Submitted:
14 April 2023
Posted:
17 April 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
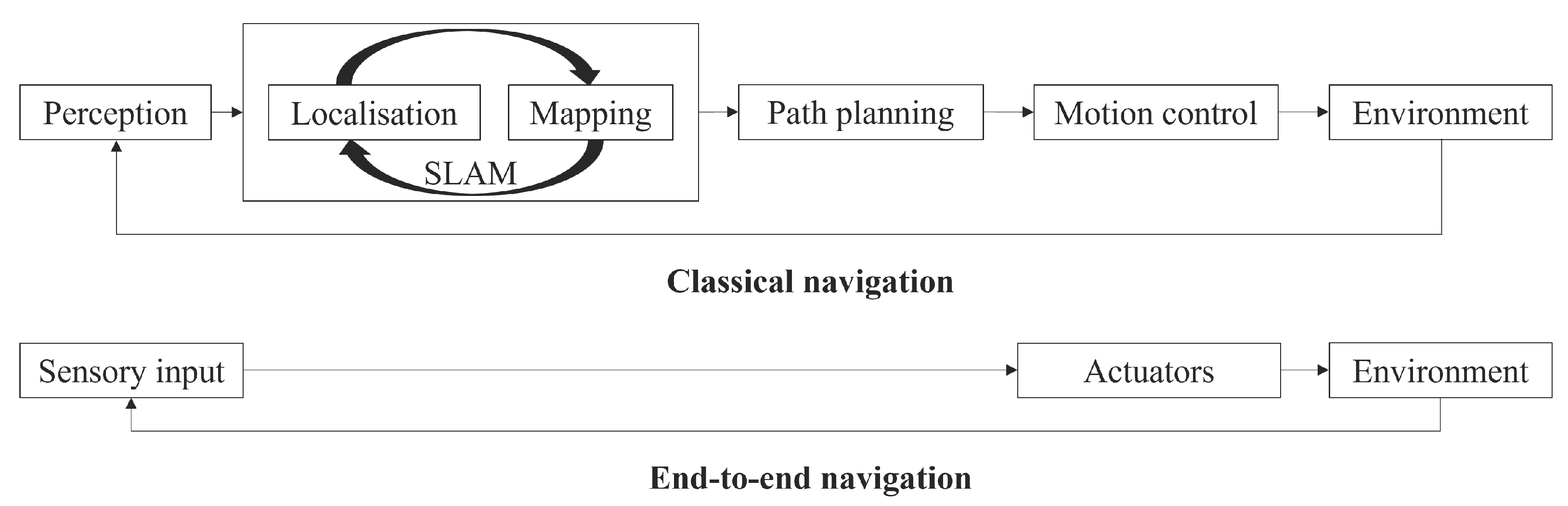
1. Introduction
- perception,
- localisation and mapping, and
- scene understanding.
2. Robot Environment Perception for Navigation
2.1. Vision and Ranging Sensors
2.1.1. Vision-based Sensor Types
2.1.2. Active Ranging Sensors
2.2. LiDAR and Camera Data Fusion
2.2.1. Dense Depth Prediction
2.2.2. Dense Depth from Monocular Camera and LiDAR Fusion
2.2.3. Dense Depth from Stereo Camera and LiDAR Fusion
2.2.4. Multimodal Object Detection
2.2.5. Multimodal Semantic Segmentation
2.2.6. Multimodal Instance Segmentation
3. Robot Scene Understanding for Navigation Planning
4. Mobile Robot Local Path Planning
5. Summary of the Current State-of-the-Art Techniques
6. Research Challenges and Future Directions in Unstructured Outdoor Environment Navigation
6.1. Research Challenges
6.2. Future Research Directions
7. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rubio, F.; Valero, F.; Llopis-Albert, C. A review of mobile robots: Concepts, methods, theoretical framework, and applications. International Journal of Advanced Robotic Systems 2019, 16, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, K.; Wang, C.; Cheng, J.; De Silva, C.W.; Meng, M.Q.H. Mobile robot path planning in dynamic environments: A survey. arXiv arXiv:2006.14195 2020.
- Quarles, N.; Kockelman, K.M.; Lee, J. America’s fleet evolution in an automated future. Research in Transportation Economics 2021, 90, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavel, M.I.; Tan, S.Y.; Abdullah, A. Vision-based autonomous vehicle systems based on deep learning: A systematic literature review. Applied Sciences 2022, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Yao, J.; Wang, R.; Liu, Z.; Ma, C.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, Y. Design of intelligent fire-fighting robot based on multi-sensor fusion and experimental study on fire scene patrol. Robotics and Autonomous Systems 2022, 154, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Kroemer, O.; Su, Z.; Veiga, F.F.; Kaboli, M.; Ritter, H.J. A review of tactile information: Perception and action through touch. IEEE Transactions on Robotics 2020, 36, 1619–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alatise, M.B.; Hancke, G.P. A review on challenges of autonomous mobile robot and sensor fusion methods. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 39830–39846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, D.; Haase-Schütz, C.; Rosenbaum, L.; Hertlein, H.; Glaeser, C.; Timm, F.; Wiesbeck, W.; Dietmayer, K. Deep multi-modal object detection and semantic segmentation for autonomous driving: Datasets, methods, and challenges. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems 2020, 22, 1341–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Yang, C.; Li, K.; Zhang, J. A forest point cloud real-time reconstruction method with single-line LiDAR based on visual-IMU fusion. Applied Sciences 2022, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.B.; Su, T.L.; Kong, J.L.; Bai, Y.T.; Miao, B.B.; Dou, C. State-of-the-art mobile intelligence: Enabling robots to move like humans by estimating mobility with artificial intelligence. Applied Sciences 2018, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Li, Y.; Zhao, C.; Yao, D.; Chen, G.; Sun, L.; Krajnik, T.; Yan, Z. 3D ToF LiDAR in mobile robotics: A review. arXiv arXiv:2202.11025 2022.
