1. Introduction
Over the past 50 years, an increasing proportion of the world's aluminium supply has come from a variety of sources. One of the major sources is ore, however, scrap aluminium from industrial waste and end-of-life products is increasingly coming to the fore. The processing of this scrap to produce a new aluminium alloy is known as recycling, and the alloy is commonly called secondary. [
1,
2]. Recycling represents increased environmental care in the aluminium industry, which is related to reducing the consumption of resources such as energy, materials, water, and soil, extending the lifetime of products, etc. [
3,
4,
5,
6]. The producers of such aluminum casts have worried about the effect of chemical composition (especially higher Fe content) on strength, hardness, wear resistance, creep, stress relaxation, or fatigue since these are influenced by the size, volume, and morphology of microstructural parameters or intermetallic [
7].
Unfortunately, even in casting processes, coarse microstructures, and various defects are commonly formed, which possibly reduce the mechanical properties and especially the fatigue strength of the final cast part, as they are discontinuity elements and act as stress concentrators. [
8]. The higher Fe content also affects the porosity of cast material. In general, the porosity parameters (percent porosity, maximum porosity) tend to increase with increasing % wt. Fe. [
9]. Although iron is very soluble in liquid aluminium and its alloys, it has very low solubility in the solid state and therefore tends to combine with other elements to form various types of intermetallic phases. As the % Fe increases, the size and density of Fe-based intermetallic phases also increase. In the absence of Si the phases Al
3Fe and Al
6Fe are dominant, with the presence of Si being dominant phases such as Al
8Fe
2Si (known as α-phase) and Al
5FeSi (known as β-phase). The higher content of Fe causes an increase in forming of a long and higher amount of Al
5FeSi phases. Hard and brittle Al
5FeSi platelets (3D morphology)/needles (2D metallography surface) have a detrimental influence on the properties of the alloy. These phases enhance porosity, reduce fluidity, act as stress concentrators, promote crack formation, and reduce impact strength, machinability, and fatigue life. In terms of corrosion, Fe reduces the corrosion resistance of materials. Despite the lower value of the electrode potential of the metal, aluminum has excellent corrosion resistance in a neutral environment owing to a passive layer. This passive layer consists of aluminium oxides and hydroxides that reduce the rate of corrosion processes by isolating the metal from the environment [
11]. If this layer is removed by mechanical or chemical means, both anodic and cathodic reactions begin immediately (<1 mS) and continue until the layer reforms [
12]. Al corrosion occurs relatively rapidly in areas of activity where the metal is oxidized to a soluble ionic product, Al 3+. At pH from 4 to 8.5, aluminum is able to form a thin stable passivation layer of hydrated aluminum oxides (Al
2O
3 · H
2O), which significantly slow corrosion reactions [
12,
13].
Whereas Fe decreases the corrosion resistance of materials, is very important to study its impact in different environments. The corrosion rate of aluminum in pure water is extremely low. The assessment of corrosion properties of Al alloys used in the automotive industry is important because in many regions cars are exposed to severe corrosive conditions during winter, due to the use of de-icing salt, but also important is how exactly Al and chloride (Cl−) ions s influence the protective character of the quasi-passive surface films [
13]. Uneven corrosion attack of aluminum alloys occurs especially in the case of higher inhomogeneities of the material, which represent the so-called. "weak spots”. The weak spots are affected by the purity of Al (i.e., the higher the purity, the higher the corrosion resistance), and therefore the course of corrosion processes depends on the chemical and structural composition of Al-alloys. Vargel [
14] describes in his work the fact that the individual components of the structure of Al-alloys have different potential values and move in both directions from the potential of the basic matrix. However, the dissolution potential of aluminum alloys is determined by its main component, the solid solution α. The value of the dissolution potential is approximately -845 mV. The values of the dissolution potentials of the most common intermetallic phases in Al alloys also differ from the value of the matrix potential. The microstructure of Al-Si alloys often leads to the formation of galvanic cells, which are places not only for the initiation but also for the growth of pitting corrosion, precisely due to the presence of intermetallic phases of different chemical compositions [
15]. In the case of the presence of Mg and Si, the Fe forms the π-phase Al
8FeMg
3Si
6, resp. Fe with Mn addition forms Al
15(Fe, Mn)
3Si
2 [
10]. Mg is an element that improves the corrosion resistance of Al alloys depending on other additive elements present in the alloy. The increased Mg content results in a higher susceptibility of Al alloys to intergranular corrosion or stress cracking. The Mg
2Si phase is even more "active" compared to the Al alloy matrix or silicon itself and contributes to pitting or intergranular corrosion [
19,
20] focused on investigating the corrosion behavior of AlSi7Mg0.3 alloy before and after heat treatment. Vargel [
14] stated that the presence of larger eutectic Si particles, in non-heat-treated alloys, caused the formation of pitting corrosion largely compared to heat-treated alloys. In general, the formation of pitting corrosion in Al-Si alloys is associated with a difference in corrosion potential, as the intermetallic phases, as well as eutectic Si, represent the sites for cathodic reactions [
16,
17]. In some cases, lead to the formation of intercrystalline corrosion or corrosion during casting stress. Vargel and Ambant et al. [
14,
18] also showed in their work that the presence of Fe-rich intermetallic phases has an adverse effect on corrosion resistance. The Fe-rich phases act as catalytic sites for cathodic reactions as well as nucleation sites for corrosion pits.
Al-Si alloys are widely used in fatigue-critical structural applications, such as engine blocks, cylinder heads, and suspension components, for their excellent combination of mechanical and technological properties, to improve automotive fuel economy [
2]. The increasing use of cast Al-components under repeated cyclic loading has focused considerable interest on the fatigue properties of cast Al-alloys. The Wöhler test is the most widely used analysis to determine the fatigue properties of a material and to determine the fatigue lifetime and fatigue strength of constant stress amplitude. The results obtained from the experiments are plotted into the graphical dependence of the amplitude of the applied nominal stress 𝜎
𝑎 depending on the number of cycles to the fracture N
f [
21,
22]. The fatigue life curve for aluminum alloys 𝜎
𝑎=
f (N) has a different shape that of steel. For aluminum alloys the fatigue life curve decreases constantly with stress amplitude, therefore aluminum alloys are characterized by a fatigue time limit (σ
c) for a certain number of cycles [
23]. The authors [
24] experimented on the AlSi9Cu3 aluminum alloy in a casting state, where was obtained the typical fatigue curve. The results show that the fatigue life increases with the decreasing of stress amplitude in the range of 160 MPa to 80 MPa and the fatigue limit was stated as a value σ
c = 80MPa. Fatigue properties of cast aluminum components strongly depend on casting defects and microstructural characteristics (especially intermetallic phases and eutectic Si needle-like forms). According to the authors [
25,
26] the material with higher Fe content has a better fatigue lifetime, while fatigue is tested at 100 MPa. Increasing Fe-content reduces the fatigue life in the long lifetime regime (> 10
6 cycles). Thus has no effect on medium fatigue lifetime (> 10
5 and < 10
6 cycles) and it slightly increases the fatigue life in the short lifetime regime (< 10
5 cycles).
For secondary Al alloys to be able to compete with primary Al alloys, it is essential that the products produced from them are of high quality and have comparable properties over their entire service life. The quality of the casting itself is affected by several factors and one of the most significant is a higher presence of Fe. As mentioned above, higher Fe content reduces the corrosion properties of castings. Therefore, this work focused on the effect of the corrosion environment on the mechanical and fatigue properties of secondary AlSi7Mg0.3 alloys with different Fe contents.
2. Materials and Methods
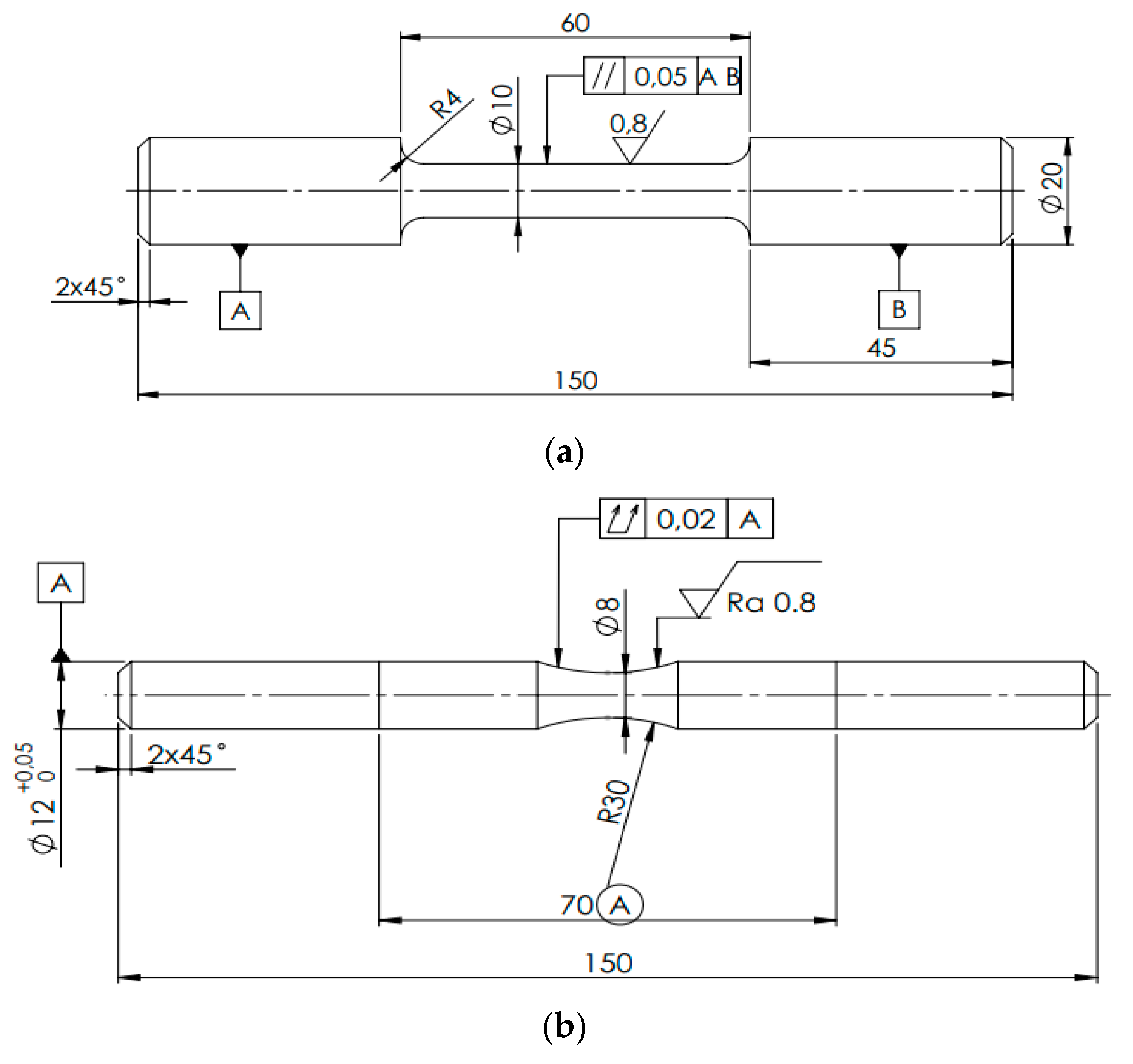
Three as-cast aluminum alloys (cast into sand molds) were studied in this work. as the casting of secondary alloys in sand molds has not been investigated so far. The alloys were manufactured in UNEKO, Zátor, Ltd. Czech Republic company with the aim to investigate if the increased Fe content will have a significant detrimental effect on fatigue and corrosion properties. The original alloy ingots were re-melted and sand-casted into the shape of bars with a diameter of 20 mm and a length of 300 mm. The investigated alloys were without modification or refinement. The chemical compositions are presented in
Table 1. As can be seen – the iron content is gradually increasing. Since the alloy designated A is a primary type of alloy without the use of scrap metal, the Fe content is the lowest. The secondary alloys designated B and C are secondary alloys, where a ratio of scrap metal was used, thus they possess higher Fe contamination. There is also a slight difference between other main alloying elements such as Si, Mg, and Cu, but these differences are not expected to have a significant influence on mechanical and corrosion properties. From the as-cast bars were manufactured specimens for tensile tests and fatigue tests per
Figure 1.
