1. Introduction
A puree is a tasty and nutritious food that can have various textures, from very light to thicker [
1]. It can be prepared by multiple combinations of different fruits, vegetables, tubers, bulbs, legumes and other herbal extracts [
2].
There are many bacteria that can contaminate these purees due to not thoroughly washing the leaves of the vegetables, from enterobacteria to spore-forming bacteria [
3]. Endospore-forming bacteria are a concern in food spoilage, especially for cooked and refrigerated foods such as purees. In commercial purées, several
Bacillus species have been identified and have been shown to cause food spoilage during storage at abuse temperatures [
4].
Bacillus cereus is the most important cause of food poisoning [
5]. The species
Bacillus licheniformis,
Bacillus amyloliquefaciens, and
Bacillus subtilis have also been linked to incidents of foodborne illness [
6,
7]. One of the current approaches under study to control food spoilage is based on the use of natural antimicrobial substances such as bacteriocins [
8].
Paenibacillus dendritiformis, is a Gram positive microorganism, which lives in the soil, forms spores and has the ability to change between different morphotypes [
9]. It has been found that when sister colonies of
P. dendritiformis are cultivated in a medium low in nutrients, they inhibit each other's growth through the secretion of a lethal factor [
10]. This fact occurs in quite a few bacteria, and during starvation, competing bacteria within the same colony can lyse their sisters and use them as a source of nutrients [
11]. The antimicrobial compounds secreted during bacterial cannibalism are called bacteriocins and generally have a narrow spectrum of activity, as they have to kill only closely related bacteria, which are competing for the same resources [
12]. About the production and isolation of antimicrobial compounds from
P. dendritiformis, it has been seen that it can produce antimicrobial substances, which were purified using various chromatographic techniques. These compounds had characteristics similar to polymyxins but with more efficacy than commercial polymyxins and at the same time much less toxicity, which makes them a good alternative for the search for new antimicrobial substances against gram-negative and multiresistant bacteria [
13].
Therefore, antimicrobial substances from Paenibacillus have a potential application in food biopreservation to avoid the deterioration of these foods, both from similar bacteria and from gram-negative bacteria. The strain P. dendritiformis UJA2219 was isolated from fresh carrot as producer of antimicrobial activity against bacteria of concern in foods, including Escherichia coli and Salmonella enterica. The genome of strain UJA2219 has been sequenced, and the genome data strongly suggest suggest that this strain may produce a variant of the lasso peptide paeninodin and also carries genetic determinants related to other putative antimicrobial peptides paenibacterin, pelgipectin and paenilamicin (Mena et al., manuscript in preparation). To the best of our knowledge, there are no previous studies addressing the possible application of P. dendritiformis for preservation of vegetable foods. The aim of the present study was to determine the effect of partially-purified extracts from P. dendritiformis UJA2219 on a vegetable puree (selected as a model food system) on the total microbial load and also on the bacterial diversity of the puree.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Partially-Purified Extracts
An overnight culture of
P. dentritiformis UJA2219 grown in brain heart infusion broth (BHI, Scharlau, Barcelona, Spain) at 30 °C with shaking was inoculated (1% wt/vol) in 2 l of complex medium CM [
14] without casamino acids. After 24 h incubation at 30 °C with shaking, the pH was measured and the entire culture was filtered through a glass funnel with Whatman filter paper. The culture filtrate was divided into two aliquots (1 l each) and mixed in bulk with the corresponding chromatography gels for 45 min under shaking at room temperature. The chromatography gels used for recovery of antimicrobial substances from the culture filtrates were cation exchange Carboxymethyl-Sephadex C-25 (Sigma-Aldrich, Madrid, Spain) and reversed-phase Waters PREP C18 55-105UM gel (Waters, Milford, MA). The gels were then washed with 50 ml distilled water. Eluants (45 ml each) were 1.5 M NaCl in distilled water (for the cation Exchange gel), 40% acetonitrile/water and 60% acetonitrile/water for the reverse-phase gel. Eluates were tested for antibacterial activity by the agar-well difusion method with Oxford towers (8 mm diameter, Scharlau) according to Tagg & McGiven, 1971 [
15]. The bacteria used for sensitivity tests were from our laboratory collection or from the Spanish Type Culture Collection (CECT, Burjasot, Valencia, Spain):
Escherichia coli E19
, Staphylococcus aureus CECT 976,
Salmonella enterica CECT 3197 and
Bacillus cereus LWL1.
2.2. Preparation of the Puree
We prepare a homemade vegetable puree by mixing the raw ingredients with skin and without washing and passing the mixture through a blender (Oster. All Metal Drive; Sunbeam Products Inc, Boca Raton FL). The following ingredients were used (wt/wt): vegetables 90% (vegetables in variable proportion: potato, carrot, leek, zucchini, green beans, chard, cabbage, spinach, peas), olive oil, salt and water.
2.3. Preparation of Puree Samples for Microbiological Counts
The puree was distributed into two sets of 4 Falcon test tubes with 5 ml of puree each (8 tubes in total). The first tube of the set was used as control (without any addition of antimicrobials). The second tube was inoculated (1% vol/vol) with an overnight culture of Paenibacillus dendritiformis strain UJA2219 in order to test the potential of the bacterium for direct antagonism in the puree. To the third tube we added 500 µl of the partially purified with NaCl eluate (E) and to the last sample we added 500 µl of the partially purified eluate obtained with 60% acetonitrile (A). One set of tubes was incubated at 4 °C and the other at 25 °C. At desired times of incubation (0 h, 24 h, 48 h and 7 days) the puree samples were tested for viable cell counts. Briefly, one aliquot of the puree (1 ml) was serially diluted in sterile saline solution and plated in triplicate on the culture media Tryptic soy agar (TSA), Eosin Methylene Blue Agar (EMB), Bacillus cereus agar and de Man, Rogosa y Sharpe agar (MRS). Viable cell counts were determined after 24-48 h of incubation at 37 °C and 30 °C for MRS medium. All culture media were provided by Scharlab (Barcelona, Spain).
2.4. Preparation of Puree Samples for Biodiversity Analysis
The puree, prepared as described above, was clarified through a strainer in order to minimize interference of solids with the process of DNA extraction. Then, the puree was distributed into 12 Falcon tubes (2 ml of puree each). The tubes were grouped in four sets (3 tubes each). The first set was used as control. The second set was inoculated (1%, vol/vol) with an overnight culture of Paenibacillus dendritiformis UJA2219 as described above. The third set was added 200 µl of the eluate E (per 2ml of puree) and the last set was added 200 µl of the eluate A (per 2 ml of puree). The samples were incubated for 24 h at 25 °C under shaking conditions. Following incubation, the purees samples were centrifuged at 13,000 x g for 5 min. in order to recover microbial cells for DNA extraction. DNA was extracted from the cell pellets with the Power food microbial extraction kit (Qiagen, Madrid, Spain). The concentration of extracted DNA was determined using Qubit 3.0 (Invitrogene, Massachusetts, USA).
2.5. DNA Sequencing and Analysis
Once it was verified that the extracted samples met the quality conditions and the established minimum DNA concentration of 5 ng/L, the massive sequencing and bioinformatic analysis were entrusted to an external service (Fisabio, Valencia, Spain). Briefly, library preparation, quality assessment and sequence joining, bioinformatic analysis and metataxonomic analysis were done as described in previous work [
16]. The libraries were sequenced using a 2x300 bp paired-end run (MiSeq Reagent kit v3 (MS-102-3001)) on a MiSeq Sequencer according to manufacturer’s instructions (Illumina). Taxonomic affiliations were assigned using the Naive Bayesian classifier integrated in quiime2 plugins, with Silva138_V3V4K as database for taxonomic assignation.