- Moon, J.; Lee, B.H. PDDL planning with natural language-based scene understanding for UAV-UGV cooperation. Applied Sciences 2019, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Rosenhahn, B.; Murino, V. Multimodal scene understanding: Algorithms, applications and deep learning; Academic Press: United Kingdom, 2019; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Sidibé, D.; Morel, O.; Mériaudeau, F. Deep multimodal fusion for semantic image segmentation: A survey. Image and Vision Computing 2021, 105, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Zhang, W.; Yu, R.; Zhang, Y. Motion planning for mobile robots—Focusing on deep reinforcement learning: A systematic review. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 69061–69081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janai, J.; Güney, F.; Behl, A.; Geiger, A.; others. Computer vision for autonomous vehicles: Problems, datasets and state of the art. Foundations and Trends® in Computer Graphics and Vision 2020, 12, 1–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Efros, A.A.; Hebert, M. Blocks world revisited: Image understanding using qualitative geometry and mechanics. In Proceedings of the 11th European Conference on Computer Vision, Heraklion, Crete, Greece, 5-11 September 2010; pp. 482–496. [Google Scholar]
- Kocić, J.; Jovičić, N.; Drndarević, V. Sensors and sensor fusion in autonomous vehicles. 26th Telecommunications Forum (TELFOR),Serbia, Belgrade, 20-, pp. 420–425. In Proceedings of the 26th Telecommunications Forum (TELFOR), Serbia, Belgrade, 20-21 November 2018; pp. 420–425. [Google Scholar]
- Muñoz-Bañón, M.Á.; Candelas, F.A.; Torres, F. Targetless camera-LiDAR calibration in unstructured environments. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 143692–143705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Cao, J.; Li, S.; Huang, Z.; Wang, J.; Liu, G. Map construction and path planning method for a mobile robot based on multi-sensor information fusion. Applied Sciences 2022, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Shen, J.; Cheng, M.M.; Shao, L. An iterative and cooperative top-down and bottom-up inference network for salient object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR); pp. 5968–5977.
- Santos, L.C.; Santos, F.N.; Pires, E.S.; Valente, A.; Costa, P.; Magalhães, S. Path planning for ground robots in agriculture: A short review. IEEE International Conference on Autonomous Robot Systems and Competitions (ICARSC), Ponta Delgada, Portugal, 15-16 April 2020; pp. 61–66. [Google Scholar]
- Fayyad, J.; Jaradat, M.A.; Gruyer, D.; Najjaran, H. Deep learning sensor fusion for autonomous vehicle perception and localization: A review. Sensors 2020, 20, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valada, A.; Oliveira, G.L.; Brox, T.; Burgard, W. Deep multispectral semantic scene understanding of forested environments using multimodal fusion. International Symposium on Experimental Robotics, Tokyo, Japan, 3-6 October 2016; pp. 465–477. [Google Scholar]
- Lei, X.; Zhang, Z.; Dong, P. Dynamic path planning of unknown environment based on deep reinforcement learning. Journal of Robotics 2018, 2018, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crespo, J.; Castillo, J.C.; Mozos, O.M.; Barber, R. Semantic information for robot navigation: A survey. Applied Sciences 2020, 10, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galvao, L.G.; Abbod, M.; Kalganova, T.; Palade, V.; Huda, M.N. Pedestrian and vehicle detection in autonomous vehicle perception systems—A review. Sensors 2021, 21, 1–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hewawasam, H.; Ibrahim, M.Y.; Appuhamillage, G.K. Past, present and future of path-planning algorithms for mobile robot navigation in dynamic environments. IEEE Open Journal of the Industrial Electronics Society 2022, 3, 353–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martini, M.; Cerrato, S.; Salvetti, F.; Angarano, S.; Chiaberge, M. Position-Agnostic Autonomous Navigation in Vineyards with Deep Reinforcement Learning. IEEE 18th International Conference on Automation Science and Engineering (CASE), 20-24 August 2022, pp. 477–484.
- Huang, Z.; Lv, C.; Xing, Y.; Wu, J. Multi-modal sensor fusion-based deep neural network for end-to-end autonomous driving with scene understanding. IEEE Sensors Journal 2020, 21, 11781–11790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamza, A. Deep reinforcement learning for mapless mobile robot navigation. Master’s thesis, Luleå University of Technology, Sweden, 2022.
- Carrasco, P.; Cuesta, F.; Caballero, R.; Perez-Grau, F.J.; Viguria, A. Multi-sensor fusion for aerial robots in industrial GNSS-denied environments. Applied Sciences 2021, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Wang, S.; Gu, D. DeepSLAM: A robust monocular SLAM system with unsupervised deep learning. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics 2020, 68, 3577–3587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguiar, A.; Santos, F.; Sousa, A.J.; Santos, L. FAST-FUSION: An improved accuracy omnidirectional visual odometry system with sensor fusion and GPU optimization for embedded low cost hardware. Applied Sciences 2019, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Brasch, N.; Wang, Y.; Navab, N.; Tombari, F. Structure-slam: Low-drift monocular slam in indoor environments. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters 2020, 5, 6583–6590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaffar, M.; Ehsan, S.; Stolkin, R.; Maier, K.M. Sensors, SLAM and long-term autonomy: A review. NASA/ESA Conference on Adaptive Hardware and Systems (AHS), United Kingdom, 6-9 August 2018, pp. 285–290.
