1. Introduction
Calcium is a very essential mineral element and one of the fundamental nutrients for plant growth and development, which has necessary physiological features such as maintaining cell morphology, regulating ion homeostasis, and osmotic pressure (Bai et al., 2022; Yang et al., 2014). Both calcium deficiency and immoderate concentrations of calcium have an effect on plant-related physiological and biochemical strategies and are detrimental to plant growth (Aras et al., 2021; Blatt, 2000). When vegetation are deficient in calcium, cell walls can't be formed, affecting cell division and formation, and additionally making ginseng much less resistant to adversity (Yang,2015). Calcium over-treatment can, to some extent, motive injury to the membrane structure of the photosynthetic system, leading to blockage of the electron transport chain and reduced light energy use efficiency in tea leaves, hence affecting the boom of new tea leaves (Wang, et al., 2010). A reasonable quantity of calcium would alleviate the poisonous outcomes of calcium, and 5 mM CaCl2 cure appreciably increased Fv/Fm in seedlings of Tung tree after drought stress (Li et al., 2017). The outcomes of preceding research confirmed that calcium deficiency and calcium excess diminished the boom of Q.acutissima and had been hazardous to the synthesis and accumulation of photosynthetic pigments, the expand of photosynthetic rate, and the synthesis of photosynthetic products, whilst reasonable calcium cure notably promoted the increase of Q.acutissima seedlings and the accumulation of photosynthetic pigments, and elevated the photosynthetic parameters and photosynthetic product content material of the plants (Han, 2018). Previous research on optimum calcium concentration in general centered on single tree species, for example, Huang (2019) determined that the increase and photosynthetic traits of Fig seedlings have been most high-quality beneath pot test conditions with 4 mmol·L-1 calcium treatment, and underneath field test conditions, 200 mmol·L-1 calcium cure used to be most tremendous in growing relative chlorophyll content, etc. Li et al. (2022) discovered that the plant height, basal diameter, and photosynthetic stage of Mongolian pine seedlings reached the most at an exogenous calcium awareness of 10 mmol·L-1. Ren et al. (2020) discovered that the growth, photosynthetic characteristics, and water use effectivity of Fraxinus mandshurica have been ideal at a calcium gradient of 200 mg·kg-1. A multi-species contrast was not conducted, and the leaf qualities of broadleaf and coniferous timber can respond differently to resource changes, and there are crucial variations between these two species in regulating their uptake, metabolism, and water and soil nutrients (Zhang, 2020). Therefore, two coniferous and broadleaf species had been chosen for study and comparison in this experiment, to discover the differences in calcium requirements of coniferous and broadleaf species, and additionally to furnish a reference for the optimum calcium application rate of different tree species. This experiment was performed to investigate the differences in calcium requirements between coniferous and broadleaf species, and to furnish a reference for the optimal amount of calcium application for different species.
Pinus tabuliformis, Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica, Populus, and Morus alba are all vital species for the Three North Protection Forest with important roles in wind control, sand fixation, and soil conservation (Wang et al., 2017; Ahmed et al., 2020). However, in Liaoning Province, improper selection of tree species has been identified as a contributing factor to forest degradation. During the early stages of afforestation, the principle of suitable tree selection for specific environments was not always followed due to outdated concepts and technologies. As a result, the afforestation survival rate was low, and even if trees managed to grow, their resistance to pests and diseases was weakened in later stages, leaving them vulnerable to invasion and significantly diminishing their protection effectiveness (Li et al., 2021; Xu, 2021).Four tree species have declined in the past decades of construction, such as experiencing large-scale decline and mortality in many introduced areas, with problems such as terminal shoot death, premature tree decay and mortality, ecosystem degradation, and frequent pests and diseases (Zhou et al., 2020; Guo et al., 2020; Zhao et al., 2021) .The selection of a suitable tree species for a given site is a fundamental principle of silviculture, and is guided by various factors including soil conditions and biological characteristics of the tree species. Some scholars have suggested the use of the soil's calcium supply potential as an evaluation index for stand quality, and the maximum growth calcium demand of tree species as a biological characteristic index for tree species selection. Matching the maximum growth calcium demand of tree species with the stand's calcium supply potential facilitates the selection of a suitable tree species for the land. In other words, the essence of selecting a suitable tree for a given site lies in selecting a tree species suitable for calcium supply. This principle is crucial for ensuring successful silvicultural production activities (Zhou et al. 2017).Thus, these four tree species were selected to explore the impact of calcium on their growth. The hypothesis being tested is that the ideal calcium concentration differs among various tree species, and that the calcium requirement of broadleaf species differs from that of conifers.
2. Materials and methods
2.1. Cultivation and treatment of seedlings of four tree species
The experiment was carried out at the Beishan Experimental Station of Shenyang Agricultural University. 3-year-old live Pinus tabuliformis seedlings and Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica seedlings, Populus cuttings of "Liao Hu No. 1" and live Morus alba seedlings of the identical dimension were selected from Fujia Forestry Farm, Changtu County, Northwest Liaoning Province, respectively.
The collected soil was sieved and processed to cast off stones and impurities. Accurately weigh 3 kg of test soil combined with 2 kg of quartz sand as potting test soil. Plants of uniform growth were selected and planted into plastic pots with an inner diameter of 15 cm, a depth of 12 cm,and a volume of about 1 L. Different treatments were carried out, and every treatment was repeated three times. After carrying out a period of slowing down, nutrient solution treatments were applied. The calcium gradient in the experiment was provided by anhydrous CaCl2 in 0, 100, 200, 400, and 800 mg·kg-1 5 gradients. Other nutrients were prepared in accordance to Xie's (2014) sand culture nutrient solution formulation with ultrapure water, using NaOH to adjust the nutrient solution pH to 5–6.
2.2. Measurement methods and indicators
2.2.1. Determination of growth
Before calcium treatment of seedlings of various tree species, measure the height of every group of seedlings to 0.10 cm with a ruler, and measure the base diameter to 0.01mm with a Vernier caliper. After calcium treatment, the plant height and basal diameter of seedlings were measured again before harvest.
2.2.2. Determination of biomass
After calcium treatment, the seedlings of every tree species are taken back, washed, and divided into three parts: root, stem, and leaf by pruning. Then put it in the envelope, put it in the 105 ℃ oven for sterilization for 0.5h, then dry it to constant weight at 80 ℃, and weigh its dry weight with a thousandth balance(Li et al., 2022).
2.2.3. Determination of calcium concentration in leaves
The leaves of four tree species seedlings were killed for 0.5h in an oven at 105 ℃ and then dried to constant weight at 80 ℃. Crush the leaves with a pulverizer, and then use a ball mill to crush the leaf samples, pass a 100-mesh sieve, and use the wet ashing method to determine the calcium concentration of plant leaves. Accurately sample 0.1g, put it into a conical flask, add 10mL of mixed acid of nitric acid and perchloric acid (HNO3: HClO4=4:1), put a funnel on the conical flask mouth, and place it on the heating plate, regulate the temperature of the heating plate to gradually increase, make the sample digest to colorless and transparent, then move it into a 50mL volumetric flask and add shielding agent (strontium chloride 30g·L-1), and then use flame atomic absorption spectrophotometer to measure the calcium content of its leaves respectively.
2.2.4. Determination of photosynthetic index
Determination of photosynthetic parameters
Photosynthetic parameters such as net photosynthetic rate (Pn), stomatal conductance (Gs), and transpiration rate (Tr) were measured under sunny weather conditions from 8:30 a.m. to 11:30 a.m. using a Li-6400 photosynthesis system (Li-Cor Inc., Lincoln, USA), and the photosynthetic active radiation (PAR) was controlled at 1000 μmol·m-2·s-1 for Pinus tabuliformis, Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica, Populus, and Morus alba seedlings, respectively. The measurements were repeated three times (Li et al., 2022).
Determination of photosynthetic pigment
Photosynthetic pigments were determined by the ethanol extraction method. Firstly, the centrifuge tubes were numbered, and 0.1g of plant leaves were collected separately according to the number, the main veins were removed and cut and then loaded into the centrifuge tubes according to the number, and 95% ethanol was rapidly added to 9mL followed by 48h extraction by immersion away from light. After that, the absorbance values were measured at 665nm and 649nm, and the contents of chlorophyll a and chlorophyll b were calculated by paying attention to avoiding light during the process.
where Ca and Cb represent chlorophyll a and chlorophyll b, respectively; FW is the fresh weight of the sample of 0.1 g;
Vt is the total volume of the extraction solution of 9 mL; A665 and A649 represent the absorbance values of photosynthetic pigment extracts at 665 nm and 649 nm (Li et al., 2022; Weng et al., 2022).
Determination of photosynthate
The soluble sugar and starch of photosynthate were determined using the anthrone colorimetric method (Zhao, 2002). Weigh 5mg of a dry sample of plant leaves, use anthrone colorimetry to measure the absorbance at 625nm with a spectrophotometer, and then calculate the content of soluble sugar and starch in the leaves of plant seedlings according to the formula:
Where C represents the sugar content found on the standard curve(μg); Vt is the total volume of the extraction solution (mL); V1 is the volume taken for determination (mL); m is the weight of the sample (mg) (Chen and Li, 2016).
2.2.5. Determination of chlorophyll fluorescence parameters
The leaves of Pinus tabuliformis, Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica, Populus, and Morus alba were dark-treated for 20 minutes from 9 a.m. to 11 a.m. under sunny weather conditions. The maximum photochemical efficiency (Fv/Fm) and potential photochemical efficiency (Fv/Fo) of their seedlings under different calcium concentrations were measured by a portable pulse-modulated fluorometer.
2.2.6. Determination of the stress tolerance
Determination of long-term water use efficiency
The long-term water use efficiency of plants was characterized by WUEL values, calculated through the use of δ
13C from the leaves of seedlings of
Pinus tabuliformis,
Pinus sylvestris var.
mongolica,
Populus, and
Morus alba, respectively. After calcium treatment, until the growth distinction occurs, destructive sampling is started. The leaves of
Pinus tabuliformis,
Pinus sylvestris var.
mongolica,
Populus, and
Morus alba seedlings are washed, and then put into an oven at 105 ℃ to kill for 0.5h, and then dried to constant mass at 80 ℃, and ground through a 100-mesh sieve to make samples for standby. Accurately weigh 0.7 mg of the sample and wrap it tightly with a tin boat, and use the DELTAV Advantage Isotope Ratio Mass Spectrometer to determine δ
13C, and then use the formula to calculate the WUEL value (Song et al., 2015; Li et al., 2022):
In the formula, A represents net photosynthetic rate, Gs represents stomatal conductance, Ca and Ci are the concentrations of CO2 in the atmosphere and leaf cells, a and b are the partial effects of CO2 diffusion to the stomata and the partial effects of stomatal photosynthetic carboxylase RUBP on carbon isotopes.
Determination of antioxidant enzymes
For the determination of antioxidant enzymes, a 0.4 g sample was extracted from fresh leaves, stored in a frozen tube, fixed with liquid nitrogen, and stored at -80°C. For measurements, samples were taken according to the markers and placed in a mortar. Then, 5 ml of pre-cooled phosphate buffer was added, and the sample was ground and centrifuged at 13,000 rpm for 15 min at 4°C. The supernatant was placed in a centrifuge tube for stock (each sample was repeated 3 times). Peroxidase (POD) levels were determined by the guaiacol method. Catalase (CAT) levels were determined by the ultraviolet absorption of hydrogen peroxide. Superoxide dismutase (SOD) levels were determined by methionine (Perveen et al., 2020; Sheng et al., 2023).