The microstructure character of experimental materials can be evaluated with different methods of quantitative metallography. In the past, the evaluation of microstructure was measured by etalons, measurement of structural parameters by coherent tests grids, and so on. Nowadays is mostly used automatic image analysis. The image analysis enables the evaluation of different structural parameters, for example, the evaluation of the volume (area) ratio of phases and structural components, the shape of particles, size of particles, count of particles per unit of area or volume, the measurement of the distance between particles, length, width, diameter, angle, area or perimeter of particles, the orientation of the structure and so on in different materials [
7,
29]. Therefore, the image analysis software NIS Elements 5.0 was used for these studies.
Specimens for metallography analysis were prepared by standard metallography procedure and as etchers were used 0.5% HF, Dix-Keller, and for highlighting of Fe intermetallic phases, H2SO4 etcher was used. For highlighting the 3D morphology of structural constituents, the deep etching method was used as well. Deep etching was performed with an HCl etcher, which dissolved the matrix so other microstructural constituents (eutectic Si, and intermetallic phases) were visible and were not dissolved in the etcher.
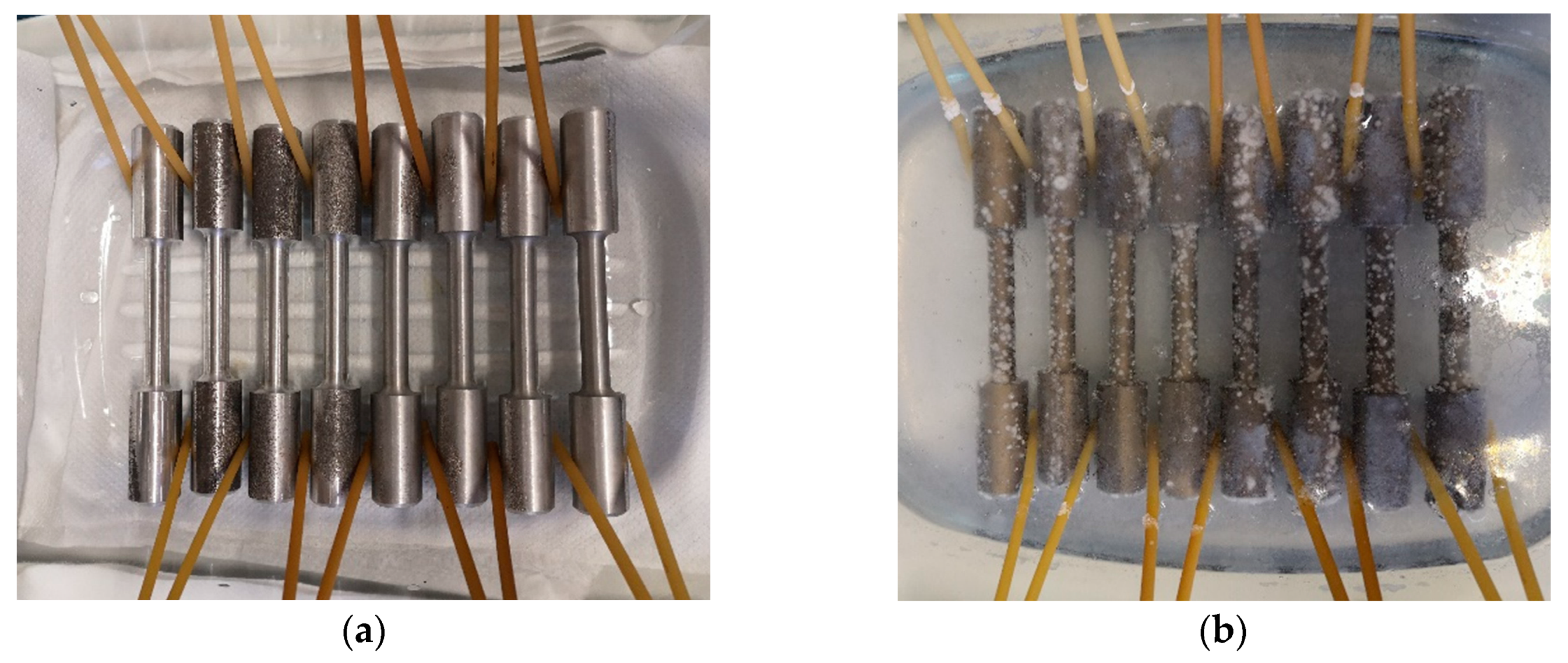
The tensile tests, hardness test, and bending impact tests were performed on experimental alloys that: (a) were in as-cast state (without being affected by the corrosion environment), and (b) after corrosion attack. The exposition of specimens to a corrosive environment was performed by immersion test. The corrosion environment was 3.5 % NaCl (aq) solution in which were samples immersed for three weeks (
Figure 2).
Tensile testing was performed on Instron 5985 device (ISO 6892-1A standard [
31]), where the test results include UTS (Ultimate Tensile Strength) and Ductility. Five test specimens per
Figure 1a for each series of materials A, B, and C were used to determine the mechanical properties and averaged.
For the assessment of alloy quality, the quality index (QI) or their derivates are commonly applied to assess comprehensively the operating durability of as-cast aluminium alloys. In this study, the QI index was calculated according to Drouzy per the following formula [
32,
33]:
where: UTS – ultimate tensile strength; A – elongation; d – experimentally chosen coefficient, depending on the alloy type (in the case of casting hypoeutectic Al-Si alloys, the most often chosen value is 150.
The hardness was obtained with the use NEXUS 3000 hardness tester per ISO 6506 – 1 standard [
34]. The used method was HBW 5/250 and the resulting values are average of total six measurements.
The Charpy impact test was performed on Charpy tester with nominal energy of 300 J. These tests provide information about resistance of the material to impact loading. The final result value at each state was obtained by an average of at least six measurements.
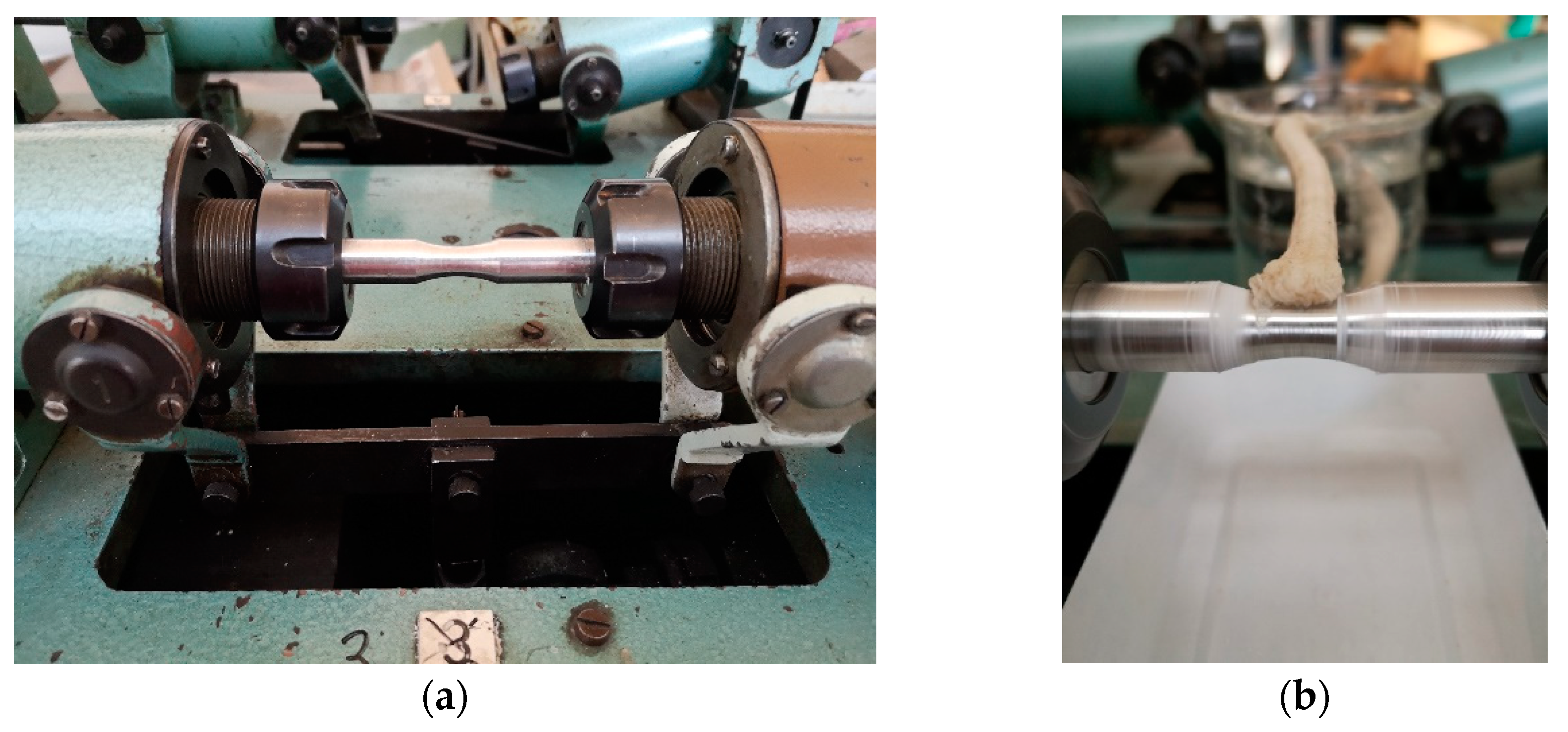
Fatigue tests were performed on the experimental device KOUPT - for rotating bending fatigue testing on specimens per
Figure 1b. All details regarding the test methodology, e.g. test setup, temperature control, data recording and others complied with STN 42 0363 [
35]. During rotation is stress at the gauge length sinus changes from maximum tension to maximum pressure. It means that it is a symmetrical load with a stress asymmetry ratio R = -1, at room temperature T = 20
5 °C. The testing device is powered by an electric motor and the load frequency depends on its speed, which in our case is 30 Hz. The recording of the number of applied cycles is determined using the revolutions counter.
Two fatigue tests types were performed: (a) fatigue test on rotation bending device at room temperature without environment (
Figure 3a), (b) fatigue test on rotation bending device at room temperature with corrosion environment (
Figure 3b). As corrosion environment was used 3.5 wt.% NaCl solution. To verify the effect of the corrosive environment during the cyclic loading of the samples, a solution of 3.5% NaCl was continuously applied to the stressed area with the use of a wick during rotation. During the fatigue test was controlled the wick, whether is a solution still transported to the stressed area. These measurements were performed under the same conditions as the fatigue tests of the specimens without the application of corrosive solution, and under the same loads.
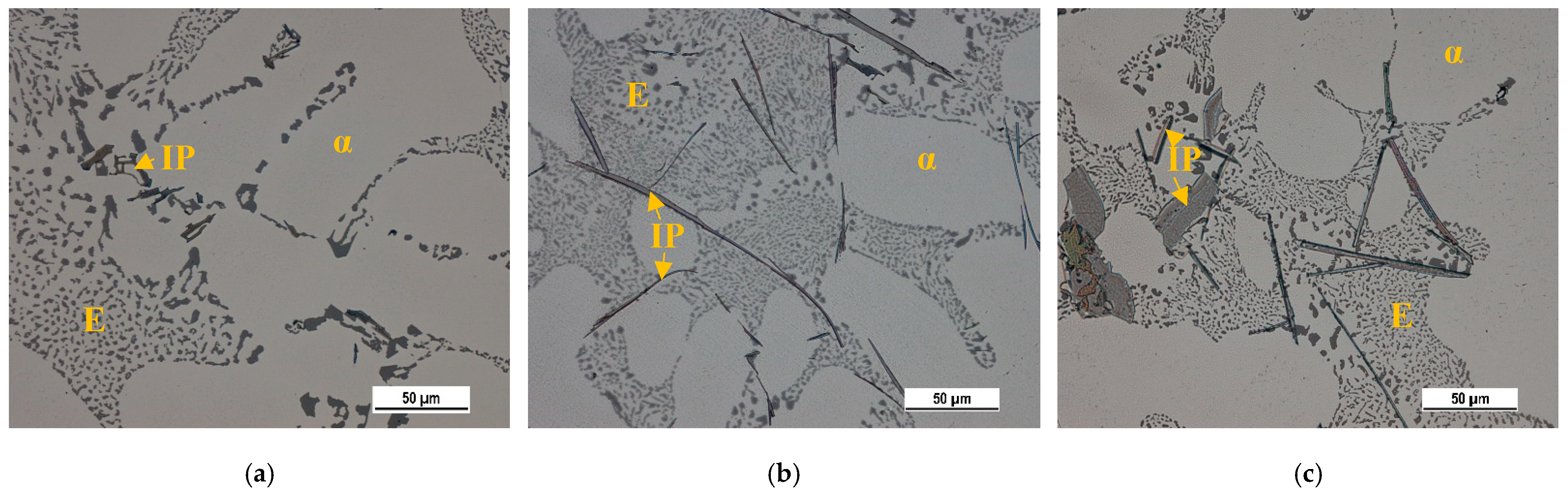
3.1. Basic Microstructure
The microstructure analysis demonstrated the presence of general microstructural constituents: matrix (α-phase), eutectic (mechanical mixture of α-phase and eutectic Si), and intermetallic phases with different chemical compositions (
Figure 4). The effect of higher Fe content on the basic microstructural features and porosity in the same experimental materials were evaluated in our previous study [
34]. Its results show the effect of increased Fe content on forming longer Fe-rich phases in form needles (
Figure 4b), eutectic Si morphology changes (
Figure 4), and porosity formation. The formation of finer eutectic Si particles was confirmed as a result of the increasing formation of the Fe plate-like phases in the microstructure (
Figure 4). The length of the Fe needle-like phases affects the pore growth, too. The longest phases (in alloy B) led to the formation of smaller pores than in alloys A and C [
36].