2.6. Statistics
The statistical significance of the data corresponding to the culture-dependent microbiological analysis was determined using one-way ANOVA and Tukey's test. Data on bacterial diversity were compared by Principal Coordinate Analysis (PCoA) and comparing the different samples by student's t test. For the different statistical analyses, the Past program (version 4.0) and R studio (version 4.2.2) were used. Krona tools [
17] were also used to represent the different percentages of diversity.
3. Results
3.1. Antimicrobial Activity of Eluates
The eluate purified with NaCl (E) produced an inhibition zone of 13 mm diameter for S. aureus CECT 976, 13 mm for S. enterica CECT 3197, 14 mm for E. coli E19 and 12 mm for B. cereus LWL1, while inhibition caused by the eluate purified with acetonitrile (A) was 16 mm in diameter for S. aureus CECT 976, 9 mm for S. enterica CECT 3197, 9 mm for E. coli E19 and 17 mm for B. cereus LWL1. The eluants E and A showed no antibacterial activities.
3.2. Microbiological Counts
The microbiological counts in the different culture media and at different temperatures are shown in
Table 1. It was observed that the total number of total aerobic mesophiles increased significantly (p<0.05) with time, more at 25 °C than at 4 °C, both in the controls and in all of the trated samples. For presumptive Enterobacteriaceae at 25 °C, highest reductions of viable cell counts were obtained for treatment A, reducing even on day 7 the number of colonies below the detection limit. Significant differences were also observed in treatment E compared to untreated controls because the viable cell concentrations of presumptive Enterobacteriaceae did not increase during incubation, but rather remained at values close to time 0. Treatment P (inoculation with the Paenibacillus strain) also seemed to delay proliferation of presumptive Enterobacteriaceae compared to controls at the end of storage. By contrast, in the samples incubated at 4 °C no significant differences were observed for presuptive Enterobacteriaceae. In the Bacillus cereus agar medium, significantly lower counts (p<0.05) were observed in treatments E and A at 25 °C with respect to the control, but not for tretment P. At 4 °C, viable cell counts decreased during incubation for all the samples, with no significant differences between controls and treated samples. The counts obtained on MRS agar (presumptive lactic acid bacteria) increased with time more at 25 °C than at 4 °C (p<0.05), but no statistically significant differences were observed between controls and treated samples.
3.3. Bacterial Biodiversity
The numbers of assigned reads and alpha diversity indices of controls and treated samples are shown in
Table 2. The indices show that there was not a great diversity of species and there was dominance of a low number of species.
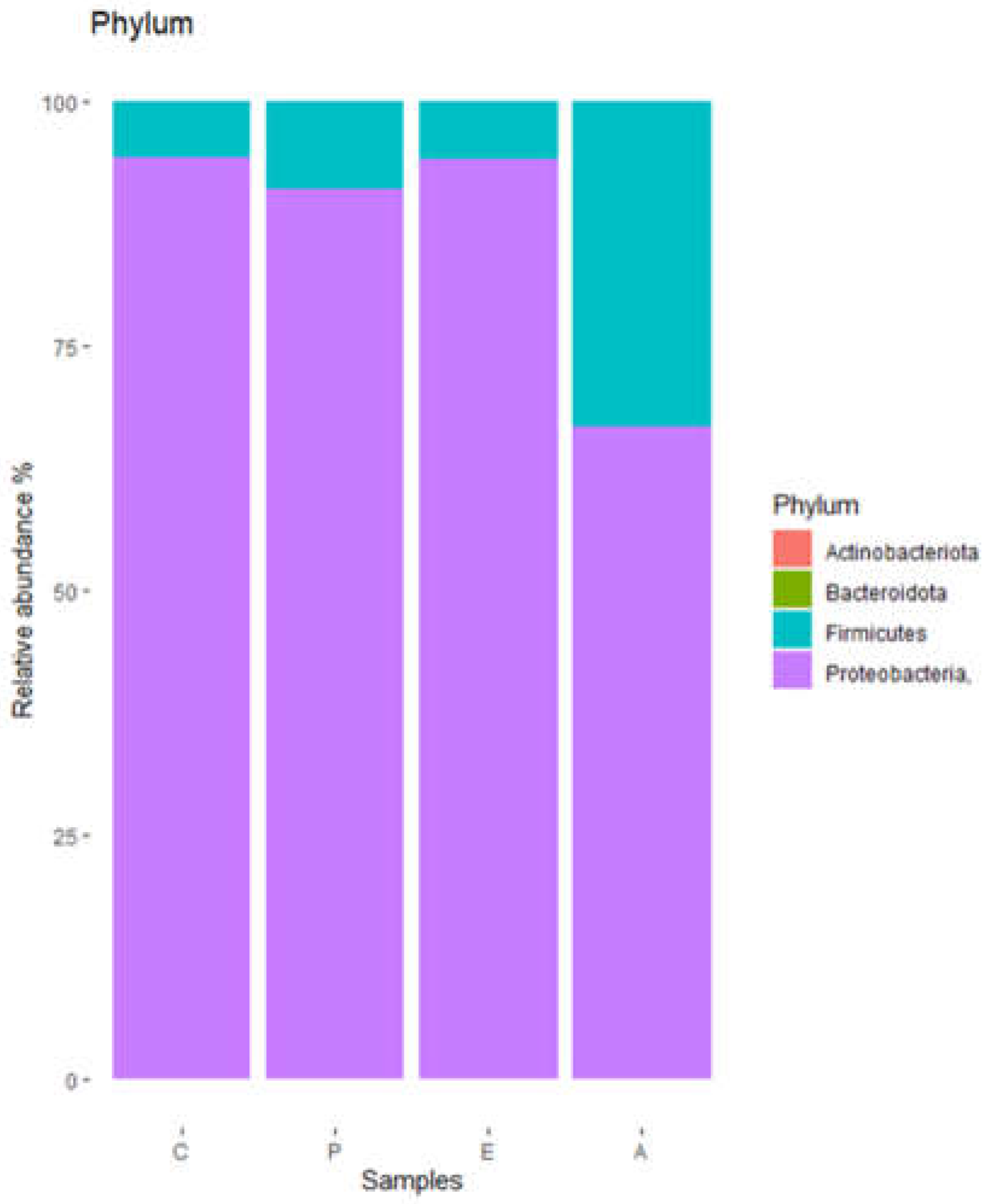
The different operational taxonomic units (OTU) found in the puree samples were grouped into 4 phyla (
Figure 1), of which
Proteobacteria were by far the main representatives, followed by
Firmicutes. Remarkably, samples corresponding to treatment A showed a lower relative abundance of
Proteobacteria and a higher relative abundance of
Firmicutes.
