Submitted:
29 April 2023
Posted:
30 April 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
| Abnormality | Description | Histology | Risk of Progression |
|---|---|---|---|
| LSIL | Low-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion | CIN1 | Low |
| CIN1 | Cervical intraepithelial neoplasia 1 | Mild dysplasia | Low |
| CIN2 | Cervical intraepithelial neoplasia 2 | Moderate dysplasia | Moderate |
| CIN3 | Cervical intraepithelial neoplasia 3 | Severe dysplasia/carcinoma in situ | High |
| HSIL | High-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion | CIN2-CIN3 | High |
| ASC-US | Atypical squamous cells of undetermined significance | - | - |
| ASC-H | Atypical squamous cells, cannot exclude HSIL | - | - |
2. Results and Discussion
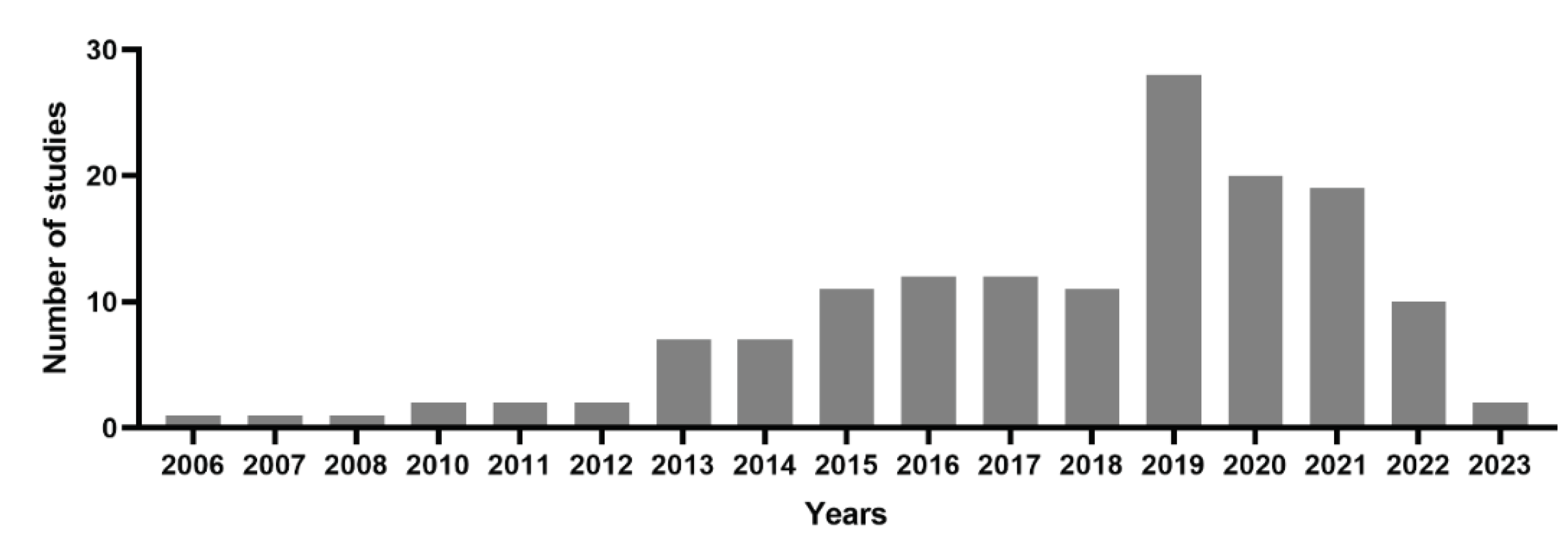
2.1. PubMed online data base analysis for PDT of cervical cancer
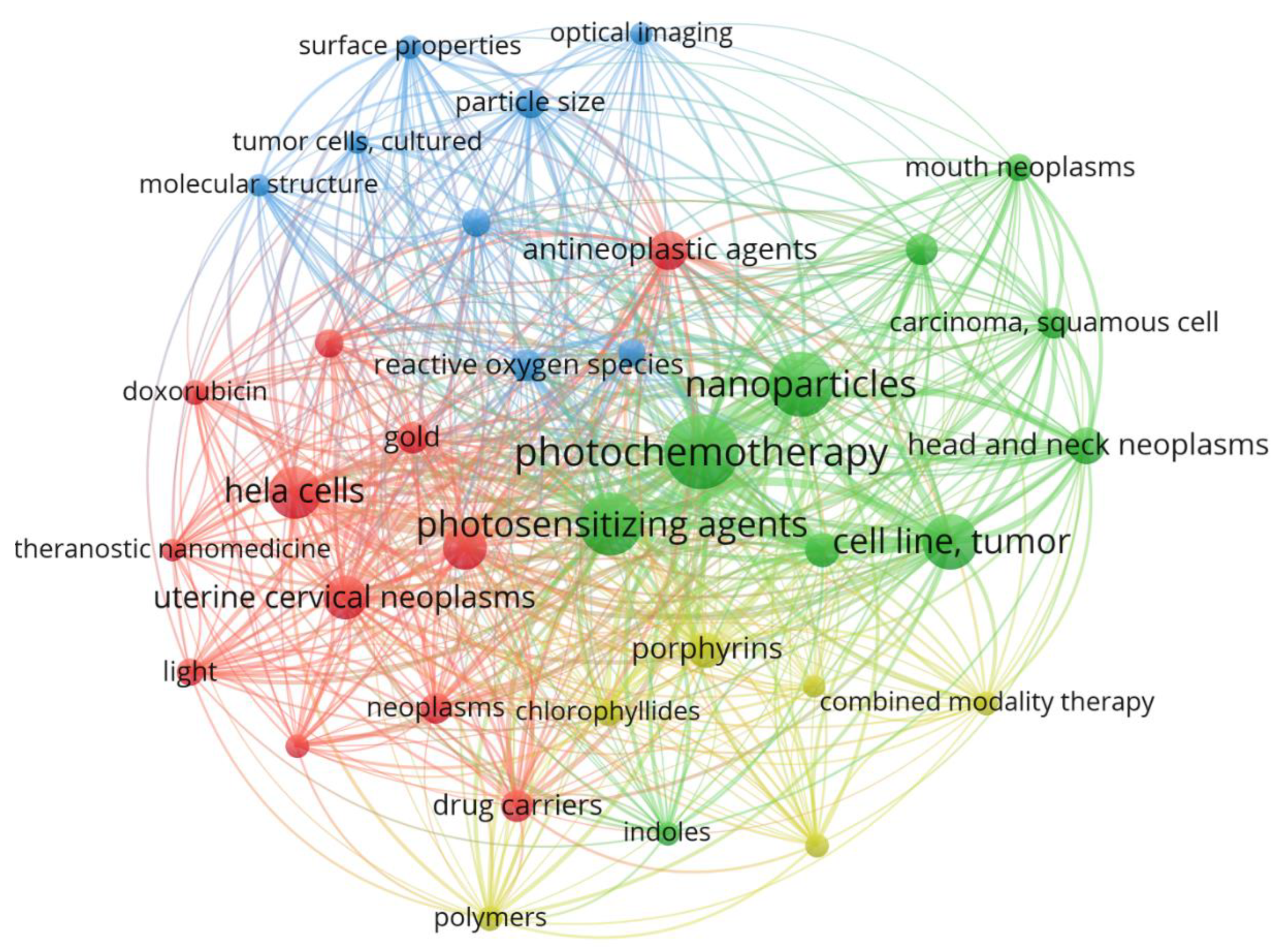
2.2. Photo chemotherapy, nanoparticles and photosensitizing agents were the most frequent MeSH keywords that have been used in the field of the usages of PDT in the field of treating cervical cancer cells
