Submitted:
05 May 2023
Posted:
06 May 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
1.1. Current Situation of OHS (Occupational Health & Safety) in the Construction Sector in Romania
1.2. Accident Situation on Romania
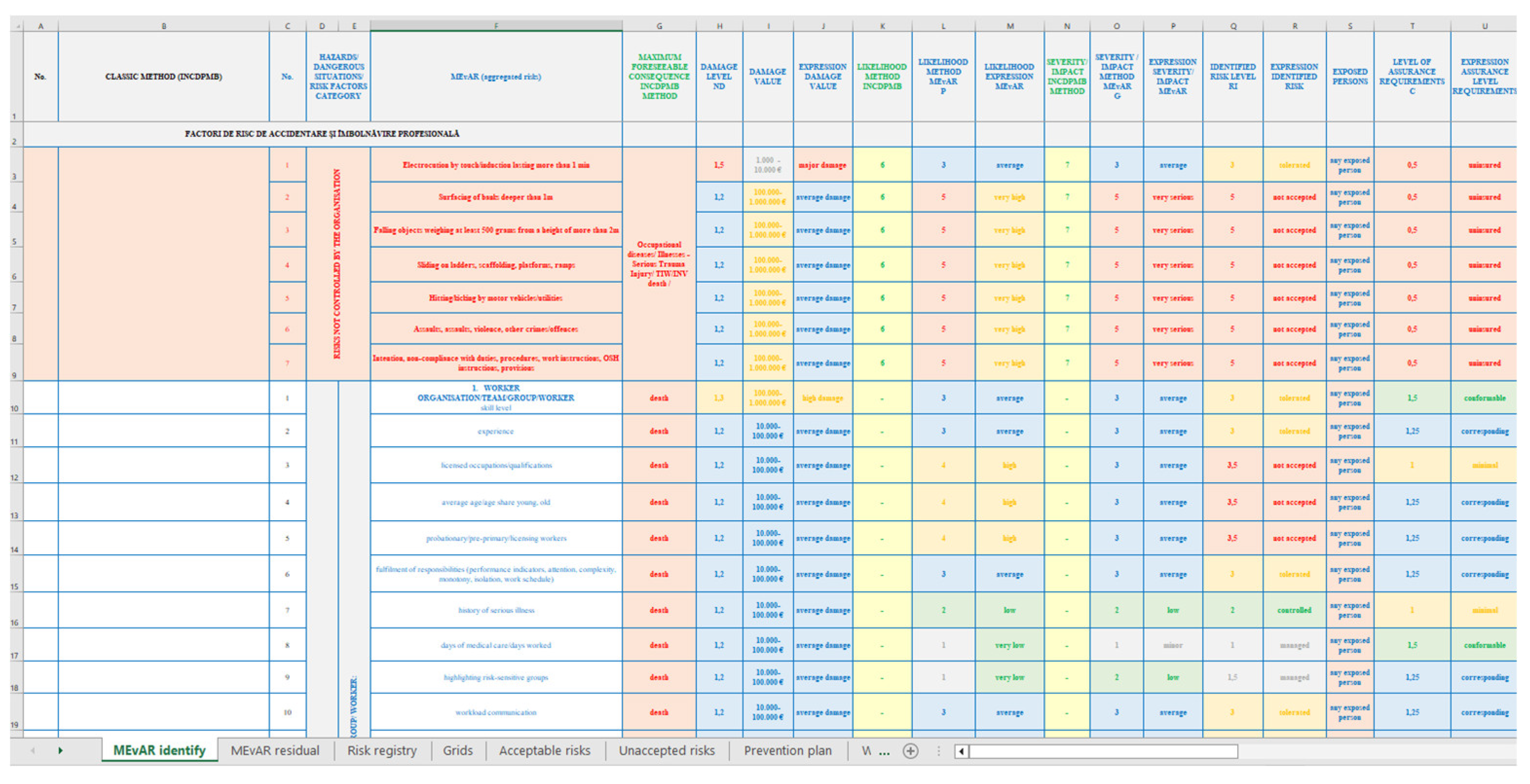
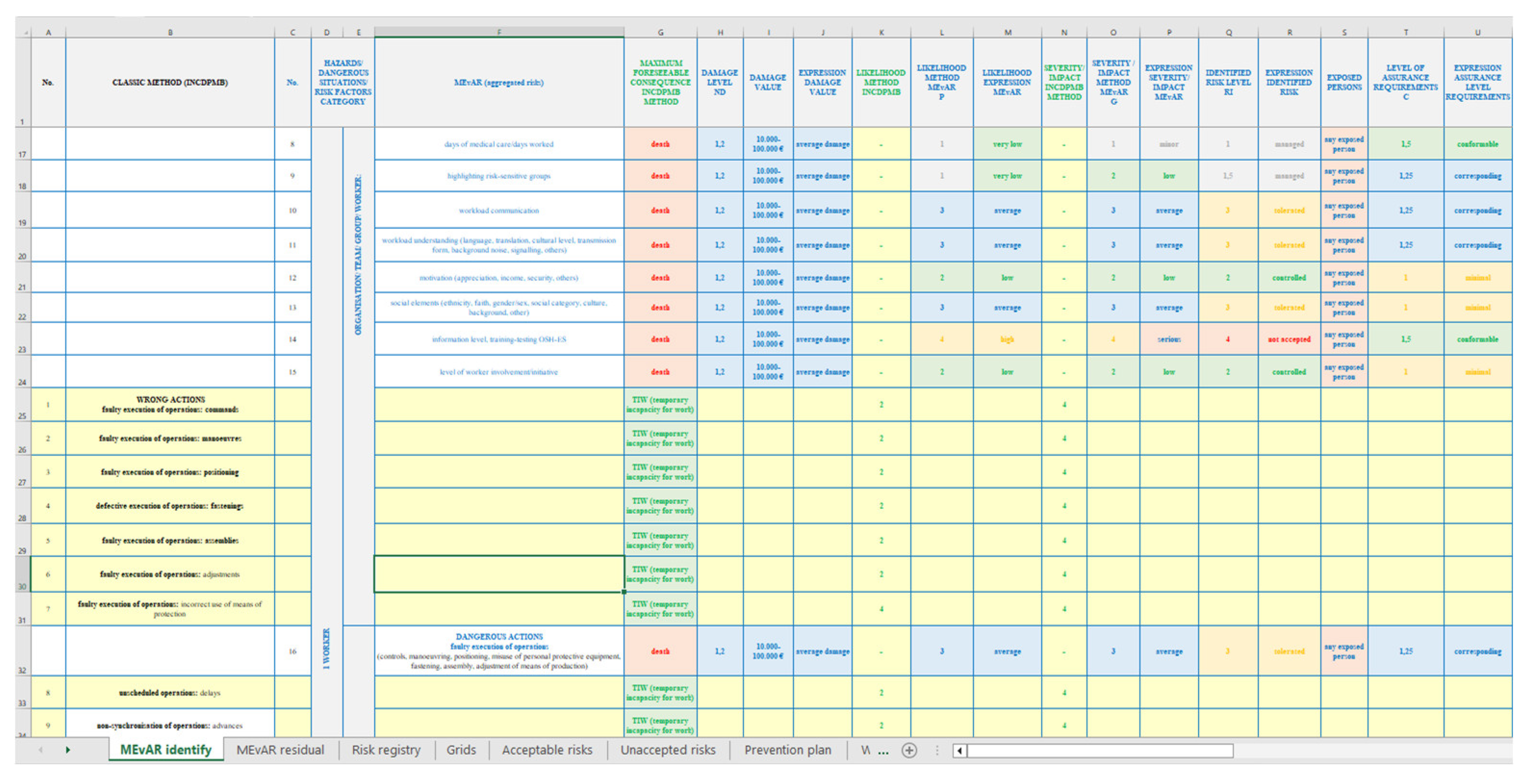
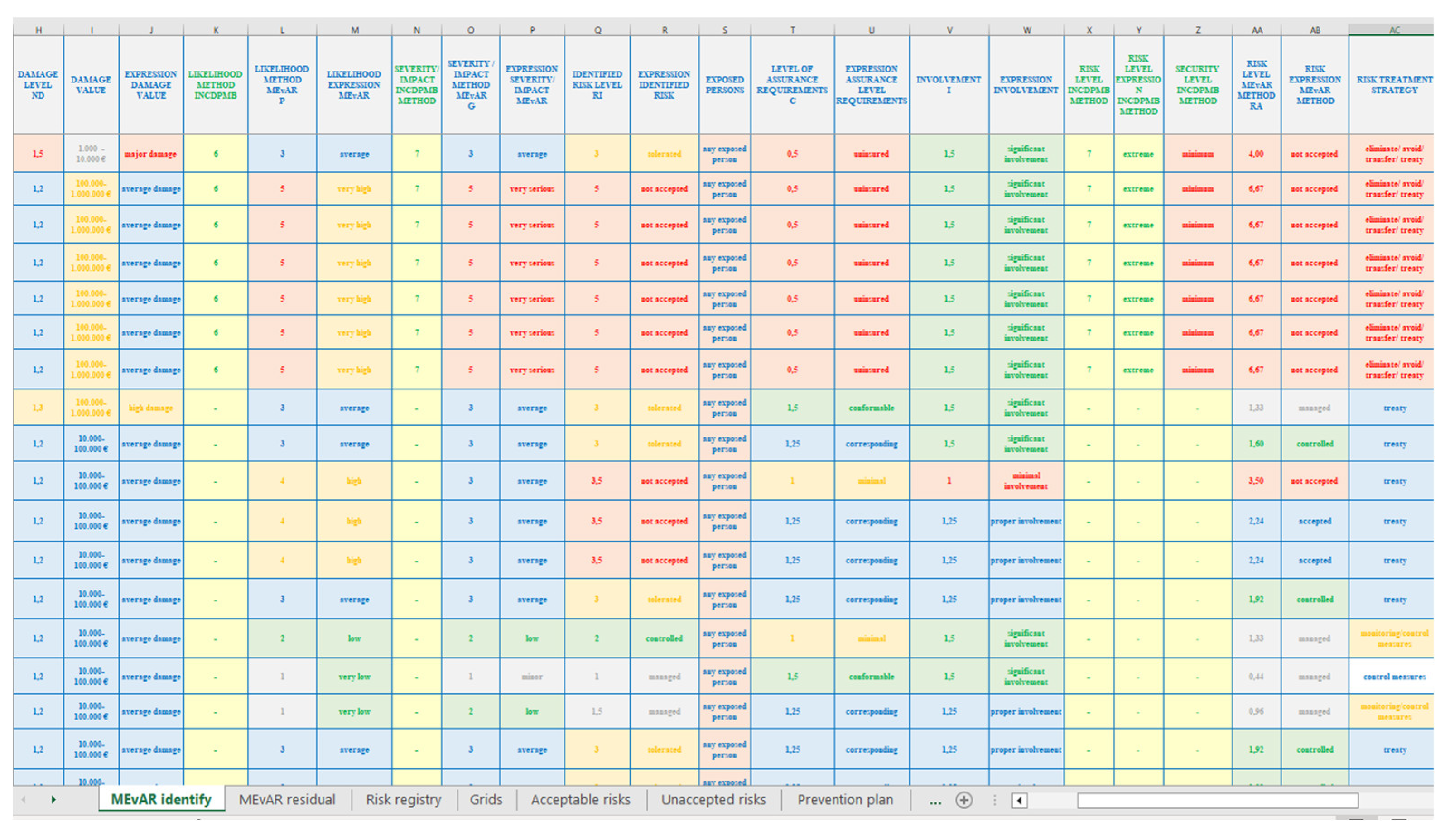
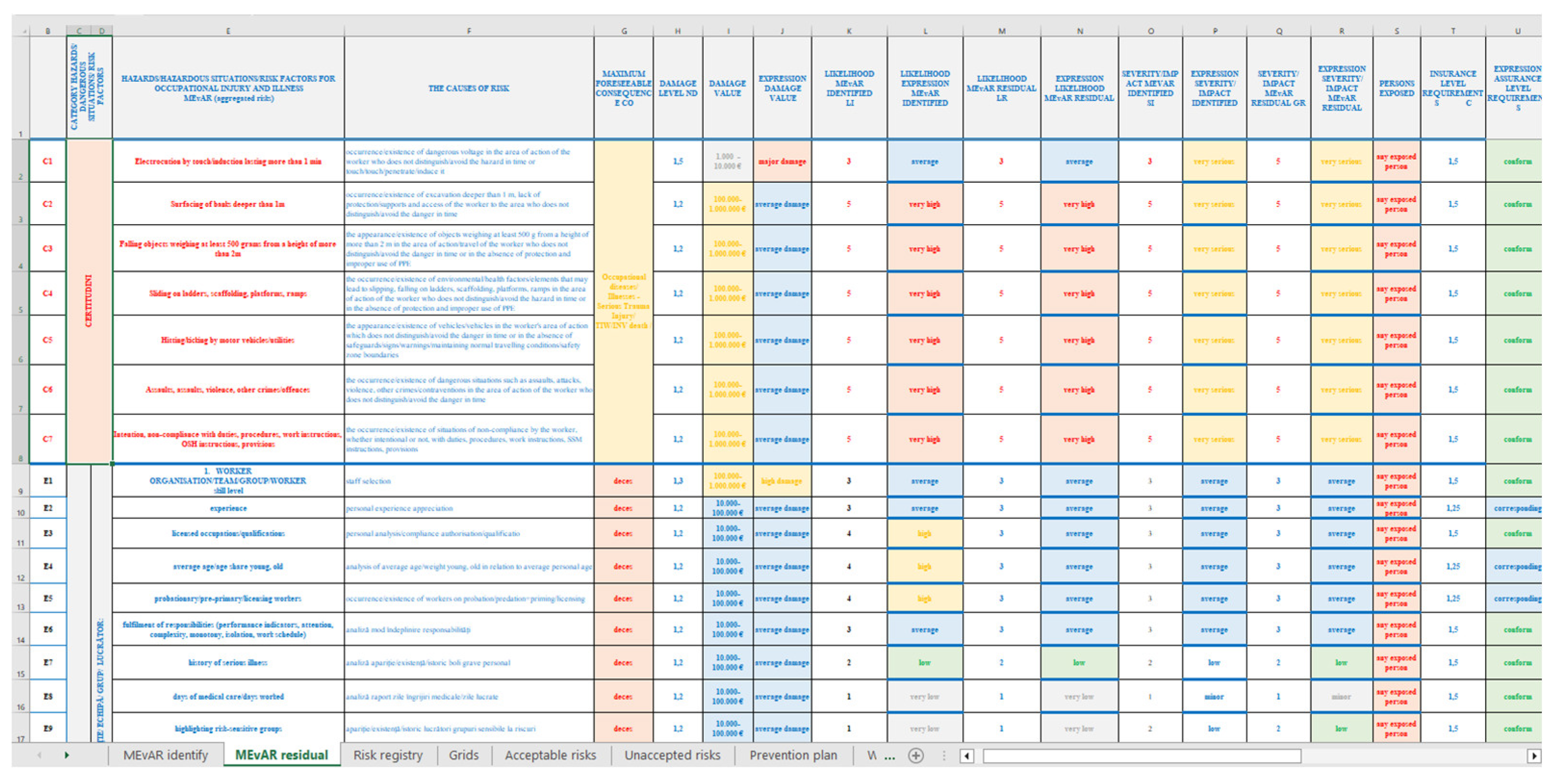
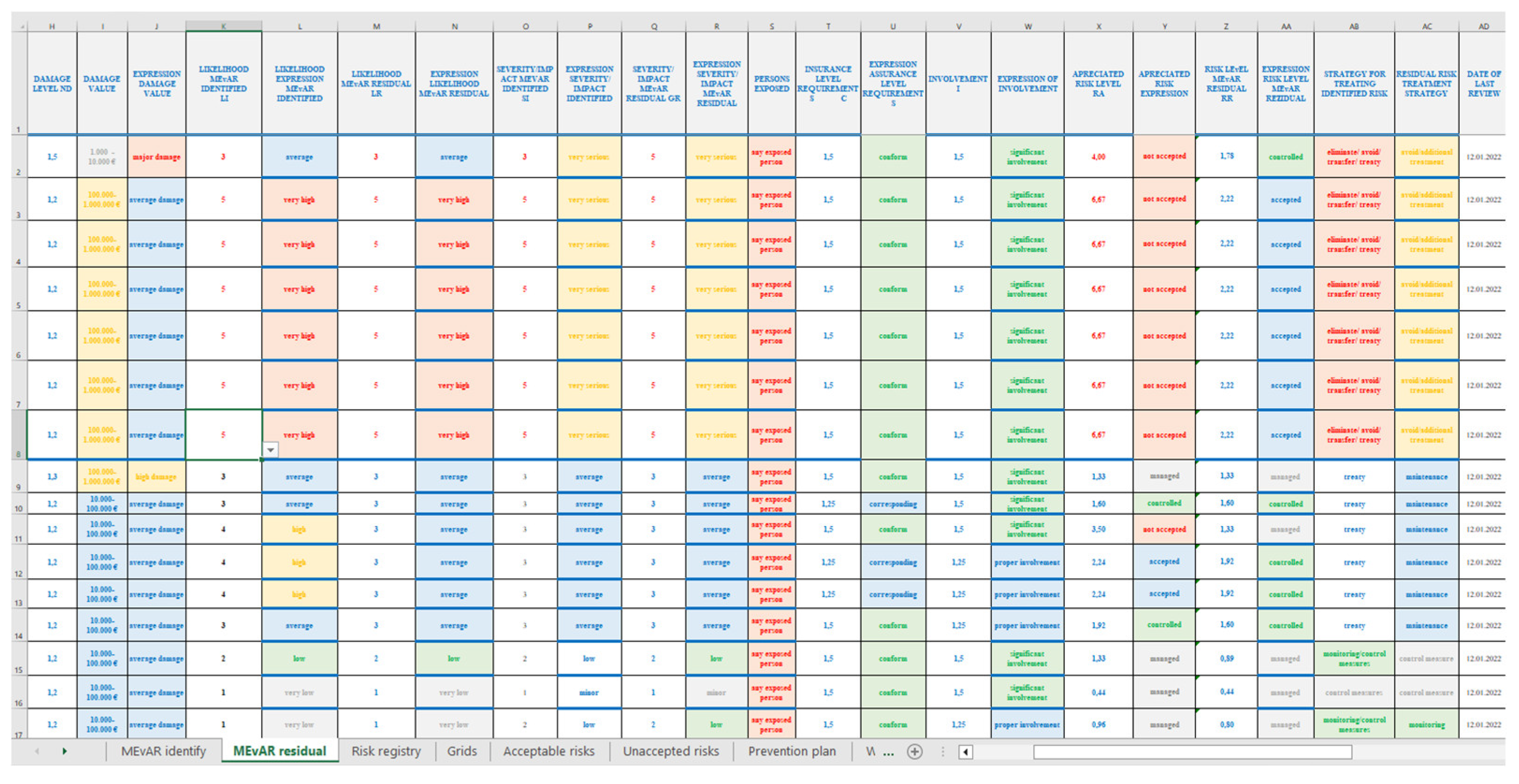
2. Short Presentation on the MEvAR Method of Occupational Risk Assessment
- -
- it has correspondence in the Community or international standards in the field;
- -
- the method takes into account elements of certainty before risks, risks are aggregated on the basis of sources, dangerous situations and hazards, elements specific to the organisation, work teams, workers, direct relationship with the organization’s management, company management and workplace managers, records and history of impact on workers;
- -
- the assessment covers the workplace/station/activity/process/sensitive group/work equipment/chemical substances and/or preparations used/workplace layout in the organization;
- -
- risks generated in the analysis and action, opportunities, vulnerabilities and capabilities are considered;
- -
- technical data, operating parameters and up to date maintenance are analyzed for failure predictions of analyzed equipment;
- -
- the work environment is separated into the workplace environment and the environment in its vicinity for better analysis of external sources and impacts;
- -
- risks in combining and adapting the main elements of SR EN ISO 31010:2019, SR EN ISO 45001: 2018 are analyzed and assessed from different assessment methods (Brainstorming, Delphi, INCDPM - Darabont, Heinrich, FMEA, AMDEC, ARAMIS, ISHIKAWA, NEBOSH, HAZOP, ELVIE, REASON, MEVA, others) considering the participation of minimum 2 assessors, analysis and identification of sources, interview, supervision and organization of process meetings, the assessed values use parameter specific mathematical models, different type 5x5, 4x4, 3x3 with associated values that are chosen by the assessor in order to realize the relevance of the risk and proposed measures;
- -
- the risk can be assessed in different forms - initial, proposed - residual, weighted with that of the basic method according to the established purpose and objectives, there is a selection of the risk treatment strategy and the risks can be reviewed during the assessment;
- -
- the method incorporates harmonized elements of classical occupational risk assessment methods, H&S management system requirements and current legislative requirements;