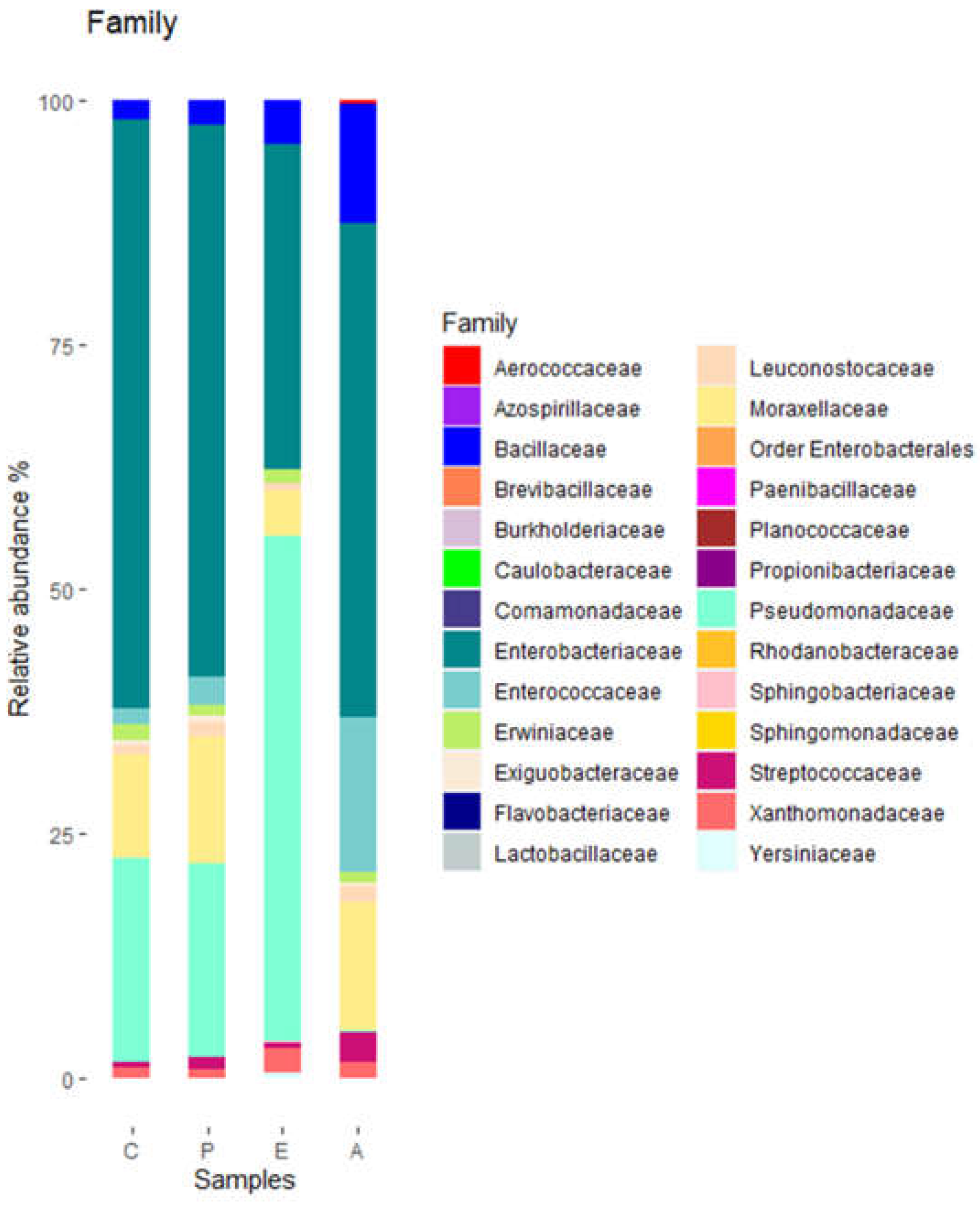
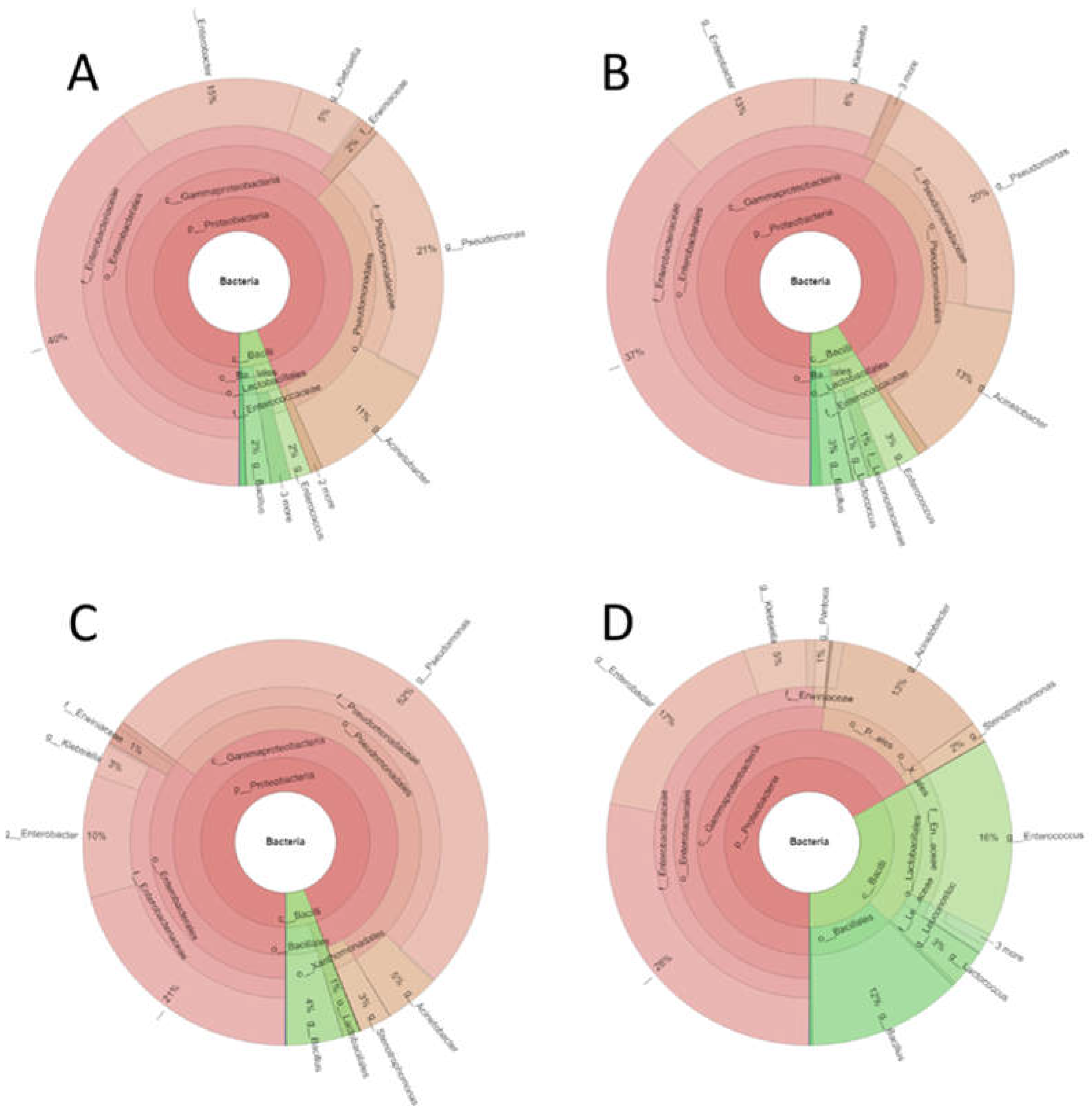
These phyla included representatives of 26 families. Of them, 8 families had relative abundances of at least 2% (
Figure 2).