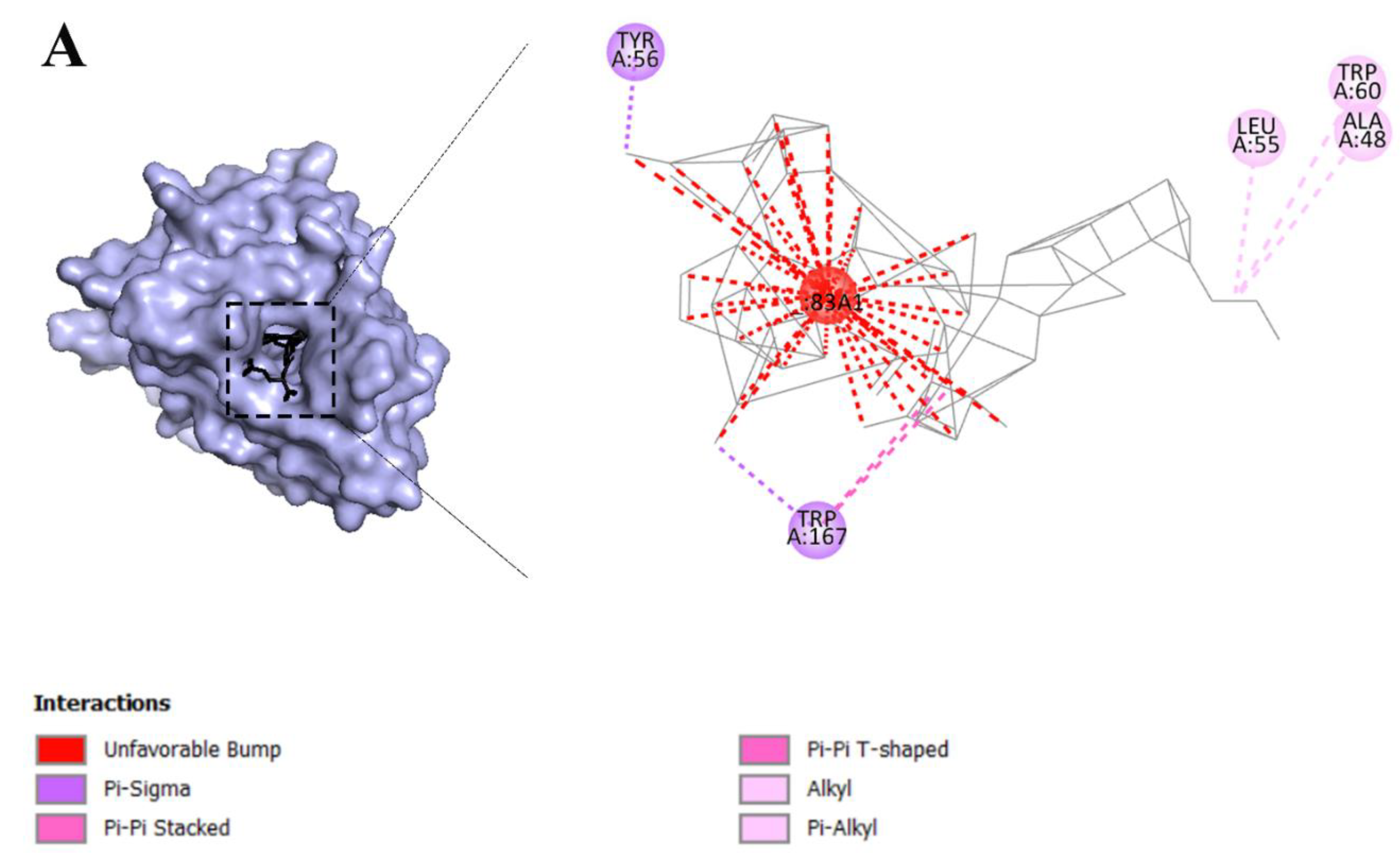
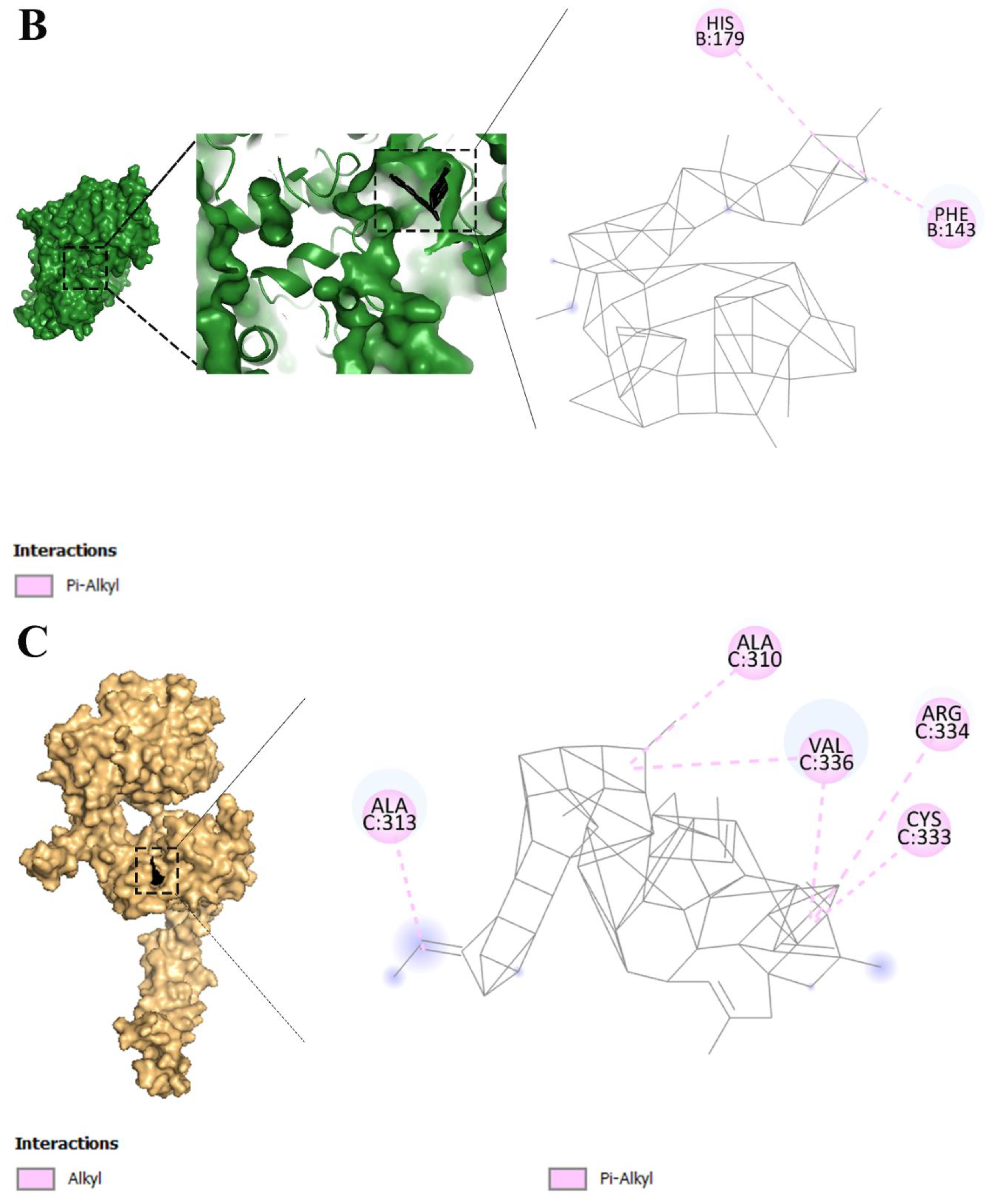
2.3. Fullerene has the most binding affinity to overexpressed receptors in cervical cancer cells
2.4. PDT as a novel approach for cervical cancer therapy
2.5. Photo chemotherapy, nanoparticles and photosensitizing agents were the most frequent MeSH keywords that have been used in the field of the usages of PDT in the field of treating cervical cancer cells
2.6. Fullerene with the best affinity to overexpressed receptors in cervical cancer
2.7. Approved dyes for clinical approaches of PDT of cervical cancer
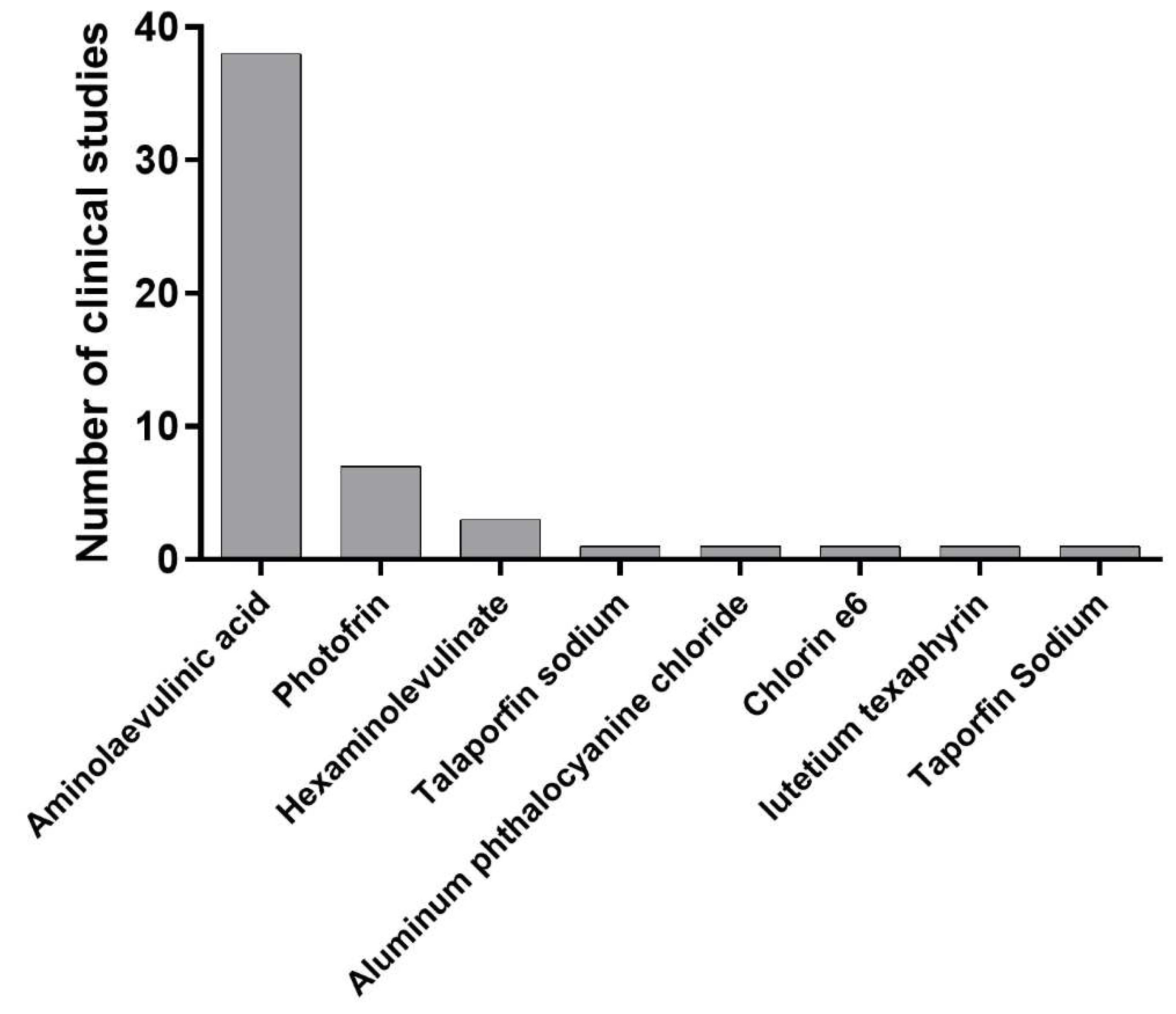
- 5-aminolevulinic acid (ALA): ALA is a photosensitizer that is used in PDT for cervical cancer [28]. A several clinical trials evaluated the safety and efficacy of ALA-PDT in patients with cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN) (). Further clinical studies are needed to evaluate the long-term efficacy of ALA-PDT in the treatment of cervical cancer.
