Submitted:
22 April 2023
Posted:
23 April 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
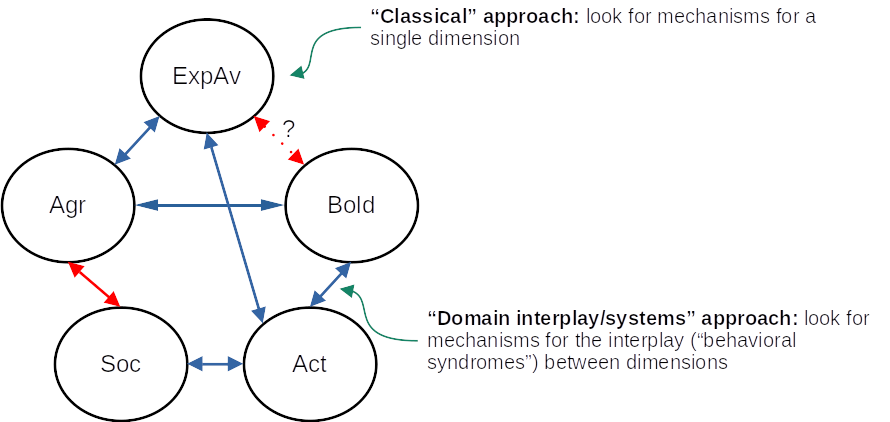
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Current issues in fish personality research
3. Dimensionality of personality in fish
3.1. Boldness-shyness
3.2. Exploration-avoidance
3.3. Activity
3.4. Aggressiveness
3.5. Sociability
4. The use of fish personality in anxiety research
5. Conclusion
Financial support
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abbey-Lee, R.N.; Kreshchenko, A.; Fernandez Sala, X.; Petkova, I.; Løvlie, H. Effects of monoamine manipulations on the personality and gene expression of three-spined sticklebacks. Journal of Experimental Biology 2019, 222, jeb211888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Abreu, M.S.; Genario, R.; Giacomini, A.C. V. V.; Demin, K.A.; Lakstygal, A.M.; Amstislavskaya, T.G.; Fontana, B.D.; Parker, M.O.; Kalueff, A.V. Zebrafish as a model of neurodevelopmental disorders. Neuroscience 2020, 445, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alfonso, S.; Peyrafort, M.; Cousin, X.; Bégout, M.-L. Zebrafish Danio rerio shows behavioural cross-context consistency at larval and juvenile stages but no consistency between stages. Journal of Fish Biology 2020, 96, 1411–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allport, F.H.; Allport, G.W. Personality traits: Their classification and measurement. Journal of Abnormal and Social Psychology 1921, 16, 6–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez, D.; Bell, A.M. Sticklebacks from streams are more bold than sticklebacks from ponds. Behavioural Processes 2007, 76, 215–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amundsen, T. Fishes as models in studies of sexual selection and parental care. Journal of Fish Biology 2003, 63, 17–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, A.M. Behavioural differences between individuals and two populations of stickleback (Gasterosteus aculeatus). Journal of Evolutionary Biology 2005, 18, 464–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, A.M.; Sih, A. Exposure to predation generates personality in threespined sticklebacks (Gasterosteus aculeatus). Ecology Letters 2007, 10, 828–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, A.M.; Stamps, J.A. Development of behavioural differences between individuals and populations of sticklebacks, Gasterosteus aculeatus. Animal Behaviour 2004, 68, 1339–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, A.M.; Backström, T.; Huntingford, F.A.; Pottinger, T.G.; Winberg, S. Variable neuroendocrine responses to ecologically-relevant challenges in sticklebacks. Physiology & Behavior 2007, 91, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, A.M.; Henderson, L.; Huntingford, F.A. Behavioral and respiratory responses to stressors in multiple populations of three-spined sticklebacks that differ in predation pressure. Journal of Comparative Physiology. B, Biochemical, Systemic, and Environmental Physiology 2010, 180, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bender, N.; Heg-bachar, Z.; Oliveira, R.F.; Canario, A.V. M.; Taborsky, M. Hormonal control of brood care and social status in a cichlid fish with brood care helpers. Steroids 2008, 94, 349–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Binder, T.R.; Wilson, A.D. M.; Wilson, S.M.; Suski, C.D.; Godin, J.-G. J.; Cooke, S.J. Is there a pace-of-life syndrome linking boldness and metabolic capacity for locomotion in bluegill sunfish? Animal Behaviour 2016, 121, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biro, P.A.; Stamps, J.A. Do consistent individual differences in metabolic rate promote consistent individual differences in behavior? Trends in Ecology & Evolution 2010, 25, 653–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaser, R.E.; Rosemberg, D.B. Measures of Anxiety in Zebrafish (Danio rerio): Dissociation of Black/White Preference and Novel Tank Test. PLOS ONE 2012, 7, e36931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyer, N.; Réale, D.; Marmet, J.; Pisanu, B.; Chapuis, J.