- Sabattini, L.; Levratti, A.; Venturi, F.; Amplo, E.; Fantuzzi, C.; Secchi, C. Experimental comparison of 3D vision sensors for mobile robot localization for industrial application: Stereo-camera and RGB-D sensor. 12th International Conference on Control Automation Robotics & Vision (ICARCV), Guangzhou, China, 5-7 December 2012, pp. 823–828.
- Tölgyessy, M.; Dekan, M.; Chovanec, L.; Hubinskỳ, P. Evaluation of the azure kinect and its comparison to kinect v1 and kinect v2. Sensors 2021, 21, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evangelidis, G.D.; Hansard, M.; Horaud, R. Fusion of range and stereo data for high-resolution scene-modeling. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence 2015, 37, 2178–2192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glover, A.; Bartolozzi, C. Robust visual tracking with a freely-moving event camera. IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 24–28 September 2017, pp. 3769–3776.
- Gallego, G.; Delbrück, T.; Orchard, G.; Bartolozzi, C.; Taba, B.; Censi, A.; Leutenegger, S.; Davison, A.J.; Conradt, J.; Daniilidis, K.; others. Event-based vision: A survey. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence 2020, 44, 154–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, W.; Li, J.; Bhatta, M.; Shi, Y.; Baenziger, P.S.; Ge, Y. Wheat height estimation using LiDAR in comparison to ultrasonic sensor and UAS. Sensors 2018, 18, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moosmann, F.; Stiller, C. Velodyne slam. IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium,Baden-Baden, Germany, 5-9 June 2011, pp. 393–398.
- Li, K.; Li, M.; Hanebeck, U.D. Towards high-performance solid-state-lidar-inertial odometry and mapping. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters 2021, 6, 5167–5174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulton, C.V.; Yaacobi, A.; Cole, D.B.; Byrd, M.J.; Raval, M.; Vermeulen, D.; Watts, M.R. Coherent solid-state LIDAR with silicon photonic optical phased arrays. Optics letters 2017, 42, 4091–4094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behroozpour, B.; Sandborn, P.A.; Wu, M.C.; Boser, B.E. Lidar system architectures and circuits. IEEE Communications Magazine 2017, 55, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Zhang, L.; Yang, J.; Cao, C.; Wang, W.; Ran, Y.; Tan, Z.; Luo, M. A review of multi-sensor fusion slam systems based on 3D LIDAR. Remote Sensing 2022, 14, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yu, A.W.; Meng, T.; Caine, B.; Ngiam, J.; Peng, D.; Shen, J.; Lu, Y.; Zhou, D.; Le, Q.V. others. Deepfusion: LiDAR-camera deep fusion for multi-modal 3D object detection. IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), New Orleans, Louisiana, USA, 18-24 June 2022, pp. 17182–17191.
- Zheng, W.; Xie, H.; Chen, Y.; Roh, J.; Shin, H. PIFNet: 3D object detection using joint image and point cloud features for autonomous driving. Applied Sciences 2022, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Chen, R.; Chu, W.; Chen, L.; Tian, D.; Li, Y.; Cao, D. Deep learning for image and point cloud fusion in autonomous driving: A review. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems 2021, 23, 722–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Ang, M.H.; Karaman, S.; Rus, D. A general pipeline for 3D detection of vehicles. 2018 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Brisbane, Australia, 21-25 May 2018, pp. 3194–3200.
- Yang, Z.; Sun, Y.; Liu, S.; Shen, X.; Jia, J. Ipod: Intensive point-based object detector for point cloud. arXiv arXiv:1812.05276 2018.
- Qi, C.R.; Liu, W.; Wu, C.; Su, H.; Guibas, L.J. Frustum pointnets for 3D object detection from RGB-D data. IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18-23 June 2018, pp. 918–927.
- Shin, K.; Kwon, Y.P.; Tomizuka, M. Roarnet: A robust 3D object detection based on region approximation refinement. IEEE intelligent vehicles symposium (IV), Paris, France, 9-12 June 2019, pp. 2510–2515.
- Qi, C.R.; Su, H.; Mo, K.; Guibas, L.J. Pointnet: Deep learning on point sets for 3D classification and segmentation. IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 21-26 July 2017, pp. 652–660.
- Tran, D.; Bourdev, L.; Fergus, R.; Torresani, L.; Paluri, M. Learning spatiotemporal features with 3D convolutional networks. IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Santiago, Chile, 2015, pp. 4489–4497.
- Maturana, D.; Scherer, S. Voxnet: A 3D convolutional neural network for real-time object recognition. IEEE/RSJ international conference on intelligent robots and systems (IROS), Hamburg, Germany, 28 Sept-2 Oct 2015, pp. 922–928.
- Xu, D.; Anguelov, D.; Jain, A. Pointfusion: Deep sensor fusion for 3D bounding box estimation. IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 18-23 June 2018, pp. 244–253.