- -
- severity is expressed as the ratio of consequence to harm, with the level of injury being a ratio of trauma to illness and the level of material damage being estimated according to the financial level of the organization;
- -
- probability is analyzed in terms of the likelihood of an event occurring and the characteristics of the exposure - route, duration and frequency ;
- -
- the number and quality of workers are included in the assessment;
- -
- the influence on processes of situations such as the Coronavirus Sars CoV-2 - Covid -19 pandemic is taken into account ;
- -
- we consider that the method is relatively easy to use, being accompanied by the Microsoft Excel software application popular among users, with which reports are obtained on the certainties and potential risks, their treatment measures, prevention and protection measures in the field of H&S ;
- -
- the contractual requirements ;
- -
- administrative requirements ;
- -
- information on regulatory compliance ;
- -
- knowledge of work processes ;
- -
- planning of activities and scheduling of the team and staff to be interacted with prior to the commencement of the risk assessment work;
- -
- staff briefing and training;
- -
- preparation of documents, equipment, facilities;
- -
- travel to the work sites.
- -
- entering the initial data into the application;
- -
- assessing, determining and estimating the levels of the risk calculation elements;
- -
- calculation of the assessed risk, which is carried out by the application;
- -
- the projection of the residual risk resulting from the recalculation of the analysis of the risk treatment, the verification of the assurance of the prevention and protection measures and the continuous improvement projected to be achieved by the input of new data and is carried out by the application [24,25].
- -
- prevention and protection plan;
- -
- risk register;
- -
- work equipment assessment sheet;
- -
- the evaluation sheet for hazardous chemical substances or preparations;
- -
- workstation layout sheet – ergonomics;
- -
- sensitive groups assessment sheet;
- -
- certainties (definite hazards);
- -
- unacceptable risks;
- -
- acceptable risks;
- -
- risk alert form;
- -
- risk tracking sheet.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Study on the Working Environment in Construction
3.2. Workplace- Installer
- -
- Activity/Process: installation, commissioning, checking, control of thermal and sanitary installations according to the construction project;
- -