-L. Personality, space use and tick load in an introduced population of Siberian chipmunks Tamias sibiricus. The Journal of Animal Ecology 2010, 79, 538–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, C.; Braithwaite, V.A. Size matters: A test of boldness in eight populations of the poeciliid Brachyraphis episcopi. Animal Behaviour 2004, 68, 1325–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, C.; Burgess, F.; Braithwaite, V.A. Heritable and experiential effects on boldness in a tropical poeciliid. Behavioral Ecology and Sociobiology 2007, 62, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, C.; Jones, F.; Braithwaite, V. In situ examination of boldness–shyness traits in the tropical poeciliid, Brachyraphis episcopi. Animal Behaviour 2005, 70, 1003–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, C.; Jones, F.; Braithwaite, V.A. Correlation between boldness and body mass in natural populations of the poeciliid Brachyrhaphis episcopi. Journal of Fish Biology 2007, 71, 1590–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Careau, V.; Thomas, D.; Humphries, M.M.; Réale, D. Energy metabolism and animal personality. Oikos 2008, 641–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, A.J.; Feeney, W.E.; Marshall, H.H.; Cowlishaw, G.; Heinsohn, R. Animal personality: What are behavioural ecologists measuring? Biological Reviews 2013, 88, 465–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castanheira, M.F.; Cerqueira, M.; Millot, S.; Gonçalves, R.A.; Oliveira, C.C. V.; Conceição, L.E. C.; Martins, C.I. M. Are personality traits consistent in fish?—The influence of social context. Applied Animal Behaviour Science 2016, 178, 96–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castanheira, M.F.; Herrera, M.; Costas, B.; Conceição, L.E. C.; Martins, C.I. M. Can We Predict Personality in Fish? Searching for Consistency over Time and across Contexts. PLOS ONE 2013, 8, e62037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cervone, D.; Shadel, W.G.; Jencius, S. Social-Cognitive Theory of Personality Assessment. Personality and Social Psychology Review 2001, 5, 33–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, C.W.; Dukas, R. Balancing Foraging and Antipredator Demands: An Advantage of Sociality. American Naturalist 1994, 144, 542–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coleman, K.; Wilson, D.S. Shyness and boldness in pumpkinseed sunfish: Individual differences are context-specific. Animal Behaviour 1998, 56, 927–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conrad, J.L.; Weinersmith, K.L.; Brodin, T.; Saltz, J.B.; Sih, A. Behavioural syndromes in fishes: A review with implications for ecology and fisheries management. Journal of Fish Biology 2011, 78, 395–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corr PJ (2002), J.A. Gray’s reinforcement sensitivity theory: Tests of the joint subsystems hypothesis of anxiety and impulsivity. Personality and Individual Differences 2002, 33, 511–532. [CrossRef]