2.2.7. Statistical Analysis
Use Excel and SPSS22 software programs to sort out and plot the test data, and conduct necessary statistical analysis and difference analysis. The data in the figure is the mean value ± standard error(SE) of three repetitions, and the single factor analysis of variance and Duncan’s new multiple extreme difference method are used. The error line in the text is expressed by the standard error, and the different letters in the chart indicate that the difference of each index between different calcium levels is up to a 5% significant level.
3. Results
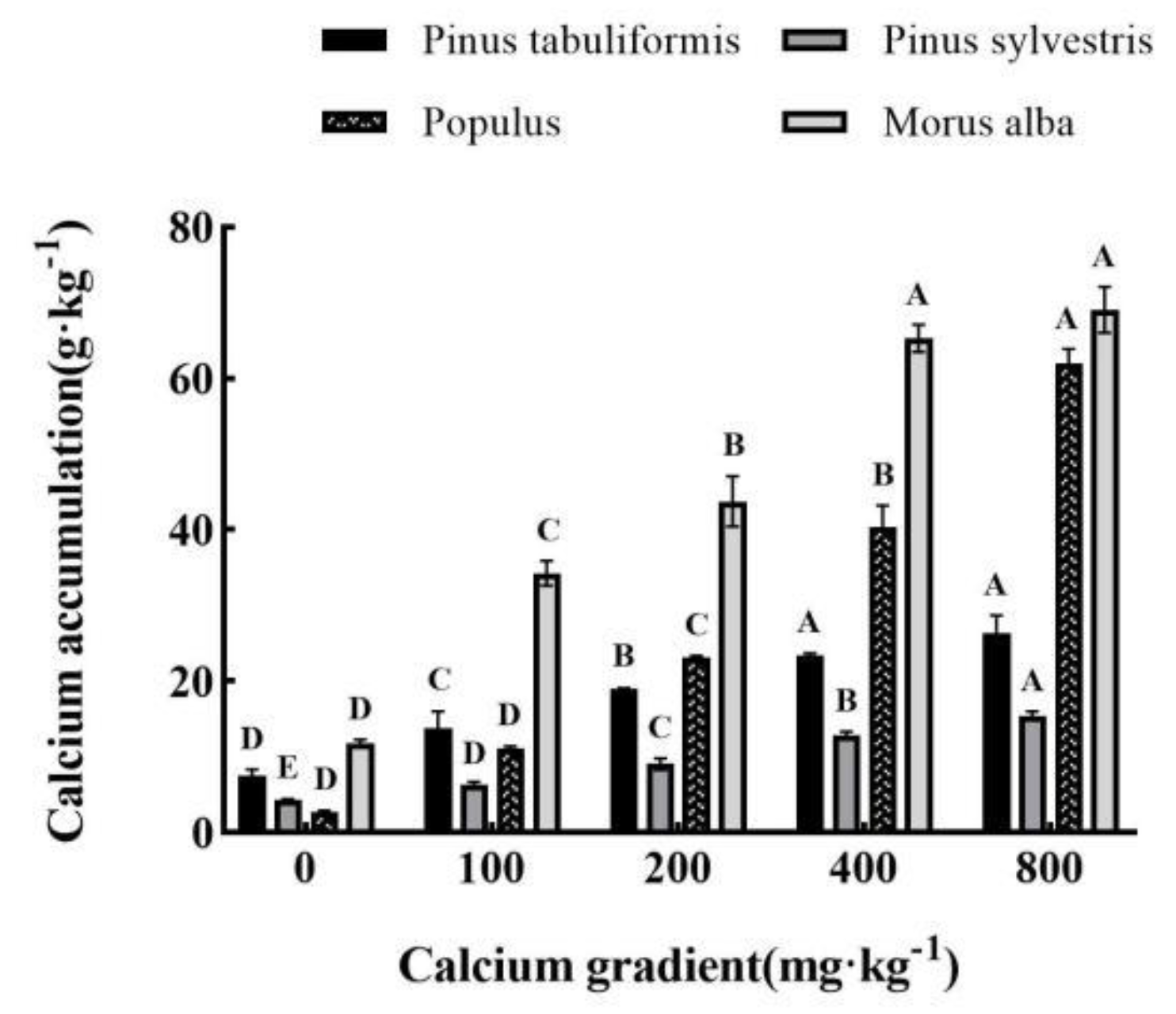
3.1. Effect of exogenous calcium on calcium content in leaves of four tree species seedlings
Under five different exogenous calcium concentrations, the calcium content in the leaves of seedlings of
Pinus tabuliformis,
Pinus sylvestris var.
mongolica,
Populus, and
Morus alba increased significantly with the increase of calcium concentration (
P<0.05). When exogenous calcium was not applied, the calcium content in the leaves of
Pinus tabuliformis,
Pinus sylvestris var.
mongolica,
Populus, and
Morus alba was the lowest, 7.50g·kg
-1, 4.29g·kg
-1, 2.79g·kg
-1 and 11.78g·kg
-1, respectively. When the concentration of exogenous calcium increased to 800 mg·kg
-1, it showed the maximum value, which was 26.32g·kg
-1, 15.44g·kg
-1, 61.97g·kg
-1 and 69.05g·kg
-1, respectively, which was significantly increased by 250.93%, 259.91%, 2121.15%, and 486.16% compared with the treatment without calcium (
P<0.05). Among them, the growth of
Populus is the largest, and the calcium content of plant leaf tissue when the exogenous calcium concentration is 800mg·kg
-1 is 22.21 times higher than that without calcium treatment (
Figure 1).
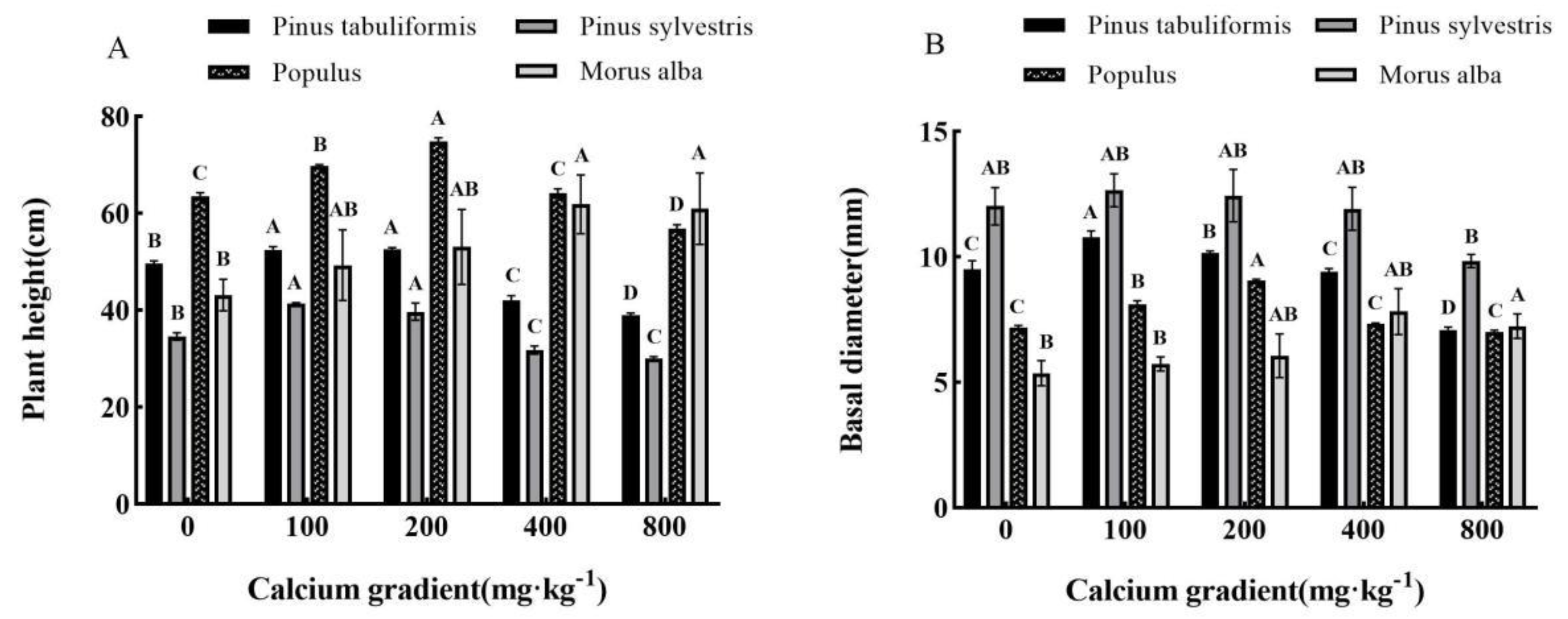
3.2. Effects of exogenous calcium on the growth of seedlings of four tree species
The plant height and basal diameter of
Pinus tabuliformis,
Pinus sylvestris var.
mongolica,
Populus, and
Morus alba were significantly different from those of the control group without calcium application (
P<0.05), which showed a trend of first increasing and then decreasing with the increase of calcium concentration (
Figure 2A,B). The plant height of
Pinus tabuliformis reached the maximum at the calcium concentration of 200mg·kg
-1, slightly higher than that at 100mg·kg
-1, and the base diameter reached the maximum at 100mg·kg
-1. The height and basal diameter of
Pinus sylvestris var.
mongolica,
Populus, and
Morus alba reached the maximum at 100mg·kg
-1, 200mg·kg
-1, and 400mg·kg
-1, respectively. However, with the continuous increase of calcium concentration, the plant height and basal diameter of the four planting plants gradually decreased, and the other three tree species, except
Morus alba, were even lower than the control without calcium application under the treatment of 800mg·kg
-1 calcium concentration, which also showed that the high concentration of calcium would inhibit the growth of plants. It can be seen that the application of exogenous calcium does promote the growth of plants, and there is an optimal calcium concentration to make all measurement indicators reach the peak. It can be seen from the above results that the most suitable calcium concentration for the growth of tree height and basal diameter of
Pinus tabuliformis,
Pinus sylvestris var.
mongolica,
Populus and
Morus alba is 100–200 mg·kg
-1, 100 mg·kg
-1, 200 mg·kg
-1 and 400 mg·kg
-1, respectively.
The total biomass of the seedlings of the four species also showed a trend of first increasing and then decreasing with the increase of exogenous calcium concentration (
Table 1). The highest total biomass was observed in
Pinus tabuliformis,
Pinus sylvestris var.
mongolica,
Populus, and
Morus alba at calcium concentrations of 100 mg·kg
-1, 100 mg·kg
-1, 200 mg·kg
-1, and 400 mg·kg
-1, respectively. These values were found to be 65.34g, 81.73g, 33.54g, and 46.75g, respectively, indicating a significant increase of 10.43%, 17.29%, 17.31%, and 94.87% compared to control without calcium treatment. However, the total biomass of
Pinus tabuliformis,
Pinus sylvestris var.
mongolica, and
Populus declined to its lowest value at a calcium concentration of 800 mg·kg
-1, which was found to be 39.96g, 27.49g, and 25.15g respectively. This was 32.47%, 60.55%, and 12.03% lower compared to no calcium application (
P<0.05).
