Submitted:
19 April 2023
Posted:
20 April 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results
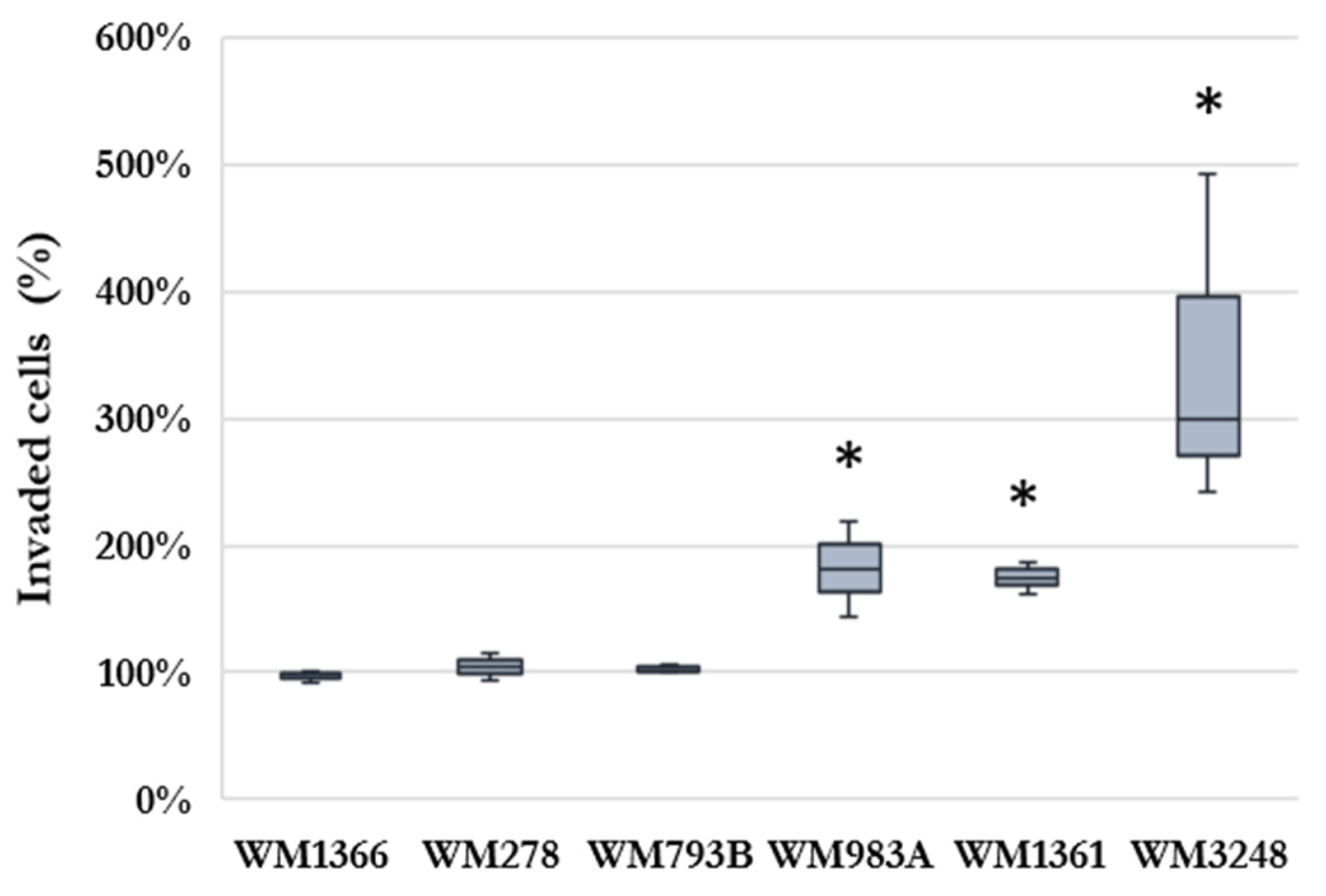
2.1. Effect of HHSEC on melanoma cell invasion
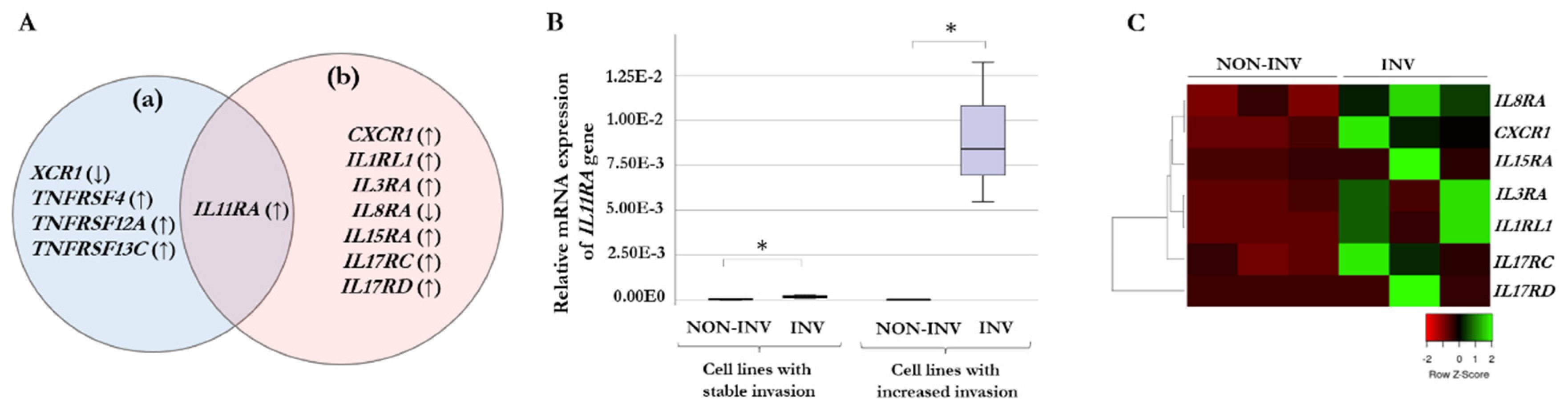
2.2. Chemokine- and cytokine receptor expression of melanoma cells
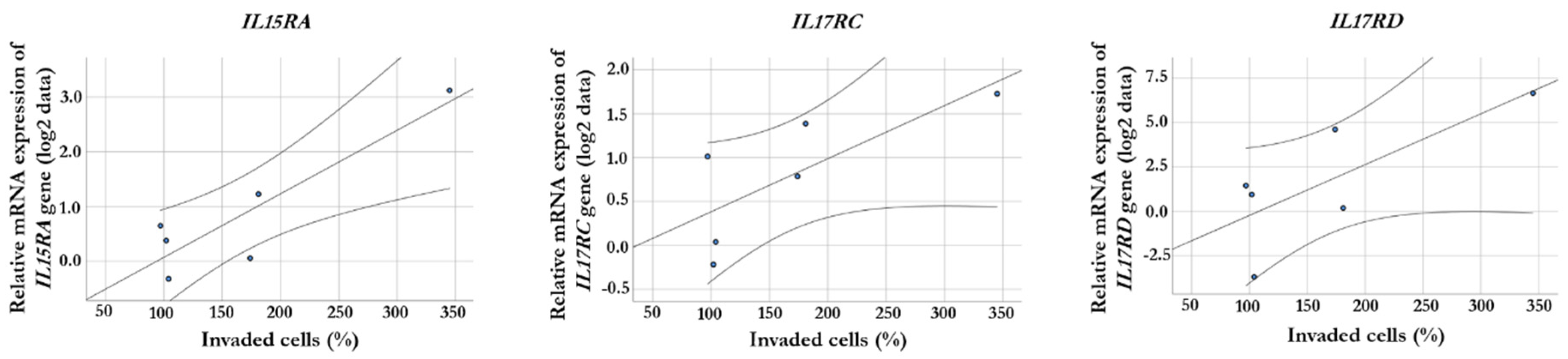
2.3. Correlation between gene expression and invasiveness
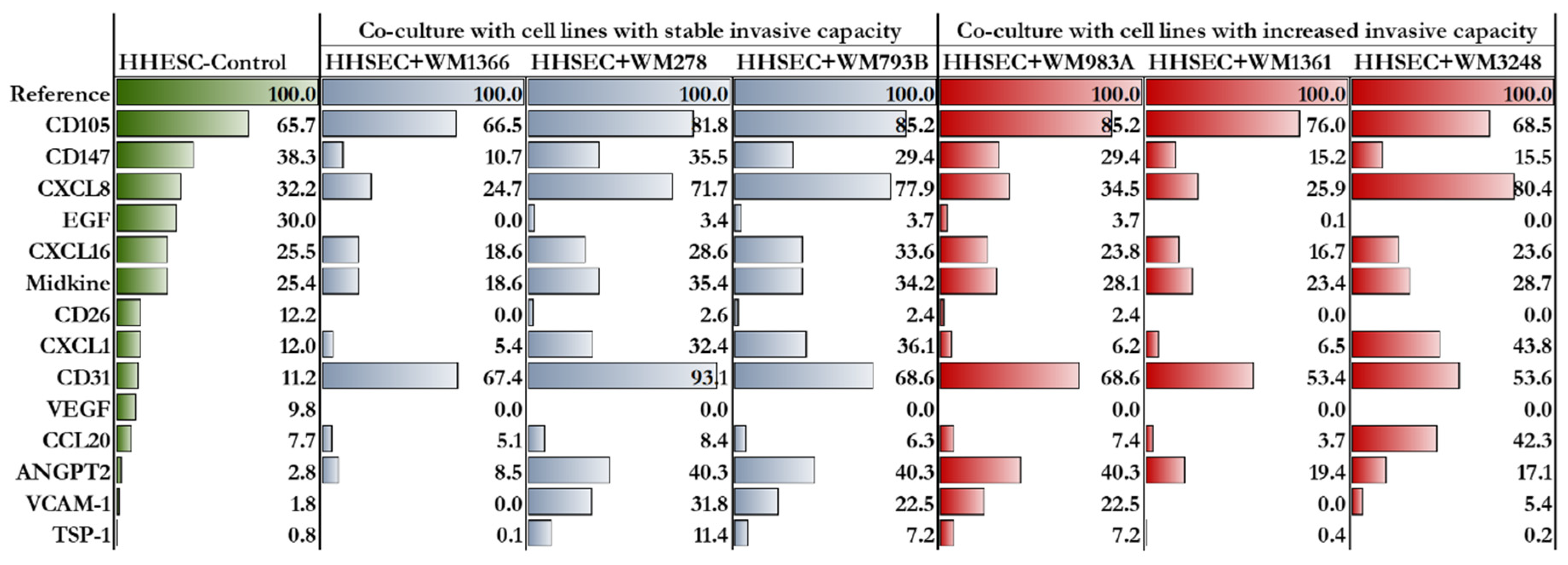
2.4. Proteome profile of HHSECs
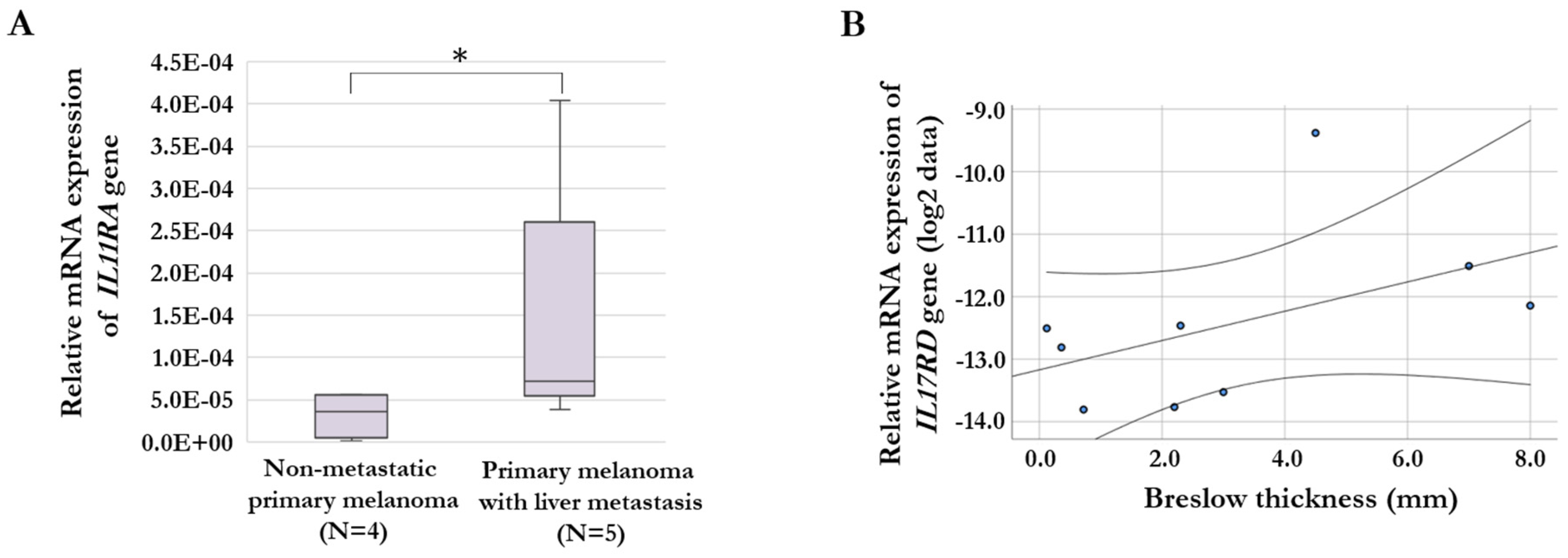
2.5. Gene expression of chemokine- and cytokine receptors in melanoma tissue samples
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell lines and culturing
4.2. Melanoma tissue samples used for qRT-PCR
4.3. In vitro invasion assay
4.4. Co-culturing of melanoma cell lines and endothelial cells
4.5. Real-time quantitative PCR analysis
4.6. Protein Expression Analysis
4.7. Statistical analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, X.; Lupardus, P.; Laporte, S.L.; Garcia, K.C. Structural biology of shared cytokine receptors. Annu Rev Immunol 2009, 27, 29–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talmadge, J.E.; Fidler, I.J. AACR centennial series: the biology of cancer metastasis: historical perspective. Cancer Res 2010, 70, 5649–5669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cucanic, O.; Farnsworth, R.H.; Stacker, S.A. The cellular and molecular mediators of metastasis to the lung. Growth Factors 2022, 40, 119–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paget, S. The distribution of secondary growths in cancer of the breast. 1889. Cancer Metastasis Rev 1989, 8, 98–101. [Google Scholar]
- Peinado, H.; Zhang, H.; Matei, I.R.; Costa-Silva, B.; Hoshino, A.; Rodrigues, G.; Psaila, B.; Kaplan, R.N.; Bromberg, J.F.; Kang, Y.; et al. Pre-metastatic niches: organ-specific homes for metastases. Nat Rev Cancer 2017, 17, 302–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerashchenko, T.S.; Schegoleva, A.A.; Khozyainova, A.A.; Choinzonov, E.L.; Denisov, E.V. Metastasis prevention: How to catch metastatic seeds. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer 2023, 1878, 188867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obenauf, A.C.; Massague, J. Surviving at a distance: organ specific metastasis. Trends Cancer 2015, 1, 76–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Signore, A.; Chianelli, M.; Bei, R.; Oyen, W.; Modesti, A. Targeting cytokine/chemokine receptors: a challenge for molecular nuclear medicine. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2003, 30, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muller, A.; Homey, B.; Soto, H.; Ge, N.; Catron, D.; Buchanan, M.E.; McClanahan, T.; Murphy, E.; Yuan, W.; Wagner, S.N.; et al. Involvement of chemokine receptors in breast cancer metastasis. Nature 2001, 410, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, D.X.; Bos, P.D.; Massague, J. Metastasis: from dissemination to organ-specific colonization. Nat Rev Cancer 2009, 9, 274–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amos, S.E.; Choi, Y.S. The Cancer Microenvironment: Mechanical Challenges of the Metastatic Cascade. Front Bioeng Biotechnol 2021, 9, 625859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Floros, T.; Tarhini, A.A. Anticancer Cytokines: Biology and Clinical Effects of Interferon-alpha2, Interleukin (IL)-2, IL-15, IL-21, and IL-12. Semin Oncol 2015, 42, 539–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ugurel, S.; Rohmel, J.; Ascierto, P.A.; Flaherty, K.T.; Grob, J.J.; Hauschild, A.; Larkin, J.; Long, G.V.; Lorigan, P.; McArthur, G.A.; et al. Survival of patients with advanced metastatic melanoma: the impact of novel therapies-update 2017. Eur J Cancer 2017, 83, 247–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damsky, W.E.; Rosenbaum, L.E.; Bosenberg, M. Decoding melanoma metastasis. Cancers (Basel) 2010, 3, 126–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kastelan, S.; Mrazovac Zimak, D.; Ivankovic, M.; Markovic, I.; Gverovic Antunica, A. Liver metastasis in uveal melanoma - treatment options and clinical outcome. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed) 2022, 27, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, D.; George, J.; Aucoin, D.; Bower, J.; Burrell, S.; Gilbert, R.; Bower, N. The Pathogenesis and Clinical Management of Cutaneous Melanoma: An Evidence-Based Review. J Med Imaging Radiat Sci 2019, 50, 460–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsilimigras, D.I.; Brodt, P.; Clavien, P.A.; Muschel, R.J.; D'Angelica, M.I.; Endo, I.; Parks, R.W.; Doyle, M.; de Santibanes, E.; Pawlik, T.M. Liver metastases. Nat Rev Dis Primers 2021, 7, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeLeve, L.D.; Maretti-Mira, A.C. Liver Sinusoidal Endothelial Cell: An Update. Semin Liver Dis 2017, 37, 377–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poisson, J.; Lemoinne, S.; Boulanger, C.; Durand, F.; Moreau, R.; Valla, D.; Rautou, P.E. Liver sinusoidal endothelial cells: Physiology and role in liver diseases. J Hepatol 2017, 66, 212–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, A.L.; Qurashi, M.; Shetty, S. The Role of Sinusoidal Endothelial Cells in the Axis of Inflammation and Cancer Within the Liver. Front Physiol 2020, 11, 990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, A.M.; Ma, B.; Taylor, D.L.; Griffith, L.; Wells, A. Liver metastases: Microenvironments and ex-vivo models. Exp Biol Med (Maywood) 2016, 241, 1639–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendt, M.; Cardier, J.E. Activation of the CXCR4 chemokine receptor enhances biological functions associated with B16 melanoma liver metastasis. Melanoma Res 2017, 27, 300–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neumann, K.; Erben, U.; Kruse, N.; Wechsung, K.; Schumann, M.; Klugewitz, K.; Scheffold, A.; Kuhl, A.A. Chemokine Transfer by Liver Sinusoidal Endothelial Cells Contributes to the Recruitment of CD4+ T Cells into the Murine Liver. PLoS One 2015, 10, e0123867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babicki, S.; Arndt, D.; Marcu, A.; Liang, Y.; Grant, J.R.; Maciejewski, A.; Wishart, D.S. Heatmapper: web-enabled heat mapping for all. Nucleic Acids Res 2016, 44, W147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whiteman, D.C.; Pavan, W.J.; Bastian, B.C. The melanomas: a synthesis of epidemiological, clinical, histopathological, genetic, and biological aspects, supporting distinct subtypes, causal pathways, and cells of origin. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res 2011, 24, 879–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damsky, W.E.; Theodosakis, N.; Bosenberg, M. Melanoma metastasis: new concepts and evolving paradigms. Oncogene 2014, 33, 2413–2422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Gupta, B.; Wong, G.Y.M. Prognostic circulating proteomic biomarkers in colorectal liver metastases. Comput Struct Biotechnol J 2023, 21, 2129–2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitsel, Y.; Cooke, T.; Sotirchos, V.; Sofocleous, C.T. Colorectal Cancer Liver Metastases: Genomics and Biomarkers with Focus on Local Therapies. Cancers (Basel) 2023, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, E.; Croce, M.; Reggiani, F.; Schinzari, G.; Ambrosio, M.; Gangemi, R.; Tortora, G.; Pfeffer, U.; Amaro, A. Uveal Melanoma Metastasis. Cancers (Basel) 2021, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karami Fath, M.; Azargoonjahromi, A.; Jafari, N.; Mehdi, M.; Alavi, F.; Daraei, M.; Mohammadkhani, N.; Mueller, A.L.; Brockmueller, A.; Shakibaei, M.; et al. Exosome application in tumorigenesis: diagnosis and treatment of melanoma. Med Oncol 2022, 39, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendas, G.; Borsig, L. Cancer cell adhesion and metastasis: selectins, integrins, and the inhibitory potential of heparins. Int J Cell Biol 2012, 2012, 676731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reymond, N.; d'Agua, B.B.; Ridley, A.J. Crossing the endothelial barrier during metastasis. Nat Rev Cancer 2013, 13, 858–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strilic, B.; Offermanns, S. Intravascular Survival and Extravasation of Tumor Cells. Cancer Cell 2017, 32, 282–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gassmann, P.; Haier, J.; Schluter, K.; Domikowsky, B.; Wendel, C.; Wiesner, U.; Kubitza, R.; Engers, R.; Schneider, S.W.; Homey, B.; et al. CXCR4 regulates the early extravasation of metastatic tumor cells in vivo. Neoplasia 2009, 11, 651–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceausu, R.A.; Cimpean, A.M.; Gaje, P.; Gurzu, S.; Jung, I.; Raica, M. CD105/Ki67 double immunostaining expression in liver metastasis from colon carcinoma. Rom J Morphol Embryol 2011, 52, 613–616. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Zhai, Z.; Liu, D.; Zhong, X.; Meng, X.; Yang, Q.; Liu, J.; Li, H. CD105 promotes hepatocarcinoma cell invasion and metastasis through VEGF. Tumour Biol 2015, 36, 737–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vidal-Vanaclocha, F.; Fantuzzi, G.; Mendoza, L.; Fuentes, A.M.; Anasagasti, M.J.; Martin, J.; Carrascal, T.; Walsh, P.; Reznikov, L.L.; Kim, S.H.; et al. IL-18 regulates IL-1beta-dependent hepatic melanoma metastasis via vascular cell adhesion molecule-1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2000, 97, 734–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrascal, M.T.; Mendoza, L.; Valcarcel, M.; Salado, C.; Egilegor, E.; Telleria, N.; Vidal-Vanaclocha, F.; Dinarello, C.A. Interleukin-18 binding protein reduces b16 melanoma hepatic metastasis by neutralizing adhesiveness and growth factors of sinusoidal endothelium. Cancer Res 2003, 63, 491–497. [Google Scholar]
- Helfrich, I.; Edler, L.; Sucker, A.; Thomas, M.; Christian, S.; Schadendorf, D.; Augustin, H.G. Angiopoietin-2 levels are associated with disease progression in metastatic malignant melanoma. Clin Cancer Res 2009, 15, 1384–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augustin, H.G.; Koh, G.Y.; Thurston, G.; Alitalo, K. Control of vascular morphogenesis and homeostasis through the angiopoietin-Tie system. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2009, 10, 165–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul Pari, A.A.; Singhal, M.; Hubers, C.; Mogler, C.; Schieb, B.; Gampp, A.; Gengenbacher, N.; Reynolds, L.E.; Terhardt, D.; Geraud, C.; et al. Tumor Cell-Derived Angiopoietin-2 Promotes Metastasis in Melanoma. Cancer Res 2020, 80, 2586–2598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urosevic, J.; Blasco, M.T.; Llorente, A.; Bellmunt, A.; Berenguer-Llergo, A.; Guiu, M.; Canellas, A.; Fernandez, E.; Burkov, I.; Clapes, M.; et al. ERK1/2 Signaling Induces Upregulation of ANGPT2 and CXCR4 