Pseudomonadaceae and
Enterobacteriace were the families with higher relative abundances. The relative abundance of
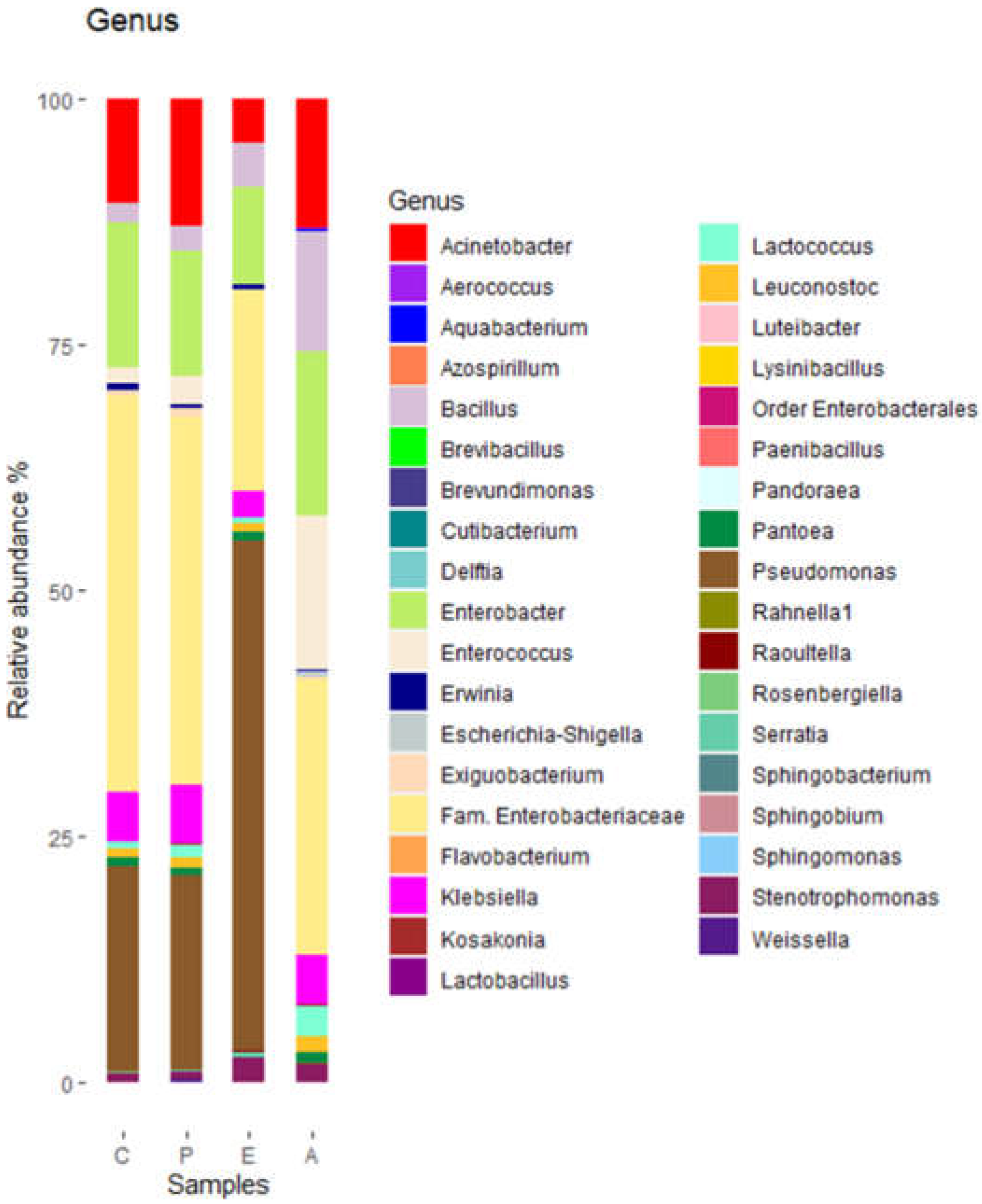
Pseudomonadaceae was highest in sample E and lowest in sample A. At the genus level, a total of 37 genera were detected. Of them, 10 had relative abundances of at least 2% (
Figure 3).
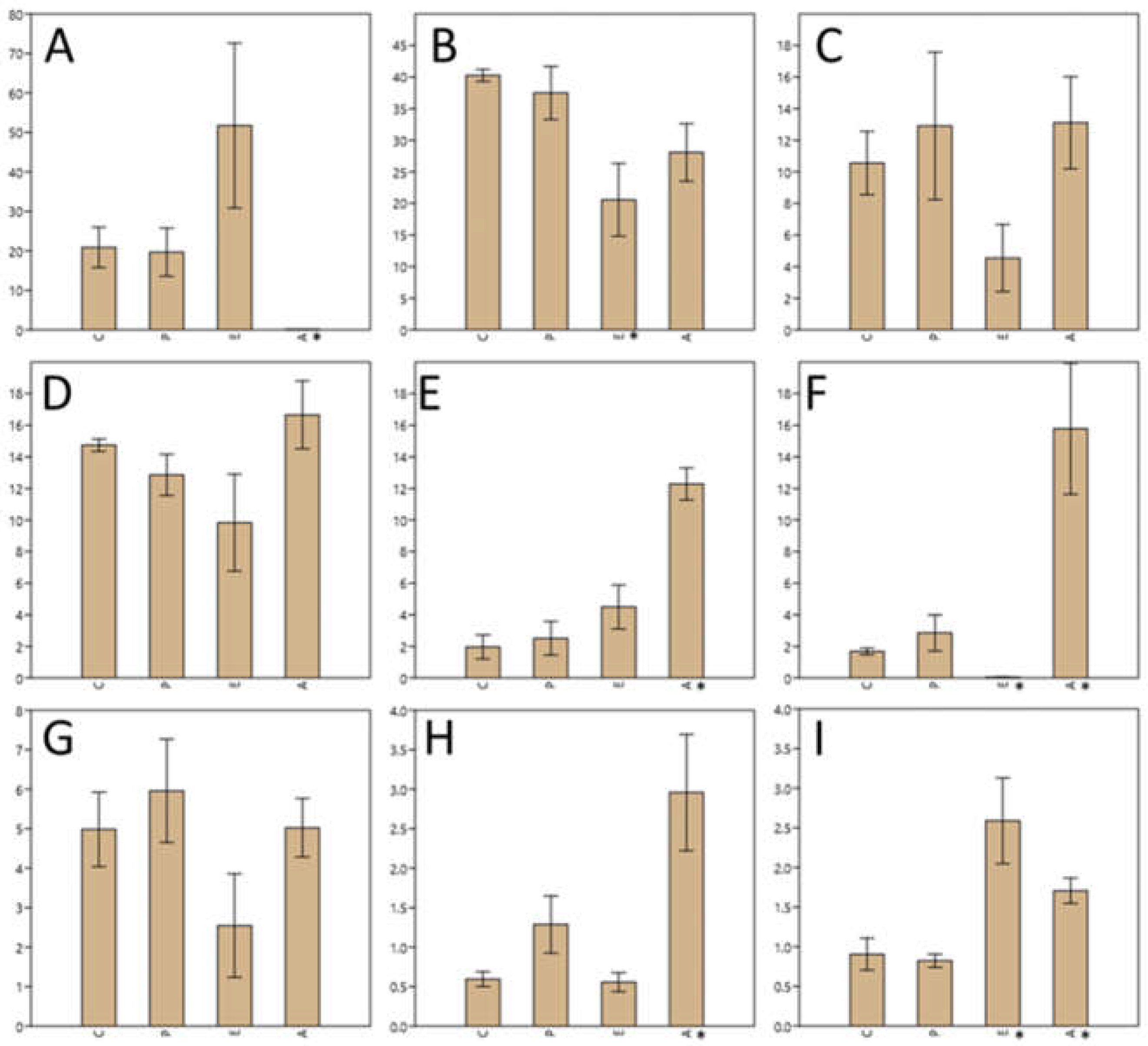
Figure 4 shows the most representative genera according to the relative abundance in the different samples, with the
Enterobacteriaceae family presenting 40% relative abundance in both the control sample and in the sample inoculated with
Paenibacillus; however, this percentage decreased significantly (p<0.05) to 20% when treated with eluate E and 30% when treated with eluate A. Genus
Pseudomonas was represented with a quite similar percentage both in the control and in the sample inoculated with
Paenibacillus (around 20%), but instead it increased up to 50% in the sample treated with eluate E and decreased significantly (p<0.05), almost to zero in the sample treated with eluate A.