- Corr, P.J. Reinforcement sensitivity theory and personality. Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews 2004, 28, 317–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corr, P.J.; McNaughton, N. Neuroscience and approach/avoidance personality traits: A two stage (valuation–motivation) approach. Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews 2012, 36, 2339–2354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corr, P.J.; Perkins, A.M. The role of theory in the psychophysiology of personality: From Ivan Pavlov to Jeffrey Gray. International Journal of Psychophysiology 2006, 62, 367–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dahlbom, S. J, Lagman, D.; Lundstedt-Enkel, K.; Sundstrom, L.F.; Winberg, S. Boldness predicts social status in zebrafish (Danio rerio). PLoS One 2011, 6, e23565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Depue, R.A.; Collins, P.F. Neurobiology of the structure of personality: Dopamine, facilitation of incentive motivation, and extraversion. Behavioural and Brain Sciences 1999, 22, 491–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Young, C.G. Personality neuroscience and the biology of traits. Social and Personality Psychology Compass 2010, 4, 1165–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dingemanse, N.J.; Wright, J.; Kazem, A.J. N.; Thomas, D.K.; Hickling, R.; Dawnay, N. Behavioural syndromes differ predictably between 12 populations of three-spined stickleback. The Journal of Animal Ecology 2007, 76, 1128–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diotel, N.; do Rego, J.-L.; Anglade, I.; Vaillant, C.; Pellegrini, E.; Vaudry, H.; Kah, O. The brain of teleost fish, a source, and a target of sexual steroids. Frontiers in Neuroscience 2011, 5, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- do Carmo Silva, R.X.; Lima-Maximino, M.G.; Maximino, C. The aversive brain system of teleosts: Implications for neuroscience and biological psychiatry. Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews 2018, 95, 123–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzieweczynski, T.L.; Eklund, A.C.; Rowland, W.J. Male 11-ketotestosterone levels change as a result of being watched in Siamese Fighting Fish. Steroids 2006, 147, 184–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edenbrow, M.; Croft, D.P. Behavioural types and life history strategies during ontogeny in the mangrove killifish, Kryptolebias marmoratus. Animal Behaviour 2011, 82, 731–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eysenck, H.J. (1967). The Biological Basis of Personality.
- Fernandes-Silva, B.W.; Leite-Ferreira, M.E.; Menezes, F.P.; Luchiari, A.C. Covariation among behavioral traits and hatching time in zebrafish. Behavioural Processes 2022, 194, 104546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrari, M.C. O.; Sih, A.; Chivers, D.P. The paradox of risk allocation: A review and prospectus. Animal Behaviour 2009, 78, 579–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, S.; Horri, K.; Allal, F.; Vergnet, A.; Benhaim, D.; Vandeputte, M.; Chatain, B.; Bégout, M.-L. Heritability of Boldness and Hypoxia Avoidance in European Seabass, Dicentrarchus labrax. PLOS ONE 2016, 11, e0168506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filby, A.L.; Paull, G.C.; Hickmore, T.F.; Tyler, C.R. Unravelling the neurophysiological basis of aggression in a fish model. BMC Genomics 2010, 11, 498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fontana, B.D.; Francescon, F.; Rosemberg, D.B.; Norton, W.H. J.; Kalueff, A.V.; Parker, M.O. Zebrafish models for attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews 2019, 100, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gosling, S. & John, O. Personality dimensions in nonhuman animals: a cross-species review. Current Directions in Psychological Science 1999, 8, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graeff, F.G. Serotonin, the periaqueductal gray and panic. Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews 2004, 28, 239–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, J.A.; McNaughton, N. (2003). The Neuropsychology of Anxiety: An Enquiry into the Functions of the Septo-Hippocampal System.
