caching networks are considered a competitive technology to offload congested mobile network traffic from base stations to mobile device direct transmissions and to improve the OTT service consumption environment [
3,
5,
28]. Wireless D2D caching networks indicate a technology that pre-stores repeatedly demanded content in mobile device storage in advance and exchanges it over D2D links among users arriving at the place at peak times [
3]. In other words, this technology significantly relieves the overloads of a mobile network traffic by caching popular content in a user device and transmitting it to the device of another user who request the content through a D2D link rather than using cellular access links.
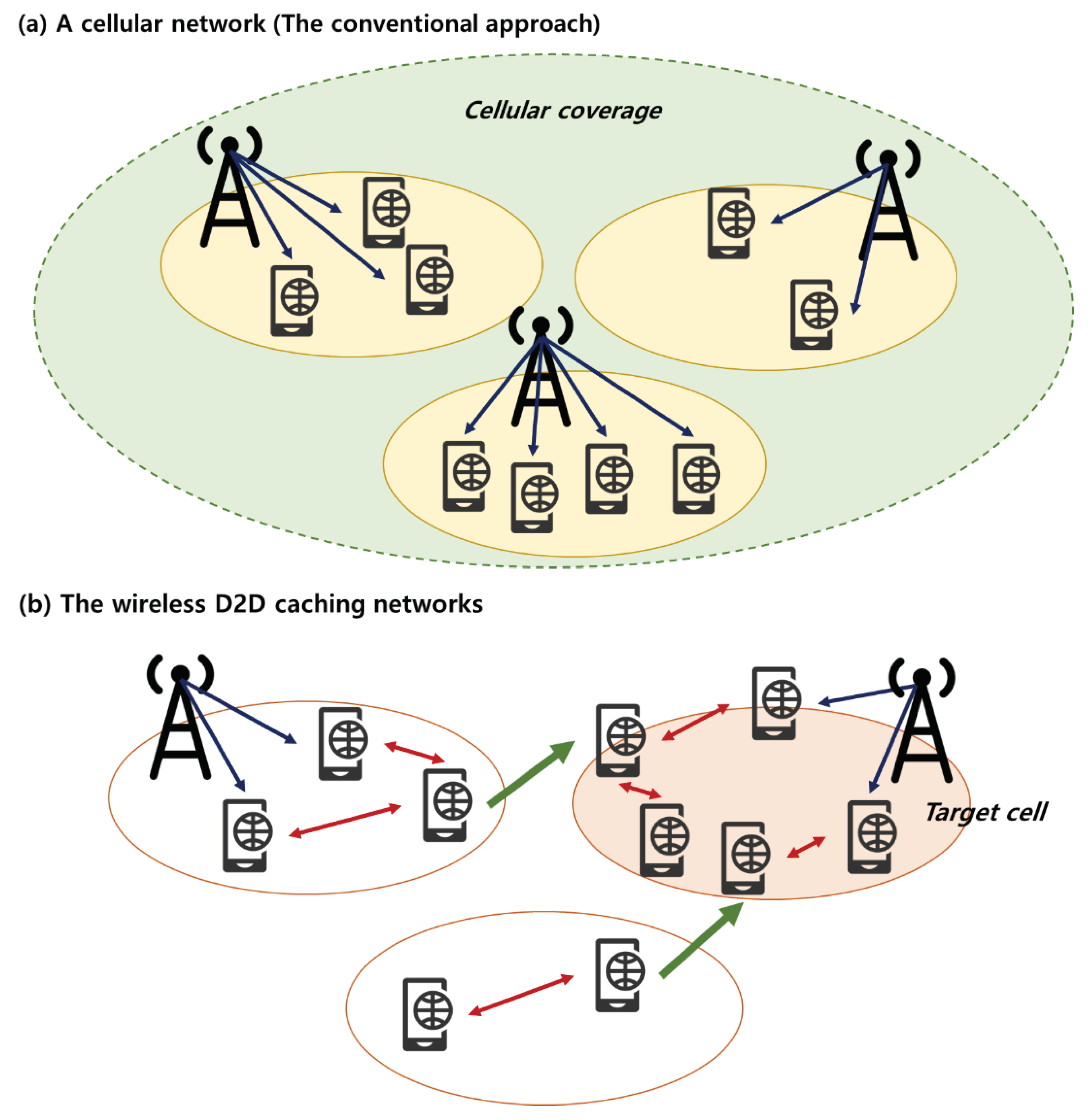
More specifically, so far, as illustrated in
Figure 1(a), a typical or representative user can be any user associated with one of multiple base stations. The conventional approach treated a system built around multiple access points or multiple base stations as a single service area when placing and delivering content, so it is difficult to optimize over the average performance throughout the entire system coverage [
3]. As a result, it fails to make use of the temporal mobility pattern, which can be tracked and predicted using user-related information or data [
3]. However, as
Figure 1(b) illustrates, wireless D2D caching networks focus on inter-cell mobility, in which a pair of end users within close proximity to each other directly communicate. It enables a proactive caching toward the target cell subject to a predictable spatiotemporal mobility profile [
3,
34]. Because wireless D2D caching networks interconnect mobile devices’ storage and users with wireless caching, traffic loads during rush hours – particularly in the case of the high-density user population, which are the potentially overloaded cells – can significantly decrease [
3,
5]. Users can communicate directly through their mobile devices regardless of whether the base station is nearby or not. Users do not need to go through any difficult training and procedures to participate in wireless D2D caching networks. If a user agrees to apply the wireless D2D caching network, a series of processes such as pre-storing and transmitting content and finding other device nearby that has the content a user wants to watch are performed automatically. Moreover, as the load on the mobile network traffic is lifted by the cache memory instead of using network resources such as the bandwidth, it is possible to deliver content quickly and stably [
5]. This implies that telecommunication operators do not need to necessarily build an expensive over-dimensioned mobile network-related infrastructure to cope with peak-hour traffic if wireless D2D caching networks are adequately applied [
3]. As such, this technology has the effect of reducing network-related overheads, saving related costs, improving energy efficiency, and protecting the environment [
11,
34].
Meanwhile, wireless D2D caching networks are a new approach that attempts to solve the issue of limiting existing mobile network infrastructure with user engagement. In the conventional approach, the infrastructures, such as base stations and bandwidth, are prepared by a telecommunication operator first. In this context, users are passive customers who pay to use the service. However, in the context of wireless D2D caching networks, the user actively engages in the process of service provision. In other words, the user’s status is changed from passive customer to service provider.
By deciding to participate in wireless D2D caching networks, a user becomes one of the service providers and will be able to store content on their mobile devices and transmit data through D2D communication when required. This contributes to relieving mobile networks’ traffic overload. Germonprez et al. [
29] called a technology that is intentionally applicated in the context of user experience “tailorable technology.” Because tailoring technology is accompanied with a user-initiated process, the user’s role in the technology consumption is crucial. Considering that OTT service users' status shifts from passive to entrepreneurial when they adopt wireless D2D caching networks on their mobile devices, wireless D2D caching networks have the characteristics of tailorable technology.
