Submitted:
24 April 2023
Posted:
25 April 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. PAT model
3. Numerical simulations
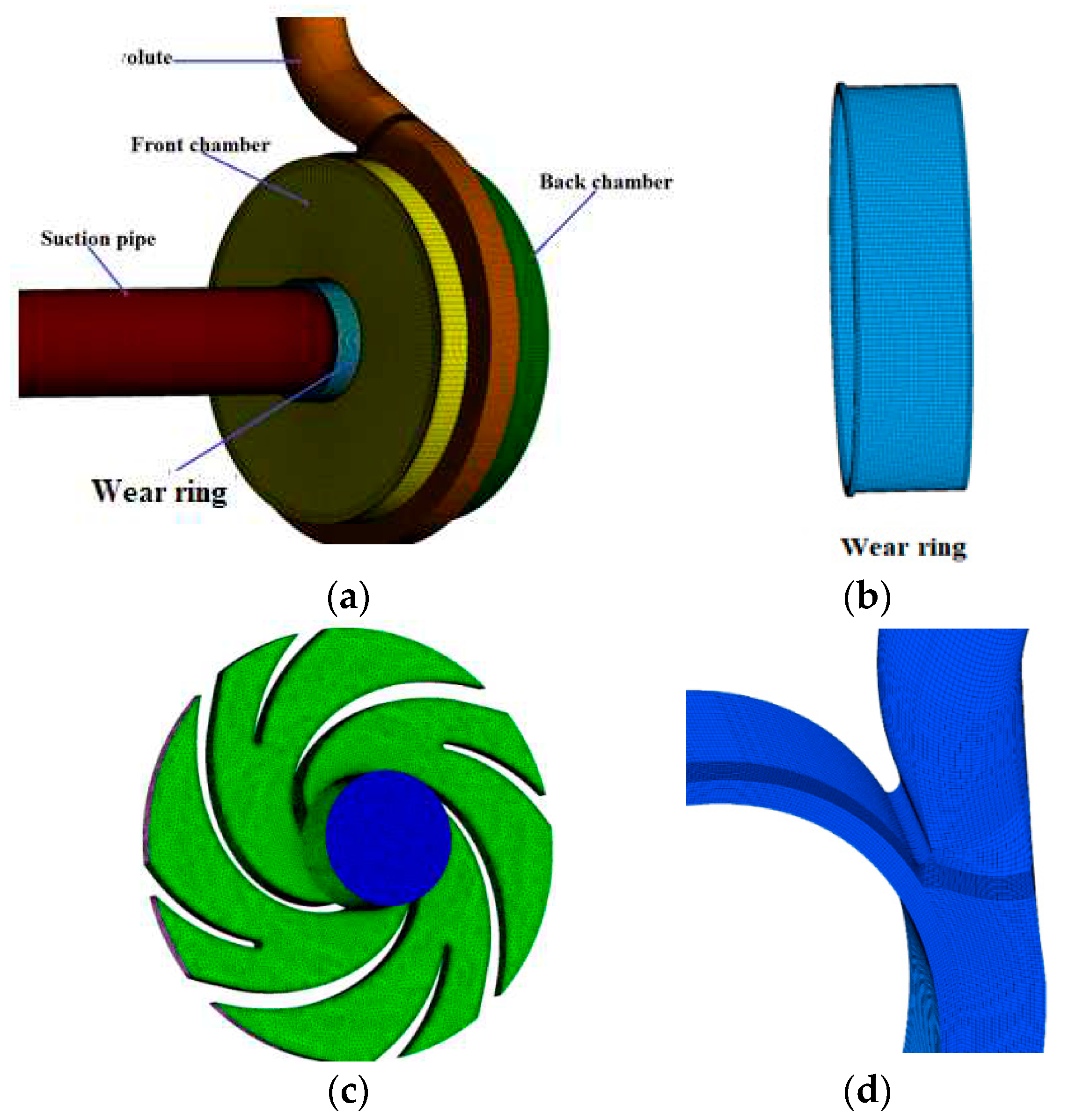
3.1. Description of entire PAT fields
3.2. Numerical simulation structure
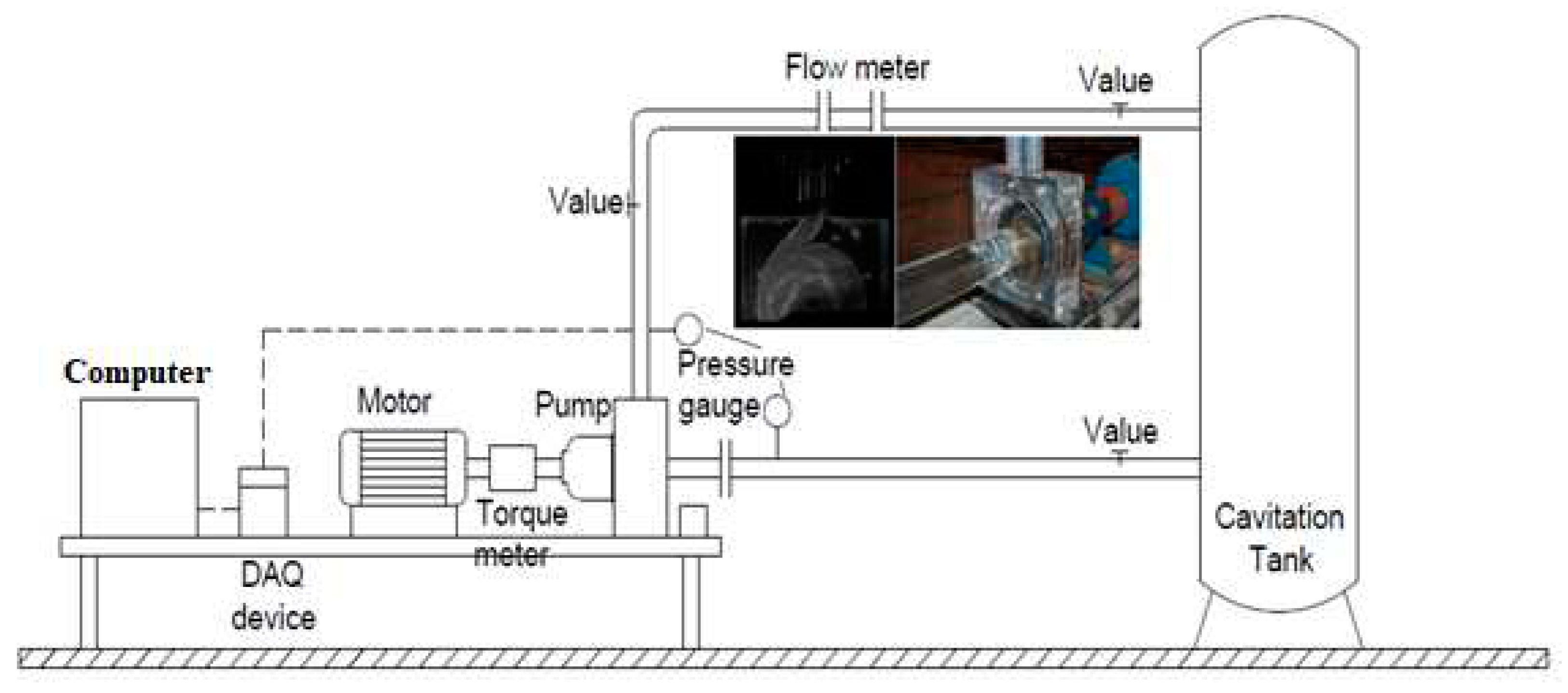
4. Experimental setup
5. Results and discussions
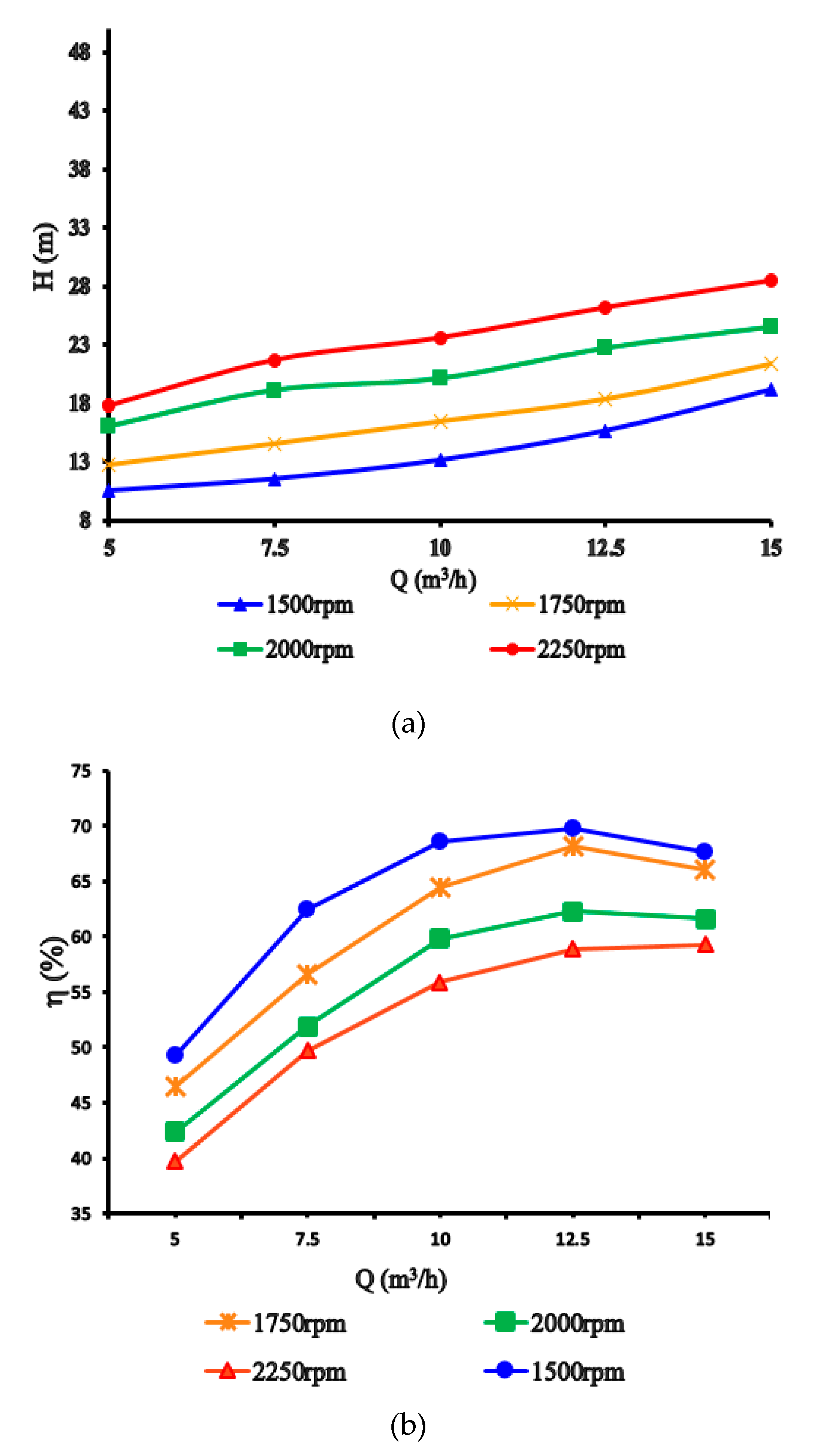
5.1. pump characteristics curves
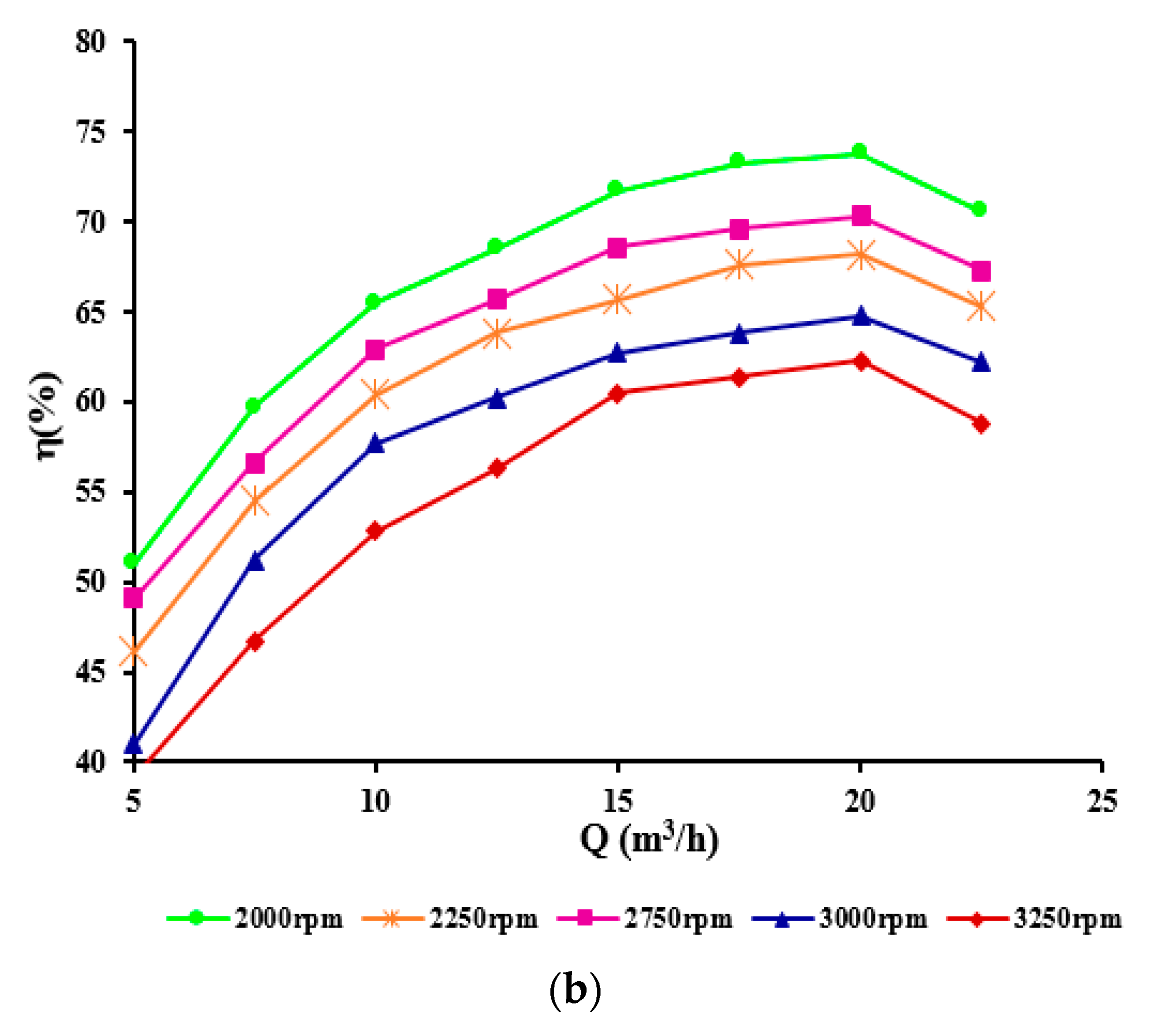
5.2. Effect of rotational speed on PAT performance
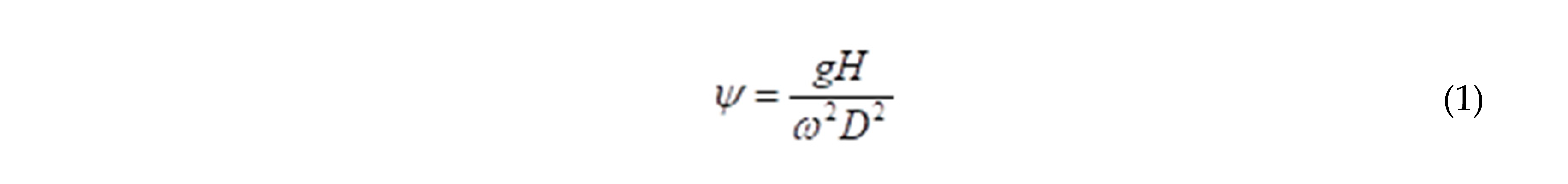

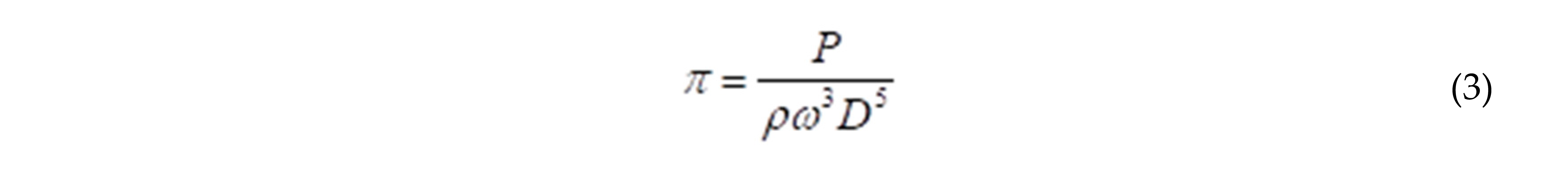
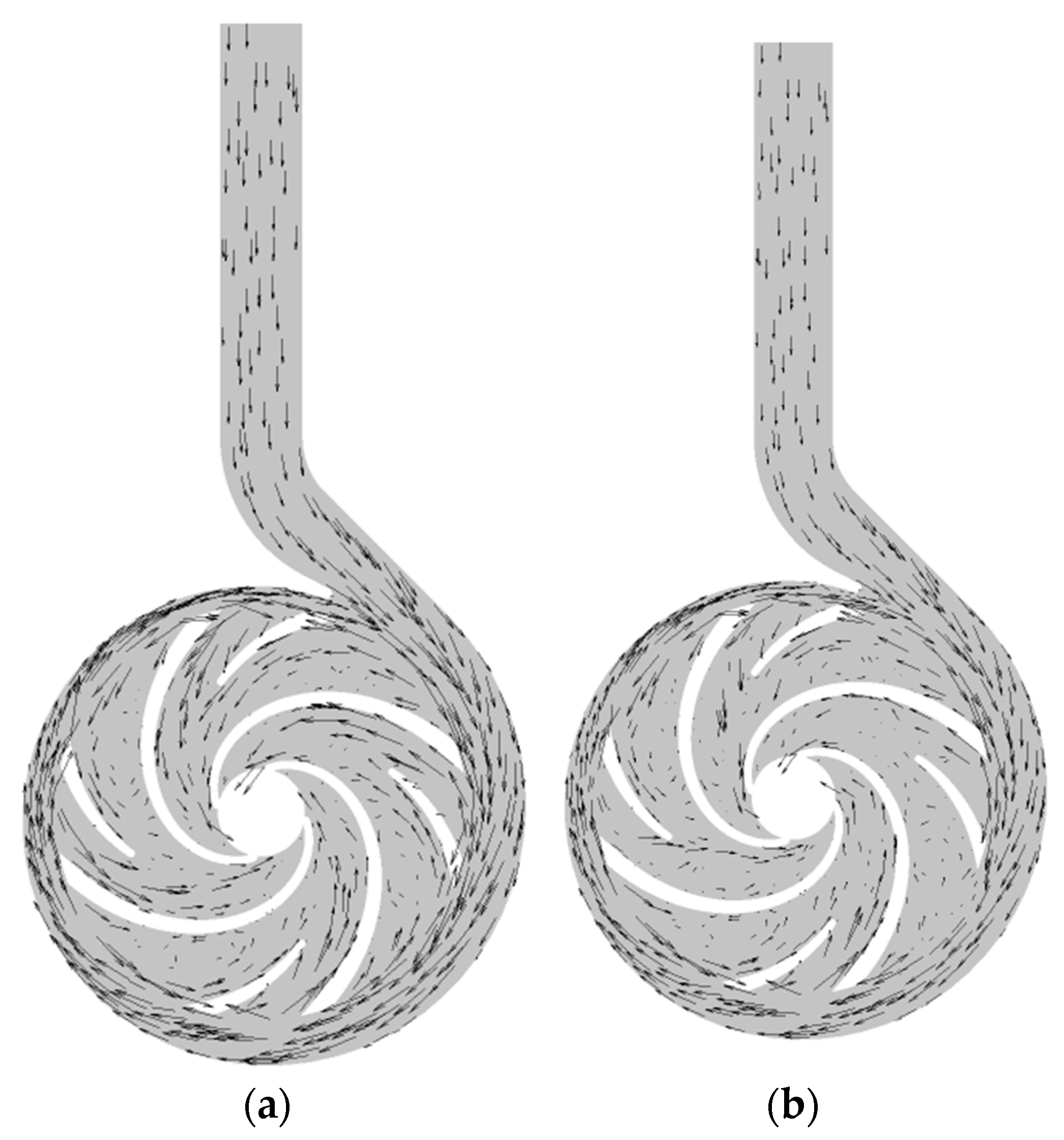
5.3. Pressure Distribution in PAT
