Submitted:
27 April 2023
Posted:
28 April 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling Procedure and Bacterial Isolation
2.2. Genomic DNA Extraction and PCRs
2.3. Pulsed-Field Gel Electrophoresis (PFGE) Typing
2.4. Multilocus Sequence Typing (MLST)
2.5. Molecular Detection of Virulence Genes
2.6. Enterotoxins A-D Production
2.7. Antibiotic Susceptibility
3. Results
3.1. Prevalence of S. aureus in Dry-Cured Meat Products Producing Facilities
3.2. Characterization of S. aureus Isolates
3.3. Detection of Virulence Genes
3.4. Antimicrobial Resistance Profiles
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Moretro, T.; Langsrud, S. Residential Bacteria on Surfaces in the Food Industry and Their Implications for Food Safety and Quality. Compr Rev Food Sci Food Saf 2017, 16, 1022–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Loir, Y.; Baron, F.; Gautier, M. Staphylococcus aureus and food poisoning. Genet Mol Res 2003, 2, 63–76. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- EFSA. The European Union One Health 2019 Zoonoses Report 1831-4732; 2021; p. e06406. [Google Scholar]
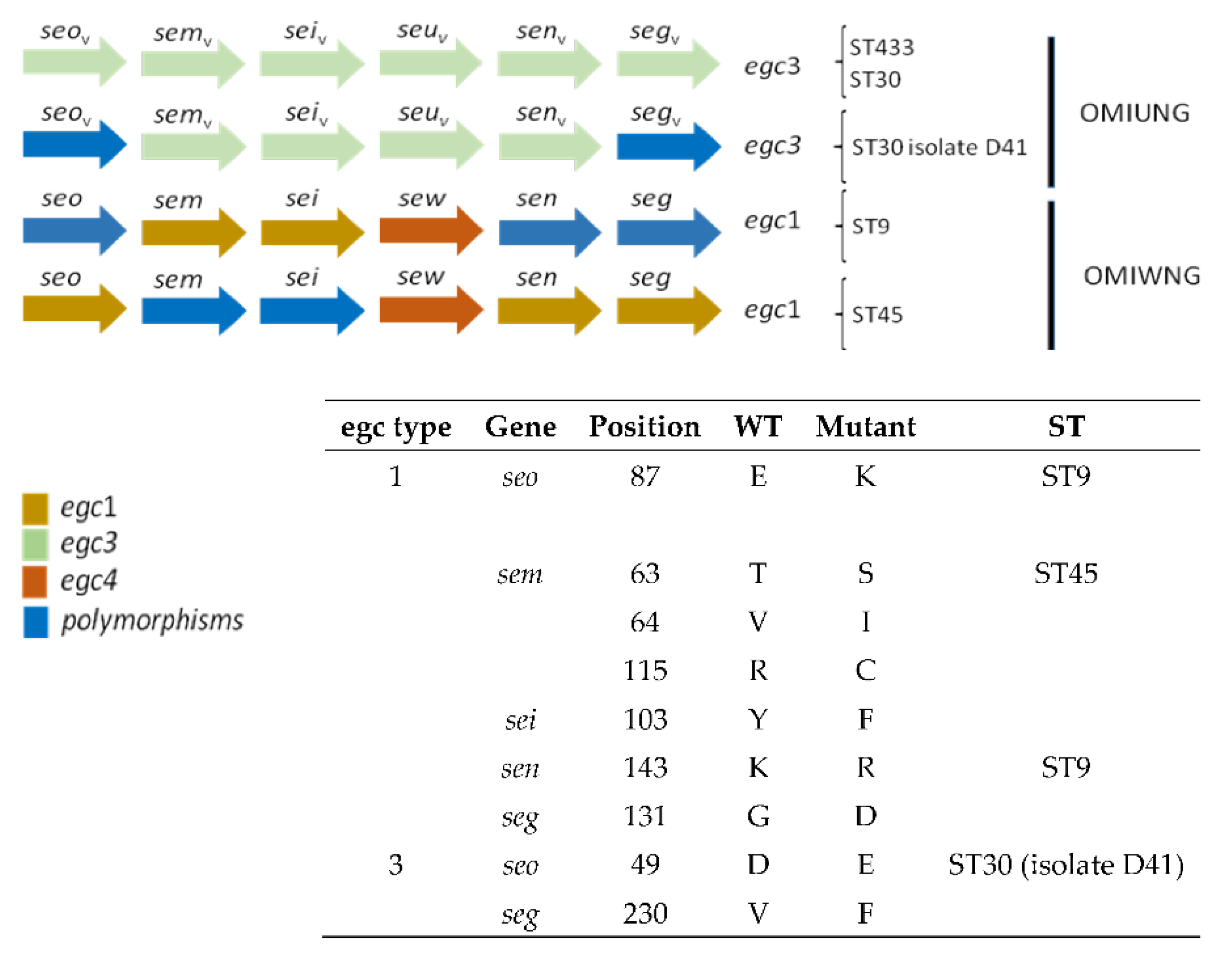
- Schwendimann, L.; Merda, D.; Berger, T.; Denayer, S.; Feraudet-Tarisse, C.; Klaui, A.J.; Messio, S.; Mistou, M.Y.; Nia, Y.; Hennekinne, J.A.; et al. Staphylococcal Enterotoxin Gene Cluster: Prediction of Enterotoxin (SEG and SEI) Production and of the Source of Food Poisoning on the Basis of vSabeta Typing. Appl Environ Microbiol 2021, 87, e0266220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Wang, Y.; Cao, Y.; Yan, W.; Niu, X.; Zhou, L.; Chen, J.; Sun, Y.; Li, C.; Zhang, X.; et al. The Distribution of 18 Enterotoxin and Enterotoxin-Like Genes in Staphylococcus aureus Strains from Different Sources in East China. Foodborne Pathog Dis 2016, 13, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Miao, X.; Zhou, L.; Cui, B.; Zhang, J.; Xu, X.; Wu, C.; Peng, X.; Wang, X. Characterization of Oxacillin-Susceptible mecA-Positive Staphylococcus aureus from Food Poisoning Outbreaks and Retail Foods in China. Foodborne Pathog Dis 2020, 17, 728–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarraud, S.; Peyrat, M.A.; Lim, A.; Tristan, A.; Bes, M.; Mougel, C.; Etienne, J.; Vandenesch, F.; Bonneville, M.; Lina, G. egc, a highly prevalent operon of enterotoxin gene, forms a putative nursery of superantigens in Staphylococcus aureus. J Immunol 2001, 166, 669–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argudin, M.A.; Mendoza, M.C.; Gonzalez-Hevia, M.A.; Bances, M.; Guerra, B.; Rodicio, M.R. Genotypes, exotoxin gene content, and antimicrobial resistance of Staphylococcus aureus strains recovered from foods and food handlers. Appl Environ Microbiol 2012, 78, 