Submitted:
21 April 2023
Posted:
21 April 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Animals and treatments
2.3. Superovulation and oocyte collection
2.4. Immunocytochemistry of γ-H2AX, RAD 51, 8-OHdG, nitrotyrosine, and microtubules
2.5. Statistical analysis
3. Results
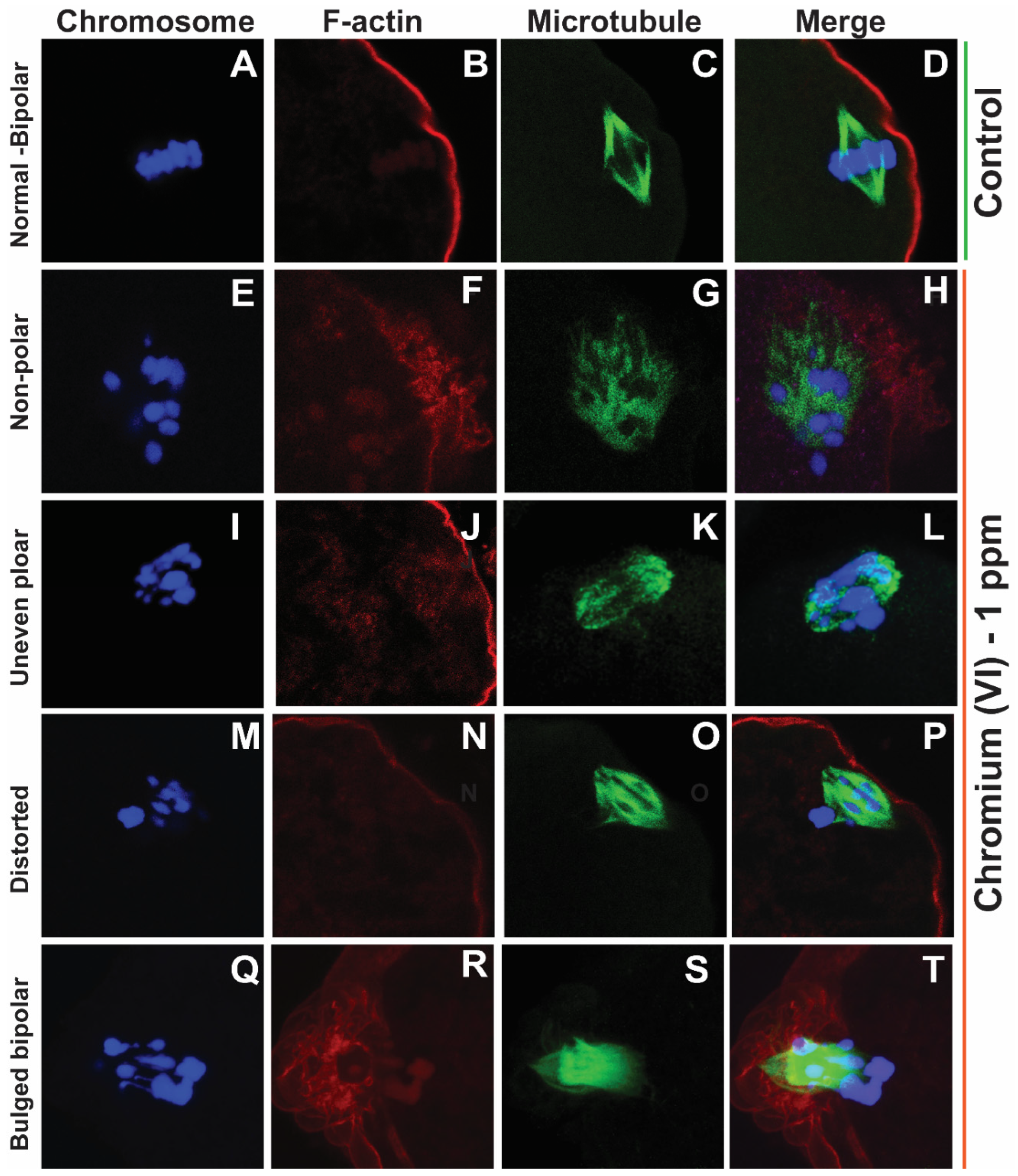
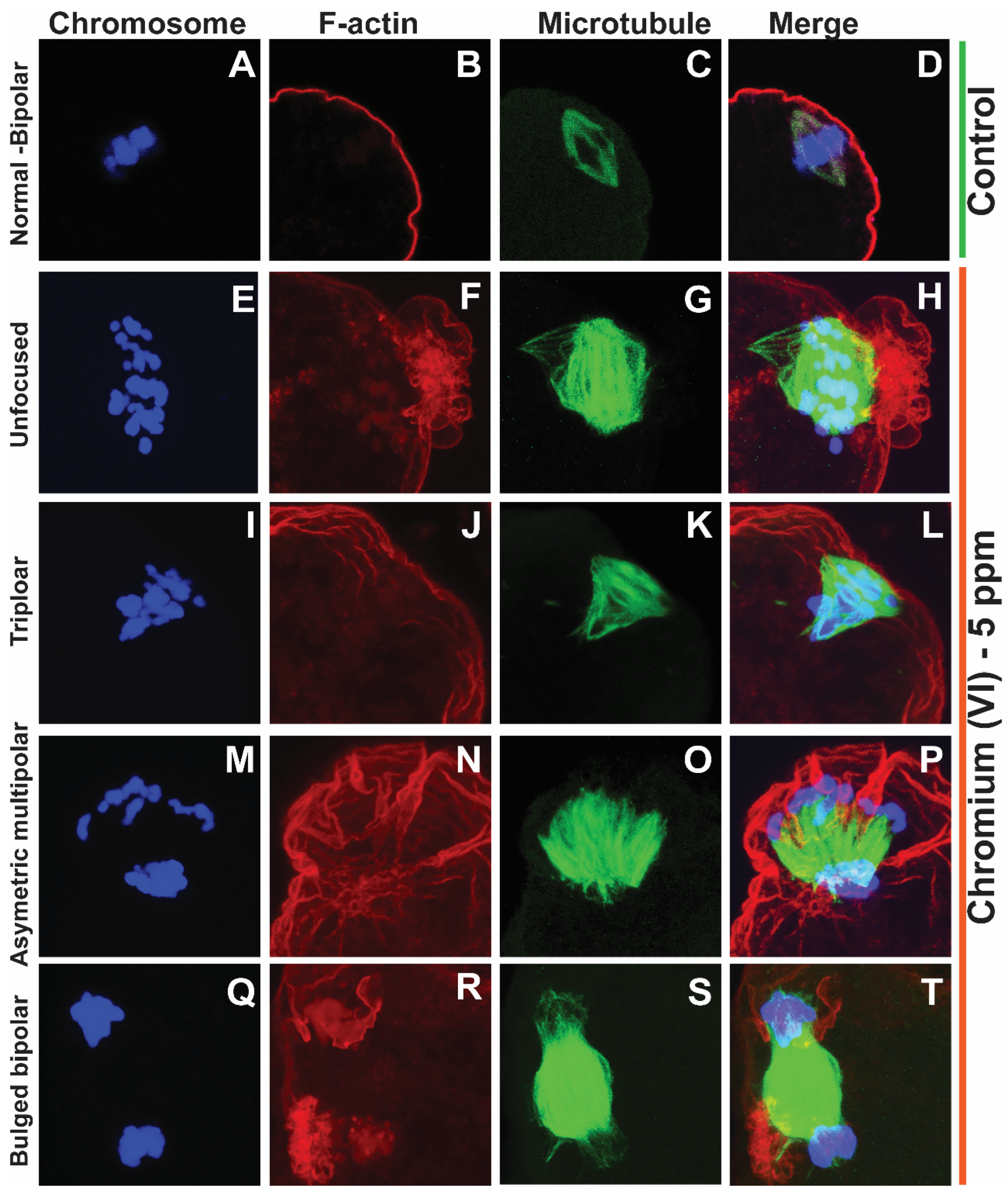
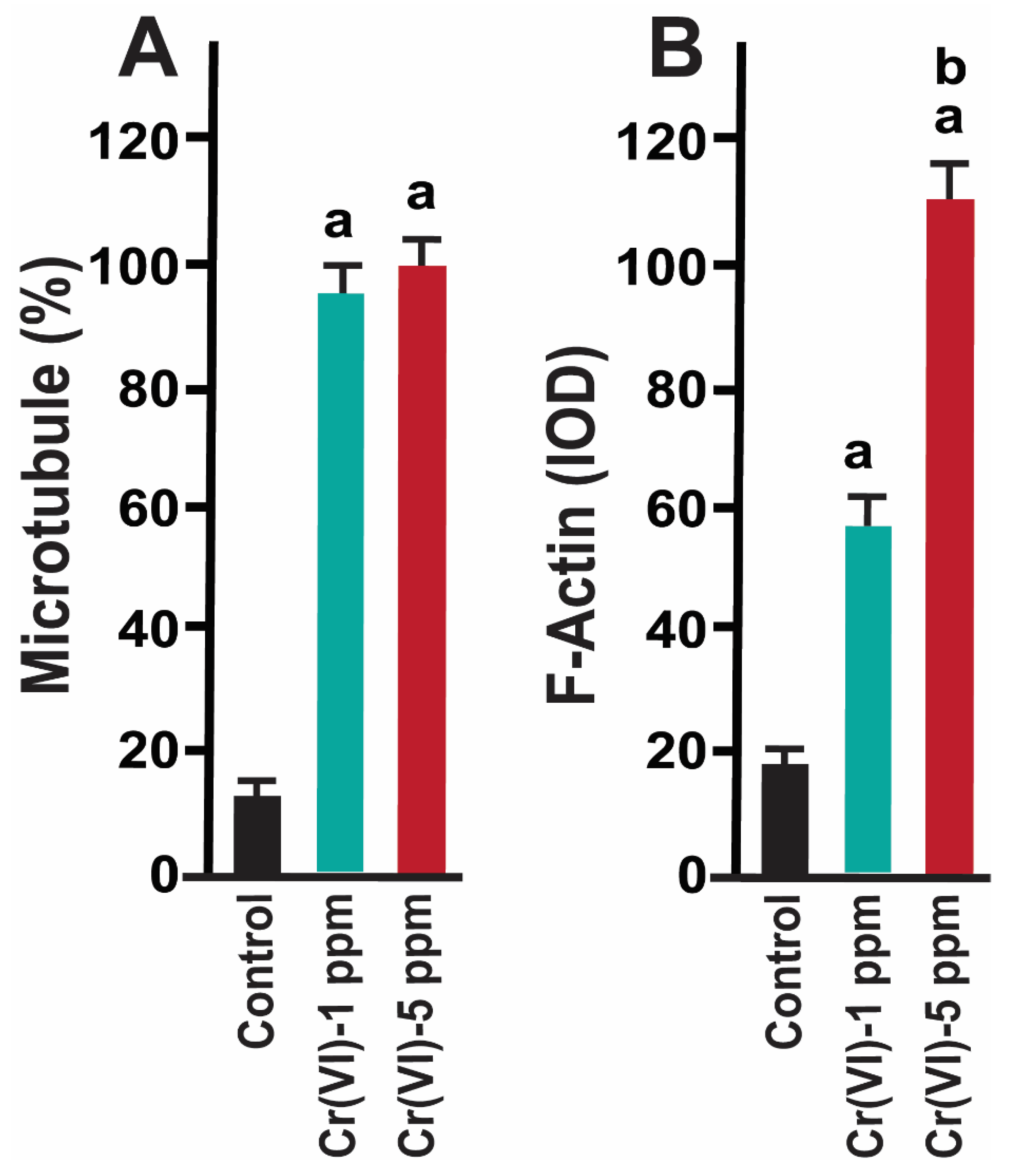
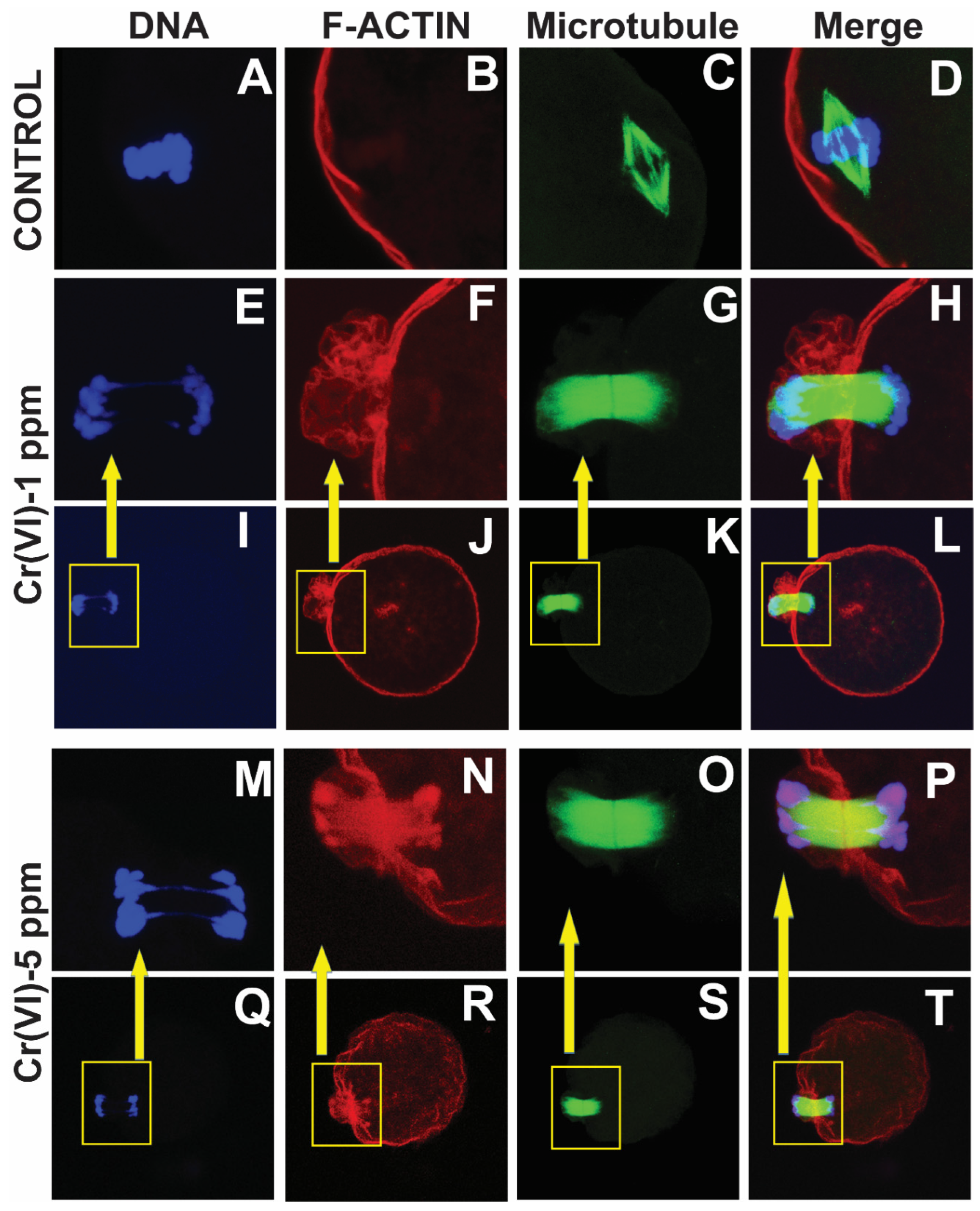
3.1. Exposure to Cr(VI) distorted the microtubule structure and chromosome arrangement in metaphase II oocytes.
3.2. Exposure to Cr(VI) delayed polar body extrusion resulted in incomplete cytokinesis in the MII oocytes
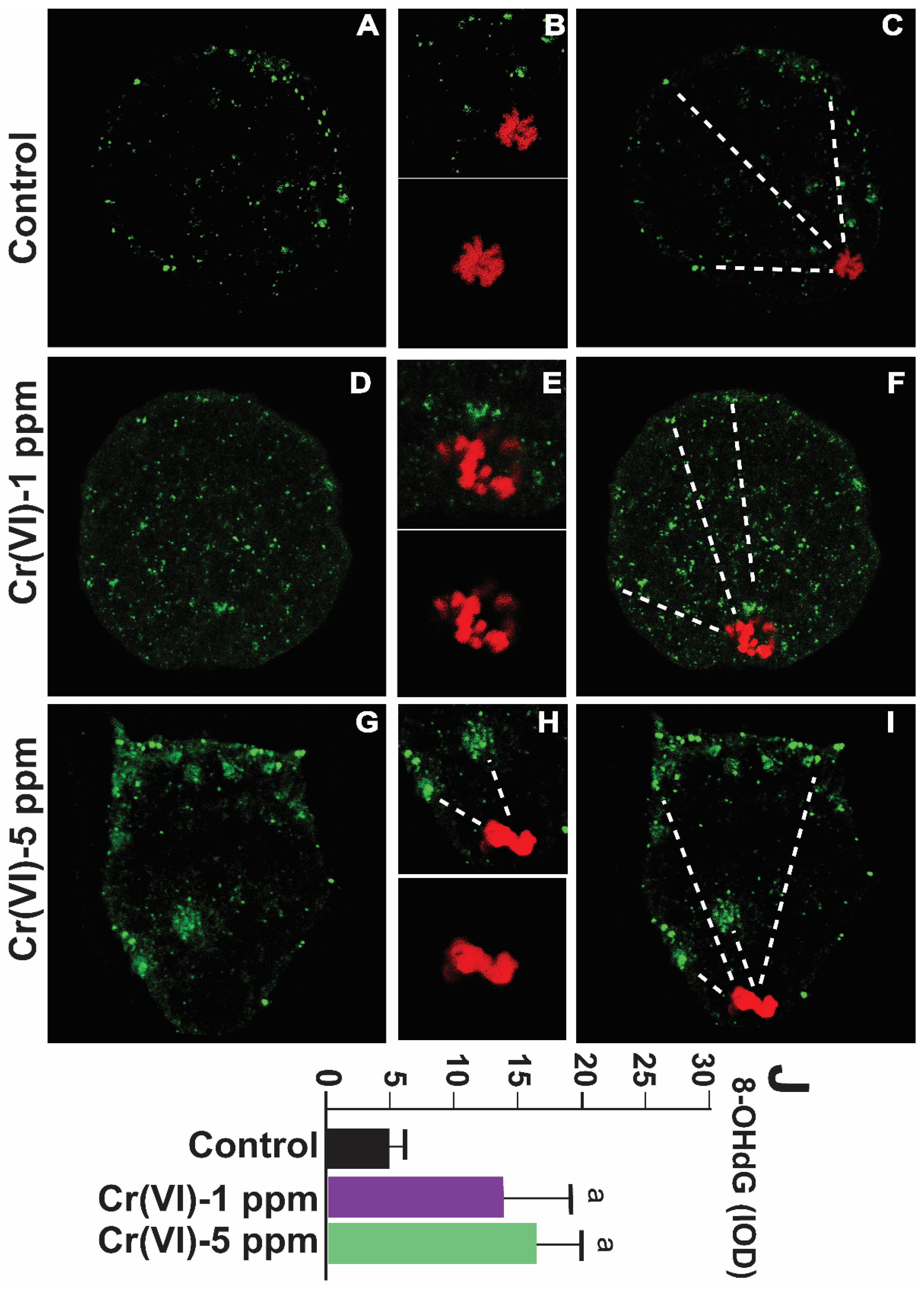
3.3. Exposure to Cr(VI) increased oxidative DNA damage in the MII oocytes
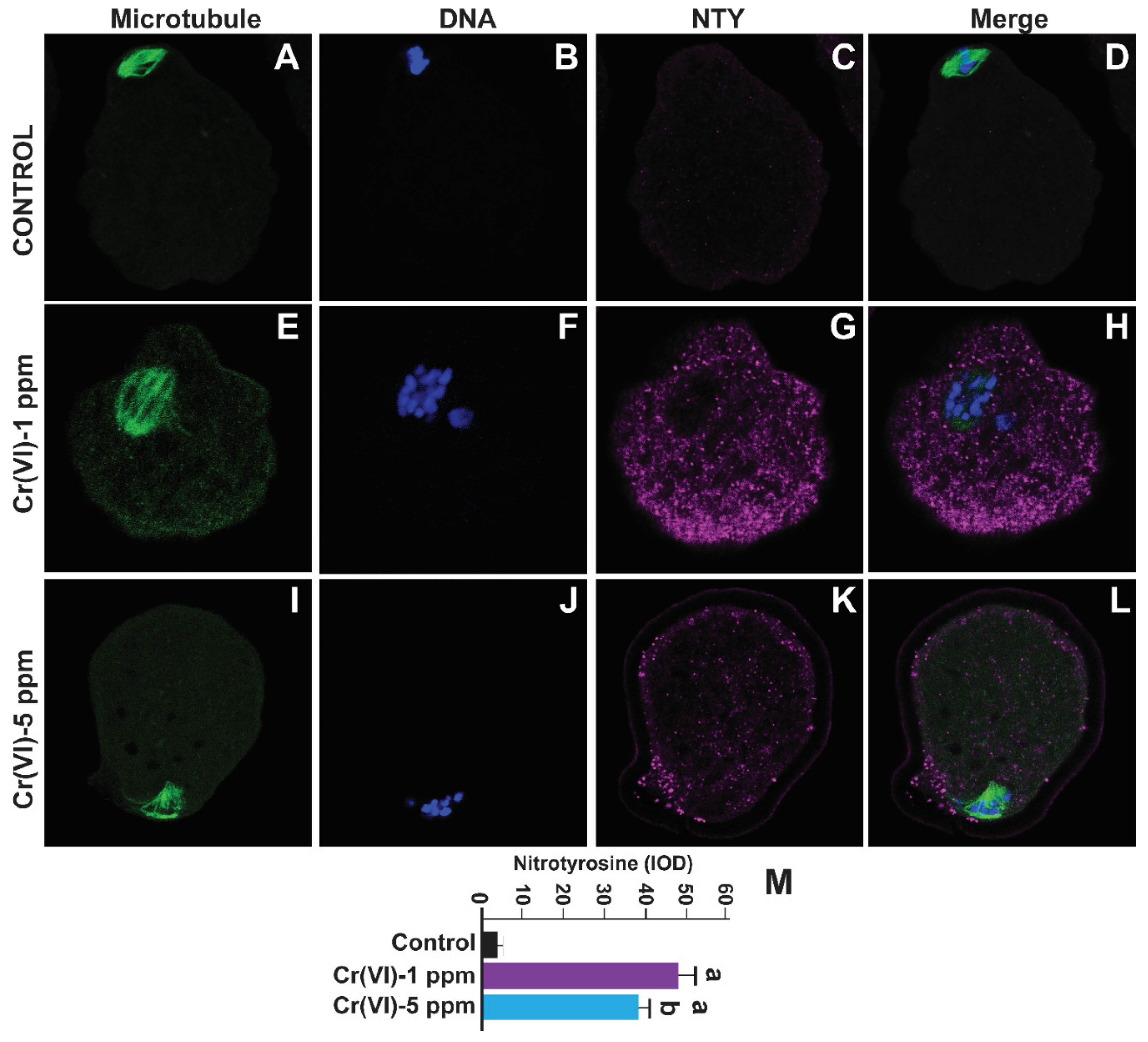
3.4. Exposure to Cr(VI) increased oxidative protein damage in the MII oocytes
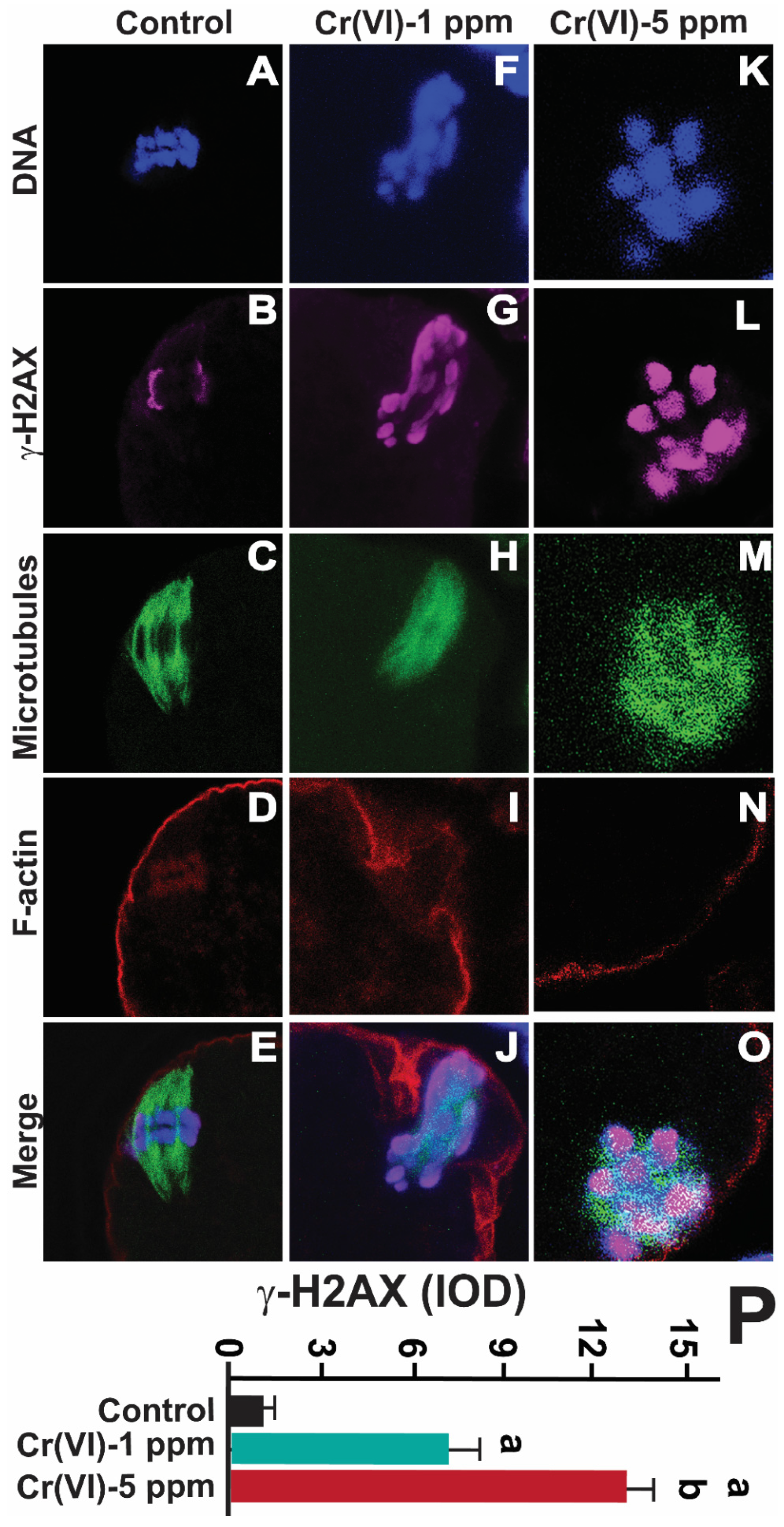
3.5. Exposure to Cr(VI) increased DNA double strand breaks in the MII oocytes
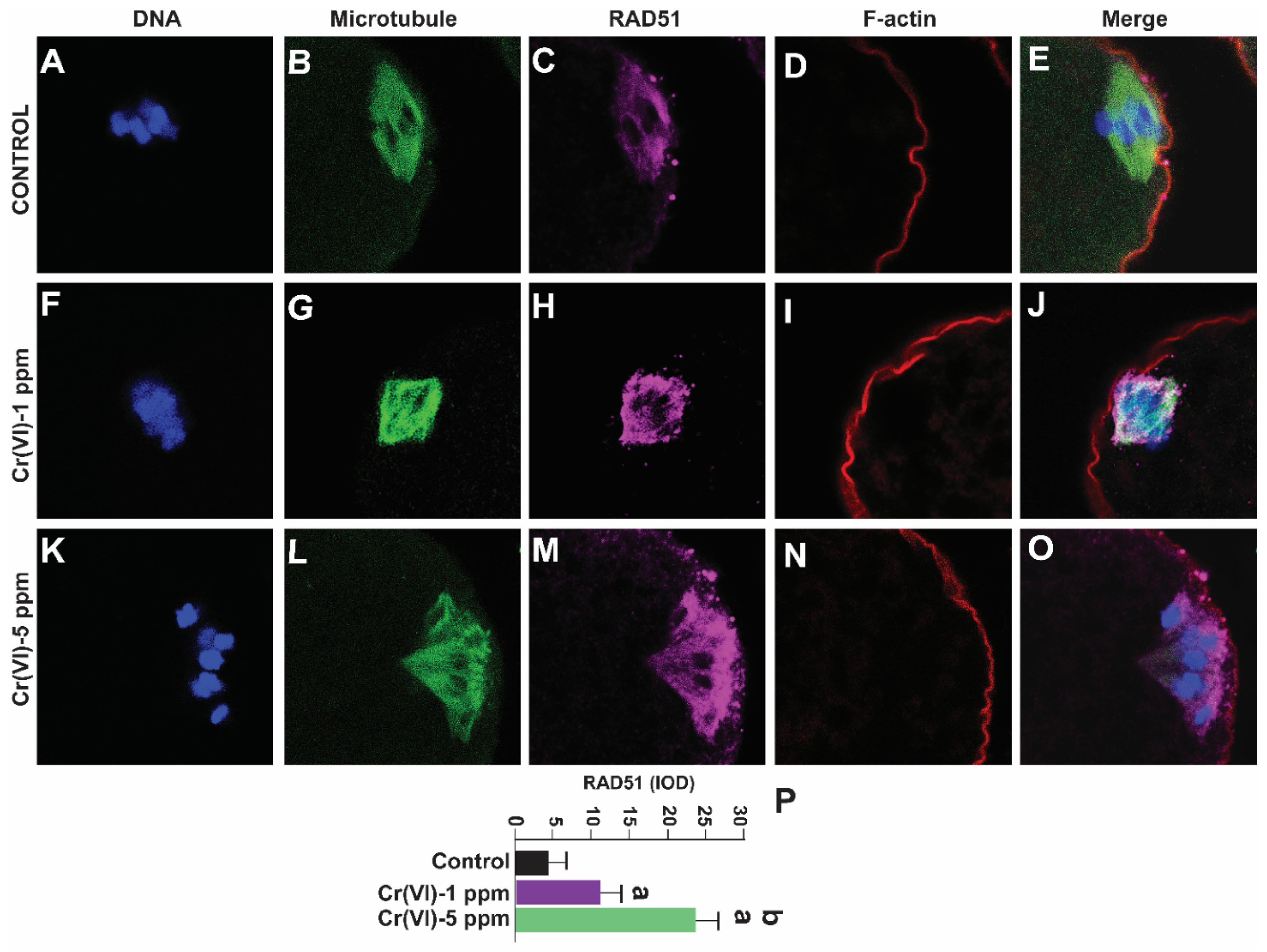
3.6. Exposure to Cr(VI) increased RAD51 expression in the MII oocytes
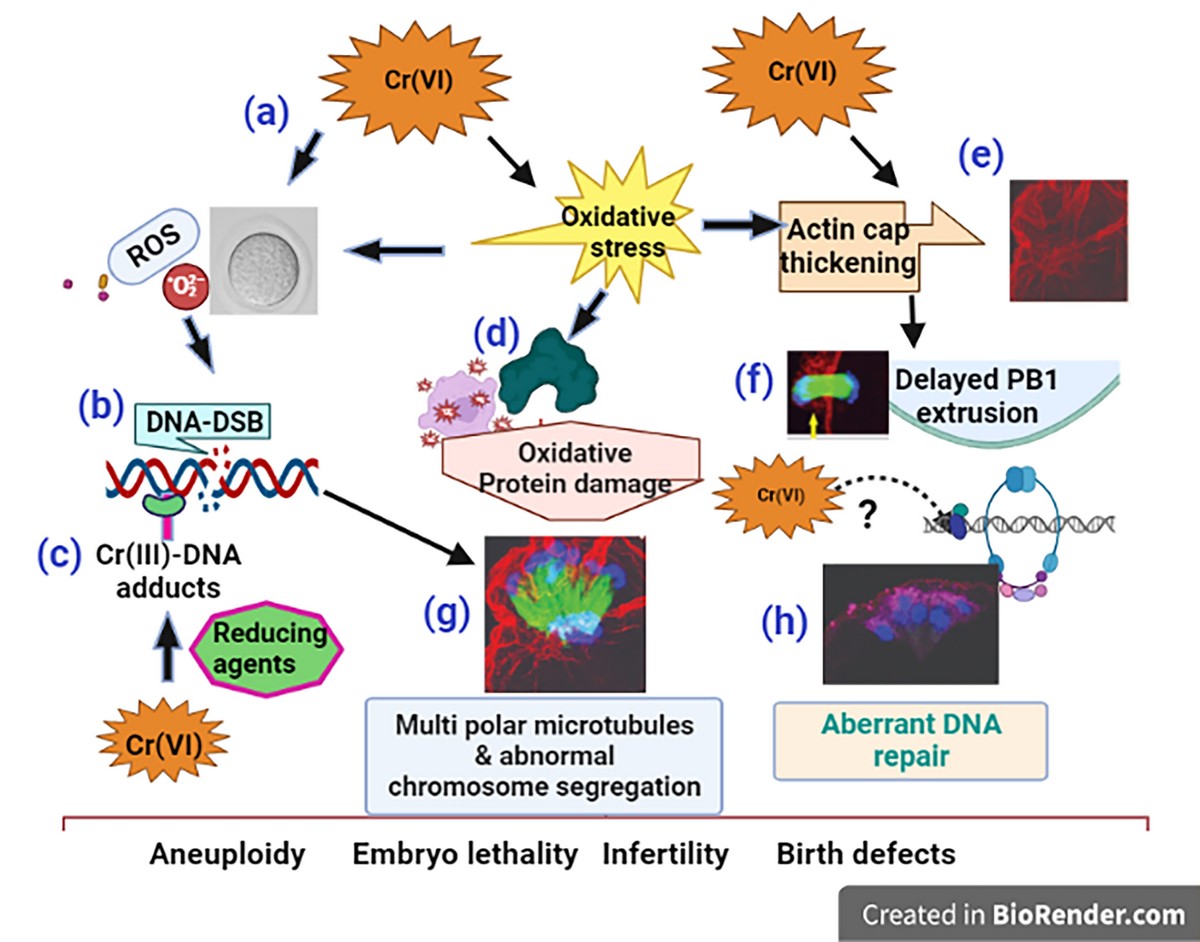
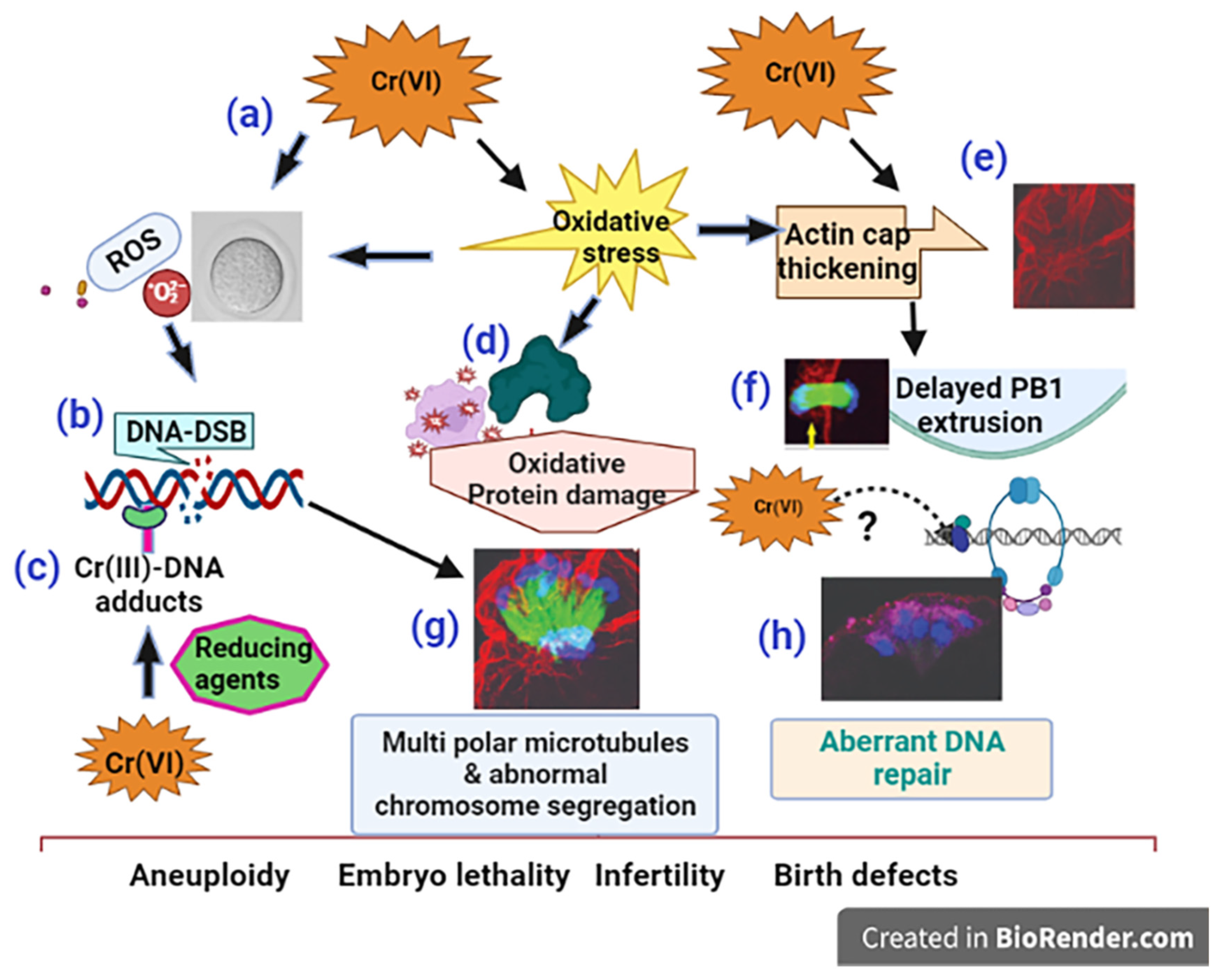
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wuri, L.; Arosh, J. A.; Wu, J. Z.; Banu, S. K. Exposure to hexavalent chromium causes infertility by disrupting cytoskeletal machinery and mitochondrial function of the metaphase II oocytes in superovulated rats. Toxicology Reports 2022, 9, 219–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stringer, J. M.; Winship, A.; Liew, S. H.; Hutt, K. The capacity of oocytes for DNA repair. Cell Mol Life Sci 2018, 75, 