Introduction
The olive oil industry is one of the most important branches of agriculture in the Mediterranean basin, producing over 90% of the global olive oil production [
1]. This industry also generates solid and liquid waste byproducts characterized by their dark color and a typical odor, which are not easily degradable. Solid waste can be recycled and used as an ingredient of several products such as fertilizers
, ethanol and high value-added biomolecules [
2] or lightweight aggregates [
3]. On the other hand, the liquid byproduct, olive mill wastewater (OMWW), is significantly more difficult to treat. This liquid is characterized by high concentrations of polyphenols and tannins, in addition to low pH and high chemical and biochemical oxygen demands. These qualities inhibit biological decomposition and place OMWW as one of the most contaminating effluents among those produced by the agrofood industries [
4].
Previous studies suggested that the high concentrations of phenols, acids and sugar derivatives associated with OMWW may be applied for crop protection in dry or saline environments [
5]. These qualities also make OMWW and its extracts potentially useful biopesticides. Some studies have shown that extracts of OMWW have the potential to inhibit the growth of bacteria, fungi and weeds [
6]. However, very few studies explored the potential of OMWW extracts as insecticides or as insect growth inhibitors. Current studies focused on phytophagous insects [7-9].
The main objective of the current study was to examine the biopesticide potential of OMWW extracts against the development and survival of mosquito larvae. We focused on two, very different, species of mosquitoes that are highly common throughout the Mediterranean basin, specifically in North Israel.
Culex laticinctus (Edwards) is distributed throughout the Middle-east and around the Mediterranean Sea. The larvae of this species are associated with artificial aquatic habitats such as cisterns and concreate pools, containing fresh and brackish water [
10]. As such we hypothesize that this species will show a relevant durability to OMWW. The Asian Tiger mosquito,
Aedes albopictus (Skuse 1894) is one of the world’s worst invasive species [
11]. This species, native to South-East Asia, was first recorded in the United states in 1985 and spread rapidly into other parts of the world [
10]. Currently, it can be found in most areas with warm and temperate climate [
12,
13].
Aedes albopictus were first reported in Israel in 2002 [
14]. Since then, they have become highly abundant in the non-arid areas of central and North Israel [
15]. Unlike
Cx. laticinctus, larval
Ae. Albopictus are associated with small, freshwater containers who are difficult to locate and treat with conventional methods such as larvicidal sprays [
10,
16]. Plant extracts could therefore be potentially excellent bio-larvicide of this species.
Methods
Larval Collection
We collected
Culex laticinctus (Edwards) egg rafts and
Aedes albopictus (Skuse 1894) eggs from plastic ovitraps placed at Oranim College Campus, Tivon, Israel. Sampled larvae from each batch were reared to 4
th instar and identified to species [
10]. First instar larvae were transferred into 400 ml plastic cups containing tap water, aged for 24 hours.
Larval Toxicity Bioassay
We performed toxicity tests according to standard larvae bioassay [
17] to determine LC
50 and LC
90values. We placed 25 2
nd instar larvae in 100 ml cups containing 5, 10, 15, 20 and 25 ppt OMWW extract. Each concentration repeated 3 times. We recorded larval mortality after 48 hours of incubation, during this time we fed the larvae with a mixture of finely ground fish flakes (42.2% crude protein, Sera-Vipan, Heinsberg, Germany) and rodent chow (17% protein, Ribos, Haifa, Israel). Cups were kept at a temperature of 24.83 ± 0.84 °C (mean ± SD).
Sublethal Effects of OMWW on Larvae
We transferred 30 larvae into 400 ml plastic cups within 24 hours of hatching. The experiment consisted of paired cups (blocks), each containing either 1 ppt OMWW extract solution or aged water control (4 blocks in total). This concentration was assumed to be sublethal based on preliminary toxicity results showing it was 10% of Cx. laticinctus LC50. The larvae in each block were sibling Cx. laticinctus (from the same egg raft) or Ae. albopictus larvae originated from the same ovitrap. We fed the larvae every three days with 0.05 ± 0.003 (mean ± SD) grams of the mixture used in the previous experiment. We removed the pupae and identified emerging adults by sex. We recorded the number of days to pupation and the number of emerging adults
Statistical Analysis
We calculated LC
50 and LC
90 values at 95% confidence intervals using Probit analysis [
18].