to Mediate Liver Metastasis in Colon Cancer. Cancer Res 2020, 80, 4668–4680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bentebibel, S.E.; Diab, A. Cytokines in the Treatment of Melanoma. Curr Oncol Rep 2021, 23, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dranoff, G. Cytokines in cancer pathogenesis and cancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer 2004, 4, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Margolin, K. Cytokines in cancer immunotherapy. Cancers (Basel) 2011, 3, 3856–3893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ardolino, M.; Hsu, J.; Raulet, D.H. Cytokine treatment in cancer immunotherapy. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 19346–19347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Li, A.; Tian, Y.; Wu, J.D.; Liu, Y.; Li, T.; Chen, Y.; Han, X.; Wu, K. The CXCL8-CXCR1/2 pathways in cancer. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 2016, 31, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuo, Y.; Raimondo, M.; Woodward, T.A.; Wallace, M.B.; Gill, K.R.; Tong, Z.; Burdick, M.D.; Yang, Z.; Strieter, R.M.; Hoffman, R.M.; et al. CXC-chemokine/CXCR2 biological axis promotes angiogenesis in vitro and in vivo in pancreatic cancer. Int J Cancer 2009, 125, 1027–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Nannuru, K.C.; Sadanandam, A.; Varney, M.L.; Singh, R.K. CXCR1 and CXCR2 enhances human melanoma tumourigenesis, growth and invasion. Br J Cancer 2009, 100, 1638–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, F.M.; Li, J. A small-molecule antagonist of CXCR1 and CXCR2 inhibits cell proliferation, migration and invasion in melanoma via PI3K/AKT pathway. Med Clin (Barc) 2019, 152, 425–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bie, Y.; Ge, W.; Yang, Z.; Cheng, X.; Zhao, Z.; Li, S.; Wang, W.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Yin, Z.; et al. The Crucial Role of CXCL8 and Its Receptors in Colorectal Liver Metastasis. Dis Markers 2019, 2019, 8023460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Wen, M.; Pan, D.; Lin, X.; Mo, J.; Dong, X.; Liao, S.; Ma, Y. IL-33/ST2 Axis Regulates Vasculogenic