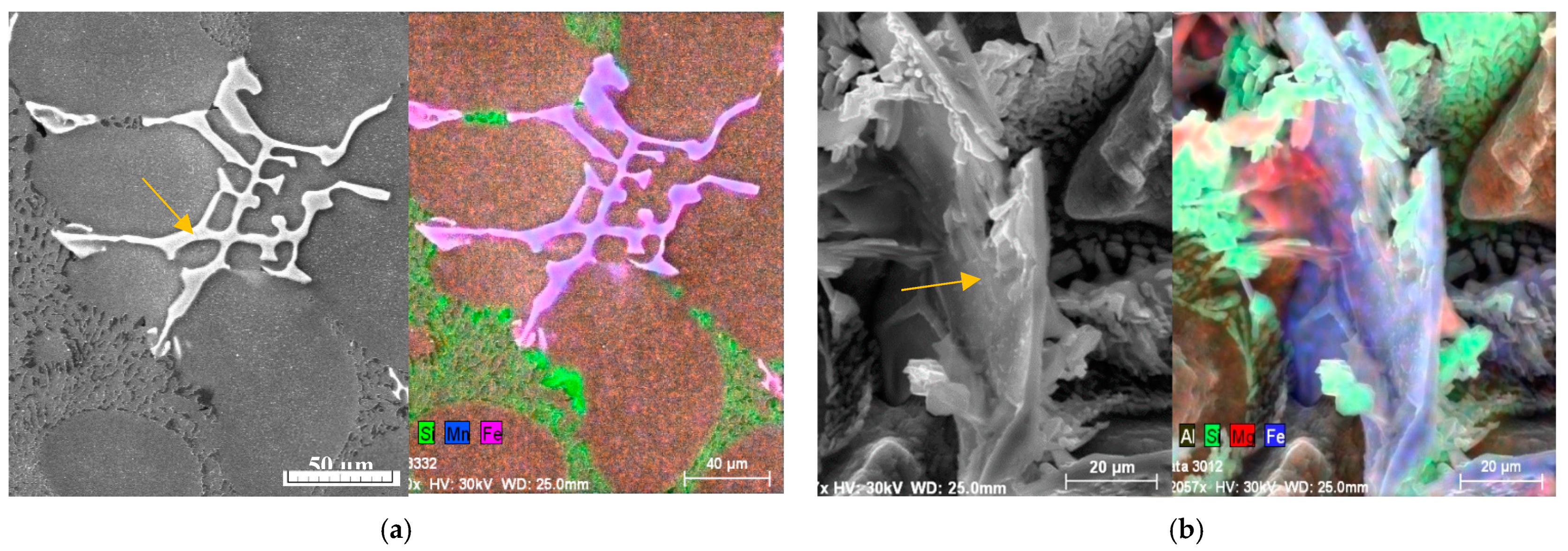
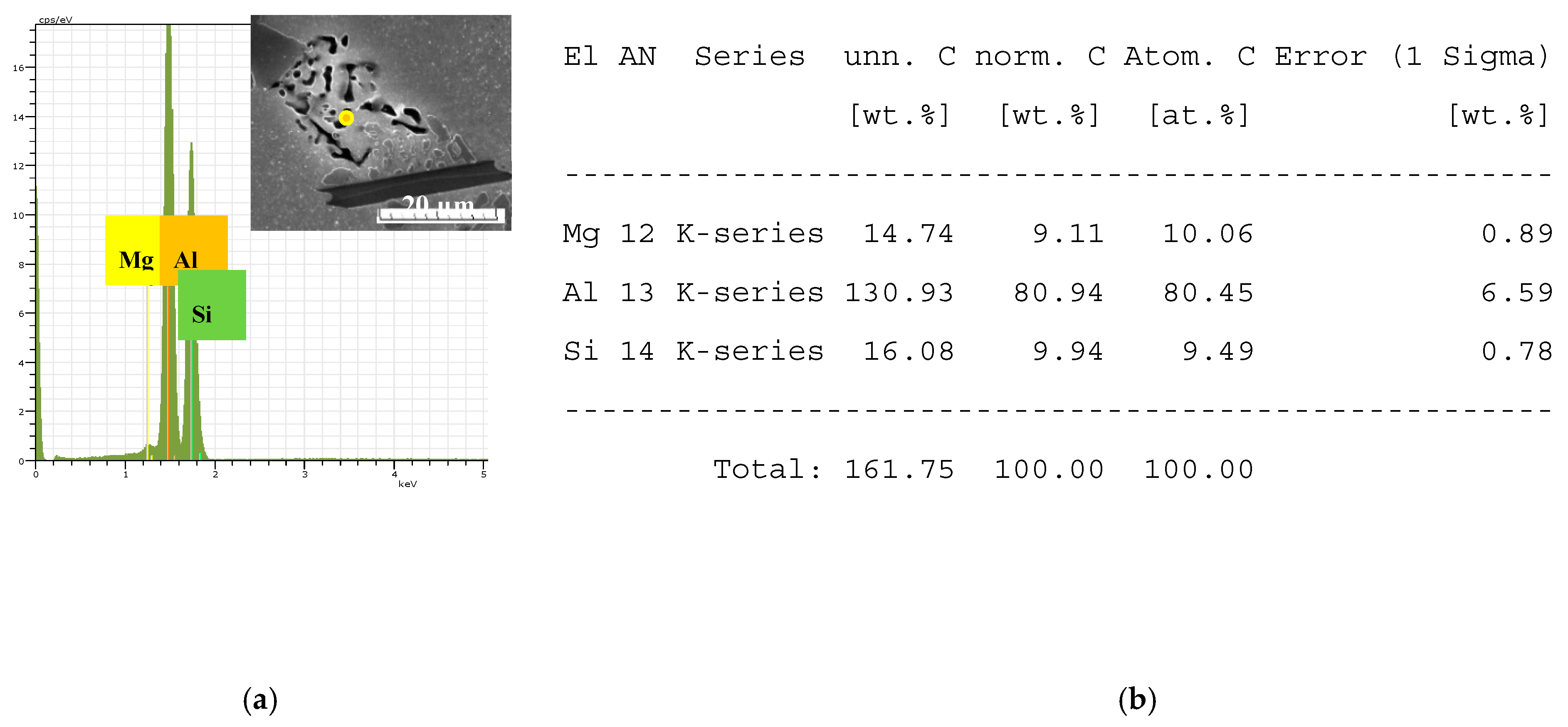
The identification of intermetallic phases’ observed in experimental AlSi7Mg0.3 materials was made with morphology study on an optical microscope and with energy dispersive X-ray analysis on a scanning electron microscope (EDX). Intermetallic phases based on Fe, Mn, and Mg were identified by EDX analysis as follows: Mg
2Si (in form of globular particles) Al
15(FeMn)
3Si
2 (in form of skeleton-particles), Al
5FeSi (in the form of platelets) documented in
Figure 5 and
Figure 6 [
9,
10,
36].
3.2. Effect of Corrosion Environment on Mechanical Properties
Results of the static tensile test and hardness test (
Table 2) have shown negligible differences between the different material melts. Immersion of specimens into a corrosive environment had minimal effect on UTS, hardness, and ductility of the alloy, the differences in the results can be considered as a standard material scatter. The influence of the Fe content and corrosion attack on the material is possible to observe in the results of the Charpy test. The impact energy (
Table 2) is decreasing with increasing Fe content in the as-cast materials and exposition to a corrosive environment causes a further decrease in the resistance to impact loading. These results correlate with the conclusions of authors [
37,
38,
39,
40] that the presence of a higher amount of Al
5FeSi Fe-rich phases increases the material tendency to brittle fracture. The effect of the corrosion environment on the decreasing of all mechanical properties in materials containing more Fe, as demonstrated by the authors [
9,
18,
19,
41] was not confirmed. Our results show, that impact energy correlates with the results of the authors [
9,
18,
19,
41].
The calculated quality index (
Table 3) per Equation (1) shows that both alloys with increased Fe content (material A and B) before exposure to corrosion environments have a higher quality index than the primary alloy (material A). When the materials were exposed to a corrosive environment, the quality index of the primary alloy (material A) is almost identical to the as-cast condition, but the index of the secondary alloys (material B and C) decreased significantly. However, there is no significant difference in the quality index of the secondary alloy despite the significant difference in the iron content. It also demonstrates that all materials affected by a corrosion environment have a quality index comparable with no relation to the Fe content. The results of mechanical tests and quality index confirmed that higher Fe content and corrosion environment are not critical for these experimental materials and they could be used for many common applications in the automotive industry.
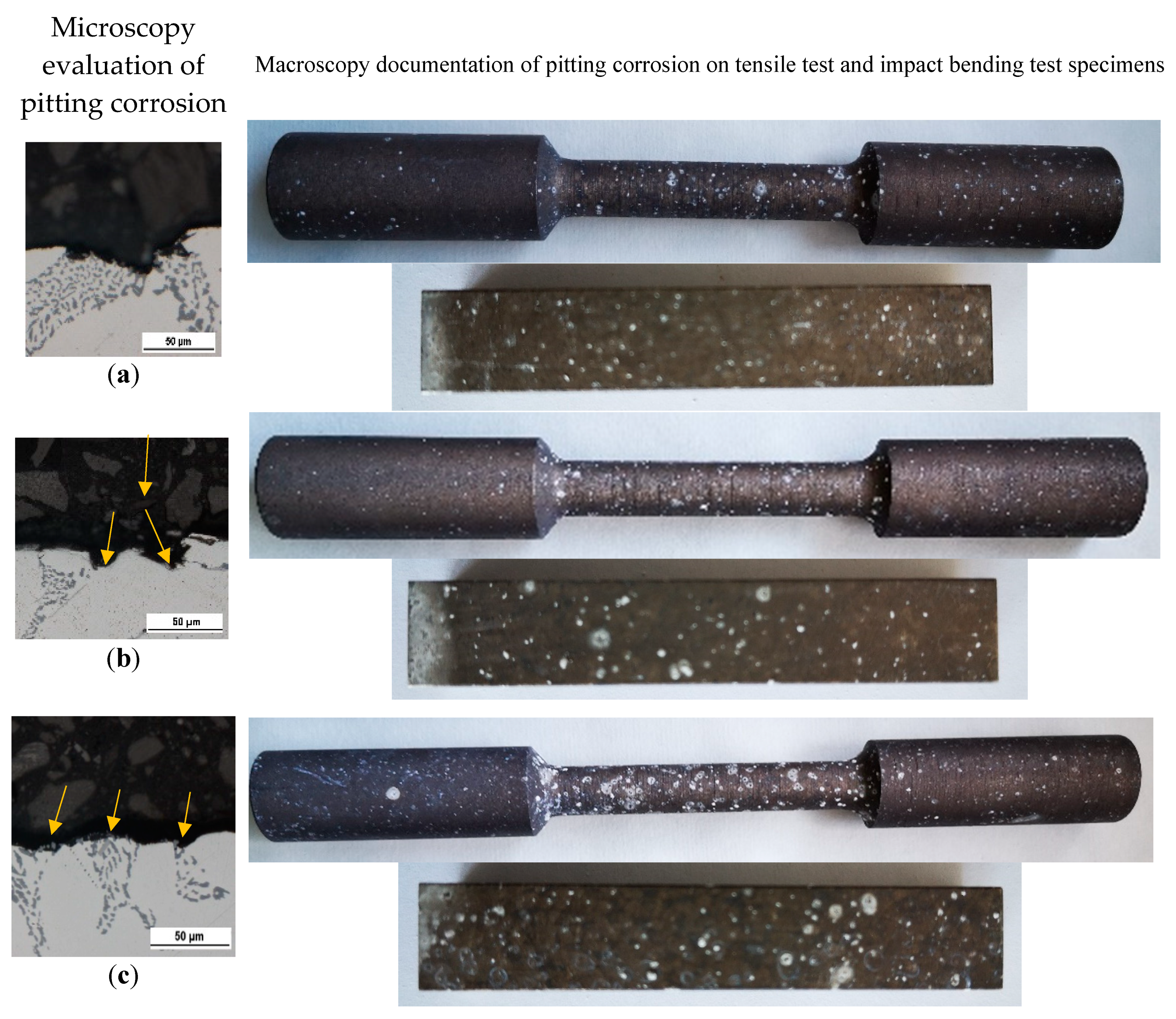
Evaluation of Corrosion Attack on Tested Specimens
The optical evaluation of corrosion attack shows presence the of pitting corrosion on each experimental material (
Figure 8). The more detailed investigation of pits in such experimental materials with higher Fe content we demonstrated in our research work [
42].