- Ku, J.; Mozifian, M.; Lee, J.; Harakeh, A.; Waslander, S.L. Joint 3D proposal generation and object detection from view aggregation. IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS),Madrid, Spain, 1-5 October 2018, pp. 1–8.
- Liang, M.; Yang, B.; Wang, S.; Urtasun, R. Deep continuous fusion for multi-sensor 3D object detection. 15th European conference on computer vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8-14 September 2018, pp. 641–656.
- Sindagi, V.A.; Zhou, Y.; Tuzel, O. Mvx-net: Multimodal voxelnet for 3D object detection. International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Montreal, Canada, 20-24 May 2019, pp. 7276–7282.
- Chen, X.; Ma, H.; Wan, J.; Li, B.; Xia, T. Multi-view 3D object detection network for autonomous driving. IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 21-26 July 2017, pp. 1907–1915.
- Geiger, A.; Lenz, P.; Stiller, C.; Urtasun, R. Vision meets robotics: The kitti dataset. The International Journal of Robotics Research 2013, 32, 1231–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, P.; Kretzschmar, H.; Dotiwalla, X.; Chouard, A.; Patnaik, V.; Tsui, P.; Guo, J.; Zhou, Y.; Chai, Y.; Caine, B. others. Scalability in perception for autonomous driving: Waymo open dataset. IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 13-19 June 2020, pp. 2446–2454.
- Geyer, J.; Kassahun, Y.; Mahmudi, M.; Ricou, X.; Durgesh, R.; Chung, A.S.; Hauswald, L.; Pham, V.H.; Mühlegg, M.; Dorn, S. ; others. A2d2: Audi autonomous driving dataset. arXiv arXiv:2004.06320 2020.
- Caesar, H.; Bankiti, V.; Lang, A.H.; Vora, S.; Liong, V.E.; Xu, Q.; Krishnan, A.; Pan, Y.; Baldan, G.; Beijbom, O. nuscenes: A multimodal dataset for autonomous driving. IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 13-19 June 2020, pp. 11621–11631.
- Cordts, M.; Omran, M.; Ramos, S.; Rehfeld, T.; Enzweiler, M.; Benenson, R.; Franke, U.; Roth, S.; Schiele, B. The cityscapes dataset for semantic urban scene understanding. IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27-30 June 2016, pp. 3213–3223.
- Ma, F.; Cavalheiro, G.V.; Karaman, S. Self-supervised sparse-to-dense: Self-supervised depth completion from lidar and monocular camera. International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Montreal, Canada, 20-24 May 2019, pp. 3288–3295.
- Ma, F.; Karaman, S. Sparse-to-dense: Depth prediction from sparse depth samples and a single image. IEEE international conference on robotics and automation (ICRA), Brisbane, Australia, 21-25 May 2018, pp. 4796–4803.
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27-30 June 2016, pp. 770–778.
- Cheng, X.; Wang, P.; Yang, R. Depth estimation via affinity learned with convolutional spatial propagation network. European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8-14 September 2018, pp. 103–119.
- Cheng, X.; Wang, P.; Guan, C.; Yang, R. CSPN++: Learning context and resource aware convolutional spatial propagation networks for depth completion. 34th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New York, USA, 7-12 February 2020, pp. 10615–10622.
- Cheng, X.; Zhong, Y.; Dai, Y.; Ji, P.; Li, H. Noise-aware unsupervised deep LiDAR-stereo fusion. IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, CA, USA, 15-20 June 2019, pp. 6339–6348.
- Jalal, A.S.; Singh, V. The state-of-the-art in visual object tracking. Informatica 2012, 36, 1–22. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, P.; Wang, X.; Wang, A.; Yan, Y.; Liu, W.; Huang, J.; Yuille, A. Weakly supervised region proposal network and object detection. 15th European conference on computer vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8-14 September 2018, pp. 352–368.
- Uijlings, J.R.; Van De Sande, K.E.; Gevers, T.; Smeulders, A.W. Selective search for object recognition. International Journal of Computer Vision 2013, 104, 154–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, M.; Li, S.; Yang, Y.; Zhu, F.; Zhao, Q.; Lu, L. SSPNet: Scale selection pyramid network for tiny person detection from UAV images. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters 2021, 19, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girshick, R. Fast R-CNN. IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Santiago, Chile, 7-13 December 2015, pp. 1440–1448.
- Ren, S.; He, K.; Girshick, R.; Sun, J. Faster R-CNN: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence 2015, 39, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Cho, J. Exploring a multimodal mixture-of-YOLOs framework for advanced real-time object detection. Applied Sciences 2020, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Girshick, R.; Arbeláez, P.; Malik, J. Learning rich features from RGB-D images for object detection and segmentation. 13th European conference on computer vision (ECCV), Zurich, Switzerland, 6-12 September 2014, pp. 345–360.
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv arXiv:1409.1556 2014.
- Zhou, Y.; Tuzel, O. Voxelnet: End-to-end learning for point cloud based 3D object detection. IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Salt Lake City, UT, USA,, 18-23 June 2018, pp. 4490–4499.
- Meyer, G.P.; Charland, J.; Hegde, D.; Laddha, A.; Vallespi-Gonzalez, C. Sensor fusion for joint 3D object detection and semantic segmentation. IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW), 16-17 June 2019, pp. 1–8.
