Submitted:
18 April 2023
Posted:
19 April 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Applications of omics technologies in forest plants
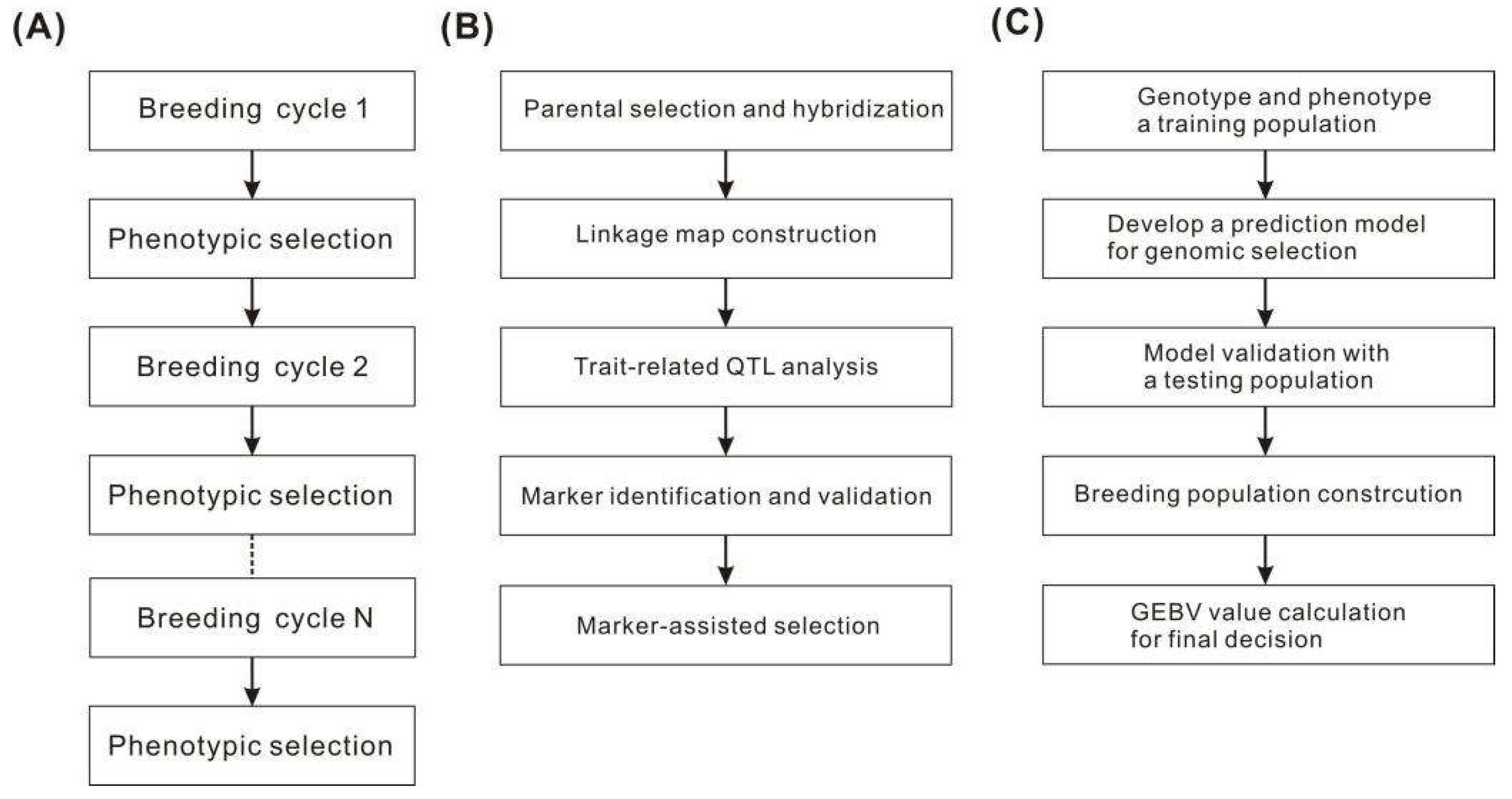
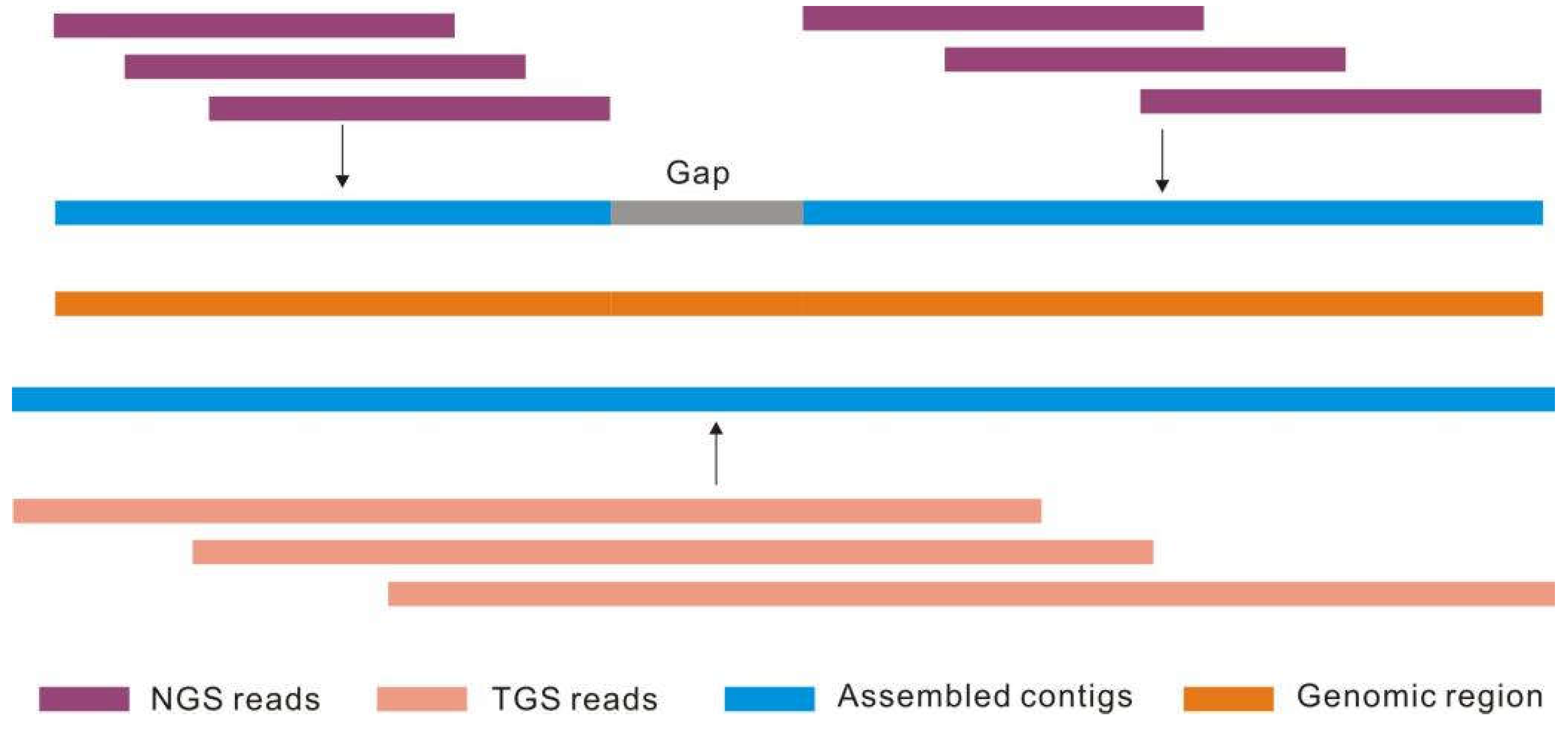
2.1. Genomics
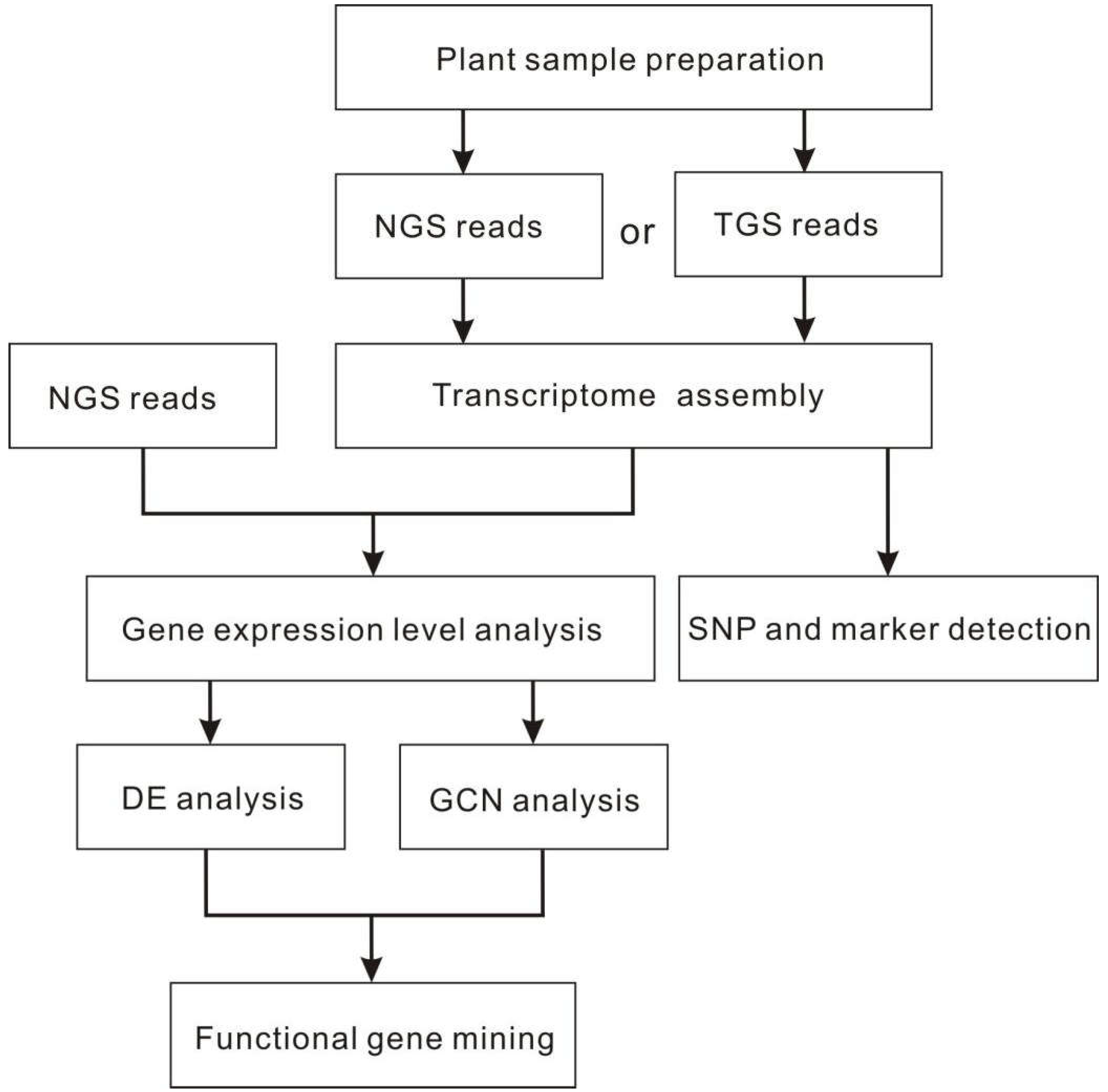
2.2. Transcriptomics
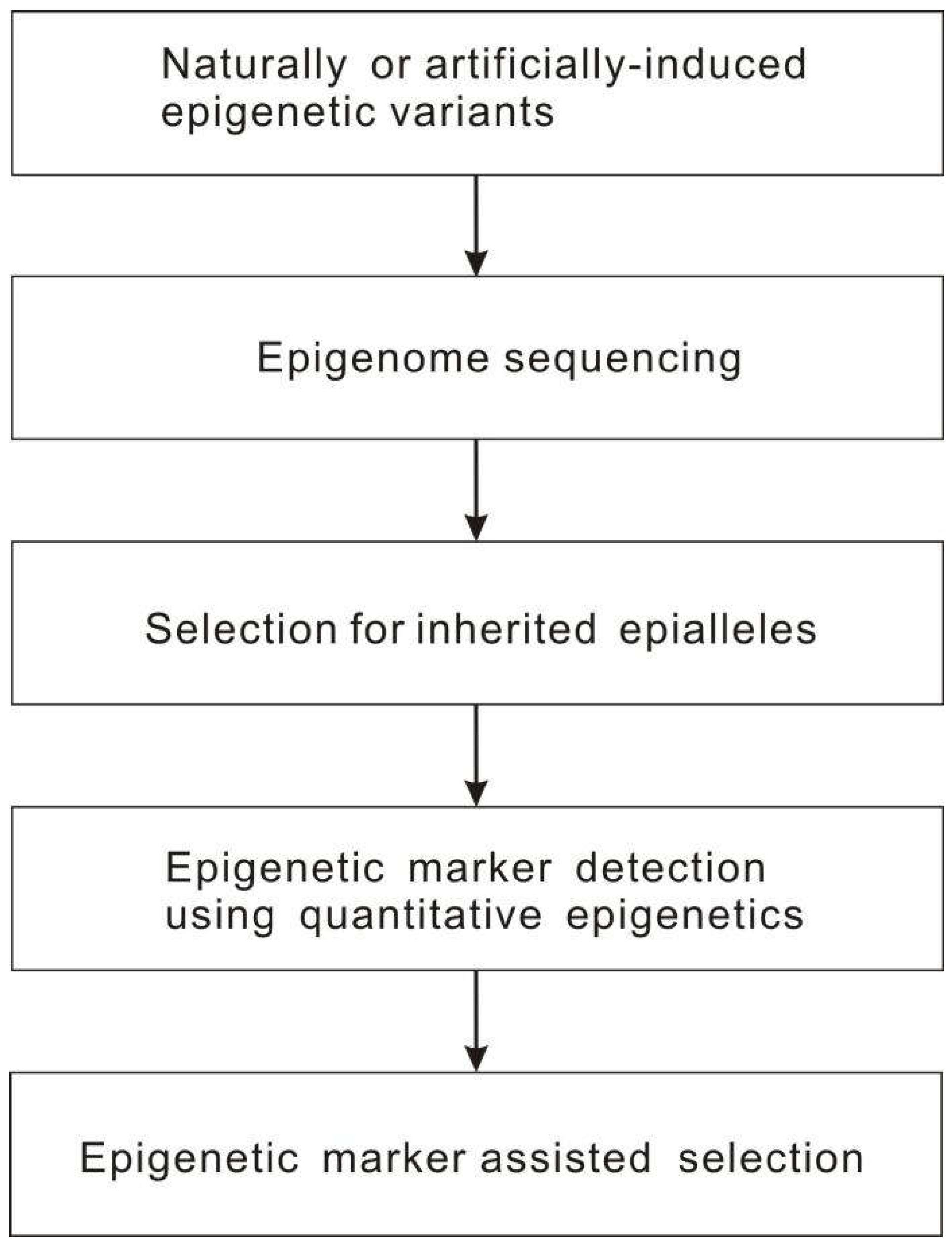
2.3. Epigenomics
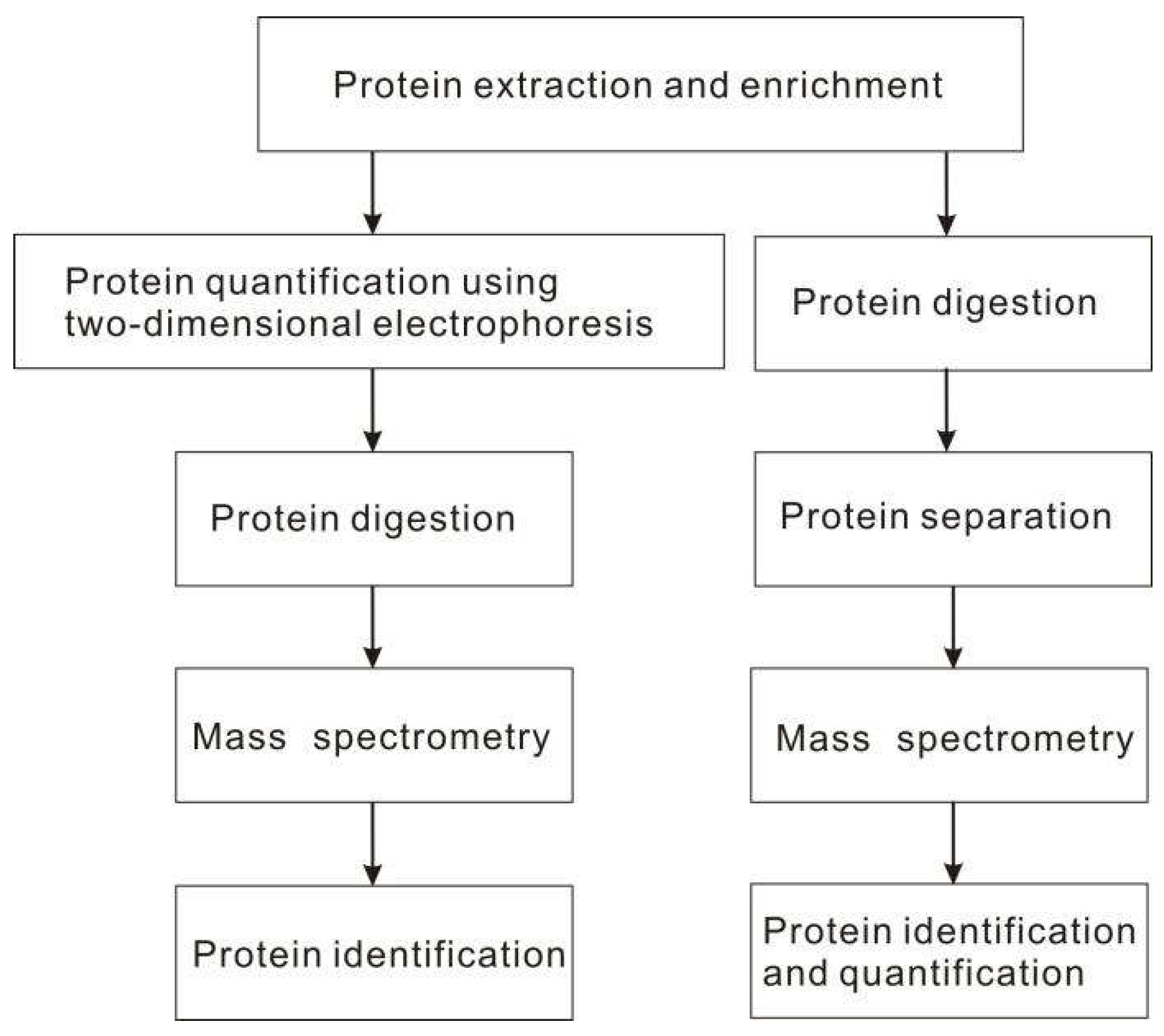
2.4. Proteomics
2.5. Metabolomics
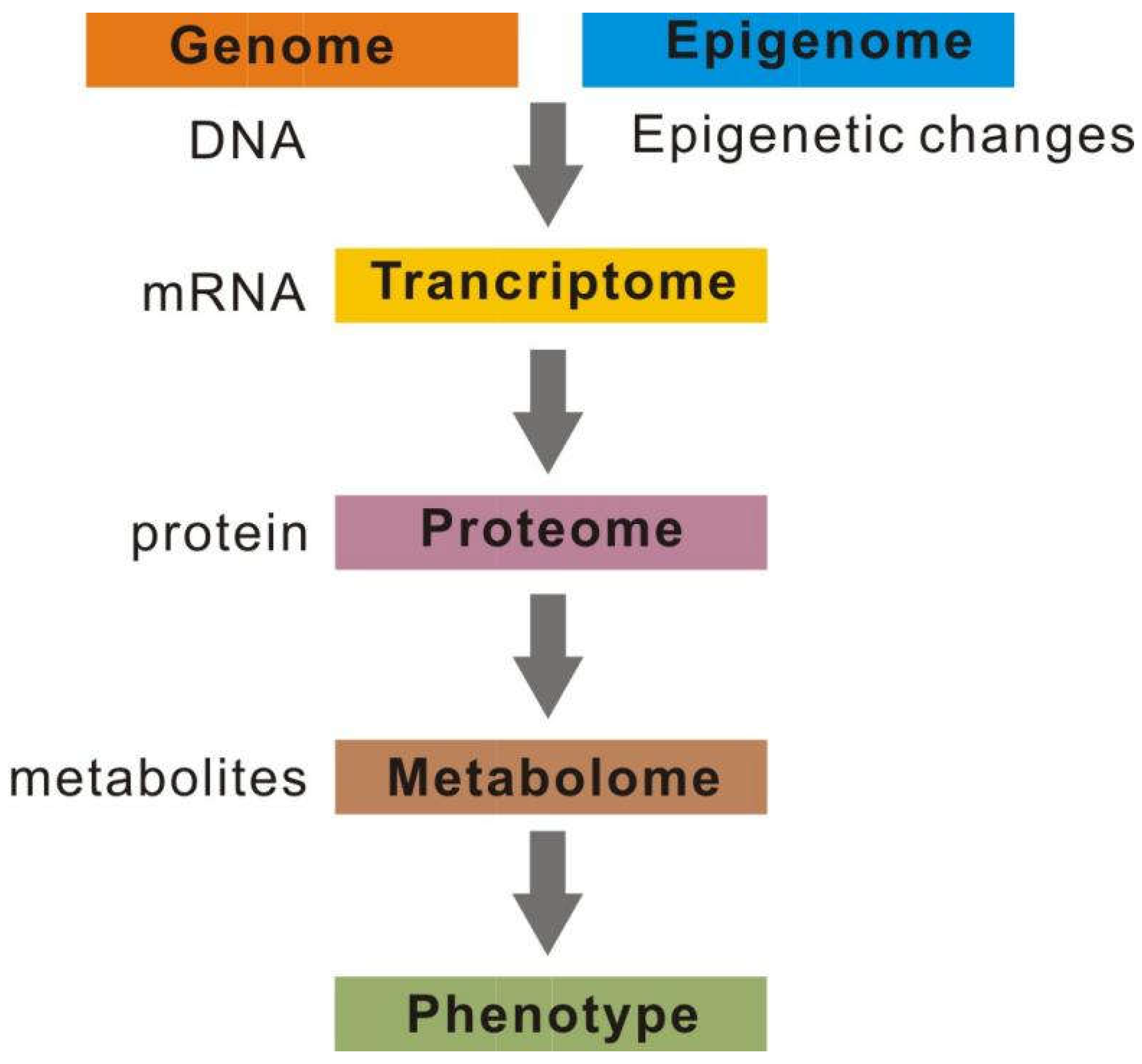
2.6. Multi-omics integration
3. Conclusions and prospects
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Keenan, R.J.; Reams, G.A.; Achard, F.; de Freitas, J.V.; Grainger, A.; Lindquist, E. Dynamics of global forest area: Results from the FAO Global Forest Resources Assessment 2015. For. Ecol. Manage. 2015, 352, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Nieto, A.P.; García-Llorente, M.; Iniesta-Arandia, I.; Martín-López, B. Mapping forest ecosystem services: from providing units to beneficiaries. Ecosyst. Serv. 2013, 4, 126–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, P.; Ashmore, M.R.; Black, H.I.; Burgess, P.J.; Evans, C.D.; Quine, T.A.; Thomson, A.M.; Hicks, k.; Orr, H.G. The role of ecosystems and their management in regulating climate, and soil, water and air quality. J. Appl. Ecol. 2013, 50, 812–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brockerhoff, E.G.; Barbaro, L.; Castagneyrol, B.; Forrester, D.I.; Gardiner, B.; González-Olabarria, J.R.; Lyver, P.O.; Meurisse, N.; Oxbrough, A.; Taki, H; et al. Forest biodiversity, ecosystem functioning and the provision of ecosystem services. Biodiversity Conserv. 2017, 26, 3005–3035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderegg, W.R.; Trugman, A.T.; Badgley, G.; Anderson, C.M.; Bartuska, A.; Ciais, P.; Cullenward, D.; Field, C.B.; Freeman, J.; Goetz, S.J.; et al. Climate-driven risks to the climate mitigation potential of forests. Science 2020, 368, eaaz7005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griscom, B.W.; Adams, J.; Ellis, P.W.; Houghton, R.A.; Lomax, G.; Miteva, D.A.; Schlesinger, W.H.; Shoch, D.; Siikamäki, J.V.; Smith, P.; et al. Natural climate solutions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2017, 114, 11645–11650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isabel, N.; Holliday, J.A.; Aitken, S.N. Forest genomics: Advancing climate adaptation, forest health, productivity, and conservation. Evol. Appl. 2020, 13, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirilenko, A.P.; Sedjo, R.A. Climate change impacts on forestry. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2007, 104, 19697–19702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betts, M.G.; Wolf, C.; Ripple, W.J.; Phalan, B.; Millers, K.A.; Duarte, A.; Butchart, S.H.M.; Levi, T. Global forest loss disproportionately erodes biodiversity in intact landscapes. Nature 2017, 547, 441–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curtis, P.G.; Slay, C.M.; Harris, N.L.; Tyukavina, A.; Hansen, M.C. Classifying drivers of global forest loss. Science 2018, 361, 1108–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trumbore, S.; Brando, P.; Hartmann, H. Forest health and global change. Science 2015, 349, 814–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koskela, J.; Vinceti, B.; Dvorak, W.; Bush, D.; Dawson, I.K.; Loo, J.; Kjaer, E.D.; Navarro, C.; Padolina, C.; Bordács, S.; et al. Utilization and transfer of forest genetic resources: A global review. For. Ecol. Manage. 2014, 333, 22–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebedev, V.G.; Lebedeva, T.N.; Chernodubov, A.I.; Shestibratov, K.A. Genomic selection for forest tree improvement: Methods, achievements and perspectives. Forests 2020, 11, 1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickmann, D; Isebrands, J. ; Eckenwalder, J.; Richardson, J. Poplar culture in North America. NRC Research Press: Ottawa, ON, Canada, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Dorman, K.W. The genetics of breeding southern pines. Agricultural handbook 471. USDA Forest Service, Washington, DC, 1976.
- Lee, S.J. Improving the timber quality of Sitka spruce through selection and breeding. Forestry 1999, 72, 123–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eldridge, K.; Davidson, J.; Harwood, C.; van Wyk, G. Eucalypt domestication and breeding. Clarendon Press: Oxford, UK, 1994.
- Lelu-Walter, M.A.; Pâques, L.E. Simplified and improved somatic embryogenesis of hybrid larches (Larix × eurolepis and Larix × marschlinsii). Perspectives for breeding. Ann. For. Sci. 2009, 66, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmar, S.; Ballesta, P.; Ali, M.; Mora-Poblete, F. Achievements and challenges of genomics-assisted breeding in forest trees: From marker-assisted selection to genome editing. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribaut, J.M.; Hoisington, D. Marker-assisted selection: new tools and strategies. Trends Plant Sci. 1998, 3, 236–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collard, B.C.; Mackill, D.J. Marker-assisted selection: an approach for precision plant breeding in the twenty-first century. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B 2008, 363, 557–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collard, B.C.; Jahufer, M.Z.Z.; Brouwer, J.B.; Pang, E.C.K. An introduction to markers, quantitative trait loci (QTL) mapping and marker-assisted selection for crop improvement: the basic concepts. Euphytica 2005, 142, 169–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crossa, J.; Pérez-Rodríguez, P.; Cuevas, J.; Montesinos-López, O.; Jarquín, D.; de Los Campos, G.; Burgueño, J.; González-Camacho, J. M.; Pérez-Elizalde, S.; Beyene, Y.; et al. Genomic selection in plant breeding: methods, models, and perspectives. In Trends Plant Sci.; 2017; Volume 22, pp. 961–975. [Google Scholar]