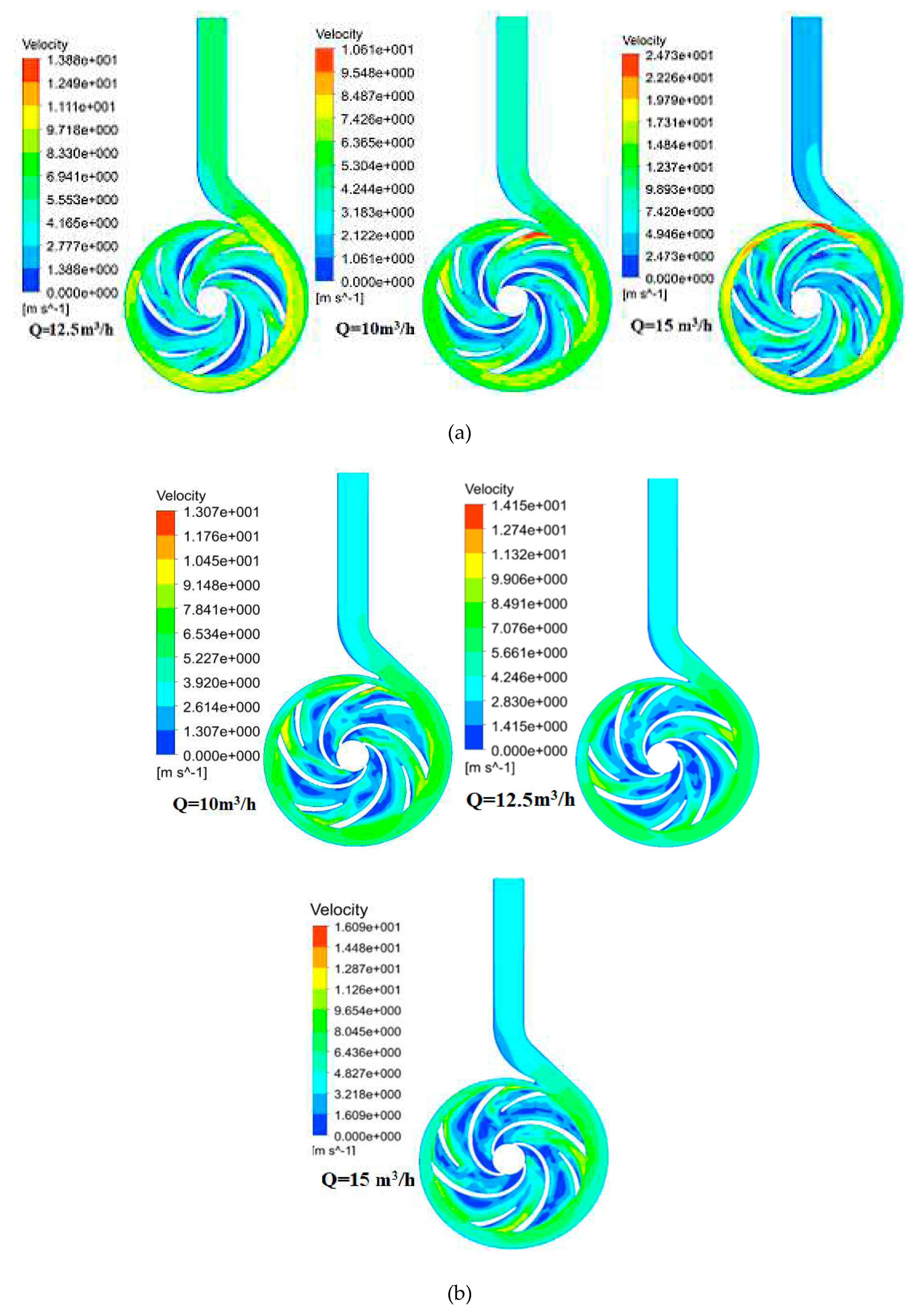
5.4. Velocity Distribution in PAT
6. Conclusion
Acknowledgments
Nomenclature
| D1 | Suction diameter[m] |
| D2 | Impeller out diameter[m] |
| b2 | Impeller out width[m] |
| Z | Number of vanes |
| P | Motor Power[kW] |
| Pin | Pressure of pump inlet [Pa] |
| η | Pump hydraulic efficiency[%] |
| n | Motor speed[rpm] |
| ns | Specific Speed |
| M | Impeller moment [Nm] |
| rpm | revolutions per minute |
| ηBEP. | efficiency at best efficient point |
| BEP | best efficient point |
| Qd | Design pump flow rate[m3/h] |
| Q | Pump flow rate[m3/h] |
| Hd | Design Pump Head[m] |
| H | pump head[m] |
| Di | Inlet diameter of splitter blades [m] |