Wireless D2D caching networks have various benefits and costs for the telecommunication operator and user, as described in
Table 1. Alongside these double-sided features, users’ recognition of this technology’s application on their mobile device might be different. Even though wireless D2D caching networks have not been commercialized yet, it is a highly plausible near-term option for telecommunication operators suffering from enormous network traffic issues. Therefore, it is meaningful for mobile OTT service users to consider whether they will adopt wireless D2D caching networks on their mobile devices or resist applying the technology. This study aims to examine mobile OTT service users’ strategic decisions in responding to the application of wireless D2D caching networks on their mobile devices and identify the factors contributing to making the decision. Therefore, the study presents the following questions.
RQ1. What are the key determinants for mobile OTT service users to adopt wireless D2D caching networks on their mobile devices?
RQ2. Among possible telecommunications alternatives to watching mobile OTT video content outside or while moving, which is most preferred by users?
3. Methodology
3.1. Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP) Model
Since Saaty proposed it in the 1970s [
30], the AHP model has been used in many studies for investigating complex decision-making processes. Largely, AHP comprises two phases: hierarchic design and evaluation [
31]. In other words, this is a process of reaching a consensus on structuring a hierarchy of the problem and on judgments and synthesis [
31]. This framework provides an overall view of the complex relationship inherent in a situation and enables accurate comparison of homogeneous elements [
32]. Vargas [
31] surmises that this model has the advantage of translating qualitative judgment into numeric analysis and an intuitive understanding of the apportionment of the whole into its components. This model speculates that choosing the factors that are important for a certain decision is the most essential task in making a decision [
32]. In detail, AHP deconstructs the problem into several steps, and the factors are arranged in a hierarchic structure descending from the overall goal to criteria, sub-criteria, and alternatives in successive levels [
32]. Then, the priorities are evaluated based on pairwise comparisons and a combination of relative and absolute scales [
33]. Based on the relative importance and priority weights, AHP accurately compares how much more important one factor is than the other [
33].
3.2. Previous Research Using AHP
AHP is used in various academic and practice settings as it efficiently identifies important factors of the problem and organizes a proper decision-making process. For example, AHP has been applied to investigate market choices related to financial interests [
34]. This research developed factors as a hierarchy and evaluated the priorities of a company when it decides whether to lease or buy. The AHP framework is also used for stakeholder-related issues; for example, Álvarez et al. [
35] used AHP to support corporate social responsibility (CSR) decisions in large infrastructure projects.
AHP is also used to investigate the impact of emerging and promising new technology. For instance, Kim and Kim [
36] examined the determinants of newspaper management in adopting robot journalism into newsrooms using AHP. Park et al. [
37] identified killer services and keystone players in the smart car market from consumer and expert perspectives based on this framework. Recently, Mohammed and Daham [
38] developed a model for the method of teaching science and used AHP to assess whether teaching-flipped classrooms affect student performance. These studies looked at users’ perceptions of new technology they had not yet experienced and derived prospects and strategies for commercializing new technology based on them. Prior studies have elucidated that AHP helps discover the core of the problem, understand the different views, and arrange relationships based on preferences.
Considering AHP’s functionality and performance, this study finds AHP to be fit in examining mobile OTT service users’ strategic decisions in response to the application of wireless D2D caching networks on their mobile devices and identifying the factors contributing to making the decision, even though it is not yet commercialized and experienced. AHP would enable suggesting a model that can help mobile OTT service users participate in wireless D2D caching networks. As for telecommunication operators, the result from this AHP analysis can be used as a valuable foundation for devising business strategies to commercialize wireless D2D caching networks.
3.3. Criteria for Responding to Wireless D2D Caching Networks
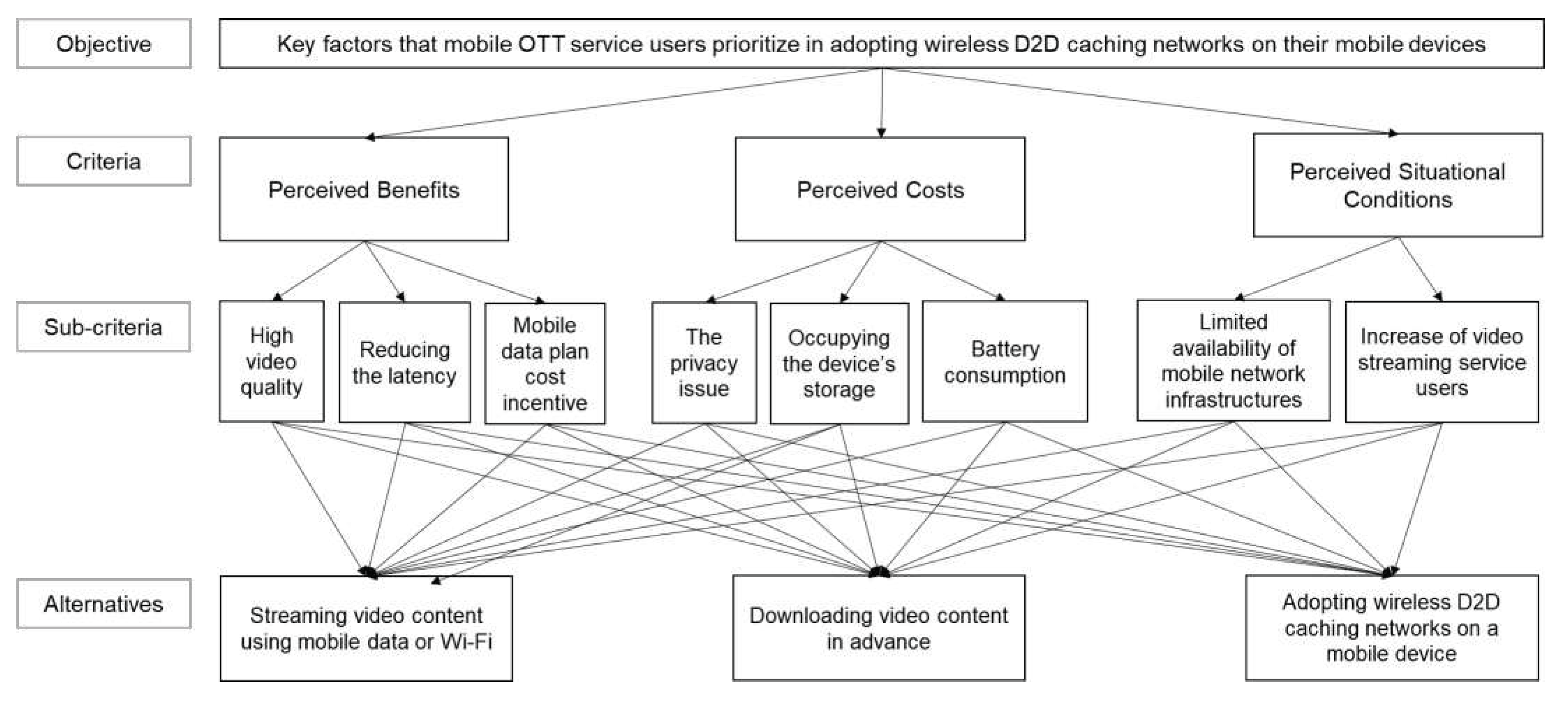
The structure of the AHP model proposed in the current study is constructed of three levels. The model is composed of criteria, sub-criteria, and alternatives in a hierarchical descending order of levels. The objective goal of this study is to use AHP to examine and understand the key factors that mobile OTT service users prioritize in adopting wireless D2D caching networks on their mobile devices.