2930–2935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajkovic, A.; Jovanovic, J.; Monteiro, S.; Decleer, M.; Andjelkovic, M.; Foubert, A.; Beloglazova, N.; Tsilla, V.; Sas, B.; Madder, A.; et al. Detection of toxins involved in foodborne diseases caused by Gram-positive bacteria. Compr Rev Food Sci Food Saf 2020, 19, 1605–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doyle, M.E.; Hartmann, F.A.; Lee Wong, A.C. Methicillin-resistant staphylococci: implications for our food supply? Anim Health Res Rev 2012, 13, 157–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argudin, M.A.; Mendoza, M.C.; Rodicio, M.R. Food poisoning and Staphylococcus aureus enterotoxins. Toxins (Basel) 2010, 2, 1751–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matyi, S.A.; Dupre, J.M.; Johnson, W.L.; Hoyt, P.R.; White, D.G.; Brody, T.; Odenwald, W.F.; Gustafson, J.E. Isolation and characterization of Staphylococcus aureus strains from a Paso del Norte dairy. J Dairy Sci 2013, 96, 3535–3542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mama, O.M.; Morales, L.; Ruiz-Ripa, L.; Zarazaga, M.; Torres, C. High prevalence of multidrug resistant S. aureus-CC398 and frequent detection of enterotoxin genes among non-CC398 S. aureus from pig-derived food in Spain. Int J Food Microbiol 2020, 320, 108510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EFSA. Assessment of the Public Health significance of meticillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) in animals and foods. EFSA J 2009, 7, 993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Boer, E.; Zwartkruis-Nahuis, J.T.; Wit, B.; Huijsdens, X.W.; de Neeling, A.J.; Bosch, T.; van Oosterom, R.A.; Vila, A.; Heuvelink, A.E. Prevalence of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in meat. Int J Food Microbiol 2009, 134, 52–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, M.A.; Parveen, S.; Rahman, M.; Huq, M.; Nabi, A.; Khan, Z.U.M.; Ahmed, N.; Wagenaar, J.A. Occurrence and Characterization of Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus aureus in Processed Raw Foods and Ready-to-Eat Foods in an Urban Setting of a Developing Country. Front Microbiol 2019, 10, 503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Huang, J.; Wu, Q.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, F.; Yang, X.; Wu, H.; Zeng, H.; Chen, M.; Ding, Y.; et al. Staphylococcus aureus Isolated From Retail Meat and Meat Products in China: Incidence, Antibiotic Resistance and Genetic Diversity. Front Microbiol 2018, 9, 2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enright, M.C.; Day, N.P.; Davies, C.E.; Peacock, S.J.; Spratt, B.G. Multilocus sequence typing for characterization of methicillin-resistant and methicillin-susceptible clones of Staphylococcus aureus. J Clin Microbiol 2000, 38, 1008–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CLSI. