Submitted:
13 April 2023
Posted:
14 April 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials
2.1. Laboratory Culture-Ware and Common Ingredients
- 6/12/24/96 well tissue culture treated dishes.
- Poly-L-Ornithine
- Laminin (Sigma L2020-1MG)
- mTeSRTM1 media for maintenance of hiPSCs (StemCell Technologies Catalog # 85850).
- Corning® Matrigel® hESC-Qualified Matrix (Corning 354277).
- 70% (vol/vol) ethanol.
- D-PBS (Without Ca++ and Mg++).
- Conical Tubes.
- Serological Pipettes 5ml/10ml/25ml.
- Rock inhibitor Y-27632 (StemCell Technologies Catalog #72302).
- Cell counter or hemocytometer.
- Trypan blue.
- Doxycycline.
- Glutamax.
- Parafilm.
- ReLeSR.
2.2. Materials for the Dual SMAD Inhibition Protocol
- STEMdiffTM SMADi Neural Progenitor Kit (StemCell Technologies #08581).
- STEMdiffTM Neural Progenitor Medium (StemCell Technologies #05833).
- STEMdiffTM Forebrain Neuron Differentiation kit (StemCell Technologies #08600).
- STEMdiffTM Forebrain Neuron Maturation kit (StemCell Technologies #08605).
- Neural Progenitor Freezing Media.
- 5ml FACS tubes with a cell strainer.
- Wide bore 200ul and 1000ul pipette tips.
- Anti-Adherence rinsing solution (StemCell Technologies Catalog #07010).
- AggreWellTM 800 (StemCell Technologies Catalog #34815) or Corning Elplasia (Corning 4441) plates for embryoid body formation.
2.3. Materials for the Generation of Neurons Using Transcription Factor Overexpression Protocol
- hiPSCs expressing doxycycline-inducible NEUROG2 (NGN2) expression cassette. The method for generating this cell line is not described in this protocol but can be found here in the article published by Schmid et al. [15]. The iPSC lines generated by Schmid et al. are available for purchase through the European Bank for Induced pluripotent Stem Cells (EBiSC).
- Knockout DMEM/F12
- Non-Essential Amino Acid supplement
- N2 supplement
- NT-3
- BDNF
- Mouse Laminin (1mg/ml stock Sigma L2020)
- Rock Inhibitor
- Gem21 supplement/ B27 supplement
- DMEM/F12
- Neurobasal medium
2.4. Materials Required for Cell Characterization by Immunofluorescence
- BSA
- TritonX-100
- PBS
- 4% Paraformaldehyde
- Fluorescence microscope
- Anti-MAP2 antibody (Abcam, catalog number: ab92434)
- Anti-DCX antibody (Cell Signaling Technology, catalog number: 4604)
- Anti-NeuN antibody (Invitrogen, catalog number: PA5-78499)
- OCT4 antibody (Cell Signaling Technology, catalog number: C52G3)
- SOX2 antibody (SantaCruz Biotechnology, catalog number: sc-365823)
- SSEA4 antibody (SantaCruz Biotechnology, catalog number: sc-59368)
- MSI1 antibody (Millipore Sigma, catalog number: AB5977)
- PAX6 antibody (Biolegend, catalog number: 901301)
3. Methods
3.1. Coating Cell Culture Plates with Matrix
3.1.1. Coating Plates with Corning Matrigel
- Thaw an aliquot of 100x stock concentration of Matrigel on ice.
- Dispense ice-cold DMEM or DMEM/F12 in a conical tube and add freshly thawed Matrigel to the conical tube to a final concentration of 1X. Mix well.
- Add the Matrigel DMEM solution to culture plates such that it covers the surface of the plate completely (See Table 1 for recommended coating volumes). Incubate at 37°C for at least an hour before plating cells. Coated plates can be sealed using parafilm stored for up to a week at 4°C.
| Plate Type | Recommended Volume of Matrix |
|---|---|
| 384 well | 30 ul |
| 96 well | 50 ul |
| 24 well | 250 ul |
| 12 well | 500 ul |
| 6 well | 1000 ul |
3.1.2. Coating Plates with Poly-L-Ornithine/Laminin
- Thaw an aliquot of the Poly-L-Ornithine (PLO) solution on ice and dilute it in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) to a final concentration of 15ug/ml.
- Add the diluted PLO solution to culture plates. Use the volumes recommended in Table 1.
- Incubate at 37°C for 1.5 to 2hr or incubate overnight at 2 – 8°C. Make sure the PLO solution does not evaporate.
- Aspirate PLO solution with a pipette. Make sure the surface of the cultureware is not scratched while aspirating.
- Wash 2-3 times with 1x PBS.
- Dilute laminin in DMEM/F12 to a final concentration of 10ug/ml.
- Add diluted laminin to the culture plates coated with PLO. Use the volumes recommended in Table 1.
- Incubate at 37°C for 1.5 to 2hr or incubate overnight at 2 – 8°C. Make sure the Laminin solution does not evaporate.
- Coated plates can be sealed using parafilm and stored for up to a week at 4°C.
3.1.3. Preparing AggreWellTM 800 Plates
- Add 500ul of anti-adherence rinsing solution to each well of the AggreWellTM plate.
- Centrifuge for 5 min at 1300 x g. Make sure that the centrifuge is balanced.
- Observe under the microscope to ensure that the bubbles are removed from the microwells of the AggreWellTM plate. If the bubbles are still trapped centrifuge again for 5 min at 1300 x g.
- Aspirate the anti-adherence rinsing solution and add 1 ml warm media to each well of a 24-well plate.
3.2. Preparing Cell Culture Media
3.2.1. mTeSRTM1 Medium
3.2.2. STEMdiffTM Neural Induction Medium + SMADi
3.2.3. Neural Progenitor Medium
3.2.4. STEMdiffTM Forebrain Neuron Differentiation Medium
3.2.5. STEMdiffTM Forebrain Neuron Maturation Medium
3.2.6. Neuron Pre-Differentiation Media
- Knockout DMEM/F12 - 50 ml
- Non-essential amino acid supplements – 500 ul
- Glutamax - 500 ul
- NT-3 (10ug/ml stock) – 50 ul
- BDNF (10ug/ml stock) – 50 ul
- Mouse Laminin (1 mg/ml stock) – 50 ul
- Rock inhibitor Y-27632 (10 uM stock) – Final concentration 10 nM
- Doxycycline (2 mg/ml stock) – Final concentration 2 ug/ml
3.2.7. Neuron Differentiation Media
- DMEM/F12 – 25 ml
- Neurobasal Media – 25 ml
- Glutamax – 500 ul
- Non-essential amino acid supplements – 500 ul
- NT-3 (10ug/ml stock) – 50 ul.
- BDNF (10ug/ml stock) – 50 ul
- Mouse Laminin (1 mg/ml stock) – 50 ul
- Doxycycline (2 mg/ml stock) – Final concentration 2 ug/ml
3.3. Differentiating hiPSCs into Forebrain Neurons via a Neural Progenitor Intermediate Using Dual SMAD Inhibition
- Aspirate media and wash with 1X PBS once to remove any dead cells.
- Add ReLeSR to the well such that it covers the surface completely. Aspirate ReLeSR solution and incubate at 37°C for 5-6 min.
- Add warm mTeSRTM1 media and passage 1:10 of the cell suspension to a new Matrigel-coated well.
- Warm enough reconstituted STEMdiffTM + SMADi Neural induction media and DMEM/F12. Add rock inhibitor (Y-27632) to the media at a final concentration of 10uM.
- Prepare a well of AggreWellTM-800 24 well plate (Section 3.1.3).
- Rinse the well of hiPSCs with 2ml of sterile PBS.