- Meyer, G.P.; Laddha, A.; Kee, E.; Vallespi-Gonzalez, C.; Wellington, C.K. Lasernet: An efficient probabilistic 3D object detector for autonomous driving. IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, California, 15-20 June 2019, pp. 12677–12686.
- Guo, Z.; Huang, Y.; Hu, X.; Wei, H.; Zhao, B. A survey on deep learning based approaches for scene understanding in autonomous driving. Electronics 2021, 10, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoph, B.; Vasudevan, V.; Shlens, J.; Le, Q.V. Learning transferable architectures for scalable image recognition. IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18-23 June 2018, pp. 8697–8710.
- Valada, A.; Mohan, R.; Burgard, W. Self-supervised model adaptation for multimodal semantic segmentation. International Journal of Computer Vision 2020, 128, 1239–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caltagirone, L.; Bellone, M.; Svensson, L.; Wahde, M. LIDAR–camera fusion for road detection using fully convolutional neural networks. Robotics and Autonomous Systems 2019, 111, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, A.; Nießner, M. 3DMV: Joint 3D-multi-view prediction for 3D semantic scene segmentation. European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8-14 September 2018, pp. 452–468.
- Chiang, H.Y.; Lin, Y.L.; Liu, Y.C.; Hsu, W.H. A unified point-based framework for 3D segmentation. International Conference on 3D Vision (3DV), Québec, Canada,, 16-19 September 2019, pp. 155–163.
- Qi, C.R.; Yi, L.; Su, H.; Guibas, L.J. Pointnet++: Deep hierarchical feature learning on point sets in a metric space. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 2017, 30, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Jaritz, M.; Gu, J.; Su, H. Multi-view pointnet for 3D scene understanding. IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision Workshop (ICCVW), Seoul, Korea (South), 27-28 October 2019, pp. 1–9.
- Su, H.; Jampani, V.; Sun, D.; Maji, S.; Kalogerakis, E.; Yang, M.H.; Kautz, J. Splatnet: Sparse lattice networks for point cloud processing. IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18-23 June 2018, pp. 2530–2539.
- Hou, J.; Dai, A.; Nießner, M. 3D-SIS: 3D semantic instance segmentation of RGB-D scans. IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, CA, USA, 15-20 June 2019, pp. 4421–4430.
- Narita, G.; Seno, T.; Ishikawa, T.; Kaji, Y. Panopticfusion: Online volumetric semantic mapping at the level of stuff and things. IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Macau, China, 4-8 November 2019, pp. 4205–4212.
- Elich, C.; Engelmann, F.; Kontogianni, T.; Leibe, B. 3D bird’s-eye-view instance segmentation. 41st DAGM German Conference on Pattern Recognition, Dortmund, Germany, 10-13 September 2019, pp. 48–61.
- Comaniciu, D.; Meer, P. Mean shift: A robust approach toward feature space analysis. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence 2002, 24, 603–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kochanov, D.; Ošep, A.; Stückler, J.; Leibe, B. Scene flow propagation for semantic mapping and object discovery in dynamic street scenes. IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Daejeon, Korea, 9-14 October 2016, pp. 1785–1792.
- Yue, Y.; Zhao, C.; Li, R.; Yang, C.; Zhang, J.; Wen, M.; Wang, Y.; Wang, D. A hierarchical framework for collaborative probabilistic semantic mapping. IEEE international conference on robotics and automation (ICRA), Paris, France, 31 May - 31 August 2020, pp. 9659–9665.
- Rosinol, A.; Violette, A.; Abate, M.; Hughes, N.; Chang, Y.; Shi, J.; Gupta, A.; Carlone, L. Kimera: From SLAM to spatial perception with 3D dynamic scene graphs. The International Journal of Robotics Research 2021, 40, 1510–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Chang, Y.; Arias, F.H.; Nieto-Granda, C.; How, J.P.; Carlone, L. Kimera-multi: Robust, distributed, dense metric-semantic slam for multi-robot systems. IEEE Transactions on Robotics 2022, 38, 2022–2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, U.H.; Park, J.M.; Song, T.J.; Kim, J.H. 3-D scene graph: A sparse and semantic representation of physical environments for intelligent agents. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics 2019, 50, 4921–4933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosinol, A.; Gupta, A.; Abate, M.; Shi, J.; Carlone, L. 3D dynamic scene graphs: Actionable spatial perception with places, objects, and humans. arXiv arXiv:2002.06289 2020.
- Liu, H.; Yao, M.; Xiao, X.; Cui, H. A hybrid attention semantic segmentation network for unstructured terrain on Mars. Acta Astronautica 2023, 204, 492–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humblot-Renaux, G.; Marchegiani, L.; Moeslund, T.B.; Gade, R. Navigation-oriented scene understanding for robotic autonomy: learning to segment driveability in egocentric images. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters 2022, 7, 2913–2920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badrinarayanan, V.; Kendall, A.; Cipolla, R. Segnet: A deep convolutional encoder-decoder architecture for image segmentation. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence 2017, 39, 2481–2495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, T.; Kothandaraman, D.; Chandra, R.; Sathyamoorthy, A.J.; Weerakoon, K.; Manocha, D. GA-Nav: Efficient terrain segmentation for robot navigation in unstructured outdoor environments. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters 2022, 7, 8138–8145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wigness, M.; Eum, S.; Rogers, J.G.; Han, D.; Kwon, H. A RUGD dataset for autonomous navigation and visual perception in unstructured outdoor environments. IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Macau, China, 4-8 November 2019, pp. 5000–5007.