We used a Pearson goodness of fit test in order to evaluate the observed distribution. We used a heterogeneity factor to calculate confidence limits when model assumptions were not met (p<0.15). We analyzed the effects of sublethal concentrations on larval time to pupation using Linear Mixed Models (LMM), with the variables “Sex” and “Treatment” (OMWW and control) as fix factors and “Block” as a random factor. These analyses considered random sampling (Block effect), and the fact that male mosquitoes usually pupate faster than females (Sex effect). All analyses used SPSS statistics for windows version 24 with Type III sums of squares [
19].
Results
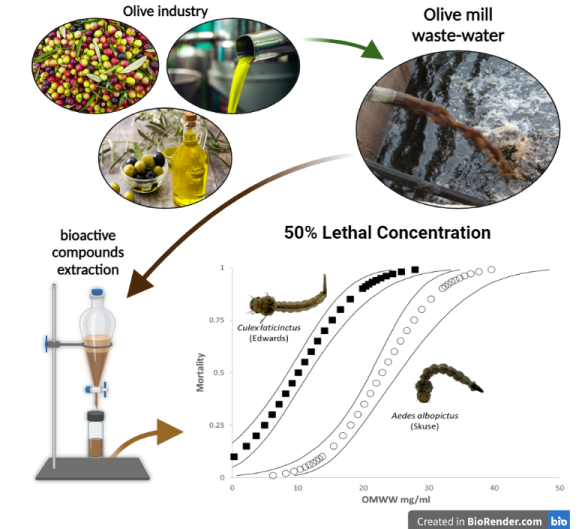
The toxicity of OMWW extract for both species are summarized in
Table 1. We found 100% mortality for
Cx. laticinctus larvae that were exposed to 25 ppt OMWW for 48 hours.
Aedes albopictus larvae expressed a stronger resistance to the extract with only ~60% mortality at the same concentration. The LC
50 value for
Ae. albopictus was 2.27 times higher than that of
Cx. laticinctus and 1.15 times higher than its LC
90 value.
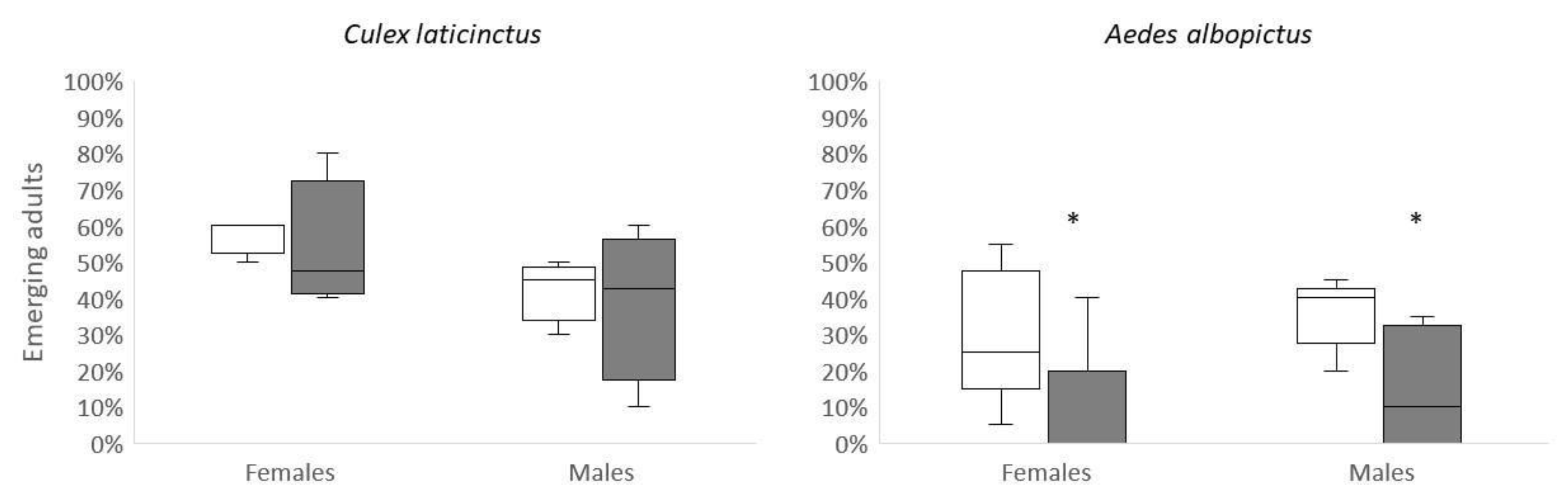
The number of larval
Cx. laticintctus surviving to adulthood in sublethal OMWW treatment did not differ in comparison to control (paired t-test: t
3=0.52; p=0.64 and t
3=0.42; p=0.7 for males and females, respectively), (
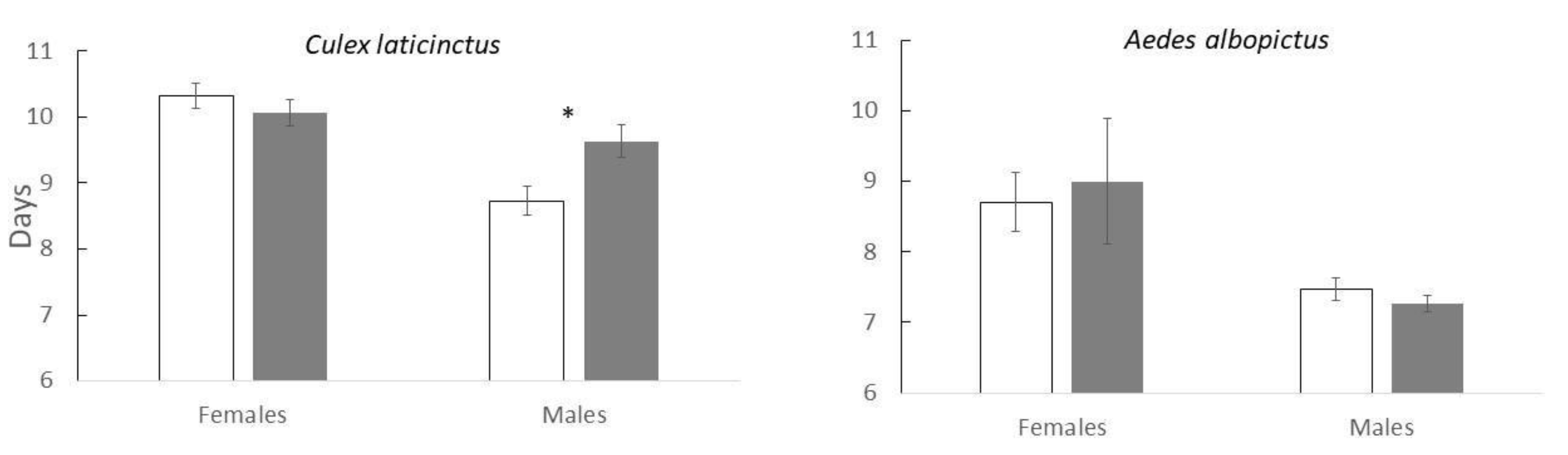