- Hintz, W.D.; Lonzarich, D.G. Maximizing foraging success: The roles of group size, predation risk, competition, and ontogeny. Ecosphere 2018, 9, e02456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, R.N. Intrinsic exploration in animals: Motives and measurement. Behavioural Processes 1997, 41, 213–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huntingford, F.A. A comparison of the reaction of sticklebacks in different reproductive conditions towards conspecifics and predators. Animal Behaviour 1976, 24, 694–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibarra-Zatarain, Z.; Rey, S.; Boglino, A.; Fatsini, E.; Duncan, N. Senegalese sole (Solea senegalensis) coping styles are consistent over time: Behavioural and physiological responses during ontogenesis. Physiology & Behavior 2020, 217, 112803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ioannou, C.C.; Bartumeus, F.; Krause, J.; Ruxton, G.D. Unified effects of aggregation reveal larger prey groups take longer to find. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences 2011, 278, 2985–2990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jolles, J.W.; Boogert, N.J.; Sridhar, V.H.; Couzin, I.D.; Manica, A. Consistent Individual Differences Drive Collective Behavior and Group Functioning of Schooling Fish. Current Biology 2017, 27, 2862–2868e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaiser, M.I.; Müller, C. What is an animal personality? Biology & Philosophy 2021, 36, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalueff, A.V.; Echevarria, D.J.; Homechaudhuri, S.; Stewart, A.M.; Collier, A.D.; Kaluyeva, A.A.; Li, S.; Liu, Y.; Chen, P.; Wang, J.; Yang, L.; Mitra, A.; Pal, S.; Chaudhuri, A.; Roy, A.; Biswas, M.; Roy, D.; Podder, A.; Poudel, M.K.; … Song, C. Zebrafish neurobehavioral phenomics for aquatic neuropharmacology and toxicology research. Aquatic Toxicology 2016, 170, 297–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalueff, A.V.; Ren-Patterson, R.F.; LaPorte, J.L.; Murphy, D.L. Domain interplay concept in animal models of neuropsychiatric disorders: A new strategy for high-throughput neurophenotyping research. Behavioural Brain Research 2008, 188, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawabata, Y.; Hiraki, T.; Takeuchi, A.; Okubo, K. Sex differences in the expression of vasotocin/isotocin, gonadotropin-releasing hormone, and tyrosine and tryptophan hydroxylase family genes in the medaka brain. Neuroscience 2012, 218, 65–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, A.J.; Fürtbauer, I.; Mamuneas, D.; James, C.; Manica, A. Sex-Differences and Temporal Consistency in Stickleback Fish Boldness. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e81116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koohlaas, J.M.; De Boer, S.F.; Coppens, C.; Buwalda, C. Neuroendocrinology of coping styles: towards understanding the biology of individual variation. Frontiers in Neuroendocrinology 2010, 31, 307–321 . [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koolhaas, J.M.; Korte, S.M.; De Boer, S.F.; Van Der Vegt, B.J.; Van Reenen, C.G.; Hopster, H.; De Jong, I.C.; Ruis, M.A. W.; Blokhuis, H.J. Coping styles in animals: Current status in behavior and stress-physiology. Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews 1999, 23, 925–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Køppe, S. A moderate eclecticism: Ontological and epistemological issues. Integrative Psychological & Behavioral Science 2012, 46, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krakauer, D.C. Groups confuse predators by exploiting perceptual bottlenecks: A connectionist model of the confusion effect. Behavioral Ecology and Sociobiology 1995, 36, 421–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krause, J.; Ruxton, G.D. (2002). Living in Groups. Oxford Series in Ecology and Evolution. Oxford and New York: Oxford University Press.
- Kysil, E.V.; Meshalkina, D.A.; Frick, E.E.; Echevarria, D.J.; Rosemberg, D.B.; Maximino, C.; Lima, M.G.; Abreu, M.S.; Giacomini, A.C.; Barcellos, L.J. G.; Song, C.; Kalueff, A.V. Comparative Analyses of Zebrafish Anxiety-Like Behavior Using Conflict-Based Novelty Tests. Zebrafish 2017, 14, 197–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larson, E.T.; O’Malley, D.M.; Melloni, R.H. Aggression and vasotocin are associated with dominant–subordinate relationships in zebrafish. Behavioural Brain Research 2006, 167, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leblond, C.; Reebs, S.G. Individual leadership and boldness in shoals of golden shiners (Notemigonus crysoleucas). Behaviour 2006, 143, 1263–1280. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.S.; Bereijikian, B.A. Stability of behavioral syndromes but plasticity in individual behavior: Consequences for rockfish stock enhancement. Environmental Biology of Fishes 2008, 82, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima-Maximino, M.; Pyterson, M.P.; Silva, R.X. do C.; Gomes, G.C. V.; Rocha, S.P.; Herculano, A.M.; Rosemberg, D.B.; Maximino, C. Phasic and tonic serotonin modulate alarm reactions and post-exposure behavior in zebrafish. Journal of Neurochemistry 2020, 153, 495–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luttbeg, B.; Sih, A. Risk, resources and state-dependent adaptive behavioural syndromes. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society Part B 2010, 365, 3977–3990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacKay, J.R. D.; Haskell, M.J. Consistent Individual Behavioral Variation: The Difference between Temperament, Personality and Behavioral Syndromes. Animals 2015, 5, Art 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, E.P.; Bhat, A. Population-level personalities in zebrafish: Aggression-boldness across but not within populations. Behavioral Ecology 2014, 25, 368–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruska, K.; Soares, M.C.; Lima-Maximino, M.; Henrique de Siqueira-Silva, D.; Maximino, C. Social plasticity in the fish brain: Neuroscientific and ethological aspects. Brain Research 2019, 1711, 156–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maximino, C.; de Brito, T.M.; da Silva Batista, A.W.; Herculano, A.M.; Morato, S.; Gouveia, A. Measuring anxiety in zebrafish: A critical review. Behavioural Brain Research 2010, 214, 157–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maximino, C.; Oliveira, D.L. de, Rosemberg, D.B.; Batista, E. de J. O.; Herculano, A.M.; Oliveira, K.R. M.; Benzecry, R.; Blaser, R. A comparison of the light/dark and novel tank tests in zebrafish. Behaviour 2012, 149, 1099–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maximino, C.; Puty, B.; Benzecry, R.; Araújo, J.; Lima, M.G.; de Jesus Oliveira Batista, E.; Renata de Matos Oliveira, K.; Crespo-Lopez, M.E.; Herculano, A.M. Role of serotonin in zebrafish (Danio rerio) anxiety: Relationship with serotonin levels and effect of buspirone, WAY 100635, SB 224289, fluoxetine and para-chlorophenylalanine (pCPA) in two behavioral models. Neuropharmacology 2013, 71, 83–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maximino, C.; Silva, A.W. B. da, Araújo, J.; Lima, M.G.; Miranda, V.; Puty, B.; Benzecry, R.; Picanço-Diniz, D.L. W.; Jr, A.G.; Oliveira, K.R. M.; Herculano, A.M. Fingerprinting of Psychoactive Drugs in Zebrafish Anxiety-Like Behaviors. PLOS ONE 2014, 9, e103943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazué, G.P. F.; Dechaume-Moncharmont, F.-X.; Godin, J.-G. J. Boldness–exploration behavioral syndrome: Interfamily variability and repeatability of personality traits in the young of the convict cichlid (Amatitlania siquia). Behavioral Ecology 2015, 26, 900–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNaughton, N.; Corr, P.J. The non-human perspective on the neurobiology of temperament, personality, and psychopathology: What’s next? Current Opinion in Behavioral Sciences 2022, 43, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metcalfe, N.B.; Thorpe, J.E. Early predictors of life-history events: The link between first feeding date, dominance and seaward migration in Atlantic salmon, Salmo salar L. Journal of Fish Biology 1992, 41, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metcalfe, N.B.; Taylor, A.C.; Thorpe, J.E. Metabolic rate, social status and life-history strategies in Atlantic salmon. Animal Behaviour 1995, 49, 431–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, J.T.; Kimbrel, N.A.; Hundt, N.E.; Cobb, A.R.; Nelson-Gray, R.O.; Lootens, C.M. An analysis of reinforcement sensitivity theory and the five-factor model. European Journal of Personality 2007, 21, 869–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momeni, S. & Roman, E. Subgroup-dependent effects of voluntary alcohol intake on behavioral profiles in outbred Wistar rats. Behavioural Brain Research 2014, 275, 288–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montgomery, K.C. The relation between fear induced by novel stimulation and exploratory drive. Journal of Comparative and Physiological Psychology 1955, 48, 254–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montgomery, K.C.; Monkman, J.A. The relation between fear and exploratory behavior. Journal of Comparative and Physiological Psychology 1955, 48, 132–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moretz, J.A.; Martins, E.P.; Robison, B.D. Behavioral syndromes and the evolution of correlated behavior in zebrafish. Behavioral Ecology 2007, 18, 556–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafa, A.; Roman, E.; Winberg, S. Boldness in Male and Female Zebrafish (Danio rerio) Is Dependent on Strain and Test. Frontiers in Behavioral Neuroscience 2019, 13, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mustafa, A.; Thörnqvist, P.