- Jiang, P.; Osteen, P.; Wigness, M.; Saripalli, S. RELLIS-3D dataset: Data, benchmarks and analysis. IEEE international conference on robotics and automation (ICRA), Xi’an, China, May 31 - June 4 2021, pp. 1110–1116.
- Ma, L.; Stückler, J.; Kerl, C.; Cremers, D. Multi-view deep learning for consistent semantic mapping with RGB-D cameras. IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 24-28 September 2017, pp. 598–605.
- Hazirbas, C.; Ma, L.; Domokos, C.; Cremers, D. Fusenet: Incorporating depth into semantic segmentation via fusion-based cnn architecture. 13th Asian Conference on Computer Vision, Taipei, Taiwan, 20-24 November 2016, pp. 213–228.
- Zhang, J.; Henein, M.; Mahony, R.; Ila, V. VDO-SLAM: A visual dynamic object-aware SLAM system. arXiv arXiv:2005.11052 2020.
- Maturana, D.; Scherer, S. Voxnet: A 3D convolutional neural network for real-time object recognition. IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Hamburg, Germany, Sept 28 - Oct 2 2015, pp. 922–928.
- Huang, J.; You, S. Point cloud labeling using 3D convolutional neural network. 23rd International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR), Cancun, Mexico, 4-8 December 2016, pp. 2670–2675.
- LeCun, Y.; Bottou, L.; Bengio, Y.; Haffner, P. Gradient-based learning applied to document recognition. Proceedings of the IEEE 1998, 86, 2278–2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Yu, F.; Zeng, A.; Chang, A.X.; Savva, M.; Funkhouser, T. Semantic scene completion from a single depth image. IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, Hawaii, 21-26 July 2017, pp. 1746–1754.
- Riegler, G.; Osman Ulusoy, A.; Geiger, A. OctNet: Learning deep 3D representations at high resolutions. IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, Hawaii, 21-26 July 2017, pp. 3577–3586.
- Tatarchenko, M.; Park, J.; Koltun, V.; Zhou, Q.Y. Tangent convolutions for dense prediction in 3D. IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, Utah, USA, 18-23 June 2018, pp. 3887–3896.
- Wang, F.; Yang, Y.; Wu, Z.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, W. Real-time semantic segmentation of point clouds based on an attention mechanism and a sparse tensor. Applied Sciences 2023, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Qi, Z.; Fuxin, L. Pointconv: Deep convolutional networks on 3D point clouds. IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, CA, USA, 15-20 June 2019, pp. 9621–9630.
- Hua, B.S.; Tran, M.K.; Yeung, S.K. Pointwise convolutional neural networks. IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18-23 June 2018, pp. 984–993.
- Zamorski, M.; Zięba, M.; Klukowski, P.; Nowak, R.; Kurach, K.; Stokowiec, W.; Trzciński, T. Adversarial autoencoders for compact representations of 3D point clouds. Computer Vision and Image Understanding 2020, 193, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.; Li, J.; Huang, H.; Du, L.; Zhang, X. 3D recurrent neural networks with context fusion for point cloud semantic segmentation. 15th European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8-14 September 2018, pp. 403–417.
- Wang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Liu, Z.; Sarma, S.E.; Bronstein, M.M.; Solomon, J.M. Dynamic graph cnn for learning on point clouds. ACM Transactions on Graphics 2019, 38, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, X.; Liao, R.; Jia, J.; Fidler, S.; Urtasun, R. 3D graph neural networks for RGB-D semantic segmentation. IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, Italy, 22-29 October 2017, pp. 5199–5208.
- Landrieu, L.; Simonovsky, M. Large-scale point cloud semantic segmentation with superpoint graphs. IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18-23 June 2018, pp. 4558–4567.
- Li, J.; Chen, B.M.; Lee, G.H. SO-Net: Self-organizing network for point cloud analysis. IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18-23 June 2018, pp. 9397–9406.
- Thrun, S. Probabilistic robotics. Communications of the ACM 2002, 45, 52–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegwart, R.; Nourbakhsh, I.R.; Scaramuzza, D. Introduction to autonomous mobile robots, 2nd ed.; MIT press, 2011.
- Sivakumar, A.N.; Modi, S.; Gasparino, M.V.; Ellis, C.; Velasquez, A.E.B.; Chowdhary, G.; Gupta, S. Learned visual navigation for under-canopy agricultural robots. 17th Robotics: Science and Systems, 12-16 July 2021.
- Atas, F.; Grimstad, L.; Cielniak, G. Evaluation of sampling-based optimizing planners for outdoor robot navigation. arXiv arXiv:2103.13666 2021.
- Wang, X.; Shi, Y.; Ding, D.; Gu, X. Double global optimum genetic algorithm–particle swarm optimization-based welding robot path planning. Engineering Optimization 2016, 48, 299–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Zhu, W.; Zhang, X.; Cao, T. Path planning of lunar robot based on dynamic adaptive ant colony algorithm and obstacle avoidance. International Journal of Advanced Robotic Systems 2020, 17, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mac, T.T.; Copot, C.; Tran, D.T.; De Keyser, R. A hierarchical global path planning approach for mobile robots based on multi-objective particle swarm optimization. Applied Soft Computing 2017, 59, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghita, N.; Kloetzer, M. Trajectory planning for a car-like robot by environment abstraction. Robotics and Autonomous Systems 2012, 60, 609–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Mottaghi, R.; Kolve, E.; Lim, J.J.; Gupta, A.; Fei-Fei, L.; Farhadi, A. Target-driven visual navigation in indoor scenes using deep reinforcement learning. IEEE international conference on robotics and automation (ICRA), Singapore, 29 May - 3 June 2017, pp. 3357–3364.