- Aluminum phthalocyanine chloride: Aluminum phthalocyanine chloride is a second-generation photosensitizer that is used in PDT for various cancers, including cervical cancer [29]. Further clinical studies are needed to evaluate the long-term efficacy of aluminum phthalocyanine chloride-mediated PDT in the treatment of cervical cancer.
- Photofrin: Photofrin is a photosensitizer that has been approved for use in PDT for various cancers, including cervical cancer [28]. Further clinical studies are needed to evaluate the long-term efficacy of photofrin-mediated PDT in the treatment of cervical cancer.
- Hexaminolevulinate: Hexaminolevulinate is a photosensitizer that is used in PDT for various cancers, including cervical cancer [28]. Further clinical studies are needed to evaluate the long-term efficacy of hexaminolevulinate-mediated PDT in the treatment of cervical cancer.
- Chlorin e6: Chlorin e6 is another photosensitizer that are used in PDT for cervical cancer [31]. It has a high absorption rate in the near-infrared region, which can penetrate deeper into tissue than other photosensitizers. It has also been shown to have high selectivity for cancer cells over healthy cells, making it a promising candidate for use in PDT [32].
- Porphyrin derivatives: Porphyrin derivatives, such as protoporphyrin IX and hematoporphyrin derivatives, are natural photosensitizers that are used in PDT for cervical cancer [33]. These compounds are naturally occurring molecules in the body and have been shown to accumulate in cancer cells at higher rates than in healthy cells. When exposed to light at a specific wavelength, these photosensitizers generate reactive oxygen species that can destroy cancer cells [34].
2.8. Clinical trials for PDT for LSIL
2.9. Clinical trials for PDT for HSIL
2.10. Preclinical approaches of PDT of cervical cancer
- Hypericin: Hypericin is a compound found in St. John's wort. It has been found to have photosensitizing properties and has been used in PDT for cervical cancer [71]. When hypericin is activated by light, it produces reactive oxygen species that can damage cancer cells. Hypericin has been shown to be effective in killing cancer cells in vitro and in animal studies [72], but more research is needed to determine its effectiveness in humans.
- Methylene blue: Methylene blue is a blue dye that has been used in medicine for many years. It has been found to be effective in PDT for cervical cancer [75]. There are evidences showed that methylene blue-mediated PDT was effective in inducing cell death in cervical cancer cells [71,76].When methylene blue is activated by light, it produces reactive oxygen species that can damage cancer cells. Methylene blue has been shown to be effective in killing cancer cells in vitro and in animal studies, but more research is needed to determine its effectiveness in humans.
- Rose Bengal: Rose Bengal is a red dye that has been used in medicine for many years. It has also been found to have photosensitizing properties and has been used in PDT for cervical cancer [72]. When Rose Bengal is activated by light, it produces reactive oxygen species that can damage cancer cells. Rose Bengal has been shown to be effective in killing cancer cells in vitro and in animal studies [72], but more research is needed to determine its effectiveness in humans.
- Zinc phthalocyanine: This is a photosensitizer that can be used in PDT for cervical cancer [32]. It has a high absorption rate in the red-light region, which makes it effective for use in PDT. When exposed to light at a specific wavelength, the photosensitizer generates reactive oxygen species that can destroy cancer cells [32].
2.11. Potential dyes for PDT of cervical cancer
- Bacteriochlorins: Bacteriochlorins are a class of photosensitizers that have been investigated for their potential use in PDT for various cancers [80]. There is no study to show that bacteriochlorin-based PDT can be effective for treating cervical cancer.
- Xanthene dyes: Xanthene dyes such as eosin and erythrosine are a class of fluorescent dyes that have been used in various applications, including as photosensitizers in PDT for various cancers [82].
2.12. Scoring of application of dyes for PDT of cervical cancer
- FDA approval status: if a dye has been approved by the FDA for clinical use, it is given a score of 5. If it is in clinical trials, it is given a score of 4. If it has only been tested in preclinical studies, it is given a score of 3. If there is no data available, it is given a score of 1.
- Efficacy: this refers to the effectiveness of the dye in treating cervical cancer. If there is strong evidence supporting its efficacy, it is given a score of 5. If there is some evidence, it is given a score of 3. If there is little or no evidence, it is given a score of 1.
- Safety: this refers to the safety profile of the dye, including its potential for side effects. If there is strong evidence supporting its safety, it is given a score of 5. If there is some evidence, it is given a score of 3. If there is little or no evidence, it is given a score of 1.
- For the preclinical and potential dyes section, the following parameters are considered:
- Preclinical efficacy: this refers to the effectiveness of the dye in preclinical studies. If there is strong evidence supporting its efficacy, it is given a score of 5. If there is some evidence, it is given a score of 3. If there is little or no evidence, it is given a score of 1.
- Preclinical safety: this refers to the safety profile of the dye in preclinical studies. If there is strong evidence supporting its safety, it is given a score of 5. If there is some evidence, it is given a score of 3. If there is little or no evidence, it is given a score of 1.
- Potential for clinical translation: this refers to the potential for the dye to be translated into clinical use. If there is strong evidence supporting its potential for clinical use, it is given a score of 5. If there is some evidence, it is given a score of 3. If there is little or no evidence, it is given a score of 1.
2.13. Challenges and solutions related to using dyes for PDT of cervical cancer
- Tumor targeting: It can be a challenge to specifically target the dye to the tumor cells, while minimizing the uptake by healthy tissues, which could lead to toxicity.
- Depth of penetration: The depth of penetration of the light used to activate the dye can be limited, which means that tumors located deeper in the body may be difficult to treat.
- Photobleaching: Dyes can undergo photobleaching, which means that they lose their ability to generate reactive oxygen species upon exposure to light. This can limit their efficacy in PDT.
- Stability: Some dyes can be unstable in biological environments, which can affect their efficacy and safety.
- Regulatory approval: The regulatory approval of dyes for clinical use can be a lengthy and expensive process, which can limit their availability for PDT of cervical cancer.
- Solubility: One challenge related to the use of dyes for PDT of cervical cancer is their solubility in biological fluids, which can affect their effectiveness and potential toxicity.
- Some potential solutions to the challenges related to the use of dyes for PDT of cervical cancer are listed below:
- Solubility: One solution could be to use lipid-based or polymeric nanocarriers to encapsulate the dye and improve its solubility and stability.
- Tissue penetration: To improve tissue penetration, different delivery methods such as intra-tumoral injection or topical application may be explored.
- Specificity: Specificity can be improved by utilizing targeting strategies such as ligand conjugation to the dye or by using activatable dyes that are only activated in cancer cells.
- Photobleaching: Photobleaching can be reduced by optimizing the dye concentration and light dose, as well as by using photostable dyes.
- Toxicity: Toxicity can be minimized by using lower doses of the dye and light, as well as by optimizing the drug delivery method to minimize off-target effects.
- Regulatory approval: It is important to follow established regulatory guidelines for drug development and clinical trials to ensure safety and efficacy before seeking regulatory approval for clinical use.
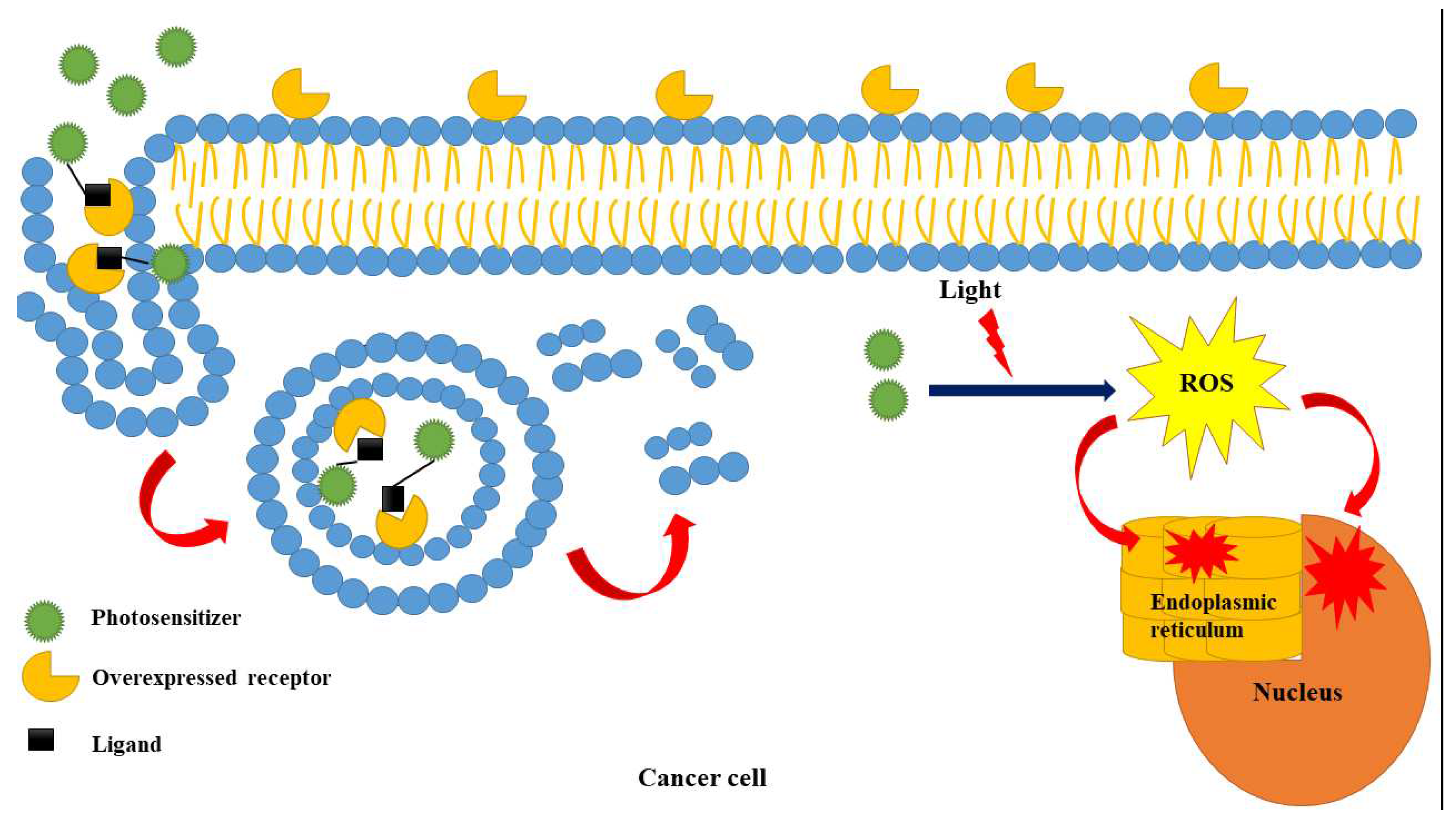
- Tumor targeting: Tumor targeting can be achieved through the use of targeted delivery systems, such as nanoparticles, stem cell derived exosomes or liposomes [84,85,86,87], which can be conjugated with specific ligands or antibodies that recognize and bind to tumor cells. This can increase the accumulation of the photosensitizer in the tumor, while minimizing its uptake in healthy tissues, thereby improving the selectivity of PDT and reducing off-target effects. Another approach is to use light sources with a specific wavelength that can selectively activate the photosensitizer in the tumor, while minimizing activation in surrounding healthy tissues.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Data collection and extraction for bibliometric analysis
3.2. Molecular interactions and docking studies of receptors that are overexpressed in cervical cancer cells and various dyes that are used in PDT
3.3. Visualization of inter-molecular interaction
3.4. Data collection and extraction for systematic analysis of dyes for PDT of cervical cancer
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Salcedo, M.P.; Phoolcharoen, N.; Schmeler, K.M. Intraepithelial neoplasia of the lower genital tract (cervix, vagina, vulva): etiology, screening, diagnosis, management. In Comprehensive Gynecology; Elsevier: 2021; p. 637.