The increase in occurrence and size of the corrosion pits were observed with increasing Fe content (
Figure 8). The appearance of corrosion attack was comparable between specimens for the tensile test and specimens for the Charpy impact test. The observation of corrosion attack (
Figure 8) confirms the results of Osório et al. [
43,
44] that increasing the Si content causes a detrimental effect on the electrochemical corrosion resistance. This correlates with the results of microstructure changes - the higher Fe content leads to a decrease in the size of eutectic Si, thus resulting in the increase of the amount of these particles. Locations with an increased number of Si particles are more prone to initiation of pitting corrosion as a result of the different potential of structural constituents as written in research [
13,
14,
15,
16,
17]. The influence of the higher content of Fe on the increasing pitting corrosion of Al-alloys is confirmed also by the research work of Samuel et al. [
9]. Results of this study confirm that the higher amount and smaller size of eutectic Si lead to the increasing amount of corrosion pit (
Figure 8). However, it should not be forgotten that these changes are related to the increasing amount of Fe platelets-phases in microstructure due to higher content of Fe.
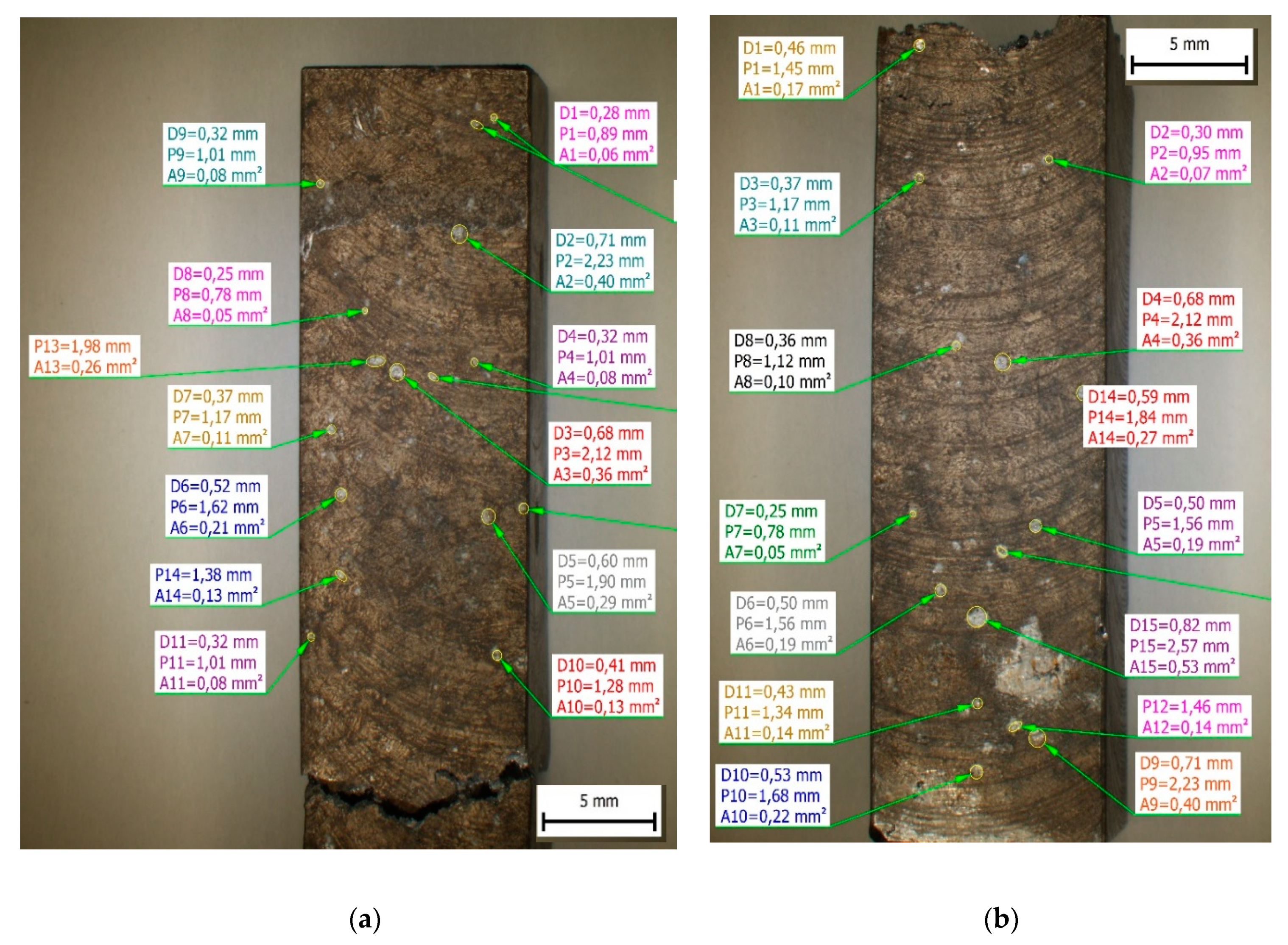
For documentation of an increasing number of point corrosion pits on the surfaces were used quantitative measurements of surface area, diameter (marked as D in
Table 4 and
Figure 9), and circumference (marked as P in
Table 4 and
Figure 9) of corrosion pits (
Figure 9 and
Table 4). The results confirm the presence of larger corrosion pits on surfaces of materials with higher Fe content and increasing the maximum area of pits with increasing Fe content. The minimum and average values of other measured parameters confirm comparable results for each experimental material.
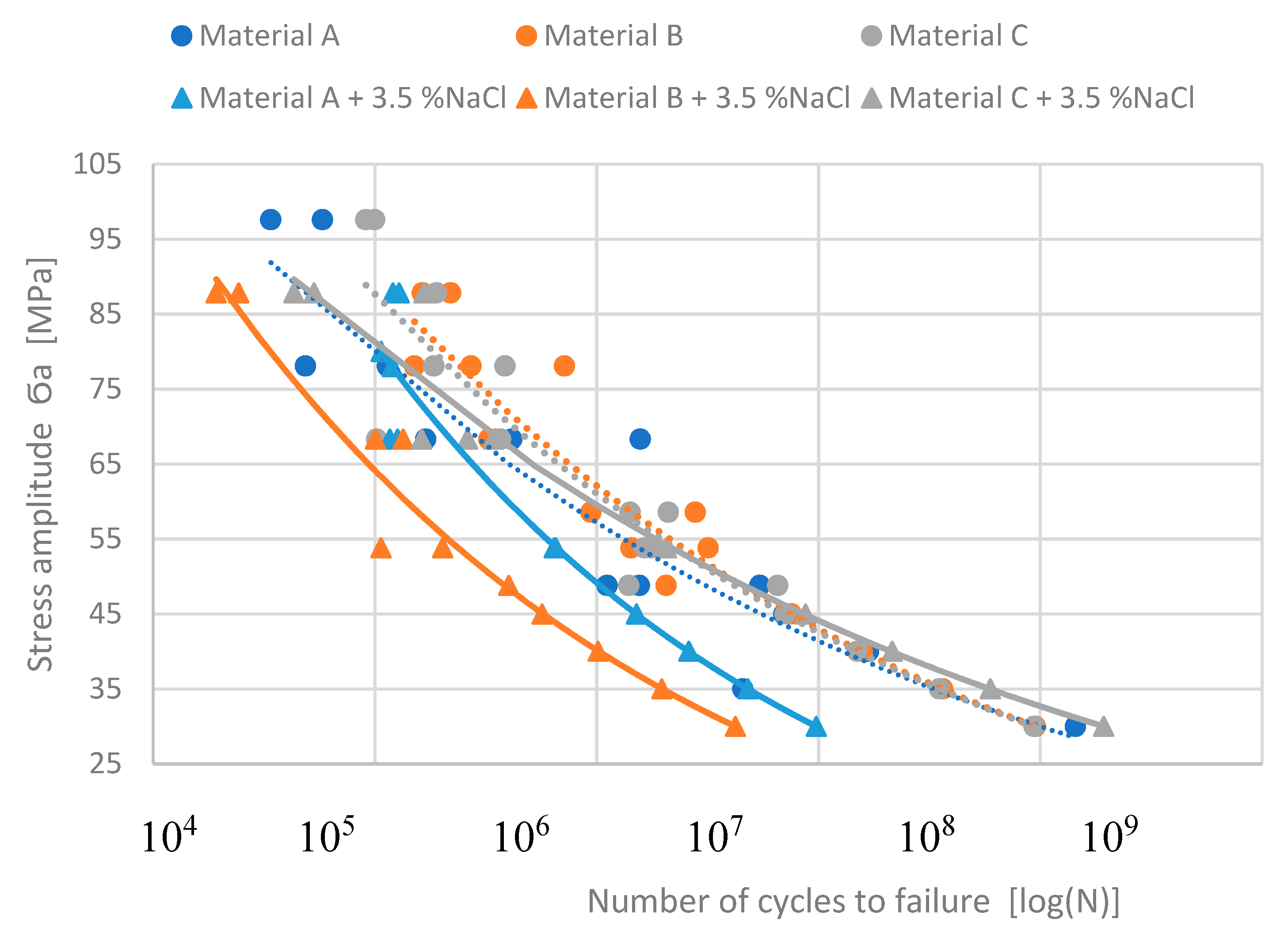
3.3. Effect of Corrosion Environment on Fatigue Properties
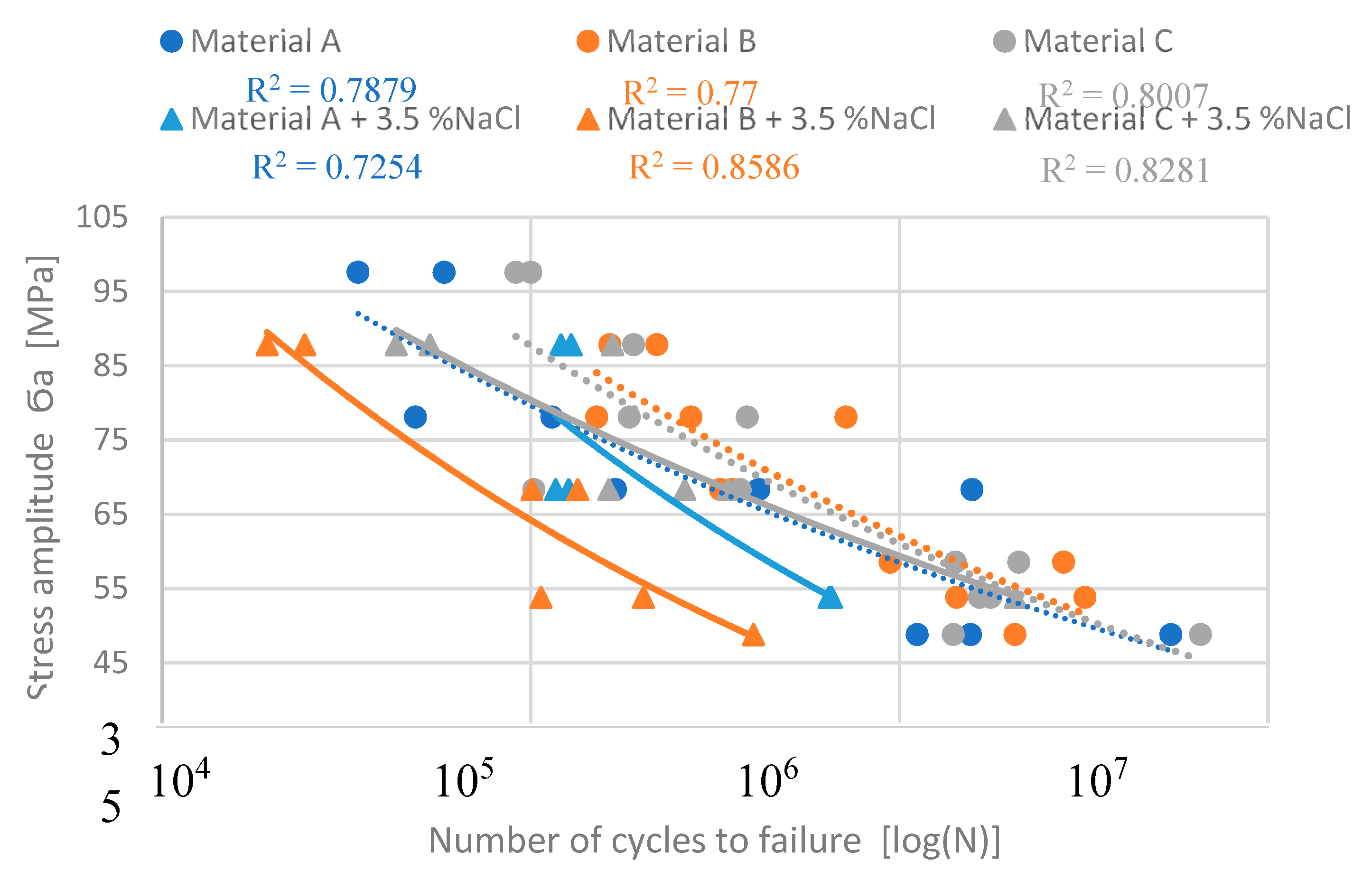
One of the main experimental interest was to determine the results of the corrosion environment on the fatigue properties of experimental alloys, which have different Fe content. The fatigue life of the experimental materials was defined as the highest applied stresses which a specimen can withstand N
c = 3 × 10
5 cycles (
Figure 10). The previous study by Kuchariková (2021) demonstrated the effect of Fe content on the fatigue properties of these experimental alloys before corrosion attack (pointed lines in
Figure 10) and they show that with a decrease of the stress amplitude, the fatigue properties of alloys with a higher content of Fe fell sharply, and were lowest in the alloys with chemical composition closest to the standard (alloy A without increased content of Fe). When materials were under higher stress amplitude as 60 MPa the better fatigue properties had materials with higher Fe content.