Mimicry via ERK1/2-MMP-2/9 Pathway in Melanoma. Dermatology 2019, 235, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, P.; Deng, S.; Ye, H.; Yu, X.; Deng, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, L.; Li, J.; Yu, Y.; Han, W. The IL-33/ST2 pathway suppresses murine colon cancer growth and metastasis by upregulating CD40 L signaling. Biomed Pharmacother 2020, 127, 110232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Davis, C.; Shah, S.; Hughes, D.; Ryan, J.C.; Altomare, D.; Pena, M.M. IL-33 promotes growth and liver metastasis of colorectal cancer in mice by remodeling the tumor microenvironment and inducing angiogenesis. Mol Carcinog 2017, 56, 272–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, X.; Wang, X.; Yang, Q.; Zhao, X.; Wen, W.; Li, G.; Lu, J.; Qin, W.; Qi, Y.; Xie, F.; et al. Tumoral expression of IL-33 inhibits tumor growth and modifies the tumor microenvironment through CD8+ T and NK cells. J Immunol 2015, 194, 438–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sotiriou, C.; Lacroix, M.; Lespagnard, L.; Larsimont, D.; Paesmans, M.; Body, J.J. Interleukins-6 and -11 expression in primary breast cancer and subsequent development of bone metastases. Cancer Lett 2001, 169, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putoczki, T.L.; Thiem, S.; Loving, A.; Busuttil, R.A.; Wilson, N.J.; Ziegler, P.K.; Nguyen, P.M.; Preaudet, A.; Farid, R.; Edwards, K.M.; et al. Interleukin-11 is the dominant IL-6 family cytokine during gastrointestinal tumorigenesis and can be targeted therapeutically. Cancer Cell 2013, 24, 257–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- To, S.Q.; Dmello, R.S.; Richards, A.K.; Ernst, M.; Chand, A.L. STAT3 Signaling in Breast Cancer: Multicellular Actions and Therapeutic Potential. Cancers (Basel) 2022, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, D.; Xu, L.; Liu, H.; Zhang, W.; Liu, W.; Liu, Y.; Fu, Q.; Xu, J. High expression of interleukin-11 is an independent indicator of poor prognosis in clear-cell renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Sci 2015, 106, 