Submitted:
26 April 2023
Posted:
28 April 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
Introduction
Methods
Protocol and registration
Eligibility criteria
Information sources
Search strategy
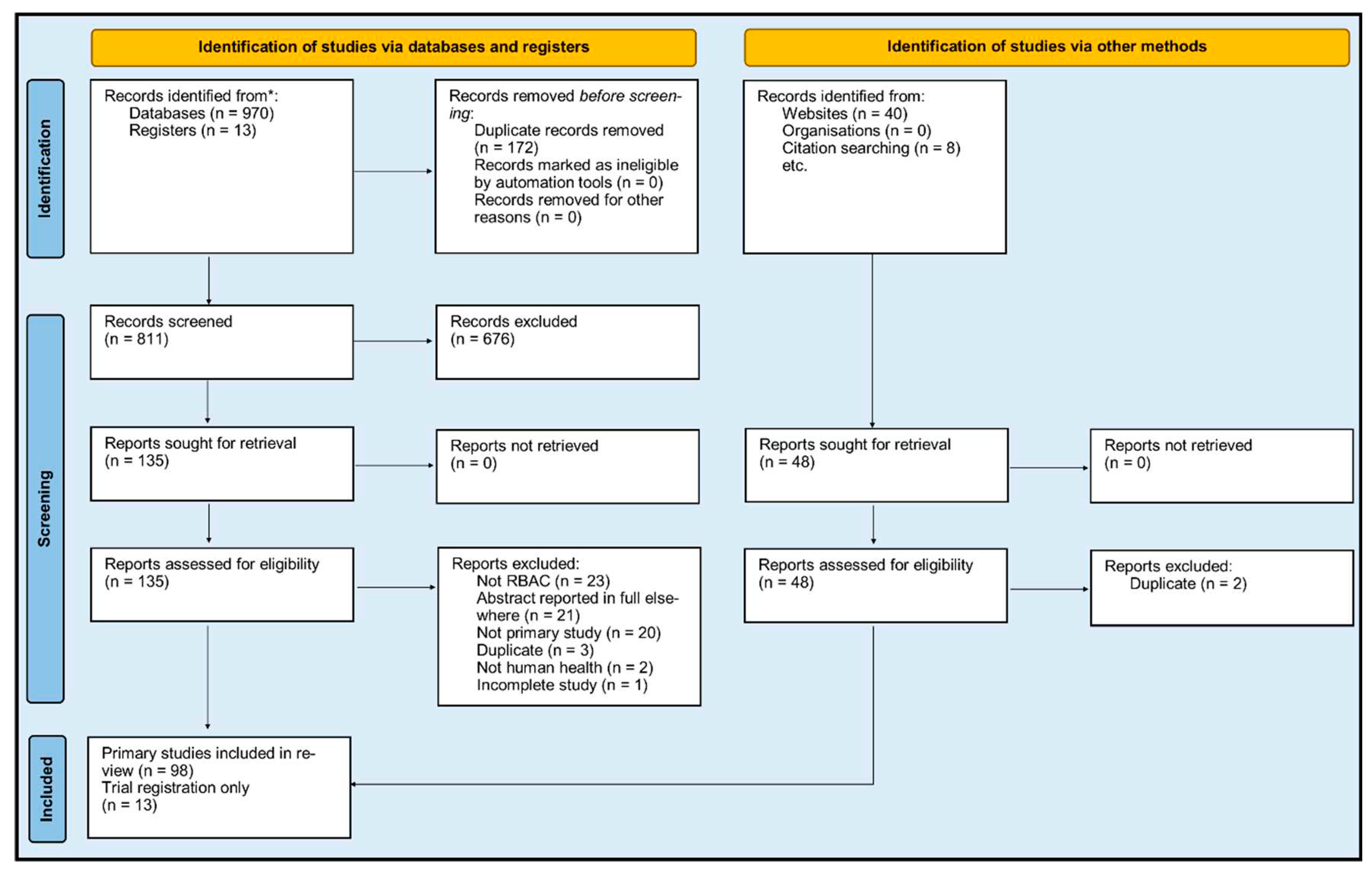
Source of evidence selection
Data extraction
Data analysis and presentation
Results
Sources of evidence
Authors
Institutions
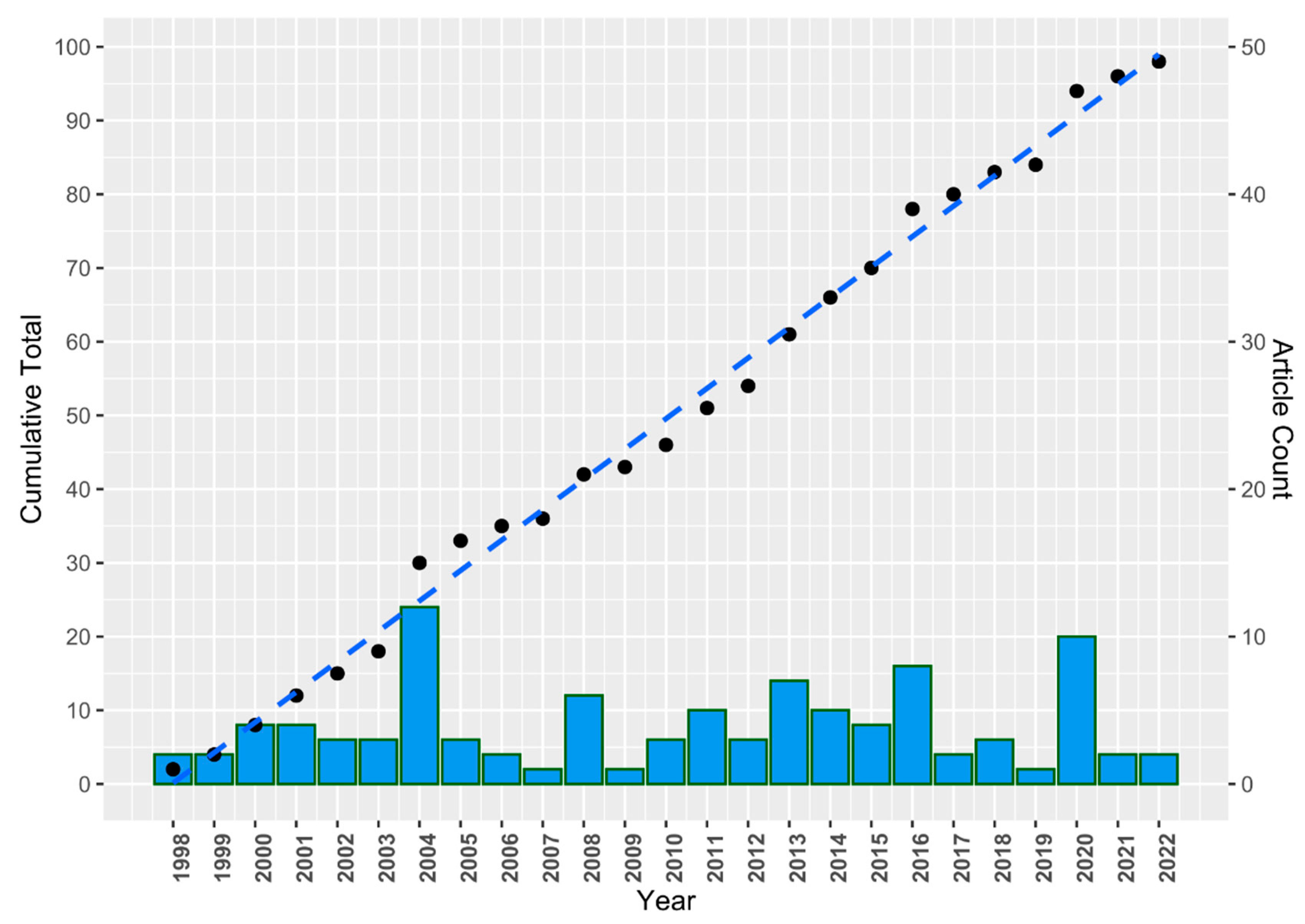
