1. Introduction
Rapeseed meal (RM) is an important agro-industrial by-product of oil extraction from rapeseeds. Global rapeseed oil production has been increasing over recent years [
1]. As rapeseed oil production increases, so does the production of waste material. Based on oil production data and market prices in the European Union, the estimated global value of RM waste biomass alone, without additional processing, is in the order of €6.36 billion [
1,
3]. Biomass enrichment can increase the nominal value of RM waste many times over. The growing world population and sustainable development goals require the valorization of waste by reusing, recycling, or composting and conversion into more useful materials, chemicals, fuels, or energy sources [
2]. These activities fit perfectly into the definition of a circular economy.
Rapeseed meal is normally used as organic fertilizer or as biofuel. It can also be dried and used as feed additive for livestock and poultry, due to its high protein content. Rapeseed meal is mainly composed of protein, fat, fibers (celluloses, hemicelluloses, and lignins), pectin, and minerals with significant amounts of calcium, magnesium, zinc, and copper [
5]. Of particular interest is the group of isoflavone compounds in RM, which exhibit a very broad spectrum of functionality. Notably, compounds such as daidzein, daidzin, genistein, genistin, glycitein, and glycitin show estrogenic, neuroprotective, cytostatic, and cytotoxic activity [
10,
11,
12]. However, the efficient utilization of RM as animal feed is limited by its low metabolizable energy, poor palatability, and high levels of fiber and anti-nutritional components, such as glucosinolates, phytic acids, and phenolic compounds.
Agroresidues such as RM offer a cheap, eco-friendly substrate for the growth of microorganisms, as both a support matrix and a nutrient medium. An example is the production of single-cell protein (SCP) by fermentation with microorganisms [
4]. However, the high contents of protein, carbohydrates, and minerals in RM cannot be assimilated by the majority of microorganisms. These nutrients can be made accessible for microorganisms by enzymatic hydrolysis. Microbial treatments can be used to detoxify RM and improve its digestibility during fermentation processes, as well as its functional properties [
6,
7]. For example, supplementation with lactic acid bacteria (
Lactobacillus plantarum and
Bacillus clausii) and yeasts (
Saccharomyces cariocanus and
Wickerhamomyces anomalus) can degrade free gossypol, improving the utilization efficiency of this substrate in the fermentation process [
8]. Other studies show that fermentation with
Saccharomyces cerevisiae or
Saccharomyces boulardii reduces the content of antinutritive factors and increases the protein content of the RM, without having major adverse effects on its overall nutritional value [
9].
In this study, we investigate the enrichment of RM with SCP by fermentation with conventional and unconventional yeasts, to make a nutritionally-improved feed component. This research is a continuation of earlier work by Dygas et al. [
13].
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Waste Material and Sample Preparation
The raw material for the research was rapeseed meal biomass after oil extraction. The waste material was provided by a rapeseed oil producer in Kruszwica, Poland. The dry material was hydrated before processing to achieve an optimal water content for enzymatic pre-hydrolysis and microbial growth. For this purpose, three different portions of waste biomass (10 g (A), 12.5 g (B), 15 g (C)) were placed in conical flasks and filled with 90 ml of distilled water. The samples were sterilized at 121°C for 15 min.
2.2. Enzymatic Pre-Hydrolysis and Simultaneous Saccharification and Fermentation (SSF)
The sterilized samples were prehydrolyzed with enzymatic preparations: Rohament® and Rohapect® by AB Enzyme. The prehydrolysis process was performed at 50°C for 4 h after adding 0.5 ml/ 10 grams of dry mass (DM) to each sample. Different doses of enzymes (0.5 ml/10g DM (D); 0.25ml/10g DM (E); 0.125 ml/10g DM (F)) were added to the samples. To prevent the negative influence of ammonium sulfate, an alternative nitrogen source was added after prehydrolysis (0.3 g per sample; 0.3% m/m). At this stage, the samples were ready for inoculation and fermentation. To avoid enzyme inactivation, the process was performed with simultaneous saccharification and fermentation (SSF). The yeast strains used are listed in
Table 1.
The samples were inoculated with the strains listed in
Table 1. Subsequently, SSF was carried out for 48 h at an ambient temperature of approx. 21°C.
2.2. Determinantion of Protein Content
The Kjeldahl method was used to determine the protein fraction. For this purpose, the solid fraction was separated from the post-culture liquid by centrifugation (3000 RCF). The biomass samples were transferred to test tubes, filled with sulfuric acid (15 ml of a solution of 95% m/v), and 4 grams of catalyst (3.5 g potassium sulfate, 0.5 g copper sulfate) were added. The samples were heated at 550°C in a SpeedDigester K-425 for 2 h until a transparent liquid was obtained. The samples were neutralized (30% NaOH) and steam distilled in a KjelFlex K-360 instrument, then titrated automatically with 0.1 mol HCl solution in a TitroLine®5000.
2.3. Determinantion of Free Amino Nitroge (FAN)
The liquid was separated from the solid fraction after culture and transferred to a test tube. Hydrolyzed unfermented rapeseed meal was used as a control sample. A detailed description of the methodology can be found in the Eppendorf protocol [
14].
2.4. Determinantion Crude Fiber (CF) Content
Crude fiber content was determined using a FOSS Fibertec
TM 8000. The samples were prepared and the analysis was performed according to EN-ISO 6865:2000 [
15].
