Submitted:
23 April 2023
Posted:
30 April 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics statement.
2.2. Animal handling and sample collection.
2.3. RNA quantitation and quality
2.4. Transcriptome sequencing.
2.5. Quantification of gene expression.
2.6. Differential expression analysis.
2.7. GO and KEGG enrichment analyses of DEGs.
2.8. Prediction of new transcripts and alternative splicing analysis.
2.9. qRT-PCR for RNA-Seq data validation.
3. Results
3.1. Gene expression profiling during testicular development in Qianbei Ma goats.
| Sample name | Exonic region | Intronic region | Intergenic region |
|---|---|---|---|
| I1 | 4466151533 (79.48%) | 611822545 (10.89%) | 541085383 (9.63%) |
| I2 | 4779622398 (78.65%) | 761383464 (12.53%) | 535946498 (8.82%) |
| I3 | 4432093997 (80.66%) | 570346947 (10.38%) | 492580965 (8.96%) |
| I4 | 4614052978 (78.53%) | 738532433 (12.57%) | 523236881 (8.90%) |
| I5 | 5160159063 (81.96%) | 605739527 (9.62%) | 530252297 (8.42%) |
| I6 | 4298336210 (78.73%) | 599791632 (10.99%) | 561800986 (10.29%) |
| S1 | 5004805293 (79.49%) | 606545683 (9.63%) | 684973145 (10.88%) |