Publications
Citations
Keywords – MeSH
Research evidence
Health or disease conditions
Beneficial actions
Positive outcome measures
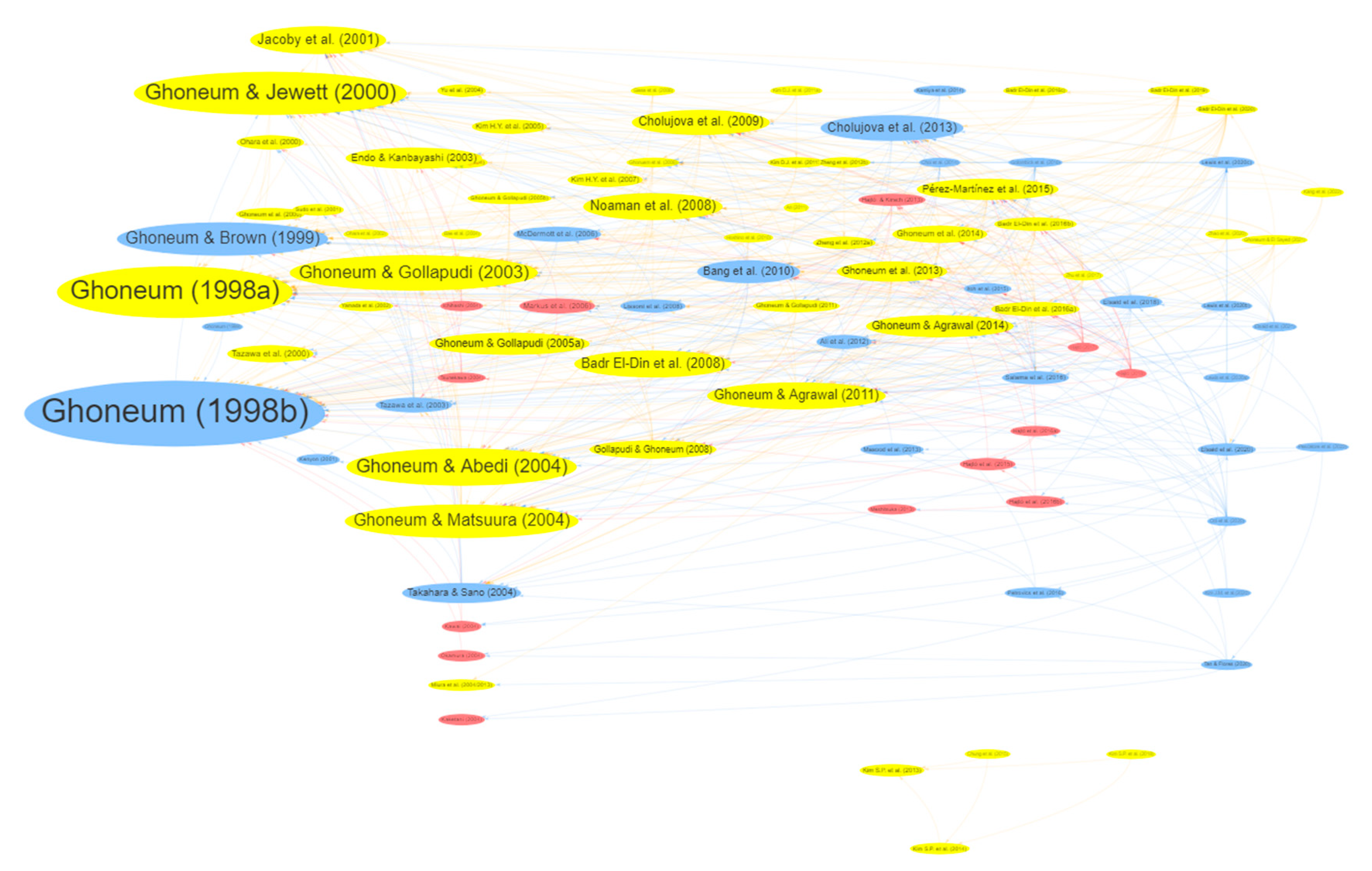
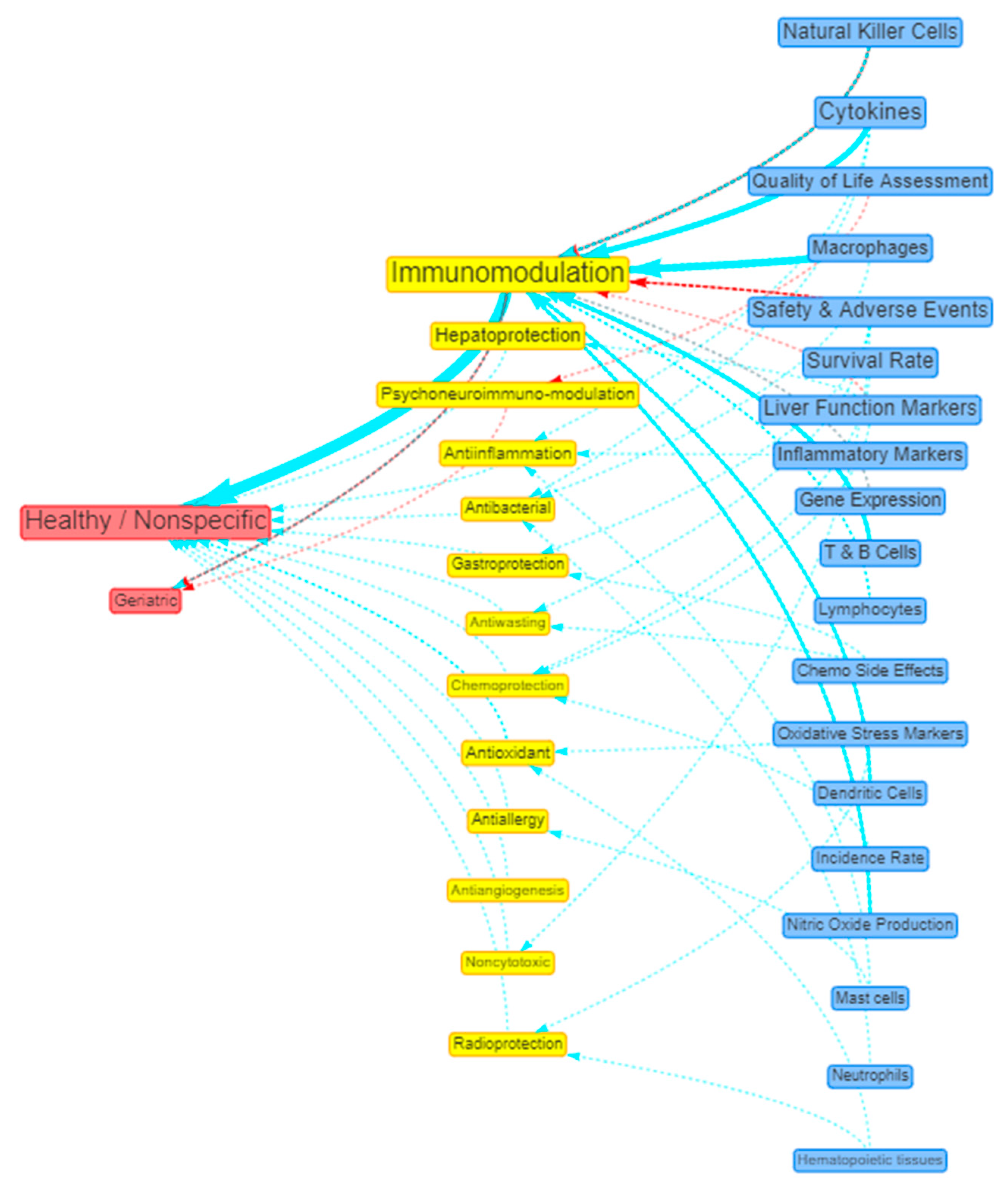
Visualisation of evidence
Discussion
Conclusion
Supporting Information
- S1.
- Supporting Materials for Methods
- S2.
- PRISMA-ScR Checklist.
- S3.
- Data Tables.
- S4.
- Additional Tables and Figures
- S5.