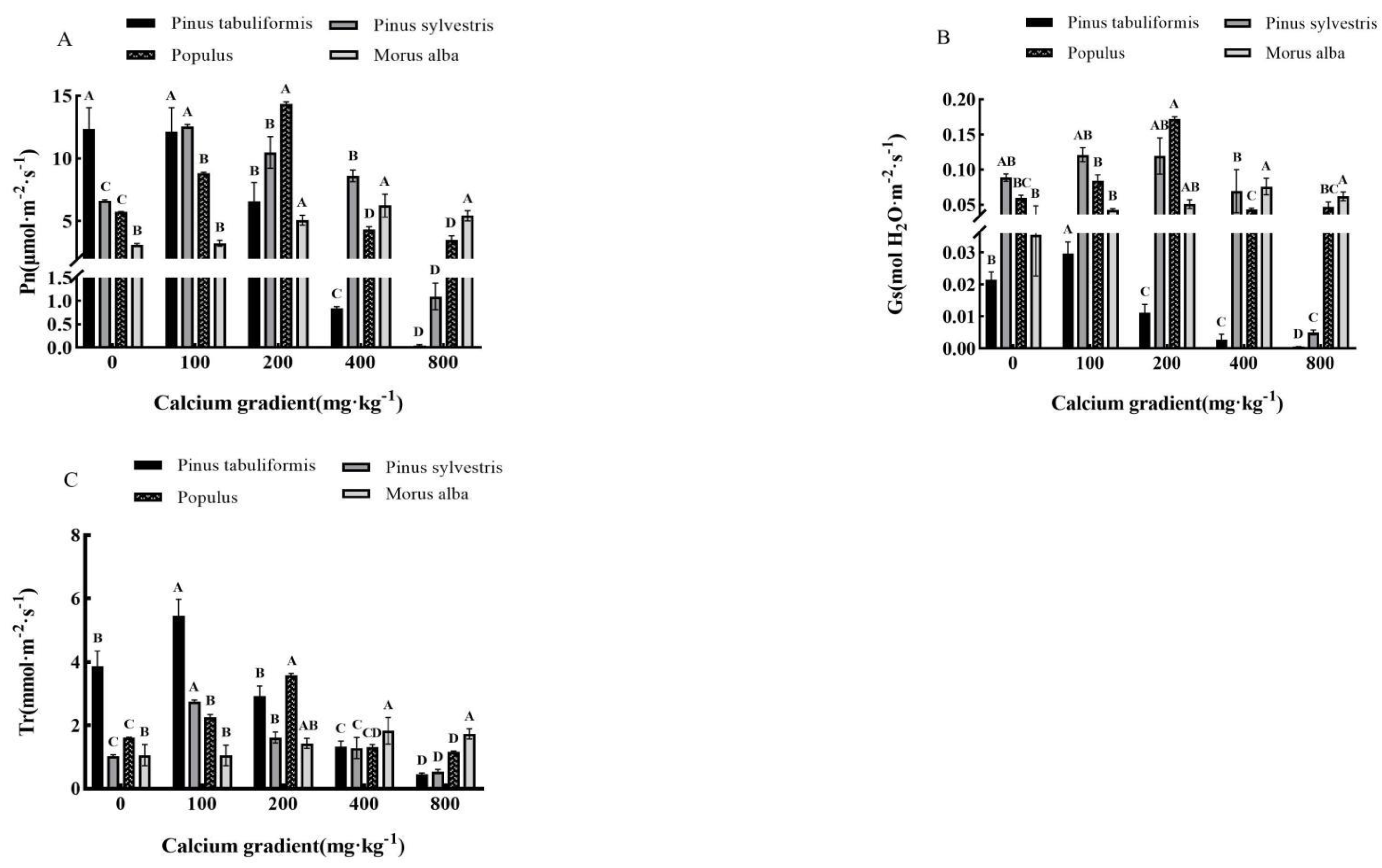
3.3. Effect of exogenous calcium on photosynthetic characteristics of seedlings of four tree species
3.3.1. Effect of exogenous calcium on photosynthetic parameters of seedlings of four tree species
Overall, different concentrations of calcium treatments had significant effects (
P<0.05) on all indicators of photosynthetic parameters of
Pinus tabuliformis,
Pinus sylvestris var.
mongolica,
Populus, and
Morus alba seedlings, which first increased and then decreased with increasing exogenous calcium concentrations (
Figure 3A–C).
However, the net photosynthetic rate of Pinus tabuliformis seedlings gradually decreased with the increase in calcium concentration. The treatment of 100−800 mg·kg-1 calcium concentration decreased 1.38%, 46.60%, 93.19%, and 99.68% compared with the treatment without calcium. Its stomatal conductance and transpiration rate showed a trend of first increasing and then decreasing after applying calcium, and both reached the maximum value when the calcium concentration was 100 mg·kg-1, which was 0.03 mol·m-2·s-1 and 5.45 mol H2O·m-2·s-1, respectively, increased by 42.86% and 41.19% compared with the treatment without calcium. The photosynthetic index of Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica, Populus and Morus alba seedlings expanded first and then reduced with the increase of calcium concentration, and reached the maximum value when the calcium concentration was 100mg·kg-1, 200mg·kg-1 and 400mg·kg-1, respectively. Under the treatment of 100 mg·kg-1 calcium concentration, the net photosynthetic rate of Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica seedlings reached 12.55 μMol·m-2·s-1, stomatal conductance reached 0.12 molH2O·m-2·s-1, and transpiration rate reached 2.75 mmol·m-2·s-1. When the calcium concentration is 800mg·kg-1, the photosynthetic index is 1.09 μMol·m-2·s-1, 0.005 mol H2O·m-2·s-1, 0.54 mol·m-2·s-1, decreased by 83.58%, 94.44%, and 47.06% respectively compared with those without calcium application. The net photosynthetic rate, stomatal conductance, and transpiration rate of Populus seedlings reached the maximum at 200 mg·kg-1, which were 14.36 μMol·m-2·s-1 respectively, 0.17 molH2O·m-2·s-1 and 3.58 mol·m-2·s-1. When calcium concentration is 800mg·kg-1, its photosynthetic index decreases to the lowest value, which is 3.49 μmol·m-2·s-1 respectively、0.05 molH2O·m-2·s-1、1.16mmol·m-2·s-1. Compared with that without calcium, it increased and decreased by 149.74% and 39.30%, 183.33% and 16.67%, 122.36% and 27.95% respectively. The net photosynthetic rate of Morus alba reached 6.24 μmol·m-2·s-1 when the calcium concentration was 400mg·kg-1, stomatal conductance 0.076 molH2O·m-2·s-1, transpiration rate 1.83 mmol·m-2·s-1, all reached the maximum value, increased by 100.64%, 117.14%, and 72.64% respectively compared with without calcium.
The above results showed that when the calcium concentrations were 0−100 mg·kg-1, 100 mg·kg-1, 200 mg·kg-1, and 400 mg·kg-1, respectively, the photosynthesis of the seedlings of the four tree species was best promoted, and these calcium concentrations were the most suitable calcium concentrations for the photosynthesis of the four tree species. Photosynthesis of seedlings of Pinus tabuliformis, Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica, Populus, and Morus alba was inhibited by calcium deficiency and calcium excess.
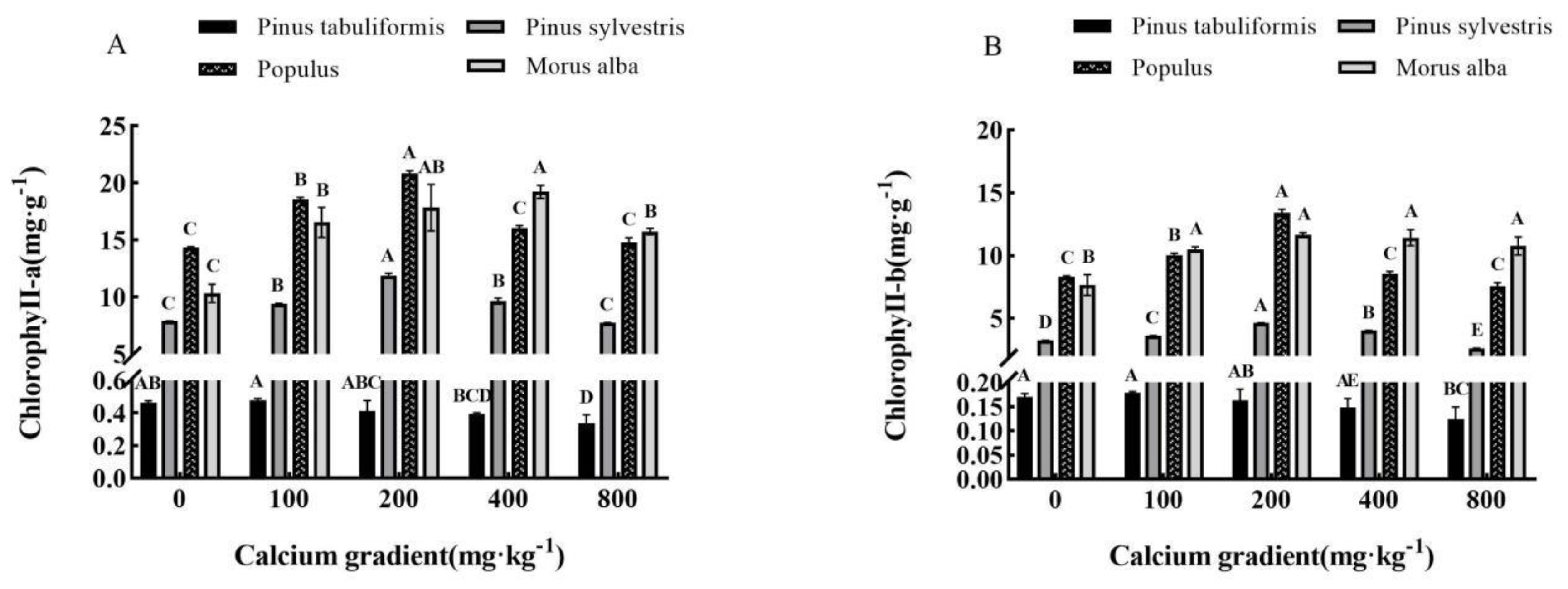
3.3.2. Effect of exogenous calcium on photosynthetic pigments of seedlings of four tree species
Overall, the levels of chlorophyll a and chlorophyll b present in the leaves of
Pinus tabuliformis,
Pinus sylvestris var.
mongolica,
Populus, and
Morus alba seedlings demonstrated a trend of initial increase followed by decrease with rising concentrations of calcium (
Figure 4A,B). The highest concentrations of Chlorophyll a and chlorophyll b were observed at calcium concentrations of 100 mg·kg
-1, 200 mg·kg
-1, 200 mg·kg
-1, and 200−400 mg·kg
-1, respectively, which were shown to be significantly different from other treatments (
P<0.05).