2777–2792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winship, A. L.; Stringer, J. M.; Liew, S. H.; Hutt, K. J. The importance of DNA repair for maintaining oocyte quality in response to anti-cancer treatments, environmental toxins and maternal ageing. Hum Reprod Update 2018, 24, 119–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vessa, B.; Perlman, B.; McGovern, P. G.; Morelli, S. S. Endocrine disruptors and female fertility: a review of pesticide and plasticizer effects. F S Rep 2022, 3, 86–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munisha, M.; Schimenti, J. C. Genome maintenance during embryogenesis. DNA Repair (Amst) 2021, 106, 103195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robertson, A. B.; Klungland, A.; Rognes, T.; Leiros, I. DNA repair in mammalian cells: Base excision repair: the long and short of it. Cell Mol Life Sci 2009, 66, 981–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rothkamm, K.; Lobrich, M. Evidence for a lack of DNA double-strand break repair in human cells exposed to very low x-ray doses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2003, 100, 5057–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J. W.; Xu, D. Q.; Feng, X. Z. The toxic effects and possible mechanisms of glyphosate on mouse oocytes. Chemosphere 2019, 237, 124435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, Y. L.; Chen, M. H.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, B. H.; Liu, R.; Xu, L.; He, S. W.; Li, F. P.; Qi, Z. Q.; Wang, H. L. Methoxychlor exposure induces oxidative stress and affects mouse oocyte meiotic maturation. Mol Reprod Dev 2016, 83, 