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing: 29th Edition. Supplement M100 In CLSI Supplement M100; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Dicks, J.; Turnbull, J.D.; Russell, J.; Parkhill, J.; Alexander, S. Genome Sequencing of a Historic Staphylococcus aureus Collection Reveals New Enterotoxin Genes and Sheds Light on the Evolution and Genomic Organization of This Key Virulence Gene Family. J Bacteriol 2021, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez, D.; Delgado, S.; Vazquez-Sanchez, D.; Martinez, B.; Cabo, M.L.; Rodriguez, A.; Herrera, J.J.; Garcia, P. Incidence of Staphylococcus aureus and analysis of associated bacterial communities on food industry surfaces. Appl Environ Microbiol 2012, 78, 8547–8554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pala, T.R.; Sevilla, A. Microbial contamination of carcasses, meat, and equipment from an Iberian pork cutting plant. J Food Prot 2004, 67, 1624–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gounadaki, A.S.; Skandamis, P.N.; Drosinos, E.H.; Nychas, G.J. Microbial ecology of food contact surfaces and products of small-scale facilities producing traditional sausages. Food Microbiol 2008, 25, 313–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelbicova, T.; Brodikova, K.; Karpiskova, R. Livestock-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in Czech retailed ready-to-eat meat products. Int J Food Microbiol 2022, 374, 109727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korenova, J.; Reskova, Z.; Veghova, A.; Kuchta, T. Tracing Staphylococcus aureus in small and medium-sized food-processing factories on the basis of molecular sub-species typing. Int J Environ Health Res 2015, 25, 384–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, Q.; Peng, Y.; Lin, D.; Bai, C.; Zhang, T.; Lin, J.; Ye, X.; Yao, Z. A Meta-Analysis of the Global Prevalence Rates of Staphylococcus aureus and Methicillin-Resistant S. aureus Contamination of Different Raw Meat Products. J Food Prot 2017, 763–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Zhang, J.; Yu, S.; Wu, Q.; Guo, W.; Huang, J.; Cai, S. Prevalence of Staphylococcus aureus and Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus in Retail Ready-to-Eat Foods in China. Front Microbiol 2016, 7, 816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adame-Gomez, R.; Castro-Alarcon, N.; Vences-Velazquez, A.; Toribio-Jimenez, J.; Perez-Valdespino, A.; Leyva-Vazquez, M.A.; Ramirez-Peralta, A. Genetic Diversity and Virulence Factors of S. aureus Isolated from Food, Humans, and Animals. Int J Microbiol 2020, 2020, 1048097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; He, Y.; Gehring, A.; Hu, Y.; Li, Q.; Tu, S.I.; Shi, X. Genotypes and toxin