| S2 | 4891821345 (81.09%) | 533206687 (8.84%) | 607543338 (10.07%) |
| S3 | 5173907638 (80.30%) | 600212860 (9.32%) | 668983341 (10.38%) |
| S4 | 4579030919 (79.56%) | 552189052 (9.59%) | 623968138 (10.84%) |
| S5 | 4488498885 (78.27%) | 613561446 (10.70%) | 632649316 (11.03%) |
| S6 | 4595667229 (79.73%) | 543550434 (9.43%) | 624459696 (10.83%) |
| P1 | 5058268703 (79.52%) | 636322977 (10.00%) | 666220762 (10.47%) |
| P2 | 4921081484 (78.42%) | 644761157 (10.27%) | 709616381 (11.31%) |
| P3 | 4871901450 (79.39%) | 593069117 (9.66%) | 671905236 (10.95%) |
| P4 | 4918914052 (80.00%) | 601562419 (9.78%) | 628332353 (10.22%) |
| P5 | 4886718972 (80.63%) | 554456620 (9.15%) | 619529425 (10.22%) |
| P6 | 4658554613 (80.75%) | 537138992 (9.31%) | 573327628 (9.94%) |
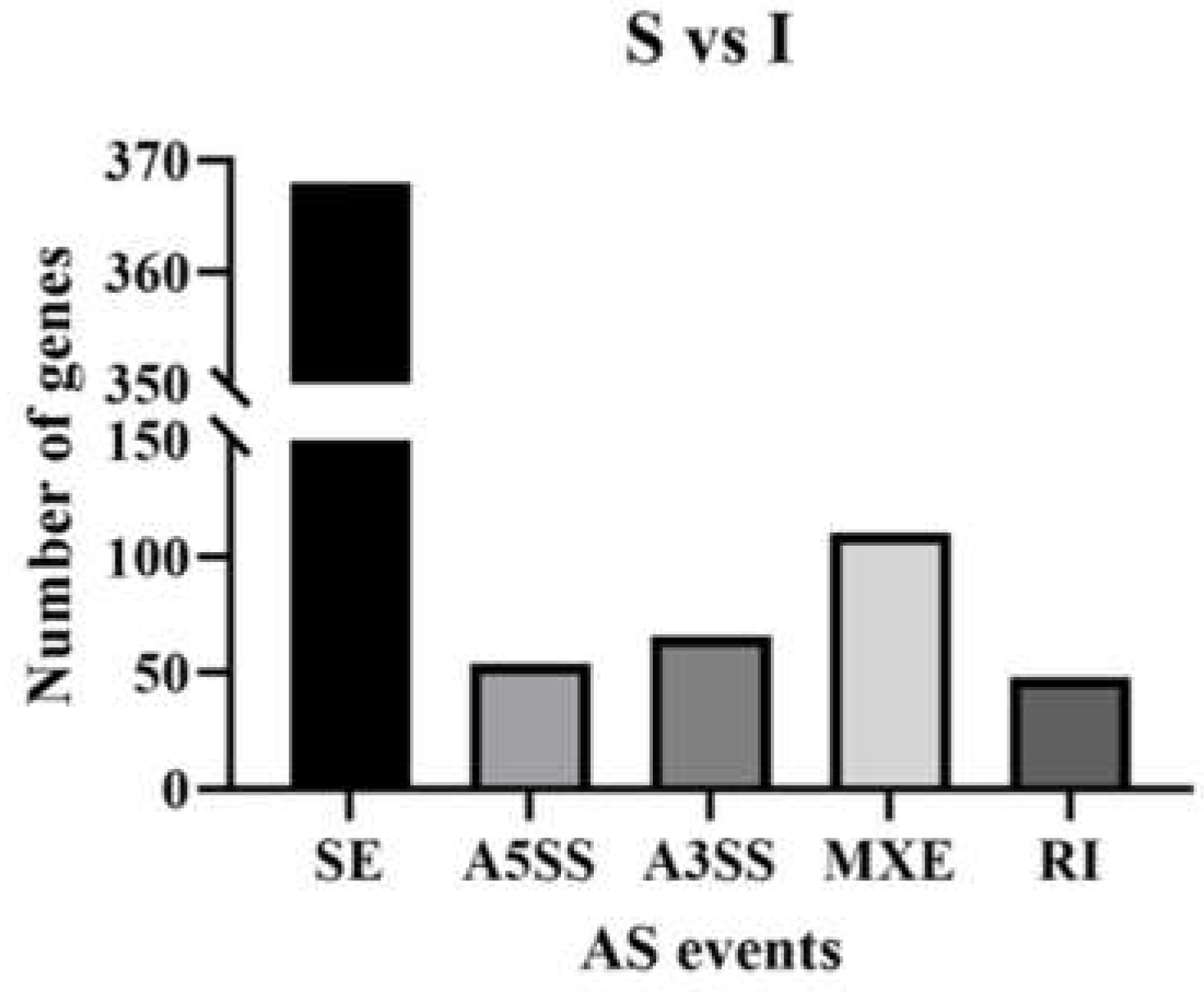
3.2. Alternative splicing data.
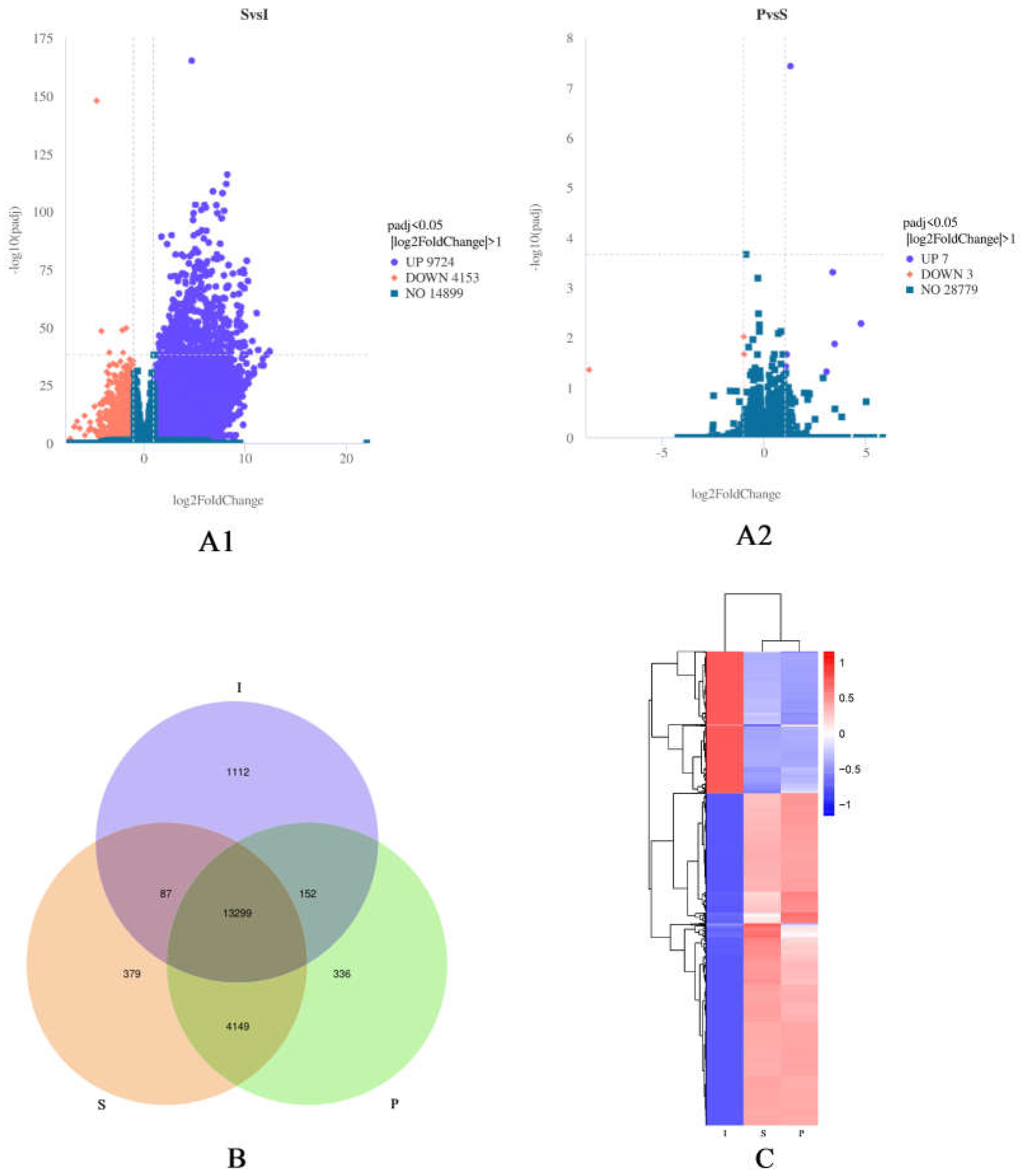
3.3. Analysis of DEGs.
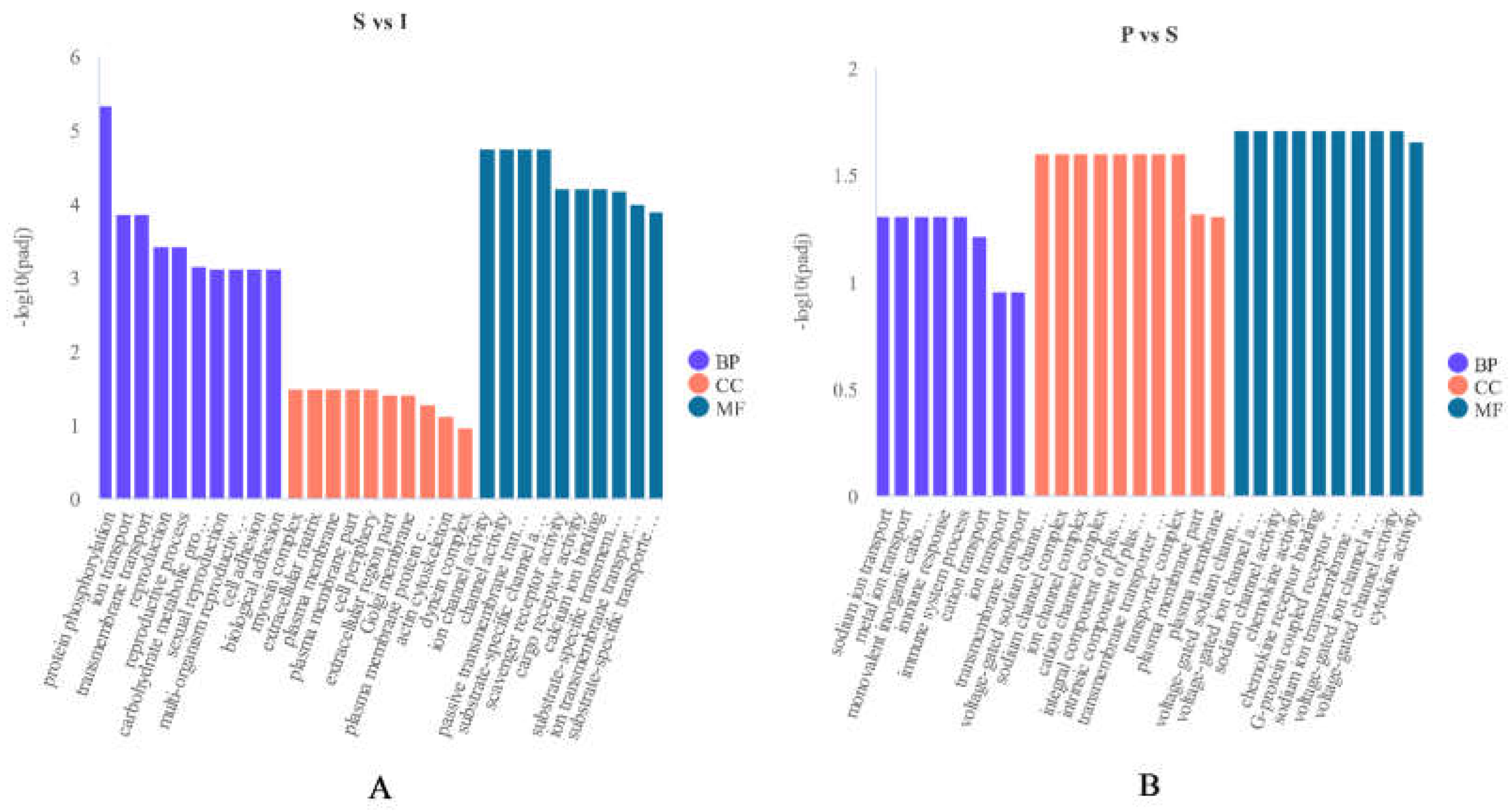
3.4. GO analysis of DEGs.
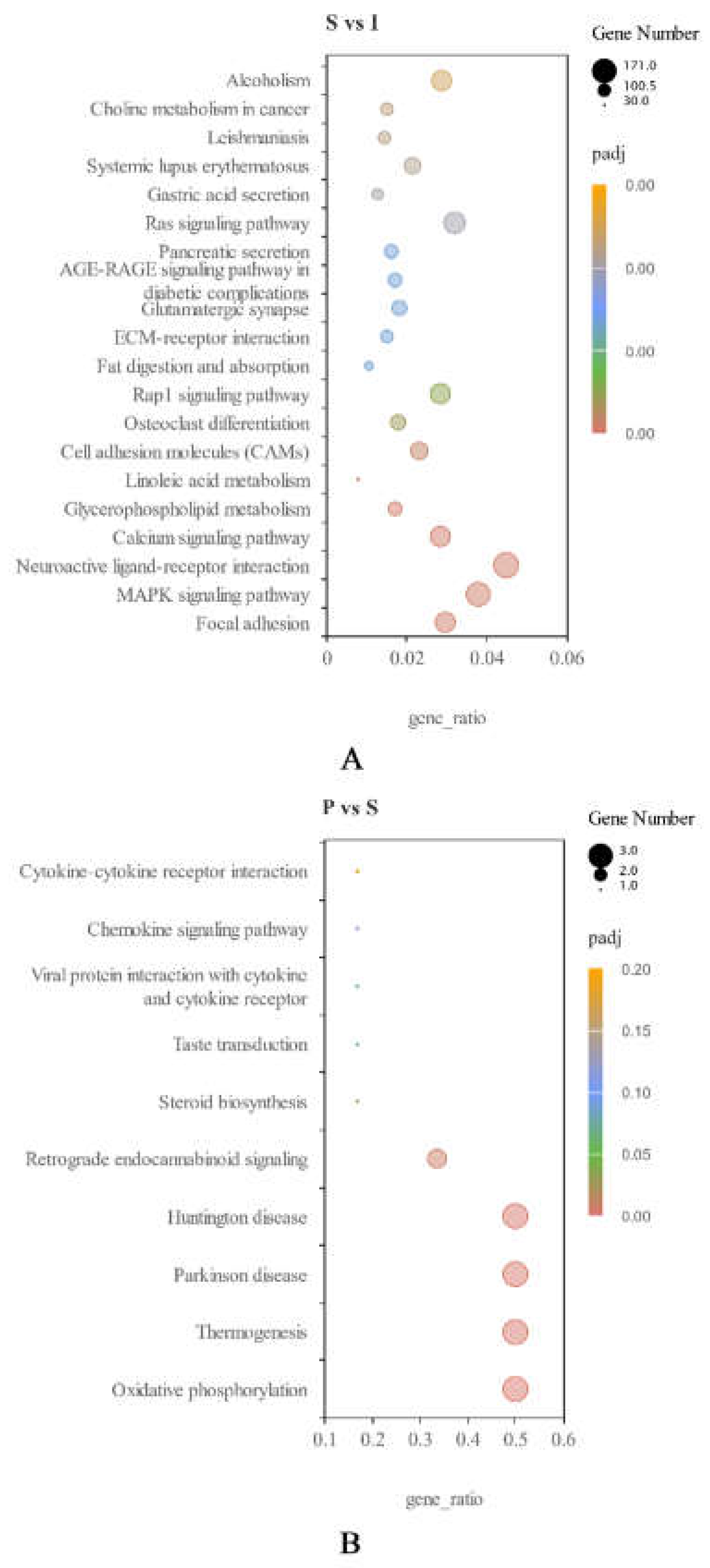
3.5. KEGG pathway analysis of DEGs.
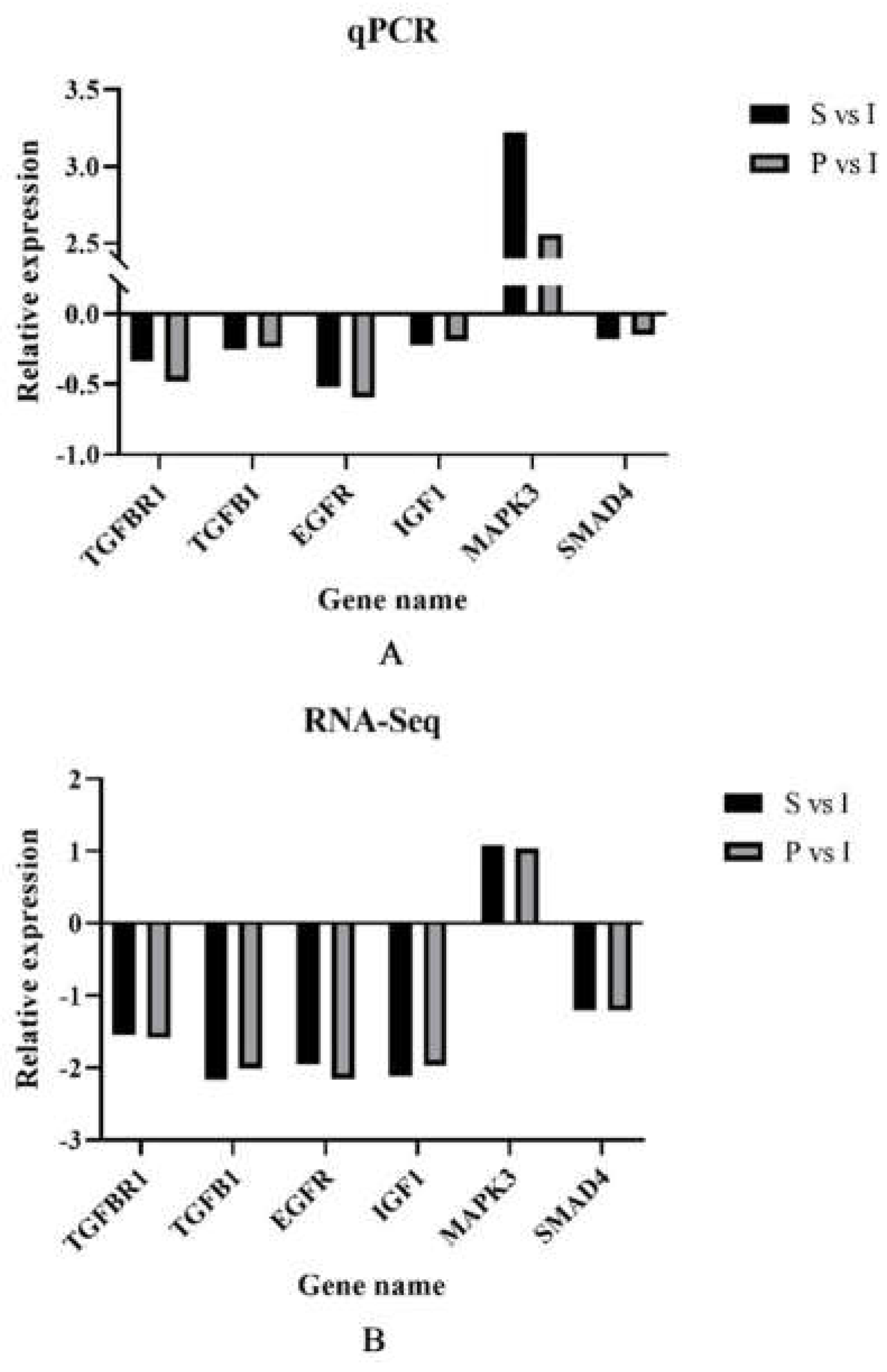
3.6. qRT-PCR validation of DEGs.