768–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghunath, A.; Sundarraj, K.; Nagarajan, R.; Arfuso, F.; Bian, J.; Kumar, A. P.; Sethi, G.; Perumal, E. Antioxidant response elements: Discovery, classes, regulation and potential applications. Redox biology 2018, 17, 297–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Li, R. Effects of environment and lifestyle factors on anovulatory disorder. Environment and Female Reproductive Health 2021, 113–136. [Google Scholar]
- Dabrowska, N.; Wiczkowski, A. Analytics of oxidative stress markers in the early diagnosis of oxygen DNA damage. Adv Clin Exp Med 2017, 26, 155–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halliwell, B. Can oxidative DNA damage be used as a biomarker of cancer risk in humans? Problems, resolutions and preliminary results from nutritional supplementation studies. Free radical research 1998, 29, 469–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, J.; Luderer, U. Oxidative damage increases and antioxidant gene expression decreases with aging in the mouse ovary. Biology of reproduction 2011, 84, 775–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wojsiat, J.; Korczyński, J.; Borowiecka, M.; Żbikowska, H. M. The role of oxidative stress in female infertility and in vitro fertilization. Postepy higieny i medycyny doswiadczalnej (Online) 2017, 71, 359–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Saleh, I.; Coskun, S.; Al-Rouqi, R.; Al-Rajudi, T.; Eltabache, C.; Abduljabbar, M.; Al-Hassan, S. Oxidative stress and DNA damage status in couples undergoing in vitro fertilization treatment. Reprod Fertil 2021, 2, 117–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banu, S. K.; Stanley, J. A.; Sivakumar, K. K.; Arosh, J. A.; Burghardt, R. C. Resveratrol