- Aspirate the PBS and add 1ml of accutase to one well of the 6 well plates. Incubate at 37°C for 4-5 min till the hiPSCs detach.
- Resuspend the cells by pipetting up and down with a 1ml pipette. Transfer the suspension to a 15ml conical tube and add 5ml of warm DMEM/F12 media to the tube.
- Centrifuge the cells at 300xg for 5min. Carefully aspirate the supernatant and resuspend the cells in 1ml of DMEM/F-12.
- Count the cells using Trypan blue and the cell counter of your choice.
- Aliquot 3 x 106 cells in 1 ml of STEMdiffTM + SMADi Neural induction medium + 10uM Y-27632 and add the suspension to the pre-prepared well of AggreWellTM800 plate.
- Centrifuge the AggreWellTM plate at 100 x g for 3 minutes. This will capture the cells in the microwells. Make sure to balance the plate during centrifugation. Observe the well under the microscope to make sure that the cells are evenly distributed in the microwells.
- Incubate the cells at 37°C.
- Uniform embryoid bodies (EBs) should be seen on day 1 (Figure 1A). More than 50% of cells should be incorporated into the EBs.
- Gently aspirate the media from a well of the AggreWellTM-800 plate. Tilt the plate a little bit and aspirate media touching the pipette tip to the wall of the well. Make sure to aspirate media very slowly so that the EBs are not disturbed. Aspirate 1.5 ml of media.
- Add 1.5 ml of warm STEMdiffTM Neural Induction medium + SMADi to the well. Add the media very slowly. Again, tilt the plate while adding media and add media by touching the pipette tip to the wall of the well. Do not add medium to the surface of the well.
- Incubate at 37°C.
- Repeat steps 2-4 until day 4.
- Warm enough DMEM/F12 and STEMdiffTM Neural Induction Medium + SMADi.
- Resuspend the EBs in the medium in the well. Use a 1ml pipettor with wide bore tips to remove the medium from the well and then firmly expel the medium onto the surface of the well. This will dislodge the EBs from the microwells.
- Aspirate the EB solution and pass it through a cell strainer on a 5ml FACS tube (sterile).
- Observe under the microscope to make sure all the EBs have been dislodged and transferred. If the well still contains EBs repeat steps 2-3 using warm DMEM/F12 till all the EBs have been dislodged and transferred.
- Remove the cell strainer and invert over a well of 6 well plate coated with Matrigel. Pass 2ml of warm STEMdiffTM Neural Induction Medium + SMADi through the strainer into the Matrigel-coated well. This should transfer all the EBs to the well.
- Move the plate in a quick back-and-forth and sideways motion to distribute the EBs in the well and incubate at 37°C.
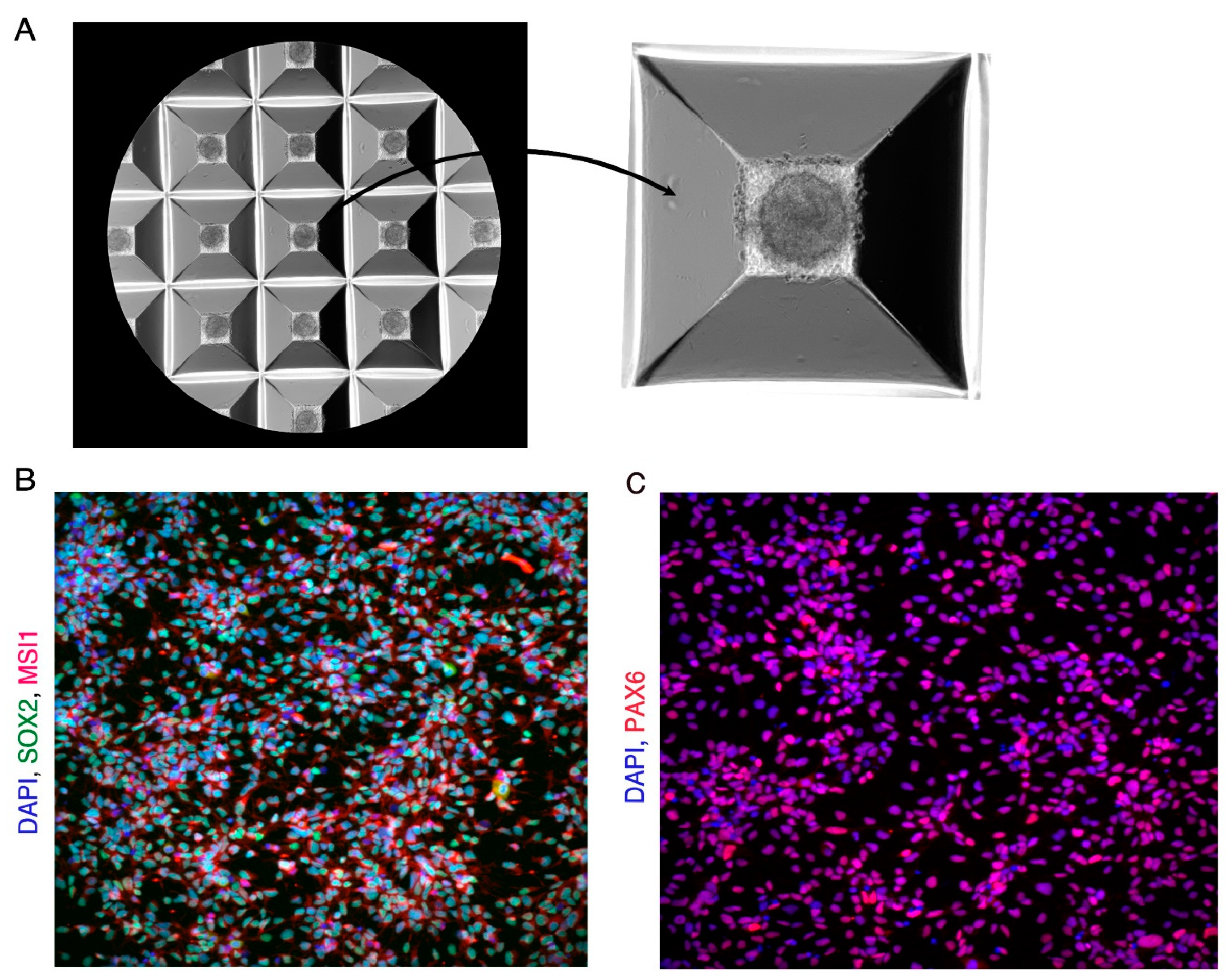
- Aspirate the medium from the well and wash the rosettes with 2ml of warm DMEM/F12.
- Aspirate DMEM/F12 and add 1ml of Neural Rosette Selection Reagent.
- Incubate the plate for 1.5 hours.
- Carefully remove the Neural Rosette Selection Reagent with a pipettor. To dislodge the neural rosettes firmly dispense 1ml of warm DMEM/F12 onto the rosettes with a 1ml pipettor. Transfer the rosettes to a 15ml conical tube. Repeat till most of the neural rosettes are dislodged. See note 5 for precautions to be taken during neural rosette selection.
- Centrifuge at 300xg for 5 minutes.
- Aspirate the supernatant and resuspend the rosettes gently in 2ml of warm STEMdiffTM Neural Induction media + SMADi.
- Transfer the rosettes and STEMdiffTM Neural Induction media + SMADi to a Matrigel-coated well of a 6-well plate. Move the plate in a quick back-and-forth and sideways motion to distribute the rosette clusters in the well and incubate at 37°C.
- Dissociate the day 19 NPCs using accutase into a single cell suspension. Briefly, aspirate the STEMdiffTM Neural Induction media + SMADi and wash the cells once with PBS. Add 1 ml accutase and incubate for 5 mins at 37 °C till the cells dissociate. Transfer the cell suspension and add 4-5ml of warm DMEM/F12.