Figure 1). We found a strong sex effect on time to pupation, i.e. males pupated faster than females (F
1,147.13=27.9; p<0.001). Female pupation time did not vary among the treatments but males exposed to OMWW prolonged time to pupation (
Figure 2). This resulted in a significant “Sex × Treatment” interaction (F
1,147.08=6.4; p<0.001). The overall effect of OMWW by itself was not statistically significant (F
1,147.04=1.5; p=0.23).
Less
Ae. albopictus larvae metamorphosed in sublethal the treatment in comparison to control. This trend was shown in males (t
8=2.5; p=0.02) and females (t
8=1.9; p=0.05), (
Figure 1). Males pupated faster than females (Sex effect: F
1,70.27=12.3; p<0.001). We did not find a significant “Sex × Treatment” interaction (F
1,70.27=0.4; p=0.52), or a significant effect of the overall treatment on time to pupation (F
1,5.03=0.03; p=0.88), (
Figure 2).
Discussion
Results showed that OMWW extract is potentially toxic to both mosquito species. Extracts from numerous plant species are known to be have potential larvicide qualities [
20]. The uniqueness in the use of OMWW extracts, is that it could proof as method for the reuse of agricultural waste products as eco-friendly larvicides. We tested the lethal effect of OMWW on early instar larvae who are more sensitive to insecticides than late instars [
21], hence efficiency is usually measured for late instars.