The levels of chlorophyll a and chlorophyll b in the leaves of Pinus tabuliformis seedlings exhibited a 3.24% and 5.29% increase, respectively, when treated with 100 mg·kg-1 calcium concentration relative to those without calcium treatment, reaching their maximum value. Subsequently, their levels gradually decreased with an increase in the concentration of calcium. Conversely, under treatments of 200, 400, and 800 mg·kg-1 calcium, the levels of chlorophyll a and chlorophyll b decreased by 11.02% and 4.12%, 15.12% and 12.35%, and 27.43% and 26.47% respectively, compared to those without calcium treatment. The highest levels of chlorophyll a and chlorophyll b in Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica seedlings were achieved with 200 mg·kg-1 calcium concentration. This resulted in a remarkable 50.57% increase in chlorophyll a content and a 42.77% increase in chlorophyll b content, compared to those without calcium application. Conversely, the content of chlorophyll b reduced by 19.38% under 800 mg·kg-1 calcium treatment. In the case of Populus seedlings, the content of chlorophyll a and chlorophyll b was highest under the 200 mg·kg-1 calcium concentration treatment, with increases of 45.49% and 61.18% respectively. This was in comparison to those without calcium application. However, the content of chlorophyll b was 8.89% lower under 800 mg·kg-1 calcium treatment as compared to those without calcium. The addition of calcium at 100 mg·kg-1, 200 mg·kg-1, and 400 mg·kg-1 concentrations resulted in significant increases in the content of chlorophyll a and chlorophyll b in Morus alba seedling leaves (P<0.05). Specifically, the content of chlorophyll a rose by 60.52%, 72.94%, and 86.32%, respectively, while the content of chlorophyll b increased by 36.95%, 52.22%, and 49.22%, respectively, compared to the control group without calcium. The highest levels of both chlorophyll a and chlorophyll b were observed at 400 mg·kg-1 and 200 mg·kg-1 concentrations of calcium. However, further addition of calcium to a concentration of 800 mg·kg-1 led to a decline in chlorophyll content.
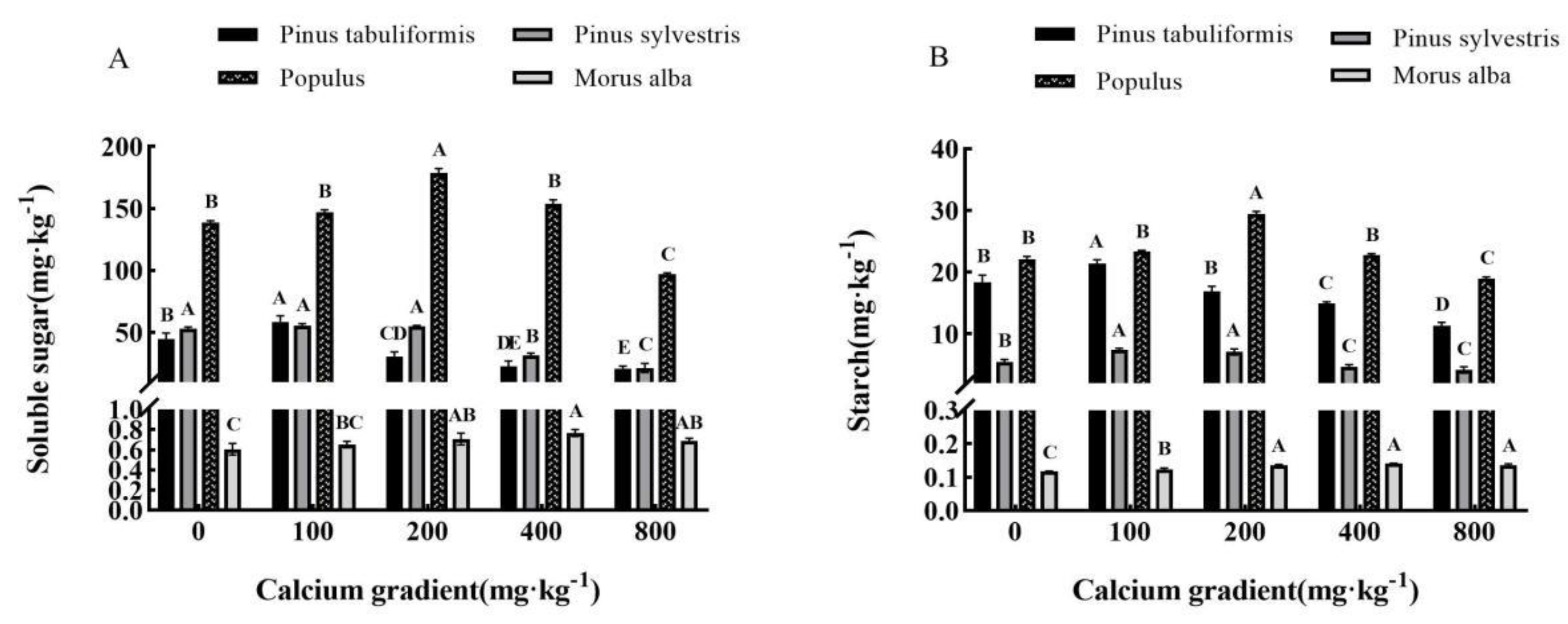
3.3.3. Effect of exogenous calcium on photosynthetic products of seedlings of four tree species
Generally, the levels of soluble sugar and starch, the photosynthetic products of
Pinus tabuliformis,
Pinus sylvestris var.
mongolica,
Populus, and
Morus alba seedlings, followed a pattern of increase and then decrease in response to varying levels of calcium concentration (
Figure 5A,B). The maximum values were observed at calcium concentrations of 100 mg·kg
-1, 100 mg·kg
-1, 200 mg·kg
-1, and 400 mg·kg
-1 for
Pinus tabuliformis,
Pinus sylvestris var.
mongolica,
Populus, and
Morus alba, respectively, which were significantly different from other treatments (
P<0.05).
When the calcium concentration was 100 mg·kg-1, the soluble sugar and starch contents of Pinus tabuliformis seedlings were 58.53 mg·kg-1 and 21.39 mg·kg-1, respectively. These values increased by 30.24% and 16.25%, respectively, compared to the calcium concentration of 0 mg·kg-1. However, as the calcium concentration increased, a gradual decrease in these values was observed. At a calcium concentration of 800 mg·kg-1, the values decreased by 70.87% and 38.64% compared to the calcium concentration of 0 mg·kg-1. The Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica seedlings had a maximum soluble sugar and starch content of 55.65 mg·kg-1 and 7.35 mg·kg-1, respectively, at a calcium concentration of 100 mg·kg-1. This represented a 4.51% and 35.36% increase, respectively, compared to the calcium concentration of 0 mg·kg-1. The soluble sugar and starch contents of Populus were significantly reduced by 59.69% and 23.20% (P<0.05), respectively, when treated with a calcium concentration of 800 mg·kg-1 compared to 0 mg·kg-1. The treatment with a calcium concentration of 200 mg·kg-1 resulted in the maximum soluble sugar and starch content for Populus, at 178.96 mg·kg-1 and 29.47 mg·kg-1, respectively. This represented an increase of 28.99% and 33.29% compared to the 0 mg·kg-1 calcium concentration. In contrast, the soluble sugar and starch content of the 800 mg·kg-1 calcium treatment decreased by 30.02% and 14.02% compared to the 0 mg·kg-1 calcium treatment. For Morus alba seedlings, the maximum content of soluble sugar and starch occurred at a calcium concentration of 400 mg·kg-1, with levels of 0.766 mg·kg-1 and 0.142 mg·kg-1, respectively. These levels were 26.40% and 20.34% higher than those observed at 0 mg·kg-1 calcium concentration.When the calcium concentration increased to 800 mg·kg-1, its value decreased to 0.690 mg·kg-1 and 0.136 mg·kg-1, respectively.
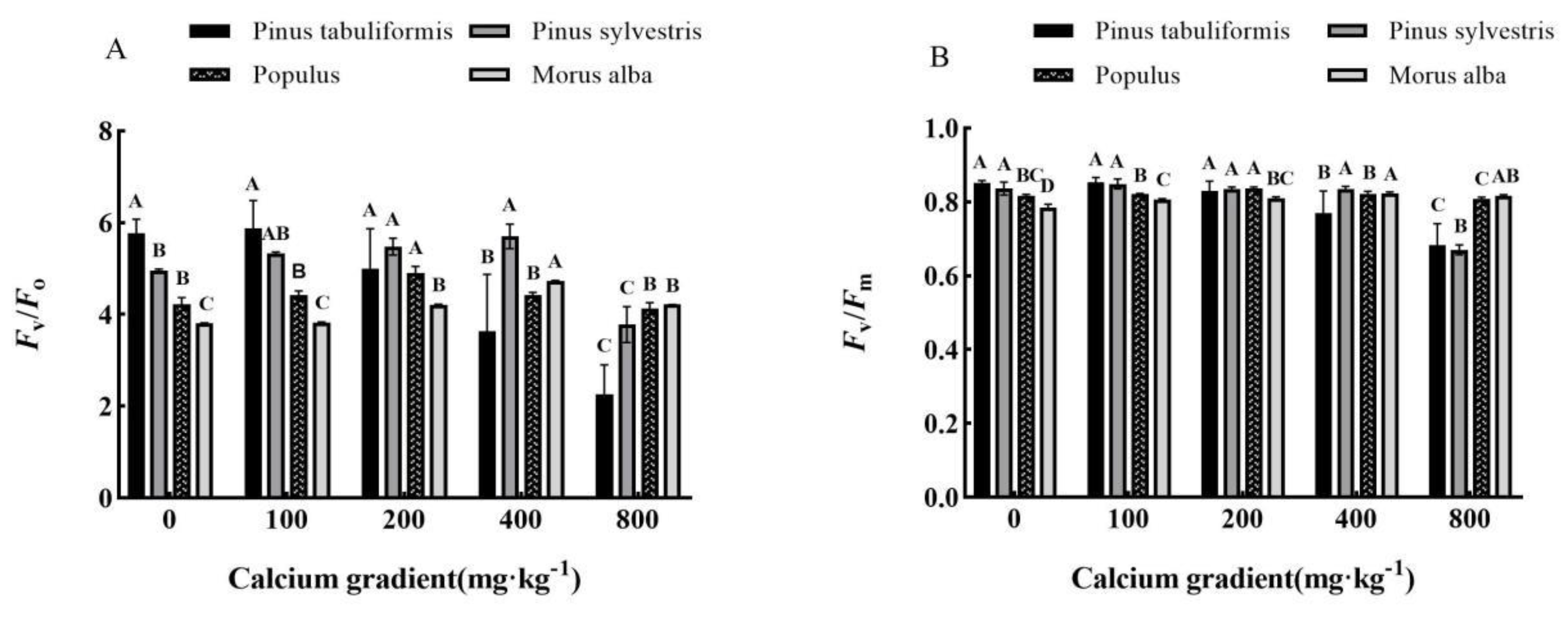
3.4. Effect of exogenous calcium on chlorophyll fluorescence of seedlings of four tree species
Generally, as the concentration of calcium increased, there was a trend of first increase and then decrease in the chlorophyll fluorescence parameters of
Pinus tabuliformis,
Pinus sylvestris var.
mongolica,
Populus, and
Morus alba seedlings (
Figure 6A,B). The maximum value was achieved when the calcium concentration was 100 mg·kg
-1, 100−400 mg·kg
-1, 200 mg·kg
-1, and 400 mg·kg
-1, respectively, which showed significant differences from the other treatments (
P<0.05).