The fatigue properties of materials affected by the corrosion show a significant drop of fatigue toughness when compared to the as-cast state (
Figure 10). Again, direct correlation between the iron content and fatigue properties was not confirmed. The experimental material C with the highest Fe content has the best fatigue properties. The values of fatigue toughness for N
c = 3 × 10
5 cycles are shown in
Table 4.
Table 4.
The results of fatigue properties.
Table 4.
The results of fatigue properties.
| Fatigue life |
Before corrosion |
After corrosion |
| A |
B |
C |
A |
B |
C |
|
σ3×105 [MPa] |
68.5 |
75.5 |
73.5 |
63.5 |
51.5 |
69.5 |
According to the S-N curves, the material with the longest and thinnest Fe platelets- phases (material B) has the worst fatigue properties after a corrosion attack, but without exposure to corrosion, the material has the best fatigue properties. A significant decrease in fatigue properties was observed in material A (primary alloy with lowest Fe contamination) at lower stress amplitudes. The material C has comparable fatigue properties at smaller stress amplitude (
Figure 6).
The Basquin equation is commonly used to model the fatigue data trend for different numbers of cycles by using the statistical calculation of the S-N curves (
Figure 10). The Basquin equation has the form [
45,
46,
47]:
where “σ
’f” is the fatigue strength coefficient, and “b” is the fatigue life exponent. Therefore, for better visualization of the corrosion environment effect, statistical calculation was used and obtained Basquin equation for experimental materials in different states are:
The application of the Basquin equation is shown in
Figure 11. These predicted curves point to the fact that the highest Fe content does not lead to decreasing fatigue properties. It also demonstrates that material C has the best fatigue life after a corrosion attack. Moreover, it seems to have better properties than the same material without corrosion attack (
Figure 11).
3.4. Effect of Corrosion Environment on Fracture Surfaces
3.4.1. Fracture Surfaces after Tensile Strength and Charpy Impact Tests
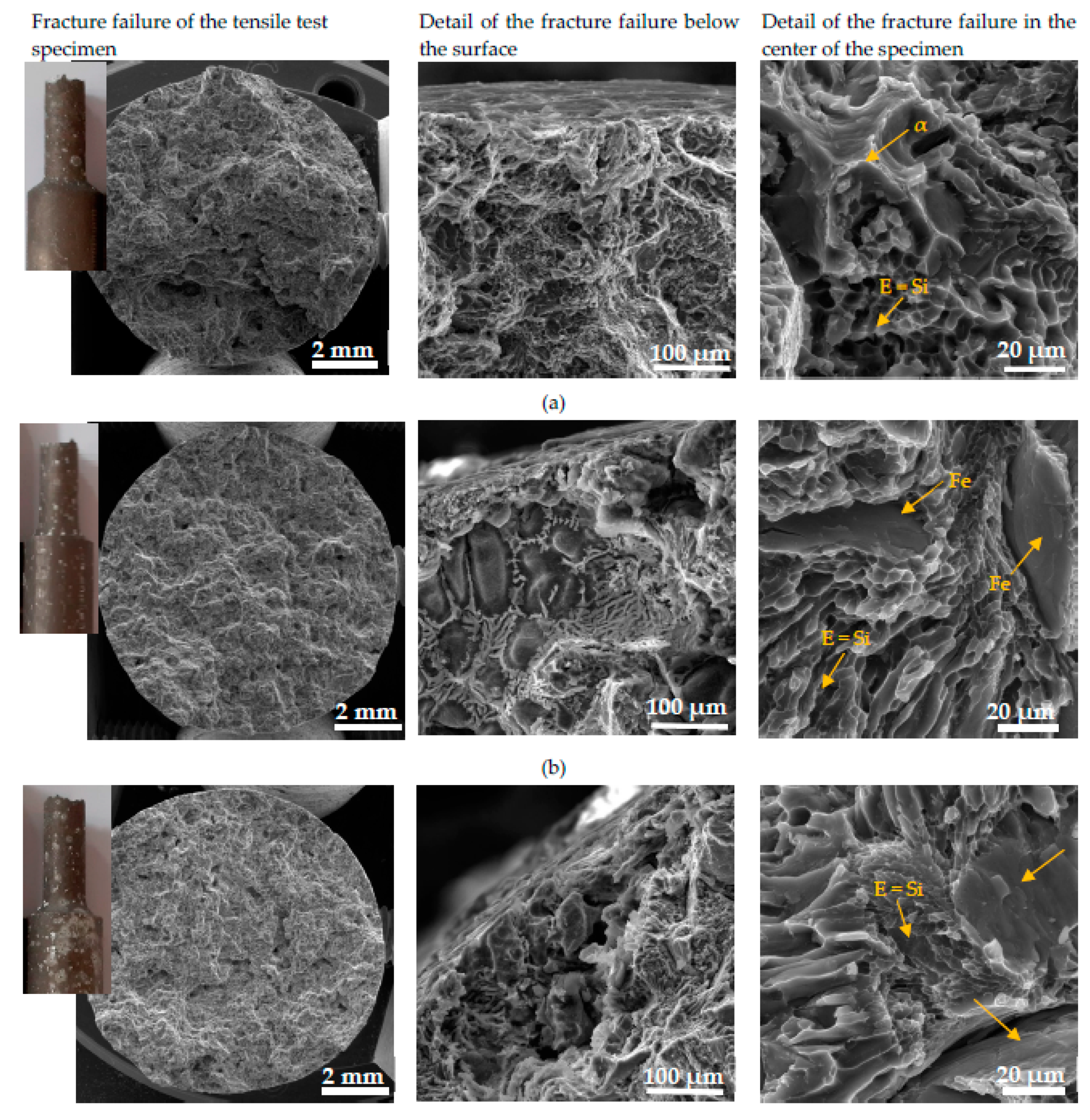
The character of the fracture surface of specimens after the tensile test is mixed and consists of the transcrystalline cleavage fracture and transcrystalline ductile fracture. This character of fracture surface correlates with results of other research works [
48,
49,
50]. Macrofractography assessment of fracture failure does not show a greater effect of the higher Fe content on the increasing fragmentation of fracture surfaces (
Figure 12). The presence of corrosion products was documented in the detail of the fracture failure below the surface (
Figure 12). This microfractographic assessment declares that material A is not affected to the greater depth by corrosion (
Figure 12a). The increasing Fe content leads to the penetration of the corrosion into greater depths (
Figure 12b,c). The microfractographic analysis of fracture surfaces in the center of the specimen also shown the presence of a mixed fracture. The fine transcrystalline ductile fracture with a higher presence of the ductile ridges of the matrix is typical for material A. Phase identification was possible to perform according the morphology of individual features based on work of Taylor [
10], where phase character reconstruction was performed. The increasing amount of brittle Fe needles-phases lead to increasing transcrystalline cleavage fracture content in materials B and C. Also changes in the finesse of the transcrystalline ductile fracture which is connected with changes in the size of the eutectic Si in the microstructure were observed (
Figure 4 and
Figure 12).