2.5. Chromatographic Analysis of Flavonoids
Chromatographic analysis of flavonoid compounds was performed according to the method described by Sulyok et al. [
16] and Steglińska et al. [
17].
2.6. Statistical Analysis
Statistical analysis was performed by analysis of variance (one-way ANOVA) at a significance level p ≤ 0.05 using STATISTICA 14.0 (StatSoft, Tulsa, OK, USA) to determine differences. Post-hoc analysis was performed when a statistical difference was detected (Tukey’ test, significance p ≤ 0.05).
3. Results
3.1. Influence of Different Biomass Loads on Various Parameters
3.1.1. Protein Content Increase with Various Biomass Loads
The biomass was separated by centrifugation and the protein content was analyzed according to the Kjeldahl method. Unfermented rapeseed meal used as a control sample.
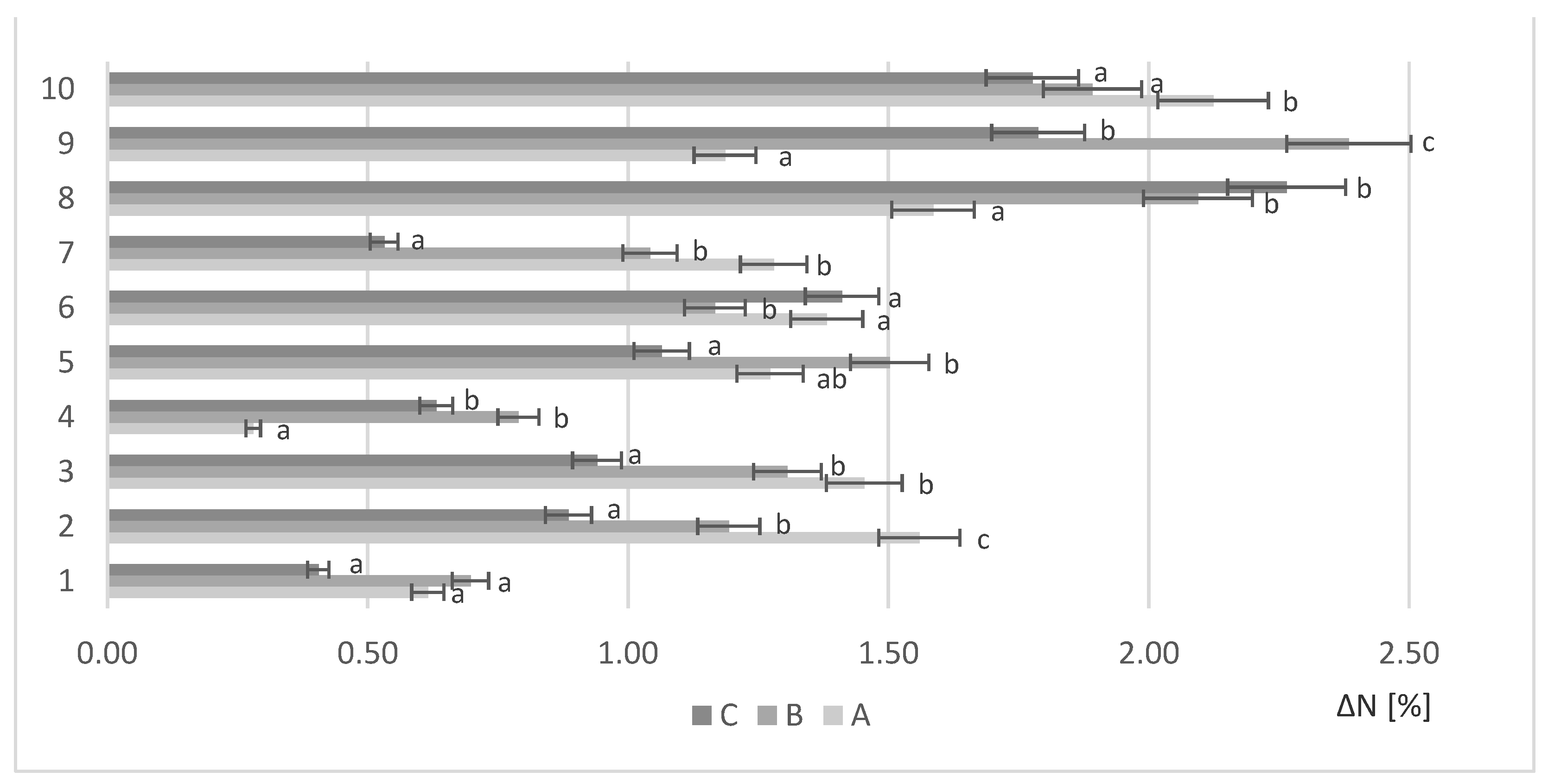
Figure 1 presents the increase in protein content after fermentation with yeasts (1–10) under various biomass loads (A,B,C) relative to the unfermented rapeseed meal.
All the yeasts studied showed the ability to grow on RM biomass and increase its protein content. The adopted conditions were favorable for cultivation for Saccharomyces cerevisiae. On the sample with 10 g (A) biomass load, the highest growth was recorded for Saccharomyces cerevisiae Tokay (10) (ΔN = 2.12%). With higher biomass load (B), Saccharomyces cerevisiae Ethanol Red (9) produced the highest amount of protein (ΔN = 2.38%). Further increasing the biomass load up to 15 g (C) resulted in the highest biosynthesis of proteins by Saccharomyces cerevisiae TT (8) (ΔN = 2.26%).