The Fv/Fo and Fv/Fm values of Pinus tabuliformis seedlings were observed to reach their maximum at a calcium concentration of 100 mg·kg-1. Specifically, the Fv/Fo value increased by 1.91% and the Fv/Fm value increased by 0.23% when compared to the values obtained without the presence of calcium. These values were found to be 5.88 and 0.854, respectively. However, when the calcium concentration exceeded 400 mg·kg-1, the Fv/Fm value of Pinus tabuliformis seedlings dropped below 0.8, which indicated that their growth was adversely affected by this increase in calcium concentration.The Fv/Fo value of Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica seedlings reaches its peak at a calcium concentration of 400 mg·kg-1, with a maximum value of 5.70—a remarkable 14.92% increase from the value without calcium. Similarly, the maximum Fv/Fm value of 0.849 is achieved at a lower calcium concentration of 100 mg·kg-1, showing a 1.56% improvement over the absence of calcium. However, as the calcium concentration increases to 800 mg·kg-1, the Fv/Fm value drops to 0.671. The Fv/Fo and Fv/Fm values of Populus seedlings exhibit noticeable peaks at a calcium concentration of 200 mg·kg-1, with Fv/Fo reaching 4.91 and Fv/Fm achieving 0.836—a significant 16.35% and 2.33% improvement, respectively, compared to the values without calcium.The Fv/Fo value of Morus alba seedlings peaked at a calcium concentration of 400 mg·kg-1, with a value of 4.73. This was a significant increase of 24.15% when compared to values without calcium(P<0.05). Additionally, the Fv/Fm value initially registered at 0.786 in the absence of calcium. However, after application of various exogenous calcium concentrations, the Fv/Fm value increased and then decreased, ultimately ranging between 0.8 and 0.84. The maximum value of 0.823 was achieved through a calcium treatment of 400 mg·kg-1.
3.5. Effect of exogenous calcium on the stress resistance of seedlings of four tree species
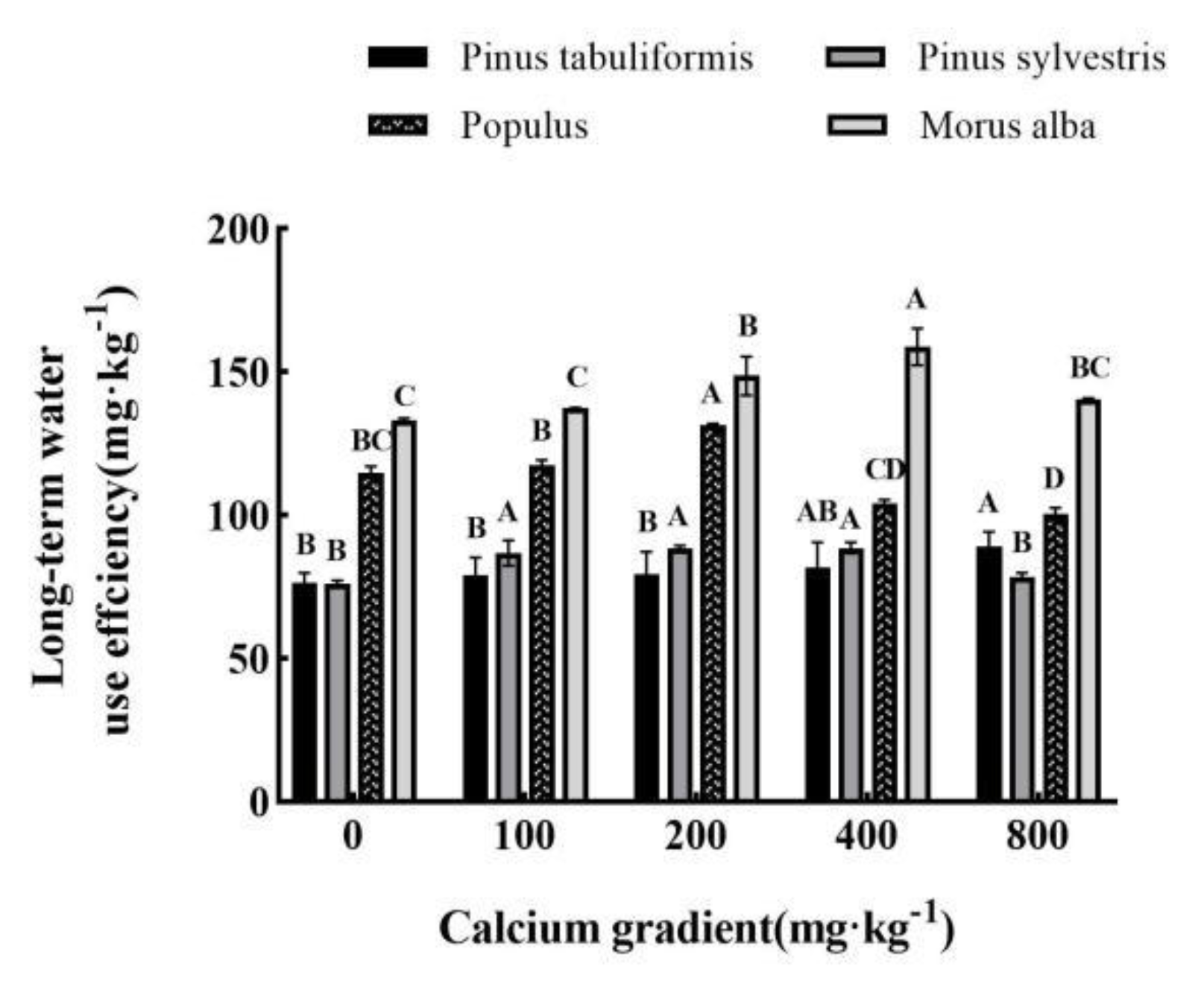
3.5.1. Effect of exogenous calcium on water use efficiency of seedlings of four tree species
In general, the long-term water use efficiency (WUEL) of
Pinus tabuliformis seedlings showed a continuous increase with an increase in calcium concentration. However, for
Pinus sylvestris var.
mongolica,
Populus, and
Morus alba seedlings, the long-term water use efficiency first increased and then decreased as the calcium concentration was increased (
Figure 7).
The long-term water use efficiency of Pinus tabuliformis seedlings was substantially increased after making use of exogenous calcium in contrast with that without calcium (P<0.05). When the calcium concentration was 800 mg·kg-1, its water use efficiency reached the maximum value of 89.25 mg·kg-1, which was 16.61% greater than that without calcium. From low calcium cure (100 mg·kg-1) to high calcium cure (800 mg·kg-1), the continuous increase of water use efficiency of Pinus tabuliformis seedlings confirmed that exogenous calcium had a significant impact on its water use efficiency. The long-term water use efficiency of Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica, Populus, and Morus alba seedlings reached the maximum value when the calcium concentration was 400 mg·kg-1, 200 mg·kg-1, and 400 mg·kg-1, respectively, which improved by means of 16.32%, 14.28%, and 19.13% in contrast with that without calcium application.
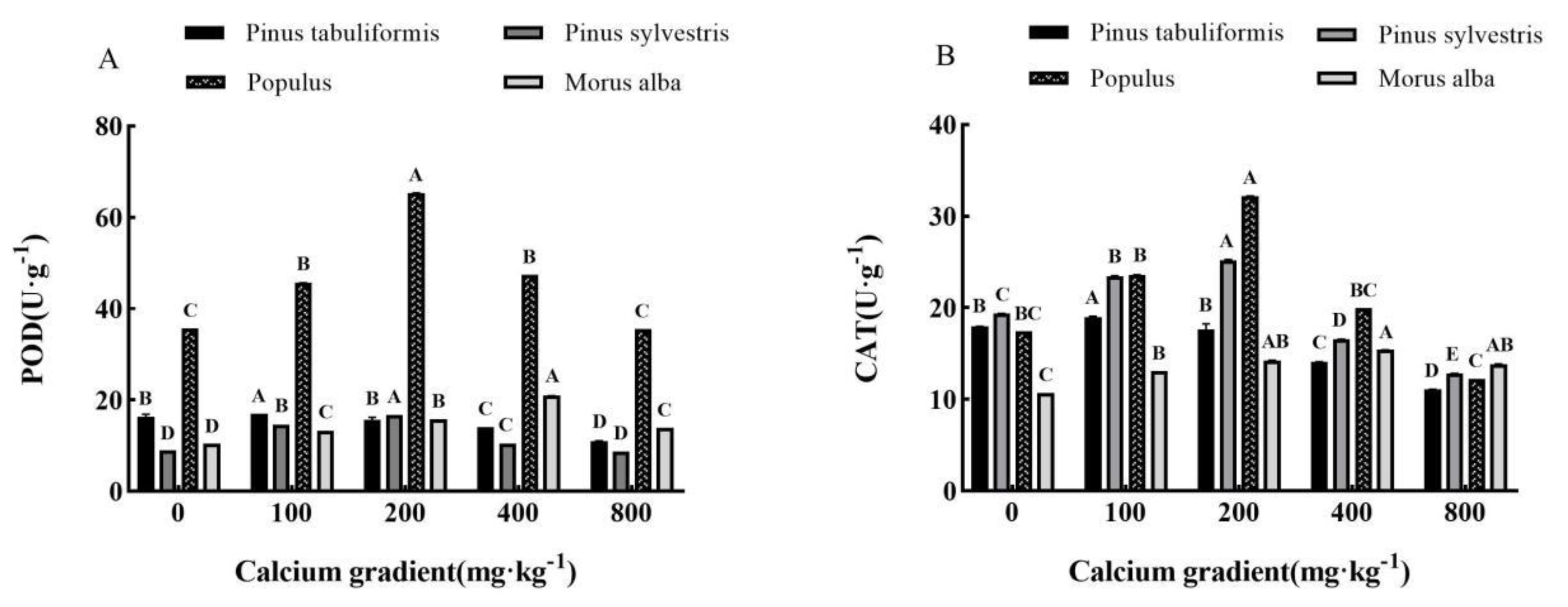
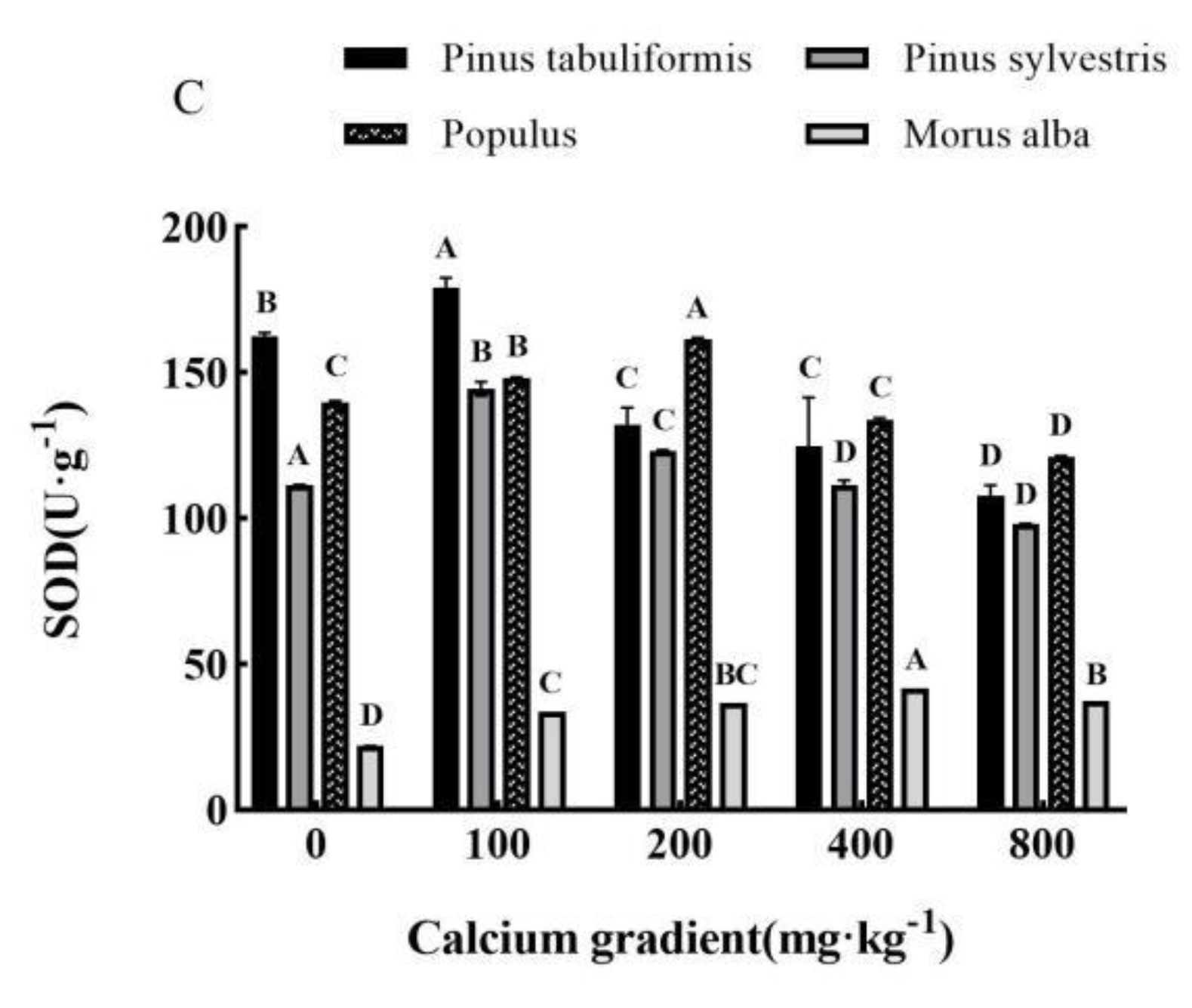
3.5.2. Effect of exogenous calcium on antioxidant enzyme activities of seedlings of four tree species
Overall, the antioxidant enzyme activities of
Pinus tabuliformis,
Pinus sylvestris var.