- Centrifuge at 300 x g for 5 min.
- Aspirate the supernatant and resuspend the cells in 1ml of DMEM/F12.
- Count the cells using trypan blue and a cell counter. Plate approximately 1 million live cells on a PLO/laminin-coated well of a 6 well plate in 2ml of warm STEMdiffTM Forebrain Neuron Differentiation Medium. For recommended seeding densities for NPCs in different culture vessels see Table 2.
- Change the media daily till day 25.
| Plate Type | Growth Area (cm2) | Seeding Density | Number of Cells |
|---|---|---|---|
| 6 well | 9.5 | 1.25E+05 | 1.19E+06 |
| 12 well | 3.8 | 1.25E+05 | 4.75E+05 |
| 24 well | 1.9 | 1.25E+05 | 2.38E+05 |
| 96 well | 0.32 | 1.25E+05 | 4.00E+04 |
| 384 well | 0.056 | 1.25E+05 | 7.00E+03 |
- Dissociate neuron precursors on day 25 using accutase into a single cell suspension. Briefly, aspirate the media and wash the cells once with PBS. Add 1 ml accutase and incubate for 5 mins at 37 °C till the cells dissociate. Transfer the cell suspension and add 4-5ml of warm DMEM/F12. Centrifuge at 300 x g for 5 min.
- Aspirate the supernatant and resuspend the cells in 1ml of DMEM/F12.
- Count the cells using trypan blue and a cell counter. Plate approximately 1 million live cells on a PLO/laminin-coated well of a 6 well plate in 2ml of warm STEMdiffTM Forebrain Neuron Maturation Medium. For recommended seeding densities for neuron precursors in different culture vessels see Table 3.
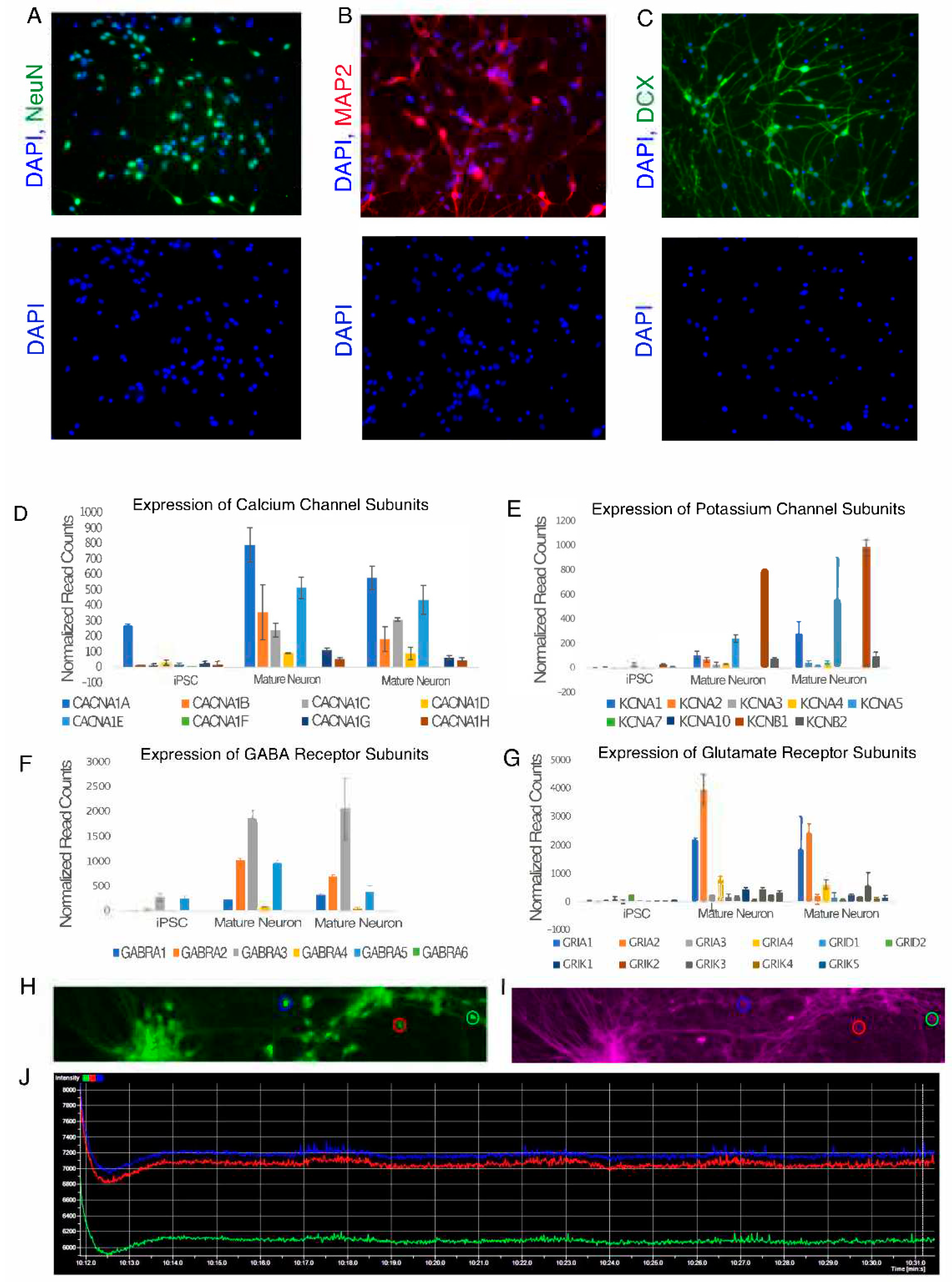
- Change the media every 3 days. Mature neurons are positive for neuron markers MAP2, DCX, and NeuN (Figure 2A–C). Mature neurons also express calcium and potassium channel subunits (Figure 2D). Mature neurons generated using this protocol express both GABA and Glutamate receptor subunits indicating the presence of both GABAergic and glutamatergic neurons in culture (Figure 2E). Mature neurons capable of exhibiting spontaneous electrical activity (Figure 2E–G) are seen around 18-22 days after culturing in maturation media. The protocols for performing functional assays on neurons are out of the scope of this publication. For more information on functional assays for neurons see note 8.
| Plate Type | Growth Area (cm2) | Seeding Density | Number of Cells |
|---|---|---|---|
| 6 well | 9.5 | 3.00E+04 | 2.85E+05 |
| 12 well | 3.8 | 3.00E+04 | 1.14E+05 |
| 24 well | 1.9 | 3.00E+04 | 5.70E+04 |
| 96 well | 0.32 | 3.00E+04 | 9.60E+03 |
| 384 well | 0.056 | 3.00E+04 | 1.68E+03 |
3.4. Differentiating hiPSCs into Neurons Using NGN2 Overexpression
- Start with undifferentiated iPSC colonies which express dox inducible NEUROG2 cassette.
- Wash the cells with PBS and add 1ml of accutase to 1 well of a six-well plate. Incubate for 5 min at 37 °C till the cells lift off. Pipette the cells with a 1 ml pipettor to make a single-cell suspension and add it to a 15ml conical tube. Add 4-5ml of PBS and mix well. Centrifuge at 300 x g for 5 min. Remove the supernatant and resuspend the cells in 1 ml of pre-differentiation media.
- Count the cells using trypan blue and a cell counter.
- Add 1x106 cells to a Matrigel-coated well of a 6 well plate and add 2ml of warm Neuron Pre-differentiation media.
- Perform half media change till day 3. Keep adding doxycycline to the media till day 3.
- Pre-differentiated cells on day 3 can be frozen in pre-differentiation media + 10% DMSO.