3.1.2. Free Amino Nitrogen Content in Sample of Post-Culture Liquid
The centrifuged post-culture liquid was analyzed to determine FAN. The liquid fraction of hydrolyzed, non-fermented RM was used as a control sample. The results showed the remaining nitrogen compounds that were not assimilated by the yeasts.
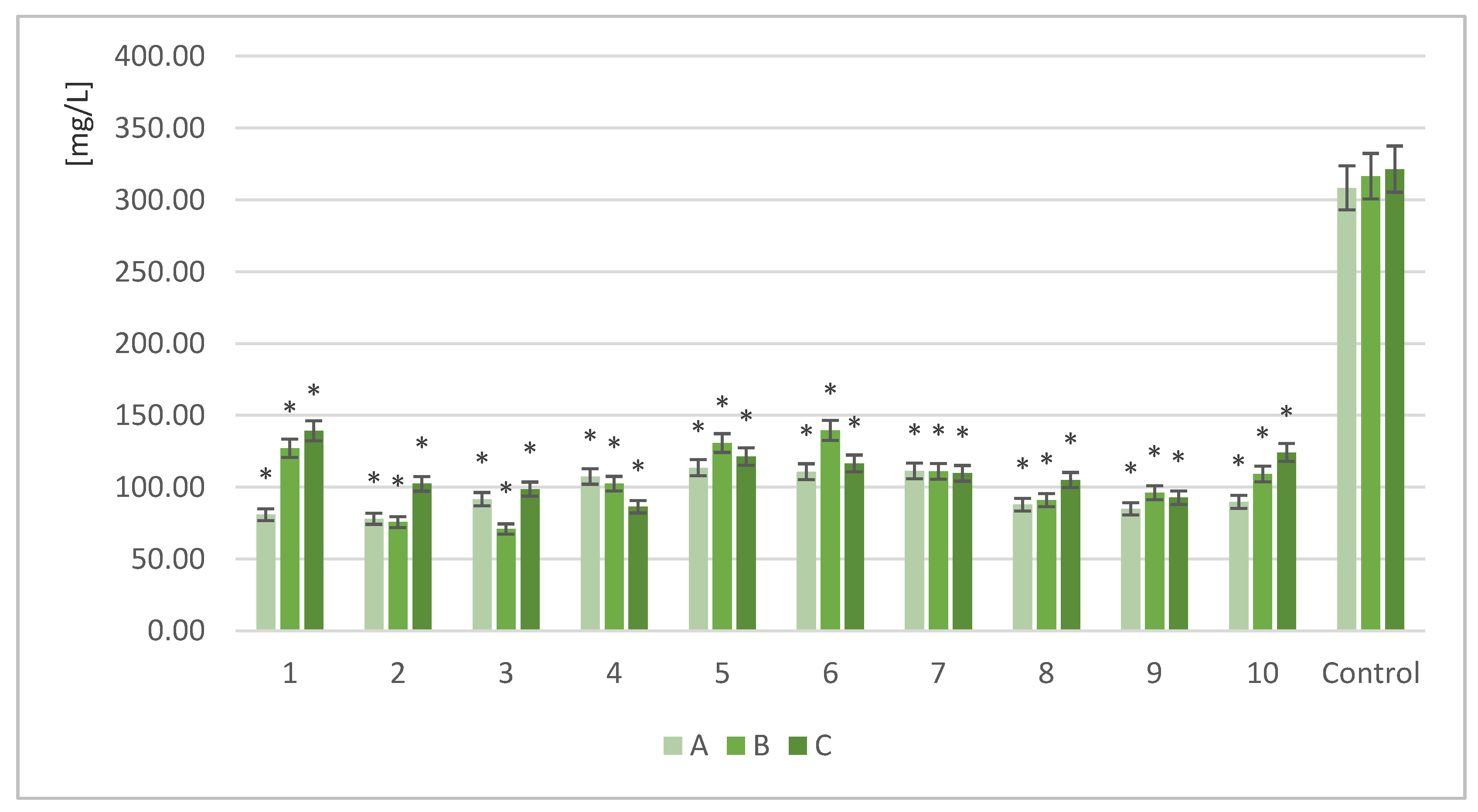
Figure 2 shows the results for each strain tested (1–10) under various biomass loads (A,B,C).
After the fermentation process, the available FAN was significantly reduced in all tested samples. All the strains were able to significantly reduce nitrogen compounds compared to the control sample.
3.2. Influence of Different Doses of Enzymatic Preparation on Production of Feeds
3.2.1. Control of Yeast Growth by Measuring Number of Cells
As a continuation of previous studies, yeast growth on different doses of enzymes was monitored using the pour plate method. An inoculated non-fermented sample (time t = 0 h) was used as a control.
Table 2 shows yeast growth (1–10) under different doses of enzymes (D,E,F) during the SSF process. The values in bold indicate a significant difference from the mean value of the control (
p ≤ 0.05).
All tested strains were able to grow on the hydrolyzed RM substrate. The highest cell number at the highest enzyme dose (D) was obtained for Yarrowia lipolytica (4.92×108 CFU/mL). Reducing the enzyme dose by half (E) provided optimal conditions for Saccharomyces bayanus, resulting in a cell number of 2.92×108 CFU/mL. Further reducing the enzyme amount (F) led to a decrease in yeast growth, with Scheffersomyces stipitis producing the highest number of cells.