592–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamazumi, K.; Nakayama, T.; Kusaba, T.; Wen, C.Y.; Yoshizaki, A.; Yakata, Y.; Nagayasu, T.; Sekine, I. Expression of interleukin-11 and interleukin-11 receptor alpha in human colorectal adenocarcinoma; immunohistochemical analyses and correlation with clinicopathological factors. World J Gastroenterol 2006, 12, 317–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koroknai, V.; Szasz, I.; Jambor, K.; Balazs, M. Cytokine and Chemokine Receptor Patterns of Human Malignant Melanoma Cell Lines. Int J Mol Sci 2022, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szasz, I.; Koroknai, V.; Kiss, T.; Vizkeleti, L.; Adany, R.; Balazs, M. Molecular alterations associated with acquired resistance to BRAFV600E targeted therapy in melanoma cells. Melanoma Res 2019, 29, 390–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Cell line | Growth phase1 | Histologic subtype2 | BRAF mutation status3 | NRAS mutation status4 |
| WM793B | RGP/VGP | SSM | V600E | wt |
| WM1361 | VGP | SSM | wt | Q61L |
| WM278 | VGP | NM | V600E | wt |
| WM983A | VGP | n.a. | V600E | wt |
| WM1366 | VGP | n.a. | wt | Q61L |
| WM3248 | VGP | n.a. | V600E | wt |
| 1RGP: radial growth phase, VGP: vertical growth phase; 2SSM: superficial spreading melanoma, NM: nodular melanoma, n.a.: data not available; 3V: valine, E: glutamic acid, wt: wild-type; 4Q: glutamine, L: leucine | ||||
| Sample number | Gender1 | Age at initial diagnosis (years) | Location | Histological subtype2 | Breslow thickness (mm) | Ulceration |
| Primary melanoma with no metastasis3 | ||||||
| 1 | F | 64 | Extremities | SSM | 0.4 | No |
| 2 | M | 67 | Head | NM | 0.1 | No |
| 3 | M | 72 | Trunk | NM | 4.5 | No |
| 4 | M | 59 | Trunk | SSM | 0.7 | No |
| Primary melanoma with liver metastasis3 | ||||||
| 5 | M | 71 | Trunk | SSM | 2.3 | No |
| 6 | M | 40 | Extremities | NM | 3.0 | No |
| 7 | M | 69 | Trunk | SSM/NM | 8.0 | Yes |
| 8 | M | 63 | Trunk | SSM | 2.2 | No |
| 9 | F | 71 | Trunk | NM | 7.0 | Yes |
| 1F: female, M: male; 2SSM: superficial spreading melanoma, NM: nodular melanoma; 3Patients with at least 5-years follow-up period | ||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