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hecht, N.B. Molecular mechanisms of male germ cell differentiation. BioEssays. 1998, 20, 555–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eddy, E.M.; O'Brien, D.A. Gene expression during mammalian meiosis. Current Topics in Developmental Biology. 1998, 37, 141–200. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hess, R.A.; De Franca, L.R. Spermatogenesis and cycle of the seminiferous epithelium. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology. 2008, 636, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mortazavi, A.; Williams, B.A.; McCue, K.; Schaeffer, L.; Wold, B. Mapping and quantifying mammalian transcriptomes by RNA-Seq. Nature Methods. 2008, 5, 621–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marioni, J.C.; Mason, C.E.; Mane, S.M.; Stephens, M.; Gilad, Y. RNA-seq: an assessment of technical reproducibility and comparison with gene expression arrays. Genome Research. 2008, 18, 1509–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Gerstein, M.; Snyder, M. RNA-Seq: a revolutionary tool for transcriptomics. Nature Reviews. Genetics. 2010, 10, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramsköld, D.; Wang, E.T.; Burge, C.B.; Sandberg, R. An abundance of ubiquitously expressed genes revealed by tissue transcriptome sequence data. PLoS Computational Biology. 2009, 5, e1000598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Djureinovic, D.; Fagerberg, L.; Hallstrom, B.; Danielsson, A.; Lindskog, C.; Uhlen, M.; Ponten, F. The human testis-specific proteome defined by transcriptomics and antibody-based profiling. Molecular Human Reproduction. 2014, 20, 476–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, M.; Prasad, B.V. The computational analysis of human testis transcriptome reveals closer ties to pluripotency. Journal of Human Reproductive Sciences. 2012, 5, 266–273. [Google Scholar]
- Mortazavi, A.; Williams, B.A.; McCue, K.; Schaeffer, L.; Wold, B. Mapping and quantifying mammalian transcriptomes by RNA-Seq. Nature Methods. 2008, 5, 621–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bray, N.L.; Pimentel, H.; Melsted, P.; Pachter, L. Erratum: Near-optimal probabilistic RNA-seq quantification. Nature Biotechnology. 2016, 34, 888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trapnell, C.; Williams, B.A.; Pertea, G.; Mortazavi, A.; Kwan, G.; van Baren, M. J.; Salzberg, S.L.; Wold, B.J.; Pachter, L. Transcript assembly and quantification by RNA-Seq reveals unannotated transcripts and isoform switching during cell differentiation. Nature Biotechnology. 2010, 28, 511–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anders, S.; Huber, W. Differential expression analysis for sequence count data. Genome Biology. 2010, 11, R106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanehisa, M.; Araki, M.; Goto, S.; Hattori, M.; Hirakawa, M.; Itoh, M.; Katayama, T.; Kawashima, S.; Okuda, S.; Tokimatsu, T.; Yamanishi, Y. KEGG for linking genomes to life and the environment. Nucleic Acids Research. 2008, 36, D480–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, K.; Chen, X.; Guo, W.; Zhou, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Ji, T.; Yang, P.; Tian, X.; Wang, W.; Zou, Y. Effects of N Acetylcysteine on the Expression of Genes Associated with Reproductive Performance in the Goat Uterus during Early Gestation. Animals. 2022, 12, 2431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shumate, Alaina. Improved Transcriptome Assembly Using a Hybrid of Long and Short Reads with StringTie. PLoS Computational Biology. 2022, 18, 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Pertea, Mihaela. StringTie Enables Improved Reconstruction of a Transcriptome from RNA-seq Reads. Nature Biotechnology. 2015, 33, 290–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, C.; Zhang, L.; Xu, D.; Ding, H.; Zheng, S.; Liu, M. MeDIP-seq and RNA-seq Analysis during Porcine Testis Development Reveals Functional DMR at the Promoter of LDHC. Genomics. 2022, 114, 110467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Li, F.; Lei, P.; Guo, M.; Liu, R.; Wang, L.; Yu, T.; Lv, Y.; Zhang, T.; Zeng, W.; Lu, H.; Zheng, Y. Single-cell RNA-sequencing Reveals the Dynamic Process and Novel Markers in Porcine Spermatogenesis. Journal of Animal Science and Biotechnology. 2021, 12, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, T.; Yang, Y.; Retzel, E.F.; Liu, W. Male-specific Region of the Bovine Y Chromosome Is Gene Rich with a High Transcriptomic Activity in Testis Development. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences – PNAS. 2013, 110, 12373–12378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Wu, M.; Fan, Y.; Li, S.; Lai, Z.; Huang, Y.; Lan, X.; Lei, C.; Chen, H.; Dang, R. Identification and Characterization of Circular RNAs in Qinchuan Cattle Testis. Royal Society Open Science. 2018, 5, 180413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Wu, P.; Beane, T.; Zamore, P.D.; Weng, Z. Elimination of PCR Duplicates in RNA-seq and Small RNA-seq Using Unique Molecular Identifiers. BMC Genomics. 