The first level includes major criteria that mobile OTT service users consider in adopting wireless D2D caching networks. We assumed that when deciding whether or not to adopt a new technology never previously experienced by and not well-known to the user, users would first and foremost consider what benefits and costs they would gain and pay by adopting it. Simultaneously, they also consider contextual conditions related to the use of the technology which may affect their choices, rather than detailed factors. Thus, this study included perceived benefits, perceived costs, and perceived situational conditions as the major criteria. The second level relates to sub-criteria are composed of factors that users can experience in relation to technology use. Accordingly, high video quality, reduced latency, mobile data plan cost incentives, the privacy issue, occupying the device’s storage, battery consumption, the limited availability of mobile network infrastructures, and increased video streaming service users are included. A pairwise comparison among sub-criteria attributes will be performed to evaluate the hierarchy of importance. The last level represents alternatives: streaming video content using mobile data or Wi-Fi, downloading video content in advance, and adopting wireless D2D caching networks on a mobile device. The alternatives were composed of only alternatives with a high probability that users could realistically choose in their daily lives.
3.3.1. Perceived Benefits
As innovative alternative telecommunication technology for wireless data transmission, wireless D2D caching networks provide various benefits for mobile OTT service users. Among the various strengths of wireless D2D caching networks, there are three standout advantages that users can experience: high video quality, reduced latency, and mobile data plan cost incentives. In the current mobile network environment, where there are many unsatisfactory points related to OTT video content playback and viewing outdoors or while moving, this study forecasts that high video quality, reduced latency, and mobile data plan cost incentives are important attributes that distinguish wireless D2D caching networks from other alternatives. As a new alternative that can solve mobile OTT service users’ dissatisfaction with using the service outside, the benefits received from wireless D2D caching networks are anticipated to influence mobile OTT service users’ decision-making processes in adopting wireless D2D caching networks on their mobile devices.
High video quality focuses on maximizing the quality of the video content. Prior research identified that OTT service users highly prefer HD content when they have a choice [
13]. In this sense, many OTT service platforms, such as Netflix and Wavve, have tried to create and provide HD content in Korea [
14]. However, it is not easy to maintain high video quality when users are outside or moving, because the network is not constantly stable. Notably, as wireless D2D caching networks transmit content stably through D2D communication, it is evaluated as a transmission technique that can maximize the quality of video content [
39]. Indeed, various methods for encoding video content at different quality levels and volumes as closely as possible to the user’s expected quality have been examined by numerous D2D caching studies [
39]. The technology’s ability to consistently provide HD video content thus distinguishes the technology from other alternatives and ultimately engages mobile OTT service users’ decision to adopt wireless D2D caching networks on their mobile devices.
Reduced latency refers to minimizing the delayed data transmission when users stream OTT video content. Mobile OTT service users experience the inconvenience of a slowed-down OTT service which keeps buffering OTT video content while they watch it outside or while moving. Because wireless D2D caching networks pre-store content in high demand in advance in a personal mobile device, the content can be provided immediately without communication with the separate server when one or the other user nearby requests the corresponding content [
39]. Wireless D2D caching networks can significantly reduce the latency of content transmission and increase the likelihood that the content will be delivered correctly, meaning it is spotlighted as an excellent alternative to support online video streaming services [
40]. Mobile OTT service users are, therefore, anticipated to adopt wireless D2D caching networks that guarantee uninterrupted and fast content transmission as it is associated with maximizing immersion while watching video content.
Mobile data plan cost incentive refers to the economic support that telecommunication operators provide to users. In Korea, telecommunication operators provide OTT services using their broadband connections [
10]. However, they have gradually reached the limit of their ability to meet the enormous demands of mobile network traffic [
3,
5]. It is becoming difficult to deploy more base stations or expand the network bandwidth because of excessively high infrastructure costs and restricted resources [
6]. Given that wireless D2D caching networks are considered adequate to reduce network-related overheads, save related costs, and improve energy efficiency [
3,
11,
34], this technology is a highly attractive option for telecommunication operators suffering from large network issues. To encourage users to adopt wireless D2D caching networks on their mobile devices, telecommunication operators can offer a cost cut to a mobile data plan. In the Korean context where the burden of expensive mobile data prices is constantly raised as an issue [
1,
41], this economic incentive thus distinguishes wireless D2D caching networks from other alternatives. It ultimately influences mobile OTT service users’ decision-making processing in accepting wireless D2D caching networks on their mobile devices.
3.3.2. Perceived Costs
Despite technical excellence, innovation or technology cannot be purely optimistic. While wireless D2D caching networks improve mobile OTT service users’ video content consumption experience, users need to bear some costs. There are three main costs that users might consider sensitive and critical when adopting wireless D2D caching networks on their mobile devices. If they do so, they need to provide their personal information, offer mobile device storage, and consume battery. In other words, users are compelled to share their sensitive and essential resources and become vulnerable to personal data breaches and mobile devices’ resource depletion. This study projects that adopting wireless D2D caching networks on mobile OTT service users’ devices is accompanied by inescapable costs, influencing users’ technology adoption decisions.
The privacy issue is a cost that users’ privacy is violated due to wireless D2D caching networks’ open nature [
42,
43]. In D2D communication, information such as users’ location and demand for content must be open to allowing other users, as a transmitter, decode the desired file and transmit it quickly and adequately [
42]. Moreover, OTT video content viewing history is also utilized when strategically deciding which content to pre-store on whose mobile device’s storage. However, such information can be considered privacy-sensitive for some users, and that privacy constraint might be critical [
43]. Indeed, a prior study shows that many people want to avoid the possibility of misuse of their personal information by online companies [
44]. Thus, mobile OTT service users may avoid the cost of personal information leakage by choosing not to adopt wireless D2D caching networks on their mobile devices. Therefore, the privacy issue caused by wireless D2D caching networks is thus a significant cost that mobile OTT service users face when adopting wireless D2D caching networks on their mobile devices.
Occupying the device’s storage is another potential cost users need to bear when adopting wireless D2D caching networks on their mobile devices. Wireless D2D caching networks pre-store repeatedly requested content in the device’s memory space in advance and transmit it on demand. This technology efficiently processes repeated requests without sending or receiving them with the core network through the base station [
45]. Therefore, it has the merit of reducing the repeated traffic generated by the transmitter. The transmission efficiency can be improved by utilizing the information stored in the receiver’s memory. In this process, the size of the content to be stored and the allocation of the mobile device’s storage are considered important factors in designing this technology [
45]. In other words, to adopt and utilize wireless D2D caching networks, users need to share their mobile device’s storage to pre-store the content. According to prior research, however, there are already high storage demands caused by the evolution of mobile apps and technology [
46]. This research indicated that this tendency would be intensified as the mobile app’s functionality and technology, including AR, AI, and 4K graphics, are continuously evolving. Therefore, additional demand for storage from wireless D2D caching networks can be a cost for users who have accumulated large amounts of data, including photos, videos, music, and apps in the mobile device with limited storage.
Battery consumption highlights the battery efficiency problem that users face while adopting wireless D2D caching networks. Due to wireless D2D caching networks’ nature that pre-store popular content in the device’s storage in advance and transmits it when requested through D2D communication, technology usage time and battery consumption are inevitably proportional. According to prior studies, however, maintaining a high battery level is essential for the majority of smartphone users [
47,
48]. They emphasized that this tendency is getting stronger as users treat smartphones as a gateway to their daily lives, providing networking access to social networking, massaging, shopping, etc. Battery consumption is thus a significant cost that users face while using wireless D2D caching network technology with their mobile devices.