- Inputs: qualified installers and unqualified personnel, installation of electric lighting, electricity, plumbing, heating, construction elements, construction site, necessary funds;
- -
- Outputs: construction and proper operation of thermal plumbing, consumption of electricity, water, fuel, spare parts, heat emissions, waste.
- -
- - means of transport and communication: Ford transit van 3.5 t;
- -
- - productive buildings/spaces: - office, warehouse, site premises;
- -
- - the containers and warehouses for storing products: - material warehouse, cabinets, boxes, cases;
- -
- - Energy, water power, steam, etc. : - electricity, water.
- -
- - instrinsic protection - compliance of products with the essential requirements of the OSH;
- -
- - collective protection - means of delimiting and marking work areas, improving microclimate, electrical security, combating noise, air currents, combating mechanical risks, improving lighting.
- -
- - training of workers, health surveillance, health and safety propaganda, organisation of work and workstation/ activities/processes/sensitive groups/ work equipment/ chemical substances and/or preparations used/ workplace layout;
- -
- - personal protection - protection of head, eyes and face, ears, respiratory tract, body, hands, feet, whole body, electrical safety protection.
- -
- - protective feeding, hygienic sanitary materials, first aid stations, changing rooms, bathrooms with showers, etc.
4. Conclusions
- -
- update and complete the uncovered and/or niche aspects of the assessment methods used by most specialists;
- -
- adaptation of occupational risk assessment methods with other general or specific risk assessment methods;
- -
- linking with the requirements of the OSH management system and the integrated quality - environment - OSH - HACCP - information management system;
- -
- adaptation with territorial administrative management systems;
- -
- awareness of hazards and prevention and protection measures on the part of the organizations' management by taking over the assessment report;
- -
- the possibility of vector development of the assessment system by ensuring the application of general and particular principles of identification, analysis, assessment, evaluation and conclusion by specialists;
- -
- the possibility of mitigating hazards by ensuring greater attention and weighting to the treatment of risks, managing and keeping under control those that are highly variable or likely to occur;
- -
- improving the resilience of OSH, Emergency situation, environmental protection to events.