2018, 19, 531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, C.D.; Ma, Q.; Manske, G.L.; Shami, A.N.; Zheng, X.; Marini, S.; Moritz, L.; Sultan, C.; Gurczynski, S.J.; Moore, B.B.; Tallquist, M.D.; Li, J.Z.; Hammoud, S.S. A Comprehensive Roadmap of Murine Spermatogenesis Defined by Single-Cell RNA-Seq. Developmental Cell. 2018, 46, 651–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, X.; Lu, T.; Zhao, Z.; Liu, G.; Lian, Z.; Guo, Y.; Sun, B.; Liu, D.; Li, Y. Comprehensive Analysis of MRNAs and MiRNAs in the Ovarian Follicles of Uniparous and Multiple Goats at Estrus Phase. BMC Genomics. 2020, 21, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zi, X.; Lu, J.; Zhou, H.; Ma, L.; Xia, W.; Xiong, X.; Lan, D.; Wu, X. Comparative Analysis of Ovarian Transcriptomes between Prolific and Non-prolific Goat Breeds via High-throughput Sequencing. Reproduction in Domestic Animals. 2018, 53, 344–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, L.; Hu, Q.; Zang, X.; Xie, Y.; Zhou, C.; Zou, X.; Li, Y.; Deng, M.; Guo, Y.; Liu, G.; Liu, D. Analysis and Screening of Reproductive Long Non-coding RNAs Through Genome-Wide Analyses of Goat Endometrium During the Pre-attachment Phase. Frontiers in Genetics. 2020, 11, 568017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Wang, C.; Li, Z.; Shang, C.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, R.; Wang, A.; Jin, Y.; Lin, P. Transcriptomic Analysis of STAT1/3 in the Goat Endometrium During Embryo Implantation. Frontiers in Veterinary Science. 2021, 8, 757759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bo, D.; Jiang, X.; Liu, G.; Hu, R.; Chong, Y. RNA-Seq Implies Divergent Regulation Patterns of LincRNA on Spermatogenesis and Testis Growth in Goats. Animals. 2021, 11, 625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Yang, P.; Yang, H.; Wang, Z.; El-Samahy, M.A.; Wang, F.; Zhang, Y. Dietary Supplementation with Metformin Improves Testis Function and Semen Quality and Increases Antioxidants and Autophagy Capacity in Goats. Theriogenology. 2022, 188, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, F.; Geng, Y.; Zhang, L.; Luo, L.; Yan, G.; Hou, R.; Yue, B.; Zhang, X. Transcriptome Analysis Reveals the Alternative Splicing Changes in the Immune-Related Genes of the Giant Panda (Ailuropoda melanoleuca), in Response to the Canine Distemper Vaccine. Zoological Science. 2022, 39, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Q.; Shai, O.; Lee, L.J.; Frey, B.J.; Blencowe, B.J. Deep surveying of alternative splicing complexity in the human transcriptome by high-throughput sequencing. Nature Genetics. 2008, 40, 1413–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagiwara, M.; Kuroyanagi, H. 2SE01 Regulatory Mechanisms of Alternative Splicing in Metazoans. Seibutsu Butsuri. 2005, 45, S23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; He, P.; Zhang, Z.; Gong, P.; Niu, Y.; Bao, Zhen. ; Yang, Y.; Gan, L.; Muhuyati. Candidate Genes and Their Alternative Splicing May Be Potential Biomarkers of Acute Myocardial Infarction: A Study of Mouse Model. BMC Cardiovascular Disorders. 2022, 22, 1–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Ni, S.; Zhang, J.; Yuan, Y.; Bai, Yun. ; Yin, X.; Zhu, Z. Genome-wide Analysis of Dysregulated RNA-binding Proteins and Alternative Splicing Genes in Keloid. Frontiers in Genetics. 2023, 14, 1118999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schomburg, L.; Liao, X.; Majed, F.A.; Abdullah, M.S.Y.; Refetoff, S.; Boran, G.; Dumitrescu, A.M.; Lado-Abeal, J.; Moeller, L.C.; Weiss, R.E. Mutations in SECISBP2 Result in Abnormal Thyroid Hormone Metabolism. Nature Genetics. 2005, 37, 1247–1252. [Google Scholar]
- Schoenmakers, E.; Chatterjee, K. Identification of Genetic Disorders Causing Disruption of Selenoprotein Biosynthesis. Methods in Molecular Biology. 2018, 1661, 325–335. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mohammadabadi, T.; Tabatbaei, S.; Ghezi, Z.; Swelum, A.A. Effect of Dietary Palm Kernel on Semen Quality, Reproductive and Thyroid Hormones and Blood Chemistry Parameters of Arabi Rams. Animal Nutrition and Feed Technology. 2020, 20, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mogheiseh, A.; Vara, N.; Ayaseh, M.; Jalali, P. Effects of Cabergoline on Thyroid Hormones and Semen Quality of Dog. Topics in Companion Animal Medicine. 2017, 32, 13–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quartuccio, M.; Fazio, E.; Medica, P.; Cristarella, S.; Emmanuele, G.; Sinagra, L.; Liotta, L. Correlation between Sperm Parameters and Circulating Thyroid Hormones and Testosterone Concentrations in Labrador Retriever Dog. Italian Journal of Animal Science. 2021, 20, 947–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemzadeh-Hasankolaei, M.; Sedighi-Gilani, M.A.; Eslaminejad, M.B. Induction of Ram Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells into Germ Cell Lineage Using Transforming Growth Factor-β Superfamily Growth Factors. Reproduction in Domestic Animals. 2014, 49, 588–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas-García, P.P.; Recabarren, M.P.; Sir-Petermann, T.; Rey, R.; Palma, S.; Carrasco, A.; Perez-Marin, C.C.; Padmanabhan, V.; Recabarren, S.E. Altered Testicular Development as a Consequence of Increase Number of Sertoli Cell in Male Lambs Exposed Prenatally to Excess Testosterone. Endocrine. 2013, 43, 705–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingman, W.V.; Robertson, S.A. The Essential Roles of TGFB1 in Reproduction. Cytokine & Growth Factor Reviews. 2009, 20, 233–239. [Google Scholar]