- Heffner, E.L.; Sorrells, M.E.; Jannink, J.L. Genomic selection for crop improvement. Crop Sci. 2009, 49, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meuwissen, T.H.; Hayes, B.J.; Goddard, M. Prediction of total genetic value using genome-wide dense marker maps. Genetics 2001, 157, 1819–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desta, Z.A.; Ortiz, R. Genomic selection: genome-wide prediction in plant improvement. Trends Plant Sci. 2014, 19, 592–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuskan, G.A.; Difazio, S.; Jansson, S.; Bohlmann, J.; Grigoriev, I.; Hellsten, U.; Putnam, N.; Ralph, S.; Rombauts, S.; Salamov, A.; et al. The genome of black cottonwood, Populus trichocarpa (Torr. & Gray). Science 2006, 313, 1596–1604. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mackay, J.; Dean, J.F.; Plomion, C.; Peterson, D.G.; Cánovas, F.M.; Pavy, N.; Ingvarsson, P.K.; Savolainen, O.; Guevara, M.A.; Fluch, S.; et al. Towards decoding the conifer giga-genome. Plant Mol. Biol. 2012, 80, 555–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nystedt, B.; Street, N.R.; Wetterbom, A.; Zuccolo, A.; Lin, Y.C.; Scofield, D.G.; Vezzi, F.; Delhomme, N.; Giacomello, S.; Alexeyenko, A.; et al. The Norway spruce genome sequence and conifer genome evolution. Nature 2013, 497, 579–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, H.; Winefield, C.; Bombarely, A.; Prentis, P.; Waterhouse, P. Tools and strategies for long-read sequencing and de novo assembly of plant genomes. Trends Plant Sci. 2019, 24, 700–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michael, T.P.; VanBuren, R. Building near-complete plant genomes. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2020, 54, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Shang, L.; Zhu, Q.H.; Fan, L.; Guo, L. Twenty years of plant genome sequencing: Achievements and challenges. Trends Plant Sci. 2022, 27, 391–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Wang, X.; Wang, G.; Cui, P.; Wu, S.; Ai, C.; Hu, N.; Li, A.; He, B.; Shao, X.; et al. The nearly complete genome of Ginkgo biloba illuminates gymnosperm evolution. Nat. Plants 2021, 7, 748–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, X.; Gou, J.; Liao, Q.; Li, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Bi, G.; Li, C.; Du, R.; Wang, X.; Sun, T.; et al. The Taxus genome provides insights into paclitaxel biosynthesis. Nat. Plants 2021, 7, 1026–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Wang, X.; Liu, X.; Zhu, X.; Li, Z.; Chu, H.; Wang, Q.; Lou, Q.; Cai, B.; Yang, Y.; et al. Chromosome-level genome of Himalayan yew provides insights into the origin and evolution of the paclitaxel biosynthetic pathway. Mol. Plant 2021, 14, 1199–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, C.; Xie, Y.H.; Li, Z.; Liu, Y.J.; Sun, X.M.; Li, J.J.; Quan, W.P.; Zeng, Q.Y.; Van de Peer, Y.; Zhang, S.G. The Larix kaempferi genome reveals new insights into wood properties. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2022, 64, 1364–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, S.; Li, J.; Bo, W.; Yang, W.; Zuccolo, A.; Giacomello, S.; Chen, X.; Han, F.; Yang, J.; Song, Y.; et al. The Chinese pine genome and methylome unveil key features of conifer evolution. Cell 2022, 185, 204–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kersey, P.J. Plant genome sequences: past, present, future. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2019, 48, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Wang, J.P.; Liu, H.; Li, H.; Lin, Y.C.J.; Shi, R.; Yang, C.; Gao, J.; Zhou, C.; Li, Q.; et al. Hierarchical transcription factor and chromatin binding network for wood formation in Populus trichocarpa. Plant Cell 2019, 31, 602–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.; Zhou, C.; Li, D.; Li, S.; Lin, Y.C.J.; Wang, J.P.; Chiang, V.L.; Li, W. A PtrLBD39-mediated transcriptional network regulates tension wood formation in Populus trichocarpa. Plant Communications 2022, 3, 100250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, C.; Li, Q.; Yao, K.; Zhang, Y.; Meng, S.; Yin, W.; Xia, X. Populus trichocarpa PtNF-YA9, a multifunctional transcription factor, regulates seed germination, abiotic stress, plant growth and development in Arabidopsis. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- André, D.; Marcon, A.; Lee, K.C.; Goretti, D.; Zhang, B.; Delhomme, N.; Schmid, M.; Nilsson, O. FLOWERING LOCUS T paralogs control the annual growth cycle in Populus trees. Curr. Biol. 2022, 32, 2988–2996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, R.; Wang, C.T.; Ma, C.; Shevchenko, O.; Dye, S.J.; Puzey, J.R.; Etherington, E.; Sheng, X.; Meilan, R.; Strauss, S.H.; et al. Populus CEN/TFL1 regulates first onset of flowering, axillary meristem identity and dormancy release in Populus. Plant J. 2010, 62, 674–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.; Xin, H.; Gu, X.; Ma, J.; Li, L. Genome-wide identification and functional analysis of the Basic Helix-Loop-Helix (bHLH) transcription family reveals candidate PtFBH genes involved in the flowering process of Populus trichocarpa. Forests 2021, 12, 1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuai, P.; Liang, D.; Tang, S.; Zhang, Z.; Ye, C.Y.; Su, Y.; Xia, X.; Yin, W. Genome-wide identification and functional prediction of novel and drought-responsive lincRNAs in Populus trichocarpa. J. Exp. Bot. 2014, 65, 