3.2.2. Protein Increase under Different Doses of Enzymatic Preparation
The next phase of the study tested the influence of different doses of enzymes on the parameters of the final product. The protein content of the samples was also analyzed. The control sample was unfermented RM biomass.
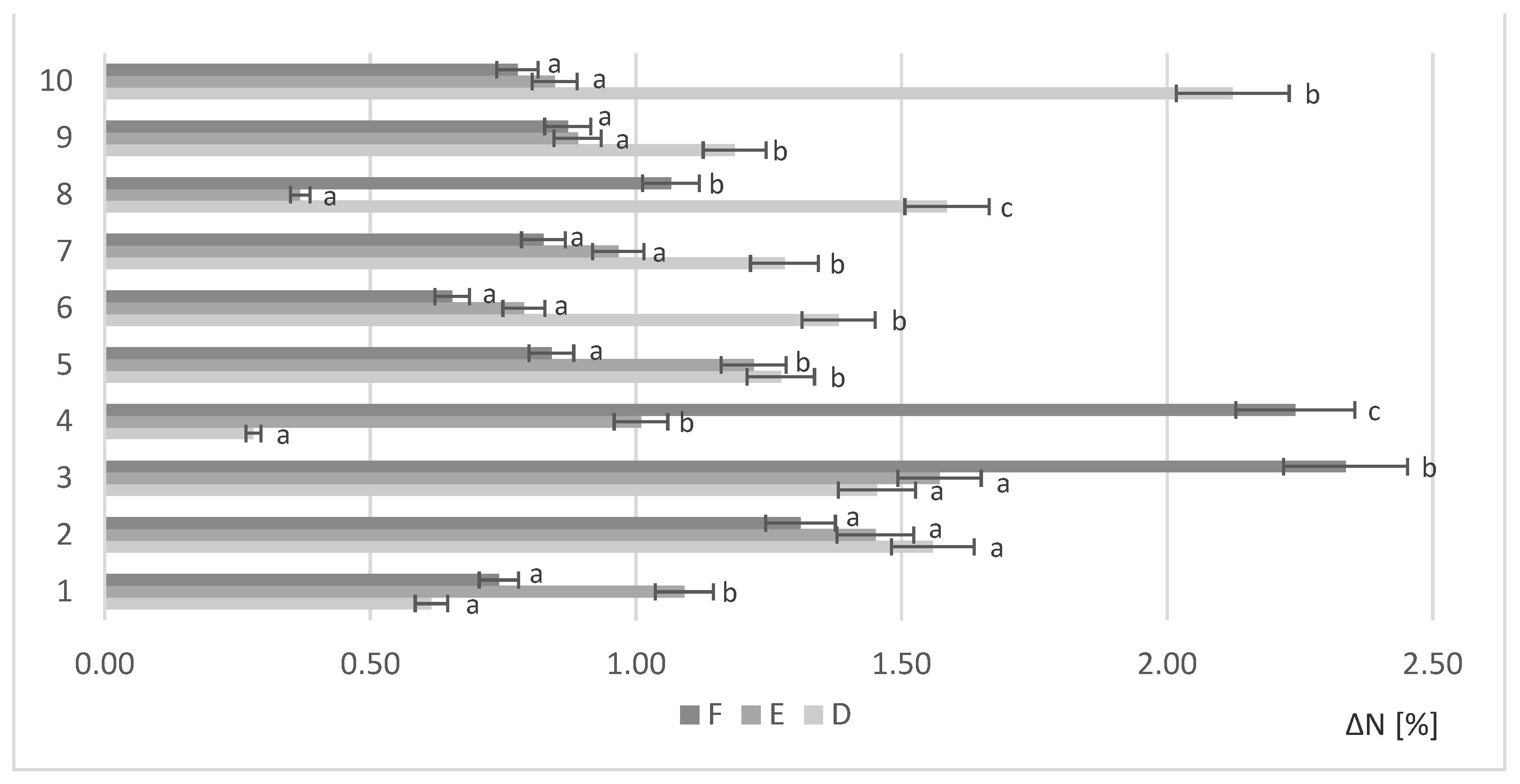
Figure 3 shows the calculated protein gain of the fermented samples with yeast (1–10) treated with different enzyme doses (D,E,F) and without enzyme treatment.
The most effective production of protein with the highest dose of enzyme (D) was noted for Saccharomyces cerevisiae Ethanol Red (ΔN = 2.12%). Reducing the volume of the enzyme dose by half (E) resulted in optimal environmental conditions for Scheffersomyces stipitis (ΔN = 1.57%). With the lowest enzyme concentration (F), Scheffersomyces stipitis produced the highest protein increase (ΔN = 2.34%). The combination of the lowest enzyme concentration with Scheffersomyces stipitis provided the best conditions for protein biosynthesis.
3.2.3. Crude Fiber Content in Samples with Different Biomass Loads and Enzyme Doses
The crude fiber (CF) content was analyzed in samples with different biomass loads and enzyme doses. The strains that produced the most favorable protein increases with various biomass loads were analyzed. For easy comparison of the results, the same strains at the variable enzyme dose stage were chosen.