- Aspirate the media from the well and wash the cells once with PBS.
- Add 1ml of accutase to 1 well of a six-well plate. Incubate for 5 min at 37 °C till the cells lift off. Pipette the cells with a 1 ml pipettor to make a single-cell suspension and add it to a 15ml conical tube. Add 4-5ml of PBS and mix well. Centrifuge at 300 x g for 5 min. Remove the supernatant and resuspend the cells in 1 ml of neuron differentiation media.
- Count the cells using trypan blue and a cell counter.
- Using Table 3 plate appropriate numbers of cells for the type of culture dish and add an appropriate amount of differentiation media to the well of the culture dish.
- Dox should be added only on the day of transition to differentiation media.
- Change half of the media every 3-4 days. While changing media aspiration and dispensing into the wells should be performed very gently. Tilt the plate and change the media by touching the pipette tip to the sides of the well.
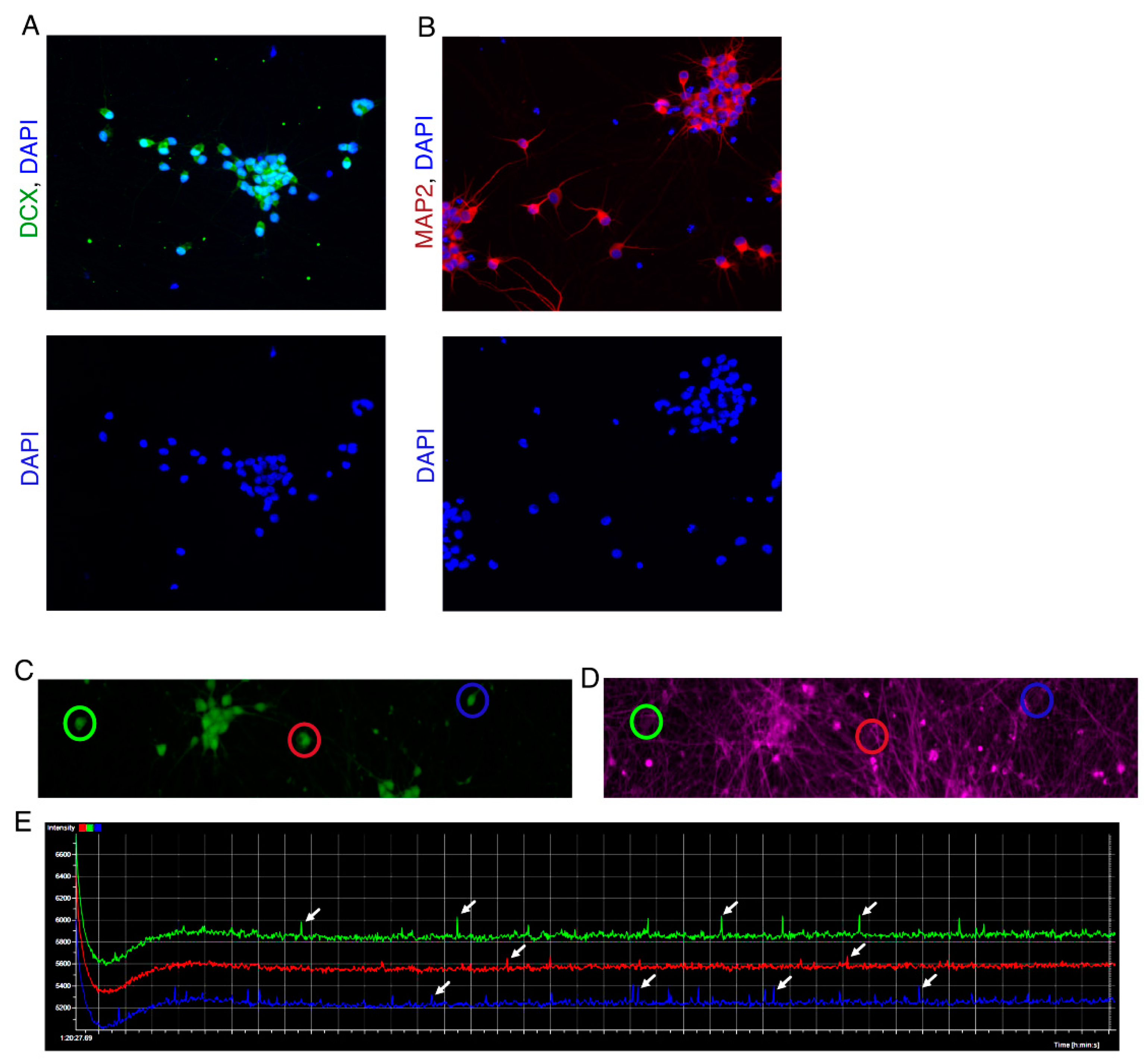
- Mature neurons which exhibit spontaneous electrical activity and are positive for MAP2 and DCX are observed between days 14-21 after switching to neuron differentiation media (Figure 3). The protocols for performing functional assays on neurons are out of the scope of this publication. For more information on functional assays for neurons see note 8.
3.5. Immunofluorescence
- 2% w/v BSA
- 0.1% v/v Triton X-100 (Make a 10% solution of Triton X-100 in water and use that as a stock solution while making the blocking buffer)
- Dissolve BSA in PBS and add Triton X100 to a final concentration of 0.1% to make the blocking buffer.
- Aspirate media from the wells of 96 well plate (Make sure to avoid touching the center of the plate to avoid disturbing the attached cells).
- Rinse gently with PBS (2 times) to remove traces of media.
- Add 100ul 4% PFA (enough to cover a well of a 96 well plate) and incubate at room temperature for 15-20 min.
- Aspirate the PFA and collect it in an appropriate waste container.
- Rinse the wells gently with PBS (2 times) and continue for incubation with primary antibody (Alternatively, cells can be stored in PBS at 4 degrees at this step and the rest of the protocol can be continued later. Seal the plates with parafilm before storing at 4 degrees to minimize evaporation of PBS). Be very gentle during the wash steps. Add PBS from the sides of the well extremely slowly.
- Aspirate the PBS and add 100 ul of blocking buffer to the wells.
- Incubate at room temperature for 45-60 min.
- Meanwhile, prepare appropriate dilutions of primary antibodies in the blocking buffer and keep them on ice.
- Aspirate the blocking buffer from the wells and add 150ul of the appropriate primary antibody per well.
- Incubate overnight at 4 degrees.
- Aspirate the primary antibody solution from the wells.
- Wash 3 times for 5 min with the blocking buffer.
- Dilute the secondary antibodies in blocking buffer usually at 1:1000 dilution.
- Aspirate blocking buffer from the wells and add 150ul of the appropriate diluted secondary antibody.
- Incubate at room temperature in dark for 45-60 min.
- Aspirate the secondary antibody solution and wash the cells with PBS twice (5 min).
- Aspirate the PBS and add with 1X DAPI solution in PBS.
- Aspirate the DAPI and wash twice with PBS. Store the cells at 4 degrees in PBS and protect them from light.
Notes
- Undifferentiated colonies are tight and compact with very little space between cells.
- Undifferentiated colonies have sharp boundaries. Cells should not be migrating away from the colonies.
- Undifferentiated hiPSCs have a large nucleus with very little cytoplasm.