- Wijmans, E.; Kadian, A.; Morcos, A.; Lee, S.; Essa, I.; Parikh, D.; Savva, M.; Batra, D. Dd-ppo: Learning near-perfect pointgoal navigators from 2.5 billion frames. arXiv arXiv:1911.00357 2019.
- Gupta, S.; Davidson, J.; Levine, S.; Sukthankar, R.; Malik, J. Cognitive mapping and planning for visual navigation. International Journal of Computer Vision 2020, 128, 1311–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datta, S.; Maksymets, O.; Hoffman, J.; Lee, S.; Batra, D.; Parikh, D. Integrating egocentric localization for more realistic point-goal navigation agents. 4th Conference on Robot Learning (CoRL), 16 - 18 November 2020, pp. 313–328.
- Kumar, A.; Gupta, S.; Fouhey, D.; Levine, S.; Malik, J. Visual memory for robust path following. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 2018, 31, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, Y.; Cheng, C.A.; Saigol, K.; Lee, K.; Yan, X.; Theodorou, E.; Boots, B. Agile autonomous driving using end-to-end deep imitation learning. arXiv arXiv:1709.07174 2017.
- Sadeghi, F.; Levine, S. CAD2RL: Real single-image flight without a single real image. Robotics: Science and Systems, Cambridge, Massachusetts, USA, 12-16 July 2017.
- Ross, S.; Melik-Barkhudarov, N.; Shankar, K.S.; Wendel, A.; Dey, D.; Bagnell, J.A.; Hebert, M. Learning monocular reactive uav control in cluttered natural environments. IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Karlsruhe, Germany, 6-10 May 2013, pp. 1765–1772.
- Gandhi, D.; Pinto, L.; Gupta, A. Learning to fly by crashing. IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 24-28 September 2017, pp. 3948–3955.
- Gasparino, M.V.; Sivakumar, A.N.; Liu, Y.; Velasquez, A.E.; Higuti, V.A.; Rogers, J.; Tran, H.; Chowdhary, G. Wayfast: Navigation with predictive traversability in the field. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters 2022, 7, 10651–10658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathyamoorthy, A.J.; Weerakoon, K.; Guan, T.; Liang, J.; Manocha, D. TerraPN: Unstructured terrain navigation using online self-supervised learning. IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Kyoto, Japan, 23-27 October 2022, pp. 7197–7204.
- Hirose, N.; Shah, D.; Sridhar, A.; Levine, S. ExAug: Robot-conditioned navigation policies via geometric experience augmentation. arXiv arXiv:2210.07450 2022.
- Heimann, D.; Hohenfeld, H.; Wiebe, F.; Kirchner, F. Quantum deep reinforcement learning for robot navigation tasks. arXiv arXiv:2202.12180 2022.
- Gyagenda, N.; Hatilima, J.V.; Roth, H.; Zhmud, V. A review of GNSS-independent UAV navigation techniques. Robotics and Autonomous Systems 2022, 152, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
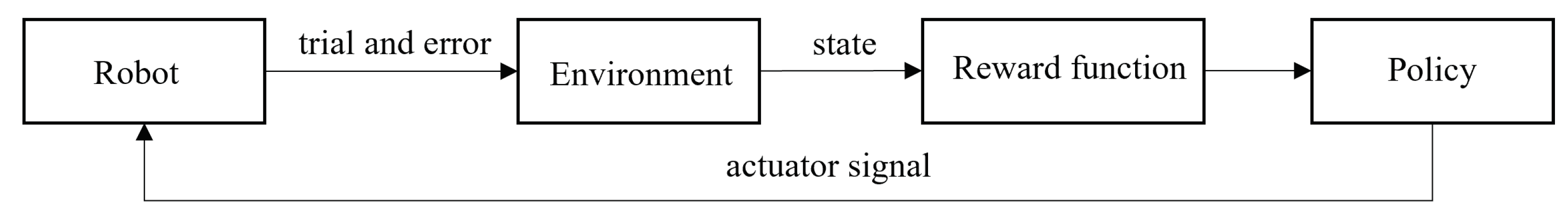
- Zhu, K.; Zhang, T. Deep reinforcement learning based mobile robot navigation: A review. Tsinghua Science and Technology 2021, 26, 674–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y. Deep reinforcement learning: An overview. arXiv arXiv:1701.07274 2017.
- Li, H.; Zhang, Q.; Zhao, D. Deep reinforcement learning-based automatic exploration for navigation in unknown environment. IEEE transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems 2019, 31, 2064–2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Ma, X.; Peng, T.; Wang, H. An improved timed elastic band (TEB) algorithm of autonomous ground vehicle (AGV) in complex environment. Sensors 2021, 21, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulhánek, J.; Derner, E.; De Bruin, T.; Babuška, R. Vision-based navigation using deep reinforcement learning. European Conference on Mobile Robots (ECMR), Prague, Czech Republic, 4-6 September 2019, pp. 1–8.