-O.; Roman, E.; Winberg, S. The aggressive spiegeldanio, carrying a mutation in the fgfr1a gene, has no advantage in dyadic fights with zebrafish of the AB strain. Behavioural Brain Research 2019, 370, 111942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nespolo, R.F.; Franco, M. Whole-animal metabolic rate is a repeatable trait: A meta-analysis. Journal of Experimental Biology 2007, 210, 2000–2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nomakuchi, S.; Park, P.J.; Bell, M.A. Correlation between exploration activity and use of social information in three-spined sticklebacks. Behavioral Ecology 2009, 20, 340–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norton, W.H. J.; Bally-Cuif, L. Unravelling the proximate causes of the aggression-boldness behavioural syndrome in zebrafish. Behaviour 2012, 149, 1063–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norton, W.H. J.; Stumpenhorst, K.; Faus-Kessler, T.; Folchert, A.; Rohner, N.; Harris, M.P.; Callebert, J.; Bally-Cuif, L. Modulation of Fgfr1a Signaling in Zebrafish Reveals a Genetic Basis for the Aggression–Boldness Syndrome. Journal of Neuroscience 2011, 31, 13796–13807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connell, L.A.; Hofmann, H.A. The Vertebrate mesolimbic reward system and social behavior network: A comparative synthesis. Journal of Comparative Neurology 2011, 519, 3599–3639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Connell, L.A.; Hofmann, H.A. Evolution of a Vertebrate Social Decision-Making Network. Science 2012, 336, 1154–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogawa, S.; Pfaff, D.W.; Parhar, I.S. Fish as a model in social neuroscience: Conservation and diversity in the social brain network. Biological Reviews 2021, 96, 999–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, R.F. Social plasticity in fish: Integrating mechanisms and function. Journal of Fish Biology 2012, 81, 2127–2150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olivier, B. Serotonin and Aggression. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences 2004, 1036, 382–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Øverli, Ø.; Sørensen, C.; Pulman, K.G. T.; Pottinger, T.G.; Korzan, W.; Summers, C.H.; Nilsson, G.E. Evolutionary background for stress-coping styles: Relationships between physiological, behavioral, and cognitive traits in non-mammalian vertebrates. Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews 2007, 31, 396–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, E.D.; Lowry, C.A. Functional topography of serotonergic systems supports the Deakin/Graeff hypothesis of anxiety and affective disorders. Journal of Psychopharmacology 2013, 27, 1090–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paul, E.D.; Johnson, P.L.; Shekhar, A.; Lowry, C.A. The Deakin/Graeff hypothesis: Focus on serotonergic inhibition of panic. Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews 2014, 46, 379–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pervin, L.A. A Critical Analysis of Current Trait Theory. Psychological Inquiry 1994, 5, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philip, J.; Dellinger, M.; Benhaïm, D. Among-individual variation of risk-taking behaviour in group and solitary context is uncorrelated but independently repeatable in a juvenile Arctic charr (Salvelinus alpinus) aquaculture strain. Applied Animal Behaviour Science 2022, 249, 105596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimentel, A.F. N.; Carvalho, T. dos S.; Lima, F.; Lima-Maximino, M.; Soares, M.C.; Maximino, C. Conditional approach as cooperation in predator inspection: A role for serotonin? Behavioural Brain Research 2019, 365, 164–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pimentel, A.F. N.; Lima-Maximino, M.G.; Soares, M.C.; Maximino, C. Zebrafish cooperate while inspecting predators: Experimental evidence for conditional approach. Animal Behaviour 2021, 177, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polverino, G.; Cigliano, C.; Nakayama, S.; Mehner, T. Emergence and development of personality over the ontogeny of fish in absence of environmental stress factors. Behavioral Ecology and Sociobiology 2016, 70, 2027–2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Réale, D.; Garant, D.; Humphries, M.M.; Bergeron, P.; Careau, V.; Montiglio, P.-O. Personality and the emergence of the pace-of-life syndrome concept at the population level. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences 2010, 365, 4051–4063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Réale, D.; Reader, S.M.; Sol, D.; McDougall, P.T.; Dingemanse, N.J. Integrating animal temperament within ecology and evolution. Biological Reviews 2007, 82, 291–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rieucau, G.; Fernö, A.; Ioannou, C.C.; Handegard, N.O. Towards of a firmer explanation of large shoal formation, maintenance and collective reactions in marine fish. Reviews in Fish Biology and Fisheries 2015, 25, 21–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, J.D.; Moore, F.L. Behavioral neuroendocrinology of vasotocin and vasopressin and the sensorimotor processing hypothesis. Frontiers in Neuroendocrinology 2002, 23, 317–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, T.; Bhat, A. Population, sex and body size: Determinants of behavioural variations and behavioural correlations among wild zebrafish Danio rerio. Royal Society Open Science 2018, 5, 170978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, T.; Bhat, A. Repeatability in boldness and aggression among wild zebrafish (Danio rerio) from two differing predation and flow regimes. Journal of Comparative Psychology 2018, 132, 349–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, P.A. Relationships Between Exploratory Behaviour and Fear: A Review. British Journal of Psychology 1973, 64, 417–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabadin, G.R.; Biasuz, E.; Canzian, J.; Adedara, I.A.; Rosemberg, D.B. A novel behavioral paradigm to measure anxiety-like behaviors in zebrafish by the concomitant assessment of geotaxis and scototaxis. Progress in Neuro-Psychopharmacology and Biological Psychiatry 2022, 118, 110579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-Tójar, A.; Moiron, M.; Niemelä, P.T. Terminology use in animal personality research: A self-report questionnaire and a systematic review. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences 2022, 289, 20212259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santangelo, N.; Bass, A.H. Individual behavioral and neuronal phenotypes for arginine vasotocin mediated courtship and aggression in a territorial teleost. Brain, Behavior and Evolution 2010, 75, 282–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuett, W.; Tregenza, T.; Dall, S.R. X. Sexual selection and animal personality. Biological Reviews 2010, 85, 217–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sih, A.; Bell, A.M.; Johnson, J.C. Behavioral syndromes: An ecological and evolutionary overview. Trends in Ecology & Evolution 2004, 19, 372–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sih, A.; Bell, A.M.; Johnson, J.C.; Ziemba, R.E. Behavioral Syndromes: An Integrative Overview. The Quarterly Review of Biology 2004, 79, 241–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silveira, M.M.; Silva, P.F.; Ferreira, R.G.; Luchiari, A.C. Fighting off the intruder: Context-dependent territory defence in the damselfish Stegastes fuscus. Environmental Biology of Fishes 2020, 103, 1091–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smillie, L.D.; Pickering, A.D.; Jackson, C.J. The new Reinforcement Sensitivity Theory: Implications for personality measurement. Personality and Social Psychology Review 2006, 10, 320–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snekser, J.L.; Leese, J.; Ganim, A.; Itzkowitz, M. Caribbean damselfish with varying territory quality: Correlated behaviors but not a syndrome. Behavioral Ecology 2009, 20, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamps, J.A.; Groothuis, T.G. G. Developmental perspectives on personality: Implications for ecological and evolutionary studies of individual differences. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences 2010, 365, 4029–4041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamps, J.; Groothuis, T.G. G. The development of animal personality: Relevance, concepts and perspectives. Biological Reviews 2010, 85, 301–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanford, S.C. The open field test: Reinventing the wheel. Journal of Psychopharmacology 2007, 21, 134–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stenberg, M.; Persson, A. Patch use behaviour in benthic fish depends on their long-term growth prospects. Oikos 2006, 112, 332–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taborsky, B.; Oliveira, R.F. Social competence: An evolutionary approach. Trends in Ecology & Evolution 2012, 27, 679–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toms, C.N.; Echevarria, D.J. Back to Basics: Searching for a Comprehensive Framework for Exploring Individual Differences in Zebrafish (Danio rerio) Behavior. Zebrafish 2014, 11, 325–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toms, C.N.; Echevarria, D.J.; Jouandot, D.J. A