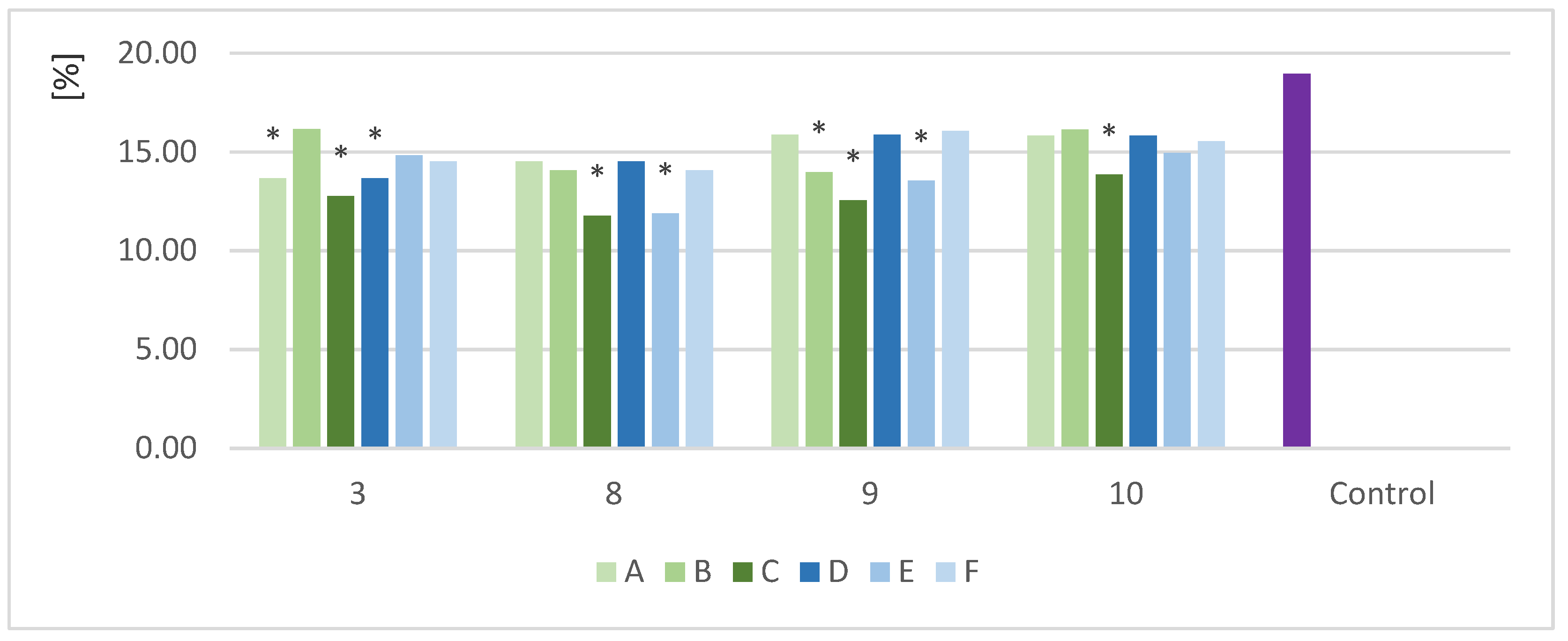
Figure 4 shows the CF content in the selected samples (3,8,9,10) after yeast fermentation with different biomass loads (A,B,C) and enzyme doses (D,E,F).
After fermentation, the biomass was separated from the liquid by centrifugation. The content CF in the solid fraction was determined. Raw material was used as the control sample. All the samples showed a reduction in CF after the SSF process. The CF content was in the range of 11.8–16.1% with different biomass loads and 11.9–15.9% with different enzyme doses. Higher biomass loads had a positive effect on the efficiency of fiber degradation. The lowest amounts of fiber were determined in the samples with biomass loads of 15 g (C). The CF content was in the range of 11.8–15.8%, with the highest fiber degradation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae TT. The results for biomass load (C) were statistically different from the control. Decreasing the load of biomass led to a decrease in efficiency. The results for the different enzyme doses ranged from 11.9% to 15.9%, with the lowest CF content also obtained for Saccharomyces cerevisiae TT (E).
3.2.4. Flavonoid Content after Fermentation
Flavonoid content was analyzed according to the methodology described by Sulyok
et al. [
13]. Two samples,
Scheffersomyces stipitis with an enzyme dose of 0.125 ml/10 g DM (3F) and
Saccharomyces cerevisiae Ethanol Red with a 12.5 g biomass load (9B), produced the greatest protein increases among all the sample variants. Untreated biomass, which is regularly used as a feed component, was used as a control.
As a result of fermentation, the daidzein content increased around 1.5 times relative to the control sample. A similar phenomenon was noticed for genistein, which increased by between 1.4 and 2.1 µg/g. The content of daidzin, a precursor of daidzein, was drastically reduced, around 250–460 times relative to the untreated biomass. A similar tendency was observed for genistin, a precursor of genistein, which reduced by between 28 and 176 times relative to the control sample. Glycitein transformation was exceptional. Fermentation with 12.5 g of biomass and Saccharomyces cerevisiae Ethanol Red resulted in a decrease of 206.1 ng/g; however, fermentation with 0.125 ml/10 g DM and Scheffersomyces stipitis led to an increase in glycitein content of 283.2 ng/g. The content of glycitin after fermentation was beneath the detection threshold (1.4 ng/g was the limit of detection [LOD]), from 53 mg/g before the process.