- Additional References
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgements
References
- Kulathunga J, Ozsisli B, Simsek S. Introduction to rice bran arabinoxylan compound. In: Pak SC, Ooi SL, Micalos PS, Ghoneum MH, editors. Modified rice bran arabinoxylan: therapeutic applications in cancer and other diseases. Singapore: Springer Nature; 2023. p. 3-11.
- Ooi, S.L.; Pak, S.C.; Micalos, P.S.; Schupfer, E.; Lockley, C.; Park, M.H.; Hwang, S.-J. The Health-Promoting Properties and Clinical Applications of Rice Bran Arabinoxylan Modified with Shiitake Mushroom Enzyme—A Narrative Review. Molecules 2021, 26, 2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BioBran Research Foundation. The summary of Biobran/MGM-3. BioBran/MGN-3 (Rice Bran Arabinoxylan Coumpound): Basic and clinical application to integrative medicine. 2nd ed. Tokyo, Japan: BioBran Research Foundation; 2013. p. 3-8.
- Hong, S. Development of immunostimulation materials from rice bran. Food Ind. Nutr. 2005, 10, 42–47. [Google Scholar]
- Kim HY, Han JT, Hong SG, Yang SB, Hwang SJ, Shin KS, et al. Enhancement of immunological activity in exo-biopolymer from submerged culture of Lentinus edodes with rice bran. Nat. Prod. Sci. 2005, 11, 183–187. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H.-Y.; Kim, J.-H.; Yang, S.-B.; Hong, S.-G.; Lee, S.-A.; Hwang, S.-J.; Shin, K.-S.; Suh, H.-J.; Park, M.-H.; Banik, S.P.; et al. A Polysaccharide Extracted from Rice Bran Fermented withLentinus edodesEnhances Natural Killer Cell Activity and Exhibits Anticancer Effects. J. Med. Food 2007, 10, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghoneum, M. Enhancement of human natural killer cell activity by modified arabinoxylane from rice bran (MGN-3). Int. J. Immunother. 1998, 14, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghoneum, M. Anti-HIV Activityin Vitroof MGN-3, an Activated Arabinoxylane from Rice Bran. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1998, 243, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fort, D.G.; Herr, T.M.; Shaw, P.L.; Gutzman, K.E.; Starren, J.B. Mapping the evolving definitions of translational research. J. Clin. Transl. Sci. 2017, 1, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghoneum, M. From bench to bedside : The growing use of arabinoxylan rice bran (MGN-3/Biobran) in cancer immunotherapy. Austin Immunol. 2016, 1, 1006. [Google Scholar]
- Ooi, S.L.; McMullen, D.; Golombick, T.; Nut, D.; Pak, S.C. Evidence-Based Review of BioBran/MGN-3 Arabinoxylan Compound as a Complementary Therapy for Conventional Cancer Treatment. Integr. Cancer Ther. 2017, 17, 165–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong Kong Trade Development Council. China’s Health Food Market Hong Kong SAR, China: Hong Kong Trade Development Council; 2022 [cited 2023 27/3/2023]. Available from: https://research.hktdc.com/en/article/MzA4NzQ3NzUw.
- Peters M, Godfrey C, McInerney P, Munn Z, Trico A, Khalil H. Chapter 11: Scoping Reviews. In: Aromataris E, Munn Z, editors. JBI Manual for Evidence Synthesis: JBI; 2020.
- Ooi SL, Micalos PS, Pak SC. Rice Bran Arabinoxylan Compound as a Nutraceutical in Health and Disease – A Scoping Review: OSF Registries; 2022. [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Trial registration: World Health Organization; n.d. [16/2/2023]. Available from: https://www.who.int/clinical-trials-registry-platform/network/trial-registration.