Genus Acinetobacter and Enterobacter, which represented between 10% and 14% of the total OTUs, treatment with NaCl eluate reduced the population by at least half. Genus Acinetobacter represents 10% of the population, this percentage increased after Paenibacillus inoculation to about 13% and remained so after treatment with acetonitrile eluate, while it decreased to 4.5% when treated with NaCl eluate.
The treatment with the acetonitrile eluate (A) significantly (p<0.05) increased the relative abundance of Bacillus, Enterococcus and Lactococcus. Treatment with NaCl eluate significantly (p<0.05) decreased the population of Enterococcus while significantly (p<0.05) increased that of Stenotrophomonas.
Figure 5 shows the biodiversity of the different samples represented using the Krona tool.
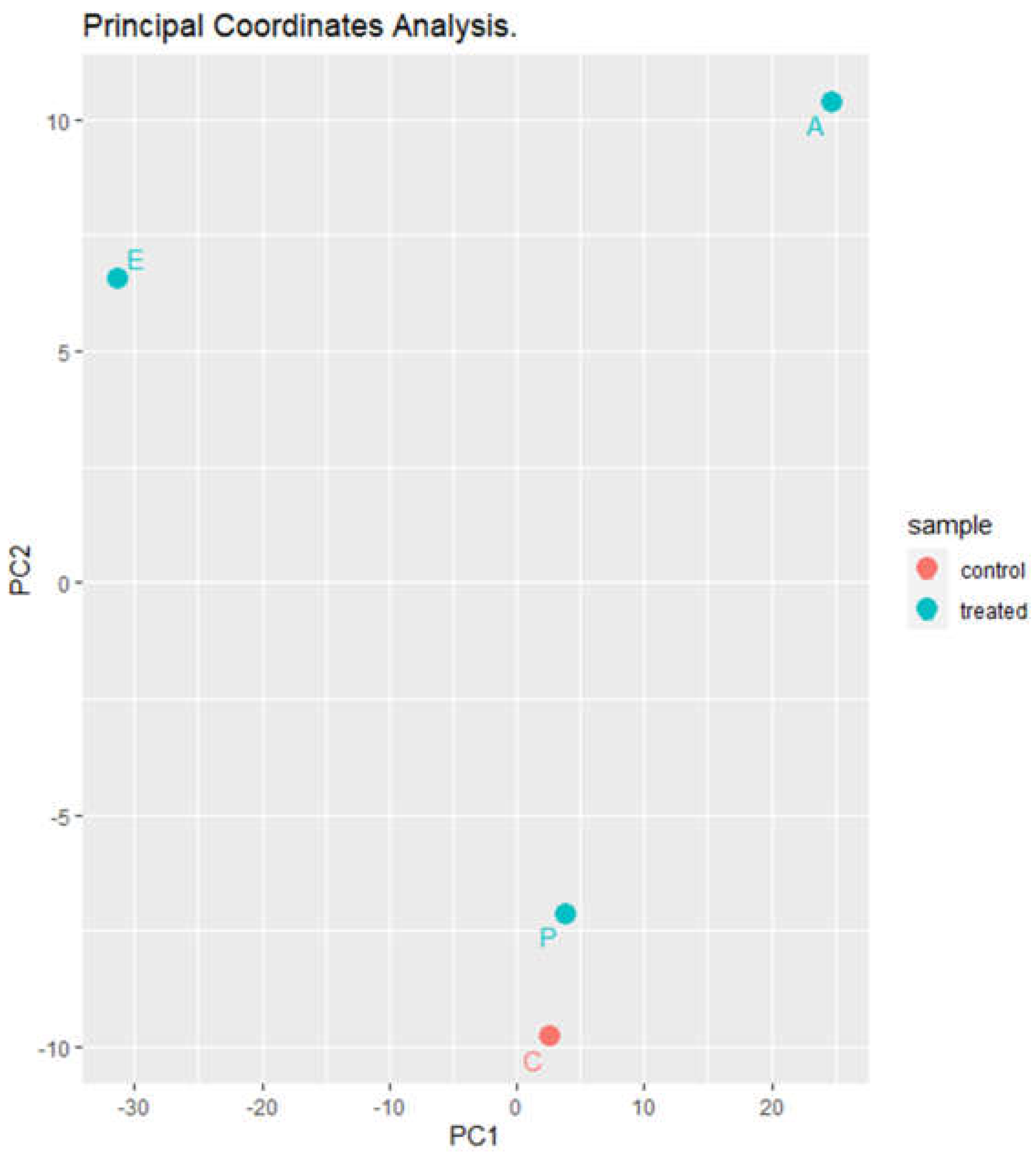
Principal coordinate analysis (PCoA) (
Figure 6) revealed that the control sample and the sample inoculated with
Paenibacillus are very similar; however, there is a large difference between the samples treated with the eluates with respect to the control and to each other.
4. Discussion
The results obtained in the present study indicate that Paenibacillus dendritiformis UJA2219 produces antimicrobial activity against bacteria of risk in foods as E. coli E19, S. enterica CECT 3197, S. aureus CECT 976 and B. cereus LWL1. The antibacterial activity can be recovered fom cultured broths by cation exchange chomatograpy and also by reversed-phase chromatography.
To study the antimicrobial effect of these partially purified fractions, a food model was chosen, which was a homemade vegetable puree. Previous studies carried out in our group [
6] indicated that the
Paenibacillus genus presented antimicrobial activity and modified the growth of pathogens present in food.
Paenibacillus dendritiformis is described to produce antimicrobial peptides [
18]. These peptides are being studied for their antifungal effect to prevent crop colonization by fungi [
19,
20]. The annotation of the genome of
P. dendritiformis UJA2219 (Mena et al., in preparation) suggests that this bacterial strain may produce secondary metabolites identified as 1 RiPP protein (paeninodin) and NRP proteins like paenibacterin, pelgipectin and paenilamicin. It could be that the addition of
Paenibacillus dendritiformis or any of its metabolites to a food model in this case a homemade vegetable puree generates an antimicrobial effect and/or a modification of microbial biodiversity.