3.3.3. Perceived Situational Conditions
Situational conditions affect the mobile OTT service user’s decisions and actions. Situational conditions refer to “all those factors particular to a time and place of observation which do not follow from a knowledge of personal (intra-individual) and stimulus (choice alternative) attributes and which have a demonstrable and systematic effect on current behavior" [
49] (p.157). Bandura [
50] emphasized that contextual factors, including the social, situational, and temporal circumstances under which events occur, have a significant influence on people’s cognitive process related to the cause and effect of their behaviors. Mobile OTT service users’ decision-making processes are also affected by situational conditions surrounding the OTT service market. Despite the technical excellence and innovativeness, technology cannot successfully operate unless the situational conditions are diversely considered. Given that wireless D2D caching networks require a permit and support from users for commercialization, situational conditions that mobile OTT service users perceive are crucial in their decisions to adopt wireless D2D caching networks on mobile devices. Thus, this study puts the following two sub-criteria under perceived situational conditions.
The limitations of mobile network infrastructures
Historically, users’ increasing video content viewing time and demand for high-quality video has been met by the development of mobile communication technology. However, the existing mobile communication technology consistently results in dissatisfying and excessive demands of mobile network traffic [
3,
5]. For instance, South Korea launched the world’s first national 5G networks in April 2019. As the number of 5G subscribers exceeded 30 million, as of April 2023, nearly 38% of mobile subscribers are on 5G networks in South Korea [
9]. However, 5G commercialization proceeds in a state where network coverage and equipment for 5G are insufficient. Consumers are raising complaints about limited service and poor quality, despite expensive rate mobile data plans [
24]. Moreover, it becomes difficult to deploy more base stations or expand the network bandwidth because of excessively high infrastructure costs and restricted resources [
6]. It means that it is difficult to dramatically improve the content consumption environment using conventional approaches with regard to increasing the area spectral efficiency, such as deploying more base stations and expanding the bandwidth [
3]. The limitation of building more mobile network infrastructure is, therefore, anticipated to contribute to an environment that persuades and motivates mobile OTT service users to adopt wireless D2D caching networks on their mobile devices.
Increase of video streaming service users
As OTT service platforms have become steadily diversified based on the development of internet technology and the spread of devices capable of connecting to the internet, the number of OTT service users proportionally has increased in Korea [
51]. Moreover, with the additional arrival of Disney+ and Apple TV+ in 2021 and the pervasiveness of multiple subscriptions to OTT services, it is expected that Korean OTT service users and their demand for mobile traffic would jump. Indeed, Lee et al. [
3] highlighted that video streaming services such as Netflix and YouTube are the primary source of mobile traffic demand, and mobile traffic continues to explode with an increase in video streaming service users. The tremendous demand for mobile traffic may eventually result in insufficient provision of smooth and seamless OTT video content streaming [
3]. The more dissatisfied mobile OTT service users become with the current mobile communication condition and seek to comfortable experience in OTT service, the more heavily influenced mobile OTT service users’ decisions are anticipated to be by the increasing number of video streaming service users.
3.3.4. Alternatives
As telecommunications alternatives to watching mobile OTT video content outside or while moving, this study tried to include alternatives that mobile OTT service users can realistically choose and use in their daily lives. As a result of examining various alternatives, this study proposed three alternatives that are most suitable for users to watch mobile OTT video content outside or while moving. The first alternative is to stream video content using mobile data or Wi-Fi. Users can instantly stream video content online when they want to watch it by using their mobile data or free Wi-Fi. When using this method, however, mobile OTT service users bear the risk of low-quality of video content, buffering, and latency due to unstable networks in outdoor places or transportation. The second alternative is to download video content to the mobile device in advance. Some OTT platforms provide services allowing users to download content in advance and watch it offline. When users expect a lack of mobile data or difficulty connecting with mobile data networks or free Wi-Fi, they can download OTT video content beforehand in a place where the network is stable, such as at home or in their workplace. Then, users can play the content when they want, even during flights. This method has the advantage of allowing users to watch OTT video content in an offline state regardless of the mobile network status, but there is also the inconvenience for a user to look for a place where they can access the network and take the time to download the content in advance. The third alternative is to adopt wireless D2D caching on a mobile device. This alternative is for mobile OTT service users willing to embrace the benefits and costs of wireless D2D caching networks. They can watch the OTT video content through D2D communication between mobile devices of other users nearby. This method does not require connection to mobile data or Wi-Fi, but consumes the battery and storage space of the mobile device of the person whose device the cache is on. In summary, a user outdoors can watch mobile OTT video content online in the first and third alternatives but through a different link and offline in the second alternative.
Based on the three criteria, eight sub-criteria, and three alternatives, this study aims to understand mobile OTT service users’ responses to wireless D2D caching networks. By using AHP, the study will first examine mobile OTT service users’ decisions to either apply or resist wireless D2D caching networks. Next, the study will utilize criteria weights to identify the key factors contributing to such decisions. The proposed framework is demonstrated in
Figure 2.
3.4. Data Collection
The study examined the AHP model by conducting an online survey. Respondents who subscribed to mobile OTT services were recruited through an online survey company. They answered questions about various options related to using mobile OTT services outside or while moving. The study collected responses during May 19–23, 2022. Firstly, a total of 110 responses were collected. However, only 94 responses were analyzed in this study after eliminating 16 that did not satisfy the statistical standard.
The profile of the respondents is presented in
Table 2, which shows the following features: the number of mobile OTT services in use, mobile OTT services in use, mobile data offered, age, gender, occupation, education, and income. Respondents subscribed to 1.66 mobile OTT services on average, and most of the respondents (46.9%) subscribed to Netflix the most. They paid an average of 15,344.84 KRW
1 (USD 11.61) per month on mobile OTT service subscription fees. Regarding smartphones, respondents spent an average of 49,163.39 KRW (USD 37.19) per month on mobile data plans and were offered an average of 37.04 GB of mobile data per month.
3.5. Data Analysis
The responses were analyzed using the technical computing language software, MatLab. The consistency ratio (CR) was examined to verify the validity of the responses. According to Saaty [
52], responses with CR values below 0.2 are acceptable, especially in social sciences where respondents have different perspectives and understandings of the hierarchies. Except for 16 responses, all responses had a CR below 0.2. The study, therefore, analyzed 94 survey responses from mobile OTT service users.