protects the ovary against chromium-toxicity by enhancing endogenous antioxidant enzymes and inhibiting metabolic clearance of estradiol. Toxicology and applied pharmacology 2016, 303, 65–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, E. D.; Detloff, M. R.; Johnson, K.; Kupina, N. C. Peroxynitrite-mediated protein nitration and lipid peroxidation in a mouse model of traumatic brain injury. Journal of neurotrauma 2004, 21, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Headlam, H. A.; Davies, M. J. Markers of protein oxidation: different oxidants give rise to variable yields of bound and released carbonyl products. Free Radical Biology and Medicine 2004, 36, 1175–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banu, S. K.; Stanley, J. A.; Taylor, R. J.; Sivakumar, K. K.; Arosh, J. A.; Zeng, L.; Pennathur, S.; Padmanabhan, V. Sexually dimorphic impact of chromium accumulation on human placental oxidative stress and apoptosis. Toxicological Sciences 2018, 161, 375–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.-H.; Zhang, X.; Wang, X.-C.; Jin, L.-F.; Yang, Z.-P.; Jiang, C.-X.; Chen, Q.; Ren, X.-B.; Cao, J.-Z.; Wang, Q. Chronic occupational exposure to hexavalent chromium causes DNA damage in electroplating workers. BMC Public Health 2011, 11, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, P.; Itankar, N.; Patil, Y. Biomanagement of hexavalent chromium: Current trends and promising perspectives. Journal of Environmental Management 2021, 279, 111547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metzger, L. New Report: CPS Energy’s Calaveras Power Station among nation’s top water polluters; Environment Texas Research & Policy Center: 2022.