- Okunade, K.S. Human papillomavirus and cervical cancer. Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology 2020, 40, 602–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilyadova, A.; Ishchenko, A.; Shiryaev, A.; Alekseeva, P.; Efendiev, K.; Karpova, R.; Loshchenov, M.; Loschenov, V.; Reshetov, I. Phototheranostics of Cervical Neoplasms with Chlorin e6 Photosensitizer. Cancers (Basel) 2022, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsui, T.; Tamoto, R.; Iwasa, A.; Mimura, M.; Taniguchi, S.; Hasegawa, T.; Sudo, T.; Mizuno, H.; Kikuta, J.; Onoyama, I. Nonlinear Optics with Near-Infrared Excitation Enable Real-Time Quantitative Diagnosis of Human Cervical CancersNovel Cancer Diagnosis with Nonlinear Optical Imaging. Cancer Research 2020, 80, 3745–3754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Y.; Tamadon, A.; Hsueh, A.J.W. Imaging the ovary. Reproductive BioMedicine Online 2018, 36, 584–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yurttaş, A.G.; Sevim, A.M.; Çınar, K.; Atmaca, G.Y.; Erdoğmuş, A.; Gül, A. The effects of zinc (II) phthalocyanine photosensitizers on biological activities of epitheloid cervix carcinoma cells and precise determination of absorbed fluence at a specific wavelength. Dyes and Pigments 2022, 198, 110012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Li, Z.; Xu, Z.; Tang, Y.; Duan, C.; Dai, H.; Dai, X.; Wei, X.; Liu, Y.; Xu, C. Reactive Oxygen Species-Based Nanotherapeutics for Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Materials & Design, 2022; 223, 111194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cang, W.; Gu, L.; Hong, Z.; Wu, A.; Di, W.; Qiu, L. Effectiveness of photodynamic therapy with 5-aminolevulinic acid on HPV clearance in women without cervical lesions. Photodiagnosis and photodynamic therapy 2021, 34, 102293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, C.; Li, L.; Wang, S.; Xu, Y.; Wang, L.; Huang, Y.; Hieawy, A.; Liu, H.; Ma, J. Advances in nanomaterials for the diagnosis and treatment of head and neck cancers: a review. Bioactive Materials 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, A.; Li, Q.; Ling, J.; Gu, L.; Hong, Z.; Di, W.; Qiu, L. Effectiveness of photodynamic therapy in women of reproductive age with cervical high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions (HSIL/CIN2). Photodiagnosis and photodynamic therapy 2021, 36, 102517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alrajjal, A.; Pansare, V.; Choudhury, M.S.R.; Khan, M.Y.A.; Shidham, V.B. Squamous intraepithelial lesions (SIL: LSIL, HSIL, ASCUS, ASC-H, LSIL-H) of uterine cervix and bethesda system. Cytojournal 2021, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, M.; Zhao, S.; Liu, W.; Lee, C.S.; Zhang, W.; Wang, P. Photosensitizers for photodynamic therapy. Advanced healthcare materials 2019, 8, 1900132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Ding, L.; Bai, L.; Chen, X.; Kang, H.; Hou, L.; Wang, J. Folate receptor alpha is associated with cervical carcinogenesis and regulates cervical cancer cells growth by activating ERK1/2/c-Fos/c-Jun. Biochemical and biophysical research communications 2017, 491, 1083–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, N.; Wei, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Wang, X.; Wang, Q.; Chen, D.; Li, W. Iron metabolism protein transferrin receptor 1 involves in cervical cancer progression by affecting gene expression and alternative splicing in HeLa cells. Genes & genomics 2022, 44, 637–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, J.L.; Martins-Cardoso, K.; Guimarães, I.S.; De Melo, A.C.; Lopes, A.H.; Monteiro, R.Q.; Almeida, V.H. Interplay between EGFR and the platelet-activating factor/PAF receptor signaling axis mediates aggressive behavior of cervical cancer. Frontiers in Oncology 2020, 10, 557280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, J.; Kim, H.; Jeong, Y.-I.; Yang, H.S. CD44 receptor-mediated/reactive oxygen species-sensitive delivery of nanophotosensitizers against cervical cancer cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2022, 23, 3594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Javed, S.; Sood, S.; Rai, B.; Bhattacharyya, S.; Bagga, R.; Srinivasan, R. ALDH1 & CD133 in invasive cervical carcinoma & their association with the outcome of chemoradiation therapy. The Indian journal of medical research 2021, 154, 367. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.; Cai, L.; Du, X.; Zhao, J.; Zhao, Y.; Zou, C.; Yu, S.; Zhang, C.; Ye, P.; Su, X. Anti-tumour effect of in situ vaccines combined with VEGFR inhibitors in the treatment of metastatic cervical cancer. International Immunopharmacology 2021, 101, 108302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- VanHeyst, K.A.; Choi, S.H.; Kingsley, D.T.; Huang, A.Y. Ectopic Tumor VCAM-1 Expression in Cancer Metastasis and Therapy Resistance. Cells 2022, 11, 3922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zou, H.; Shen, Y.; Deng, S.; Wu, Y. Synthesis and evaluation of 68Ga-labeled dimeric cNGR peptide for PET imaging of CD13 expression with ovarian cancer xenograft. Journal of Cancer 2021, 12, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Ma, X.; Jin, Y.; Zhang, J.; Li, Y.; Tang, Y.; Song, Y.; Wang, S. Chlorin e6-biotin conjugates for tumor-targeting photodynamic therapy. Molecules 2021, 26, 7342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trott, O.; Olson, A.J. AutoDock Vina: improving the speed and accuracy of docking with a new scoring function, efficient optimization, and multithreading. Journal of computational chemistry 2010, 31, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Chen, J.; Cheng, T.; Gindulyte, A.; He, J.; He, S.; Li, Q.; Shoemaker, B.A.; Thiessen, P.A.; Yu, B. PubChem 2023 update. Nucleic Acids Research 2023, 51, D1373–D1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- BIOVIA, D.S. Software product name. Software version], San Diego: Dassault Systèmes,[Year]. Please note that all current BIOVIA software products start with the company name, and should be referenced as such. All products can be found at https://3ds. com/products-services/biovia/products 2019.