gene profiles of Staphylococcus aureus clinical isolates from China. PLoS One 2011, 6, e28276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Andersen, P.S.; Stegger, M.; Sieber, R.N.; Ingmer, H.; Staubrand, N.; Dalsgaard, A.; Leisner, J.J. Antimicrobial Resistance and Virulence Gene Profiles of Methicillin-Resistant and -Susceptible Staphylococcus aureus From Food Products in Denmark. Front Microbiol 2019, 10, 2681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waters, A.E.; Contente-Cuomo, T.; Buchhagen, J.; Liu, C.M.; Watson, L.; Pearce, K.; Foster, J.T.; Bowers, J.; Driebe, E.M.; Engelthaler, D.M.; et al. Multidrug-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus in US Meat and Poultry. Clin Infect Dis 2011, 52, 1227–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Neeling, A.J.; van den Broek, M.J.; Spalburg, E.C.; van Santen-Verheuvel, M.G.; Dam-Deisz, W.D.; Boshuizen, H.C.; van de Giessen, A.W.; van Duijkeren, E.; Huijsdens, X.W. High prevalence of methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus in pigs. Vet Microbiol 2007, 122, 366–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wattinger, L.; Stephan, R.; Layer, F.; Johler, S. Comparison of Staphylococcus aureus isolates associated with food intoxication with isolates from human nasal carriers and human infections. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 2012, 31, 455–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, V.; Lopes, C.; Castro, A.; Silva, J.; Gibbs, P.; Teixeira, P. Characterization for enterotoxin production, virulence factors, and antibiotic susceptibility of Staphylococcus aureus isolates from various foods in Portugal. Food Microbiol 2009, 26, 278–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sankomkai, W.; Boonyanugomol, W.; Kraisriwattana, K.; Nutchanon, J.; Boonsam, K.; Kaewbutra, S.; Wongboot, W. Characterisation of Classical Enterotoxins, Virulence Activity, and Antibiotic Susceptibility of Staphylococcus aureus Isolated from Thai Fermented Pork Sausages, Clinical Samples, and Healthy Carriers in Northeastern Thailand. J Vet Res 2020, 64, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Q.; Zhu, Z.; Chang, Y.; Shen, X.; Gao, H.; Yang, Y. Prevalence and Characteristics of Enterotoxin B-Producing Staphylococcus aureus Isolated from Food Sources: A Particular Cluster of ST188 Strains was Identified. J Food Sci 2016, 81, M715–M718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, H.R.; Lee, Y.J. Characterization of Virulence Factors in Enterotoxin-Producing Staphylococcus aureus from Bulk Tank Milk. Animals (Basel) 2022, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.; Shi, C.; Xu, X.; Shi, X. Molecular Typing and Virulence Gene Profiles of Enterotoxin Gene Cluster (egc)-Positive Staphylococcus