- Xi, A.; Mudiyanselage, T.W.; Tao, D.; Chen, C. Balance control of a biped robot on a rotating platform based on efficient reinforcement learning. IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica 2019, 6, 938–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.; Vlahov, B.; Gibson, J.; Rehg, J.M.; Theodorou, E.A. Approximate inverse reinforcement learning from vision-based imitation learning. IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Xi’an, China, 31 May - 4 June 2021, pp. 10793–10799.
- Qi, W.; Mullapudi, R.T.; Gupta, S.; Ramanan, D. Learning to move with affordance maps. arXiv arXiv:2001.02364 2020.
- Zendel, O.; Honauer, K.; Murschitz, M.; Steininger, D.; Dominguez, G.F. Wilddash-creating hazard-aware benchmarks. 15th European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8-14 September 2018, pp. 402–416.
- Tang, J.; Chen, Y.; Kukko, A.; Kaartinen, H.; Jaakkola, A.; Khoramshahi, E.; Hakala, T.; Hyyppä, J.; Holopainen, M.; Hyyppä, H. SLAM-aided stem mapping for forest inventory with small-footprint mobile LiDAR. Forests 2015, 6, 4588–4606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Shang, G.; Ji, A.; Zhou, C.; Wang, X.; Xu, C.; Li, Z.; Hu, K. An overview on visual SLAM: From tradition to semantic. Remote Sensing 2022, 14, 1–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chghaf, M.; Rodriguez, S.; Ouardi, A.E. Camera, LiDAR and multi-modal SLAM systems for autonomous ground vehicles: A survey. Journal of Intelligent & Robotic Systems 2022, 105, 1–35. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, H.; Hein, B.; Bakr, M.; Schildbach, G.; Abel, B.; Rueckert, E. Using deep reinforcement learning with automatic curriculum learning for mapless navigation in intralogistics. Applied Sciences 2022, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Technique | Typical Sensors | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Structured light | Kinect v1, Xtion PROLive, RealSense SR300 and F200 | High accuracy and precision in indoor environments | Limited range, not suitable for outdoor environment due to noise from ambient light, interference from reflections and other light sources |
| ToF | Kinect v2 | Good for indoor outdoor applications, long range, robust to illumination changes | Lower image resolution than structured light cameras, high power consumption, cost varies with resolution, rain fog can affect sensor performance |
| Active infrared stereo | RealSense R200, RealSense D435, D435i | Compact, lightweight, dense depth images | Stereo matching requires high processing power, struggle at high occlusions and featureless environments, relatively low range especially outdoors |
| Configuration | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Monocular | Compactness, low hardware requirements | No direct depth measurements |
| Stereo | Depth measurements, low occlusions | Fails in featureless environments, CPU intensive, accuracy/range depends on camera quality |
| RGB-D | Color and depth information per pixel | Limited range, reflection problems on transparent, shiny, or very matte and absorbing objects |
| Event | High temporal resolution, suitable for changing light intensities, low latency [41] | No direct depth information, costly, not suitable for static scenes, requires non-traditional algorithms |
| Omni-directional | Wide angle view (alternative to rotating cameras) | Lower resolution, need special methods to compensate for image distortions |
| Configuration | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Pulsed | High frame rate | Low depth resolution, higher inference from other LiDAR sensors |
| AMCW | Not limited by low SNRs, however, not effective at very low SNRs | Low accuracy than FMCW, lower depth resolution than FMCW |
| FMCW | Velocity and range detection in a single shot, higher accuracy than AMCW, higher depth resolution | Currently at the research and development stage |
| Algorithms | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Dijkstra | The calculation strategy is not complex and give the shortest path | The increment of traversal nodes complicates the calculations |
| A* | In static environments the algorithm search efficiency is high | Not appropriate for dynamic environments |
| D* | Good for dynamic environment path planning and more efficient than A* | Planning longer paths via D* creates challenges |
| RRT | Fast convergence, high search capability | Algorithm efficiency is low in unstructured environments |
| Genetic | Appropriate for complex environments, good for finding optimal paths | Low algorithm convergence speed, low search ability in local paths |
| Ant colony | Appropriate for complex environments, can be combined with other heuristic-based path planners | Slow convergence rate, easily trapped in local minima |
| Particle swarm optimisation | High convergence rate, good robustness | Frequently, solutions converge into local optimal solutions |
| Algorithms | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Artificial potential field | Can be implemented for 3D path planning, and can solve the local minimum problem | Cannot guarantee the optimal solution |
| Simulated annealing | Flexible and easy implementation, can deal with noisy data and non-linear models | Can produce unstable results, the trade-off between accuracy and speed |
| Fuzzy logic | Strong robustness, decrease the dependencies between environmental data | Needs accurate prior knowledge, poor learning capabilities |
| Neural network | Strong robustness, and learning ability from experiences | Low path planning efficiency |
| Dynamic window | Good self-adaptation to environments | Not appropriate for unstructured complex environments |
| Algorithms | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| DQN | Updates are done offline, are not complex, and are reliable | Only discrete motions |
| DDPG | High sample efficiency, less data correlation and faster convergence compared to DQN | The poor generalisation of novel environments |
| TRPO | Ensure stable convergence | Too many assumptions, may create large errors |
| PPO | Simplified solution process, good performance and easier to implement compared to TRPO | Low sampling efficiency |
| A3C | Asynchronous parallel network training, fast convergence, suitable for multi-robot systems | Require large training data, Difficult to migrate model to real world |
| SAC | Better robustness and sample efficiency compared to the above methods | Bulky model size |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