Funding
Acknowledgments
References
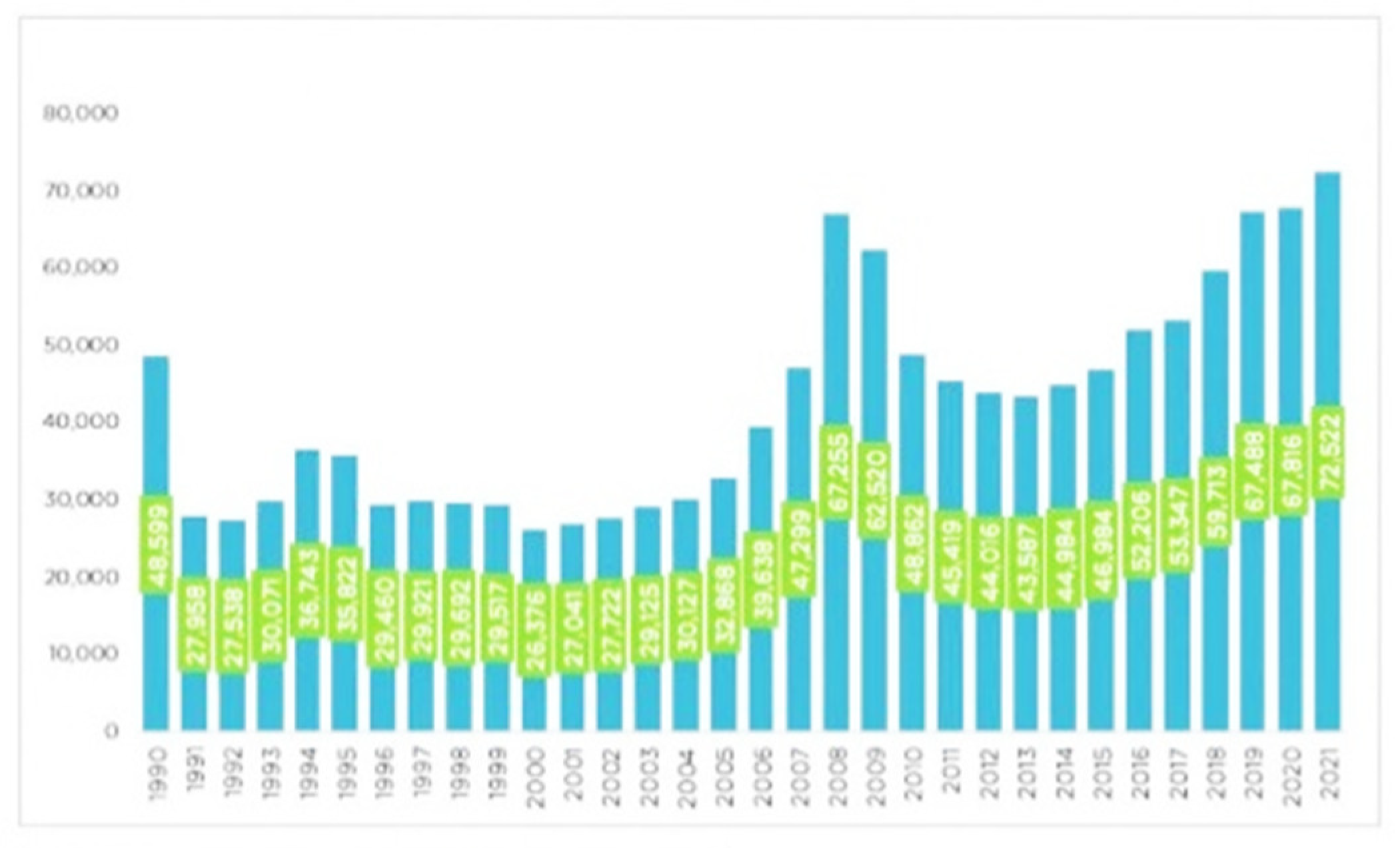
- In 2021 the most homes were built in the last 30 years - 2022 is the sign of uncertainty. Available online: https://www.wall-street.ro/articol/Real-Estate/284340/in-2021-au-fost-construite-cele-mai-multe-locuinte-in-ultimii-30-de-ani-2022-sta-sunt-semnul-incertitudinii.html (accessed on 17 November 2022).
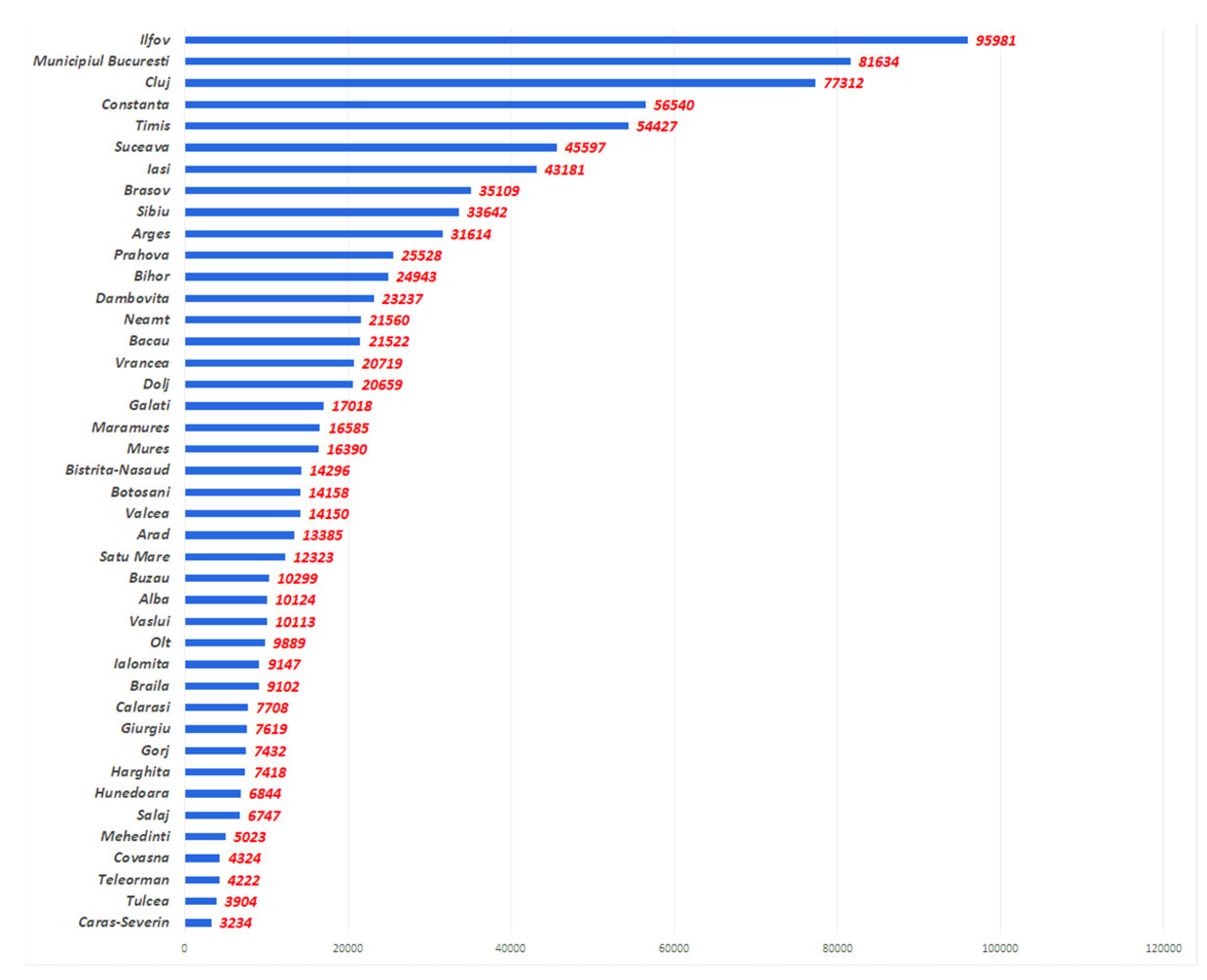
- The places where the most houses were built in Romania in the last 10 years / Counties where fewer houses are built and those where their number has exploded. Available online: https://economie.hotnews.ro/stiri-finante_banci-25674715-locurile-care-construit-cele-mai-multe-locuinte-din-romania-ultimilor-10-ani-judetele-care-construiesc-mai-putine-locuinte-cele-care-numarul-lor-explodat.htm (accessed on 17 November 2022).