- Dubey, R.; Verma, P.; Kumar, S. Cr (III) genotoxicity and oxidative stress: An occupational health risk for leather tannery workers of South Asian developing countries. Toxicol Ind Health 2022, 38, 112–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yatera, K.; Morimoto, Y.; Ueno, S.; Noguchi, S.; Kawaguchi, T.; Tanaka, F.; Suzuki, H.; Higashi, T. Cancer risks of hexavalent chromium in the respiratory tract. Journal of UOEH 2018, 40, 157–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Remy, L. L.; Byers, V.; Clay, T. Reproductive outcomes after non-occupational exposure to hexavalent chromium, Willits California, 1983-2014. Environmental Health 2017, 16, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roeles, J.; Tsiavaliaris, G. Actin-microtubule interplay coordinates spindle assembly in human oocytes. Nature communications 2019, 10, 4651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacLennan, M.; Crichton, J. H.; Playfoot, C. J.; Adams, I. R. Oocyte development, meiosis and aneuploidy. Semin Cell Dev Biol 2015, 45, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, A.; Fishel, S.; Bowman, N.; Duffy, S.; Sedler, M.; Thornton, S. Retrospective analysis of outcomes after IVF using an aneuploidy risk model derived from time-lapse imaging without PGS. Reproductive BioMedicine Online 2013, 27, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cimini, D.; Degrassi, F. Aneuploidy: a matter of bad connections. Trends in cell biology 2005, 15, 442–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.; Li, J.; Zhang, C.; Qian, W. Octocrylene exposure impairs mouse oocyte quality by inducing spindle defects and mitochondria dysfunction. Toxicology 2022, 479, 153306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.