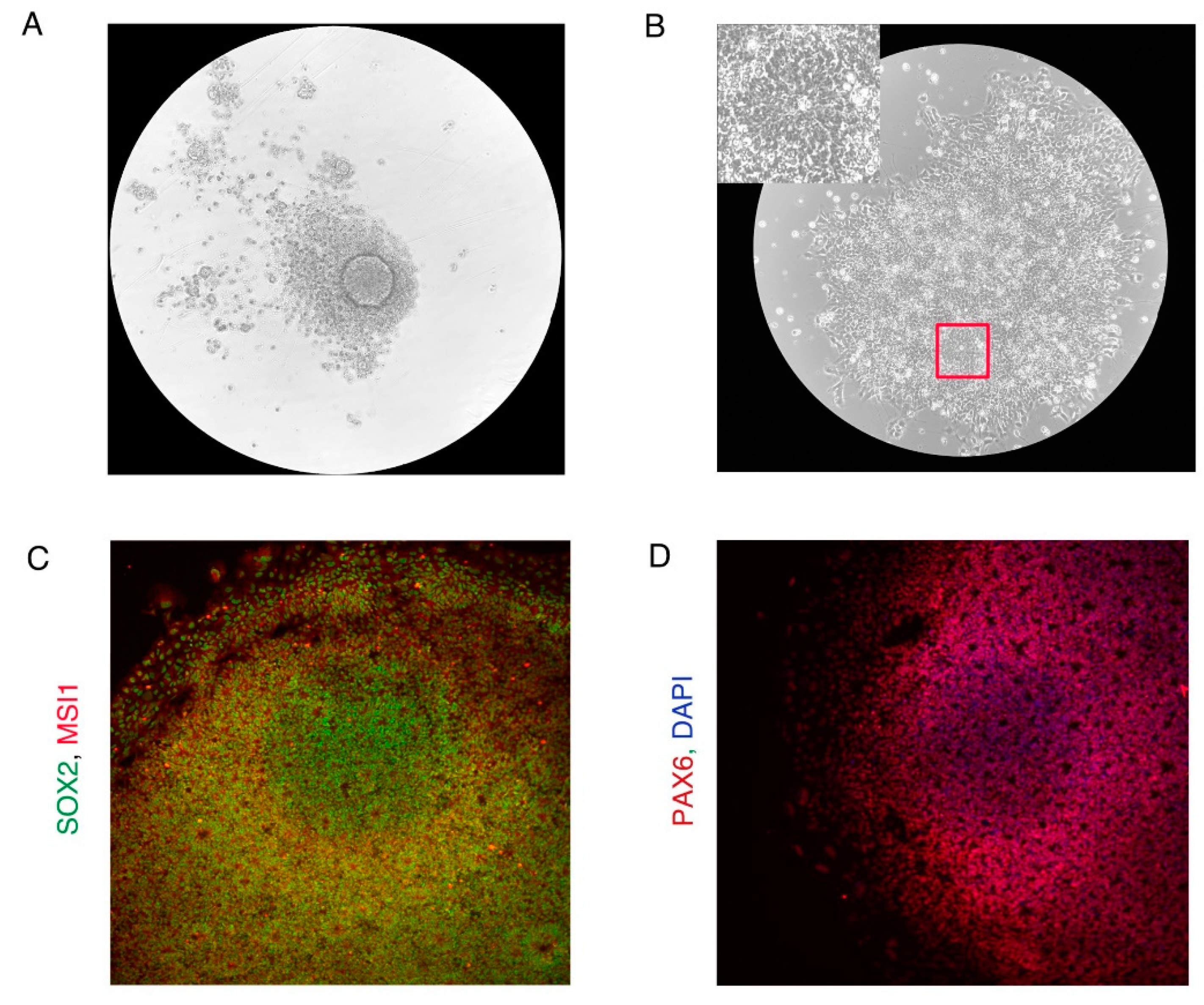
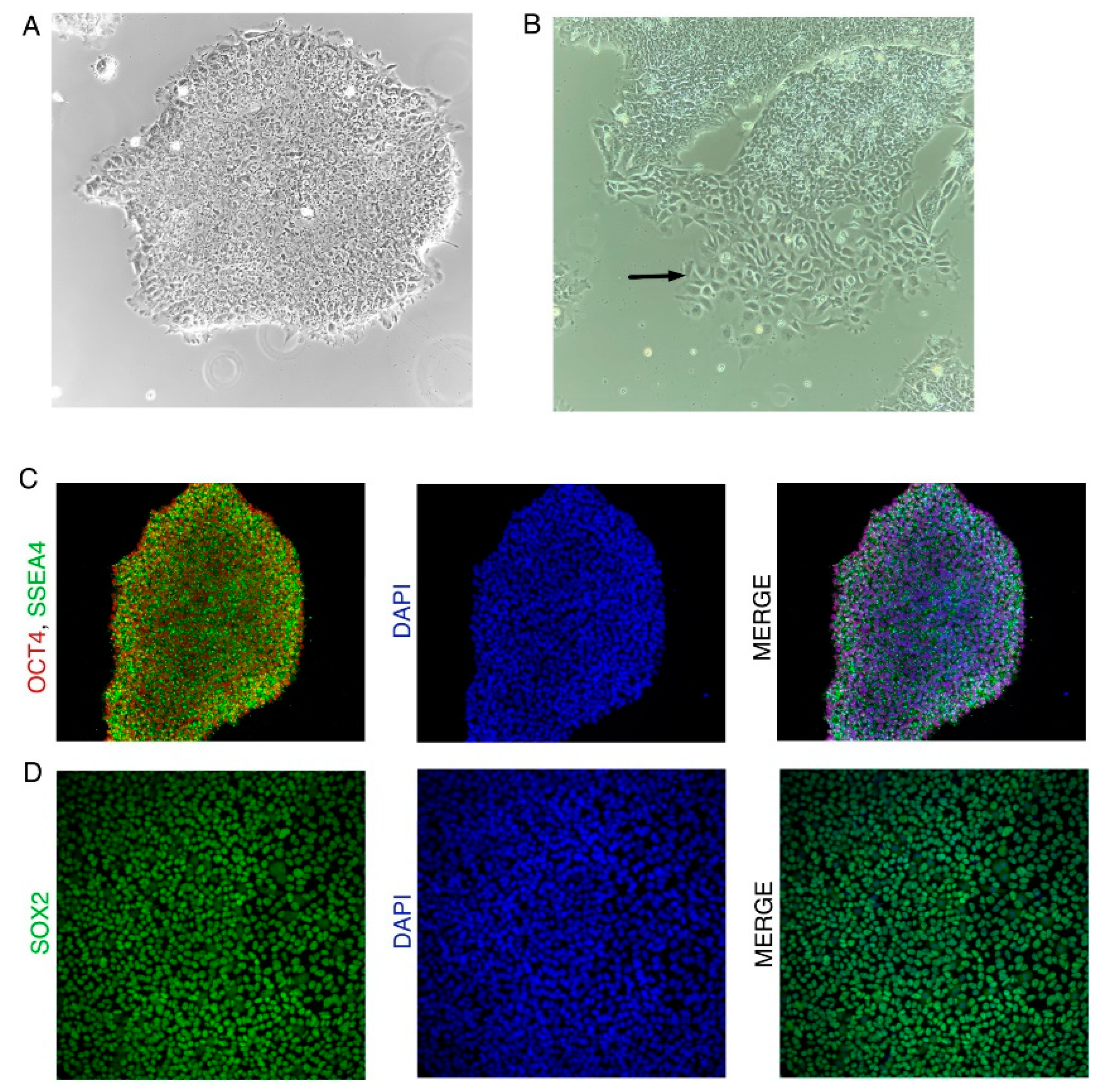
- Undifferentiated hiPSCs should be positive for iPSC markers OCT4, SOX2, and SSEA3/4 (Figure N2B). (Figure N2 near here)
- Count all attached EBs
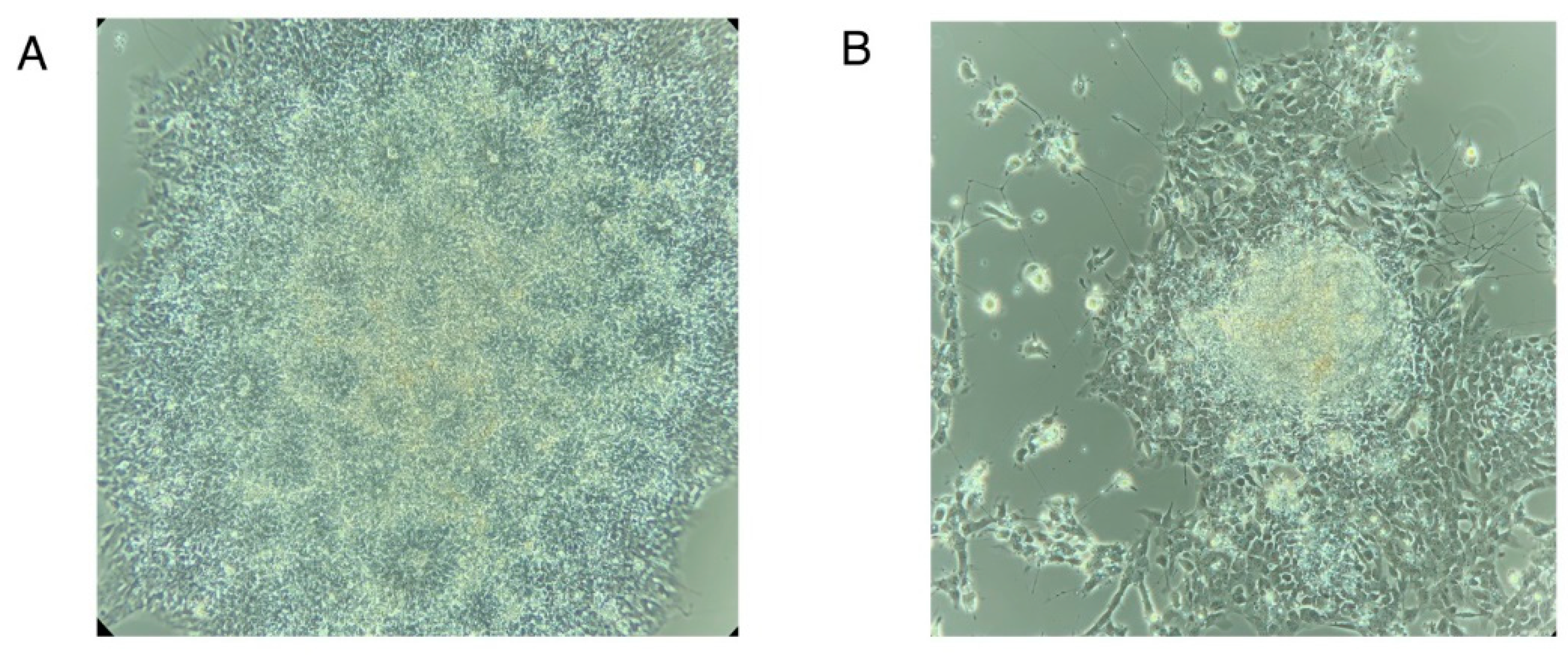
- Count all EBs in which at least 50-70% of the area is filled with neural rosettes. See Figure N3A for a representative image of EBs with 100% neural rosettes and Figure N3B for a representative image of EBs with less than 50% neural rosettes. (Figure N3 near here)
- Calculate % neural induction using the following formula
- Make sure you incubate the cells with a neural rosette selection reagent for at least an hour and not more than 1.5 hours. The neural rosettes should start dislodging when you shake the plate, but increased incubation time can release the cells that have migrated out of the neural rosettes.