- The evolution of trial registration. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2009, 8, 755–755. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biobran MGN-3 - An Overview: Clear Publications (Biobran.org); n.d. [24/4/2023]. Available from: https://www.biobran.org/overview.
- BioBran Research Foundation. BioBran/MGN-3 (Rice Bran Arabinoxylan Coumpound): Basic and clinical application to integrative medicine. 2nd ed. Tokyo, Japan: BioBran Research Foundation; 2013.
- Institute for Progressive Research of RBAC Immunomodulator Compounds: iPraxic; [24/4/2023]. Available from: https://www.ipraxic.org/.
- Zhang, C. A proposal for calculating weighted citations based on author rank. 2009, 10, 416–417. [CrossRef]
- Institute for Clinical and Translational Research. What are the T0 to T4 research classifications? : Institute for Clinical and Translational Research; n.d. Available from: https://ictr.wisc.edu/what-are-the-t0-to-t4-research-classifications/.
- Tricco, A. C.; Lillie, E.; Zarin, W.; O’Brien, K. K.; Colquhoun, H.; Levac, D.; Moher, D.; Peters, M. D. J.; Horsley, T.; Weeks, L.; et al. PRISMA Extension for Scoping Reviews (PRISMA-ScR): Checklist and Explanation. Ann Intern Med 2018, 169, 467–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Almende BV, Contributors. Network Visualization using 'vis.js' Library. R package version 2.1.2 2022. Available from: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/visNetwork/index.html.
- Ooi SL, Micalos PS, Pak SC. Network Analysis of RBAC Research 2023 [24/4/2023]. Supplementary materials to "Modified Rice Bran Arabinoxylans by Lentinus Edodes Mycelial Enzyme as a Nutraceutical in Health and Disease: “ A Scoping Review with Bibliometric Analysis"]. Available from: https://resource.rbac-qol.info/.
- Cholujova, D.; Jakubikova, J.; Czako, B.; Martisova, M.; Hunakova, L.; Duraj, J.; Mistrik, M.; Sedlak, J. MGN-3 arabinoxylan rice bran modulates innate immunity in multiple myeloma patients. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2012, 62, 437–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Martínez, A.; Valentín, J.; Fernández, L.; Hernández-Jiménez, E.; López-Collazo, E.; Zerbes, P.; Schwörer, E.; Nuñéz, F.; Martín, I.G.; Sallis, H.; et al. Arabinoxylan rice bran (MGN-3/Biobran) enhances natural killer cell–mediated cytotoxicity against neuroblastoma in vitro and in vivo. Cytotherapy 2014, 17, 601–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghoneum, M.; Abdulmalek, S.; Fadel, H.H. Biobran/MGN-3, an Arabinoxylan Rice Bran, Protects against Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2): An In Vitro and In Silico Study. Nutrients 2023, 15, 453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwyer, J.T.; Coates, P.M.; Smith, M.J. Dietary Supplements: Regulatory Challenges and Research Resources. Nutrients 2018, 10, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Database Type | Count | List |
|---|---|---|
| English databases | 6 | MEDLINE (via PubMed), ProQuest, Cochrane Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL), Emcare (via Ovid), Cumulative Index to Nursing & Allied Health Literature (CINAHL plus, via EBSCO), and Web of Science (exclude MEDLINE & KCI). |
| Chinese databases | 2 | Chinese National Knowledge Infrastructure Database (CNKI) and Wanfang. |
| Korean databases | 3 | Korean Journal Database (KCI, via Web of Science), Research Information Service System (RISS), and ScienceON. |
| Japanese databases | 2 | CiNii and J-Stage. |