- Unanyan, A.; Pivazyan, L.; Davydova, J.; Murvatova, K.; Khrapkova, A.; Movsisyan, R.; Ishchenko, A.; Ishchenko, A. Efficacy of photodynamic therapy in women with HSIL, LSIL and early stage squamous cervical cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Photodiagnosis and photodynamic therapy 2021, 36, 102530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, W.; Sun, C.; Jiang, G.; Xin, Y. Recent developments of nanoparticles in the treatment of photodynamic therapy for cervical cancer. Anti-Cancer Agents in Medicinal Chemistry (Formerly Current Medicinal Chemistry-Anti-Cancer Agents) 2019, 19, 1809–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gierlich, P.; Mata, A.I.; Donohoe, C.; Brito, R.M.; Senge, M.O.; Gomes-da-Silva, L.C. Ligand-targeted delivery of photosensitizers for cancer treatment. Molecules 2020, 25, 5317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Su, Y.; Tang, Y.; Qin, L.; Shen, Y.; Wang, B.; Zhou, M.; Zhou, Y.; Cao, L.; Zhang, T. Comparative study of topical 5-aminolevulinic acid photodynamic therapy (5-ALA-PDT) and surgery for the treatment of high-grade vaginal intraepithelial neoplasia. Photodiagnosis and Photodynamic Therapy 2022, 39, 102958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vendette, A.C.F.; Piva, H.L.; Muehlmann, L.A.; de Souza, D.A.; Tedesco, A.C.; Azevedo, R.B. Clinical treatment of intra-epithelia cervical neoplasia with photodynamic therapy. International Journal of Hyperthermia 2020, 37, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murakami, H.; Matsuya, M.; Adachi, M.; Itoh, T.; Shibata, T.; Nakayama, T.; Okazaki, S.; Itoh, H.; Kanayama, N. Photodynamic Therapy Using Talaporfin Sodium for Cervical Intraepithelial Neoplasia. The Journal of Japan Society for Laser Surgery and Medicine 2020, 40, 381–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, H.; Yan, J.; Zhou, Z.; Shen, S.; Wu, Y.; Liu, P.; Zhang, H.; Wang, X. A chlorin e6 derivative-mediated photodynamic therapy for patients with cervical and vaginal low-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions: a retrospective analysis. Translational Biophotonics 2022, e202200006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodgkinson, N.; Kruger, C.A.; Mokwena, M.; Abrahamse, H. Cervical cancer cells (HeLa) response to photodynamic therapy using a zinc phthalocyanine photosensitizer. Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology B: Biology 2017, 177, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichimura, H.; Yamaguchi, S.; Kojima, A.; Tanaka, T.; Niiya, K.; Takemori, M.; Hasegawa, K.; Nishimura, R. Eradication and reinfection of human papillomavirus after photodynamic therapy for cervical intraepithelial neoplasia. International journal of clinical oncology 2003, 8, 322–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallegos, E.R.; Rodrı́guez, I.D.; Guzmán, L.A.M.n.; Zapata, A.J.P. In vitro study of biosynthesis of protoporphyrin IX induced by δ-aminolevulinic acid in normal and cancerous cells of the human cervix. Archives of Medical Research 1999, 30, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenthal, D.I.; Nurenberg, P.; Becerra, C.R.; Frenkel, E.P.; Carbone, D.P.; Lum, B.L.; Miller, R.; Engel, J.; Young, S.; Miles, D. A phase I single-dose trial of gadolinium texaphyrin (Gd-Tex), a tumor selective radiation sensitizer detectable by magnetic resonance imaging. Clinical cancer research 1999, 5, 739–745. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cheng, M.H.; Overchuk, M.; Rajora, M.A.; Lou, J.W.; Chen, Y.; Pomper, M.G.; Chen, J.; Zheng, G. Targeted Theranostic 111In/Lu-Nanotexaphyrin for SPECT Imaging and Photodynamic Therapy. Molecular pharmaceutics 2021, 19, 1803–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Xiong, Z.; Wu, D. 5-aminolevulinic acid-mediated photodynamic therapy effectively ameliorates HPV-infected cervical intraepithelial neoplasia. Am J Transl Res 2022, 14, 2443–2451. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yuehui, S.; Zhang, Y.; Tong, Y.; Zhang, L.; Li, P.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, X.; Tang, Y.; Qin, L.; Shen, Y. Effect and rational application of topical photodynamic therapy (PDT) with 5-aminolevulinic acid (5-ALA) for treatment of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia with vaginal intraepithelial neoplasia. Photodiagnosis and photodynamic therapy 2022, 37, 102634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Zheng, H.; Chen, X.; Qi, N. Comparison of the efficacy of ALA and high-frequency electric ion operating on cervical intraepithelial neoplasia grade I. Int J Clin Exp Med 2016, 9, 16782–16786. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, L.; Gao, X.; Geng, L.; You, K.; Wu, Z.; Li, Y.; Han, Q.; Wang, Y.; Guo, H. Efficacy and safety of photodynamic therapy mediated by 5-aminolevulinic acid for the treatment of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia 2: A single-center, prospective, cohort study. Photodiagnosis Photodyn Ther 2021, 36, 102472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizuno, M.; Mitsui, H.; Kajiyama, H.; Teshigawara, T.; Inoue, K.; Takahashi, K.; Ishii, T.; Ishizuka, M.; Nakajima, M.; Kikkawa, F. Efficacy of 5-aminolevulinic acid and LED photodynamic therapy in cervical intraepithelial neoplasia: A clinical trial. Photodiagnosis and Photodynamic Therapy 2020, 32, 102004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, J.; Cheng, M.; Hong, Z.; Ling, J.; Di, W.; Gu, L.; Qiu, L. The effect of 5-Aminolaevulinic Acid Photodynamic Therapy versus CO(2) laser in the Treatment of Cervical Low-grade Squamous Intraepithelial Lesions with High-Risk HPV Infection: A non-randomized, controlled pilot study. Photodiagnosis Photodyn Ther 2021, 36, 102548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; You, L.; Zhang, W.; Ma, Y.; Tang, Y.; Xu, W. Evaluation of 5-aminolevulinic acid-mediated photodynamic therapy on cervical low-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions with high-risk HPV infection. Photodiagnosis Photodyn Ther 2022, 38, 102807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Xu, J.; Wu, H.; Wang, Y.; Zeng, J.; Li, H.; Chi, H.; Qiu, H.; Gu, Y. Topical 5-Aminolevulinic Acid-Mediated Photodynamic Therapy versus Loop Electrosurgical Excision Procedure in the Treatment of Cervical Intraepithelial Neoplasia: A retrospective study, 2012–2019. Authorea Preprints 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Inada, N.M.; Buzzá, H.H.; Leite, M.F.M.; Kurachi, C.; Trujillo, J.R.; de Castro, C.A.; Carbinatto, F.M.; Lombardi, W.; Bagnato, V.S. Long term effectiveness of photodynamic therapy for CIN treatment. Pharmaceuticals 2019, 12, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Y.; Bao, Y.; Hui, Y.; Gao, X.; Yang, M.; Chang, J. Topical