mongolica,
Populus, and
Morus alba seedlings showed a trend of increasing and then decreasing with growing calcium concentration(
Figure 8A–C), achieving the maximum values at 100 mg·kg
-1, 100–200 mg·kg
-1, 200 mg·kg
-1 and 400 mg·kg
-1, respectively, with significant differences from other treatments (
P< 0.05).
The activities of POD, CAT, and SOD in Pinus tabuliformis seedlings peaked at a calcium concentration of 100 mg·kg-1, showing increases of 4.10%, 5.69%, and 10.13%, respectively, over the concentration of 0 mg·kg-1. Meanwhile, in Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica seedlings, the maximum activities of POD and CAT were recorded at a calcium concentration of 200 mg·kg-1, with an increase of 29.98% and 85.08%, respectively, compared to no calcium addition. Similarly, the maximum SOD activity occurred at a concentration of 100 mg·kg-1 calcium, showing a 29.65% increase over no calcium addition. Populus seedlings also exhibited their maximum POD, CAT, and SOD activities under the 200 mg·kg-1 calcium treatment, with increases of 83.03%, 84.36%, and 15.57%, respectively, compared with no addition of calcium. Finally, the activities of POD, CAT, and SOD in Morus alba seedlings reached their peak values when subjected to a calcium concentration of 400 mg·kg-1, showing increases of 100.38%, 44.06%, and 89.59%, respectively, when compared to a concentration of 0 mg·kg-1.
4. Discussion
4.1. There is an optimum calcium concentration for plant growth
Ca2+ is a crucial nutrient and signal molecule that plays pivotal roles in the regulation of stomatal movement, responses to various biotic and abiotic stresses, and the growth and development of plants (Zhang et al., 2020). Previous studies have shown that the fresh biomass of Zoysia japonica increased with CaCl2 pretreatment, with the highest increase observed in the group treated with 10 mmol·L−1 CaCl2 (Xu et al., 2013). Supplementation of Ca2+ also promoted the growth of cucumber stem and root biomass, with 10 mmol·L−1 Ca2+ proving to be the most effective (Wang et al., 2021). Moreover, the foliar application of Ca2+ enhanced the growth and photosynthesis of peanuts (Liu et al., 2013; Song et al., 2020) and improved the quality of sweet cherries (Correia et al., 2019).A lack of calcium can result in the inability to form cell walls due to impaired cell division and formation. Calcium is also necessary for the structural construction of cell walls and membranes, and its deficiency can lead to lysine degradation, the accumulation of pipecolic acid, and reduced biomass accumulation, as well as potential physiological diseases (Xing et al., 2021; Činčerová,1976; Liu et al., 2019). However, excessive Ca2+ can disrupt normal biochemical metabolism and nutrient metabolism in plants, as well as affect their morphology and internal structure. High concentrations of Ca are known to cause cytotoxicity and abnormal plant development (Conn et al., 2011; Cybulska et al., 2011), with Ca deficiency or overload in tomato plants resulting in reduced leaf size and plant biomass (Hao and Papadopoulos, 2004).
The current study yielded similar findings, indicating that plant height, basal diameter, and total biomass of Pinus tabuliformis, Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica, Populus, and Morus alba seedlings increased then decreased with increasing calcium concentration across varying treatments. Maximum values were observed in response to 100 mg·kg-1, 100 mg·kg-1, 200 mg·kg-1, and 400 mg·kg-1 calcium treatments, respectively. Thus, calcium content levels have a significant impact on plant growth and biomass accumulation. The application of exogenous calcium leads to significant changes in the levels of nutrients such as Mg, N, and P in the leaves, which further leads to an increase in the levels of photosynthetic pigments and photosynthetic products, ultimately increasing plant growth and biomass (Weng et al., 2022).
Chlorophyll fluorescence parameters are instrumental in describing the photosynthetic functioning and physiological status of plants. They are commonly used to investigate the correlation between a plant's photosynthetic activities and its environmental conditions (Zhao, et al.,2021). Changes in chlorophyll fluorescence are closely linked to how light energy is absorbed, transferred, dissipated, and distributed. Hence, measuring these parameters can help identify the adaptation mechanisms of plants in stressful environments. A Fv/Fm ratio less than 0.8 indicates that a plant is under stress, leading to severe growth and developmental restrictions (Peng et al., 2021; Zheng et al., 2021; Weng et al., 2022). Furthermore, leaf water use efficiency is crucial for determining optimal water supply requirements for plant growth and development (Song et al., 2012; YAN et al., 1998). This efficiency represents the efficiency of water consumption in generating organic matter during plant physiological activities and can be used to assess the impact of environmental factors on plants. Plant species that exhibit high water use efficiency values often thrive in low water availability environments (Ma et al., 2004). Environmental stress can lead to an increase in the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS), compared to the number produced under normal metabolic processes (Mittler 2006; Hu et al., 2017). These ROS usually comprise hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), superoxide (), and hydroxyl radicals (OH-) (Zeng et al., 2010). Plants have innate defense mechanisms to neutralize the overproduction of ROS, including enzymatic (SOD, POD, CAT, etc.) and non-enzymatic (glutathione, proline, carotenoids, tocopherols, etc.) antioxidants (Melorose et al., 2015).
The photosynthetic characteristics of seedlings from four tree species studied were significantly influenced by the application of calcium. Chlorophyll content, photosynthetic parameters, photosynthetic products and chlorophyll fluorescence parameters increased initially, but then decreased with higher calcium concentrations. Fv/Fm of Morus alba without calcium and Fv/Fm of Pinus tabuliformis and Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica with excessive calcium concentrations were below 0.8; this indicates that the plants were under stress and their growth and development were severely inhibited. Additionally, long-term water use efficiency and antioxidant enzyme activities also exhibited an increasing and decreasing trend with calcium concentrations, reaching their maximum values at a certain calcium concentration. These results suggest that the presence of suitable calcium concentrations promoted the growth of seedlings of the four species and achieved optimal growth. However, excessive calcium in the cells reacts chemically with phosphate substances, producing impurities such as precipitation, which interferes with phosphorus metabolism and other related processes, leading to the blockage of calcium signaling and ultimately affecting plant photosynthesis and respiration (Li et al., 2021). Adequate amounts of calcium ions can improve the structural integrity and stability of chloroplasts, enhance the activities of Rubisco and PEP carboxylases, and increase the carboxylation efficiency of CO2 and the activity of membrane ATPases, resulting in improved photosynthetic levels of plants (Weng et al., 2022).
4.2. Different plants have different optimal calcium concentrations
The findings of the study revealed that photosynthesis in the leaves of Pinus tabuliformis and Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica seedlings was significantly inhibited in comparison to Populus and Morus alba, under identical temperature and light conditions. Specifically, the net photosynthetic rates of Pinus tabuliformis, Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica, and Populus were reduced by 99.68%, 83.58%, and 39.3%, respectively, when treated with 800 mg·kg-1 calcium, as compared to the control group. Moreover, as the calcium concentration was gradually increased, a significant decrease was observed in the measured values of Pinus tabuliformis seedlings, while Morus alba seedlings did not show such a decrease. A previous study showed that broadleaf and coniferous trees exhibit different responses to changes in factors like precipitation, nutrients and light, due to their distinct leaf habits (Zhang, 2020; Yuan et al, 2021). Leaf nitrogen content and photosynthetic efficiency are correlated (Ellsworth and Reich, 1992; Maire, et al, 2012). Broadleaf species are plants with high leaf nitrogen content, high specific leaf area, and high photosynthetic capacity, and conifer species are plants with low leaf nitrogen content, low specific leaf area, and low photosynthetic capacity (Walters and Reich, 1999; Díaz, et al, 2016). This, to some extent, may explain the differential response of coniferous species to calcium concentration.
Our study has discovered that an ideal calcium concentration exists for the growth of seedlings in all four tree species. What's more, this optimal calcium concentration differs among varying species of seedlings, with broadleaf plants requiring more calcium than coniferous ones. The author has provided a hypothesis that this occurrence may be attributed to the distinct functional traits of the various plants and their diverse responses to alterations in resources. This theory is supported by previous studies (Chapin, 1980; Westoby and Wright, 2006; Reich, 2014; Luo, et al, 2019). The dissimilar features of needle and broad-leaved tree species that employ resources may account for this difference. Broadleaf species show traits of "rapid growth" leaves, featuring high specific leaf area and a low leaf carbon to nitrogen ratio. On the other hand, conifer species exhibit typical "slow growing" characteristics with low specific leaf area and a high carbon to nitrogen ratio (Reich et al., 1999; Reich, 2014; Salguero-Gómez 2017).The "fast" strategy offers the advantage of efficient use of abundant resources, enabling plants to outcompete those following the "slow" strategy. On the other hand, the "slow" strategy facilitates survival under conditions of limited resources and low growth capacity (Grime, 1979; Craine, 2009; Reich, 2014; Damián et al., 2020). Similar to our findings, numerous studies have reported that different concentrations of calcium produce varying effects on plant growth, and that an optimal calcium concentration exists for optimal plant growth. For instance, the optimal calcium concentration for Mongolian pine seedlings grown in dark brown soil is 100−200 mg·kg-1 (Li et al., 2022). Guo et al. (2021) also discovered that supplementing 10 mmol·L-1 of exogenous calcium chloride under salt stress has a beneficial effect on the growth and photosynthetic characteristics of Gleditsia sinensis. Among the different calcium application treatments ranging from 0 to 12 g·plant-1 CaCl2, the 9 g·plant-1 treatment resulted in the highest levels of chlorophyll and soluble protein contents in the leaves of Ilex rotunda Thunb, according to Zhang's (2022) findings. Therefore, it can be concluded that, in silvicultural production activities, it is important to select silvicultural species based on their calcium requirements and apply an appropriate concentration of calcium fertilizer to regulate growth and achieve optimal growth results.