The results obtained on microbial counts in puree inoculated with
P. dendriformis UJA2219 indicated that the bacterium failed to inhibit the puree microbiota, except for the weak decrease of presumptive
Enterobacteriaceae detected at day 7 of incubation at 25 °C. These results could be due to a low production of antimicrobials in the puree by the inoculated strain. In situ production of antimicrobial substances is markedly influenced by many factors like pH, aeration, incubation temperature, time of incubation, available nutrients, the food matrix, and the competing microbiota [
21].
The treatments carried out with partially-purified preparations from P. dendriformis UJA2219 cultured broths exerted an antimicrobial effect on the vegetable puree incubated at 4 °C and 25 °C that depended on the microbial group. Although this activity was more pronounced at 25 °C than under refrigerated conditions, it helps the preservation of these purees outside of refrigeration. At 25 °C, for all mesophilic aerobic bacteria and lactic acid bacteria, an efficacy of the eluate from NaCl was observed during the first two days, but this was no longer observed after 7 days; for presumptive Bacillus, an efficacy of the two eluates (A and E) was observed after 7 days, and in presumptive Enterobacteriaceae there was a great reduction in both the sample inoculated with Paenibacillus and the eluate (E), and even the CFU/ml levels decreased below the detection limits after 7 days with eluate (A). On the other hand, at 4 °C, there were no differences with respect to the control sample in total aerobic mesophilic counts, presumptive lactic acid bacteria or Bacillus, but we did observe a decrease in the number of presumptive Enterobacteriaceae with the treatments applied.
In published studies of the efficacy of
Paenibacillus as an antibacterial in food, it has been shown to reduce the populations of
Bacillus subtilis and
Listeria in milk, which makes it promising for the biopreservation of dairy products [
22].
Paenibacillus has also been shown to be effective against other bacterial groups such as
Clostridium or
E. coli [
23]. Most of these studies are based on assays performed with the strain in question, not with the purified fractions. The present study shows that the production of these metabolites and their subsequent purification could be used as preservatives in this food model.
Regarding the impact of Paenibacillus and its partially-purified extracts on bacterial diversity, the results we have obtained so far indicate that inoculation with UJA2219 strain had no remarkable impact on the microbiota of the puree. These results agree with those obtained in the culture-dependent experiments in which the inoculated strain failed to inhibit microbial proliferation. Regarding treatments with culture extracts, for the most representative genera of the samples such as Pseudomonas and Enterobacteriaceae the observed effect was different depending on the treatments: in the case of the genus Pseudomonas the eluate with NaCl (E) makes the population increase in relative abundance almost twice while the treatment with the eluate of acetonitrile (A) decreases it to undetectable limits. In the case of Enterobacteriaceae, it was the treatment with the NaCl eluate (E) that had the greatest effect, reducing the relative abundance of this group by half, while the eluate from the purification with acetonitrile (A) did not have such a marked effect on this population. These results seem to be contradictory with those obtained by the culture-dependent approach (according to which eluate A had a remarkable effect on the population of presumptive Enterobacteriaceae). However, we should take into account that the selective medium used (EMB) also supports growth of Pseudomonas and, while Pseudmomonas are non-fermentative, they may be difficult to differentiate from the true fermentative Enterobacteriaceae in mixed growth. Therefore, the results could be explained assuming that the counts obtained on EMB agar as presumptive Enterobacteriaceae include, at least in part, Pseudomonas.
Furthermore, the observed differences in the effects of partially purified culture extracts on bacterial diversity could also be interpreted considering that Paenibacillus UJA2219 may produce different antimicrobial substances. Thus, it is possible that the antimicrobial peptides recovered in the acetonitrile eluate are different from those recovered by cation exchange chromatography. Paenibacillus may produce a mixture of lasso peptides, lipopeptides and bacteriocins. Many of these peptides are cationic and could be recovered from culture supernatants by cation exchange. Others, however, may be amphipathic or hydrophobic (as in the case of lipopeptides) and show a low solubility in the water used as eluant for cation exchange. Instead, hydrophobic peptides would have a higher solubility in acetonitrile. Therefore, it is tempting to suggest that the different eluates are enriched in different peptides that act differently on each microbial population and therefore have different effects on bacterial diversity. Furthermore, the eluant itself may also have an effect on the peptide solubility and final activity. We must also keep in mind that the results were expressed in terms of relative abundance and therefore the observed increase in relative abundance for a given population may simply be the result of a decrease in the relative abundance of the other populations in the sample.
At present it is important for the food industry not only to evaluate the relationships between the different microbial populations present in a food, but also to know their behavior when they are subjected to treatments with secondary metabolites with antimicrobial potential as is the case of Paenibacillus dendritiformis UJA2219. Further experiments with the purified peptides are needed in order to understand better their impact on the bacterial communities of food systems and their potential as new biopreservatives.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.J.G.; methodology, M.J.G., L.M.; formal analysis, L.M., M.J.G. and A.G.; investigation, L.M. and M.J.G.; writing—review and editing, M.J.G., L.M. and A.G.; supervision, M.J.G.; project administration, M.J.G.; funding acquisition, M.J.G. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Ministerio de Ciencia e Innovación (Unión Europea, Agencia Estatal de Investigación, Programa Ramón y Cajal), grant number RYC-2017-23077. L.M. received a research grant from University of Jaén (Ayudas Predoctorales para la Formación de Personal Investigador del Plan de Apoyo a la Investigación de la Universidad de Jaén 2019-2020), grant number PIPFP91. The APC was funded by University of Jaén (AGR230).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author. The data are not publicly available due to privacy.