4975–4983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, X.; Wang, S.; Zhao, X.; Gao, N.; Wang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Wu, E.; Jiang, C.; Cheng, Y.; Wu, W.; et al. Role of lncRNAs in cis- and trans-regulatory responses to salt in Populus trichocarpa. Plant J. 2022, 110, 978–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Lin, Y.C.J.; Wang, P.; Zhang, B.; Li, M.; Chen, S.; Shi, R.; Tunlaya-Anukit, S.; Liu, X.; Wang, Z.; et al. The AREB1 transcription factor influences histone acetylation to regulate drought responses and tolerance in Populus trichocarpa. Plant Cell 2019, 31, 663–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Y.; Han, Y.; Jin, Q.; Lin, Y.; Cai, Y. Comparative genomic analysis of the GRF genes in Chinese pear (Pyrus bretschneideri Rehd), poplar (Populous), grape (Vitis vinifera), Arabidopsis and rice (Oryza sativa). Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, H.; Movahedi, A.; Liu, G.; Li, Y.; Liu, S.; Yu, C.; Chen, Y.; Zhong, F.; Zhang, J. Comprehensive analysis of carotenoid cleavage dioxygenases gene family and its expression in response to abiotic stress in poplar. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennetzen, J.L. Transposable element contributions to plant gene and genome evolution. Plant Mol. Biol. 2020, 42, 251–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Tian, Z.; Hans, C.S.; Laten, H.M.; Cannon, S.B.; Jackson, S.A.; Shoemaker, R.C.; Ma, J. Evolutionary conservation, diversity and specificity of LTR-retrotransposons in flowering plants: Insights from genome-wide analysis and multi-specific comparison. Plant J. 2010, 63, 584–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingvarsson, P.K.; Hvidsten, T.R.; Street, N.R. Towards integration of population and comparative genomics in forest trees. New Phytol. 2016, 212, 338–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Sun, S.; Ding, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yue, X.; Du, X.; Wei, Q.; Fan, G.; Sun, H.; Lou, Y.; et al. Analysis of 427 genomes reveals moso bamboo population structure and genetic basis of property traits. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 5466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salojärvi, J.; Smolander, O.P.; Nieminen, K.; Rajaraman, S.; Safronov, O.; Safdari, P.; Lamminmäki, A.; Immanen, J.; Lan, T.; Tanskanen, J.; et al. Genome sequencing and population genomic analyses provide insights into the adaptive landscape of silver birch. Nat. Genet. 2017, 49, 904–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davey, J.W.; Hohenlohe, P.A.; Etter, P.D.; Boone, J.Q.; Catchen, J.M.; Blaxter, M.L. Genome-wide genetic marker discovery and genotyping using next-generation sequencing. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2011, 12, 499–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caballero, M.; Lauer, E.; Bennett, J.; Zaman, S.; McEvoy, S.; Acosta, J.; Jackson, C.; Townsend, L.; Eckert, A.; Whetten, R.W.; et al. Toward genomic selection in Pinus taeda: Integrating resources to support array design in a complex conifer genome. Appl. Plant Sci. 2021, 9, e11439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varas-Myrik, A.; Sepúlveda-Espinoza, F.; Fajardo, A.; Alarcón, D.; Toro-Núñez, Ó.; Castro-Nallar, E.; Hasbún, R. Predicting climate change-related genetic offset for the endangered southern South American conifer Araucaria araucana. For. Ecol. Manage. 2022, 504, 119856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goto, S.; Kajiya-Kanegae, H.; Ishizuka, W.; Kitamura, K.; Ueno, S.; Hisamoto, Y.; Kudoh, H.; Yasugi, M.; Nagano, A.J.; Iwata, H. Genetic mapping of local adaptation along the altitudinal gradient in Abies sachalinensis. Tree Genet. Genomes 2017, 13, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuentes-Utrilla, P.; Goswami, C.; Cottrell, J.E.; Pong-Wong, R.; Law, A.; A’Hara, S.W.; Lee, S.J.; Woolliams, J.A. QTL analysis and genomic selection using RADseq derived markers in Sitka spruce: the potential utility of within family data. Tree Genet. Genomes 2017, 13, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, N.; Zhang, M.; Xiao, Y.; Han, D.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yi, F.; Zhu, T.; Ma, W.; Fan, E.; et al. Construction of a high-density genetic map and QTL mapping of leaf traits and plant growth in an interspecific F1 population of Catalpa bungei × Catalpa duclouxii Dode. BMC Plant Biol. 2019, 19, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayakodi, M.; Schreiber, M.; Stein, N.; Mascher, M. Building pan-genome infrastructures for crop plants and their use in association genetics. DNA Res. 2021, 28, dsaa030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxena, R.K.; Edwards, D.; Varshney, R.K. Structural variations in plant genomes. Briefings Funct. Genomics 2014, 13, 296–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Bayer, P.E.; Batley, J.; Edwards, D. Current status of structural variation studies in plants. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2021, 19, 2153–2163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Della Coletta, R.; Qiu, Y.; Ou, S.; Hufford, M.B.; Hirsch, C.N. How the pan-genome is changing crop genomics and improvement. Genome Biol. 2021, 22, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Tian, Z.; Lai, J.; Huang, X. Plant pan-genomics and its applications. Mol. Plant 2023, 16, 168–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinosio, S.; Giacomello, S.; Faivre-Rampant, P.; Taylor, G.; Jorge, V.; Le Paslier, M.C.; Zaina, G.; Bastien, C.; Cattonaro, F.; Marroni, F.; et al. Characterization of the poplar pan-genome by genome-wide identification of structural variation. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 2706–2719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lovell, J.T.; Bentley, N.B.; Bhattarai, G.; Jenkins, J.W.; Sreedasyam, A.; Alarcon, Y.; Bock, C.; Beth Boston, L.; Carlson, J.; Cervantes, K.; et al. Four chromosome scale genomes and a pan-genome annotation to accelerate pecan tree breeding. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doğan, E.S.; Liu, C. Three-dimensional chromatin packing and positioning of plant genomes. Nat. Plants 2018, 4, 521–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniell, H.; Lin, C.S.; Yu, M.; Chang, W.J. Chloroplast genomes: diversity, evolution, and applications in genetic engineering. Genome Biol. 2016, 17, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maliga, P. Engineering the plastid and mitochondrial genomes of flowering plants. Nat. Plants 2022, 8, 996–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Wang, T.; He, X.; Cai, X.; Lin, R.; Liang, J.; Wu, J.; King, G.; Wang, X. BRAD V3.0: an upgraded Brassicaceae database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, D1432–D1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tello-Ruiz, M.K.; Naithani, S.; Gupta, P.; Olson, A.; Wei, S.; Preece, J.; Jiao, Y.; Wang, B.; Chougule, K.; Garg, P.; et al. Gramene 2021: harnessing the power of comparative genomics and pathways for plant research. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D1452–D1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGettigan, P.A. Transcriptomics in the RNA-seq era. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2013, 17, 4–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Gerstein, M.; Snyder, M. RNA-Seq: a revolutionary tool for transcriptomics. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2009, 10, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagalakshmi, U.; Waern, K.; Snyder, M. RNA-Seq: a method for comprehensive transcriptome analysis. Curr. Protoc. Mol. Biol. 2010, 89, 4–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trapnell, C.; Roberts, A.; Goff, L.; Pertea, G.; Kim, D.; Kelley, D.R.; Pimentel, H.; Salzberg, S.L.; Rinn, J.L.; Pachter, L. Differential gene and transcript expression analysis of RNA-seq experiments with TopHat and Cufflinks. Nat. Protoc. 2012, 7, 562–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pertea, M.; Pertea, G.M.; Antonescu, C.M.; Chang, T.C.; Mendell, J.T.; Salzberg, S.L. StringTie enables improved reconstruction of a transcriptome from RNA-seq reads. Nat. Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 290–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guttman, M.; Garber, M.; Levin, J.Z.; Donaghey, J.; Robinson, J.; Adiconis, X.; Fan, L.; Koziol, M.J. Gnirke, A.; Nusbaum, C. et al. Ab initio reconstruction of cell type–specific transcriptomes in mouse reveals the conserved multi-exonic structure of lincRNAs. Nat. Biotechnol. 2010, 28, 503–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haas, B.J.; Papanicolaou, A.; Yassour, M.; Grabherr, M.; Blood, P.D.; Bowden, J.; Couger, M.B.; Eccles, D.; Li, B.; Lieber, M.; et al. De novo transcript sequence reconstruction from RNA-seq using the Trinity platform for reference generation and analysis. Nat. Protoc. 2013, 8, 1494–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Y.; Wu, G.; Tang, J.; Luo, R.; Patterson, J.; Liu, S.; Huang, W.; He, G.; Gu, S.; Li, S.; et al. SOAPdenovo-Trans: de novo transcriptome assembly with short RNA-Seq reads. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 1660–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, M.H.; Zerbino, D.R.; Vingron, M.; Birney, E. Oases: robust de novo RNA-seq assembly across the dynamic range of expression levels. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 1086–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, J.A.; Wang, Z. Next-generation transcriptome assembly. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2011, 12, 671–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, D.; Cao, H.X.; Li, C.; Humbeck, K.; Wang, W. Isoform sequencing and state-of-art applications for unravelling complexity of plant transcriptomes. Genes 2018, 9, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Zhang, H.; Kohnen, M.V.; Prasad, K.V.; Gu, L.; Reddy, A.S. Analysis of transcriptome and epitranscriptome in plants using PacBio Iso-Seq and nanopore-based direct RNA sequencing. Front. Genet. 2019, 10, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shumate, A.; Wong, B.; Pertea, G.; Pertea, M. Improved transcriptome assembly using a hybrid of long and short reads with StringTie. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2022, 18, e1009730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishima, K.; Hirakawa, H.; Iki, T.; Fukuda, Y.; Hirao, T.; Tamura, A.; Takahashi, M. Comprehensive collection of genes and comparative analysis of full-length transcriptome sequences from Japanese larch (Larix kaempferi) and Kuril larch (Larix gmelinii var. japonica). BMC Plant Biol. 2022, 22, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, X.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, J.; Zhou, J.; Jiao, Z.; Wang, B.; Zhuge, Q. Full-length transcriptome characterization and comparative analysis of Chosenia arbutifolia. Forests 2022, 13, 543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Xiao, M.; Li, J.; Zhao, Q.; Wang, M.; Zhu, Z. Transcriptome Analysis of CYP450 Family Members in Fritillaria cirrhosa D. Don and Profiling of Key CYP450s Related to Isosteroidal Alkaloid Biosynthesis. Genes 2023, 14, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.; Wang, Z.; Li, M.; Su, Y.; Wang, T. First multi-organ full-length transcriptome of tree fern Alsophila spinulosa highlights the stress-resistant and light-adapted genes. Front. Genet. 