4. Results
4.1. Criteria Weight
The respective weight of the criteria used in the model is analyzed in
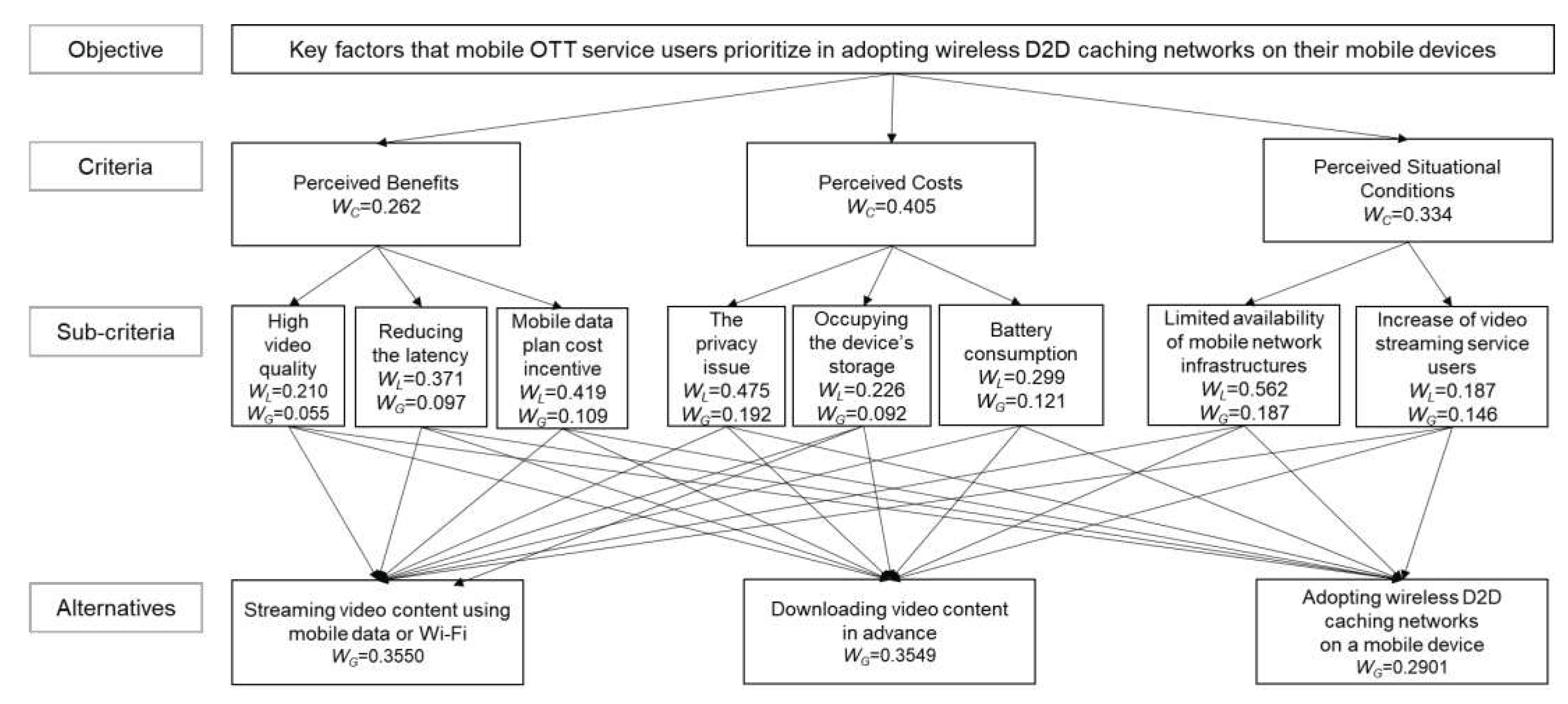
Table 3. Results demonstrate that perceived costs (.405) are the most important factor followed by perceived situational conditions (.334) and perceived benefits (.262). Within the perceived costs, the privacy issue (.475) had the highest weight, followed by battery consumption (.299) and occupying the device’s storage (.226). In the perceived situational conditions, the limited availability of mobile network infrastructures had the most weight, with .562. Under the perceived benefits criteria, the mobile data plan cost incentive (.419) was found to be more important than reducing the latency (.371) and high video quality (.210).
Global weights symbolize the relative importance of each sub-criteria. The value was calculated by multiplying the first-level criteria’s weights with the local score of each sub-criterion. The global weights of eight variables demonstrated that the privacy issue (.192) is the most important factor influencing mobile OTT service users’ responses to adopting wireless D2D caching networks on a mobile device. Two variables in the perceived situational conditions, the limited availability of mobile network infrastructures (.187) and the increase of video streaming service users (.146), were also emphasized as influential factors. High video quality (.055) was the least important criterion.
4.2. Alternatives
The priority among the alternatives is measured by first examining the local score of each sub-criterion under the given alternatives. The local score is then multiplied by the global weight score, which is the product of first-level criteria weights and sub-criteria local scores. The multiplied values become the global weight for alternatives, and the sum of global weight values is regarded as the total weight of each alternative criterion.
Table 4 shows the sub-criteria’s local values under each alternative. The alternative option, related to streaming video content using mobile data or Wi-Fi, was found to be strongly influenced by occupying the device’s storage (.517). Benefits related to high video quality (.421) and reducing the latency (.358) and cost related to the privacy issue (.379) were also important predictors to stream video content using mobile data or Wi-Fi. For the alternative of downloading video content in advance, costs related to battery consumption (.427) and the privacy issue (.387) were found to be important factors that mobile OTT service users consider. Situational conditions related to the limited availability of mobile network infrastructures (.390) and increase of video streaming service users (.338), as well as benefits related to mobile data plan cost incentive (.360) and reducing the latency (.344), were also important predictors to download video content in advance. The alternative to adopting wireless D2D caching on a mobile device was strongly correlated with situational conditions related to the increase of video streaming service users (.336) and the limited availability of mobile network infrastructures (.310). Benefits related to mobile data plan cost incentive (.327) and high video quality (.302) were also important predictors to adopt wireless D2D caching networks on a mobile device. However, battery consumption (.254) and the privacy issue (.234) showed weak relations.
The global weights of the alternatives are measured using the first-level criteria weights from
Table 3 and the sub-criteria local weights from
Table 4. The total weight of adopting wireless D2D caching networks on a mobile device was .2901, the lowest among the three proposed alternatives. Downloading video content in advance ranked second with a global weight of .3549. The most probable alternative had a global weight of .3550 and was to stream video content using mobile data or Wi-Fi.
Table 5 and
Figure 3 present the results of the AHP analysis.
5. Discussion and Conclusion
5.1. Summary of Findings
This study aimed to provide a model to help develop mobile OTT service users’ decision-making concerning adopting wireless D2D caching networks on a mobile device. By using an AHP approach, this study devised an evaluation model that includes three major factors: perceived benefits, perceived costs, and perceived situational conditions. The first criterion – perceived benefits – had sub-criteria of high video quality, reduced latency, and mobile data plan cost incentive. The second criterion – perceived costs – had sub-criteria of the privacy issue, occupying the device’s storage, and battery consumption. Lastly, the third criterion – perceived situational conditions – had two sub-criteria: the limited availability of mobile network infrastructures and the increase of video streaming service users.