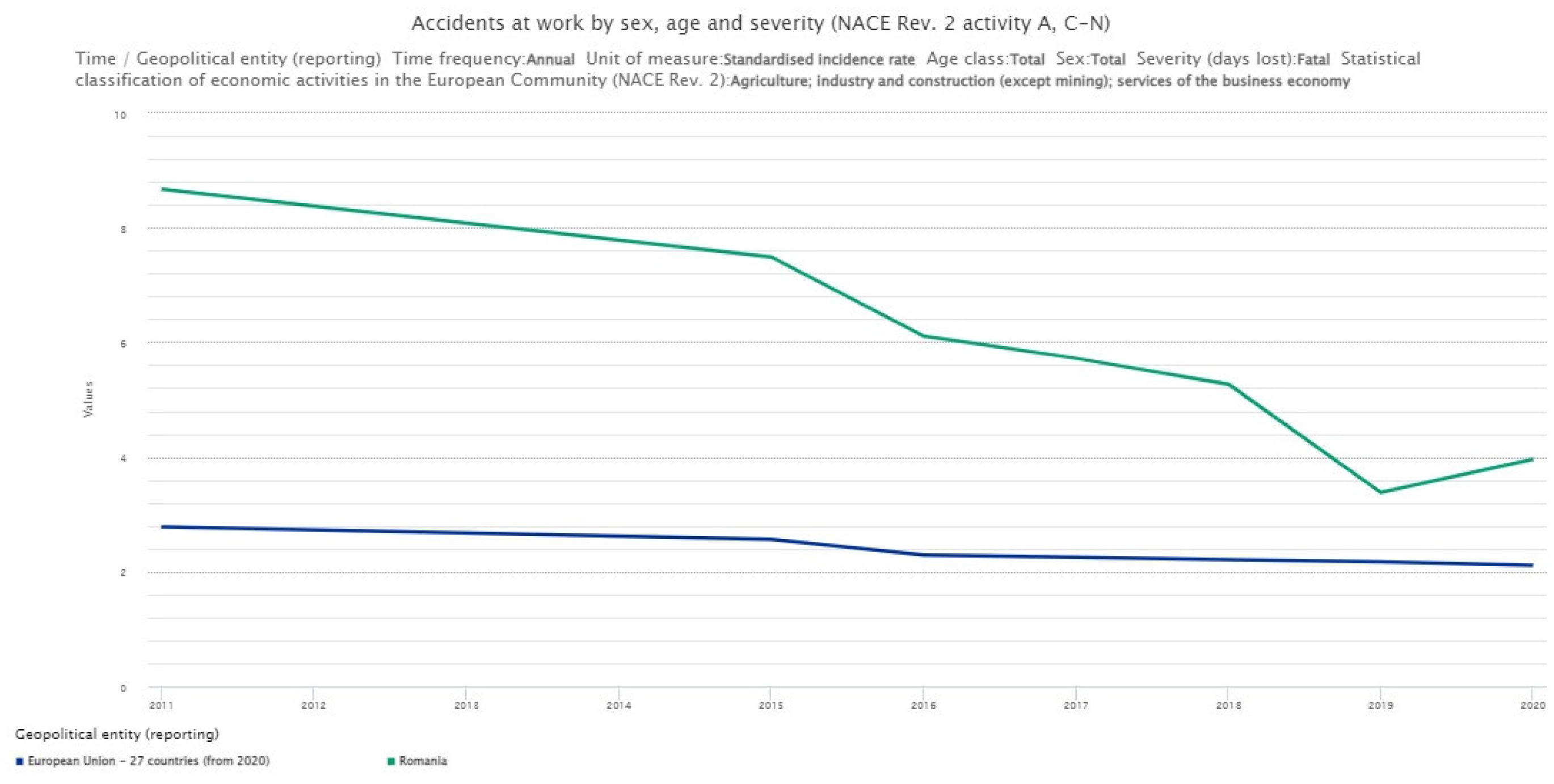
- France among most dangerous places to work in EU, figures show. Available online: https://www.rfi.fr/en/france/20221031-france-among-most-dangerous-places-to-work-in-eu-figures-show (accessed on 17 November 2022).
- Accidents at work by sex, age and severity (NACE Rev. 2 activity A, C-N). Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/databrowser/view/HSW_MI01/bookmark/line?lang=en&bookmarkId=9edf396d-7316-4e72-93c7-a84acac4d9fb (accessed on 17 November 2022).
- More than 2,000 people were injured at work in the first half of 2021. Most fatal accidents are in construction. Available online: https://www.digi24.ro/stiri/actualitate/peste-2-000-de-oameni-au-suferit-accidente-de-munca-in-prima-jumatate-a-lui-2021-cele-mai-multe-accidente-mortale-sunt-in-constructii-1709721 (accessed on 17 November 2022).
- Available online: https://dexonline.ro/definitie/mediu/definitii (accessed on 17 November 2022).
- Law 319/2006 of Occupational Health and Safety; Romanian Government: Bucharest, Romania, 2006.
- Penal code, adopted by Law 286/2009, Romania, 2014.
- Cioca L.I., Moraru R., Băbuţ, G., 2010. Occupational Risk Assessment: A Framework for Understanding and Practical Guiding the Process in Romania, Proc. Int. Conference on Risk Management, Assessment and Mitigation (RIMA ’10), 56-61, Bucharest, Romania, 20-22.04.2010, WSEAS Press.
- Matei I., Bǎbuţ G., Moraru R., Hanna C., 1995. The use of the FOCUS program for the assessment of safety conditions with the reope. ning of areas isolated as a result of spontaneous combustions in the Valea Jiului coal basin. In Proceedings of the 3rd Canadian Conference on Computer Applications in the Mineral Industry (CAMI 95); pp. 720-724.
- Moraru R., Băbuţ G., Cioca L.I., 2010a. Human Reliability Model and Application for Mine Dispatchers in Valea Jiului Coal Basin, Proceedings of the International Conference on RISK MANAGEMENT, ASSESSMENT and MITIGATION (RIMA ’10), 45-50, Bucharest, Romania, WSEAS Press, 2010; ISSN: 1790-2769, ISBN: 978-960-474-182-3.
- Moraru R., Băbuţ G., Cioca L.I. Adressing the human error assessment and management. Arch. Min. Sci. 2010, 55, 873-878.
- Cioca L.I., Moraru R.I. The importance of occupational health and safety in the framework of corporate social responsibility. Manag. Sustain. Dev. 2010, 2, 71-77.
- Cioca L.I., Moraru R.I. Explosion and/or fire risk assessment methodology: a common approach structured for underground coalmine environments. Arch. Min. Sci. 2012, 57, 53-60. [CrossRef]
- Masi, D.; Cagno, E. Barriers to OHS interventions in Small and Medium-sized Enterprises. Saf. Sci. 2015, 71, 226–241. [CrossRef]
- Hadjimanolis, A.; Boustras, G.; Economides, A.; Yiannaki, A.; Nicolaides, L. Work attitudes and safety performance in microfirms—Results from a nationwide survey: (the opinion of the employees). Saf. Sci. 2015, 80, 135–143. [CrossRef]
- Cagno, E.; Masi, D.; Leão, C.P. Drivers for OSH interventions in small and medium-sized enterprises. Int. J. Occup. Saf. Ergon. 2016, 22, 102–115. [CrossRef]
- Bonafede, M.; Corfiati, M.; Gagliardi, D.; Boccuni, F.; Ronchetti, M.; Valenti, A.; Marinaccio, A.; Iavicoli, S. OHS management and employers’ perception: Differences by firm size in a large Italian company survey. Saf. Sci. 2016, 89, 11–18. [CrossRef]
- Cunningham, T.R.; Sinclair, R. Application of a model for delivering occupational safety and health to smaller businesses: Case studies from the US. Saf. Sci. 2015, 71, 213–225. [CrossRef]
- Cioca, L.-I.; Ivascu, L. Risk Indicators and Road Accident Analysis for the Period 2012–2016. Sustainability 2017, 9, 1530. [CrossRef]
- Babut, G.B.; Cioca, L.I. Rationale and Criteria Development for Risk Assessment Tool Selection in Work Environments. Environ. Eng. Manag. J. 2014, 13, 1371–1376. [CrossRef]
- Bao, J.; Johansson, J.; Zhang, J. An Occupational Disease Assessment of the Mining Industry’s Occupational Health and Safety Management Based on FMEA and an Improved AHP Model. Sustainability 2017, 9, 94.