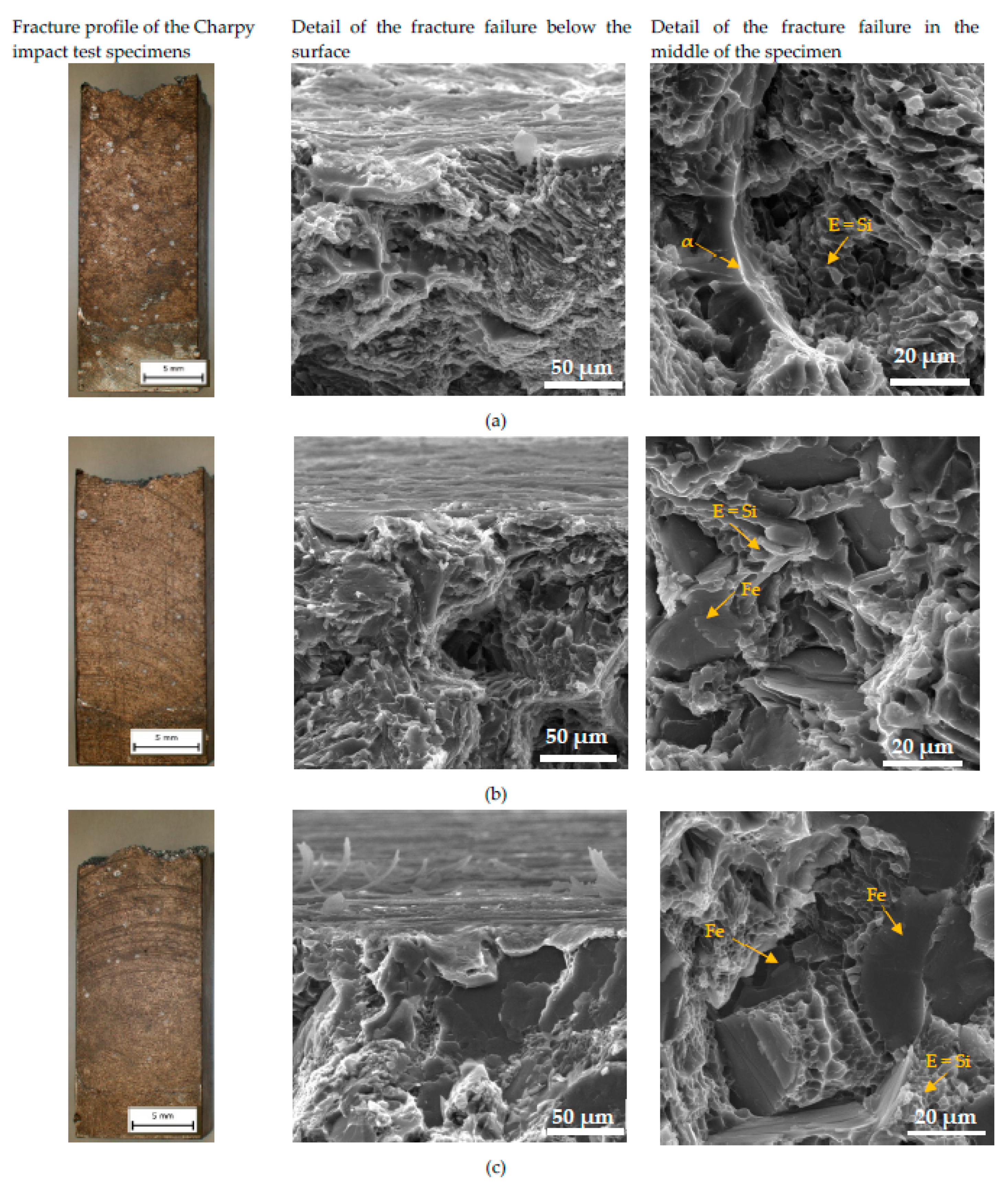
The character of the fracture surface of specimens after the Charpy impact test is comparable with the observation of specimens after tensile tests - fracture surface with mixed crack propagation mechanisms. It also consists of transcrystalline cleavage fracture and transcrystalline ductile fracture. Macrofractography assessment of fracture surfaces does not show a greater effect of the higher Fe content on the increasing fragmentation of fracture surfaces. The character of the fracture profile is similar for each experimental material (
Figure 13). The presence corrosion products was documented in detail in
Figure 13. This microfractographic assessment declares that material C has a lot of corrosion products on the surfaces, but material B is comparable with material A. The microfractographic analysis of fracture surfaces in the center of the specimen again demonstrated the presence of a mixed fracture as in tensile test specimens. The fine transcrystalline ductile fracture with a higher presence of the ductile ridges of the matrix is typical for material A (
Figure 13a). The increasing amount of brittle Fe platelets lead to increasing of the transcrystalline cleavage fracture in materials B and C (
Figure 13b,c). Also changes in the finesse of the transcrystalline ductile fracture which relates to changes in the size of the eutectic Si in the microstructure were observed (
Figure 4 and
Figure 13).
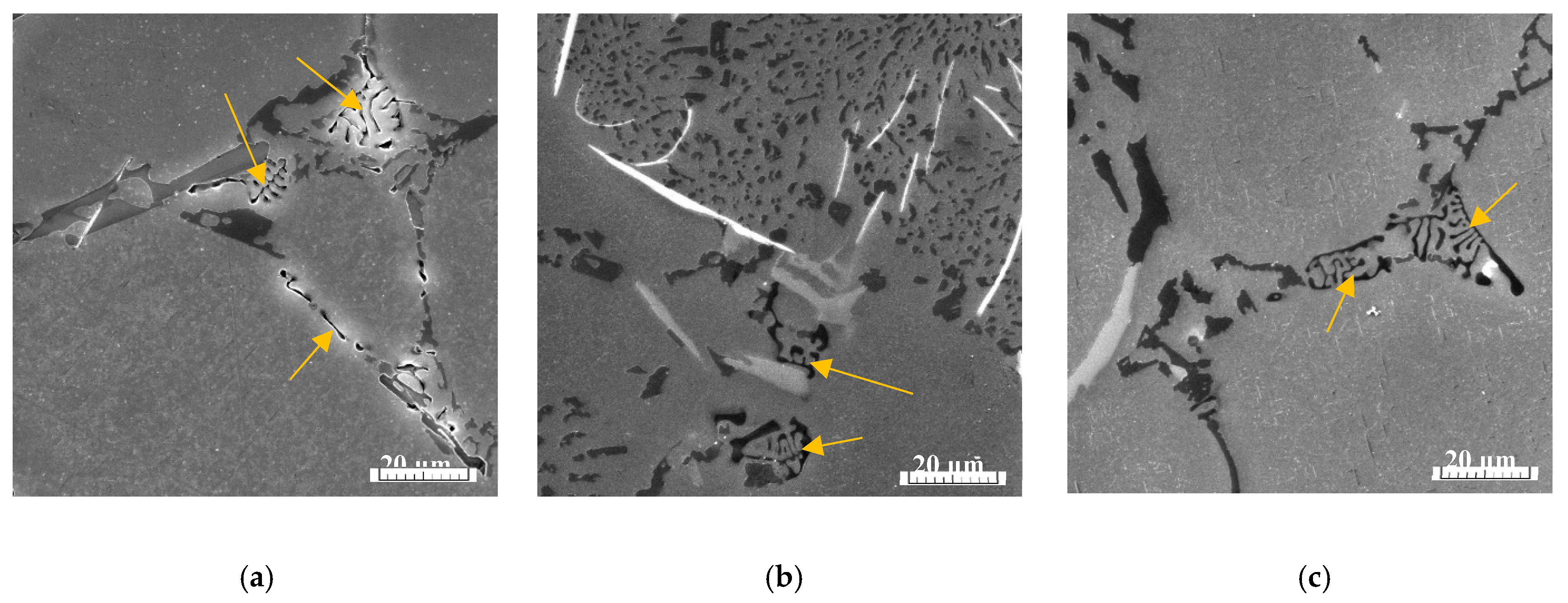
3.4.2. Fracture Surfaces after Fatigue Tests
The effect of higher Fe content on the fatigue fracture was studied in previous research work [
36].
These fatigue results and fractography analysis have not confirmed the results of Wang et al. [
51]
or Caceres et al. [
52]
suggesting that large Fe-rich phase particles are the main contributing factor for fatigue failure. As declared in our work [
36]
, the crack initiation sites were locations of surface or near-surface porosity. The presence of Fe-rich phases did not lead to initiation of fracture, but in all the experimental materials, fatigue cracks initiated on pores. The presence of a higher number of initiations locations in specimens with higher Fe content correlates with the results of the porosity ratio and their size.
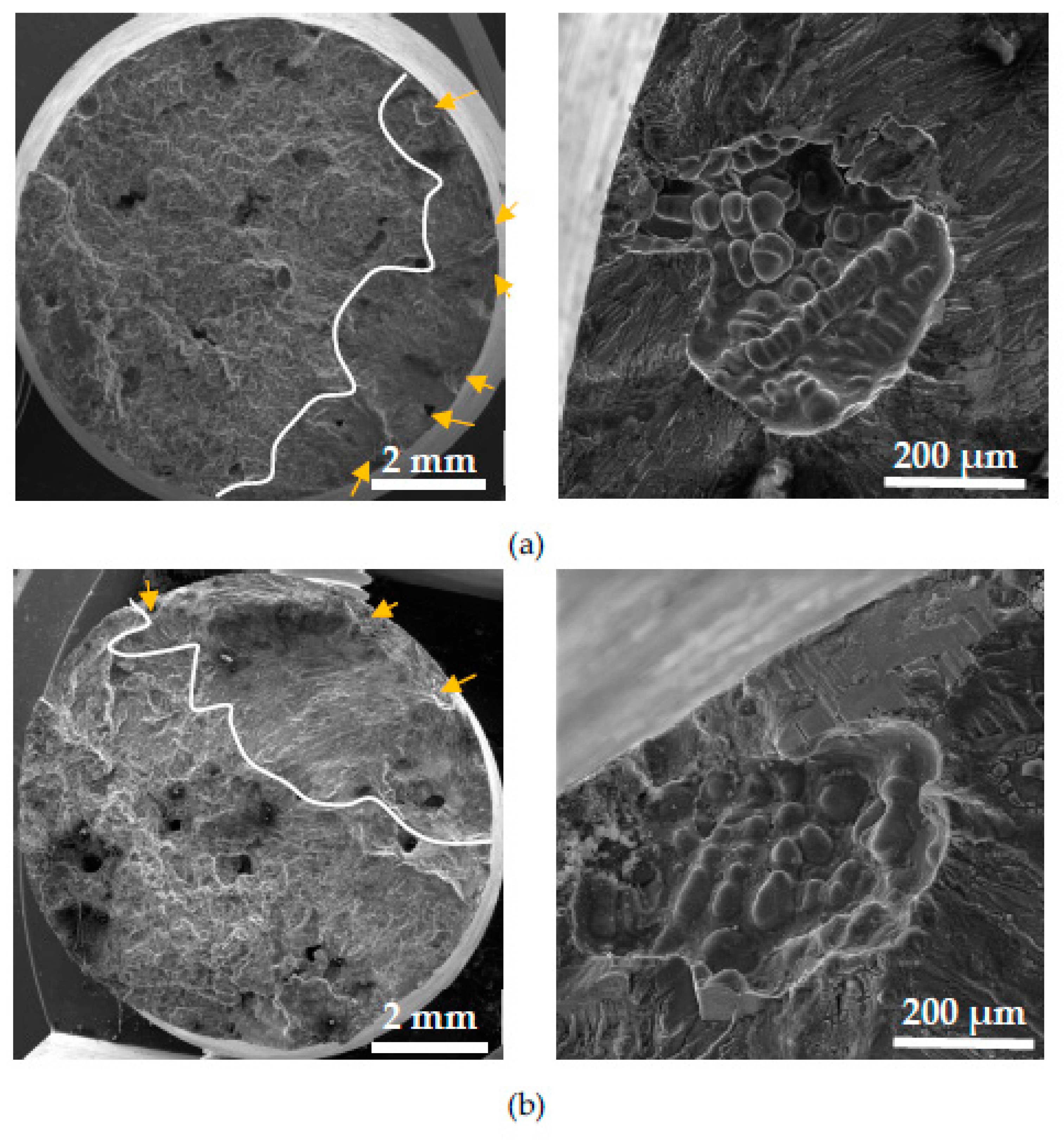
This study of the corrosion environment attack on fatigue fracture surfaces confirms, that the same microstructural parameters relate to initiation but around these places were observed corrosion products (
Figure 14). The initiation places were near-surface pores. An increase in the number of initiation locations (
Figure 14), as a result of higher porosity, is connected with higher Fe content as was mentioned previously.