Table 3.
Concentration of flavonoids in biomass samples (ng/g).
Table 3.
Concentration of flavonoids in biomass samples (ng/g).
| Flavonoid compound |
Control |
9 B |
3 F |
| Daidzein |
2019.5 |
3258.9 |
3740.7 |
| Daidzin |
12868.3 |
52.3 |
28.2 |
| Genistein |
2596.1 |
4020.9 |
4699.6 |
| Genistin |
15200.0 |
534.5 |
86.9 |
| Glycitein |
1108.3 |
901.4 |
1391.5 |
| Glycitin |
5377.561 |
<LOD |
<LOD |
| Sum |
39169.8 |
8768.0 |
9946.9 |
4. Discussion
Rapeseed meal as a waste product of the oil extraction process. It is rich in proteins and carbohydrates [
18]. In this study, we investigated the possibility of enriching the protein content of RM in the process of simultaneous saccharification and fermentation, with different strains of yeast and doses of biomass. The greatest increase in protein content was observed in the samples fermented with
Saccharomyces cerevisiae. This was due to the adaptive and metabolic capabilities of the noble yeast, which also make it a common ingredient used in brewing and distilling processes, as well as in the dairy industry [
19]. The lower the protein content using unconventional strains was due to the limited adaptability of the yeasts.
Yarrowia lipolytica is able to metabolize different hydrophilic and hydrophobic carbon sources [
20]. However, our results indicate that it does not excel in its ability to increase the protein content of RM. Yeasts of the
Candida genus also did not increase the protein content dramatically. Their productivity depends on the presence of oxygen in the environment and the composition of the medium, which contains both simple sugars and polysaccharides [
21,
22]. A similar metabolism was demonstrated by the yeast
Metschnikowia sp. The use of
Metschnikowia pulcherrima yeast, which inhibits the growth of fungi, can improve the nutritional value of the feed, as well as increase its health safety by ensuring microbiological stability [
23].
Free Amino Nitrogen content was analyzed in the post-culture liquid. Controlling the FAN content in the liquid fraction of the waste material after fermentation makes it possible to control the efficiency of nitrogen assimilation and protein synthesis. The FAN content showed statistically significant differences for all strains compared to the non-fermented sample. It can be concluded that all strains are able to convert the inorganic and organic form of nitrogen in the form of proteins at different rates. The amount of FAN in wort is regularly monitored in the brewing industry. Depending on the FAN content of the wort, the final product is characterized by a different flavor and aroma [
24].
An identical procedure was used to study the effect of different enzyme dosages on protein content. The cell count determined by the pour plate method indicated balanced growth of both the conventional and unconventional yeasts. However, lowering the dosage of the enzyme preparation during pre-hydrolysis decreased the number of cells produced by the tested yeasts. This was due to the fact that a lower enzyme dose leads to a lower rate of depolymerization of the compounds present in the RM. With a lower dosage of enzyme, the rich composition of nutrients in RM are less available to microorganisms [
25]. The increase in protein content was not strongly correlated with a decreasing enzyme dose. It can be assumed that the efficiency of nitrogen bioconversion is a strain-specific property. Depending on the environmental conditions, the strains used in the study reach their maxima of protein synthesis efficiency at different enzyme concentrations. As strains originally isolated from the environment, unconventional yeasts show a greater ability to grow in an environment that mimics natural conditions. Forced to degrade macromolecular components themselves, they synthesize their own enzymes that initiate the hydrolysis process [
26].
The SSF process successively led to the decomposition of the crude fiber contained in the biomass, as a result of the action of enzymes present in applied enzymatic preparations and yeast enzymes. The reduction of the CF content increased the potential for use as an animal feed component. One of the most important parameters for the use of a waste material as a feed component is the CF content. Crude fiber content determines the use of material as feed for a particular animal. According to the life stage of the animal, it requires a feed different composition, including a specific CF content. A fibrous diet possibility reduces the feeding motivation of sows. However, it simultaneously extends the feeding time [
27,
28]. In the case of cattle, feed additives resulted in increased daily milk yield and improved milk quality [
29].
The nutritional value of the feed can be improved not only by increasing the protein content but also by changing the content of key isoflavones. Genistein, daidzein, and glycitein show interesting biological activities in animals. They reside as glycosides with low estrogenic activity compared to their deglycosylated form, also referred to as aglycone. Upon ingestion, these compounds are metabolically hydrolyzed by the intestinal microbiota to their aglycones [
30]. However, several different factors may influence the biokinetics and bioavailability of isoflavones, such as the kind of animal, intestinal microflora, age, composition of feed, and duration of feed consumption [
31]. The phenolic hydroxyl group in isoflavones can react with free radicals. The literature data show that eliminating soybean isoflavones from the diet decreased body weight and antioxidant capacity. Replenishing soybean isoflavones prevents a decrease in these parameters, indicating that isoflavones are beneficial for pig growth and play an essential role in antioxidation [
32]. These isoflavones have also been shown to prevent atherosclerotic cardiovascular diseases in hyper-tensive rats [
33].