5. Conclusion
In conclusion, optimal calcium concentrations for tree growth were identified and found to differ among tree species. Pinus tabuliformis, Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica, Populus, and Morus alba exhibited maximum growth at exogenous calcium concentrations of 100 mg·kg-1, 100 mg·kg-1, 200 mg·kg-1, and 400 mg·kg-1, respectively. Furthermore, the study found that broadleaf and conifer species have different calcium requirements, with Morus alba exhibiting the highest requirement, followed by Populus and then Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica and Pinus tabuliformis. It is important to note that excess calcium in tree seedlings can lead to stress and inhibit growth and development.
Author Contributions
Hui Li: Conceptualization, Investigation, Methodology, Visual-Ization, Writing – review & editing. Yaoyao Zhao: Data analysis and sorting, testing, writing – original draft, cultivating seedlings. Xiaohang Weng: Cultivating seedlings, Writing–review & editing. Yongbin Zhou, Conceptualization, Methodology. Songzhu, Zhang: Methodology. Liying Liu: Methodology. Jiubo Pei: Methodology, Writing – review & editing; Conceptualization.
Acknowledgments
This thesis supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China-Research (No. 3170030160, No. 41450007, No.31800364, No.31400611) and Doctoral research start-up fund (No.880416020).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
References
- Ahmed, A. K. M., Fu, Z., Ding, C., Jiang, L., Han, X., Yang, A., et al. (2020). Growth and wood properties of a 38-year-old Populus simonii × P. nigra plantation established with different densities in semi-arid areas of northeastern China. Journal of forestry research, 31(2), 497-506. [CrossRef]
- Aras, S., Keles, H., and Bozkurt, E. (2021). Physiological and histological responses of peach plants grafted onto different rootstocks under calcium deficiency conditions. Scientia Horticulturae, 281, 109967. [CrossRef]
- Bai, R., Bai, C., Han, X., Liu, Y., and Yong, J. W. H. (2022). The significance of calcium-sensing receptor in sustaining photosynthesis and ameliorating stress responses in plants. Frontiers in Plant Science, 3998. [CrossRef]
- Blatt, M. R. (2000). Ca2+ signalling and control of guard-cell volume in stomatal movements. Current opinion in plant biology, 3(3), 196-204. [CrossRef]
- Chang-Rong, Y. A. N., Xing-Guo, H. A. N., Ling-Zhi, C. H. E. N., Jian-Hui, H. U. A. N. G., and Bo, S. U. (1998). Foliar δ13C Within Temperate Deciduous Forest: Its Spatial Change and Interspecies Variation. Journal of Integrative Plant Biology, 40(9).
- Chapin III, F. S. (1980). The mineral nutrition of wild plants. Annual review of ecology and systematics, 11(1), 233-260. [CrossRef]
- Chen, G., and Li, S. (2016). “Plant Physiology Experiment”, Beijing: Higher Education Press. p. 2.
- Činčerová, A. (1976). Effect of calcium deficiency on L-lysine-α-ketoglutarate aminotransferase in wheat plants. Zeitschrift für Pflanzenphysiologie, 80(4), 348-353. [CrossRef]
- Conn, S. J., Gilliham, M., Athman, A., Schreiber, A. W., Baumann, U., Moller, I., et al. (2011). Cell-specific vacuolar calcium storage mediated by CAX1 regulates apoplastic calcium concentration, gas exchange, and plant productivity in Arabidopsis. The Plant Cell, 23(1), 240-257. [CrossRef]
- Correia, S., Queirós, F., Ribeiro, C., Vilela, A., Aires, A., Barros, A. I., et al. (2019). Effects of calcium and growth regulators on sweet cherry (Prunus avium L.) quality and sensory attributes at harvest. Scientia Horticulturae, 248, 231-240. [CrossRef]
- Craine, J. M. (2009). Resource strategies of wild plants. In Resource Strategies of Wild Plants. Princeton University Press. [CrossRef]
- Cybulska, J., Zdunek, A., and Konstankiewicz, K. (2011). Calcium effect on mechanical properties of model cell walls and apple tissue. Journal of Food Engineering, 102(3), 217-223. [CrossRef]
- Damián, X., Ochoa-López, S., Gaxiola, A., Fornoni, J., Domínguez, C. A., and Boege, K. (2020). Natural selection acting on integrated phenotypes: covariance among functional leaf traits increases plant fitness. New Phytologist, 225(1), 546-557. [CrossRef]
- Díaz, S., Kattge, J., Cornelissen, J. H., Wright, I. J., Lavorel, S., Dray, S., et al. (2016). The global spectrum of plant form and function. Nature, 529(7585), 167-171. [CrossRef]
- Ellsworth, D. S., and Reich, P. B. (1992). Leaf mass per area, nitrogen content and photosynthetic carbon gain in Acer saccharum seedlings in contrasting forest light environments. Functional Ecology, 423-435. [CrossRef]
- Grime, J. P. (1979). Plant Strategies and Vegetation Processes Vegetation Processes. John Wiley and Sons, Limited.
- Guo, M., Gao, G., Ding, G., and Zhang, Y. (2020). Drivers of ectomycorrhizal fungal community structure associated with Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica differ at regional vs. local spatial scales in northern China. Forests, 11(3), 323. [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y., Liu, Y., Zhang, Y., Liu, J., Gul, Z., Guo, X. R., et al. (2021). Effects of exogenous calcium on adaptive growth, photosynthesis, ion homeostasis and phenolics of Gleditsia sinensis Lam. plants under salt stress. Agriculture, 11(10), 978. [CrossRef]
- Han,F.Y.(2018). The optimum concentration of calcium of Q.acutissima seedlings and its effect on growth and physiology (Master's thesis, Shenyang Agricultural University).
- Hao, X., and Papadopoulos, A. P. (2004). Effects of calcium and magnesium on plant growth, biomass partitioning, and fruit yield of winter greenhouse tomato. HortScience, 39(3), 512-515. [CrossRef]
- Huang,Y.B. (2019). Effect of calcium on the growth and physiological characteristics of fig (Master's thesis, Nanjing Agricultural University). [CrossRef]
- Hu, S., Li, Y., Wang, W., Jiao, J., Kou, M., Yin, Q., & Xu, H. (2017). The antioxidation-related functional structure of plant communities: understanding antioxidation at the plant community level. Ecological Indicators, 78, 98-107. [CrossRef]
- Li, H., Huang, S., Ren, C., Weng, X., Zhang, S., Liu, L., and Pei, J. (2022). Optimal exogenous calcium alleviates the damage of Snow-melting agent to Salix matsudana seedlings. Frontiers in Plant Science, 13. [CrossRef]
- Li, H., Huo, Y., Weng, X., Zhou, Y., Sun, Y., Zhang, G., et al. (2022). Regulation of the growth of Mongolian pine (Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica) by calcium-water coupling in a semiarid region. Ecological Indicators, 137, 108736. [CrossRef]
- Li, H., Li, X., Zhang, G., Weng, X., Huang, S., Zhou, Y., et al. (2022). The Optimum Calcium Concentration for Seedling Growth of Mongolian Pine (Pinus Sylvestris Var. Mongolica) Under Different Soil Types in Northern Semi-Arid Areas of China. Frontiers in Environmental Science, 10, 812. [CrossRef]
- Li, X. J., Zhang, G. Q., Li, H., Sun, Y., Huo, Y., Huang, S. L., and Zhou, Y. (2021). Effect of exogenous calcium on the growth and physiological characteristics of sandy camphor pine seedlings. Soil Bulletin (05), 1095-1103. [CrossRef]
- Li, Z., Tan, X. F., Lu, K., Liu, Z. M., and Wu, L. L. (2017). The effect of CaCl2 on calcium content, photosynthesis, and chlorophyll fluorescence of tung tree seedlings under drought conditions. Photosynthetica, 55, 553-560. [CrossRef]
- Li,Z.Y. (2021). An analysis of the causes and definition criteria of forest degradation in the Three Northern Protected Forests in Liaoning Province. Liaoning Forestry Science and Technology (04), 51-53.
- Liu, Y., Riaz, M., Yan, L., Zeng, Y., and Cuncang, J. (2019). Boron and calcium deficiency disturbing the growth of trifoliate rootstock seedlings (Poncirus trifoliate L.) by changing root architecture and cell wall. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 144, 345-354. [CrossRef]
- LIU, Y. F., HAN, X. R., ZHAN, X. M., YANG, J. F., WANG, Y. Z., SONG, Q. B., and Xin, C. (2013). Regulation of calcium on peanut photosynthesis under low night temperature stress. Journal of Integrative Agriculture, 12(12), 2172-2178. [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y., Hu, H., Zhao, M., Li, H., Liu, S., and Fang, J. (2019). Latitudinal pattern and the driving factors of leaf functional traits in 185 shrub species across eastern China. Journal of plant ecology, 12(1), 67-77. [CrossRef]
- Ma, C. C., Gao, Y. B., Guo, H. Y., and Wang, J. L. (2004). Photosynthesis, transpiration, and water use efficiency of Caragana microphylla, C. intermedia, and C. korshinskii. Photosynthetica, 42, 65-70. [CrossRef]
- Maire, V., Martre, P., Kattge, J., Gastal, F., Esser, G., Fontaine, S., and Soussana, J. F. (2012). The coordination of leaf photosynthesis links C and N fluxes in C3 plant species. PloS one, 7(6), e38345. [CrossRef]
- Melorose, J., Perroy, R., and Careas, S. 2015. Brassinosteriods: a class of plant hormone. Statewide agricultural land use baseline 2015. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK. [CrossRef]
- Mittler, R. (2006). Abiotic stress, the field environment and stress combination. Trends in plant science, 11(1), 15-19. [CrossRef]
- Peng, J., Feng, Y., Wang, X., Li, J., Xu, G., Phonenasay, S., et al. (2021). Effects of nitrogen application rate on the photosynthetic pigment, leaf fluorescence characteristics, and yield of indica hybrid rice and their interrelations. Scientific Reports, 11(1), 1-10. [CrossRef]
- Perveen, S., Saeed, M., Parveen, A., Javed, M. T., Zafar, S., and Iqbal, N. (2020). Modulation of growth and key physiobiochemical attributes after foliar application of zinc sulphate (ZnSO4) on wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) under cadmium (Cd) stress. Physiology and Molecular Biology of Plants, 26, . [CrossRef]
- Reich, P. B. (2014). The world-wide ‘fast–slow’plant economics spectrum: a traits manifesto. Journal of ecology, 102(2), 275-301. [CrossRef]
- Reich, P. B., Ellsworth, D. S., Walters, M. B., Vose, J. M., Gresham, C., Volin, J. C., and Bowman, W. D. (1999). Generality of leaf trait relationships: a test across six biomes. Ecology, 80(6), 1955-1969. [CrossRef]
- Ren, C.S., Li, H., Weng, S.H., Zhang, S.S., Liu, L.Y. and Zhou, Y.B.. (2020). Effect of exogenous calcium on growth, photosynthetic characteristics and water use efficiency of Fraxinus mandshurica. Journal of Shenyang Agricultural University (06), 663-669. [CrossRef]
- Salguero-Gómez, R. (2017). Applications of the fast–slow continuum and reproductive strategy framework of plant life histories. New Phytologist, 213(4), 1618-1624. [CrossRef]
- Sheng, L., Sun, X., Mo, C., Hao, M., Wei, X., and Ma, A. (2023). Relationship between antioxidant enzymes and sclerotial formation of Pleurotus tuber-regium under abiotic stress. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 1-14. [CrossRef]
- Song, F. H., Wu, Z. B., Yu, T., Shi, Y. J., Zhuo, Z., and Luo, Q. H.. (2012). Seasonal variation in carbon isotope composition and WUEi correspond with weather factors for five cultivars of Chinese jujube in Xinjiang. Journal of Fruit Trees (01), 66-70. [CrossRef]
- Song, L., Zhu, J., Yan, Q., Li, M., and Yu, G. (2015). Comparison of intrinsic water use efficiency between different aged Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica wide windbreaks in semiarid sandy land of northern China. Agroforestry Systems, 89, 477-489. [CrossRef]
- Song, Q., Liu, Y., Pang, J., Yong, J. W. H., Chen, Y., Bai, C., et al. (2020). Supplementary calcium restores peanut (Arachis hypogaea) growth and photosynthetic capacity under low nocturnal temperature. Frontiers in Plant Science, 10, 1637. [CrossRef]
- Walters, M. B., and Reich, P. B. (1999). Low-light carbon balance and shade tolerance in the seedlings of woody plants: do winter deciduous and broad-leaved evergreen species differ?. The New Phytologist, 143(1), 143-154. [CrossRef]
- Wang, X., Lan, Z., Tian, L., Li, J., Yang, G., Gao, Y., and Zhang, X. (2021). Change of physiological properties and ion distribution by synergistic effect of Ca2+ and grafting under salt stress on cucumber seedlings. Agronomy, 11(5), 848. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y. H., Zhang, L. X., and Sun, Q. Y. (2010). Effect of calcium excess on photosynthetic properties and chloroplast ultrastructure of tea plants. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer (02), 432-438.