The study examined 94 survey responses from mobile OTT service subscribers. The results were analyzed based on the perspectives of mobile OTT service users who are aware of mobile OTT service quality and their satisfaction with the service in response to adopting wireless D2D caching networks on their mobile devices. Among the three criteria on the first layer of the model, perceived costs showed the highest score, followed by perceived situational conditions and perceived benefits. Rather than the situational conditions or the benefits that the users receive from using mobile OTT service, it was the costs that mostly affected mobile OTT service users’ behavioral intentions and strategies. This indicates that telecommunication operators who want to commercialize wireless D2D caching networks should start putting effort into mitigating the sacrifice of user resources. How superior the technology is in terms of its performance or network is not the key consideration for mobile OTT service users. Rather, handling costs related to applying the technology is more important. In particular, mobile OTT service users’ decisions strongly correlated with privacy issues. Users tend to stream video content using their mobile data or W-Fi, or download it in advance, rather than adopt wireless D2D caching networks on their mobile devices due to the concerns around privacy issues. To adopt wireless D2D caching networks on mobile OTT service user devices, users need to share their information, such as location, content preference information, and content viewing history. However, the result implies that the concern for personal information leakage or misuse is critical for users in determining which alternative to choose when they watch mobile OTT video content outside or while moving. Thus, users who do not want to bear the possibility of personal data breach accidents hesitate to adopt wireless D2D caching networks and choose another alternative with a low possibility of that kind of accident. This signifies that telecommunication operators should reduce users’ concerns about personal information leakage or misuse by collecting and using only the minimum amount of personal information and preparing a reliable method to safely protect the obtained personal information. It is about building trust of the users and promoting the privacy features, as well as building them in.
The situational conditions accompanied by using mobile OTT service outside or while moving were perceived as the next significant factor affecting mobile OTT service users’ decisions. In all three alternatives, situational conditions were commonly considered one of the high priorities. This can be seen as a reflection of the character of the mobile service, which is highly influenced by situational factors such as time, place, and people around. Notably, among the three alternatives, the relative importance of the situational conditions in adopting wireless D2D caching networks was higher than other alternatives. Given that situational factors have a considerable impact on choosing an alternative to watch OTT video content outside or while moving, if a significant change in situational conditions occurs, users’ choice might change to adopt wireless D2D caching networks. Of the two major sub-criteria, the limited availability of mobile network infrastructures was perceived as the biggest concern for users. In the situation that the conventional approaches to resolving the mobile data traffic overloads are insufficient and that this fact is felt while using 5G service, this study finds that mobile OTT service users fear the limit of mobile network infrastructure and uneasy use of services as a result. The increase in video streaming service users was also perceived to be a concern that motivates users to seek viable options. Mobile OTT service subscribers have continuously increased, and consequently, mobile communication network traffic is soaring [
1,
3]. Considering mobile data traffic is significantly driven by users who stream video content, the study validates that the rise of video streaming service users is a critical concern for mobile OTT service users.
The study findings demonstrate that benefits from adopting wireless D2D caching networks are less highly prioritized when making decisions about using mobile OTT services. High video quality was ranked as the lowest priority, followed by reducing the latency and mobile data plan cost incentive. Contrary to studies emphasizing how mobile OTT service users are heavily reliant on the high quality of OTT video content consumption [
13], the study finds that the benefits are of lower priority when making decisions to adopt or reject wireless D2D caching networks on a mobile device.
Among the three suggested alternatives, streaming video content using mobile data or Wi-Fi was perceived to be the most viable option. Mobile OTT service users were also shown to prefer downloading video content in advance rather than adopting wireless D2D caching networks on a mobile device. However, as discussed above, the high weights on the limited availability of mobile network infrastructures and the increase of video streaming services strongly imply that mobile OTT service users’ decisions are heavily dependent on situational conditions related to using mobile OTT services that make the quality of service consumption different. The decision to adopt any of the three alternatives was also influenced by concerns related to privacy issues and battery consumption. The study findings carefully suggest that with the change of situational factors and assurance of protecting users’ resources, mobile OTT service users are willing to divert and adopt wireless D2D caching networks that guarantee autonomy from mobile network infrastructures and more user-oriented benefits.
5.2. Implications
The continuous growth of mobile OTT services and overloads of mobile data traffic are not separable issues. To provide a stable video content consumption experience to users, reliable alternatives must be found to resolve the limitation of the conventional approach. Accordingly, wireless D2D caching networks have gained attention as a reliable alternative. Considering that this technology can reduce network-related overheads, save related costs, and improve OTT service users’ video consumption environment [
3,
11], there is a high possibility that telecommunication operators want to commercialize this technology. To commercialize wireless D2D caching networks, users need to share their resources, such as personal information, smartphone storage, and battery. Based on the previous literature, this study explored decision factors associated with adopting wireless D2D caching networks on mobile OTT service user devices. Among various factors, situational conditions such as the limited availability of mobile network infrastructures and the increase of video streaming service users are found to be the most determining factors affecting mobile OTT service users’ decisions. As one of the first to examine mobile OTT service users’ responses to adopting wireless D2D caching networks on their mobile devices, this study offers findings with academic and practical implications.
From an academic perspective, the study integrates various literature to explain mobile OTT services and the issues associated with the OTT service market and telecommunication operators. Along with prevailing literature on OTT service and its market, concepts related to online video streaming and mobile network are used to explain telecommunication operators and OTT platforms’ tug-of-war. While previous studies on mobile OTT services focus on the growth of the OTT market and user’s perception of the service, this study specifically focuses on wireless D2D caching networks, which are a desirable alternative to resolving the mobile network traffic overloads and depicts the perceptions of mobile OTT service users through AHP analysis. The findings provide a guideline for understanding the responses of mobile OTT service users and their priorities in responding to adopting wireless D2D caching networks on their mobile devices. The analysis, therefore, contributes to extending the concept of mobile OTT service market ecosystems and specifying the features that users value when adopting a new alternative technology.
From a practical perspective, the study offers viable solutions to telecommunication operators and OTT platforms. First, the revolutionary role of the telecommunication operator is the most critical prerequisite in the motivation to adopt wireless D2D caching networks. Meanwhile, telecommunication operators have relied on conventional methods, such as deploying more base stations and expanding the bandwidth to address increasing mobile network traffic. However, consumers have felt that these methods are not obviously effective as they are left feeling not entirely satisfied with 4G and 5G services. They empathized with the limitation of existing mobile network infrastructure, and this problem would be more serious with the consistent increase in the number of mobile OTT service users. It means that users do not give credit for the “original and traditional” approach of telecommunication operators; they look for credible and competent alternative technology with the capability to deal with the soaring demand. Telecommunication operators are, therefore, encouraged to strengthen their competitiveness by developing strategies and options to motivate users to adopt wireless D2D caching networks and experience improved communication service. The innovative and exclusive value of wireless D2D caching networks is anticipated to help telecommunication operators save the cost related to CAPEX and OPEX and retain their subscribers. The deep concern for privacy issues imply that users are sensitive to personal information protection and management strategies of telecommunication operators. Thus, telecommunication operators must prepare a surefire safeguard of personal information and compensation plan for unexpected breach accidents. Furthermore, they need to provide improved and advanced communication and customer service to subscribers based on saved costs earned from subscribers’ cooperation, so subscribers understand the benefits of their sacrifice.