After yeast fermentation daidzein and genistein content increased, indicating positive isoflavone conversion processes. Glycitein remained rather constant. Ho and co-workers showed that dietary supplementation with glycitein in sows during late pregnancy and lactation can elevate antioxidative indices, improving milk composition and enhancing the growth performance of sucking piglets [
34]. The results for total isoflavone content before and after yeast fermentation are also interesting. The content of these compounds was reduced about fourfold. Reducing the amount of flavonoids and changing the proportions of glycolsides and aglycones is therefore more beneficial in terms of nutrition. After yeast fermentation, the ratios of glycosides : genistein and of daidzein : daidzin and genistin changed. Daidzein has lower estrogenic activity compared to its deglycosylated forms. Glycitin content was reduced after fermentation to below detection limit. This is of nutritional importance, because excessive isoflavones in the diet can have negative effects animal reproduction. There are reports of negative outcomes after the high consumption of isoflavones, including enhanced rate of endometriosis, the inability to become pregnant, and miscarriages [
30]. Discrepancies between the content of isoflavone compounds in the control sample and the samples after fermentation were due to the fact that intermediate forms of flavonoids, such as dihydrodaidzein or dihydrogenistein, were not determined in the analysis [
35].
5. Conclusions
Rapeseed meal is a very valuable waste product of oil production, with high management potential. Using a simple technology, it is possible to obtain a full-value product and increase profit many times over. The process of simultaneous saccharification and fermentation makes it possible to improve the parameters of the waste biomass, especially the protein content, the amount of crude fiber, and the biotransformation of isoflavone compounds present in the waste material. As a result of the experiments, the protein content of the biomass increased, and the nutrient content also increased. The amount of crude fiber was reduced, increasing the availability of the compounds and making the material easier to use as a feed component. At the same time, processing the biomass enables the bioconversion of inorganic nitrogen into organic forms of proteins, as well as the conversion of flavonoids into derivatives with health-promoting properties required for feed additives.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.B.; methodology, J.B. and D.D; investigation, D.D., A.S., W.L. and M.S.; resources, D.D.; data curation, D.D.; writing—original draft preparation, D.D.; writing—review and editing, D.D. and J.B.; supervision, J.B. and D.K.; project administration, J.B.; funding acquisition, J.B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The APC was funded by Lodz University of Technology.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
This research was completed while the first three authors were a doctoral candidates at the Interdisciplinary Doctoral School, Lodz University of Technology (Poland).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Shahbandeh, M. Rapeseed Oil: Global Production Volume 2012/13-2022/23. Statista 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Lemaire, A.; Limbourg, S. How Can Food Loss and Waste Management Achieve Sustainable Development Goals? Journal of Cleaner Production 2019, 234, 1221–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zentrale Markt- und Preisinformationen Rapeseed Meal Current Stock Exchange Prices & Charts Rapeseed Meal Available online:. Available online: https://www.zmp.de/en/oilseeds/rapeseed-meal_future (accessed on 3 April 2023).
- Tropea, A.; Ferracane, A.; Albergamo, A.; Potortì, A.G.; Lo Turco, V.; Di Bella, G. Single Cell Protein Production through Multi Food-Waste Substrate Fermentation. Fermentation 2022, 8, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Corato, U.; Viola, E. Biofuel Co-Products for Livestock Feed. In Agricultural Bioeconomy; Academic Press, 2023; pp. 245–286.
- Gong, Y.; Liu, J.; Jiang, M.; Liang, Z.; Jin, H.; Hu, X.; Wan, X.; Hu, C. Improvement of Omega-3 Docosahexaenoic Acid Production by Marine Dinoflagellate Crypthecodinium Cohnii Using Rapeseed Meal Hydrolysate and Waste Molasses as Feedstock. PLoS One 2015, 10, e0125368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lomascolo, A.; Uzan-Boukhris, E.; Sigoillot, J.C.; Fine, F. Rapeseed and Sunflower Meal: A Review on Biotechnology Status and Challenges. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2012, 95, 1105–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yusuf, H.A.; Piao, M.; Ma, T.; Huo, R.; Tu, Y. Effect of Lactic Acid Bacteria and Yeast Supplementation on Anti-Nutritional Factors and Chemical Composition of Fermented Total Mixed Ration Containing Cottonseed Meal or Rapeseed Meal. Anim. Biosci. 2022, 35, 556–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vlassa, M.; Filip, M.; Țăranu, I.; Marin, D.; Untea, A.E.; Ropotă, M.; Dragomir, C.; Sărăcilă, M. The Yeast Fermentation Effect on Content of Bioactive, Nutritional and Anti-Nutritional Factors in Rapeseed Meal. Foods 2022, 11, 2972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafii, F. The Role of Colonic Bacteria in the Metabolism of the Natural Isoflavone Daidzin to Equol. Metabolites 2015, 5, 56–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.-Y.; Ye, Y.; Xiao, L.; Rahman, K.; Xia, W.; Zhang, H. Daidzein: A Review of Pharmacological Effects. African Journal of Traditional, Complementary and Alternative Medicines 2016, 13, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, T.; Javed, S.; Tariq, A.; Budzyńska, B.; D’Onofrio, G.; Daglia, M.; Fazel Nabavi, S.; Mohammad Nabavi, S. Daidzein and Its Effects on Brain. Curr Med Chem. 2017, 24, 4–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dygas, D.; Janicka, P.; Berłowska, J.; Kręgiel, D. Conventional and Unconventional Yeasts Able to Grow on Rapeseed Meal Hydrolysates. BioResources 2022, 17, 3082–3094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geisler, J.; Weiß, N. Free Amino Nitrogen (FAN) Measurement in Beer. Short Protoc. 2015, 9, 10–12. [Google Scholar]
- ISO 6865:2000 - Determination of Crude Fibre Content — Method with Intermediate Filtration. In Animal Feed stuffs; 2000; p. 10.