photodynamic therapy with 5-aminolevulinic acid for cervical high-risk HPV infection. Photodiagnosis and photodynamic therapy 2016, 13, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnett, A.A.; Haller, J.C.; Cairnduff, F.; Lane, G.; Brown, S.B.; Roberts, D.J. A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of photodynamic therapy using 5-aminolaevulinic acid for the treatment of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia. International journal of cancer 2003, 103, 829–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ran, R.; Wang, M.; Li, X.; Liu, Q. A prospective study of photodynamic therapy for cervical squamous intraepithelial lesion. Photodiagnosis and photodynamic therapy 2021, 34, 102185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, H.; Che, Y.; Sun, X.; Yu, X.; Yu, F.; Hou, F.; Wang, Y.; Ma, T. Clinical outcome of photodynamic therapy for the treatment of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia grade 2. Photodiagnosis and Photodynamic Therapy 2022, 39, 102906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Tong, Y.; Zhang, L.; Li, P.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, X.; Tang, Y.; Qin, L.; Shen, Y.; et al. Effect and rational application of topical photodynamic therapy (PDT) with 5-aminolevulinic acid (5-ALA) for treatment of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia with vaginal intraepithelial neoplasia. Photodiagnosis and Photodynamic Therapy 2022, 37, 102634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maldonado Alvarado, E.; Osorio Peralta, M.O.; Moreno Vázquez, A.; Martínez Guzmán, L.A.; Melo Petrone, M.E.; Enriquez Mar, Z.I.; Jovel Galdamez, D.E.; Carrión Solana, B.; Balderas Martínez, G.; Parra, E. Effectiveness of photodynamic therapy in elimination of HPV-16 and HPV-18 associated with CIN I in Mexican women. Photochemistry and photobiology 2017, 93, 1269–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afanasiev, M.S.; Dushkin, A.D.; Grishacheva, T.G.; Afanasiev, S.S.; Academician, A.V.K. Photodynamic therapy for early-stage cervical cancer treatment. Photodiagnosis and Photodynamic Therapy 2022, 37, 102620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillemanns, P.; Garcia, F.; Petry, K.U.; Dvorak, V.; Sadovsky, O.; Iversen, O.E.; Einstein, M.H. A randomized study of hexaminolevulinate photodynamic therapy in patients with cervical intraepithelial neoplasia 1/2. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2015, 212, 465.e461–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, S.; Tsuda, H.; Takemori, M.; Nakata, S.; Nishimura, S.; Kawamura, N.; Hanioka, K.; Inoue, T.; Nishimura, R. Photodynamic therapy for cervical intraepithelial neoplasia. Oncology 2005, 69, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, Y.; Qin, L.; Shen, Y.; Wang, B.; Zhang, L.; Cao, L.; Zhou, Y.; Su, Y.; et al. The effect of high-risk HPV E6/E7 mRNA on the efficacy of topical photodynamic therapy with 5-aminolevulinic acid for cervical high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions. Photodiagnosis Photodyn Ther 2022, 39, 102974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keefe, K.A.; Tadir, Y.; Tromberg, B.; Berns, M.; Osann, K.; Hashad, R.; Monk, B.J. Photodynamic therapy of high-grade cervical intraepithelial neoplasia with 5-aminolevulinic acid. Lasers in Surgery and Medicine: The Official Journal of the American Society for Laser Medicine and Surgery 2002, 31, 289–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hillemanns, P.; Korell, M.; Schmitt-Sody, M.; Baumgartner, R.; Beyer, W.; Kimmig, R.; Untch, M.; Hepp, H. Photodynamic therapy in women with cervical intraepithelial neoplasia using topically applied 5-aminolevulinic acid. International journal of cancer 1999, 81, 34–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Xu, J.; Chen, J.; He, Q.; Xiang, L.; Huang, X.; Ding, G.; Xu, S. Successful photodynamic therapy with topical 5-aminolevulinic acid for five cases of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia. Archives of gynecology and obstetrics 2010, 282, 307–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Liu, X.; Zhang, J.; Huang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Jia, L.; Zhang, Y.; Jia, L. Evaluation of the efficacy and safety of 5-aminolevulinic acid-mediated photodynamic therapy in women with high-risk HPV persistent infection after cervical conization. Photodiagnosis Photodyn Ther 2022, 40, 103144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Su, Y.; Zhang, C.; Zhou, M.; Yuan, S.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, Y.; Cao, L.; Zhang, M.; et al. The effect of local photodynamic therapy with 5-aminolevulinic acid in treating different grades of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia. Photodiagnosis Photodyn Ther 2022, 40, 103196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, Z.; Wang, Z.; Qiu, S.; Cui, G.; Li, C. Efficacy of photodynamic therapy with 5-aminolevulinic acid for the treatment of cervical high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions with high-risk HPV infection: A retrospective study. Photodiagnosis Photodyn Ther 2022, 40, 103068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Su, Y.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, Y.; Qin, L.; Zhang, L.; Cao, L.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, T.; et al. Therapeutic effects of topical photodynamic therapy with 5-aminolevulinic acid on cervical high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions. Photodiagnosis Photodyn Ther 2022, 39, 102884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, Y.-K.; Park, C.-H. Clinical efficacy of photodynamic therapy. Obstetrics & gynecology science 2016, 59, 479–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Istomin, Y.P.; Lapzevich, T.P.; Chalau, V.N.; Shliakhtsin, S.V.; Trukhachova, T.V. Photodynamic therapy of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia grades II and III with Photolon®. Photodiagnosis and Photodynamic Therapy 2010, 7, 144–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, M.C.; Jung, S.G.; Park, H.; Lee, S.Y.; Lee, C.; Hwang, Y.Y.; Kim, S.J. Photodynamic therapy for management of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia II and III in young patients and obstetric outcomes. Lasers in Surgery and Medicine 2013, 45, 564–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.; Choi, M.C.; Lee, C.; Na, Y.J.; Kim, S.J. Long-term outcomes of photodynamic therapy for a positive resection margin after conization for cervical intraepithelial neoplasia grade 3. Photodiagnosis and Photodynamic Therapy 2022, 37, 102639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trushina, O.I.; Novikova, E.G.; Sokolov, V.V.; Filonenko, E.V.; Chissov, V.I.; Vorozhtsov, G.N. Photodynamic