- While dislodging the rosettes with DMEM/F12 do not pipette too many times to try and get each rosette dislodged. This might result in the release of contaminating non-neural cells. Under-selection is better.
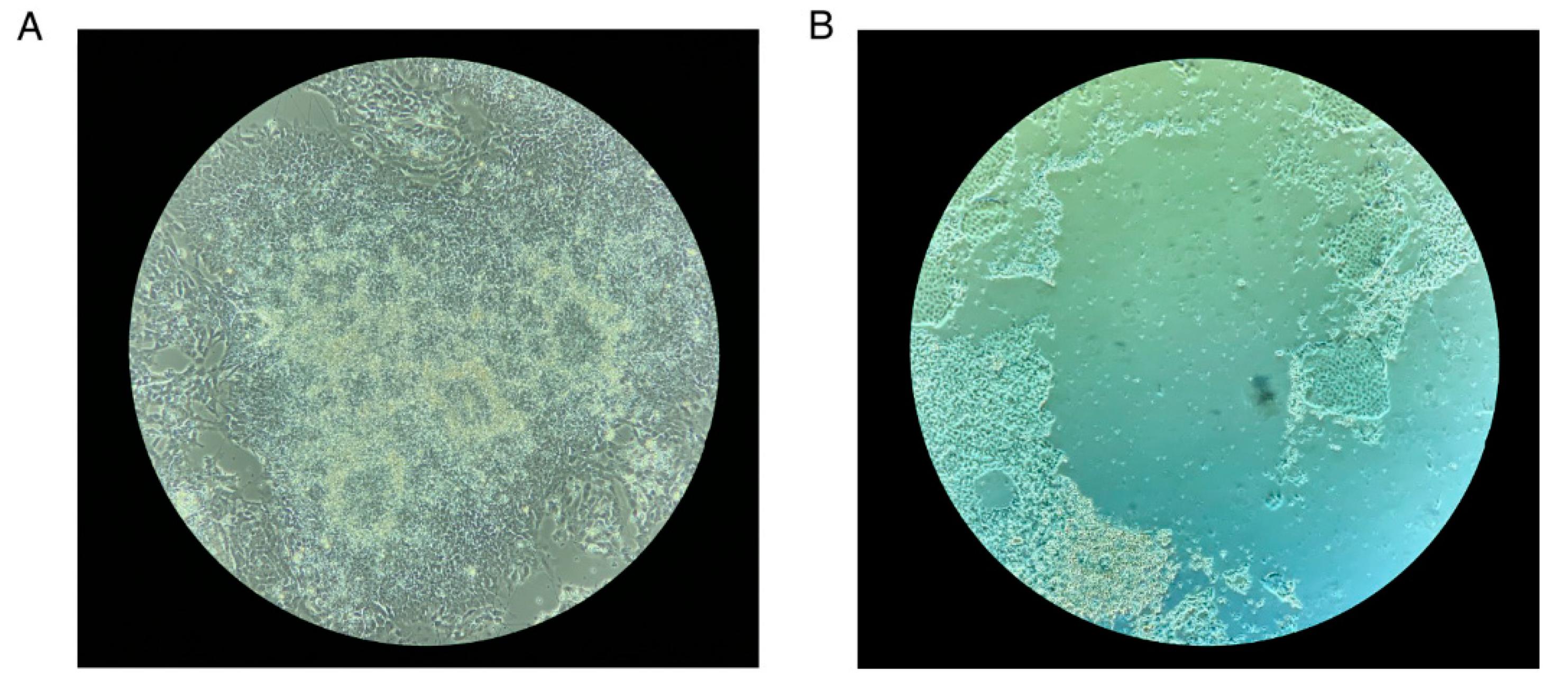
- Figure N4 shows an image of a neural rosette before and after neural rosette selection. (Figure N4 near here)
- Dissociate the cells into a single cell suspension using accutase as described before.
- Count viable cells using a cell counter.
- Centrifuge cells at 300 x g for 5 minutes.
- Aspirate the supernatant and resuspend the ~2 x 106 cells in 1 ml of cold STEMdiffTM neural progenitor freezing medium.