| SST k-ω | Shear Stress Transport |
| g | gravity acceleration [m/s2] |
| ρ | fluid density [kg/m3] |
| RANS | Reynolds- Averaged Navier–Stokes |
| CFD | Computational fluid dynamics |
| PAT | Pump as turbine |
| SHP | small hydropower |
| H | pump head[m] |
| Di | Inlet diameter of splitter blades [m] |
| SST k-ω | Shear Stress Transport |
References
- Zhang, J.; Adu, D.; Fang, Y.; Yin, T. Review of the sub-Saharan African small hydropower situation. Proc. Inst. Civ. Eng. Energy 2018, 171, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adu, D.; Zhang, J.; Fang, Y.; Suoming, L.; Darko, R.O. A Case Study of Status and Potential of Small Hydro-Power Plants in Southern African Development Community. Energy Procedia 2017, 141, 352–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karekezi S, Kimarii J the Potential Contribution of Non-Electrified Renewable Energy Technologies for Poverty Reduction in East Africa. 2005.
- European Small Hydropower Association Small Hydropower Roadmap-Condensed Research Data for EU-27[R/OL], Brussels: ESHA. ( 2013.
- Mosè Rossi et al. Pump-as-Turbine for energy recovery applications: the case study of an aqueduct ATI2016, Turin, Italy Energy Procedia. t: for energy recovery applications, 2016; 101, 1207–1214.