Culex laticinctus is one of the most common mosquito species in the Mediterranean region, and their breeding sites often consist of small, artificial water bodies [
10]. Hence, we may assume that larval
Cx. laticinctus are often exposed to olive foliage and are relatively resistant to OMWW. Therefore, we expect that OMWW extracts should be more lethal for larval mosquito species that are not associated with that region.
By contrast to our original hypothesis, the LC
50 and LC
90 levels of OMWW were significantly lower for
Cx. laticinctus in comparison to
Ae. albopictus (
Table 1). We can expect that the lethal effect of OMWW extracts will increase further by removal of some of the compounds by different types of fractionation, [
22]. For example, fractions containing mainly polyphenols from OMWW cause mortality to
Euphyllura olivina and
Aphis citricola by direct spraying of liquid solutions. The LC
50 in these studies were recorded at 0.36 and 2.12 ppt for the two Hemipterans respectively [
7].
Low concentrations of pesticide may reduce pest population fecundity over time without causing immediate mortality. For example, inhalation of OMWW extracts by pupae of the Mediterranean flour moth,
Ephestia kuehniella (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae) resulted in extended pupal duration period. In addition, emerging adults delayed time to oviposition and oviposited less eggs over fewer days [
8]. Crude extract of OMWW caused weight loss for larvae of the palm tree pest
Potosia opaca (Coleoptera: Scarabeidae). Increased larval mortality was recorded well over a week following multiple treatments [
9].
The two mosquito species in this study also varied in their response to what we originally assumed to be a sublethal OMWW concentration. This concentration, was indeed not lethal to larval
Cx. laticinctus (Fig 1). The same concentration significantly reduced the survival of
Ae. albopictus larvae whose LC
50 concentration was ~23 times higher (Fig 1; table 1). This response to relatively low OMWW concentration may point to the possibility that OMWW extracts can be applied by spraying urban areas that may contain
Ae. albopictus breeding sites with limited danger to nontarget species. Although
Cx. laticinctus survival was not reduced after a long exposure to low concentration extract, we did find a sex-specific effect on pupation time. Time for pupation was extended for males by almost a full day whereas females were not significantly affected. This resulted in an almost simultaneous emergence of males and females from OMWW treated cups (Fig 2). In most mosquito species, males have a shorter larval stage, emerge 1-2 days before the females and are significantly smaller than them [
10]. However, males become sexually mature only a day after emergence, at the same time as later emerging female of the same cohort [
10]. A situation where males and females emerge simultaneously following exposure to OMWW may result in delayed mating and a reduction of the overall number of mating couples.
Overall, our results support the possibility that OMWW, or its fractions, may be a potential source for the development of mosquito larvicide. Future research should focus on fractionation, isolation and identification of compounds from different fractions of OMWW with strong insecticidal activity. It is important to emphasize that this approach suits well the circular bio-economy and green chemistry models that concern the importance of valorization of agro-wastes and by-products generated by agricultural and agro-industries.
Acknowledgments
Avi Bar-Massada, and Elad Chiel helped with several aspects of this study. This work was supported by the program for University of Haifa and Shamir Research Institute joined research, and the Margolin grant awarded to Maram Halabi.
References
- International Olive council- Olive oil & table olive figures.