| Summary Characteristics | N (% total) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| All included articles | 98 (100%) | |||
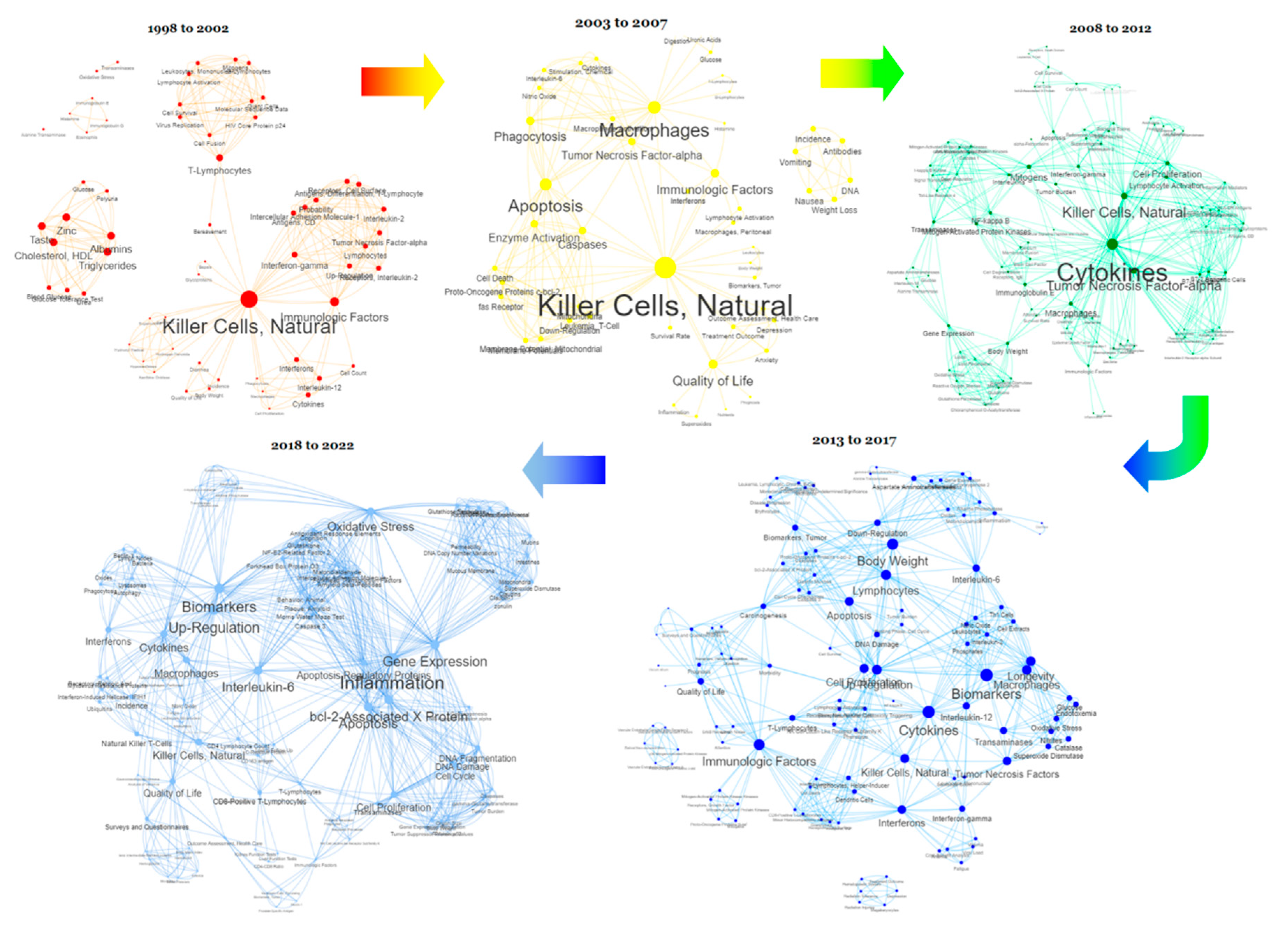
| Publication Years | ||||
| 2018-2022 | 18 (18.37%) | |||
| 2013-2017 | 26 (26.53%) | |||
| 2008-2012 | 18 (18.37%) | |||
| 2003-2007 | 21 (21.43%) | |||
| 1998-2002 | 15 (15.31%) | |||
| Country | ||||
| United States of America (USA) | 29 (29.59%) | |||
| Japan | 22 (22.45%) | |||
| South Korea | 15 (15.31%) | |||
| Egypt | 11 (11.22%) | |||
| Hungary | 7 (7.14%) | |||
| Others | 15 (14.29%) | |||
| Language | ||||
| English | 81 (82.65%) | |||
| Japanese | 11 (11.22%) | |||
| Korean | 6 (6.12%) | |||
| Publication Type | ||||
| Full paper | 85 (86.73%) | |||
| Abstract | 8 (8.16%) | |||
| Book Chapter | 2 (2.04%) | |||
| Short communication | 1 (1.02%) | |||
| Study protocol | 1 (1.02%) | |||
| Thesis | 1 (1.02%) | |||
| Summary Characteristics | N (% total) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| All included articles | 98 (100%) | |||||
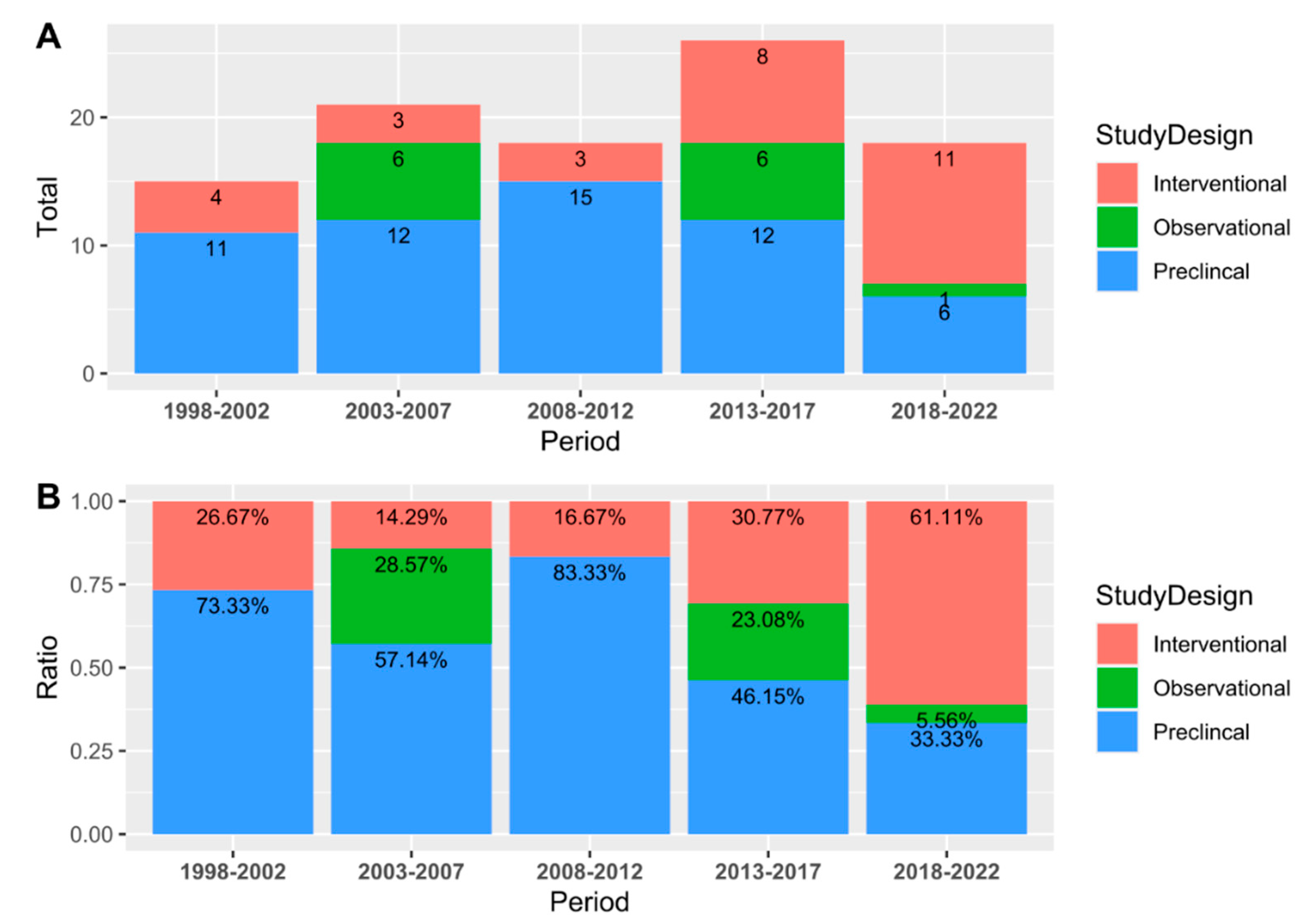
| Study Design | ||||||
| Preclinical | 56 (57.14%) | |||||
| Animal | 25 (25.51%) | |||||
| Animal + Cell | 6 (6.12%) | |||||
| Animal + Cell + Chemical | 3 (3.06%) | |||||
| Cell | 19 (19.39%) | |||||
| Cell + Chemical | 2 (2.04%) | |||||
| Chemical | 1 (1.02%) | |||||
| Clinical | 42 (42.86%) | |||||
| Interventional | ||||||
| Randomised controlled trial | 21 (21.43%) | |||||
| Non-randomised controlled trial | 1 (1.02%) | |||||
| Before and after study | 7 (7.14%) | |||||
| Observational | ||||||
| Descriptive cross-sectional study | 1 (1.02%) | |||||
| Case series | 4 (4.08%) | |||||
| Case report | 8 (8.16%) | |||||
| Translational Stage | ||||||
| T0 – Basic biomedical research | 56 (57.14%) | |||||
| T1 – Translation to humans | 38 (38.78%) | |||||
| T2 – Translation to patients | 4 (4.08%) | |||||
| Summary Characteristics | N (% total) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| All included articles | 98 (100%) | ||||
| Commercial Source of RBAC | |||||
| Daiwa Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd. | 85 (86.73%) | ||||
| Erom Co. Ltd. | 8 (8.16%) | ||||
| STR Biotech Co. Ltd. | 5 (5.10%) | ||||
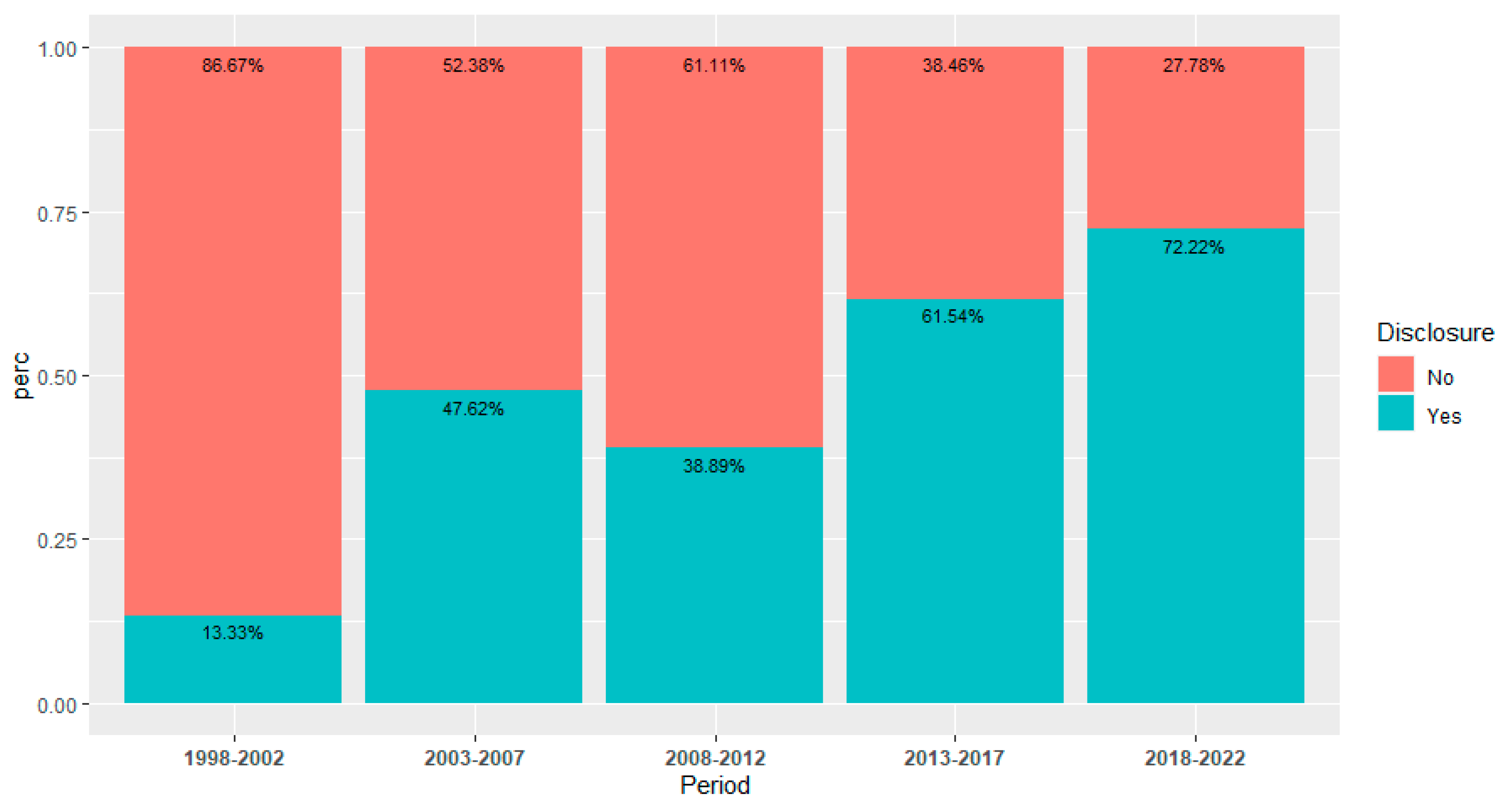
| Funding Sources | |||||
| Not Disclosed | 50 (51.02%) | ||||
| Disclosed * | 48 (48.98%) | ||||
| Commercial – Daiwa | 26 (26.53%) | ||||
| Public | 17 (17.35%) | ||||
| Commercial – Daiwa (Product Only) | 8 (8.16%) | ||||
| Private / Nonprofit | 6 (6.12%) | ||||
| Commercial – Erom | 5 (5.10%) | ||||
| Commercial – Others | 2 (2.04%) | ||||
| Publishing | TWC | Article | Clinical | Preclinical | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| # | Author | Period | Count (% Total) | Intervention | Observation | Animal | In Vitro | Chemical | |
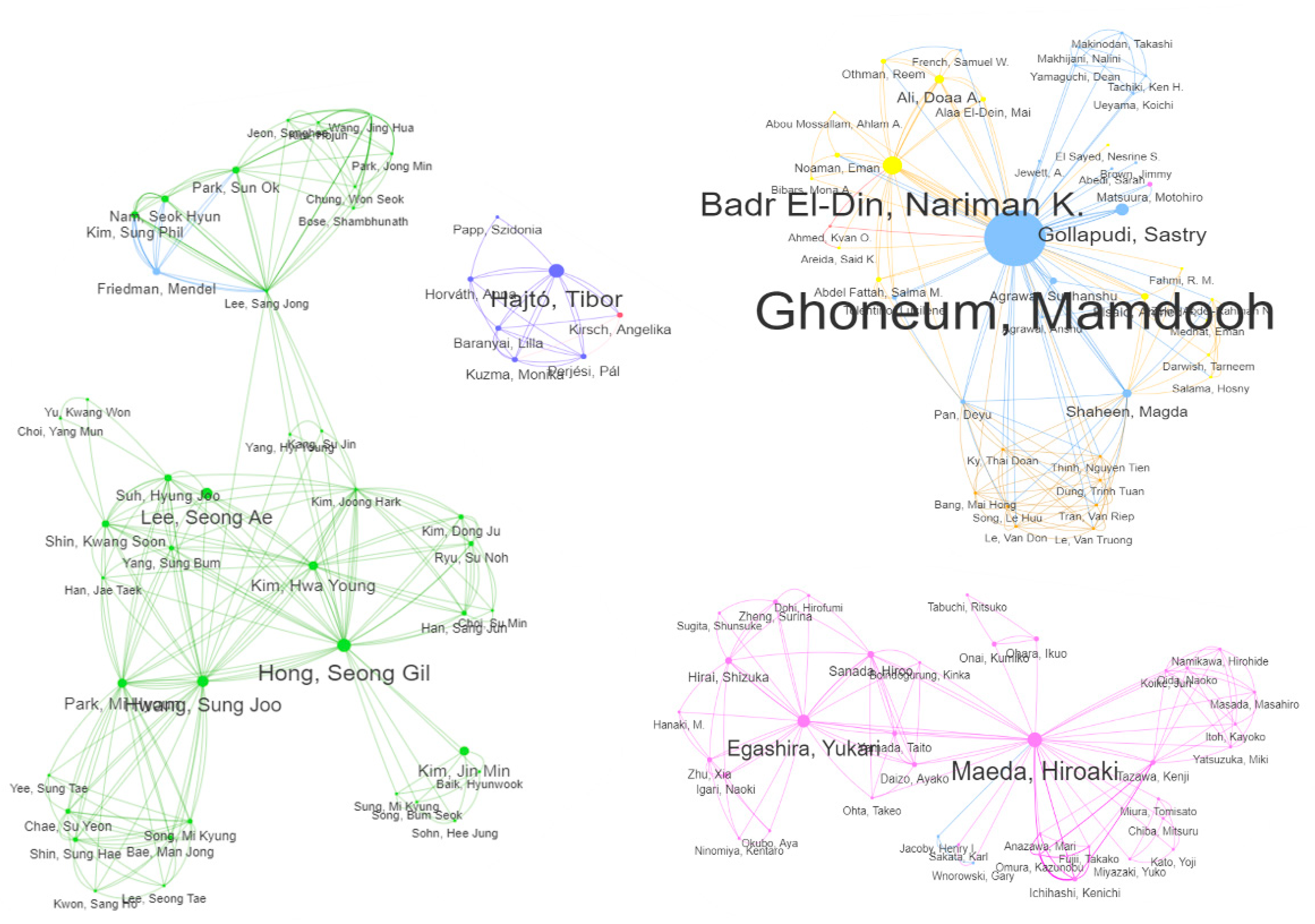
| 1 | Ghoneum, Mamdooh | 1998 - 2021 | 30.00 | 30 (30.61%) | 26.7% | - | 30.0% | 53.3% | - |
| 2 | Badr El-Din, Nariman K. | 2008 - 2020 | 7.64 | 9 (9.18%) | - | - | 88.9% | 11.1% | - |
| 3 | Gollapudi, Sastry | 2003 - 2011 | 6.00 | 6 (6.12%) | - | - | - | 100% | - |
| 3 | Hajtó, Tibor | 2013 - 2018 | 6.00 | 6 (6.12%) | - | 100% | - | - | - |
| 5 | Maeda, Hiroaki | 2000 - 2004 | 5.36 | 7 (7.14%) | 14.3% | - | 57.1% | 14.3% | 28.6% |
| 6 | Egashira, Yukari | 2001 - 2017 | 4.50 | 6 (6.12%) | - | - | 83.3% | 16.7% | - |
| 7 | Lewis, John E. | 2012 - 2020 | 4.00 | 4 (4.08%) | 100% | - | - | - | - |
| 8 | Hong, Seong Gil | 2005 - 2022 | 3.75 | 6 (6.12%) | 16.7% | - | 66.7% | 50.0% | - |