-X.; Ding, Z.-M.; Ahmad, M. J.; Wang, Y.-S.; Duan, Z.-Q.; Miao, Y.-L.; Xiong, J.-J.; Huo, L.-J. Bisphenol B exposure disrupts mouse oocyte meiotic maturation in vitro through affecting spindle assembly and chromosome alignment. Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology 2020, 8, 616771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gumus, E.; Sisko, A.; Abas, B. I.; Demirkan, B.; Cevik, O. Quercetin protects mouse oocytes against chromium-induced damage in vitro and in vivo. Journal of Trace Elements in Medicine and Biology 2023, 75, 127087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, A. L.; Colaiácovo, M. P. Exposure to phthalates: germline dysfunction and aneuploidy. Prenatal Diagnosis 2021, 41, 610–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, P. A.; Koehler, K. E.; Susiarjo, M.; Hodges, C. A.; Ilagan, A.; Voigt, R. C.; Thomas, S.; Thomas, B. F.; Hassold, T. J. Bisphenol A exposure causes meiotic aneuploidy in the female mouse. Current biology 2003, 13, 546–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wellbrock, R.; Rattonetti, A. IS IT CHROMIUM III OR CHROMIUM VI? ARE YOU SURE? ENERGY & AIR, 2013; 113. [Google Scholar]
- Zhitkovich, A. Chromium in drinking water: sources, metabolism, and cancer risks. Chemical research in toxicology 2011, 24, 1617–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honeycutt, M. E. Hexavalent chromium in Texas drinking water. Toxicol Sci 2011, 119, 423–4, author reply 