- Muscolo, A.; Romeo, F.; Marra, F.; Mallamaci, C. Recycling agricultural, municipal and industrial pollutant wastes into fertilizers for a sustainable healthy food production. J Environ Manage 2021, 300, 113771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno-Maroto, J.M.; Uceda-Rodríguez, M.; Cobo-Ceacero, C.J.; de Hoces, M.C.; MartínLara, M.Á.; Cotes-Palomino, T.; García, A.B.L.; Martinez-Garcia, C. Recycling of ‘alperujo’(olive pomace) as a key component in the sintering of lightweight aggregates. J Clean Prod 2019, 239, 118041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messineo, A.; Maniscalco, M.P.; Volpe, R. Biomethane recovery from olive mill residues through anaerobic digestion: A review of the state of the art technology. Sci Total Environ 2020, 703, 135508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azzaz, A.A.; Jeguirim, M.; Kinigopoulou, V.; Doulgeris, C.; Goddard, M.; Jellali, S.; Ghimbeu, C.M. Olive mill wastewater: From a pollutant to green fuels, agricultural and water source and bio-fertilizer–Hydrothermal carbonization. Sci Total Environ 2020, 733, 139314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Abbassi, A.; Saadaoui, N.; Kiai, H.; Raiti, J.; Hafidi, A. Potential applications of olive mill wastewater as biopesticide for crops protection. Sci Total Environ 2017, 576, 10–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larif, M.; Zarrouk, A.; Soulaymani, A.; Elmidaoui, A. New innovation in order to recover the polyphenols of olive mill wastewater extracts for use as a biopesticide against the Euphyllura olivina and Aphis citricola. Research on Chemical Intermediates 2013, 39, 4303–4313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahcene, S.; Taibi, F.; Mestar, N.; Ahmed, S.A.; Boumendjel, M.; Ouafi, S.; Houali, K. Insecticidal effects of the Olea europaea subsp. laperrinei extracts on the flour Pyralid Ephestia kuehniella. Cell Mol Biol 2018, 64, 6–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boutaj, H.; Boutasknit, A.; Anli, M.; Ahmed, M.A.; El Abbassi, A.; Meddich, A. Insecticidal Effect of Olive Mill Wastewaters on Potosia opaca (Coleoptera: Scarabeidae) Larva. Waste and Biomass Valorization 2020, 11, 3397–3405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, N.; Petric, D.; Zgomba, M.; Boase, C.; Madon, M.; Dahl, C.; Kaiser, A. SpringerLink Mosquitoes and Their Control, 2nd ed.; Springer: Berlin, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Lowe, S.; Browne, M.; Boudjelas, S.; De Poorter, M. 100 of the world's worst invasive alien species: a selection from the global invasive species database; Invasive Species Specialist Group: Auckland, New Zealand, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Bonizzoni, M.; Gasperi, G.; Chen, X.; James, A.A. The invasive mosquito species Aedes albopictus: current knowledge and future perspectives. Trends Parasitol 2013, 29, 460–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamal, M.; Kenawy, M.A.; Rady, M.H.; Khaled, A.S.; Samy, A.M. Mapping the global potential distributions of two arboviral vectors Aedes aegypti and Ae. albopictus under changing climate. PloS one 2018, 13, e0210122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pener, H.; Wilamowski, A.; Schnur, H.; Orshan, L.; Shalom, U.; Bear, A. Aedes albopictus in Israel. European Mosquito Bulletin 2003, 14, 32. [Google Scholar]
- Müller, G.C.; Kravchenko, V.D.; Junnila, A.; Schlein, Y. Tree-hole breeding mosquitoes in Israel. Journal of Vector Ecology 2012, 37, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandel, K.; Suman, D.S.; Wang, Y.; Unlu, I.; Williges, E.; Williams, G.M.; Gaugler, R. Targeting a hidden enemy: pyriproxyfen autodissemination strategy for the control of the container mosquito Aedes albopictus in cryptic habitats. PLoS neglected tropical diseases 2016, 10, e0005235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization Guidelines for laboratory and field testing of mosquito larvicides. WHO/CDS/WHOPES/GCDPP/2005.13 2005.
- Finney, D.J. Probit analysis: a statistical treatment of the sigmoid response curve; Cambridge university press: Cambridge, England, 1952. [Google Scholar]
- IBM, C. IBM SPSS Statistics for Windows, version 24; NY-IBM Corp.: Armonk, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Pavela, R.; Maggi, F.; Iannarelli, R.; Benelli, G. Plant extracts for developing mosquito larvicides: From laboratory to the field, with insights on the modes of action. Acta Trop 2019, 193, 236–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulla, M.S. Susceptibility of various larval instars of Culex p. quinquefasciatus Say to insecticides. Mosquito News 1961, 21, 320–323. [Google Scholar]
- Tafesh, A.; Najami, N.; Jadoun, J.; Halahlih, F.; Riepl, H.; Azaizeh, H. Synergistic antibacterial effects of polyphenolic compounds from olive mill wastewater. Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine 2011, 2011, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).