| Publishing | No. | TWC | Article | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| # | Institution | Country | Type | Period | Authors | Authors | Count (% Total) |
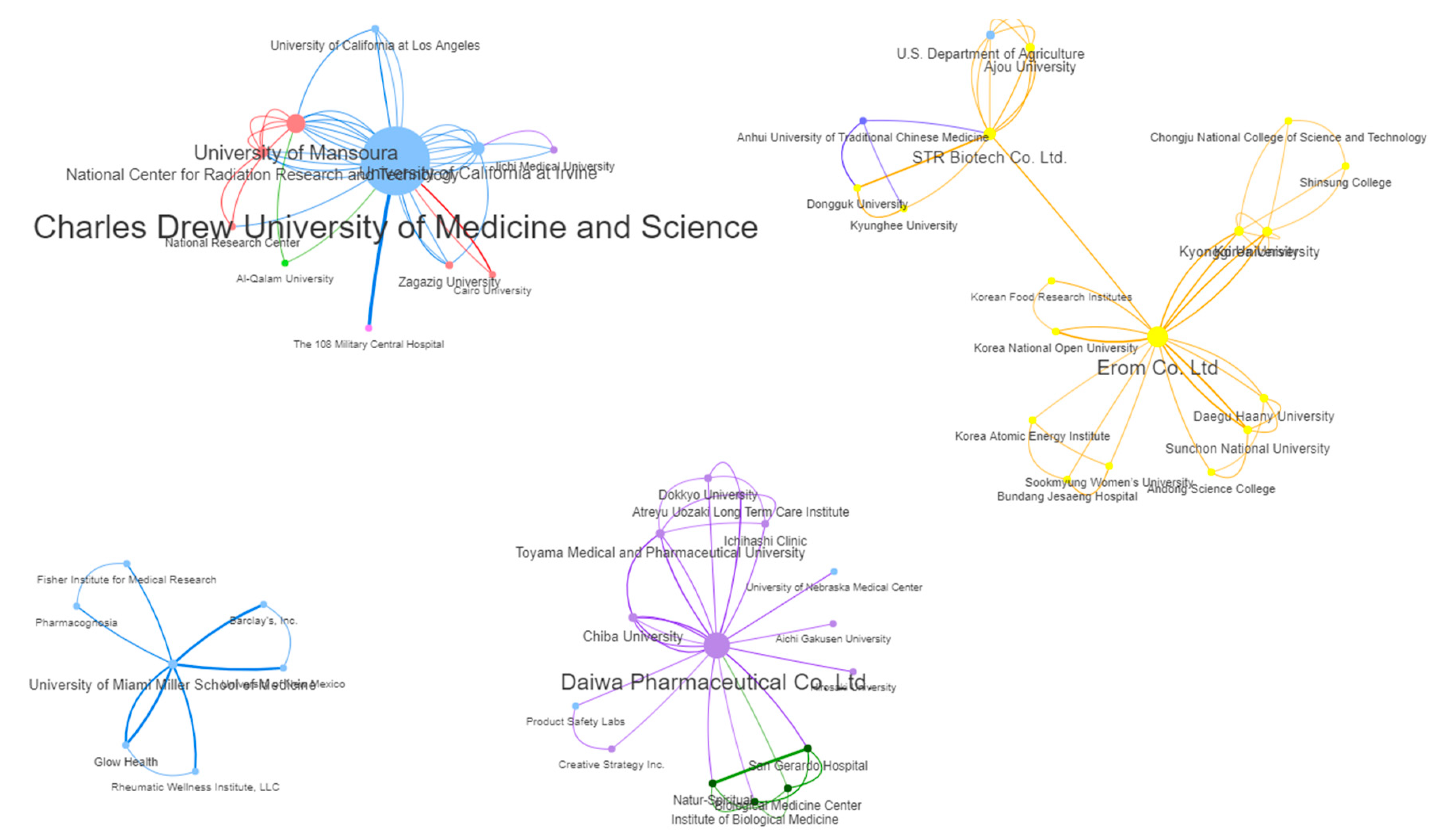
| 1 | Charles Drew University of Medicine and Science | USA | Academic | 1998 - 2021 | 6 | 35.03 | 30 (30.61%) |
| 2 | Daiwa Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd. | Japan | Commercial | 2000 – 2017 | 10 | 10.64 | 11 (11.22%) |
| 3 | University of California at Irvine | USA | Academic | 2003 - 2021 | 3 | 9.00 | 9 (9.18%) |
| 3 | University of Mansoura | Egypt | Academic | 2008 – 2020 | 5 | 13.12 | 9 (9.18%) |
| 5 | Erom Co. Ltd. | South Korea | Commercial | 2004 – 2022 | 13 | 15.49 | 8 (8.16%) |
| 6 | Chiba University | Japan | Academic | 2000 - 2017 | 12 | 14.49 | 7 (7.14%) |
| 7 | University of Pécs | Hungary | Academic | 2013 – 2018 | 12 | 14.36 | 7 (7.14%) |
| 8 | University of Miami Miller School of Medicine | USA | Academic | 2013 - 2022 | 21 | 10.59 | 4 (4.08%) |
| # | Publications | IF | Cite Score | Publisher | Quartile: Category | Art Count (% Total) | Publishing Period |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Clinical Pharmacology and Therapy (Yakuri to Rinsho) | NA | NA | Iyaku Shuppan | NA | 6 (6.12%) | 2004 - 2004 |
| 2 | International Journal of Immunopathology and Pharmacology | 3.219 | 4.1 | Sage Publications | Q1: Medicine (all) | 5 (5.10%) | 2004 - 2016 |
| 3 | Anticancer Research | 2.48 | 3.8 | International Institute of Anticancer Research | Q3: Cancer Research; Q3: Oncology | 4 (4.08%) | 2005 - 2014 |
| 4 | Evidence-based Complementary and Alternative Medicine | 2.629 | 3.0 | Hindawi Publishing | Q1: CAM | 3 (3.06%) | 2014 - 2020 |
| 4 | Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition | 0.548 | 0.9 | The Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition | Q3: Food Science; Q4: Nutrition & Dietetic | 3 (3.06%) | 2004 - 2022 |
| 5 | Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy | 6.529 | 9.3 | Elsevier | Q1: Pharmacology | 2 (2.04%) | 2020 - 2020 |
| 5 | Cancer Detection and Prevention (Continued as Cancer Epidemiology from 2009) | 2.984 | 3.9 | Elsevier | Q3: Cancer Research; Q3: Epidemiology; Q3 – Oncology | 2 (2.04%) | 2000 - 2008 |
| 5 | Cancer Letters | 8.679 | 14 | Elsevier | Q1: Cancer Research: Q1: Oncology | 2 (2.04%) | 2003 - 2008 |
| 5 | Clinical Case Reports and Reviews | NA | NA | Open Access Text | NA | 2 (2.04%) | 2015 - 2016 |
| 5 | Integrative Cancer Therapies | 3.279 | 4.0 | Sage Publications | Q1: CAM; Q2: Oncology | 2 (2.04%) | 2016 – 2016 |
| 5 | International Congress on Anti-Aging & Biomedical Technologies | NA | NA | American Academy of Anti-Aging Medicine | NA | 2 (2.04%) | 1999 - 2000 |
| 5 | Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry | 5.279 | 7.3 | ACS Publications | Q1: Agricultural & Biological Sciences (all): Q1: Chemistry (all) | 2 (2.04%) | 2013 - 2014 |
| 5 | Journal of Dietary Supplements | 2.272 | 3.9 | Informa Healthcare | Q2: Food Science: Q2: Nutrition & Dietetic; Q2: Pharmacology | 2 (2.04%) | 2008 - 2020 |
| 5 | Journal of Japanese Association for Dietary Fiber Research | NA | NA | Japanese Association for Dietary Fiber Research | NA | 2 (2.04%) | 2001 - 2002 |
| 5 | Journal of Radiation Research | 2.724 | 3.5 | Oxford Academic | Q2:HTM; Q2: RadiationQ2: Radiology, Nuclear Medicine and Imaging | 2 (2.04%) | 2013 - 2019 |
| 5 | Neoplasma | 2.757 | 3.3 | AEPress | Q1: Medicine (all); Q3: Oncology | 2 (2.04%) | 2009 - 2011 |