- Derakhshan, S.; Nourbakhsh, A. Theoretical, numerical and experimental investigation of centrifugal pumps in reverse operation. Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 2008, 32, 1620–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- POPESCU, D. et al. Study of Centrifugal Pump Operating as Turbine in Small Hydropower Plants, Recent Researches in Electric Power and Energy Systems. ISBN: 978-960-474-328-5.
- Sanjay, V. Jain a, Abhishek S., et al. Effects of impeller diameter and rotational speed on performance of pump running in turbine mode. Energy Conversion and Management 2015, 89, 808–824. [Google Scholar]
- Suarda, M.; Suarnadwipa, N.; AdnyanaW.B., *!!! REPLACE !!!*. , Suarnadwipa N., and AdnyanaW.B. In Assessment Performance of Pumps as Hydro-Turbines‖, International Conference on Energy and Environment; ICEE, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, M.; Tan, L.; Cao, S. Performance Prediction and Geometry Optimization for Application of Pump as Turbine: A Review. Front. Energy Res. 2022, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbarelli, S.; Amelio, M.; Florio, G.; Scornaienchi, N. Procedure Selecting Pumps Running as Turbines in Micro Hydro Plants. Energy Procedia 2017, 126, 549–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramer, M. , Terheiden K., Wieprecht S., Pumps as turbines for efficient energy recovery in water supply networks. Renewable Energy 2018, 122, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frosina, E.; Buono, D.; Senatore, A. A Performance Prediction Method for Pumps as Turbines (PAT) Using a Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) Modeling Approach. Energies 2017, 10, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derakhshan, S.; Mohammadi, B.; Nourbakhsh, A. Efficiency Improvement of Centrifugal Reverse Pumps. J. Fluids Eng. 2009, 131, 021103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suarda, M.; Suarnadwipa, N.; Adnyana, W. Experimental Work on Modification of Impeller Tips of a Centrifugal Pump as a Turbine. Udayana University Denpasar, Bali, Indonesia.