- Wang, Y. T., Li, R. X., Xia, J. F. and Wang, T. C. (2017). Economic value of mulberry tree and its application in ecological conservation. China Market (11), 239-240. [CrossRef]
- Weng, X., Li, H., Ren, C., Zhou, Y., Zhu, W., Zhang, S., and Liu, L. (2022). Calcium regulates growth and nutrient absorption in poplar seedlings. Frontiers in Plant Science, 13. [CrossRef]
- Westoby, M., and Wright, I. J. (2006). Land-plant ecology on the basis of functional traits. Trends in ecology and evolution, 21(5), 261-268. [CrossRef]
- Xie, X. M. (2014). Soil and Plant Nutrition Experiments. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University Press.
- Xing, Y., Zhu, Z. L., Wang, F., Zhang, X., Li, B. Y., Liu, Z. X., et al. (2021). Role of calcium as a possible regulator of growth and nitrate nitrogen metabolism in apple dwarf rootstock seedlings. Scientia Horticulturae, 276, 109740. [CrossRef]
- Xu, C., Li, X., and Zhang, L. (2013). The effect of calcium chloride on growth, photosynthesis, and antioxidant responses of Zoysia japonica under drought conditions. PloS one, 8(7), e68214. [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.. (2021). Problems and countermeasures of the Three Northern Protective Forests in Liaoning Province. Modern Agriculture (01), 94-95. [CrossRef]
- Yang, S., Wang, F., Guo, F., Meng, J. J., Li, X. G., and Wan, S. B. (2015). Calcium contributes to photoprotection and repair of photosystem II in peanut leaves during heat and high irradiance. Journal of Integrative Plant Biology, 57(5), 486-495. [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z. (2015). Study on The effect of calcium on the growth and development of ginseng (Master's thesis, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences).
- Yuan, D., Zhu, L., Cherubini, P., Li, Z., Zhang, Y., and Wang, X. (2021). Species-specific indication of 13 tree species growth on climate warming in temperate forest community of northeast China. Ecological Indicators, 133, 108389. [CrossRef]
- Zeng, H., Tang, Q., and Hua, X. (2010). Arabidopsis brassinosteroid mutants det2-1 and bin2-1 display altered salt tolerance. Journal of Plant Growth Regulation, 29, 44-52. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.G. (2022). Effect of exogenous calcium on physiological characteristics of iron holly seedlings at high temperature. Green Technology (19), 76-79. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X. P., Ma, C. X., Sun, L. R., and Hao, F. S. (2020). Roles and mechanisms of Ca2+ in regulating primary root growth of plants. Plant signaling and behavior, 15(5), 1748283. [CrossRef]
- Zhang,Y.L. (2020). Study on Leaf functional traits of eight European conifer and broadleaved seedlings (Master's thesis, China Academy of Forestry Science). [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S. J. (2002). The Experimental Guide for Plant Physiology, third ed.Beijing.
- Zhao, Y., Cai, L. X., Jin, Y. T., Li, J. X., Cui, D., and Chen, Z. J. (2021). Warming-drying climate intensifies the restriction of moisture on radial growth of Pinus tabuli-formis plantation in semi-arid area of Northeast China. Ying Yong Sheng tai xue bao= The Journal of Applied Ecology, 32(10), 3459-3467. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y., Wu, M., Deng, P., Zhou, X.W. and Huang, S.Y.. (2021). Effect of salt stress on growth and chlorophyll fluorescence parameters of seedlings of Luo Han Guo. Fruit Trees of Southern China (02), 103-107. [CrossRef]
- Zheng, E., Zhang, C., Qi, Z., and Zhang, Z. (2021). The effects of different water and nitrogen methods on fluorescence characteristic and growth of rice in black soil region on songnen plain, northeast China. Agricultural Research, 1-10. [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H., Chen, Y., Zhu, C., Li, Z., Fang, G., Li, Y., and Fu, A. (2020). Climate change may accelerate the decline of desert riparian forest in the lower Tarim River, Northwestern China: Evidence from tree-rings of Populus euphratica. Ecological Indicators, 111, 105997. [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.B. and Zou, X.M.. (2017). From matching site with trees towards matching calcium with trees. Journal of Nanjing Forestry University (Natural Science Edition) (02), 1-8. [CrossRef]
Figure 1.
Effect of exogenous calcium on calcium content in leaves of seedlings of different tree species. Note: Every column shows the average value ± SE, n=3. Different capital letters indicate significant differences between different treatments of the same tree species(P<0.05).
Figure 1.
Effect of exogenous calcium on calcium content in leaves of seedlings of different tree species. Note: Every column shows the average value ± SE, n=3. Different capital letters indicate significant differences between different treatments of the same tree species(P<0.05).
Figure 2.
Effect of exogenous calcium on seedling growth index of different tree species. Note: Every column shows the mean ± SE, n=3.Different capital letters indicate significant differences between different treatments of the same tree species (P<0.05). (A) Plant height; (B)Basal diameter.
Figure 2.
Effect of exogenous calcium on seedling growth index of different tree species. Note: Every column shows the mean ± SE, n=3.Different capital letters indicate significant differences between different treatments of the same tree species (P<0.05). (A) Plant height; (B)Basal diameter.
Figure 3.
Effect of exogenous calcium on photosynthetic parameters of seedlings of different tree species. Note: Every column shows the mean ± SE, n=3. Different capital letters indicate significant differences between different treatments of the same tree species (P<0.05). (A) Pn (Photosynthetic rate); (B) Gs (Stomatal conductivity); (C) Tr (Transpiration rate).
Figure 3.
Effect of exogenous calcium on photosynthetic parameters of seedlings of different tree species. Note: Every column shows the mean ± SE, n=3. Different capital letters indicate significant differences between different treatments of the same tree species (P<0.05). (A) Pn (Photosynthetic rate); (B) Gs (Stomatal conductivity); (C) Tr (Transpiration rate).
Figure 4.
Effect of exogenous calcium on photosynthetic pigments of seedlings of different tree species. Note: Every column shows the mean ± SE, n=3. Different capital letters indicate significant differences between different treatments of the same tree species(P<0.05). (A) Chlorophyll a; (B) Chlorophyll b.
Figure 4.
Effect of exogenous calcium on photosynthetic pigments of seedlings of different tree species. Note: Every column shows the mean ± SE, n=3. Different capital letters indicate significant differences between different treatments of the same tree species(P<0.05). (A) Chlorophyll a; (B) Chlorophyll b.
Figure 5.
Effect of exogenous calcium on photosynthetic products of seedlings of different tree species. Note: Every column shows the mean ± SE, n=3. Different capital letters indicate significant differences between different treatments of the same tree species (P<0.05). (A) Soluble sugar; (B) Starch.
Figure 5.
Effect of exogenous calcium on photosynthetic products of seedlings of different tree species. Note: Every column shows the mean ± SE, n=3. Different capital letters indicate significant differences between different treatments of the same tree species (P<0.05). (A) Soluble sugar; (B) Starch.
Figure 6.
Effect of exogenous calcium on chlorophyll fluorescence of seedlings of different tree species. Note:Every column shows the mean ± SE, n=3. Different capital letters indicate significant differences between different treatments of the same tree species (P<0.05). (A) Fv/Fo (Potential photochemical efficiency). (B) Fv/Fm (Maximal photochemical efficiency).
Figure 6.
Effect of exogenous calcium on chlorophyll fluorescence of seedlings of different tree species. Note:Every column shows the mean ± SE, n=3. Different capital letters indicate significant differences between different treatments of the same tree species (P<0.05). (A) Fv/Fo (Potential photochemical efficiency). (B) Fv/Fm (Maximal photochemical efficiency).
Figure 7.
Effect of exogenous calcium on long-term water use efficiency of seedlings of different tree species. Note: Every column shows the mean ± SE, n=3. Different capital letters indicate significant differences between different treatments of the same tree species (P<0.05).
Figure 7.
Effect of exogenous calcium on long-term water use efficiency of seedlings of different tree species. Note: Every column shows the mean ± SE, n=3. Different capital letters indicate significant differences between different treatments of the same tree species (P<0.05).
Figure 8.
Effect of exogenous calcium on antioxidant enzyme activities of seedlings of different tree species. Note: Every column shows the mean ± SE, n=3. Different capital letters indicate significant differences between different treatments of the same tree species (P<0.05).(A) SOD (Superoxide dismutase); (B) CAT (Catalase); (C) POD (Peroxidase).
Figure 8.
Effect of exogenous calcium on antioxidant enzyme activities of seedlings of different tree species. Note: Every column shows the mean ± SE, n=3. Different capital letters indicate significant differences between different treatments of the same tree species (P<0.05).(A) SOD (Superoxide dismutase); (B) CAT (Catalase); (C) POD (Peroxidase).
Table 1.
Effect of exogenous calcium on total biomass of seedlings of different tree species.
Table 1.
Effect of exogenous calcium on total biomass of seedlings of different tree species.
| Calcium gradient/mg·kg-1
|
Pinus tabuliformis seedlings |
Pinus sylvestris
var. mongolica seedlings |
Populus
seedlings |
Morus alba seedlings |
| 0 |
59.17±0.35 B |
69.68±0.70 C |
28.59±0.08 C |
23.99±0.82 D |
| 100 |
65.34±0.72 A |
81.73±0.04 A |
30.27±0.17 B |
27.44±0.40 BD |
| 200 |
53.74±1.41 C |
75.21±0.44 B |
33.54±0.23 A |
30.26±2.93 C |
| 400 |
45.07±0.80 D |
45.38±0.40 D |
28.46±0.10 C |
46.75±1.13 A |
| 800 |
39.96±0.63 E |
27.49±0.38 E |
25.15±0.29 D |
35.15±8.38 B |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).