- Byon, Y.D. Season-dependent condition-based maintenance for a wind turbine using a partially observed markove decision process. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2010, 25, 1823–1834.
- Moraru, R. I.; Babut, G. B.; Cioca, L. I. An Inventory of Environmental Risks Induced by Tailing Dams and Sytematic Mitigation Measures. In 12th International Multidisciplinary Scientific Geoconference, SGEM 2012, Vol. V; Stef92 Technology Ltd.: Sofia, Bulgaria, 2012; pp. 43–49. [CrossRef]
- Choong, S. W. J., Ng, P. K., Yeo, B. C., Draghici, A., Gaureanu, A., Ng, Y. J., Selvan, H. K. T., A Preliminary Study on Ergonomic Contribution to the Engineering Design Approach of a Wheel Loader Control Lever System, Sustainability 2021, 14, 122. [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Xue, S.; An, K.; Cao, Y. Physiological Indices and Subjective Thermal Perception of Heat Stress-Exposed Workers in an Industrial Plant. Sustainability 2022, 14, 5019.



| Year | 2021 | |||
| Category | No. injured | Percent from total | Fatalities | Percent from total |
| Total | 2055 | - | 41 | 1.99 |
| Retail trade, except motor vehicles and motorcycles | 189 | 9.2 | - | - |
| Building construction | 130 | 6.3 | 6 | 14.6 |
| Manufacture of road transport vehicles, trailers and semi-trailers | 96 | 4.7 | - | - |
| Forestry and logging | - | - | 4 | 9.8 |
| Works of civil engineering | - | - | 4 | 9.8 |
| Year | 2021 | |||
| Place/County of injury | Bucharest | Brasov | Maramureș | Sibiu |
| No. injured | 493 | 122 | 81 | 78 |
| Percent from total | 24.0 | 5.9 | 3.9 | 3.8 |
| Year | 2021 | |
| Age of injury (first 6 month of year) | 40-50 years | 50-60 years |
| Percent from total | 27.9 | 26.7 |
| Year | 2021 | ||
| seniority | Under 5 years | 5-10 years | 10-20 years |
| No. injured | 1386 | 303 | 242 |
| Percent from total | 67.5 | 14.7 | 11.8 |
| CERTAINTY OF THE WHOLE WORKING SYSTEM | |
| FACTORS HAZARDS/ HAZARDOUS SITUATIONS/ RISK FACTORS FOR OCCUPATIONAL INJURY AND ILLNESS | CAUSES OF RISK |
| electrocution by touch/induction lasting more than 1 min | occurrence/existence of dangerous voltage in the area of action of the worker who does not distinguish/avoid the hazard in time or touch/touch/penetration/induction of the hazard |
| bank overtopping deeper than 1m | occurrence/existence of excavation more than 1 m deep, lack of protection/ supports and access of the worker to the area not recognizing/ avoiding the danger in time |
| falling objects weighing at least 500 grams from a height of more than 2m | the appearance/existence of objects weighing at least 500 g at a height of more than 2 m in the area of action/travel of the worker who does not distinguish/avoid the danger in time or in the absence of protection and improper use of PPE |
| slipping on ladders, scaffolding, platforms, ramps | occurrence/existence of environmental/health factors/elements that may cause slipping, falling on ladders, scaffolding, platforms, ramps in the area of action of the worker who does not recognize/avoid the danger in time or in the absence of protection and improper use of PPE |
| being hit/struck by vehicles/tools | the appearance/existence of vehicles/tools in the worker's area of action which do not recognize/avoid the danger in good time, or in the absence of safeguards/ signs/warnings/maintaining normal conditions of movement/ safety zone boundaries |
| assaults, attacks, violence, other offences/contraventions | the occurrence/existence of dangerous situations such as assaults, attacks, violence, other crimes/contraventions in the area of action of the worker who does not recognize/avoid the danger in time |
| intent, non-compliance with duties, procedures, work instructions, OSH instructions, provisions | occurrence/existence of situations where the worker intentionally or unintentionally fails to comply with the worker's duties, procedures, work instructions, OSH instructions, provisions |
| unauthorized/unconscious/ access to dangerous areas | occurrence/existence of situations of intentional or unintentional non-compliance by the worker with duties, procedures, work instructions, OSH instructions, provisions in hazardous areas |
| RISKS/ENVIRONMENTAL ISSUES | WORK ENVIRONMENT SPECIFIC RISKS (MEvAR) |
| general environmental requirements, permits, authorisations, other | authorisation, endorsements, OSH audit |
| authorised trades/qualifications | |
| work permits and other recognition and control methods | |
| technical data: equipment conformity | |
| emissions into the air | air temperature: high/low |
| air humidity: high/low/ presence of steam/condensation | |
| air currents: in the environment/ at head level/ at torso level/ at feet level | |
| air quality: natural ventilation/ventilation/stationary/filtered/conditioned/with supply/without supply of fresh air | |
| air pressure: high/low | |
| air ionization | |
| soil contamination | specific risks: chemical pollution |
| spills into water | precipitation: rain/snow |
| hazardous substances | materials hazardous chemical substances and/or preparations used (classified according to hazard/ precaution phrases): materials with physical hazards: explosive substances/ flammable gases, aerosols, liquids, solids/ gases, liquids, oxidising solids/ liquids under pressure/ self-reactive substances and mixtures/ liquids, pyrophoric solids/ self-heating substances and mixtures/ substances and mixtures which in contact with water emit flammable gases/ organic peroxides/ corrosive to metals |
| materials with health hazards: toxic, corrosive/irritating to skin, harmful/irritating to eyes, sensitising to respiratory tract, mutagenic, carcinogenic, toxic for reproduction, toxic to an organ, toxic by aspiration | |
| materials with environmental hazards: hazards to the aquatic environment, to the ozone layer | |
| waste management, packaging | waste management, packaging |
| use of energy, raw materials and natural resources | energy fluids: electricity, gas, fuels, pressurised water, steam |
| hazardous energies: electrical voltages, pressures, kinetic energies, potentials | |
| work objects: raw materials, materials, semi-finished products for processes: powders, liquids, chemicals, stabilisers, reagents, others | |
| objects of work: natural resources: air/water/wood/coal/ natural gas | |
| detergents, plant protection products | specific risks: chemical pollution |
| noise | noise |
| radiation | electromagnetic radiation: infrared/ ultraviolet/ microwave/ high/medium/low frequency/ laser |
| ionizing radiation: alpha/beta/gamma | |
| buildings, equipment, containers, packaging | productive buildings: office, administrative building, production hall, circulation area, parking lot, buildings, premises of institutions/customers/beneficiaries/authorities; means of work/work equipment (as per attached list): installations/tools/instruments; |
| means of work processes (as per attached list): (as per attached list); | |
| means of transport and means of communication: means of public/proprietary/service transport; containers and stores for the storage of products (as per attached list) | |
| flora | dangerous plants (poisonous plants, irritants, etc.) |
| fauna | biological risk factors airborne micro-organisms: bacteria, viruses (including SARS CoV 2), rickets, spirochaetes, protozoan, fungi, etc. ; |
| dangerous animals or insects (diseased, aggressive, venomous animals, etc.) | |
| dusts, vapours aerosols | irritant/pneumoconiogenic/carcinogenic dusts: nanomaterials/toxic/toxic dusts/flammable dusts/smoke/mist |
| chemical risk factors: toxic or caustic gases, vapors, aerosols; airborne dusts, flammable or explosive gases or vapors | |
| odors | - |
| human health | regular occupational health checks |
| history of serious diseases | |
| days of medical care/days worked | |
| risk-sensitive group records | |
| sensitive groups: pregnant women/childbirth/breastfeeding/young people/disabled people | |
| climate change | natural disasters: (lightning, flood, wind, hail, hailstorm, blizzards, landslides, landslides, landslides, avalanches, earthquakes, etc.); other foreseeable risks: falling of atmospheric, cosmic objects |
| community, local environment and stakeholder issues | social elements (ethnicity, faith, gender/sex, social category, culture, background, other) |
| active participation in forums on occupational health and safety issues | |
| social factors | |
| external risks: relations with external stakeholders and their perceptions and values |
| Type of risk | Associated risk |
| Storms and blizzards | Blizzards |
| Thunderstorms - strong wind and/or heavy rainfall | |
| Hailstorms | |
| Flooding | Flooding as a result of natural overflows of watercourses caused by increased flows from precipitation and/or snowmelt or blockages due to undersized drainage sections of bridges and culverts, blockages caused by ice or flotsam (waste and timber), landslides, avalanches and snow avalanches, and flooding by runoff from slopes |
| Floods caused by incidents, accidents or damage to hydro-technical constructions | |
| Floods caused by rising groundwater levels | |
| Floods caused by sea storms | |
| Massive snowfall | Heavy snowfall |
| Internal/external road and rail blockages | |
| Tornado | Swirling air currents |
| Drought | Hydrological |