OTT platforms are advised to cooperate with telecommunication operators to provide more customized and seamless service to their subscribers. Considering the features of wireless D2D caching networks that offload the content that is expected to be repeatedly requested at a specific time and place by a large population of users [
3], hit-ratio of offloading could get higher when utilizing an OTT platform’s data. When the hit ratio increases, telecommunication operators can save more costs, and OTT platforms can provide more smooth streaming services. Then, subscribers’ satisfaction with both service providers would increase, and those two service providers could obtain more subscribers. It would directly lead to an increase in profit. This means that they can maintain a good-neighbor relationship. Of course, the OTT platforms should clarify a plan of personal information utilization and ask for subscribers’ agreement, considering the privacy issue is a critical concern for users. Through collaborative efforts in providing more customized and enhanced service, we believe that wireless D2D caching networks can become a viable alternative for users. Moreover, commercializing wireless D2D caching networks would help decrease socioeconomic costs and increase both service providers’ and users’ convenience. For instance, telecommunication operators can relieve the burden of traffic overload caused by OTT video content streaming services. In addition, given the legal dispute between SK Broadband and Netflix over the network usage fee, wireless D2D caching networks may pose a reasonable alternative to resolve the bilateral conflict between telecommunication operators and OTT platforms. Meanwhile, OTT platforms can further enhance the quality of recommendation services by being able to consider the user’s spatiotemporal context through the application of wireless D2D caching networks. As for users, if users are willing to concede resources such as mobile device storage space and battery so that wireless D2D caching networks can be well-commercialized, it can contribute to significant savings in social and environmental costs incurred when using existing mobile communication technology infrastructures. Also, by contributing to resolving legal disputes between telecommunication operators and OTT platforms and thus promoting their business improvement, personal benefits in terms of service use and cost can be expected. Lastly, in the mobile communication service market, as the user makes a significant contribution to service provision and use by adopting wireless D2D caching networks, they can improve the user’s status and take the initiative to a certain level in terms of mobile data plan design.
Taking this study as a stepping-stone, scholars and practitioners can conduct further research using the current AHP model. This study investigated the mobile OTT service industry, but it is only a start. The convergence with other forms of online video streaming service market has no limits, so scholars or business practitioners can take inspiration from this study and examine other markets. It is hoped that more research like this study will be published and shared to provide useful business implications to the business practitioners and policymakers in the related field.
5.2. Limitations and Future Research
The study is not without limitations. First, the study focuses on Korean mobile OTT service markets and telecommunication operators; the results are, therefore, refined to market conditions and the regulatory environment in Korea. Studies in different geographical conditions with various mobile network environments can be conducted to compare the diverse needs of mobile OTT service users internationally. Second, the AHP model’s criteria in this study mostly consist of rational and objective factors; psychological or emotional reasons that users feel in the decision-making process were undervalued. Prior business and consumer research studies emphasized that consumer behavior is not only affected by rational and objective reasons but also by irrational and emotional factors. Sometimes, irrational and emotional aspects have a more decisive influence on behavior than rational and objective factors. For example, Manhas and Gulzar [
53] covered consumers’ irrational purchase behavior and its universal application. Besides, other factors like the influence of advertisement and the peer influence (“my friends use this technology, so I use it, too”) also can be considered. Regarding using mobile OTT service outside or while moving, for instance, factors can be considered such as average time of outdoor stay, the influence of a person who accompanies outdoor activities, the level of impatience of being behind the trend related to media content, the vulnerability of OTT services’ outdoor or transit advertisement that can be seen in a subway, bus stop, or park. In this sense, future studies can investigate the effects of these factors mentioned above on the adoption of wireless D2D caching networks on a mobile device. Third, this study examined users’ recognition of wireless D2D caching networks, a new technology that has not yet been commercialized. Although numerous previous studies showed the functionality and feasibility of applying AHP analysis to newly emerging technology, the limitation remains that users’ perceptions or preferences when wireless D2D caching networks are actually commercialized and applied to users’ mobile OTT service consumption may differ from the results of this study.
Notwithstanding its limitations, this study expands the literature on understanding new ICT convergence services and potential users’ perceptions and preferences. Along with this study’s implications and suggestions, more interest and efforts are required to resolve various issues surrounding the mobile OTT service market and mobile network traffic and to ensure that adjacent markets continue to grow soundly. We hope that telecommunication operators, mobile OTT platforms, the government, and users will all become key players contributing to the mobile OTT service and telecommunication market’s stability, productivity, and sustainability.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.J. and S.K.; methodology, Y.J. and S.K.; formal analysis, Y.J.; investigation, Y.J.; resources, Y.J.; data curation, Y.J.; writing—original draft preparation, Y.J.; writing—review and editing, Y.J. and S.K.; visualization, Y.J.; supervision, S.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded work by the Ministry of Education of the Republic of Korea, the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF-2019S1A3A2099973), and the MSIT (Ministry of Science and ICT), Korea, under the ITRC (Information Technology Research Center) support program (IITP-2023-2020-0-01749) supervised by the IITP (Institute of Information & Communications Technology Planning & Evaluation).
Institutional Review Board Statement
The survey conducted was determined exempt by the Institutional Review Board of Korea University.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The data are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Note
| 1 |
The Korean Won or KRW is the monetary unit of South Korea. On March 8, 2023, USD 1 was approximately 1322.10 KRW. |
References
- Korea Communications Commission. Available online: https://www.kcc.go.kr/user.do;jsessionid=f0BZa4KrNjZJNCao58yVl-HlyXeSafOYSWLiQL1B.servlet-aihgcldhome10?mode=view&page=A02060100&dc=K02060100&boardId=1027&cp=2&boardSeq=50589 (accessed on 9 August 2022).
- Korea Communications Commission. Available online: https://www.kcc.go.kr/user.do;jsessionid=-MuHoukQytSCF6n7c1ZI3tcg1So3T0MOa0xl97Iw.servlet-aihgcldhome10?mode=view&page=A02060400&dc=60400&boardId=1027&cp=1&boardSeq=52581 (accessed on 9 August 2022).
- Lee, J.; Lee, S.H.; Rim, M.; Kang, C.G. System-level spatiotemporal offloading with inter-cell mobility model for device-to-device (D2D) communication-based mobile caching in cellular network. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 51570–51581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cisco. Available online: http://media.mediapost.com/uploads/CiscoForecast.pdf (accessed on 11 August 2022).
- Ali, A.S.; Naguib, K.M.; Mahmoud, K.R. Optimized resource and power allocation for sum rate maximization in D2D- assisted caching networks. In Proceedings of the 2019 14th International Conference on Computer Engineering and Systems (ICCES), Cairo, Egypt, 17 December 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, M.; Choi, S.; Lee, Y. A study on the adoption of UHD for users perceived usefulness and ease of use of UHDTV. J. Broadcast Eng. 2015, 20, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heimerl, K.; Hasan, S.; Ali, K.; Brewer, E.; Parikh, T. Local, sustainable, small-scale cellular networks. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Information and Communication Technologies and Development: Full Papers-Volume 1, Cape Town, South Africa, 7-10 December 2013. [Google Scholar]
- The Wall Street Journal. Available online: https://www.wsj.com/articles/what-consumers-business-do-5g-south-korea-success-11646854941 (accessed on 1 September 2022).
- The JoongAng. Available online: https://www.joongang.co.kr/article/25160752 (accessed on 11 May 2023).
- Kim, Y. Impact of OTT service on the content creation, distribution and consumption. Studies of Broadcasting Culture 2015, 27, 75–102. Available online: https://www.dbpia.co.kr/pdf/pdfView.do?nodeId=NODE06366055&mark=0&useDate=&ipRange=N&accessgl=Y&language=ko_KR&hasTopBanner=true.