Acknowledgments
Acknowledgments: This work was supported by the Ramón y Cajal Program, Action co-financed by Ministry of Economy and Competitiveness (MINECO) and European Union and Pre-doctoral grants for the training of research personnel under Action 9a of the Operational Plan for Research Support in the University of Jaén.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Fern, J.; Botella-mart, C.; Navarro-rodr, C.; Vera, D.; Viuda-martos, M.; Elena, S.; Angel, P. Vegetable Soups and Creams: Raw Materials, Processing, Health Benefits, and Innovation Trends. Plants 2020, 9. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, R.H. Health-Promoting Components of Fruits and Vegetables in the Diet. Adv. Nutr. 2013, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalska, B.; Szczech, M. Differences in Microbiological Quality of Leafy Green Vegetables. Ann. Agric. Environ. Med. 2022, 29, 238–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlin, F.; Guinebretiere, M.H.; Choma, C.; Pasqualini, R.; Braconnier, A.; Nguyen-The, C. Spore-Forming Bacteria in Commercial Cooked, Pasteurised and Chilled Vegetable Purees. Food Microbiol. 2000, 17, 153–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoeni, J.L.; Lee Wong, A.C. Bacillus Cereus Food Poisoning and Its Toxins. J. Food Prot. 2005, 68, 636–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grande, M.J.; Abriouel, H.; López, R.L.; Valdivia, E.; Omar, N. Ben; Martínez-Cañamero, M.; Gálvez, A. Efficacy of Enterocin AS-48 against Bacilli in Ready-to-Eat Vegetable Soups and Purees. J. Food Prot. 2007, 70, 2339–2345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, P.B.; Bjørnvad, M.E.; Rasmussen, M.D.; Petersen, J.N. Cytotoxic Potential of Industrial Strains of Bacillus sp. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2002, 36, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumariya, R.; Garsa, A.K.; Rajput, Y.S.; Sood, S.K.; Akhtar, N.; Patel, S. Bacteriocins: Classification, Synthesis, Mechanism of Action and Resistance Development in Food Spoilage Causing Bacteria. Microb. Pathog. 2019, 128, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirota-Madi, A.; Olender, T.; Helman, Y.; Finkelshtein, I.B.; Roth, D.; Hagai, E.; Leshkowitz, D.; Brodsky, L.; Galatenko, V.; Nikolaev, V.; et al. Genome Sequence of the Pattern-Forming Social Bacterium: Paenibacillus dendritiformis C454 Chiral Morphotype. J. Bacteriol. 2012, 194, 2127–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Be’er, A.; Ariel, G.; Kalisman, O.; Helman, Y.; Sirota-Madi, A.; Zhang, H.P.; Florin, E.L.; Payne, S.M.; Ben-Jacob, E.; Swinney, H.L. Lethal Protein Produced in Response to Competition between Sibling Bacterial Colonies. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2010, 107, 6258–6263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-pastor, J.E.; Hobbs, E.C.; Losick, R. Cannibalism by Sporulating Bacteria. Science (80-. ). 2003, 301, 510–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claverys, J.P.; Håvarstein, L.S. Cannibalism and Fratricide: Mechanisms and Raisons d’être. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2007, 5, 219–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jangra, M.; Randhawa, H.K.; Kaur, M.; Srivastava, A.; Maurya, N.; Patil, P.P.; Jaswal, P.; Arora, A.; Patil, P.B.; Raje, M.; et al. Purification, Characterization and in Vitro Evaluation of Polymyxin a from Paenibacillus dendritiformis: An Underexplored Member of the Polymyxin Family. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abriouel, H.; Valdivia, E.; Martínez-Bueno, M.; Maqueda, M.; Gálvez, A. A Simple Method for Semi-Preparative-Scale Production and Recovery of Enterocin AS-48 Derived from Enterococcus faecalis subsp. liquefaciens A-48-32. J. Microbiol. Methods 2003, 55, 599–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tagg, J.R.; McGiven, A.R. Assay System for Bacteriocins. Appl. Microbiol. 1971, 21, 943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-López, J.; Grande, M.J.; Pérez-Pulido, R.; Galvez, A.; Lucas, R. Impact of High-Hydrostatic Pressure Treatments Applied Singly or in Combination with Moderate Heat on the Microbial Load, Antimicrobial Resistance, and Bacterial Diversity of Guacamole. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ondov, B.D.; Bergman, N.H.; Phillippy, A.M. Interactive Metagenomic Visualization in a Web Browser. BMC Bioinformatics 2011, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Hegemann, J.D.; Fage, C.D.; Zimmermann, M.; Xie, X.; Linne, U.; Marahiel, M.A. Insights into the Unique Phosphorylation of the Lasso Peptide Paeninodin. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 13662–13678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, K.; Verma, A.; Pal, G.; Anubha; White, J. F.; Verma, S.K. Seed Endophytic Bacteria of Pearl Millet (Pennisetum glaucum L.) Promote Seedling Development and Defend Against a Fungal Phytopathogen. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, M.; Dubey, M.K.; Upadhyay, R.S. Systemic Resistance in Chilli Pepper against Anthracnose (Caused by Colletotrichum truncatum) Induced by Trichoderma harzianum, Trichoderma asperellum and Paenibacillus dendritiformis. J. Fungi 2021, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gálvez, A.; Abriouel, H.; López, R.L.; Omar, N. Ben Bacteriocin-Based Strategies for Food Biopreservation. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2007, 120, 51–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sharoud, W.M.; Zalma, S.A.; Yousef, A.E. Inducing the Production of the Bacteriocin Paenibacillin by Paenibacillus polymyxa through Application of Environmental Stresses with Relevance to Milk Bio-Preservation. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2022, 371, 109637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girardin, H.; Albagnac, C.; Dargaignaratz, C.; Nguyen-The, C.; Carlin, F. Antimicrobial Activity of Foodborne Paenibacillus and Bacillus spp. against Clostridium botulinum. J. Food Prot. 2002, 65, 806–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Figure 1.
Bacterial diversity of puree samples at phylum level. C, untreated controls. P, puree inoculated with Paenibacillus dendritiformis UJA2219. E, puree treted with partially-purified extract (1.5 M eluate). A, puree treted with partially-purified extract (60% acetonitrile).
Figure 1.
Bacterial diversity of puree samples at phylum level. C, untreated controls. P, puree inoculated with Paenibacillus dendritiformis UJA2219. E, puree treted with partially-purified extract (1.5 M eluate). A, puree treted with partially-purified extract (60% acetonitrile).
Figure 2.
Bacterial diversity of puree samples at family level. C, untreated controls. P, puree inoculated with Paenibacillus dendritiformis UJA2219. E, puree treted with partially-purified extract (1.5 M eluate). A, puree treted with partially-purified extract (60% acetonitrile). .
Figure 2.
Bacterial diversity of puree samples at family level. C, untreated controls. P, puree inoculated with Paenibacillus dendritiformis UJA2219. E, puree treted with partially-purified extract (1.5 M eluate). A, puree treted with partially-purified extract (60% acetonitrile). .
Figure 3.
Bacterial diversity of puree samples at genus level. C, untreated controls. P, puree inoculated with Paenibacillus dendritiformis UJA2219. E, puree treted with partially-purified extract (1.5 M eluate). A, puree treted with partially-purified extract (60% acetonitrile).
Figure 3.
Bacterial diversity of puree samples at genus level. C, untreated controls. P, puree inoculated with Paenibacillus dendritiformis UJA2219. E, puree treted with partially-purified extract (1.5 M eluate). A, puree treted with partially-purified extract (60% acetonitrile).
Figure 4.
Comparison of the differences in relative abundance of the most representative genera found in the puree samples. Y axis represents relative abundance (average of three replicates ± standard deviation). X axis indicates sample type (C, controls; P, treatment with Paenibacillus strain; E, treatment with NaCl eluate; A, treatment with acetonitrile eluate. Asterisk denotes statatistically significant (p<0.05) differences with controls. Each graphic represents a different genus or taxonomic group: A, Pseudomonas; B, fam. Enterobacteriaceae; C, Acinetobacter; D, Enterobacter; E, Bacillus; F, Enterococcus; G, Klebsiella; H, Lactococcus; I, Stenotrophomonas.
Figure 4.
Comparison of the differences in relative abundance of the most representative genera found in the puree samples. Y axis represents relative abundance (average of three replicates ± standard deviation). X axis indicates sample type (C, controls; P, treatment with Paenibacillus strain; E, treatment with NaCl eluate; A, treatment with acetonitrile eluate. Asterisk denotes statatistically significant (p<0.05) differences with controls. Each graphic represents a different genus or taxonomic group: A, Pseudomonas; B, fam. Enterobacteriaceae; C, Acinetobacter; D, Enterobacter; E, Bacillus; F, Enterococcus; G, Klebsiella; H, Lactococcus; I, Stenotrophomonas.
Figure 5.
Comparison of the means different biodiversity percentages using Krona Tools. A, untreated controls. B, puree inoculated with Paenibacillus dendritiformis UJA2219. C, puree treted with partially-purified extract (1.5 M eluate). D, puree treted with partially-purified extract (60% acetonitrile). .