| Pedological | |
| Temperature extremes | Deposition of ice, frost, early or late frosts |
| Ice | |
| Ice bridges and dams on water (ice floes) | |
| Ice bridges and dams on the Danube | |
| Heatwave | |
| Vegetation fires | Forest fires |
| Fires in grass and/or shrub vegetation | |
| Fires in cereal crops | |
| Avalanches | |
| Landslides | |
| Earthquakes | |
| Accidents, breakdowns, explosions and fires in industry, including landslides caused by mining or other technological activities | |
| Accidents, damage, explosions and fires in transport and storage of dangerous goods | Major accidents involving the site |
| Major accidents with off-site implications | |
| Accidents involving dangerous goods during transport activity | |
| Accidents, damage, explosions and fires in transport activities | Land |
| Air | |
| Naval | |
| Accidents, damage, explosions and fires in transport activities | Railway tunnels |
| Road tunnels | |
| Subway | |
| By cable | |
| Accidents, breakdowns, explosions, fires or other events in nuclear or radiological activities | |
| Water pollution | Endangering human life, the aquatic environment and major water supply targets |
| With major transboundary impact | |
| Accidental pollution of watercourses | |
| Marine pollution in the coastal zone | |
| Marine pollution | |
| Collapse of buildings, installations or fittings | |
| Failure of public utilities | Major radio and television networks |
| Major communications and IT networks | |
| Major electricity and gas networks | |
| Major heat networks | |
| Major water supply networks | |
| Major sewerage and storm water networks | |
| Dam failures or other incidents leading to outflows of water endangering human life | |
| Falling objects from the atmosphere and the cosmos | |
| Unexploded or unexploded ordnance left over from military conflicts | |
| Epidemics | |
| Epidemics/Zonoses | |
| Radiological risk | |
| Fires | |
| Situations caused by attack by organisms harmful to plants | |
| WORK SYSTEM ELEMENTS/ RISKS | CATEGORIES RISK FACTORS | |
| INCDPM methods | MEvAR method | |
| worker | - | organisation/ team/ group/ worker |
| wrong actions | dangerous actions | |
| omissions | omissions | |
| workload | - | day-to-day operations and decisions |
| - | OSH opportunities | |
| inadequate content of the work task in relation to safety requirements | requests | |
| under/oversized task in relation to the worker's capacity | ||
| means of production | - | means of work |
| - | objects of work | |
| - | hazardous materials | |
| - | technical data | |
| mechanical risk factors | mechanical risk factors | |
| thermal risk factors | thermal risk factors | |
| electrical risk factors | electrical risk factors | |
| chemical risk factors | chemical risk factors | |
| biological risk factors | biological risk factors | |
| work environment | - | own workplace environment/ environment in the vicinity |
| - | job details | |
| physical risk factors | physical risk factors | |
| chemical risk factors | chemical risk factors | |
| biological risk factors | biological risk factors | |
| special nature of the environment | special risk factors | |
| other risks | - | sensitive, financial, specific, external, other |
| RISK FACTORS SPECIFIC TO THE EXTERNAL WORKPLACE ENVIRONMENT | |
| the cultural, social, political, legal, financial, technological, economic and natural environment, as well as market competition at | social/religious/cultural/political/group affiliation/ psychological pressure on management/workers/ demotivation/competitive stress/decreased |
| international, national, regional or local level, environmental dynamics | |
| the emergence of new competitors, contractors, subcontractors, suppliers, partners and providers, new technologies, new laws and new occupations | income/predictability/major changes in business dynamics/risk of job loss/employees/significant environmental changes/other competitive environment/ psychological pressure on management/ workers/ demotivation/ competitive stress/ prediction failure/short-term solutions/ major changes in business dynamics/ legislative changes/ industry uncertainties/ emergence of new activities/ trades/occupations |
| new knowledge about products and their effect on health and safety | emergence/modification/updating of products/knowledge of products and effects on environment and workers//lack of adaptation to new developments/lack of short-term solutions/ insufficient analysis of influences |
| key drivers and trends relevant to the industry or sector impacting the organisation | emergence/introduction/modification/updating of new trends relevant to industry or sector/lack of adaptation to new development vectors/lack of short-term solutions/insufficient analysis impact |
| relationships with external stakeholders and their perceptions and values | analysis of stakeholder relations, perceptions and values/insufficient development of external relations/poor adaptation to external values/ superficial market research |
| changes relating to any of the external issues | emergence/analysis and provision of measures on changes to external aspects/lack of/weaknesses/ adaptation measures on change analysis |
| overlapping activities | emergence of overlapping activities/superficial/weak analysis on impact |
| WORK SYSTEM ELEMENTS /WORK ENVIRONMENT | ||
| CATEGORY HAZARDS/ HAZARDOUS SITUATIONS/ RISK FACTORS | HAZARDS/ HAZARDOUS SITUATIONS/ RISK FACTORS FOR OCCUPATIONAL INJURY AND ILLNESS | CAUSES OF RISK |
| OWN WORKPLACE ENVIRONMENT/ ENVIRONMENT IN THE VICINITY | HIGH AND SPECIFIC RISK AREAS: | |
| areas exposed to natural hazards | the occurrence/existence of work areas exposed to natural hazards (working in open air areas, snow clearing, construction site, landscaping, others) regular/predicted/random |
|
| hazardous weather events: storms, floods, tornadoes, drought, frost, forest fires, avalanches | occurrence/existence of hazardous weather events affecting the working environment | |
| destructive phenomena: landslides, earthquakes | regular/predicted/random occurrence/existence of destructive phenomena such as landslides or earthquakes | |
| areas exposed to technological risks industry, transport, dangerous products, storage: accidents, damage, explosions, fires, water pollution, collapse of buildings, installations, installations, failure/damage to public utilities, falling objects from the atmosphere or cosmos, ship grounding/sinking, unexploded ordnance | the regular/predicted/ random/ random occurrence/occurrence of technological hazards affecting the working environment caused by careless performance of work tasks | |
| CBRN/NBC risks: chemical contamination, biological contamination, epidemics, epizootics, irradiation, nuclear contamination | regular/predicted/random occurrence/existence of CBRN/NBC hazards | |
| risk areas for visitor security | regular/planned/random occurrence/existence of hazards in the visitors' area of operation | |
| general risks: (fall, slip, hit, road accident, others) | occurrence/regular/planned/random occurrence of other general risks not specific to the working environment | |
| WORKPLACE ENVIRONMENT DETAILS | DETAILS/LOCATION/SIZING OF WORK ENVIRONMENT/WORKPLACE LAYOUT: | |
| environment: building/ outdoors/site/mixed/on premises/means of transport/underground/other | influence of the type of environment on the working environment | |
| access zones: in administration premises/clients, beneficiaries/ institutions/at home/on site/means of transport/other | influence of access areas on the working environment | |
| height regime: high/max. 4 levels/floor/ground floor/ subsurface/ underground/ other | influence of height regime on the working environment | |
| working level: underground/ ground/ floor/floor/ gondola/ scaffolding/ pit/ overhead/ underwater/ underwater/ hoists | influence of working level on the working environment | |
| structure: concrete/brick/ metal/wood/enclosure/slabs | influence of structure on the working environment | |
| facade: glazed/classic/ without/altars | influence of the façade on the working environment | |
| partitioning: office/ rooms/workshop/ hall/warehouse/storage/storage/mixed/ booth/altars | influence of partitioning on the working environment | |
| interior access: normal/ double/ revolving/automatic door/ other: | influence of indoor access on the working environment | |
| circulation routes: corridor/hollow/elevator/ concrete slabs/steel slabs/rolling slabs/alley/parking/others: | influence of traffic routes on the working environment | |
| access restrictions : no access control/access control/card or human identification/barrier/turnstiles/ others | influence of access restrictions on the working environment | |
| furniture: ergonomic/classic/ metal/ wood/ PFL/PVC/bureau/ table/ rotating chair/ rigid chair/ closed armchair/ open armchair/ locker/altars | influence of furniture on the working environment | |
| installation/cable route: protected/unprotected/on route/level floor/within human action area/maintained/ unmaintained/other | the influence of the route of installations/wiring on the working environment | |
| energy fluids/facilities: air/water/steam/electricity/ natural gas/LPG/pressure/ fuels/thermal/other | influence of energy fluids on the working environment | |