- McGrath, L.J.; Ingman, W.V.; Robker, R.L.; Robertson, S.A. Exogenous Transforming Growth Factor Beta1 Replacement and Fertility in Male Tgfb1 Null Mutant Mice. Reproduction Fertility and Development. 2009, 21, 561–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Dong, C.; You, R.; Zhu, Z.; Lv, L.; Smith, G.W. Localization of Epidermal Growth Factor (EGF) and Its Receptor (EGFR) during Postnatal Testis Development in the Alpaca (Lama Pacos). Animal Reproduction Science. 2009, 116, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Cui, Y.; Yu, S.; Zhang, Q.; Fan, J.; Abdul, R. B.; Yang, K. The Expression of Epidermal Growth Factor (EGF) and Its Receptor (EGFR) During Post-Natal Testes Development in the Yak. Reproduction in Domestic Animals. 2014, 49, 970–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassab, M.; Abd-Elmaksoud, A.; Ali, M.A. Localization of the Epidermal Growth Factor (EGF) and Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) in the Bovine Testis. Journal of Molecular Histology. 2007, 38, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannarella, R.; Condorelli, R.A.; La Vignera, S.; Calogero, A.E. Effects of the Insulin-like Growth Factor System on Testicular Differentiation and Function: A Review of the Literature. Andrology. 2018, 6, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pitetti, J.; Calvel, P.; Zimmermann, C.; Conne, B.; Papaioannou, M.D.; Aubry, F.; Cederroth, C.R.; Urner, F.; Fumel, B.; Crausaz, M.; Docquier, M.; Herrera, P.L.; Pralong, F.; Germond, M.; Guillou, F.; Jégou, B.; Nef, S. An Essential Role for Insulin and IGF1 Receptors in Regulating Sertoli Cell Proliferation, Testis Size, and FSH Action in Mice. Molecular Endocrinology. 2013, 27, 814–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cannarella, R.; La Vignera, S.; Condorelli, R.A.; Calogero, A.E. The IGF1/FSH Ratio Correlates with Sperm Count and Testicular Volume. Endocrines. 2022, 3, 624–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, L.; Kowalewski, M.P.; Reichler, I.M.; Kollár, E.; Balogh, O. Different Expression of Leptin and IGF1 in the Adult and Prepubertal Testis in Dogs. Reproduction in Domestic Animals. 2017, 52, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radovic, S.M.; Starovlah, I.M.; Capo, I.; Miljkovic, D.; Nef, S.; Kostic, T.S.; Andric, S.A. Insulin/IGF1 Signaling Regulates the Mitochondrial Biogenesis Markers in Steroidogenic Cells of Prepubertal Testis, but Not Ovary. Biology of Reproduction. 2019, 100, 253–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neirijnck, Y.; Calvel, P.; Kilcoyne, K.R.; Kühne, F.; Stévant, I.; Griffeth, R.J.; Pitetti, J.; Andric, S.A.; Hu, M.; Pralong, F.; Smith, L.B.; Nef, S. Insulin and IGF1 Receptors Are Essential for the Development and Steroidogenic Function of Adult Leydig Cells. The FASEB Journal. 2018, 32, 3321–3335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rojas, M.; Conei, D.; Bustos-Obregon, E. Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transitions in the Development of Testis/Interacciones Epitelio-Mesenquimaticas En El Desarrollo Testicular. International Journal of Morphology. 2017, 35, 1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stratikopoulos, E.; Szabolcs, M.; Dragatsis, I.; Klinakis, A.; Efstratiadis, A. Hormonal Action of IGF1 in Postnatal Mouse Growth. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences – PNAS. 2008, 105, 19378–19383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitetti, J.; Calvel, P.; Romero, Y.; Conne, B.; Vy, T.; Papaioannou, M.D.; Schaad, O.; Docquier, M.; Herrera, P.L.; Wilhelm, D.; Nef, S. Insulin and IGF1 Receptors Are Essential for XX and XY Gonadal Differentiation and Adrenal Development in Mice. PLoS Genetics. 2013, 9, E1003160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warr, N.; Carre, G.; Siggers, P.; Faleato, J.V. , Brixey, R.; Pope, M.; Bogani, D.; Childers, M.; Wells, S.; Scudamore, C.L.; Tedesco, M.; Del Barco, B.I.; Nebreda, A.R.; Trainor, P.A.; Greenfield, A. Gadd45γ and Map3k4 Interactions Regulate Mouse Testis Determination via P38 MAPK-Mediated Control of Sry Expression. Developmental Cell. 2012, 23, 1020–1031. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Ren, L.; Wei, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, Y.; Li, X.; Jing, Li.; Duan, J.; Zhou, X.; Sun, Z. Fine Particle Matter Disrupts the Blood–testis Barrier by Activating TGF-β3/p38 MAPK Pathway and Decreasing Testosterone Secretion in Rat. Environmental Toxicology. 2018, 33, 711–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Tang, X.; Wei, Y.; Long, C.; Tan, B.; Wu, S.; Sun, M.; Zhou, Y.; Cao, X.; Wei, G. Vitamin E and Vitamin C Attenuate Di-(2-ethylhexyl) Phthalate-induced Blood-testis Barrier Disruption by P38 MAPK in Immature SD Rats. Reproductive Toxicology. 2018, 81, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, D.; He, Z.; Yu, C.; Guan, Q. Role of P38 MAPK Signalling in Testis Development and Male Fertility. Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity. 2022, 2022, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, X.; Sun, K.; Wang, S.; Gong, D. Polystyrene Microplastics Induce Apoptosis and Necroptosis in Swine Testis Cells via ROS/MAPK/HIF1α Pathway. Environmental Toxicology. 2022, 37, 2483–2492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, C.R.; Dorfman, V.B.; Vitullo, A.D. IGF1 Regulation of BOULE and CDC25A Transcripts via a Testosterone-independent Pathway in Spermatogenesis of Adult Mice. Reproductive Biology. 2015, 15, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Shan, B.; Duan, Y.; Zhu, J.; Jiang, L.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Qi, F.; Niu, S. Effects of Heshouwuyin on Gene Expression of the Insulin/IGF Signalling Pathway in Rat Testis and Spermatogenic Cells. Pharmaceutical Biology. 2020, 58, 1208–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Primer name | Gene ID | Primer sequence | Fragment length | annealing temperature |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GAPDH-F GAPDH-R |
XM_005680968.3 | ATGTTTGTGATGGGCGTGAA GGCGTGGACAGTGGTCATAAGT |
153 bp | 60 ℃ |
| TGFBR1-F TGFBR1-R |
XM_018052233.1 | TTCAAACGTGCTGACATCTATGC ACTGATGGATCGGAAGGTACAAG |
128 bp | 60 ℃ |
| SMAD4-F SMAD4-R |
XM_018039535.1 | CATAACAGCACTACCACCTGGACT GGATGATTAGAAATAGGAGGCTGG |
173 bp | 60 ℃ |
| TGFB1-F TGFB1-R |
NM_001314142.1 | CAACAATTCCTGGCGCTACCT ATGTCCACTTGAAGCGTGTTATCC |
183 bp | 60 ℃ |
| EGFR-F EGFR-R |
XM_018067044.1 | CCGTGCGATTCAGTAACAACC GGTCAATTTCTGGCAGTTCTCCTC |
194 bp | 60 ℃ |
| IGF1-F IGF1-R |
NM_001285697.1 | AATCAGCAGTCTTCCAACCCAA AGCAAGCACAGGGCCAGATA |
114 bp | 60 ℃ |
| MAPK3-F MAPK3-R |
XM_018040780.1 | CTGGACCGGATGTTGACCTTTA CTCCTTCAGTCGTTCCTTGGG |
138 bp | 60 ℃ |
| Sample name | Library number | Raw reads (n) | Clean reads (n) | Error rate | Q20 | Q30 | GC pct |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I1 | 1 | 40405582 | 39128916 | 0.03 | 97.36 | 93.09 | 50.99 |
| I2 | 2 | 43841646 | 42366502 | 0.03 | 97.41 | 93.2 | 51.16 |
| I3 | 3 | 39433208 | 38237518 | 0.03 | 97.42 | 93.25 | 51.42 |
| I4 | 4 | 42396474 | 40926952 | 0.03 | 97.43 | 93.23 | 51.26 |
| I5 | 5 | 45463988 | 43854898 | 0.03 | 97.41 | 93.19 | 51.1 |
| I6 | 6 | 39351212 | 38000364 | 0.03 | 97.48 | 93.36 | 50.91 |
| S1 | 7 | 44934642 | 43739660 | 0.03 | 97.51 | 93.41 | 52.09 |
| S2 | 8 | 43025142 | 41894994 | 0.03 | 97.39 | 93.17 | 52.36 |
| S3 | 9 | 45845898 | 44647422 | 0.03 | 97.59 | 93.55 | 52.15 |
| S4 | 10 | 41237336 | 40020062 | 0.03 | 97.37 | 93.11 | 52.29 |
| S5 | 11 | 41130946 | 39901252 | 0.03 | 97.36 | 93.09 | 51.09 |
| S6 | 12 | 41242240 | 40019490 | 0.03 | 97.51 | 93.4 | 51.9 |
| P1 | 13 | 45377178 | 44131516 | 0.03 | 97.48 | 93.34 | 52.27 |
| P2 | 14 | 44664918 | 43577078 | 0.03 | 97.49 | 93.36 | 52.06 |
| P3 | 15 | 43792502 | 42601198 | 0.03 | 97.47 | 93.32 | 51.98 |
| P4 | 16 | 43921138 | 42702250 | 0.03 | 97.5 | 93.39 | 52.17 |
| P5 | 17 | 43223452 | 42134186 | 0.03 | 97.44 | 93.27 | 52.14 |
| P6 | 18 | 45571906 | 44622618 | 0.03 | 97.3 | 92.91 | 50.37 |
| SAMPLE | TOTAL READS | TOTAL MAP | UNIQUE MAP | MULTI MAP | POSITIVE MAP | NEGATIVE MAP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I1 | 39128916 | 37563635(96.00%) | 35626251(91.05%) | 1937384(4.95%) | 17793049(45.47%) | 17833202(45.58%) |
| I2 | 42366502 | 40625554(95.89%) | 38612044(91.14%) | 2013510(4.75%) | 19294015(45.54%) | 19318029(45.60%) |
| I3 | 38237518 | 36735876(96.07%) | 34685761(90.71%) | 2050115(5.36%) | 17323488(45.30%) | 17362273(45.41%) |
| I4 | 40926952 | 39282398(95.98%) | 37389786(91.36%) | 1892612(4.62%) | 18672350(45.62%) | 18717436(45.73%) |
| I5 | 43854898 | 42092675(95.98%) | 40255938(91.79%) | 1836737(4.19%) | 20105549(45.85%) | 20150389(45.95%) |
| I6 | 38000364 | 36500392(96.05%) | 34501227(90.79%) | 1999165(5.26%) | 17230278(45.34%) | 17270949(45.45%) |
| S1 | 43739660 | 42076928(96.20%) | 40551689(92.71%) | 1525239(3.49%) | 20259699(46.32%) | 20291990(46.39%) |
| S2 | 41894994 | 40318684(96.24%) | 39006285(93.10%) | 1312399(3.13%) | 19484346(46.51%) | 19521939(46.60%) |
| S3 | 44647422 | 43061457(96.45%) | 41514183(92.98%) | 1547274(3.47%) | 20739259(46.45%) | 20774924(46.53%) |
| S4 | 40020062 | 38465949(96.12%) | 36829538(92.03%) | 1636411(4.09%) | 18396451(45.97%) | 18433087(46.06%) |
| S5 | 39901252 | 38334062(96.07%) | 36942595(92.59%) | 1391467(3.49%) | 18452256(46.24%) | 18490339(46.34%) |
| S6 | 40019490 | 38522907(96.26%) | 36912252(92.24%) | 1610655(4.02%) | 18439977(46.08%) | 18472275(46.16%) |
| P1 | 44131516 | 42514601(96.34%) | 41073585(93.07%) | 1441016(3.27%) | 20518750(46.49%) | 20554835(46.58%) |
| P2 | 43577078 | 41944011(96.25%) | 40303516(92.49%) | 1640495(3.76%) | 20133389(46.20%) | 20170127(46.29%) |
| P3 | 42601198 | 41016519(96.28%) | 39440892(92.58%) | 1575627(3.70%) | 19701050(46.25%) | 19739842(46.34%) |
| P4 | 42702250 | 41098071(96.24%) | 39528322(92.57%) | 1569749(3.68%) | 19745068(46.24%) | 19783254(46.33%) |
| P5 | 42134186 | 40510371(96.15%) | 38849502(92.20%) | 1660869(3.94%) | 19405731(46.06%) | 19443771(46.15%) |
| P6 | 44622618 | 38550615(86.39%) | 37036723(83.00%) | 1513892(3.39%) | 18501103(41.46%) | 18535620(41.54%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