therapy of virus-associated precancer and early stages cancer of cervix uteri. Photodiagnosis and Photodynamic Therapy 2008, 5, 256–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soergel, P.; Wang, X.; Stepp, H.; Hertel, H.; Hillemanns, P. Photodynamic therapy of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia with hexaminolevulinate. Lasers in Surgery and Medicine: The Official Journal of the American Society for Laser Medicine and Surgery 2008, 40, 611–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Matos, R.P.A.; Calmon, M.F.; Amantino, C.F.; Villa, L.L.; Primo, F.L.; Tedesco, A.C.; Rahal, P. Effect of curcumin-nanoemulsion associated with photodynamic therapy in cervical carcinoma cell lines. BioMed research international 2018, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, G.; Mu, T.; Yuan, Y.; Yang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Q.; Bian, M.; Pan, Y.; Xiang, Q.; Chen, Z. Effects of notch signaling pathway in cervical cancer by curcumin mediated photodynamic therapy and its possible mechanisms in vitro and in vivo. Journal of Cancer 2019, 10, 4114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Jiao, R.; Chen, X.; Zhong, J.; Ji, J.; Shen, P. Methylene blue-mediated photodynamic therapy induces mitochondria-dependent apoptosis in HeLa Cell. Journal of cellular biochemistry 2008, 105, 1451–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, B.C.L.; Dharmaratne, P.; Wang, B.; Lau, K.M.; Lee, C.C.; Cheung, D.W.S.; Chan, J.Y.W.; Yue, G.G.L.; Lau, C.B.S.; Wong, C.K. Hypericin and pheophorbide a mediated photodynamic therapy fighting MRSA wound infections: a translational study from in vitro to in vivo. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.; Chen, S.; Du, Z.; Yan, T.; Alimu, G.; Zhu, L.; Ma, R.; Alifu, N.; Zhang, X. New indocyanine green therapeutic fluorescence nanoprobes assisted high-efficient photothermal therapy for cervical cancer. Dyes and Pigments 2022, 200, 110174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorbani, F.; Attaran-Kakhki, N.; Sazgarnia, A. The synergistic effect of photodynamic therapy and photothermal therapy in the presence of gold-gold sulfide nanoshells conjugated Indocyanine green on HeLa cells. Photodiagnosis and photodynamic therapy 2017, 17, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, D.-J. Methylene Blue-Based Nano and Microparticles: Fabrication and Applications in Photodynamic Therapy. Polymers 2021, 13, 3955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.; Hsu, C.-H.; Huang, C.-C.; Chang, P.-Y. Development of therapeutic Au–methylene blue nanoparticles for targeted photodynamic therapy of cervical cancer cells. ACS applied materials & interfaces 2015, 7, 432–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaturvedi, P.K.; Kim, Y.-W.; Kim, S.S.; Ahn, W.S. Phototoxic effects of pyropheophorbide-a from chlorophyll-a on cervical cancer cells. Journal of Porphyrins and Phthalocyanines 2014, 18, 182–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.B.; Minocha, T.; Yadav, S.K.; Parmar, A.S. Therapeutic Potential of Chlorophyll Functionalized Carbon Quantum Dots against Cervical Cancer. ChemistrySelect 2022, 7, e202204562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiriyanthan, R.M.; Sharmili, S.A.; Balaji, R.; Jayashree, S.; Mahboob, S.; Al-Ghanim, K.A.; Al-Misned, F.; Ahmed, Z.; Govindarajan, M.; Vaseeharan, B. Photocatalytic, antiproliferative and antimicrobial properties of copper nanoparticles synthesized using Manilkara zapota leaf extract: A photodynamic approach. Photodiagnosis and Photodynamic Therapy 2020, 32, 102058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.Y.; Balasubramanian, T.; Yang, E.; Luo, D.; Diers, J.R.; Bocian, D.F.; Lindsey, J.S.; Holten, D.; Hamblin, M.R. Stable synthetic bacteriochlorins for photodynamic therapy: role of dicyano peripheral groups, central metal substitution (2H, Zn, Pd), and Cremophor EL delivery. ChemMedChem 2012, 7, 2155–2167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.-Y.; Sharma, S.K.; Yin, R.; Agrawal, T.; Chiang, L.Y.; Hamblin, M.R. Functionalized fullerenes in photodynamic therapy. Journal of biomedical nanotechnology 2014, 10, 1918–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otake, E.; Sakuma, S.; Torii, K.; Maeda, A.; Ohi, H.; Yano, S.; Morita, A. Effect and mechanism of a new photodynamic therapy with glycoconjugated fullerene. Photochemistry and photobiology 2010, 86, 1356–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baghban, N.; Khoradmehr, A.; Nabipour, I.; Tamadon, A.; Ullah, M. The potential of marine-based gold nanomaterials in cancer therapy: A mini-review. Gold Bulletin 2022, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baghban, N.; Khoradmehr, A.; Afshar, A.; Jafari, N.; Zendehboudi, T.; Rasekh, P.; Abolfathi, L.G.; Barmak, A.; Mohebbi, G.; Akmaral, B. MRI Tracking of Marine Proliferating Cells In Vivo Using Anti-Oct4 Antibody-Conjugated Iron Nanoparticles for Precision in Regenerative Medicine. Biosensors 2023, 13, 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afshar, A.; Zare, M.; Farrar, Z.; Hashemi, A.; Baghban, N.; Khoradmehr, A.; Habibi, H.; Nabipour, I.; Shirazi, R.; Behzadi, M.A. Exosomes of mesenchymal stem cells as nano-cargos for anti-SARS-CoV-2 asRNAs. Modern Medical Laboratory Journal 2021, 4, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehpour, A.; Balmagambetova, S.; Mussin, N.; Kaliyev, A.; Rahmanifar, F. Mesenchymal stromal/stem cell-derived exosomes and genitourinary cancers: A mini review. Frontiers in cell and developmental biology 2023, 10, 1115786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nowzari, F.; Wang, H.; Khoradmehr, A.; Baghban, M.; Baghban, N.; Arandian, A.; Muhaddesi, M.; Nabipour, I.; Zibaii, M.I.; Najarasl, M.; et al. Three-Dimensional Imaging in Stem Cell-Based Researches. Frontiers in Veterinary Science 2021, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
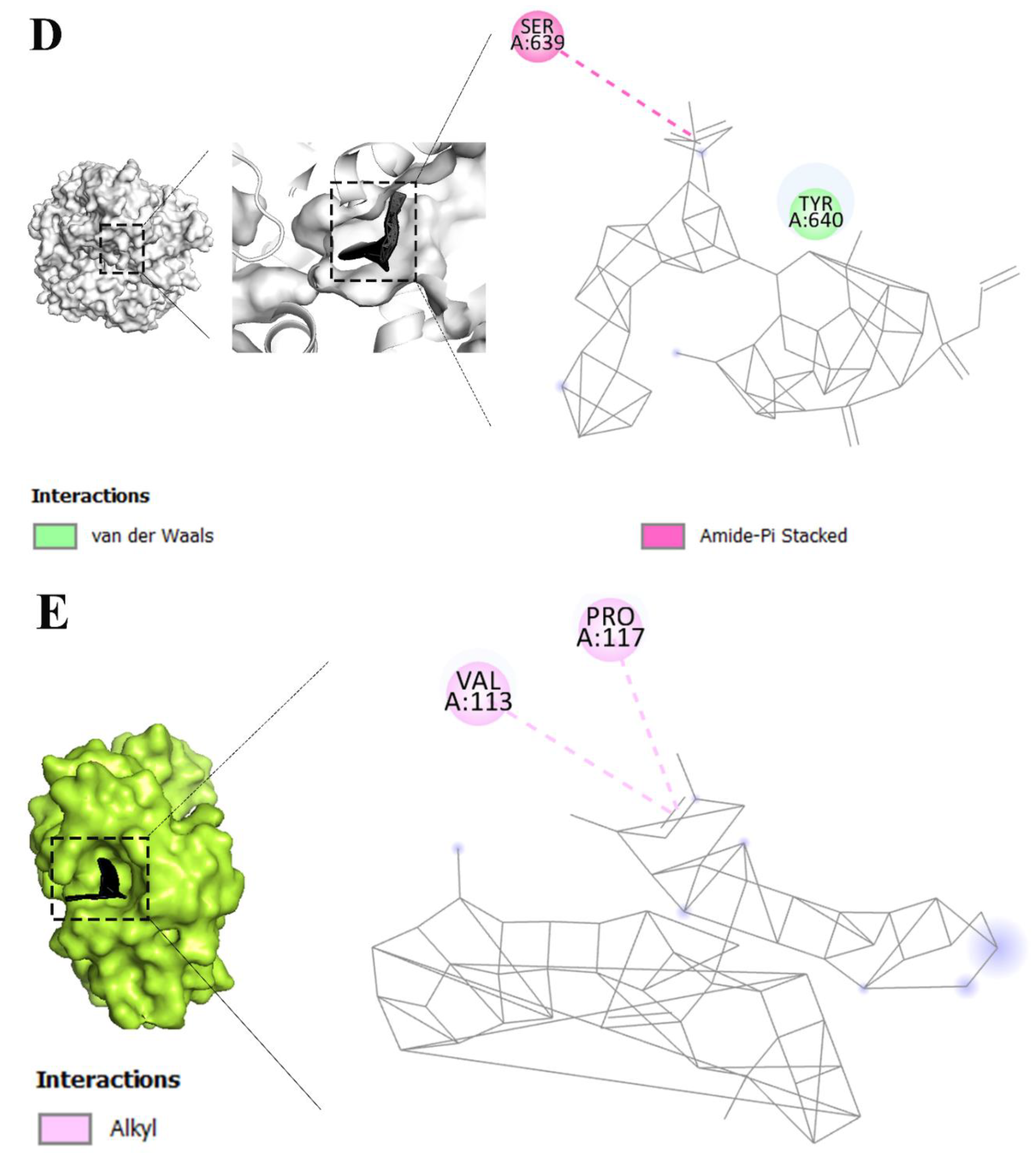

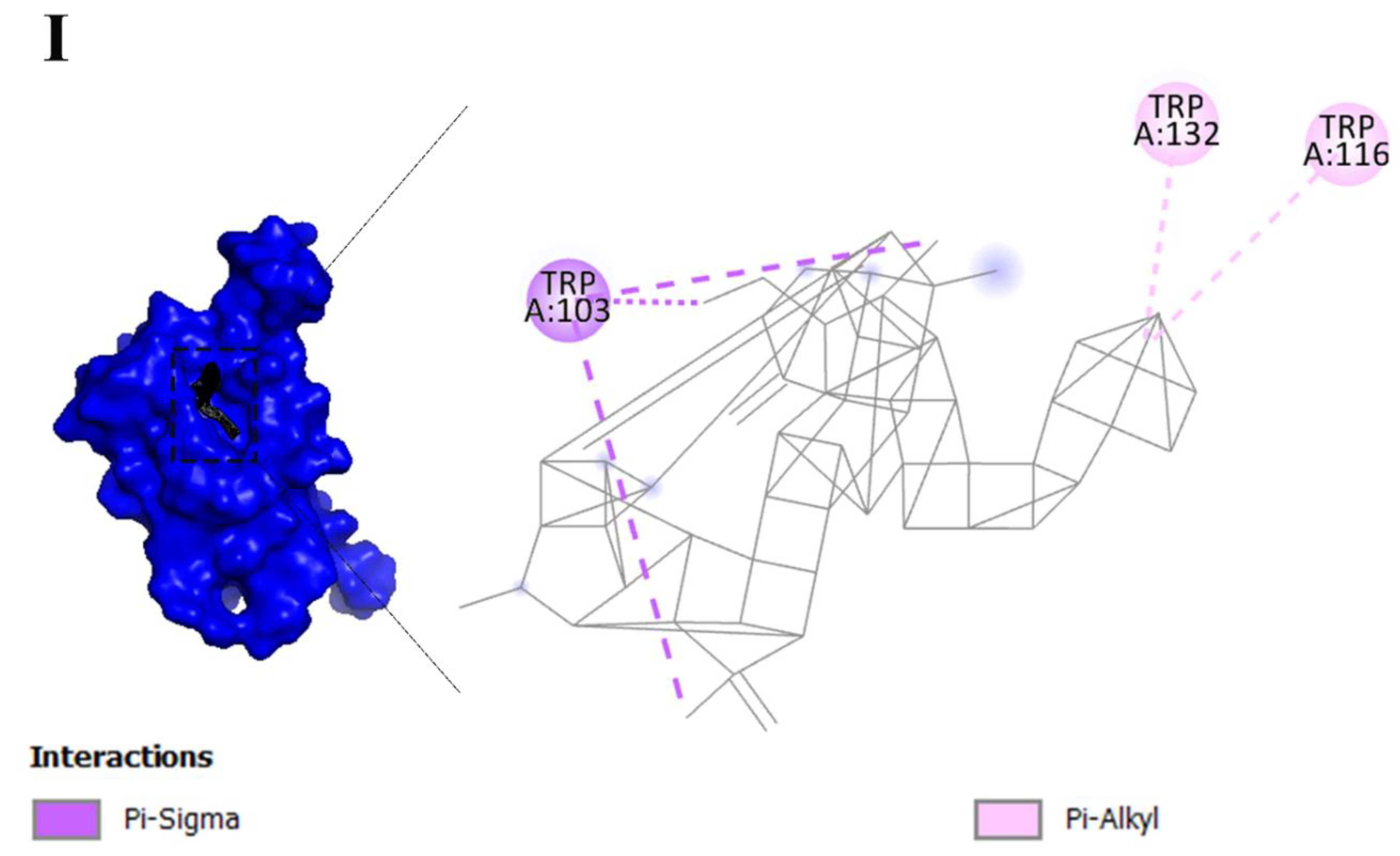
| Keywords | Cluster | Link | Total link strength | Occurrence |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Photo chemotherapy | 2 | 35 | 692 | 110 |
| Nanoparticles | 2 | 35 | 525 | 84 |
| Photosensitizing agents | 2 | 35 | 523 | 78 |
| Receptor | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dye | FRα* | TR1 | EGFR | CD13 | CD44 | CD133 | VCAM-1 | VEGFR | BR |
| 5-aminolevulinic acid | -5.3 | -5.0 | -4.4 | -5.3 | -4.5 | -3.2 | -4.2 | -3.2 | -5.1 |
| Protoporphyrin IX | -10.1 | -9.9 | -11.0 | -11.5 | -8.6 | -5.5 | -8.4 | -6.6 | -10.1 |
| Hematoporphyrin | -8.4 | -9.9 | -10.7 | -11.0 | -8.5 | -5.6 | -8.7 | -6.4 | -9.5 |
| Zinc phthalocyanine | -14.8 | -13.9 | -15.9 | -15.7 | -12.3 | -8.4 | -11.5 | -9.7 | -15.0 |