- Qian, F.; Quah, K.S.; Huang, J.; Erman, J.; Gerber, A.; Mao, Z.; Sen, S.; Spatscheck, O. Web caching on smartphones: Ideal vs. reality. In Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Mobile Systems, Applications, and Services, Low Wood Bay Lake District, UK, 25-29 June 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Gonçalves, V.; Evens, T.; Alves, A.P.; Ballon, P. Power and control strategies in online video services. proceedings of the 25th European Regional Conference of the International Telecommunications Society (ITS). “Disruptive Innovation in the ICT Industries: Challenges for European Policy and Business”, Brussels, Belgium, 22-25 June 2014; Available online: http://hdl.handle.net/10419/101438.
- Kim, M.S.; Kim, E.; Hwang, S.; Kim, J.; Kim, S. Willingness to pay for Over-the-top services in China and Korea. Telecomm. Policy. 2017, 41, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Baek, H.; Kim, D.H. OTT and live streaming services: Past, present, and future. Telecomm. Policy. 2021, 45, 102–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henten, A.; Tadayoni, R. Increasing Dominance of IT in ICT Convergence. In Proceedings of the IAMCR conference, Dublin, Ireland, 25-29 June 2013; Available online: http://www.iamcr2013dublin.org/content/increasing-dominance-it-ict-convergence.
- Mordor Intelligence. Available online: https://www.mordorintelligence.com/industry-reports/over-the-top-market. (accessed on 3 September 2022).
- Moyler, A.; Hooper, M. Over the Top TV (OTT TV) Platform Technologies. BCi Ltd. and Endurance Technology Ltd.
- Shin, S.; Park, J. Factors affecting users’ satisfaction and dissatisfaction of OTT services in South Korea. Telecomm. Policy. 2021, 45, 102–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reuters. Available online: https://www.reuters.com/business/media-telecom/skorea-broadband-firm-sues-netflix-after-traffic-surge-squid-game-2021-10-01/ (accessed on 3 September 2022).
- The Korea Herald. Available online: http://www.koreaherald.com/view.php?ud=20210628000798 (accessed on 4 September 2022).
- Bush, S. A Survey of Audience Reaction to NHK 1125 Line Color Television: Conducted at the US Public Demonstration, Washington, DC, February 3-16; Advanced Television Pub: Portland, USA, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Neuman, W.R. The Mass Audience Looks at HDTV: An Early Experiment; The annual meeting of the NAB: Las Vegas, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Massaro, M.; Kim, S. Why is South Korea at the forefront of 5G? Insights from technology systems theory. Telecomm. Policy. 2022, 46, 102–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korea Consumer Agency. Available online: https://www.kca.go.kr/home/board/download.do?menukey=4002&fno=10027481&bid=00000013&did=1002981971 (accessed on 10 September 2022).
- Seymour, T.; Shaheen, A. History of wireless communication. Rev. Bus. Inf. Syst. 2011, 15, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chlamtac, I.; Conti, M.; Liu, J.J.-N. Mobile ad hoc networking: Imperatives and challenges. Ad. Hoc. Netw. 2003, 1, 13–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.; Kim, S. Understanding user resistance to participation in multihop communications. J. Comput-Mediat. Comm. 2009, 14, 328–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Zhao, P.; Zhou, F.; Yin, M.; Yu, P.; Li, W.; Qiu, X. Resource allocation for 5G D2D multicast content sharing in social-aware cellular networks. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2018, 56, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Germonprez, M.; Hovorka, D.; Collopy, F. A theory of tailorable technology design. J. Assoc. Inf. Syst. 8, 351–367. [CrossRef]
- Saaty, R.W. The analytic hierarchy process—What it is and how it is used. Math. Model. 1987, 9, 161–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas, L.G. An overview of the analytic hierarchy process and its applications. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 1990, 48, 2–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saaty, T.L. How to make a decision: The analytic hierarchy process. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 1990, 48, 9–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saaty, T.L. Decision making with the analytic hierarchy process. Int. J. Serv. Sci. Manag. Eng. Technol. 2008, 1, 83–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas, L.G.; Saaty, T.L. Financial and intangible factors in fleet lease or buy decision. Ind. Mark. Manag. 1981, 10, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez, M.; Moreno, A.; Mataix, C. The analytic hierarchy process to support decision-making processes in infrastructure projects with social impact. Total Qual. Manag. Bus. Excell. 2013, 24, 596–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Kim, S. Newspaper companies’ determinants in adopting robot journalism. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change. 2017, 117, 184–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Nam, C.; Kim, H. Exploring the key services and players in the smart car market. Telecomm. Policy. 2019, 43, 101–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, H.J.; Daham, H.A. Analytic hierarchy process for evaluating flipped classroom learning. Comput. Mater. Contin. 2021, 66, 2229–2239. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, M. Device caching strategy maximizing expected content quality. Journal of the Korea Society of Computer and Information 2021, 26, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Lee, I.; Guan, L. Distributed throughput maximization in P2P VoD applications. IEEE. Trans. Multimedia. 2009, 11, 509–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Korea Herald. Available online: http://www.koreaherald.com/view.php?ud=20180507000098 (accessed on 11 September 2022).
- Wan, K.; Sun, H.; Ji, M.; Tuninetti, D.; Caire, G. On the Fundamental Limits of Device-to-Device Private Caching under Uncoded Cache Placement and User Collusion. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Communications, Dublin, Ireland, 7 June 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.; Lin, X. Security-aware and privacy-preserving D2D communications in 5G. IEEE Netw. 2017, 31, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Slyke, C.; Shim, J.T.; Johnson, R.; Jiang, J.J. Concern for information privacy and online consumer purchasing. J. Assoc. Inf. Syst. 2006, 7, 415–444. [Google Scholar]
- Institute of Information & Communications Technology Planning & Evaluation. Available online: https://www.itfind.or.kr/publication/regular/weeklytrend/weekly/view.do?boardParam1=7925&boardParam2=7925 (accessed on 5 September 2022).
- Bijlani, A.; Ramachandran, U.; Campbell, R. Where Did My 256 GB Go? A Measurement Analysis of Storage Consumption on Smart Mobile Devices. In Proceedings of the Abstract Proceedings of the ACM on Measurement and Analysis of Computing Systems, Virtual Event China, 31 May 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, D.; Dey, A.K.; Kostakos, V. Understanding Human-Smartphone Concerns: A Study of Battery Life. In Proceedings of the Pervasive Computing: 9th International Conference, Pervasive 2011, San Francisco, USA, 12-15 June 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, E. The Challenges in Large-Scale Smartphone User Studies. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 2nd ACM International Workshop on Hot Topics in Planet-scale Measurement, San Francisco, USA, 15-18 June 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belk, R.W. An Exploratory Assessment of situational effects in buyer behavior. J. Mark. Res. 1974, 11, 156–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandura, A. Self-efficacy: Toward a unifying theory of behavioral change. Psycho. Rev. 1977, 84, 191–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Press Arbitration Commission. Available online: https://www.pac.or.kr/_common/new_download_file.asp?menu=magazine_sub&sub_idx=6697 (accessed on 15 September 2022).
- Saaty, T.L. Priority setting in complex problems. IEEE Trans. Eng. Manage. 1983, 3, 140–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manhas, P.S.; Gulzar, F. A Review and a conceptual framework of ‘irrational influences’ on consumer purchase behavior (CPB). Pranjana: The Journal of Management Awareness. 2012, 15, 47–53. Available online: https://www.proquest.com/scholarly-journals/review-conceptual-framework-irrationalinfluences/docview/1430264146/se-2.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).