- Transfer 1ml of cell suspension into a cryovial.
- Transfer the vial to a Mr. Frosty cooler and place the cooler at -80°C. Transfer the cryovials to liquid nitrogen storage the next day.
| Method | Cellular Resolution | Throughput |
|---|---|---|
| Patch Clamp | Single cell | Low can sample from 10-12 cells at the most in one experiment. |
| Multi-electrode arrays | Groups of cells | High throughput can be scaled to 96 well plate |
| Optical Electrophysiology (Voltage Sensing Dyes and GEVIs) | Single Cell | High throughput can be scaled to 96/384 well plate |
| Neuronal Subtype | Source/Species | Transcription Factors Used and Method of Delivery | NGN2 Induction Duration | Time to Functional Neurons | Developmental Patterning | Growth Factors and Co-Culture | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bipolar neurons | Human ESCs and iPSCs | Ngn2 and Ngn1 via lentiviral gene delivery | 1–4 days | 4 days for single action potentials, 14 days for action potentials trains | NA | Co-cultured with rat astrocytes | [20] |
| Glutamatergic excitatory neurons | Human ESC and iPSCs | Ngn2 via lentiviral gene delivery | Entire duration | 2 weeks | NA | BDNF | [17] |
| Mouse ESCs | Transient Ngn2 expression and clonal transgenic line | Entire duration | 7 days | NA | NA | [21] | |
| NPCs derived from human iPSCs | Ngn2 or NGN2 via lentiviral gene delivery | 2 days–3 weeks | 2 weeks | SB431542 and LDN193189 | NA | [22] | |
| Human iPSCs | NGN2 transgenic line (i3 neurons) | 72 h | 2 weeks | NA | BDNF, NT-3 co-cultured with primary mouse astrocytes (also recommend using astrocyte conditioned media) | [23] | |
| Human ESCs and iPSCs | Ngn2 via lentiviral gene delivery | Entire duration | 2–3 weeks | SB431542, XAV939, and LDN193189 | Co-cultured with mouse primary cortical glial cells | [24] | |
| Human ESCs or ESC-derived anterior and posterior NPCs | NGN2 alone or in addition to one of the following: EMX1, EMX2, OTX1, OTX2, EOMES (TBR2), LHX2, or FOXG1 | 4 days or for single-cell RNA sequencing 14 days | 28 days | SB431542, LDN193189 and CHIR99021 | Co-cultured with mouse glia for long term cultures | [25] | |
| Dopaminergic neuron-like | Human fibroblasts | NGN2, ASCL1, SOX2, NURR1, PITX3 via lentiviral gene delivery | Transient | 20 days | SHH, FGF8 | NA | [26] |
| Midbrain dopaminergic neurons | Human iPSCs | NGN2, ATOH1 via synthetic mRNA delivery | Multiple mRNA transfections: ATOH1 for 3 days, NGN2 for 1 day | 20–49 days | SHH, FGF8b, and DAPT | BDNF, GDNF, TGFb-3, cAMP, ascorbic acid, and DAPT | [27] |
| Dopaminergic neuron | Mouse ESC-derived NPCs | Ngn2, Nurr1 via retroviral gene delivery | 3–10 days | 9–16 + days | bFGF, EGF | NA | [28] |
| Serotonergic neurons | Human dermal fibroblasts | NGN2, ASCL1, NKX2.2, FEV, GATA2, LMX1B via lentiviral gene delivery | 3–4 weeks | 6 weeks | Dibutyryl cyclic-AMP, noggin, LDN193189, A83-1, CHIR99021, SB431542, forskolin | GDNF, BDNF, dibutyryl cyclic-AMP co-culture with primary rodent astrocytes for electrophysiological analyses | [29] |
| Motor neurons | Human ESC and iPSCs | NGN2 NGN1, NGN3, ND1, ND2 via synthetic mRNA delivery | 2–4 transient transfections | 7–10 days | Forskolin, SB431542, dorsomorphin, retinoic acid | BDNF, GDNF, NT-3 | [30] |
| Human ESC and iPSC-derived NPCs | NGN2, ISL1, LHX3 via adenoviral gene delivery | Transduce day 0 and 4 | 21 days | Retinoic acid, forskolin, SHH | Retinoic acid, SHH | [31] | |
| Spinal motor neurons | Mouse ESC-derived EBs | Ngn2, Isl1, Lhx3 via inducible transgenic line | 2 days | 7–11 day | NA | Co-culture with mouse astrocytes 7–10 days | [32] |
| Mouse and human fibroblasts | Ngn2, Ascl1, Brn2, Mytl1, Lhx3, Hb9, Isl1 via retroviral transduction | Undefined | 21 + days | NA | GDNF, BDNF, CNTF | [33] | |
| Human iPSCs | Ngn2, Isl1, Lhx3 inducible line via a piggyBac transposon vector | 5 days | 13 days | DAPT, SU5402 | BDNF, GDNF, L-ascorbic acid | [34] | |
| Cranial motor neurons | Mouse ESCs-derived EBs | Ngn2, Isl1, Phox2a via inducible transgenic line | 2 days | 11 days | NA | Co-culture with mouse astrocytes 7–10 days | [32] |
| Human iPSCs | Ngn2, Isl1, Phox2a inducible line via a piggyBac transposon vector | 5 days | 13 days | DAPT, SU5402 | BDNF, GDNF, L-ascorbic acid | [34] | |
| Lower motor neurons | Human iPSCs | NGN2, ISL1, LHX3 inducible transgenic line | 72 h | 14 + days | NA | Optional co-culture of astrocytes | [23] |
| Cholinergic motor neurons | Human fetal lung fibroblasts or human postnatal and adult skin fibroblasts | NGN2 (+Sox11 for skin fibroblasts) using retroviral gene delivery | 2–35 days | 50 days | Dorsomorphin and forskolin | Co-cultured with C2C12 murine myoblast line | [35] |
| Mixed population of sensory neurons | Human and mouse fibroblasts | Ngn2 and BRN3A or Ngn1 and BRN3A via lentiviral transduction | 8 days | 14–22 days | NA | BDNF, GDNF, NGF | [36] |
| Mixed population of sensory neurons | Human ESC neural crest progenitors | NGN2 via lentiviral transduction | 4 days | 32 days | SB431524, CHIR99021, BMP2, FGF2 | BDNF, GDNF, NT-3, bNGF, Y-27632 | [37] |
| Cold-sensing mechanoreceptors | Human iPSCs or iPSC-derived neural crest cells | NGN2 and BRN3A via an inducible line | 14 days | 20 days | Y-27632, bFGF, EGF, SB431524 | BDNF, GDNF, NT-3, bNGF, Y-27632 | [38] |
| Mechanoreceptors | Human iPSC-derived neural crest cells | NGN2 and BRN3A via an inducible line | 1 day | 20 days | Y-27632, bFGF, EGF, SB431524 | BDNF, GDNF, NT-3, bNGF Retinoic acid | [38] |
| Human ESC and iPSC neural crest progenitors | NGN2 via lentiviral transduction | 1 day | 21– 30 days | FGF, EGF | BDNF, GDNF, NT-3, bNGF Retinoic acid | [39] |
References
- Avery S, Inniss K, Moore H (2006) The Regulation of Self-Renewal in Human Embryonic Stem Cells. Stem Cells and Development 15:729–740. [CrossRef]
- Shenghui H, Nakada D, Morrison SJ (2009) Mechanisms of Stem Cell Self-Renewal. Annual Review of Cell and Developmental Biology 25:377–406. [CrossRef]