| Chlorin e6 | -11.5 | -10.9 | -9.9 | -12.7 | -9.5 | -6.6 | -9.3 | -7.4 | -11.8 |
| Talaporfin Sodium | -13.1 | -13.3 | -13.5 | -17.0 | -12.3 | -8.2 | -12.4 | -8.6 | -13.3 |
| Indocyanine Green (ICG) | -15.8 | -10.7 | -10.7 | -12.7 | -8.9 | -7.5 | -8.1 | -6.6 | -11.2 |
| Rose Bengal | -11.9 | -12.6 | -9.9 | -13.4 | -11.4 | -7.4 | -10.2 | -7.9 | -9.6 |
| Photofrin | -9.8 | -9.6 | -10.8 | -11.2 | -8.5 | -5.6 | -8.5 | -6.6 | -9.7 |
| Hypericin | -13.3 | -13.8 | -16.0 | -15.3 | -14.1 | -7.8 | -12.2 | -10.0 | -12.4 |
| Methylene Blue | -10.5 | -8.1 | -8.1 | -8.2 | -6.8 | -5.0 | -6.6 | -4.9 | -8.6 |
| Curcumin | -10.9 | -8.8 | -7.8 | -8.2 | -7.3 | -5.6 | -6.7 | -5.5 | -8.9 |
| Texaphyrin | -10.9 | -11.6 | -11.8 | -11.8 | -10.7 | -7.1 | -8.6 | -7.2 | -10.7 |
| Bacteriochlorin | -12.6 | -10.3 | -11.0 | -10.8 | -10.3 | -6.5 | -8.3 | -7.2 | -9.4 |
| Fullerene | -39.1 | -30.1 | -22.7 | -28.4 | -26.8 | -19.9 | -22.3 | -23.0 | -29.3 |
| Eosin | -13.0 | -13.1 | -14.0 | -13.6 | -12.1 | -7.4 | -10.2 | -8.6 | -11.5 |
| Erythrosine | -10.7 | -11.2 | -10.7 | -11.9 | -10.2 | -6.9 | -8.6 | -7.5 | -9.8 |
| Methyl Violet | -11.7 | -8.4 | -7.6 | -8.4 | -7.0 | -5.5 | -6.5 | -5.7 | -8.0 |
| Aluminum phthalocyanine chloride | -15.3 | -15.6 | -15.0 | -16.2 | -12.9 | -9.0 | -11.5 | -10.2 | -15.1 |
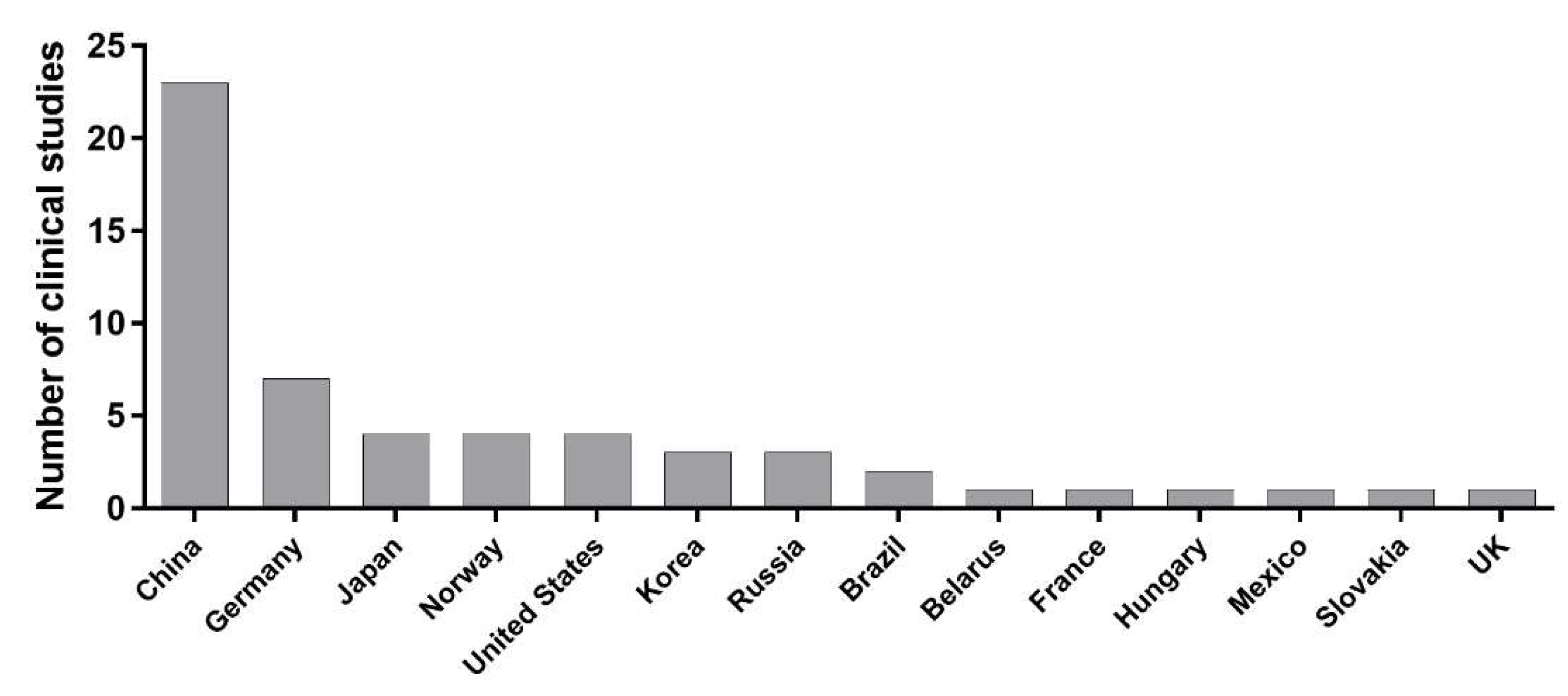
| Dye | Patients | CR (%) | Type | Country | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5-aminolevulinic acid | 115 | 79.0 | Phase 3 | China Hungary Germany Slovakia |
[37] |
| 48 | 88.6 | Retrospective | China | [38] | |
| 110 | 81.8 | Prospective | China | [39] | |
| 97 | 92.0 | Prospective | China | [40] | |
| 51 | 79.4 | Prospective | Japan | [41] | |
| 176 | 84.7 | Pilot | China | [42] | |
| 46 | 65.2 | Retrospective | China | [43] | |
| 30 | 73.3 | Retrospective | China | [44] | |
| 66 | 75.0 | Retrospective | Brazil USA |
[45] | |
| 39 | 76.9 | Prospective | China | [46] | |
| 12 | 33.0 | Prospective | UK | [47] | |
| 22 | 63.6 | Prospective | China | [48] | |
| 79 | 90.7 | Prospective | China | [49] | |
| 44 | 88.6 | Retrospective | China | [50] | |
| 30 | 80.0 | Prospective | Mexico |
[51] | |
| 55 | 90.0 | Retrospective | China | [43] | |
| Aluminum phthalocyanine chloride | 11 | 91.7 | Prospective | Brazil | [29] |
| Chlorin e6 | 18 | 88.9 | Prospective | China | [31] |
| 18 | 100 | Prospective | Russia | [3] | |
| Chlorin e6 + Photofrin | 28 | 82.0 | Retrospective | Russia | [52] |
| Hexaminolevulinate | 262 | 95.0 | Phase 2 | Germany Norway |
[53] |
| Photofrin | 105 | 90.0 | Prospective | Japan | [54] |
| Talaporfin sodium | 9 | 88.9 | Prospective | Japan | [30] |
| Dye | Patients | CR (%) | Date | Type | Country | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5-aminolevulinic acid | 148 | 86.5 | 2022 | Retrospective | China | [55] |
| 32 | 31.0 | 2002 | Phase 1&2 | United States | [56] | |
| 7 | 42.0 | 1999 | Prospective | Germany | [57] | |
| 8 | 50.0 | 2021 | Prospective | China | [48] | |
| 5 | 80.0 | 2010 | Prospective | China | [58] | |
| 68 | 88.2 | 2022 | Retrospective | China | [59] | |
| 183 | 71.0 | 2022 | Prospective | China | [60] | |
| 96 | 89.5 | 2022 | Retrospective | China | [61] | |
| 99 | 88.9 | 2022 | Retrospective | China | [62] | |
| Porphyrin | 20 | 91.0 | 2016 | Retrospective | Korea | [63] |
| 88 | 53.4 | 2010 | Prospective | Belarus | [64] | |
| 46 | 87.0 | 2013 | Retrospective | Korea | [65] | |
| 34 | 97.1 | 2022 | Retrospective | Korea | [66] | |
| 49 | 90.4 | 2008 | Prospective | Russia | [67] | |
| 28 | 90.0 | 2003 | Prospective | Japan | [33] | |
| Chlorin e6 | 18 | 72.2 | 2022 | Prospective | China | [31] |
| 24 | 70.0 | 2022 | Prospective | Russia | [3] | |
| Hexaminolevulinate | 24 | 63.0 | 2008 | Prospective | Germany | [68] |
| Dye | NCT number | Type of cancer | Status | Country | Start Date | Phase |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lutetium texaphyrin | NCT00005808 | CIN 2 &3 | Terminated | United States | 2000 | 1 |
| Taporfin Sodium | NCT00028405 | CIN | Completed | United States | 2001 | 1 |
| Aminolaevulinic acid | NCT00369018 | CIN | Completed | Germany Norway |
2006 | 1&2 |
| NCT00708942 | CIN | Terminated | France Germany Norway |
2009 | 2 | |
| NCT01256424 | CIN | Completed | Germany Norway |
2011 | 2 | |
| NCT02304770 | Persistent High-Risk HPV Infection CIN |
Completed | China | 2015 | 2 | |
| NCT02631863 | CIN LSIL Papillomavirus Infections |
Completed | China | 2016 | 2 | |
| NCT04484415 | CIN 2 &3 | Completed | China | 2022 | 3 |
| Dye | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Curcumin | Natural compound with low toxicity Anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties Has been shown to induce cell death in cancer cells Potential for tumor-selective accumulation |
Limited water solubility Low bioavailability Requires activation by light |
| Hypericin | High tumor selectivity Good tissue penetration |
Requires activation by light Potential skin photosensitivity |
| Methylene blue | FDA-approved Low toxicity |
Low tumor selectivity Requires high concentrations |
| Indocyanine green | FDA-approved for clinical use High water solubility Can be activated by near-infrared light Allowing for deeper tissue penetration |
Limited tumor selectivity Rapid clearance from the body May require high doses for therapeutic effect Potential for skin photosensitivity and allergic reactions. |
| Rose Bengal | Good tumor selectivity Low toxicity |
Requires activation by light Potential skin photosensitivity |
| Zinc phthalocyanine | High absorbance in the red spectrum Good tumor selectivity |
Low water solubility Potential toxicity |
| Dye | Clinical Studies* | Preclinical Studies | Potential Use | Overall Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5-aminolevulinic acid | 5 | 5 | 5 | 15 |
| Porphyrin derivatives | 5 | 5 | 5 | 15 |
| Zinc phthalocyanine | 5 | 5 | 3 | 13 |
| Chlorin e6 | 4 | 5 | 4 | 13 |
| Talaporfin Sodium | 4 | 4 | 4 | 12 |
| Indocyanine Green (ICG) | 3 | 5 | 4 | 12 |
| Rose Bengal | 4 | 4 | 3 | 11 |
| Photofrin | 5 | 4 | 2 | 11 |
| Hypericin | 2 | 5 | 4 | 11 |
| Methylene Blue | 3 | 4 | 3 | 10 |
| Curcumin | 2 | 4 | 4 | 10 |
| Texaphyrins | 3 | 3 | 3 | 9 |
| Chlorophyll Derivatives | 2 | 3 | 3 | 8 |
| Bacteriochlorins | 2 | 3 | 3 | 8 |
| Fullerenes | 1 | 3 | 2 | 6 |
| Xanthene Dyes (Eosin, Erythrosine) | 1 | 2 | 2 | 5 |
| Methyl Violet | 1 | 2 | 2 | 5 |
| Receptor | Reference |
|---|---|
| Folate receptor α | [13] |
| Transferrin receptor 1 | [14] |
| Epidermal growth factor receptor | [15] |
| CD44 | [16] |
| Prominin 1 (CD133) | [17] |
| Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 | [18] |
| Vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 | [19] |
| Aminopeptidase-N (CD13) | [20] |
| Biotin receptor | [21] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