| 5 | Nutrition and Cancer | 2.9 | 4.1 | Routledge | Q3: Cancer Research; Q2: Medicine (misc); Q2: Nutrition & Dietetic; Q2: Oncology | 2 (2.04%) | 2008 - 2016 |
| Ranking By: | Article | Publication | Study Design | Year | Citations: | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Others | Others | ||||||
| 1 | 1 | Ghoneum (1998b) | International Journal of Immunotherapy | Before & after | 1998 | 180 | 59 |
| 2 | 2 | Ghoneum (1998a) | Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications | Cell | 1998 | 146 | 44 |
| 3 | 3 | Ghoneum & Jewett (2000) | Cancer Detection and Prevention | Cell | 2000 | 132 | 35 |
| 4 | 6 | Ghoneum & Matsuura (2004) | International Journal of Immunopathology and Pharmacology | Cell | 2004 | 124 | 25 |
| 5 | 4 | Ghoneum & Abedi (2004) | Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology | Animal + Cell | 2004 | 100 | 29 |
| 6 | 9 | Noaman et al. (2008) | Cancer Letters | Animal | 2008 | 98 | 18 |
| 7 | 5 | Ghoneum & Gollapudi (2003) | Cancer Letters | Cell | 2003 | 93 | 27 |
| 8 | - | Kim H.Y. et al. (2007) | Journal of Medicinal Food | Animal | 2007 | 85 | 5 |
| 9 | - | Pérez-Martínez et al. (2015) | Cytotherapy | Animal + Cell | 2015 | 73 | 12 |
| 10 | 9 | Badr El-Din et al. (2008) | Nutrition and Cancer | Animal | 2008 | 69 | 18 |
| - | 6 | Ghoneum & Brown (1999) | Anti-aging Medical Therapeutics | Before & after | 1999 | 61 | 25 |
| - | 9 | Ghoneum & Agrawal (2011) | International Journal of Immunopathology and Pharmacology | Cell | 2011 | 60 | 18 |
| - | 8 | Jacoby et al. (2001) | Journal of Nutraceuticals, Functional & Medical Foods | Animal | 2001 | 41 | 19 |
| Context | Method | Intervention | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| Humans (59) Animals (43) Male (32) Female (27) Aged (14) Middle Aged (11) Adult (9) Neoplasms (9) |
Mice (29) Liver (15) Rats (14) Lipopolysaccharides (10) Spleen (9) Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (9) Cell Line (8) Cell Line, Tumor (8) Rats, Wistar (6) |
Polysaccharide MGN3 (62) Arabinoxylan (59) Xylans (39) Oryza (25) Shiitake Mushrooms (19) Immunologic Factors (15) Dietary Supplements (12) Hemicellulose (11) Polysaccharides (11) Water (11) Antineoplastic Agents (10) Injections, Intraperitoneal (9) Antioxidants (7) Adjuvants, Immunologic (6) Dose-Response Relationship, Drug (6) Hydrolysis (6) |
Killer Cells, Natural (30) Cytokines (21) Macrophages (16) Quality of Life (15) Apoptosis (12) Cell Proliferation (10) Body Weight (9) Inflammation (9) Interferons (9) Tumour Necrosis Factor-alpha (9) Biomarkers (8) Interleukin-6 (7) T-Lymphocytes (7) Transaminases (7) Up-Regulation (7) Gene Expression (6) Interferon-gamma (6) Lymphocytes (6) Oxidative Stress (6) Phagocytosis (6) |
| # | Condition | Count (%) | Preclinical (%) | Observational (%) | Interventional (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
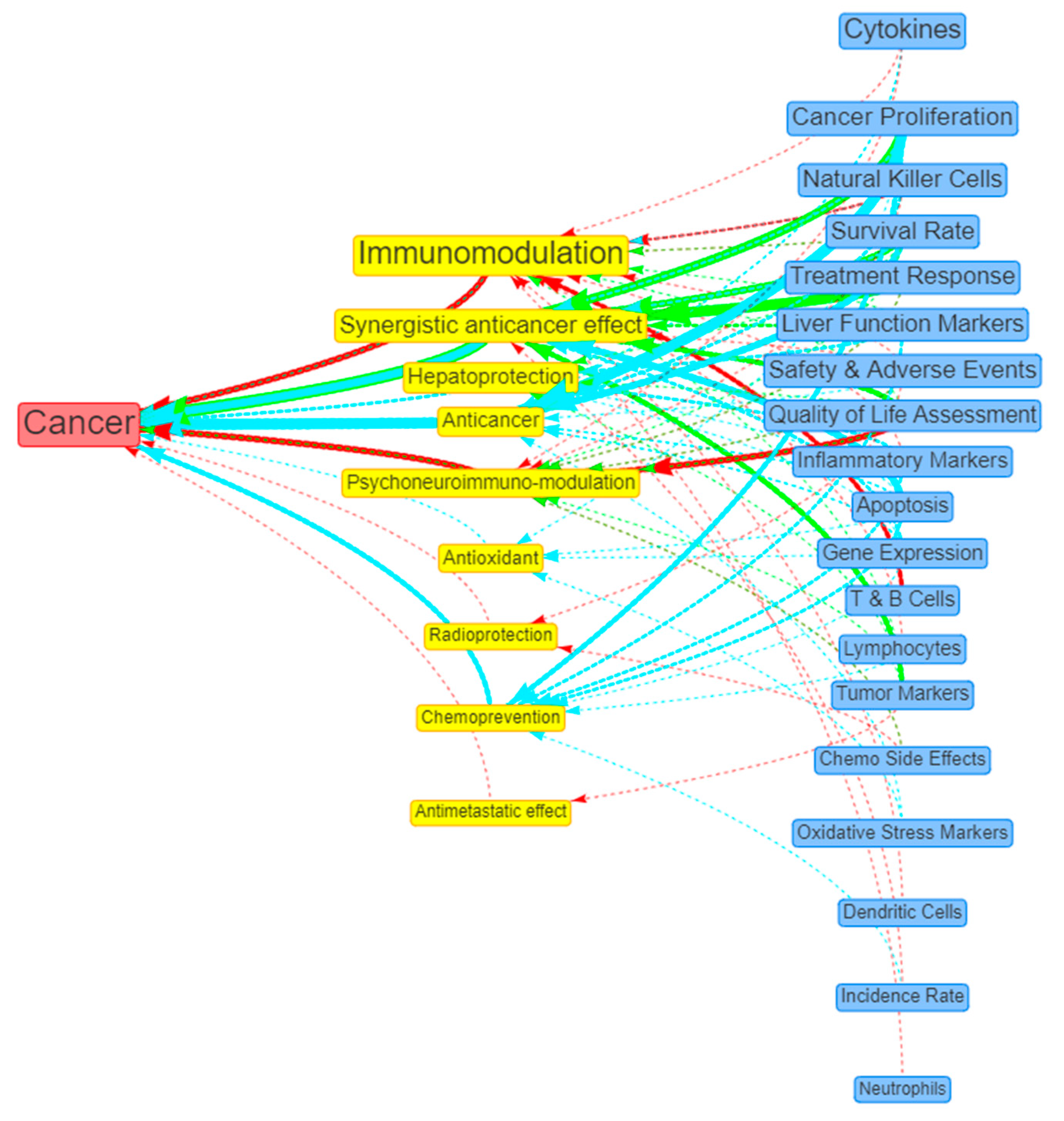
| 1 | Cancer | 45 (45.92%) | 20 (44.44%) | 12 (26.67%) | 13 (28.89%) |
| 2 | Healthy / Nonspecific | 31 (31.63%) | 28 (90.32%) | - | 3 (9.68%) |
| 3 | Hepatitis / Liver Disease | 9 (9.18%) | 7 (77.78%) | - | 2 (22.22%) |
| 4 | Geriatric | 6 (6.12%) | 2 (33.33%) | - | 4 (66.67%) |
| 5 | HIV / AIDS | 4 (4.08%) | 1 (25%) | - | 3 (75%) |
| 6 | Allergy | 4 (4.08%) | 4 (100%) | - | - |
| 7 | CFS | 3 (3.06%) | - | - | 3 (100%) |
| 8 | Gastroenteritis | 3 (3.06%) | 2 (66.67%) | - | 1 (33.33%) |
| 9 | Cold / Flu | 2 (2.04%) | - | - | 2 (100%) |