Methodological Review of Personality-Related Studies in Fish: Focus on the Shy-Bold Axis of Behavior. International Journal of Comparative Psychology 2010, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trofimova, I.; Bajaj, S.; Bashkatov, S.A.; Blair, J.; Brandt, A.; Chan, R.C. K.; Clemens, B.; Corr, P.J.; Cyniak-Cieciura, M.; Demidova, L.; Filippi, C.A.; Garipova, M.; Habel, U.; Haines, N.; Heym, N.; Hunter, K.; Jones, N.A.; Kanen, J.; Kirenskaya, A.; … Pickering, A.D. What is next for the neurobiology of temperament, personality and psychopathology? Current Opinion in Behavioral Sciences 2022, 45, 101143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uher, J. Three methodological core issues of comparative personality research. European Journal of Personality 2008, 22, 475–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uher, J. Individual behavioral phenotypes: An integrative meta-theoretical framework. Why “behavioral syndromes” are not analogs of “personality”. Developmental Psychobiology 2011, 53, 521–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uher, J. Personality Psychology: Lexical Approaches, Assessment Methods, and Trait Concepts Reveal Only Half of the Story—Why it is Time for a Paradigm Shift. Integrative Psychological & Behavioral Science 2013, 47, 1–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uher, J. Conceiving “personality”: Psychologist’s challenges and basic fundamentals of the Transdisciplinary Philosophy-of-Science Paradigm for Research on Individuals. Integrative Psychological and Behavioral Science 2015, 49, 398–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uher, J.; Werner, C.S.; Gosselt, K. From observations of individual behaviour to social representations of personality: Developmental pathways, attribution biases, and limitations of questionnaire methods. Journal of Research in Personality 2013, 47, 647–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, R.N.; Cummins, R.A. The open-field test: A critical review. Psychological Bulletin 1976, 83, 482–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- War, R.; Surendra, V.; Paul, S.; Sharma, U.R.; Suresh, J.; Manjunatha, P.M. Zebrafish as an emerging alternative tool for studying anxiety disorders. Journal of Advanced Scientific Research 2022, 13, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, A. Personality Traits: A View From the Animal Kingdom. Journal of Personality 2018, 86, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, A. ; Adams MJ (2013) Differential behavioral ecology: The structure life history evolution of primate personality Em, C. Carere & D. Maestripieri (Orgs.), Animal personalities: Behavior, physiology and evolution. University of Chicago Press. [CrossRef]
- Whitham, W. ; Washburn DA (2017) AHistory of Animal Personality Research Em, J. Vonk, A. Weiss, & S. A. Kuczaj (Orgs.), Personality in Nonhuman Animals (p. 3–16). Springer International Publishing. [CrossRef]
- Wilson, D.S.; Clark, A.B.; Coleman, K.; Dearstyne, T. Shyness and boldness in humans and other animals. Trends in Ecology and Evolution 1994, 9, 442–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Dimension | Behavioral tests | Example of operational definition | Neurotransmitter system involved |
|---|---|---|---|
| Shyness-boldness (Bold) | Responses to predators | Avoidance or inspection of the predator Time spent foraging under risk |
Serotonin |
| Response to threatening stimuli | Frequency of freezing Latency to feed after introduction of stimulus |
||
| Exploration-avoidance (ExpAv) | Emergence test | Latency to emerge from a refuge | Serotonin, dopamine, histamine, glucocorticoids |
| Novel object test | Latency to approach a novel object Proportion of time spent in contact with the object |
||
| Light/dark test | Proportion of time spent in the non-preferred compartment (e.g., black in adult zebrafish) | ||
| Novel tank test | Proportion of time spent in the bottom third of the tank | ||
| Activity (Act) |
Novel tank test | Distance covered Swimming speed Squares crossed |
|
| Other tests (Virtually every behavioral test in other dimensions can also incorporate activity measures) |
Distance covered Swimming speed Squares crossed |
||
| Sociability (Soc) |
Social preference test | Time spent near conspecific | Sexual steroids, nonapeptides, dopamine |
| Social novelty test | Time spent near novel conspecific | ||
| Shoaling | Inter-fish distance | ||
| Conditional approach | Time spent inspecting predator when conspecific is present | ||
| Aggressiveness (Agr) |
Mirror test | Aggressive display or contact | Serotonin, dopamine, histamine |
| Aggressive encounters | Aggressive display or contact |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