aureus Isolates Obtained from Various Food and Clinical Specimens. Foodborne Pathog Dis 2016, 13, 592–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekhloufi, O.A.; Chieffi, D.; Hammoudi, A.; Bensefia, S.A.; Fanelli, F.; Fusco, V. Prevalence, Enterotoxigenic Potential and Antimicrobial Resistance of Staphylococcus aureus and Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) Isolated from Algerian Ready to Eat Foods. Toxins (Basel) 2021, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Xie, S. Genotypes, Enterotoxin Gene Profiles, and Antimicrobial Resistance of Staphylococcus aureus Associated with Foodborne Outbreaks in Hangzhou, China. Toxins (Basel) 2019, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johler, S.; Giannini, P.; Jermini, M.; Hummerjohann, J.; Baumgartner, A.; Stephan, R. Further evidence for staphylococcal food poisoning outbreaks caused by egc-encoded enterotoxins. Toxins (Basel) 2015, 7, 997–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerouanton, A.; Hennekinne, J.A.; Letertre, C.; Petit, L.; Chesneau, O.; Brisabois, A.; De Buyser, M.L. Characterization of Staphylococcus aureus strains associated with food poisoning outbreaks in France. Int J Food Microbiol 2007, 115, 369–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Cai, R.; Shi, L.; Li, C.; Yan, H. Prevalence of Enterotoxin Genes in Staphylococcus aureus Isolates from Pork Production. Foodborne Pathog Dis 2018, 15, 437–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Yu, S.; Wu, Q.; Zhang, J.; Wu, S.; Rong, D. Multilocus Sequence Typing and Virulence-Associated Gene Profile Analysis of Staphylococcus aureus Isolates From Retail Ready-to-Eat Food in China. Front Microbiol 2018, 9, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, M.T.; Lauderdale, T.L.; Chou, C.C. Characteristics and virulence factors of livestock associated ST9 methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus with a novel recombinant staphylocoagulase type. Vet Microbiol 2013, 162, 779–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lina, G.; Piemont, Y.; Godail-Gamot, F.; Bes, M.; Peter, M.O.; Gauduchon, V.; Vandenesch, F.; Etienne, J. Involvement of Panton-Valentine leukocidin-producing Staphylococcus aureus in primary skin infections and pneumonia. Clin Infect Dis 1999, 29, 1128–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argudin, M.A.; Mendoza, M.C.; Mendez, F.J.; Martin, M.C.; Guerra, B.; Rodicio, M.R. Clonal complexes and diversity of exotoxin gene profiles in methicillin-resistant and methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus isolates from patients in a Spanish hospital. J Clin Microbiol 2009, 47, 2097–2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohde, H.; Knobloch, J.K.; Horstkotte, M.A.; Mack, D. Correlation of Staphylococcus aureus icaADBC genotype and biofilm expression phenotype. J Clin Microbiol 2001, 39, 4595–4596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrascosa, C.; Raheem, D.; Ramos, F.; Saraiva, A.; Raposo, A. Microbial Biofilms in the Food Industry-A Comprehensive Review. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2021, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Kim, S.; Lee, H.; Ha, J.; Lee, J.; Choi, Y.; Oh, H.; Yoon, Y.; Choi, K.H. icaA Gene of Staphylococcus aureus Responds to NaCl, Leading to Increased Biofilm Formation. J Food Prot 2018, 81, 412–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Sanz, E.; Torres, C.; Lozano, C.; Fernandez-Perez, R.; Aspiroz, C.; Ruiz-Larrea, F.; Zarazaga, M. Detection, molecular characterization, and clonal diversity of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus CC398 and CC97 in Spanish slaughter pigs of different age groups. Foodborne Pathog Dis 2010, 7, 1269–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Wu, F. Livestock-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (LA-MRSA) colonisation and infection among livestock workers and veterinarians: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Occup Environ Med 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuny, C.; Kock, R.; Witte, W. Livestock associated MRSA (LA-MRSA) and its relevance for humans in Germany. Int J Med Microbiol 2013, 303, 331–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sergelidis, D.; Angelidis, A.S. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: a controversial food-borne pathogen. Lett Appl Microbiol 2017, 64, 409–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadopoulos, P.; Papadopoulos, T.; Angelidis, A.S.; Kotzamanidis, C.; Zdragas, A.; Papa, A.; Filioussis, G.; Sergelidis, D. Prevalence, antimicrobial susceptibility and characterization of Staphylococcus aureus and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolated from dairy industries in north-central and north-eastern Greece. Int J Food Microbiol 2019, 291, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parisi, A.; Caruso, M.; Normanno, G.; Latorre, L.; Sottili, R.; Miccolupo, A.; Fraccalvieri, R.; Santagada, G. Prevalence, antimicrobial susceptibility and molecular typing of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) in bulk tank milk from southern Italy. Food Microbiol 2016, 58, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Titouche, Y.; Hakem, A.; Houali, K.; Meheut, T.; Vingadassalon, N.; Ruiz-Ripa, L.; Salmi, D.; Chergui, A.; Chenouf, N.; Hennekinne, J.A.; et al. Emergence of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) ST8 in raw milk and traditional dairy products in the Tizi Ouzou area of Algeria. J Dairy Sci 2019, 102, 6876–6884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, C.H.; Tuckman, M.; Howe, A.Y.; Orlowski, M.; Mullen, S.; Chan, K.; Bradford, P.A. Diagnostic PCR analysis of the occurrence of methicillin and tetracycline resistance genes among Staphylococcus aureus isolates from phase 3 clinical trials of tigecycline for complicated skin and skin structure infections. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2006, 50, 505–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Price, L.B.; Stegger, M.; Hasman, H.; Aziz, M.; Larsen, J.; Andersen, P.S.; Pearson, T.; Waters, A.E.; Foster, J.T.; Schupp, J.; et al. Staphylococcus aureus CC398: host adaptation and emergence of methicillin resistance in livestock. mBio 2012, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poulsen, A.B.; Skov, R.; Pallesen, L. Detection of low-level methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus with commercially available tests. J Clin Microbiol 2003, 41, 3458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becker, K.; Roth, R.; Peters, G. Rapid and specific detection of toxigenic Staphylococcus aureus: use of two multiplex PCR enzyme immunoassays for amplification and hybridization of staphylococcal enterotoxin genes, exfoliative toxin genes, and toxic shock syndrome toxin 1 gene. J Clin Microbiol 1998, 36, 2548–2553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monday, S.R.; Bohach, G.A. Use of multiplex PCR to detect classical and newly described pyrogenic toxin genes in staphylococcal isolates. J Clin Microbiol 1999, 37, 3411–3414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLauchlin, J.; Narayanan, G.L.; Mithani, V.; O'Neill, G. The detection of enterotoxins and toxic shock syndrome toxin genes in Staphylococcus aureus by polymerase chain reaction. J Food Prot 2000, 63, 479–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omoe, K.; Ishikawa, M.; Shimoda, Y.; Hu, D.L.; Ueda, S.; Shinagawa, K. Detection of seg, seh, and sei genes in Staphylococcus aureus isolates and determination of the enterotoxin productivities of S. aureus isolates Harboring seg, seh, or sei genes. J Clin Microbiol 2002, 40, 857–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasudevan, P.; Nair, M.K.; Annamalai, T.; Venkitanarayanan, K.S. Phenotypic and genotypic characterization of bovine mastitis isolates of Staphylococcus aureus for biofilm formation. Vet Microbiol 2003, 92, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarraud, S.; Mougel, C.; Thioulouse, J.; Lina, G.; Meugnier, H.; Forey, F.; Nesme, X.; Etienne, J.; Vandenesch, F. Relationships between Staphylococcus aureus genetic background, virulence factors, agr groups (alleles), and human disease. Infect Immun 2002, 70, 631–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