| utilities: dining room/kitchen/bathroom/ dressing room/lounging area/ bedroom/network/surveillance system/detection system/others | influence of utilities on the working environment | |
| Workplace dimensions: area - under 5 m2/ 10 m2/50 m2/100 m2/500 m2/ 1000 m2/10000 m2/ over 10000 m, height - under 2.0 m/ between 2.0-3.0 m/ over 3.0 m | the influence of workplace size on the working environment | |
| PHYSICAL RISK FACTORS | season: hot/cold | variation in seasonal characteristics |
| air temperature: high/low | variation in the influence of air temperature | |
| temperature of objects/ materials/ work equipment: high/ low | variation in the influence of the temperature of objects | |
| precipitation: rain/snow | variation in the influence of precipitation | |
| air humidity: high/low/ presence of steam/condensation | variation in the influence of air humidity | |
| draughts: in the environment/at head level/ at torso level/at feet level | variation in the influence of air currents | |
| air quality: natural ventilation/ventilation/stationary/filtered/conditioned/with fresh air supply/without fresh air supply | variation in the influence of air quality | |
| air pressure: high/low | variation of air pressure influence | |
| air ionization | air ionization influence variation | |
| overpressure in water depth | variation in the influence of overpressure in water depth | |
| noise | noise influence variation | |
| ultrasound | ultrasound influence variation | |
| vibration | vibration influence variation | |
| lighting: low light level/natural/ artificial/mixed/ glow/ flicker | variation in the influence of ambient lighting | |
| electromagnetic radiation: infrared/ ultraviolet/ microwave/ high/medium/low frequency/ laser | variation in the influence of electromagnetic radiation | |
| ionizing radiation: alpha/beta/gamma | variation in the influence of ionizing radiation | |
| electrostatic potential | variation in the influence of electrostatic potential | |
| natural disasters: (lightning, flood, wind, hail, hailstorm, blizzard, landslides, landslides, landslides, avalanches, earthquakes, etc.) | variation in the influence of natural disasters | |
| irritant/ pneumoconiogenic/ carcinogenic dusts: nanomaterials/ toxic/harmful dusts/flammable dusts/smoke/mist | variation in the influence of irritant dusts | |
| CHEMICAL RISK FACTORS | toxic or caustic gases, vapors, aerosols | variation in the influence of toxic or caustic gases, vapors, aerosols |
| airborne dusts, flammable or explosive gases or vapors | variation in the influence of flammable or explosive airborne dusts, gases or vapors | |
| BIOLOGICAL RISK FACTORS | airborne micro-organisms: bacteria, viruses (including Sars CoV-2), fungi, spirochetes, protozoan fungi, etc. | variation in the influence of airborne micro-organisms |
| dangerous plants (poisonous, irritant plants, etc.) | variation in the influence of contact with hazardous plants | |
| dangerous animals or insects (diseased, aggressive, venomous animals, etc.) | variation in the influence of contact with dangerous animals or insects | |
| SPECIAL ENVIRONMENTAL RISK FACTORS | underground/aquatic/underwater/swampy/aerial/cosmic/others | variation in the influence of the particular environment |
| SENSITIVE RISK FACTORS | risks identified/previous/on record | the influence of the number and consequences of risks observed/previous/on record |
| pregnant women/childbirth/breastfeeding/young people/disabled people | influence on the number and needs of sensitive categories of workers | |
| FINANCIAL RISK FACTORS | financial means: cash, bank cards, vouchers, bank cheque | influence of financial means |
| damage: loss of money, loss of turnover | influence and effects of damage | |
| SPECIFIC RISK FACTORS | chemical pollution | influence of chemical pollution |
| risks arising from ensuring prevention and protection measures | influence of risks associated with the provision of prevention and protection measures | |
| damage to reputation | influence on the organization’s reputation | |
| dangerous actions of workers, visitors, neighbors | influence of dangerous actions of workers, visitors, neighbors and their consequences | |
| reduced yield following an event | influence of workers' performance following an event | |
| EXTERNAL RISK FACTORS | cultural, social, political, legal, financial, technological, economic and natural environment, as well as market competition at international, national, regional or local level, environmental dynamics | influence of the contextual environment |
| the emergence of new competitors, contractors, subcontractors, suppliers, partners and providers, new technologies, new laws and new occupations | influence of competition, new technologies or occupations | |
| new knowledge about products and their effect on health and safety | the influence of new knowledge | |
| key drivers and trends relevant to the industry or sector impacting the organisation | the influence of factors and trends impacting on the organisation | |
| relationships with external stakeholders and their perceptions and values | influence of stakeholder relationships | |
| changes relating to any of the external issues | influence of changes in external aspects | |
| overlapping activities | influence of overlapping activities | |
| OTHER FORE SEEABLE RISK FACTORS |
atmospheric, cosmic object falls | periodic/predicted/random occurrence/existence of atmospheric, cosmic object falls |
| Activity | Estimated impact of OSH |
| Administrative activities (training, information, record-keeping, computer work, completion of documentation, files, medical examinations, other) | Risk of injury and potential occupational illness from/through: - specific team/ group/ worker risks non-compliance with employment requirements, mode of travel, workload, work procedures and instructions, OSH - non-use or misuse of PPE. - nervous solicitation, relations with beneficiaries - traffic/route accidents - impact caused by falling or projecting objects, collision with an obstacle, high pressure jets (cutting, hitting) - risks of being caught and trapped (puncture, cut, abrasion) - dangerous movements of technical equipment (moving machinery parts, fluid flows, movement of means of transport) - self-initiation or self-locking of machinery or fluids - movements under the effect of gravity, propulsion (slipping, rolling, rolling on wheels, overturning, free falling, free flowing, spilling, surging, collapsing, sinking, movements under the effect of propulsion, projection of bodies or particles, deviation from normal trajectory, rocking, rebounding) - static compression of a body part (shock, impact, impact, compression) - mechanical injuries (abrasion, puncture, cuts, bites, wounds or stab wounds) - falls caused by slipping/falling from height - noise - vibrations - accidental electrocution - inhalation of chemical/biological aerosols in powder form - direct/indirect contact with biological agents contained in materials people, animals, other - improper operation of equipment - incorrect operation of equipment - pressure vessels (particle design, jet) - outdoor ambient temperature - level slippage - musculoskeletal disorders - change in visual acuity - performing other activities not foreseen in the workload The environment in the vicinity of the workplace - high and specific risk areas Occupational illnesses Additional expenses Material or financial losses in case of technological breakdowns Reputational damage Contravention and/or criminal activities |
| Receiving, handling, transporting, storing materials and thermal and sanitary installations required on site (specific job activities) | |
| Moving around the site (accessing the entrance, moving along the site's horizontal and/or vertical traffic routes, use of mechanized means - lift, bucket, pallet truck as appropriate, leaving the site) transport, cutting, positioning, fitting, fixing, commissioning, handover to the beneficiary of the materials and the necessary heating and plumbing installations | |
| Use of collective means of protection (ladders, scaffolding, parapets, gangways, panels, etc.) | |
| Use of PPE. (reception, adjustment, checking, use, maintenance, replacement, etc.) | |
| Other activities within the compartment (emergency action, hazard, outdoor area maintenance, other) | |
| Transport of materials, movement of workers from site to site/other workplace/household |
| Risks specific to organization | |||
| Risk assessment expression INCDPM methods |
Risk assessment expression MEvAR method |
||
| Number of risks value 7 | 0 | ||
| Number of risks value 6 | 0 | 7 | Number of certainties |
| Number of risks value 5 | 1 | 1 | Number of unaccepted risks |
| Number of risks value 4 | 13 | 7 | Number of risks tolerated |
| Number of risks value 3 | 83 | 32 | Number of accepted risks |
| Number of risks value 2 | 0 | 108 | Number of risks controlled |
| Number of risks value 1 | 11 | 43 | Number of risks managed |
| Total number of risks | 108 | 191 | Total number of risks |
| General risk level | 3,13 | 4,12 | General level of risk assessed |
| 1,82 | General level of residual risk | ||
| Expression risk level | medium | controlled | Expression risk level |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