2022, 12, 2812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDermaid, A.; Monier, B.; Zhao, J.; Liu, B.; Ma, Q. Interpretation of differential gene expression results of RNA-seq data: review and integration. Briefings Bioinf. 2019, 20, 2044–2054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, M.D.; McCarthy, D.J.; Smyth, G.K. edgeR: a Bioconductor package for differential expression analysis of digital gene expression data. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 139–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Tibshirani, R. Finding consistent patterns: a nonparametric approach for identifying differential expression in RNA-Seq data. Stat. Methods Med. Res. 2013, 22, 519–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, N.; Rivero, R.M.; Shulaev, V.; Blumwald, E.; Mittler, R. Abiotic and biotic stress combinations. New Phytol. 2014, 203, 32–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhu, J.; Gong, Z.; Zhu, J.K. Abiotic stress responses in plants. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2022, 23, 104–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Liu, Z.; Feng, H.; Yang, J.; Li, C. Characterization of the gene expression profile response to drought stress in Populus ussuriensis using PacBio SMRT and Illumina Sequencing. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23(7), 3840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovalchuk, A.; Zeng, Z.; Ghimire, R.P.; Kivimäenpää, M.; Raffaello, T.; Liu, M.; Mukrimin, M.; Kasanen, R.; Sun, H.; Julkunen-Tiitto, R.; et al. Dual RNA-seq analysis provides new insights into interactions between Norway spruce and necrotrophic pathogen Heterobasidion annosum sl. BMC Plant Biol. 2019, 19, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klepikova, A.V.; Penin, A.A. Gene expression maps in plants: Current state and prospects. Plants 2019, 8, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serin, E.A.; Nijveen, H.; Hilhorst, H.W.; Ligterink, W. Learning from co-expression networks: possibilities and challenges. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langfelder, P.; Horvath, S. WGCNA: an R package for weighted correlation network analysis. BMC Bioinf. 2008, 9, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.J.; Chen, X.; Song, Y.T.; Zhang, G.F.; Zhou, X.Q.; Que, S.P.; Mao, F.; Pervaiz, T.; Lin, J.X.; Li, Y.; et al. MADS-box transcription factors MADS11 and DAL1 interact to mediate the vegetative-to-reproductive transition in pine. Plant Physiol. 2021, 187, 247–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Xie, M.; Zhao, W.; Yan, P.; Wang, Y.; Gu, Y.; Jiang, T.; Qu, G. WGCNA reveals genes associated with lignification in the secondary stages of wood formation. Forests 2023, 14, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francisco, F.R.; Aono, A.H.; da Silva, C.C.; Gonçalves, P.S.; Scaloppi Junior, E.J.; Le Guen, V.; Fritsche-Neto, R.; Souza, L.M.; de Souza, A.P. Unravelling rubber tree growth by integrating GWAS and biological network-based approaches. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 768589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Tong, S.; Ma, T.; Xi, Z.; Liu, J. Chromosome-level genome assembly of Sichuan pepper provides insights into apomixis, drought tolerance, and alkaloid biosynthesis. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2021, 21, 2533–2545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ovens, K.; Eames, B.F.; McQuillan, I. Comparative analyses of gene co-expression networks: Implementations and applications in the study of evolution. Front. Genet. 2021, 12, 695399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younessi-Hamzekhanlu, M.; Gailing, O. Genome-wide SNP markers accelerate perennial forest tree breeding rate for disease resistance through marker-assisted and genome-wide selection. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 12315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rich-Griffin, C.; Stechemesser, A.; Finch, J.; Lucas, E.; Ott, S.; Schäfer, P. Single-cell transcriptomics: a high-resolution avenue for plant functional genomics. Trends Plant Sci. 2020, 25, 186–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Tong, S.; Jiang, Y.; Ai, F.; Feng, Y.; Zhang, J.; Gong, J.; Qin, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, Y.; et al. Transcriptional landscape of highly lignified poplar stems at single-cell resolution. Genome Biol. 2021, 22, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burgess, D.J. Spatial transcriptomics coming of age. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2019, 20, 317–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giacomello, S. A new era for plant science: spatial single-cell transcriptomics. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2021, 60, 102041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S. Epigenomics of plant responses to environmental stress. Epigenomes 2018, 2, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, D.; Chaudhary, P.; Taunk, J.; Singh, C.K.; Sharma, S.; Singh, V. J.; Singh, D.; Chinnusamy, V.; Yadav, R.; Pal, M. Plant epigenomics for extenuation of abiotic stresses: challenges and future perspectives. J. Exp. Bot. 2021, 72, 6836–6855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amaral, J.; Ribeyre, Z.; Vigneaud, J.; Sow, M.D.; Fichot, R.; Messier, C.; Pinto, J.; Nolet, P.; Maury, S. Advances and promises of epigenetics for forest trees. Forests 2020, 11, 976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouil, Q.; Keniry, A. Latest techniques to study DNA methylation. Essays Biochem. 2019, 63, 639–648. [Google Scholar]