425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maddox, A. S.; Azoury, J.; Dumont, J. Polar body cytokinesis. Cytoskeleton 2012, 69, 855–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valavanidis, A.; Vlachogianni, T.; Fiotakis, C. 8-hydroxy-2′-deoxyguanosine (8-OHdG): a critical biomarker of oxidative stress and carcinogenesis. Journal of environmental science and health Part C 2009, 27, 120–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lord, T.; Aitken, R. J. Fertilization stimulates 8-hydroxy-2′-deoxyguanosine repair and antioxidant activity to prevent mutagenesis in the embryo. Developmental biology 2015, 406, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valko, M.; Morris, H.; Cronin, M. Metals, toxicity and oxidative stress. Current medicinal chemistry 2005, 12, 1161–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kujjo, L. L.; Ronningen, R.; Ross, P.; Pereira, R. J.; Rodriguez, R.; Beyhan, Z.; Goissis, M. D.; Baumann, T.; Kagawa, W.; Camsari, C.; Smith, G. W.; Kurumizaka, H.; Yokoyama, S.; Cibelli, J. B.; Perez, G. I. RAD51 plays a crucial role in halting cell death program induced by ionizing radiation in bovine oocytes. Biol Reprod 2012, 86, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crain, D. A.; Janssen, S. J.; Edwards, T. M.; Heindel, J.; Ho, S.-m.; Hunt, P.; Iguchi, T.; Juul, A.; McLachlan, J. A.; Schwartz, J. Female reproductive disorders: the roles of endocrine-disrupting compounds and developmental timing. Fertility and sterility 2008, 90, 911–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guillette Jr, L.; Crain, D. Endocrine disrupting contaminants: an evolutionary perspective. Francis and Taylor Inc., Philadelphia 2000, 355.