| 10 | Diabetes mellitus | 2 (2.04%) | 2 (100%) | - | - |
| 11 | Endotoxemia | 2 (2.04%) | 2 (100%) | - | - |
| 12 | Chemical exposure | 1 (1.02%) | - | - | 1 (100%) |
| 13 | IBS | 1 (1.02%) | - | - | 1 (100%) |
| 14 | Rheumatism | 1 (1.02%) | - | 1 (100%) | - |
| 15 | Alzheimer's disease | 1 (1.02%) | 1 (100%) | - | - |
| 16 | Bacterial infection | 1 (1.02%) | 1 (100%) | - | - |
| 17 | Oxidative stress | 1 (1.02%) | 1 (100%) | - | - |
| # | Beneficial Actions | Count (%) | Preclinical (%) | Observational (%) | Interventional (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Immunomodulation | 36 (36.73%) | 21 (58.33%) | 1 (2.78%) | 14 (38.89%) |
| 2 | Synergistic anticancer effect | 19 (19.39%) | 7 (36.84%) | 10 (52.63%) | 2 (10.53%) |
| 3 | Hepatoprotection | 13 (13.27%) | 10 (76.92%) | 1 (7.69%) | 2 (15.38%) |
| 4 | Anticancer | 10 (10.20%) | 9 (90%) | 1 (10%) | - |
| 5 | Psychoneuroimmuno-modulation | 8 (8.16%) | - | 2 (25%) | 6 (75%) |
| 6 | Antiinflammation | 8 (8.16%) | 7 (87.50%) | 1 (12.5%) | - |
| 7 | Antioxidant | 7 (7.14%) | 7 (100%) | - | - |
| 8 | Radioprotection | 3 (3.06%) | 2 (66.67%) | - | 1 (33.33%) |
| 9 | Chemoprevention | 3 (3.06%) | 3 (100%) | - | - |
| 10 | Antiallergy | 3 (3.06%) | 3 (100%) | - | - |
| 11 | Antibacterial | 3 (3.06%) | 3 (100%) | - | - |
| 12 | Antifatigue | 2 (2.04%) | - | - | 2 (100%) |
| 13 | Antiflu | 2 (2.04%) | - | - | 2 (100%) |
| 14 | No significant effect | 2 (2.04%) | - | - | 2 (100%) |
| 15 | Gastroprotection | 2 (2.04%) | 1 (50%) | - | 1 (50%) |
| 16 | Antihyperlipidemic effect | 2 (2.04%) | 2 (100%) | - | - |
|
Other benefits that have one count each: Antiangiogenesis; Antiasthma; Antihyperglycemic effect; Antimetastatic effect; Antiretroviral; Antiviral; Antirheumatic effect; Antiwasting; Chemoprotection; Endothelial improvement; Memory enhancer; Noncytotoxic, Taste influencer. |
|||||
| # | Positive Outcomes | Count (%) | Preclinical (%) | Observational (%) | Interventional (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Cytokines | 25 (25.51%) | 19 (76%) | - | 6 (24%) |
| 2 | Cancer Proliferation | 21 (21.43%) | 14 (66.67%) | 7 (33.33%) | - |
| 3 | Safety & Adverse Events | 19 (19.39%) | 4 (21.05%) | 1 (5.26%) | 14 (73.68%) |
| 4 | Natural Killer Cells | 19 (19.39%) | 9 (47.37%) | - | 10 (52.63%) |
| 5 | Treatment Response | 19 (19.39%) | 1 (5.26%) | 9 (47.37%) | 9 (47.37%) |
| 6 | Survival Rate | 19 (19.39%) | 9 (47.37%) | 8 (42.11%) | 2 (10.53%) |
| 7 | Liver Function Markers | 18 (18.37%) | 12 (66.67%) | 2 (11.11%) | 4 (22.22%) |
| 8 | QoL Assessment | 15 (15.31%) | - | 8 (53.33%) | 7 (46.67%) |
| 9 | Inflammatory Markers | 13 (13.27%) | 10 (76.92%) | 1 (7.69%) | 2 (15.38%) |
| 10 | Macrophages | 13 (13.27%) | 13 (100%) | - | - |
| 11 | T & B Cells Proliferation | 11 (11.22%) | 8 (72.73%) | - | 3 (27.27%) |
| 12 | Gene Expression | 11 (11.22%) | 10 (90.91%) | - | 1 (9.09%) |
| 13 | Apoptosis | 11 (11.22%) | 11 (100%) | - | - |
| 14 | Lymphocytes | 9 ((9.18%) | 5 (55.56%) | - | 4 (44.44%) |
| 15 | Tumour Markers | 8 (8.16%) | - | 6 (75%) | 2 (25%) |
| 16 | Chemo Side Effects | 6 (6.12%) | 2 (33.33%) | 1 (16.67%) | 3 (50%) |
| 17 | Oxidative Stress Markers | 6 (6.12%) | 6 (100%) | - | - |
|
Other positive outcome measures: Incidence Rate (5), Dendritic Cells (5), Nitric Oxide Production (5), Mast Cells (3), Neutrophils (2), Histamine (2), Immunoglobulins (2), Eosinophils (1), Hematopoietic Tissues (1). |
|||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