- Bartels, A.; Han, Q.; Nair, P.; Stacey, L.; Gaynier, H.; Mosley, M.; Huang, Q.Q.; Pearson, J.K.; Hsieh, T.F.; An, Y.Q.C.; et al. Dynamic DNA methylation in plant growth and development. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Mohapatra, T. Dynamics of DNA methylation and its functions in plant growth and development. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 596236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Ma, K.; Bo, W.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, D. Sex-specific DNA methylation and gene expression in andromonoecious poplar. Plant Cell Rep. 2012, 31, 1393–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sow, M.D.; Le Gac, A.L.; Fichot, R.; Lanciano, S.; Delaunay, A.; Le Jan, I.; Lesage-Descauses, M.C.; Citerne, S.; Caius, J.; Brunaud, V.; et al. RNAi suppression of DNA methylation affects the drought stress response and genome integrity in transgenic poplar. New Phytol. 2021, 232, 80–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, C.; Cheng, H.; Tian, S.; Liu, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhang, H.; Saqib, M.; Wei, H.; Wei, Z. DNA methylation and its effects on gene expression during primary to secondary growth in poplar stems. BMC genomics 2020, 21, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, D.; Zhou, K.; Yang, X.; Yang, Y.; Ma, Y.; Wang, Y. Crosstalk of DNA methylation triggered by pathogen in poplars with different resistances. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 4098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karemaker, I.D.; Vermeulen, M. Single-cell DNA methylation profiling: technologies and biological applications. Trends Biotechnol. 2018, 36, 952–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, C.M.; Henikoff, S. Histone variants: dynamic punctuation in transcription. Genes Dev. 2014, 28, 672–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, M.; Daujat, S.; Schneider, R. Lateral thinking: how histone modifications regulate gene expression. Trends Genet. 2016, 32, 42–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Thakur, J.K.; Prasad, M. Histone acetylation dynamics regulating plant development and stress responses. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2021, 78, 4467–4486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Cao, X.; Deng, X. Histone methylation in epigenetic regulation and temperature responses. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2021, 61, 102001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borg, M.; Jiang, D.; Berger, F. Histone variants take center stage in shaping the epigenome. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2021, 61, 101991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, S.; Zhang, Y. Profiling chromatin regulatory landscape: Insights into the development of ChIP-seq and ATAC-seq. Mol. Biomed. 2020, 1, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, D.; Chen, M.; Yang, X.; Bao, H.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Y. The intersection of non-coding RNAs contributes to forest trees’ response to abiotic stress. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 6365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yakovlev, I.A.; Fossdal, C.G.; Johnsen, Ø. MicroRNAs, the epigenetic memory and climatic adaptation in Norway spruce. New Phytol. 2010, 187, 1154–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalakouras, A.; Vlachostergios, D. Epigenetic approaches to crop breeding: current status and perspectives. J. Exp. Bot. 2021, 72, 5356–5371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- 131. Gahlaut, V; Zinta, G; Jaiswal, V; Kumar, S. Quantitative epigenetics: a new avenue for crop improvement. Epigenomes 2020, 4, 25. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, M.; Gao, Y.; Dominguez, A.A.; Qi, L.S. CRISPR technologies for precise epigenome editing. Nat. Cell Biol. 2021, 23, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuñez, J.K.; Chen, J.; Pommier, G.C.; Cogan, J.Z.; Replogle, J.M.; Adriaens, C.; Ramadoss, G.N.; Shi, Q.; Hung, K.L.; Samelson, A.J.; et al. Genome-wide programmable transcriptional memory by CRISPR-based epigenome editing. Cell 2021, 184, 2503–2519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Song, X.; Wei, L.; Liu, C.; Cao, X. Epigenetic regulation and epigenomic landscape in rice. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2016, 3, 309–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raju, S.K.K.; Shao, M.R.; Sanchez, R.; Xu, Y.Z.; Sandhu, A.; Graef, G.; Mackenzie, S. An epigenetic breeding system in soybean for increased yield and stability. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2018, 16, 1836–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Q.; Liu, S.; Yu, L.; Xiao, Y.; Zhang, S.; Wang, X.; Xu, Y.; Yu, H.; Li, Y.; Yang, J.; et al. RNA demethylation increases the yield and biomass of rice and potato plants in field trials. Nat. Biotechnol. 2021, 39, 1581–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Murillo, L.; Valencia-Lozano, E.; Priego-Ranero, N.A.; Cabrera-Ponce, J.L.; Duarte-Aké, F.P.; Vizuet-de-Rueda, J.C.; Rivera-Toro, D.M.; Herrera-Ubaldo, H.; de Folter, S.; Alvarez-Venegas, R. CRISPRa-mediated transcriptional activation of the SlPR-1 gene in edited tomato plants. Plant Sci. 2023, 329, 111617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aslam, B.; Basit, M.; Nisar, M.A.; Khurshid, M.; Rasool, M.H. Proteomics: technologies and their applications. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 2016, 55, 182–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mergner, J.; Kuster, B. Plant proteome dynamics. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2022, 73, 67–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conibear, A.C. Deciphering protein post-translational modifications using chemical biology tools. Nat. Rev. Chem. 2020, 4, 674–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Auerbach, D.; Thaminy, S.; Hottiger, M.O.; Stagljar, I. The post-genomic era of interactive proteomics: Facts and perspectives. Proteomics 2002, 2, 611–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Harmon, A.C. Advances in plant proteomics. Proteomics 2006, 6, 5504–5516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traversari, S.; Giovannelli, A.; Emiliani, G. Wood formation under changing environment: Omics approaches to elucidate the mechanisms driving the early-to-latewood transition in Conifers. Forests 2022, 13, 608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, D.; Zhang, J.; Xia, Y.; Kong, L.; OuYang, F.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, H.; Wang, J. Proteomic analysis of stress-related proteins and metabolic pathways in Picea asperata somatic embryos during partial desiccation. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2017, 15, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yang, J.; Zhou, W.; Dai, S. Exploring the diversity of plant proteome. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2021, 63, 1197–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mund, A.; Brunner, A.D.; Mann, M. Unbiased spatial proteomics with single-cell resolution in tissues. Mol. Cell 2022, 82, 2335–2349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zivy, M.; de Vienne, D. Proteomics: a link between genomics, genetics and physiology. Plant Mol. Biol. 2000, 44, 575–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kage, U.; Kumar, A.; Dhokane, D.; Karre, S.; Kushalappa, A.C. Functional molecular markers for crop improvement. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2016, 36, 917–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agregán, R.; Echegaray, N.; López-Pedrouso, M.; Aadil, R.M.; Hano, C.; Franco, D.; Lorenzo, J.M. Proteomic advances in cereal and vegetable crops. Molecules 2021, 26, 4924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodziewicz, P.; Chmielewska, K.; Sawikowska, A.; Marczak, Ł.; Łuczak, M.; Bednarek, P.; Mikołajczak, K.; Ogrodowicz, P.; Kuczyńska, A.; Krajewski, P.; et al. Identification of drought responsive proteins and related proteomic QTLs in barley. J. Exp. Bot. 2019, 70, 2823–2837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Yang, B.; Huang, R.; Suo, H.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, W.; Dai, X.; Zou, X.; Ou, L. Transcriptome- and proteome-wide association of a recombinant inbred line population revealed twelve core QTLs for four fruit traits in pepper (Capsicum annuum L.). Hortic. Res 2022, 9, uhac015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Lu, S.; Liu, K.; Wang, S.; Huang, L.; Guo, L. Proteomics: a powerful tool to study plant responses to biotic stress. Plant Methods 2019, 15, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorrin Novo, J.V. Proteomics and plant biology: contributions to date and a look towards the next decade. Expert Rev. Proteomics 2021, 18, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schauer, N.; Fernie, A.R. Plant metabolomics: towards biological function and mechanism. Trends Plant Sci. 2006, 11, 508–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourgaud, F.; Gravot, A.; Milesi, S.; Gontier, E. Production of plant secondary metabolites: a historical perspective. Plant Sci. 2001, 161, 839–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macel, M.; Van Dam, N.M.; Keurentjes, J.J. Metabolomics: the chemistry between ecology and genetics. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2010, 10, 583–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guijas, C.; Montenegro-Burke, J.R.; Warth, B.; Spilker, M.E.; Siuzdak, G. Metabolomics activity screening for identifying metabolites that modulate phenotype. Nat. Biotechnol. 2018, 36, 316–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, J.; Yang, L.; Zhang, D.; Shi, J. Plant metabolomics: an indispensable system biology tool for plant science. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagel, J.M.; Facchini, P.J. Plant metabolomics: analytical platforms and integration with functional genomics. Phytochem. Rev. 2008, 7, 479–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obata, T.; Fernie, A.R. The use of metabolomics to dissect plant responses to abiotic stresses. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2012, 69, 3225–3243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribbenstedt, A.; Ziarrusta, H.; Benskin, J.P. Development, characterization and comparisons of targeted and non-targeted metabolomics methods. PLoS One 2018, 13, e0207082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zenobi, R. Single-cell metabolomics: analytical and biological perspectives. Science 2013, 342, 1243259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C.; Fernie, A.R.; Luo, J. Exploring the diversity of plant metabolism. Trends Plant Sci. 2019, 24, 83–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Bohra, A.; Pandey, A.K.; Pandey, M.K.; Kumar, A. Metabolomics for plant improvement: status and prospects. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H. , Guo, L. , Zha, R., Gao, Z., Yu, F., & Wei, Q. (2022). Histological, metabolomic and transcriptomic analyses reveal mechanisms of cold acclimation of the Moso bamboo (Phyllostachys edulis) leaf. Tree Physiology 2022, 42, 2336–2352. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ren, S.; Ma, K.; Lu, Z.; Chen, G.; Cui, J.; Tong, P.; Wang, L.; Teng, N.; Jin, B. Transcriptomic and metabolomic analysis of the heat-stress response of Populus tomentosa Carr. Forests 2019, 10, 383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, C.; Li, L.; Yang, T.; Gui, M.; Li, X.; Zhang, F.; Zhao, Q.; Wu, Y. Transcriptomics integrated with widely targeted metabolomics reveals the cold resistance mechanism in Hevea brasiliensis. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 13, 1092411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soltis, N.E.; Kliebenstein, D.J. Natural variation of plant metabolism: genetic mechanisms, interpretive caveats, and evolutionary and mechanistic insights. Plant Physiol. 2015, 169, 1456–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, S.A.; Chibon, P.Y.; de Vos, R.C.; Schipper, B.A.; Walraven, E.; Beekwilder, J.; van Dijk, T.; Finkers, R.; Visser, R.G.F.; van de Weg, E.W.; et al. Genetic analysis of metabolites in apple fruits indicates an mQTL hotspot for phenolic compounds on linkage group 16. J. Exp. Bot. 2012, 63, 2895–2908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, W.; Du, Q.; Xiao, L.; Lv, C.; Quan, M.; Li, P.; Yao, L.; Song, F.; Zhang, D. Multi-omics analysis provides insights into genetic architecture of flavonoid metabolites in Populus. Ind. Crops Prod. 2021, 168, 113612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Yang, Y.; Huang, L.; Cui, X.; Liu, Y. From single-to multi-omics: future research trends in medicinal plants. Briefings Bioinf. 2023, 24, bbac485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jamil, I.N.; Remali, J.; Azizan, K.A.; Nor Muhammad, N.A.; Arita, M.; Goh, H.-H.; Aizat, W.M. Systematic multi-omics integration (MOI) approach in plant systems biology. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarazona, S.; Arzalluz-Luque, A.; Conesa, A. Undisclosed, unmet and neglected challenges in multi-omics studies. Nat. Comput. Sci. 2021, 1, 395–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanian, I.; Verma, S.; Kumar, S.; Jere, A.; Anamika, K. Multi-omics data integration, interpretation, and its application. Bioinf. Biol. Insights 2020, 14, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Drton, M.; Promislow, D.E.; Shojaie, A. CorDiffViz: an R package for visualizing multi-omics differential correlation networks. BMC bioinf. 2021, 22, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, D.; Bansal, G.; Narang, A.; Basak, T.; Abbas, T.; Dash, D. Integrating transcriptome and proteome profiling: Strategies and applications. Proteomics 2016, 16, 2533–2544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerrero-Sánchez, V.M.; Castillejo, M.Á.; López-Hidalgo, C.; Alconada, A.M.M.; Jorrín-Novo, J.V.; Rey, M.-D. Changes in the transcript and protein profiles of Quercus ilex seedlings in response to drought stress. J. Proteomics 2021, 243, 104263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pierre-Jean, M.; Deleuze, J.-F.; Le Floch, E.; Mauger, F. Clustering and variable selection evaluation of 13 unsupervised methods for multi-omics data integration. Briefings Bioinf. 2020, 21, 2011–2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pascual, J.; Cañal, M.J.; Escandon, M.; Meijon, M.; Weckwerth, W.; Valledor, L. Integrated physiological, proteomic, and metabolomic analysis of ultra violet (UV) stress responses and adaptation mechanisms in Pinus radiata. Mol. Cell. Proteomics 2017, 16, 485–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rai, A.; Saito, K.; Yamazaki, M. Integrated omics analysis of specialized metabolism in medicinal plants. Plant J. 2017, 90, 764–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obudulu, O.; Mähler, N.; Skotare, T.; Bygdell, J.; Abreu, I.N.; Ahnlund, M.; Gandla, M.L.; Petterle, A.; Moritz, T.; Hvidsten, T.R.; et al. A multi-omics approach reveals function of Secretory Carrier-Associated Membrane Proteins in wood formation of Populus trees. BMC genomics 2018, 19, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altman, T.; Travers, M.; Kothari, A.; Caspi, R.; Karp, P.D. A systematic comparison of the MetaCyc and KEGG pathway databases. BMC bioinf. 2013, 14, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Hidalgo, C.; Guerrero-Sanchez, V.M.; Gómez-Gálvez, I.; Sánchez-Lucas, R.; Castillejo-Sánchez, M.A.; Maldonado-Alconada, A.M.; Valledor, L.; Jorrin-Novo, J.V. A multi-omics analysis pipeline for the metabolic pathway reconstruction in the orphan species Quercus ilex. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoppi, J.; Guillaume, J.-F.; Neunlist, M.; Chaffron, S. MiBiOmics: an interactive web application for multi-omics data exploration and integration. BMC bioinf. 2021, 22, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Campbell, M.T.; Yeats, T.H.; Zheng, X.; Runcie, D.E.; Covarrubias-Pazaran, G.; Broeckling, C.; Yao, L.; Caffe-Treml, M.; Gutiérrez, L.; et al. Multi-omics prediction of oat agronomic and seed nutritional traits across environments and in distantly related populations. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2021, 134, 4043–4054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarazona, S.; Arzalluz-Luque, A.; Conesa, A. Undisclosed, unmet and neglected challenges in multi-omics studies. Nat. Comput. Sci. 2021, 1, 395–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).