- Bullach, A.; Trapphoff, T.; Zühlke, S.; Spiteller, M.; Dieterle, S. Impact of Nonylphenols and Polyhalogenated Compounds in Follicular Fluid on the Outcome of Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection. Reproductive Sciences 2021, 28, 2118–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eichenlaub-Ritter, U.; Vogt, E.; Cukurcam, S.; Sun, F.; Pacchierotti, F.; Parry, J. Exposure of mouse oocytes to bisphenol A causes meiotic arrest but not aneuploidy. Mutat Res 2008, 651, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grossman, D.; Kalo, D.; Gendelman, M.; Roth, Z. Effect of di-(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate and mono-(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate on in vitro developmental competence of bovine oocytes. Cell Biol Toxicol 2012, 28, 383–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sunderam, S.; Kissin, D. M.; Crawford, S. B.; Folger, S. G.; Jamieson, D. J.; Warner, L.; Barfield, W. D. Assisted reproductive technology surveillance—United States, 2012. Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report: Surveillance Summaries 2015, 64, 1–29. [Google Scholar]
- Gilchrist, R. B.; Lane, M.; Thompson, J. G. Oocyte-secreted factors: regulators of cumulus cell function and oocyte quality. Hum Reprod Update 2008, 14, 159–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nickens, K. P.; Patierno, S. R.; Ceryak, S. Chromium genotoxicity: A double-edged sword. Chem Biol Interact 2010, 188, 276–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banu, S. K.; Stanley, J. A.; Sivakumar, K. K.; Arosh, J. A.; Barhoumi, R.; Burghardt, R. C. Identifying a novel role for X-prolyl aminopeptidase (Xpnpep) 2 in CrVI-induced adverse effects on germ cell nest breakdown and follicle development in rats. Biol Reprod 2015, 92, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mogessie, B.; Schuh, M. Actin protects mammalian eggs against chromosome segregation errors. Science 2017, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanley, J. A.; Sivakumar, K. K.; Arosh, J. A.; Burghardt, R. C.; Banu, S. K. Edaravone mitigates hexavalent chromium-induced oxidative stress and depletion of antioxidant enzymes while estrogen restores antioxidant enzymes in the rat ovary in F1 offspring. Biology of reproduction 2014, 91, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banu, S. K.; Stanley, J. A.; Sivakumar, K. K.; Arosh, J. A.; Taylor, R. J.; Burghardt, R. C. Chromium VI− Induced developmental toxicity of placenta is mediated through spatiotemporal dysregulation of cell survival and apoptotic proteins. Reproductive Toxicology 2017, 68, 171–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banu, S. K.; Samuel, J. B.; Arosh, J. A.; Burghardt, R. C.; Aruldhas, M. M. Lactational exposure to hexavalent chromium delays puberty by impairing ovarian development, steroidogenesis and pituitary hormone synthesis in developing Wistar rats. Toxicology and applied pharmacology 2008, 232, 180–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elizur, S. E.; Lebovitz, O.; Orvieto, R.; Dor, J.; Zan-Bar, T. Reactive oxygen species in follicular fluid may serve as biochemical markers to determine ovarian aging and follicular metabolic age. Gynecol Endocrinol 2014, 30, 705–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carpenter, D. O. Effects of persistent and bioactive organic pollutants on human health; John Wiley & Sons: 2013.
- Amadi, C. N.; Igweze, Z. N.; Orisakwe, O. E. Heavy metals in miscarriages and stillbirths in developing nations. Middle East Fertility Society Journal 2017, 22, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goud, P. T.; Goud, A. P.; Joshi, N.; Puscheck, E.; Diamond, M. P.; Abu-Soud, H. M. Dynamics of nitric oxide, altered follicular microenvironment, and oocyte quality in women with endometriosis. Fertil Steril 2014, 102, 151–159 e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, J.; Shaeib, F.; Maitra, D.; Saed, G. M.; Dai, J.; Diamond, M. P.; Abu-Soud, H. M. Peroxynitrite affects the cumulus cell defense of metaphase II mouse oocytes leading to disruption of the spindle structure in vitro. Fertil Steril 2013, 100, 578–84 e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goud, A. P.; Goud, P. T.; Diamond, M. P.; Gonik, B.; Abu-Soud, H. M. Reactive oxygen species and oocyte aging: role of superoxide, hydrogen peroxide, and hypochlorous acid. Free Radic Biol Med 2008, 44, 1295–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; Wise, S. S.; Wise, J. P., Sr. Deficient repair of particulate hexavalent chromium-induced DNA double strand breaks leads to neoplastic transformation. Mutat Res 2008, 649, 230–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namgoong, S.; Kim, N. H. Meiotic spindle formation in mammalian oocytes: implications for human infertility. Biol Reprod 2018, 98, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, A.; Tripathy, A.; Ghosh, D. In Impact of endocrine disrupting chemicals (EDCs) on reproductive health of human, Proceedings of the Zoological Society, 2022; Springer: 2022; pp 16-30. [CrossRef]
- La Marca, A.; Mastellari, E. Infertility: Epidemiology and etiology. Female Reproductive Dysfunction 2020, 211–233. [Google Scholar]
- Winship, A. L.; Stringer, J. M.; Liew, S. H.; Hutt, K. J. The importance of DNA repair for maintaining oocyte quality in response to anti-cancer treatments, environmental toxins and maternal ageing. Human Reproduction Update 2018, 24, 119–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganesan, S.; Keating, A. F. Bisphenol A-Induced Ovotoxicity Involves DNA Damage Induction to Which the Ovary Mounts a Protective Response Indicated by Increased Expression of Proteins Involved in DNA Repair and Xenobiotic Biotransformation. Toxicol Sci 2016, 152, 169–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, K. H.; Sun, X. F.; Feng, Y. Z.; Cheng, S. F.; Li, B.; Li, Y. P.; Shen, W.; Li, L. The impact of Zearalenone on the meiotic progression and primordial follicle assembly during early oogenesis. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 2017, 329, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