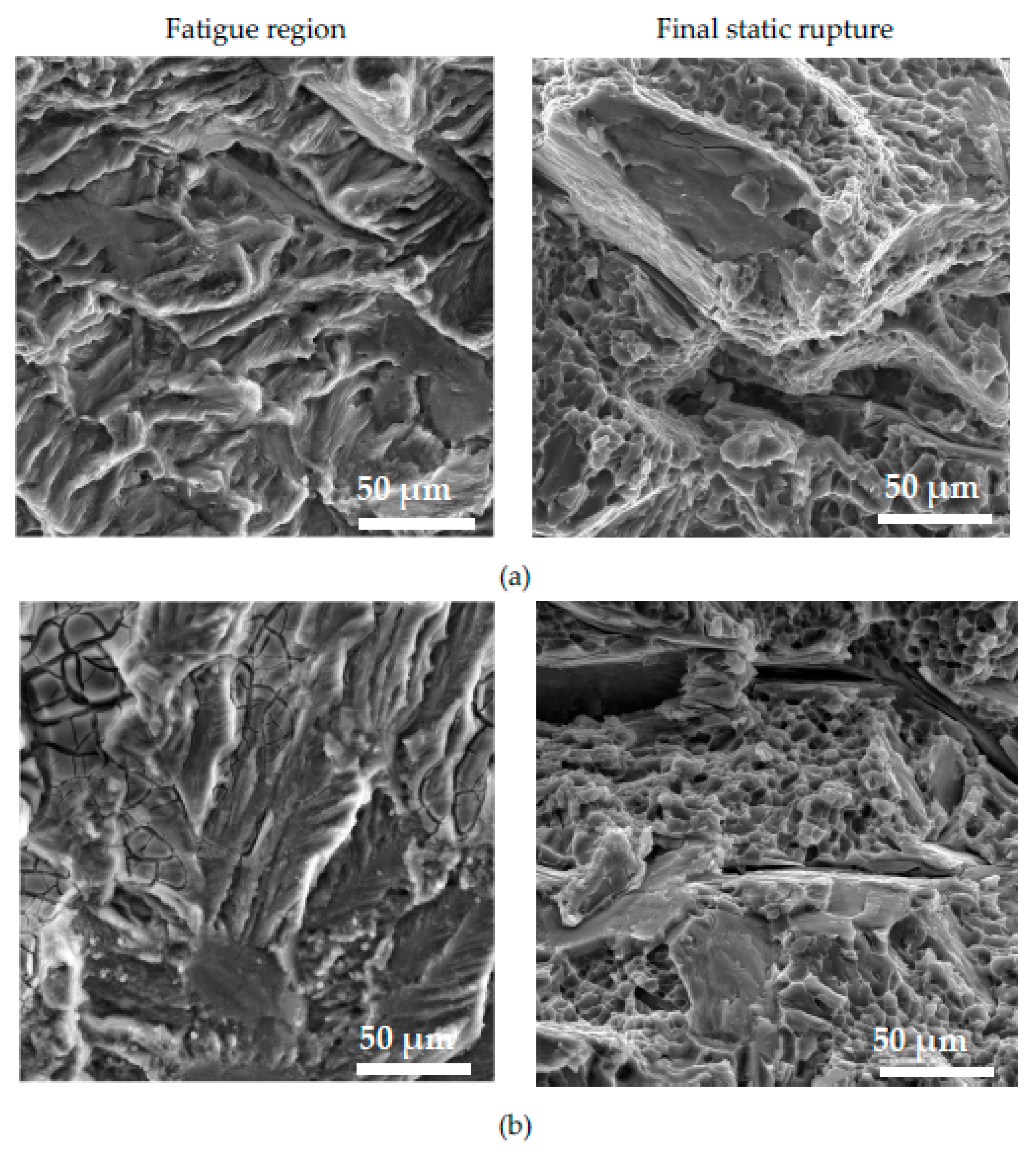
The fractography analysis of the fatigue region shows the presence of the typical fatigue fracture of a matrix on each specimen (
Figure 15), but the presence of striation was difficult to observe, because of the presence of oxide films on the failure of specimens without corrosion attack (
Figure 15a) and with affecting the fatigue region after corrosion attack (
Figure 15b). The smooth area in the fatigue region relates to the presence of the long Fe platelet-like phases in this type of experimental material.
The final static rupture (
Figure 15) shows a mixed transcrystalline ductile and transcrystalline cleavage fracture as after tensile test and Charpy impact tests. Transcrystalline ductile fractures relate to the matrix and the size of dimple depends on the fineness of the eutectic Si particles [
53,
54,
55,
56]. Transcrystalline cleavage fractures depend on the size and amount of Fe phases and eutectic Si particles. The presence of corrosion product on the static rupture of the fatigue specimens was not observed (
Figure 15b).
4. Conclusions
This study was focused on the effect of the corrosion environment on the basic mechanical properties and fatigue properties changes of the aluminum cast made from secondary alloys. The study was chosen with respect to industrial application of sand castings from AlSi7Mg0.3 and brings these results:
The microstructure of secondary materials (with higher Fe content) is completely comparable with the base microstructure of primary alloys and contains the same microstructural constituents. The difference was observed in the increased amount and size of Fe platelet phases. The presence of long phases leads to decreasing size of the eutectic Si which affects the results of the mechanical properties in a positive direction.
The UTS and HBW of all alloys are comparable – with and without a corrosion environment. Ductility in the materials without affecting by corrosion environment increase is again very similar for all three alloys. After corrosion attack, a general decrease of the Ductility can be observed for all materials. Impact energy decrease with increasing Fe content in both states of experimental materials – with and without exposure to a corrosion environment. In view of these results could be stated that secondary materials have comparable strength properties (UTS and HBW) as primary alloys.
Exposure to a corrosive environment caused, that each material was attacked by pitting corrosion. The increasing content of Fe leads to the formation of a higher amount and size of corrosion pits, however, it must be noted, that locations which are more prone to corrosion are, where eutectic phase is present (mechanical mixture of eutectic Si and matrix). The decrease in size of eutectic Si and the associated increase in their share in the microstructure correlates with creating a higher number of places with corrosion pits. Therefore, it should be noted that corrosion attacks (size and amount of pits) increase with increasing Fe content.
The fatigue properties after corrosion attack were lower, when compared to the as-cast state of experimental materials. A great decrease was observed in material B, which has the best mechanical properties of each experimental material. The best fatigue properties after corrosion attack had material C, the one with the highest content of Fe. Material A (compared to typical primary alloys) has a very low fatigue life at lower stress amplitude. Therefore, could be stated that the higher Fe content does not lead to a greater decrease in fatigue properties, but under a corrosion environment, the material behaviour changes differently, and it does not depend on the Fe content.
The investigation of tensile and impact test specimens fracture surfaces showed presence of a mixed fracture character, which consists of the transcrystalline cleavage fracture and transcrystalline ductile fracture. This character of fracture correlates with common knowledge. Corrosion environment leads to affecting the surface of experimental specimens for tensile tests and impact bending tests. The corrosion products were visible not only on the surface, but on the fracture surfaces, too. The higher content of Fe leads to violation of the protective layer which creates the locations in which the corrosion environment attacks the microstructure which is also visible on the fracture surfaces of materials B and C. More corrosion products were visible on fatigue test specimens fracture surfaces, in the fatigue region of fatigue crack propagation, because the corrosion environment acted during the fatigue test.
The results of these studies do not confirm a significant negative effect of the combination of higher Fe content and corrosion environment on the greater decreasing of AlSI7Mg0.3 castings properties, but it is necessary to make a complementary experiment, because these materials were in the as-cast state and their common application is after heat treatment.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, L.K., L.P., E.T.; methodology, L.K., V.Z., M.U. and L.P.; software, L.K., M.U., L.P. and M.Š.; validation, L.K., M.U. and L.P.; formal analysis, L.K., M.U., V.Z. and L.P.; investigation, L.K., M.U. and L.P.; resources, E.T. and L.K.; data curation, L.K. and L.P.; writing—original draft preparation, L.K.; writing—review and editing, L.K. and L.P.; visualization, L.K.; supervision, E.T.; project administration, L.K. and E.T.; funding acquisition, L.K. and E.T.
Funding
This research was funded by following grants: KEGA no. 004ŽU-4/2023 and project to support young researches at UNIZA, ID project 12715 (Kuchariková).
Data Availability Statement
Data sharing not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The authors thanks grants KEGA no. 004ŽU-4/2023 and project to support young researches at UNIZA, ID project 12715 (Kuchariková).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Schlesinger, M. Aluminum recycling: Second edition, 2nd edition; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2014; p. 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicoletto, G.; Anzelotti, G.; Konečná, R. X-ray Computed Tomography vs. Metallography for Pore Sizing and Fatigue of Cast Al-alloys. Procedia Eng. 2 2010, 2, 547–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senčáková, L.; Virčíková, E. Life cycle assessment of primary aluminium production. Acta Metall. Slovaca 2007, 13, 412–419. [Google Scholar]
- Das, K.S. Designing Aluminum Alloys for a Recycling Friendly World. Mater. Sci. Forum 2006, 519–521, 1239–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Roven, H.R. Recycling of automotive aluminium. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2010, 20, 2057–2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakedano, A.; Niklas, A.; Fernández-Calvo, A.I.; Plata, G.; Lozares, J.; Berlanga-Labari, C. Comparative Study of the Metallurgical Quality of Primary and Secondary AlSi10MnMg Aluminium Alloys. Metals 2021, 11, 1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tillová, E.; Chalupová, M.; Hurtalová, L. Evolution of the Fe-rich phases in recycled AlSi9Cu3 cast alloy during solution treatment. Communications 2010, 12, 95–101, https://komunikacie.uniza.sk/pdfs/csl/2010/04/16.pdf. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boromei, L.; Ceschini, L.; Morri, A.; Nicoletto, G.; Riva, E. Influence of the solidification microstructure and porosity on the fatigue strength of Al-Si-Mg casting alloys. Metall. Sci. Technol. 2010, 2, 18–24. [Google Scholar]
- Samuel, A.M.; Samuel, F. H.; Doty, H.W.; Valtierra, S. Beta Al5FeSi phase platelets-porosity formation relationship in A319.2 type alloys. Int. J. Met. Cast. 2018, 12, 55–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, J. Iron-containing intermetallic phases in Al-Si based casting alloys. Procedia Mater. Sci. 2012, 1, 19–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadzima, B., Liptáková, T. Fundamentals of electrochemical corrosion of metals, 1st edition; Edis: Žilina, Slovakia, 2008; 116 (in Slovak).
- Ricker, R.; Duquette, D. Corrosion Fatigue of Aluminum Alloys. Conference: The First Joint DoD/FAA/NASA Conference on Aging Aircraft 8-10 July 1997, Ogden, UT, J. Gallagher et al. edts., pps 465-473 Universal Technology Corp., Dayton OH (1999) Project: Corrosion and Environmental Induced Cracking of Al Alloys.
- Esmaily, M.; Blüche, D.B.; Svensson, J.E.; Halvarsson, M.; Johansson, L.G. New insights into the corrosion of magnesium alloys — The role of aluminum. Scr. Mater. 2016, 115, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargel, C. Corrosion of Aluminium, 1st edition; Elsevier: Paris, France, 2004; p. 626. [Google Scholar]
- Torbati-Sarraf, H.; Stannard, T.; Callagon La Plante, E.; Sant, G.N.; Chawla, N. Direct observations of microstructure-resolved corrosion initiation in AA7075-T651 at the nanoscale using vertical scanning interferometry (VSI). Mater. Charact. 2020, 161, 110166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkler, S.L.; Ryan, M.; Flower, H.M. Pitting corrosion in cast 7XXX aluminium alloys and fibre reinforced MMCs. Corros. Sci. 2004, 46, 893–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roodbari, M.K. Effect of Microstructure on the Performance of Corrosion Resistant Alloys. Light Metals, Silicon and Ferroalloy Production Supervisor: Jan Halvor Nordlien, IMTE 2015, 74. http://hdl.handle.net/11250/2377272. /.
- Ambat, R.; Davenport, A.J.; Scamans, G.M.; Afseth, A. A Effect of iron-containing intermetallic particles on the corrosion behaviour of aluminium. Corros. Sci. 2006, 48, 3455–3471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, W.J.; Rometsch, P.A.; Cao, L.F.; Birbilis, N. General aspects related to the corrosion of 6xxx series aluminium alloys: Exploring the influence of Mg/Si ratio and Cu. Corros. Sci. 2013, 76, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebril, M.A.; Omar, M.Z.; Othman, N.K.; Mohamed, I.F. Microstructural Refinement and Corrosion Resistance Improvement of Heat-Treated A356 Alloy Processed by Equal Channel Angular Pressing. Sains Malays. 2019, 48, 2749–2757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, G.; Pohl, M. Systematische Beurteilung technischer Schadensfälle, 1st edidition; Wiley – VCH Verlag GmbH: Weinheim, Germany, 2014; p. 548. [Google Scholar]
- Činčala, M. High cycle fatigue of bearing steel 14 109: Doctorate dissertation thesis, ZU:Žilina, Slovakia, 2005; 91.
- Caton, M.J.; Jones, J.W.; Mayer, H.; Stanzl-Tschegg, S.E.; Allison, J.E. Demonstration of an endurance limit in cast 319 aluminum. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2003, 34, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; YI, J.Z.; Jones, J.W.; Allison, J.E. A Probabilistic Model of Fatigue Strength Controlled by Porosity Population in a 319-Type Cast Aluminum Alloy: Part I. Model Development. Miner. Met. Mater. Soc. ASM Int. 2007, 1111–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, J.Z. Effect of microstructure and defects on the fatigue behavior of cast A356- T6 aluminium-silicon alloy. Department of Materials. 2004, Imperial College: London, UK.