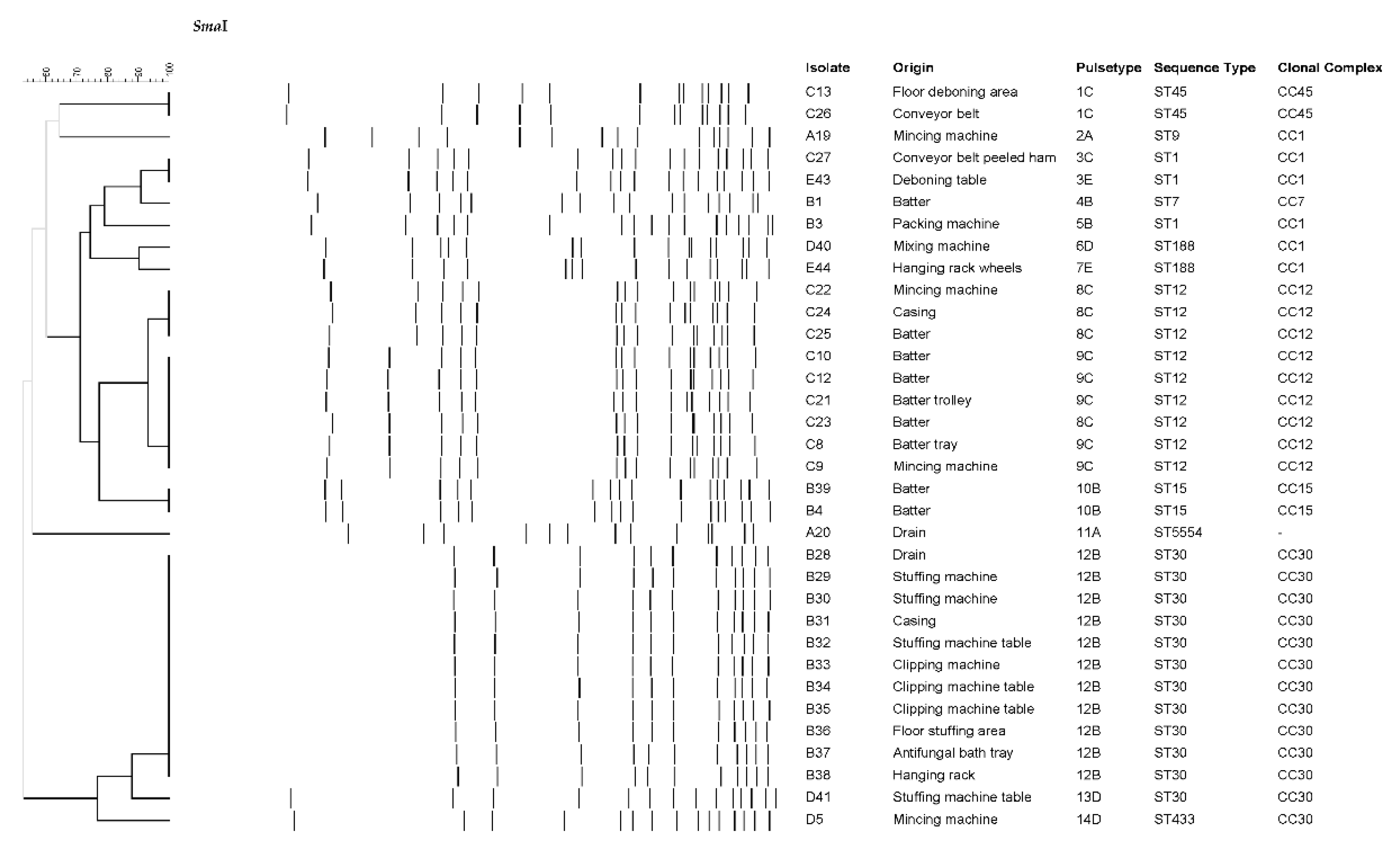
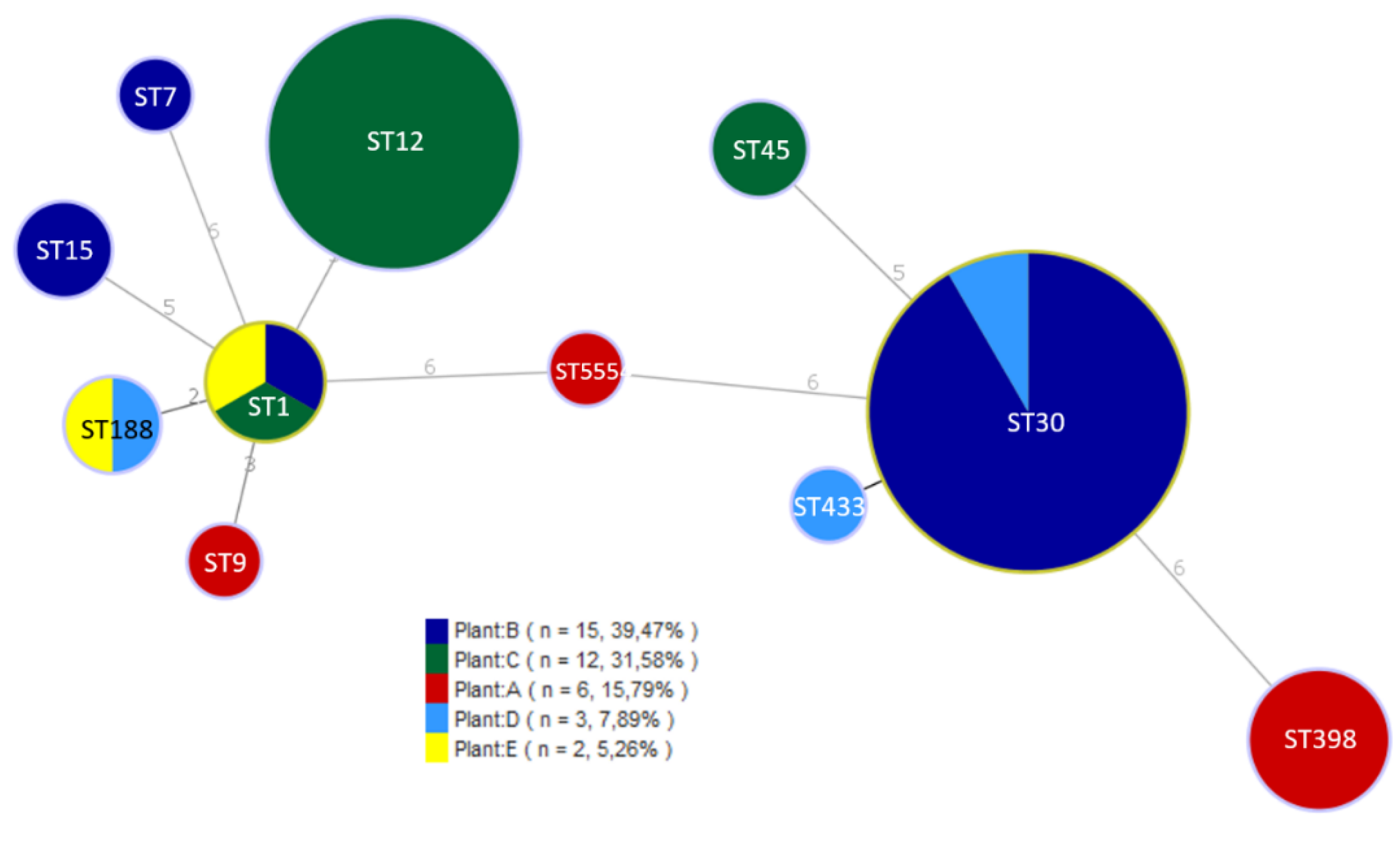
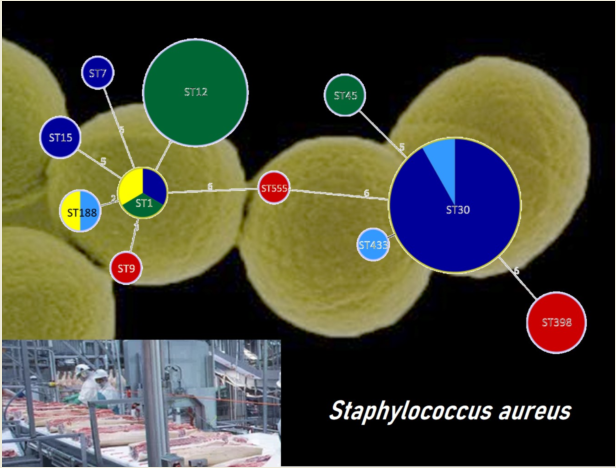
| Plant | ES | DP | ACD | FCS | NFCS | IMB | FP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. positives/ No. samples |
No. positives/ No. samples |
No. positives/ No. samples |
No. positives/ No. samples |
No. positives/ No. samples |
No. positives/ No. samples |
No. positives/ No. samples |
|
| A | 4/123 | 3/122 | 1/1 | 3/49 | 1/74 | 2/18 | 0/4 |
| B | 11/183 | 11/129 | 0/54 | 6/98 | 5/85 | 4/29 | 0/7 |
| C | 7/139 | 6/71 | 1/68 | 4/60 | 3/79 | 5/11 | NA |
| D | 3/104 | 2/53 | 1/51 | 2/49 | 1/55 | 0/10 | 0/3 |
| E | 2/97 | 2/60 | 0/37 | 1/61 | 1/36 | NA | NA |
| F | 0/74 | 0/69 | 0/5 | 48 | 26 | NA | NA |
| Total | 27/720 | 24/504 | 3/216 | 16/365 | 11/355 | 11/68 | 0/14 |
| Isolate | Plant | ST | Toxin genes | Antibiotic resistance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A42 | A | ST398 | - | PEN, FOX, ERY, TET, CIP |
| A6 | A | ST398 | - | PEN, FOX, TET |
| A17 | A | ST398 | - | PEN, TET |
| A18 | A | ST398 | - | PEN, FOX, ERY, TET |
| A19 | A | ST9 | seg, sei, sem, sen, seo, sew, tst | PEN, TET |
| A20 | A | ST5554 | tst | - |
| B1 | B | ST7 | - | - |
| B3 | B | ST1 | seb, seh, tst | PEN |
| B4 | B | ST15 | tst | PEN, TET |
| B28 | B | ST30 | sea, seg, sei, sem, sen, seo, seu, tst | PEN |
| B29 | B | ST30 | sea, seg, sei, sem, sen, seo, seu, tst | PEN |
| B30 | B | ST30 | sea, seg, sei, sem, sen, seo, seu, tst | PEN |
| B31 | B | ST30 | sea, seg, sei, sem, sen, seo, seu, tst | PEN |
| B32 | B | ST30 | sea, seg, sei, sem, sen, seo, seu, tst | PEN |
| B33 | B | ST30 | sea, seg, sei, sem, sen, seo, seu, tst | PEN |
| B34 | B | ST30 | sea, seg, sei, sem, sen, seo, seu, tst | PEN |
| B35 | B | ST30 | sea, seg, sei, sem, sen, seo, seu, tst | PEN |
| B36 | B | ST30 | sea, seg, sei, sem, sen, seo, seu, tst | PEN |
| B37 | B | ST30 | sea, seg, sei, sem, sen, seo, seu, tst | PEN |
| B38 | B | ST30 | sea, seg, sei, sem, sen, seo, seu, tst | PEN |
| B39 | B | ST15 | tst | PEN, TET |
| C8 | C | ST12 | tst | - |
| C9 | C | ST12 | tst | - |
| C10 | C | ST12 | tst | - |
| C12 | C | ST12 | tst | - |
| C13 | C | ST45 | sec, seg, sei, sem, sen, seo, sew, tst | PEN |
| C21 | C | ST12 | tst, lukED | - |
| C22 | C | ST12 | tst, lukED | - |
| C23 | C | ST12 | tst, lukED | - |
| C24 | C | ST12 | tst, lukED | - |
| C25 | C | ST12 | tst, lukED | - |
| C26 | C | ST45 | sec, seg, sei, sem, sen, seo, sew, tst | PEN |
| C27 | C | ST1 | seh, tst | PEN, ERY |
| D5 | D | ST433 | seg, sei, sem, sen, seo, seu | - |
| D40 | D | ST188 | sea, tst | PEN |
| D41 | D | ST30 | sea, seg, sei, sem, sen, seo, seu, tst | PEN |
| E43 | E | ST1 | seh | PEN, ERY |
| E44 | E | ST188 | tst | PEN |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