- Sulyok, M.; Stadler, D.; Steiner, D.; Krska, R. Validation of an LC-MS/MS-Based Dilute-and-Shoot Approach for the Quantification of > 500 Mycotoxins and Other Secondary Metabolites in Food Crops: Challenges and Solutions. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2020, 412, 2607–2620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steglińska, A.; Sulyok, M.; Janas, R.; Grzesik, M.; Liszkowska, W.; Kręgiel, D.; Gutarowska, B. Metabolite Formation by Fungal Pathogens of Potatoes (Solanum Tuberosum L.) in the Presence of Bioprotective Agents. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 5221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bell, J.M. Nutrients and Toxicants in Rapeseed Meal: A Review. J. Anim. Sci. 1984, 58, 996–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parapouli, M.; Vasileiadis, A.; Afendra, A.-S.; Hatziloukas, E.; Parapouli, M.; Vasileiadis, A.; Afendra, A.-S.; Hatziloukas, E. Saccharomyces Cerevisiae and Its Industrial Applications. AIMS Microbiol. 2020 11 2020, 6, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.H.; Ji, X.J.; Huang, H. Biotechnological Applications of Yarrowia Lipolytica: Past, Present and Future. Biotechnol. Adv. 2015, 33, 1522–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Postma, E.; Kuiper, A.; Tomasouw, W.F.; Scheffers, W.A.; Van Dijken, J.P. Competition for Glucose between the Yeasts Saccharomyces Cerevisiae and Candida Utilis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1989, 55, 3214–3220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carranza-Méndez, R.C.; Chávez-González, M.L.; Sepúlveda-Torre, L.; Aguilar, C.N.; Govea-Salas, M.; Ramos-González, R. Production of Single Cell Protein from Orange Peel Residues by Candida Utilis. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2022, 40, 102298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freimoser, F.M.; Rueda-Mejia, M.P.; Tilocca, B.; Migheli, Q. Biocontrol Yeasts: Mechanisms and Applications. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019 3510 2019, 35, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, A.; Stewart, G. Free Amino Nitrogen in Brewing. Fermentation 2019, 5, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, H.S.; Kim, H.Y.; Ahn, S.H.; Oh, S.C.; Yang, I.; Choi, I.G. Optimization of Enzymatic Hydrolysis Conditions for Extraction of Pectin from Rapeseed Cake (Brassica Napus L.) Using Commercial Enzymes. Food Chem. 2014, 157, 332–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández, M.; Úbeda, J.F.; Briones, A.I. Typing of Non-Saccharomyces Yeasts with Enzymatic Activities of Interest in Wine-Making. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2000, 59, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramonet, Y.; Meunier-Salaün, M.C.; Dourmad, J.Y. High-Fiber Diets in Pregnant Sows: Digestive Utilization and Effects on the Behavior of the Animals. J. Anim. Sci. 1999, 77, 591–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guillemet, R.; Hamard, A.; Quesnel, H.; Père, M.C.; Etienne, M.; Dourmad, J.Y.; Meunier-Salaün, M.C. Dietary Fibre for Gestating Sows: Effects on Parturition Progress, Behaviour, Litter and Sow Performance. Animal 2007, 1, 872–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grigorev, M.; Grigoreva, A.; Sharvadze, R.; Chernogradskaya, N.; Stepanova, S. The Effectiveness of Unconventional Feed Additives at Feeding Cattle in Conditions Yakutia. Lect. Notes Networks Syst. 2023, 574 LNNS, 156–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grgic, D.; Varga, E.; Novak, B.; Müller, A.; Marko, D. Isoflavones in Animals: Metabolism and Effects in Livestock and Occurrence in Feed. Toxins (Basel). 2021, 13, 836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Jiang, X.; Cai, L.; Zhang, Y.; Ding, H.; Yin, J.; Li, X. Effects of Daidzein on Antioxidant Capacity in Weaned Pigs and IPEC-J2 Cells. Anim. Nutr. 2022, 11, 48–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.P.; Jiang, X.R.; Wei, Z.X.; Cai, L.; Yin, J.D.; Li, X.L. Effects of Soybean Isoflavones on the Growth Performance, Intestinal Morphology and Antioxidative Properties in Pigs. Animal 2020, 14, 2262–2270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, W.; Ikeda, K.; Takebe, M.; Yamori, Y. Genistein, Daidzein and Glycitein Inhibit Growth and DNA Synthesis of Aortic Smooth Muscle Cells from Stroke-Prone Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats. J. Nutr. 2001, 131, 1154–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.J.; Gao, K.G.; Zheng, C.T.; Wu, Z.J.; Yang, X.F.; Wang, L.; Ma, X.Y.; Zhou, A.G.; Jiang, Z.J. Effect of Dietary Supplementation with Glycitein during Late Pregnancy and Lactation on Antioxidative Indices and Performance of Primiparous Sows. J. Anim. Sci. 2015, 93, 2246–2254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, B.N.; Dilger, R.N. Immunomodulatory Potential of Dietary Soybean-Derived Isoflavones and Saponins in Pigs1. Journal of Animal Science 2018, 96, 1288–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).