- Wang, Q.G.; Apelian, D.; Lados, D.A. Fatigue behavior of A356/357 aluminum cast alloys. Part II - Effect of microstructural constituents. J. Light Met. 2001, 1, 85–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Rawajfeh, A.E.; Al Qawabah, S.M.A. Investigation of cooper addition on the mechanical properties and corrosion resistance of commercially pure aluminum. Emir. J. Eng. Res. 2009, 14, 47–52. [Google Scholar]
- Adeosun, S.O.; Sekunowo, O.I.; Balogun, S.A.; Obiekea, V.D. Corrosion Behaviour of Heat-Treated Aluminum-Magnesium Alloy in Chloride and EXCO Environments. Hindawi Publ. Corp. Int. J. Corros. 2012, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markovičová, L.; Hurtalová, L.; Zatkalíková, V.; Garbacz, T. Evolution of composite structures by light microscopy and image analysis. Manuf. Technol. 2014, 14/3, 351-355. [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Uggowitzer, P.J.; Nagasekhar, A.V.; Schmutz, P.; Easton, M.; Song, G.; Atrens, A. Calculated phase diagrams and the corrosion of die-cast Mg–Al alloys. Corros. Sci. 2009, 51, 602–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 6892-1A, Metallic materials — Tensile testing — Part 1: Method of test at room temperature.
- Czekaj, E.; Zych, J.; Kwak, Z.; Garbacz-Klempka, A. Quality Index of the AlSi7Mg0.3 Aluminium Casting Alloy Depending on the Heat Treatment Parameters. Arch. Foundry Eng. 2016, 16, 25–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiryakioglu, M.; Staley, J.T.; Campbell, J. Evaluating structural integrity of cast Al–7%Si–Mg alloys via work hardening characteristics II. A new quality index. Mater. Sci. Eng. A368 2004, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- STN EN ISO 6506 – 1, Metallic materials: Brinell hardness test. Part 1, Test method (ISO 6506-1: 2005).
- STN 42 0363 – Metal testing. Fatigue testing of metals. Methodology of testing.
- Kuchariková, L.; Medvecká, D.; Tillová, E.; Belan, J.; Kritikos, M.; Chalupová, M.; Uhríčik, M. The Effect of the β-Al5FeSi Phases on Microstructure. Mechanical and Fatigue Properties in A356.0 Cast Alloys with Higher Fe Content without Additional Alloying of Mn. Materials 2021, 14, 1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irizalp, S.G.; Saklakoglu, N. Effect of Fe-rich intermetallic on the microstructure and mechanical properties of thixoformed A380 aluminium alloy. Eng. Sci. Technol. Int. J. 2014, 17, 58–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew, J.; Remy, G.; Williams, M.A.; Tang, F.; Srirangam, P. Effect of Fe Intermetallics on Microstructure and Properties of Al-7Si Alloys. J. Miner. Met. Mater. Soc. 2019, 71, 4362–4369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, J.A. The effect of iron in Al-Si casting alloys, 35th Australian Foundry Institute National Conference 2004, 148-157.
- Seifeddine, S. The influence of Fe on the microstructure and mechanical properties of cast Al-Si alloys. "Literature review - Vilmer project". 2007, Jönköping University, Sweden.
- Yasakau, K.A.; Zheludkevich, M.L.; Ferreira, M.G.S. Role of intermetallics in corrosion of aluminum alloys. Smart corrosion protection. Intermetallic Matrix Composites, Woodhead Publishing,: Duxford, United Kingdom, 2018, 425-462. [CrossRef]
- Kuchariková, L.; Liptáková, T.; Tillová, E.; Kajánek, D.; Schmidová, E. Role of Chemical Composition in Corrosion of Aluminum Alloys. Metals 2018, 8, 581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osório, W.R.; Garcia, L.R.; Goulart, P.R.; Garcia, A. Effects of eutectic modification and T4 heat treatment on mechanical properties and corrosion resistance of an Al–9 wt. % Si casting alloy. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2007, 106, 343–349. [CrossRef]
- Osório, W.R.; Goulart, P.R.; Garcia, A. Effect of silicon content on microstructure and electrochemical behavior of hypoeutectic Al–Si alloys. Mater. Lett. 2008, 62, 365–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trško, L., Hadzima, B.; Fintová, S. Influence of nano-grained surface layer on fatigue properties of structural materials. Pearson publishing house: Great Britain, 2020.
- Trško, L.; Guagliano, M.; Bokůvka, O.; Nový, F. Fatigue life of AW 7075 Aluminium Alloy after Severe Shot Peening Treatment with Different Intensities. Procedia Eng. 2014, 74, 246–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Retraint, D.; Gao, P.; Xue, H.; Gao, T.; Sun, Z. Effect of Surface Mechanical Attrition Treatment on Torsional Fatigue Properties of a 7075 Aluminum Alloy. Metals 2022, 12, 785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Zhang, J.; LI, B.; Cai, W. Characterization of tensile fracture in heavily alloyed Al−Si piston alloy. Prog. Nat. Sci. 2011, 21, 380–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maceka, W.; Owsińskib, R.; Trembaczc, J.; Branco, R. Three-dimensional fractographic analysis of total fracture areas in 6082 aluminium alloy specimens under fatigue bending with controlled damage degree. Mech. Mater. 2020, 147, 103410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, M. Introduction to Metal Fatigue. Department of Engineering, Aarhus University:Denmark, Denmark, 2018; 91.
- Wang, Q.G.; Caceres, C.H.; Griffiths, J.R. Damage by eutectic particle cracking in aluminum casting alloys A356/357. Met. Mater. Trans 2003, 34, 2901–2912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caceres, C.; Griffiths, J. Damage by the cracking of silicon particles in an Al-7Si-0.4Mg casting alloy. Acta Mater. 1996, 44, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Campbell, J. Morphology of β-Al5FeSi Phase in Al-Si Cast Alloys. Mater. Trans. 2006, 47, 1303–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurtalová, L.; Tillová, E.; Chalupová, M. The Changes of Fatigue Properties in Aluminium Cast Alloy during Solution Treatment. Key Eng. Mater. 2013, 592–593, 433–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tillová, E.; Chalupová, M.; Borko, K.; Kuchariková, L. Changes of Fracture Surface in Recycled A356 Cast Alloy. Mater. Today Proc. 2016, 3, 1183–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurtalová, L.; Tillová, E.; Chalupová, M.; Belan, J.; Uhríčik, M. The Influence of Two Different Casting Moulds on the Fatigue Properties of the Al–Si–Cu Cast Alloy. Adv. Struct. Mater. 2016, 61, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Figure 1.
The specimens for (a) tensile tests, and (b) fatigue tests. Dimensions are given in mm.
Figure 1.
The specimens for (a) tensile tests, and (b) fatigue tests. Dimensions are given in mm.
Figure 2.
The example of (a) placing samples into the container, and(b) embedded in a solution.
Figure 2.
The example of (a) placing samples into the container, and(b) embedded in a solution.
Figure 3.
The fatigue test (a) without corrosion environment, (b) with corrosion environment3. Results and discussion.
Figure 3.
The fatigue test (a) without corrosion environment, (b) with corrosion environment3. Results and discussion.
Figure 4.
The basic microstructural constituents’ matrix (α), eutectic (E) and intermetallic phases (IP) in (a) material A, (b) material B, and (c) material C., LM.
Figure 4.
The basic microstructural constituents’ matrix (α), eutectic (E) and intermetallic phases (IP) in (a) material A, (b) material B, and (c) material C., LM.
Figure 5.
The point EDX analysis of Mg2Si phases (a) the place of measurements and concentration of elements; (b) numerical results of point measurements.
Figure 5.
The point EDX analysis of Mg2Si phases (a) the place of measurements and concentration of elements; (b) numerical results of point measurements.
Figure 6.
The mapping EDX analysis (a) of Al15(FeMn)3Si phases; (b) of Al5FeSi phases in deep etched samples.
Figure 6.
The mapping EDX analysis (a) of Al15(FeMn)3Si phases; (b) of Al5FeSi phases in deep etched samples.
Figure 7.
The effect of increasing Fe content on Mg2Si phases in (a) material A; (b) material B; (c) material C.
Figure 7.
The effect of increasing Fe content on Mg2Si phases in (a) material A; (b) material B; (c) material C.
Figure 8.
The evaluation of pitting corrosion of experimental materials (a) A; (b) B; (c) C before mechanical tests.
Figure 8.
The evaluation of pitting corrosion of experimental materials (a) A; (b) B; (c) C before mechanical tests.
Figure 9.
The quantitative measurements of corrosion pits in (a) material A; (b) material C after on specimens after Charpy impact test: D – diameter, P – Circumference, A – area.
Figure 9.
The quantitative measurements of corrosion pits in (a) material A; (b) material C after on specimens after Charpy impact test: D – diameter, P – Circumference, A – area.
Figure 10.
The S-N curves from really measured data.
Figure 10.
The S-N curves from really measured data.
Figure 11.
The predicted S-N curves by using the Basquine equation for stress under 45 MPa.
Figure 11.
The predicted S-N curves by using the Basquine equation for stress under 45 MPa.
Figure 12.
The fractography analysis of fracture surfaces after tensile tests of (a) material A; (b) material B; (c) material C after corrosion attack.
Figure 12.
The fractography analysis of fracture surfaces after tensile tests of (a) material A; (b) material B; (c) material C after corrosion attack.
Figure 13.
The fractography analysis of fracture surface after Charpy impact test of (a) material A; (b) material B; (c) material C after corrosion attack.
Figure 13.
The fractography analysis of fracture surface after Charpy impact test of (a) material A; (b) material B; (c) material C after corrosion attack.
Figure 14.
The fractography analysis of initiation places (marked by arrows) in material C (a) without corrosion environment and (b) with corrosion environment.
Figure 14.
The fractography analysis of initiation places (marked by arrows) in material C (a) without corrosion environment and (b) with corrosion environment.
Figure 15.
The fractography analysis of fatigue and static region in material C (a) without corrosion environment and (b) with corrosion environment.
Figure 15.
The fractography analysis of fatigue and static region in material C (a) without corrosion environment and (b) with corrosion environment.
Table 1.
The chemical compositions of the experimental materials (in wt. %).
Table 1.
The chemical compositions of the experimental materials (in wt. %).
| type |
material |
Si |
Fe |
Cu |
Mn |
Mg |
Zn |
Ti |
Al |
| primary |
A |
7.028 |
0.123 |
0.013 |
0.009 |
0.354 |
0.036 |
0.123 |
92.253 |
| secondary |
B |
7.340 |
0.454 |
0.021 |
0.009 |
0.302 |
0.020 |
0.118 |
91.673 |
| secondary |
C |
7.315 |
0.655 |
0.030 |
0.010 |
0.292 |
0.028 |
0.120 |
91.486 |
Table 2.
The results of basic mechanical properties.
Table 2.
The results of basic mechanical properties.
| Measured properties |
Before corrosion |
After corrosion |
| A |
B |
C |
A |
B |
C |
| UTS [MPa] |
141 |
150 |
147 |
130 |
140 |
144 |
| HBW 5/250/15 |
52 |
55 |
54 |
58 |
59 |
59 |
| Ductility [%] |
1.45 |
1.91 |
1.55 |
1.7 |
1.5 |
1.3 |
| Impact energy [J] |
14 |
12 |
10.5 |
10.5 |
8 |
7.8 |
Table 3.
The results of the quality index.
Table 3.
The results of the quality index.
| Quality index |
Before corrosion |
After corrosion |
| A |
B |
C |
A |
B |
C |
| QI |
165.21 |
192.16 |
175.55 |
164.57 |
166.41 |
161.09 |
Table 4.
The results of quantitative measurements of corrosion pits in experimental material after a corrosion attack: D – diameter, P – Circumference, A – area.
Table 4.
The results of quantitative measurements of corrosion pits in experimental material after a corrosion attack: D – diameter, P – Circumference, A – area.
| |
Material A |
Material B |
Material C |
A
[mm2] |
D
[mm] |
P
[mm] |
A
[mm2] |
D
[mm] |
P
[mm] |
A
[mm2] |
D
[mm] |
P [mm] |
| Minimum |
48.66 |
0.25 |
0.78 |
48.66 |
0.25 |
0.78 |
24.83 |
0.18 |
0.56 |
| Maximum |
339.91 |
0.66 |
2.07 |
397.26 |
0.71 |
2.23 |
437.98 |
0.75 |
2.35 |
| Average value |
115.99 |
0.402 |
1.21 |
161.34 |
0.434 |
1.39 |
144.73 |
0.403 |
1.34 |
| Mean deviation |
71.74 |
0.120 |
0.33 |
105.31 |
0.15 |
0.44 |
91.09 |
0.15 |
0.42 |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).