- Singh, P., Ph. D. thesis: Optimization of the Internal Hydraulic and of System Design in Pumps as Turbines with Field Implementation and Evaluation,” University of Karlsruhe, Germany, 05. 20 June.
- Singh, P.; Nestmann, F. Internal hydraulic analysis of impeller rounding in centrifugal pumps as turbines. Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 2011, 35, 121–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, R. , ―Performance analysis of modified pump used as turbine‖, M.Tech. Dissertation, ; AHEC, IIT Roorkee.
- Anantharaj, S. , Ede S.R., Karthick K., Sam Sankar S., Sangeetha K., Karthik, Subrata Kundu P.E., Precision and correctness in the evaluation of electrocatalytic water splitting: revisiting activity parameters with a critical assessment. Energy Environ. Sci. 2018, 4, 744–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, X.; Li, Y.; Yang, T. Hierarchical micro-reactor as electrodes for water splitting by metal rod tipped carbon Nano capsule self-assembly in carbonized wood Applied Catalysis B: Environmental. E: Hierarchical micro-reactor as electrodes for water splitting by metal rod tipped carbon Nano capsule self-assembly in carbonized wood Applied Catalysis B, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Shiva Kumar, S. , Ramakrishna S.U.B., Bhagawan D., Himabindu V., Preparation of RuxPd1-xO2 electro catalysts for the oxygen evolution reaction (OER) in PEM water electrolysis Ionics. 24; 2018, 2411–2419. [Google Scholar]
- Rathinam, N.K.; Sani, R.K. Salem, Extremophilic Microbial Processing of Lignocellulosic Feedstocks to Biofuels, Value-Added Products, and Usable Power. Springer: Cham, 2018; pp. 229–245. [Google Scholar]
- Kannan, Sekar & Kumar, N & Pandian, Vasanthakumar. (2017). Centrifugal Pump as Turbine for Micro-Hydro Power Scheme in Rural Areas of India: A Review. In International Journal of ChemTech Research; 1: International Journal of ChemTech Research, (14), 2017; Volume 14, pp. 106–109.
- Bentum-Micah, G.; Atuahene, S.A.; Cai, L.; Adu, D.; Sheng, Q.X. Experimental investigation and performance prediction modeling of a single stage centrifugal pump operating as turbine. Energy Procedia 2017, 126, 589–596. [Google Scholar]
- Kan, K.; Zhang, Q.; Xu, Z.; Zheng, Y.; Gao, Q.; Shen, L. Energy loss mechanism due to tip leakage flow of axial flow pump as turbine under various operating conditions. Energy 2022, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Ji, L.; Li, E.; Shi, W.; Agarwal, R.; Zhou, L. Numerical investigation of energy loss mechanism of mixed-flow pump under stall condition. Renew. Energy 2020, 167, 740–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuele S, Mose R,et al, Energy recovery in gravity addiction pipelines of a water supply system (WSS) for urban areas using Pumps-as-Turbines. Sustainable Energy Technologies and Assessments 2021, 45, 101040. [CrossRef]
- Kadier, A.; Sahaid Kalil, Md.; Abdeshahian, P.; Chandrasekhar, K.; Mohamed, A.; Farhana Azman, N.; Logroño, W.; Simayi, Y.; Abdul Hamid, A. Recent advances and emerging challenges in microbial electrolysis cells (MECs) for microbial production of hydrogen and value-added chemicals. Renewable Sustainable Energy Rev. 2016, 61, 501–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang Y L, Yuan S Q, Zhang J F, et.al Numerical investigation of the effects of splitter blades on the cavitation performance of a centrifugal pump 2014 IOP Conf. Ser.: Earth Environ. Sci. 22 052003.






| (a) Geometric parameters. | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameter | Symbol | Value | Unit | ||
|
Suction diameter outer Impeller diameter outer Impeller width long blades splitter blades splitter blades Inlet diameter |
D1 D2 b2 - - Di |
0.05 0.16 0.06 4 4 0.104 |
m m m - - m |
||
| (b) Operational parameters at design condition. | |||||
| Parameter | Symbol | Value | Unit | ||
|
Flow rate Head Efficiency Specific Speed Rotational speed |
QD HD η ns n |
12.5 32 56 47 2900 |
m3/h m - - rpm |
||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