Figure 5.
Comparison of the means different biodiversity percentages using Krona Tools. A, untreated controls. B, puree inoculated with Paenibacillus dendritiformis UJA2219. C, puree treted with partially-purified extract (1.5 M eluate). D, puree treted with partially-purified extract (60% acetonitrile). .
Figure 6.
Principal coordinates analysis of puree samples treatred with elutes or with Paenibacillus dentritiformis. C, untreated controls. P, puree inoculated with Paenibacillus dendritiformis UJA2219. E, puree treted with partially-purified extract (1.5 M eluate). A, puree treted with partially-purified extract (60% acetonitrile).
Figure 6.
Principal coordinates analysis of puree samples treatred with elutes or with Paenibacillus dentritiformis. C, untreated controls. P, puree inoculated with Paenibacillus dendritiformis UJA2219. E, puree treted with partially-purified extract (1.5 M eluate). A, puree treted with partially-purified extract (60% acetonitrile).
Table 1.
Viable cell counts of puree samples during incubation at 4 °C or 25 °C.
Table 1.
Viable cell counts of puree samples during incubation at 4 °C or 25 °C.
| |
T0 |
T1 |
T2 |
T7 |
Enterobacteriaceae
25 °C
|
|
|
|
|
| C |
5.37±0.02 h
|
4.70±0.004 f g h i
|
4.48±0.00 f g h i
|
7.48±0.00 g h
|
| P |
5.29±0.03 h
|
5.84±0.03 a f g h
|
4.48±0.00 f g h i
|
6.59±0.007 a g h
|
| E |
4.11±0.01 a b d h
|
4.95±0.05 b g h i
|
4.48±0.00 f g h i
|
4.48±0.00 a b g h i
|
| A |
5.25±0.04 |
1.00±0 a b c f g h i
|
1.15±0.15 a b c f g h i
|
<1 |
Bacillus cereus
Agar 25 °C
|
|
|
|
|
| C |
3.60±0.03 e g h
|
5.31±0.01 g h
|
6.65±0.02 g h
|
4.48±0.00 e g h
|
| P |
5.05±0.01 a c d e h
|
5.27±0.007 g h
|
5.05±0.03 a g h
|
4.48±0.00 e g h
|
| E |
3.61±0.01 e g h
|
4.38±0.02 a b d e g h
|
5.15±0.06 a g h
|
2.63±0.15 a b d e g h
|
| A |
3.61±0.03 e g h
|
5.35±0.12 g h
|
5.31±0.05 a g h
|
3.09±0.05 a b g h
|
Lactic acid bacteria
25 °C
|
|
|
|
|
| C |
4.25±0.03 e h
|
7.48±0.00 |
7.94±0.08 |
8.72±0.02 |
| P |
4.37±0.05 e f h
|
7.48±0.00 |
7.37±0.01 a d h
|
8.42±0.12 |
| E |
4.09±0.01 b h
|
6.48±0 a b d
|
7.36±0.002 a d h
|
8.57±0.09 |
| A |
4.25±0.005 e h
|
7.48±0.00 |
8.17±0.02 |
8.44±0.04 |
Total Aerobic
Mesophiles 25 °C
|
|
|
|
|
| C |
5.61±0.01 |
7.48±0.00 |
8.06±0.00 |
8.64±0.05 |
| P |
5.84±0.08 |
7.48±0.00 |
8.00±0.05 |
8.37±0.06 |
| E |
4.96±0.002 a b d
|
6.48±0.00 a b d
|
7.82±0.03 a
|
8.46±0.06 |
| A |
5.33±0.03 a b
|
7.48±0.00 |
8.01±0.05 |
8.35±0.04 |
Enterobacteriaceae
4 °C
|
|
|
|
|
| C |
5.37±0.02 h
|
5.05±0.05 |
5.49±0.01 g h
|
6.85±0.03 g h i
|
| P |
5.29±0.03 h
|
4.76±0.02 g h
|
5.53±0.04 g h
|
5.57±0.08 a c g h i
|
| E |
4.11±0.01 a b d h
|
4.39±0.01 a g h
|
5.30±0.04 b d h g
|
6.03±0.01 a g h
|
| A |
5.25±0.04 |
4.74±0.14 g h
|
5.61±0.04 h
|
4.45±0.04 a b c g h
|
Bacillus cereus
Agar 4 °C
|
|
|
|
|
| C |
3.60±0.03 e g h
|
3.17±0.06 e g h i
|
3.78±0.04 e g h i
|
2.26±0.08 e h i
|
| P |
5.05±0.01 a e h
|
3.95±0.05 a e g h i
|
3.71±0.03 e g h i
|
2.27±0.04 d e h i
|
| E |
3.61±0.01 b e g h
|
3.26±0.06 b e g h i
|
3.61±0.04 e g h i
|
2.41±0.08 d e h
|
| A |
3.61±0.03 b g e h
|
3.17±0.13 b e g h i
|
3.58±0.05 e g h i
|
2.85±0.04 a e h
|
Lactic acid bacteria
4 °C
|
|
|
|
|
| C |
4.25±0.03 e h
|
5.36±0.06 i
|
6.05±0.01 i
|
7.36±0.005 h i
|
| P |
4.37±0.05 e f h
|
5.16±0.03 h i
|
5.87±0.01 a h i
|
7.29±0.02 d h i
|
| E |
4.09±0.01 b h
|
5.14±0.04 i
|
5.66±0.02 a b h i
|
7.43±0.01 h i
|
| A |
4.25±0.00 e
|
5.08±0.02 a i
|
5.61±0.03 a b h i
|
7.39±0.02 h i
|
Total Aerobic
Mesophiles 4 °C
|
|
|
|
|
| C |
5.61±0.01 |
5.39±0.03 i
|
6.17±0.03 i
|
7.64±0.10 i
|
| P |
5.84±0.08 |
6.10±0.04 a i
|
6.44±0.03 c i
|
7.36±0.02 d i
|
| E |
4.96±0.002 a b d
|
5.26±0.02 b i
|
6.02±0.07 b i
|
7.32±0.08 d i
|
| A |
5.33±0.03 a b
|
5.10±0.03 a b i
|
5.99±0.03 b i
|
8.02±0.02 a i
|
Table 2.
Number of readings and alpha diversity indices at the genus level.
Table 2.
Number of readings and alpha diversity indices at the genus level.
| Sample |
Nº Reads |
Chao1 |
Shannon |
Simpson |
| C1 |
123226 |
25 |
1.703 |
0.749 |
| C2 |
119676 |
30 |
1.849 |
0.777 |
| C3 |
127885 |
29 |
1.724 |
0.739 |
| P1 |
130156 |
25 |
1.532 |
0.702 |
| P2 |
112884 |
28 |
1.885 |
0.787 |
| P3 |
130114 |
28 |
2.050 |
0.822 |
| E1 |
124532 |
28 |
1.224 |
0.494 |
| E2 |
113295 |
27 |
1.422 |
0.626 |
| E3 |
119261 |
26 |
1.814 |
0.787 |
| A1 |
125674 |
26 |
2.056 |
0.822 |
| A2 |
121055 |
29 |
1.988 |
0.812 |
| A3 |
122216 |
33 |
2.029 |
0.835 |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).