- Nagy A, Gocza E, Diaz EM, Prideaux VR, Ivanyi E, Markkula M, Rossant J (1990) Embryonic stem cells alone are able to support fetal development in the mouse. Development 110:815–821. [CrossRef]
- Bradley A, Evans M, Kaufman MH, Robertson E (1984) Formation of germ-line chimaeras from embryo-derived teratocarcinoma cell lines. Nature 309:255–256. [CrossRef]
- Amit M, Carpenter MK, Inokuma MS, Chiu C-P, Harris CP, Waknitz MA, Itskovitz-Eldor J, Thomson JA (2000) Clonally Derived Human Embryonic Stem Cell Lines Maintain Pluripotency and Proliferative Potential for Prolonged Periods of Culture. Developmental Biology 227:271–278. [CrossRef]
- Thomson JA, Itskovitz-Eldor J, Shapiro SS, Waknitz MA, Swiergiel JJ, Marshall VS, Jones JM (1998) Embryonic stem cell lines derived from human blastocysts. Science 282:1145–1147. [CrossRef]
- Fernandes AM, Meletti T, Guimarães R, Stelling MP, Marinho PAN, Valladão AS, Rehen SK (2010) Worldwide Survey of Published Procedures to Culture Human Embryonic Stem Cells. Cell Transplant 19:509–523. [CrossRef]
- Vazin T, Freed WJ (2010) Human embryonic stem cells: Derivation, culture, and differentiation: A review. Restor Neurol Neurosci 28:589–603. [CrossRef]
- Unger C, Skottman H, Blomberg P, Sirac Dilber M, Hovatta O (2008) Good manufacturing practice and clinical-grade human embryonic stem cell lines. Human Molecular Genetics 17:R48–R53. [CrossRef]
- Ghosh D, Mehta N, Patil A, Sengupta J (2016) Ethical issues in biomedical use of human embryonic stem cells (hESCs). Journal of Reproductive Health and Medicine 2:S37–S47. [CrossRef]
- Takahashi K, Yamanaka S (2006) Induction of Pluripotent Stem Cells from Mouse Embryonic and Adult Fibroblast Cultures by Defined Factors. Cell 126:663–676. [CrossRef]
- Kitada M, Wakao S, Dezawa M (2012) Muse cells and induced pluripotent stem cell: implication of the elite model. Cell Mol Life Sci 69:3739–3750. [CrossRef]
- Tao Y, Zhang S-C (2016) Neural Subtype Specification From Human Pluripotent Stem Cells. Cell Stem Cell 19:573–586. [CrossRef]
- Hulme AJ, Maksour S, St-Clair Glover M, Miellet S, Dottori M (2022) Making neurons, made easy: The use of Neurogenin-2 in neuronal differentiation. Stem Cell Reports 17:14–34. [CrossRef]
- Schmid B, Holst B, Poulsen U, Jørring I, Clausen C, Rasmussen M, Mau-Holzmann UA, Steeg R, Nuthall H, Ebneth A, Cabrera-Socorro A (2021) Generation of two gene edited iPSC-lines carrying a DOX-inducible NGN2 expression cassette with and without GFP in the AAVS1 locus. Stem Cell Research 52:102240. [CrossRef]
- Chambers SM, Fasano CA, Papapetrou EP, Tomishima M, Sadelain M, Studer L (2009) Highly efficient neural conversion of human ES and iPS cells by dual inhibition of SMAD signaling. Nat Biotechnol 27:275–280. [CrossRef]
- Zhang Y, Pak C, Han Y, Ahlenius H, Zhang Z, Chanda S, Marro S, Patzke C, Acuna C, Covy J, Xu W, Yang N, Danko T, Chen L, Wernig M, Südhof TC (2013) Rapid Single-Step Induction of Functional Neurons from Human Pluripotent Stem Cells. Neuron 78:785–798. [CrossRef]
- Tian R, Gachechiladze MA, Ludwig CH, Laurie MT, Hong JY, Nathaniel D, Prabhu AV, Fernandopulle MS, Patel R, Abshari M, Ward ME, Kampmann M (2019) CRISPR Interference-Based Platform for Multimodal Genetic Screens in Human iPSC-Derived Neurons. Neuron 104:239-255.e12. [CrossRef]
- Yang HH, St-Pierre F (2016) Genetically Encoded Voltage Indicators: Opportunities and Challenges. J Neurosci 36:9977–9989. [CrossRef]
- Volker Busskamp, Nathan E Lewis, Patrick Guye, Alex HM Ng, Seth L Shipman, Susan M Byrne, Neville E Sanjana, Jernej Murn, Yinqing Li, Shangzhong Li, Michael Stadler, Ron Weiss, George M Church (2014) Rapid neurogenesis through transcriptional activation in human stem cells. Molecular Systems Biology 10:760. [CrossRef]
- Thoma EC, Wischmeyer E, Offen N, Maurus K, Sirén A-L, Schartl M, Wagner TU (2012) Ectopic Expression of Neurogenin 2 Alone is Sufficient to Induce Differentiation of Embryonic Stem Cells into Mature Neurons. PLOS ONE 7:e38651. [CrossRef]
- Ho S-M, Hartley BJ, Tcw J, Beaumont M, Stafford K, Slesinger PA, Brennand KJ (2016) Rapid Ngn2-induction of excitatory neurons from hiPSC-derived neural progenitor cells. Methods 101:113–124. [CrossRef]
- Fernandopulle MS, Prestil R, Grunseich C, Wang C, Gan L, Ward ME (2018) Transcription Factor–Mediated Differentiation of Human iPSCs into Neurons. Current Protocols in Cell Biology 79:e51. [CrossRef]
- Nehme R, Zuccaro E, Ghosh SD, Li C, Sherwood JL, Pietilainen O, Barrett LE, Limone F, Worringer KA, Kommineni S, Zang Y, Cacchiarelli D, Meissner A, Adolfsson R, Haggarty S, Madison J, Muller M, Arlotta P, Fu Z, Feng G, Eggan K (2018) Combining NGN2 Programming with Developmental Patterning Generates Human Excitatory Neurons with NMDAR-Mediated Synaptic Transmission. Cell Reports 23:2509–2523. [CrossRef]
- Ang CE, Olmos VH, Zhou B, Lee QY, Sinha R, Narayanaswamy A, Mall M, Chesnov K, Sudhof T, Wernig M (2020) The Dynamic Interplay Between Homeodomain Transcription Factors and Chromatin Environment Regulates Proneural Factor Outcomes. 2020.12.02.398677.
- Liu X, Li F, Stubblefield EA, Blanchard B, Richards TL, Larson GA, He Y, Huang Q, Tan A-C, Zhang D, Benke TA, Sladek JR, Zahniser NR, Li C-Y (2012) Direct reprogramming of human fibroblasts into dopaminergic neuron-like cells. Cell Res 22:321–332. [CrossRef]
- Xue Y, Zhan X, Sun S, Karuppagounder SS, Xia S, Dawson VL, Dawson TM, Laterra J, Zhang J, Ying M (2019) Synthetic mRNAs Drive Highly Efficient iPS Cell Differentiation to Dopaminergic Neurons. STEM CELLS Translational Medicine 8:112–123. [CrossRef]
- Park C-H, Kang JS, Yoon E-H, Shim J-W, Suh-Kim H, Lee S-H (2008) Proneural bHLH neurogenin 2 differentially regulates Nurr1-induced dopamine neuron differentiation in rat and mouse neural precursor cells in vitro. FEBS Lett 582:537–542. [CrossRef]
- Vadodaria KC, Mertens J, Paquola A, Bardy C, Li X, Jappelli R, Fung L, Marchetto MC, Hamm M, Gorris M, Koch P, Gage FH (2016) Generation of functional human serotonergic neurons from fibroblasts. Mol Psychiatry 21:49–61. [CrossRef]
- Goparaju SK, Kohda K, Ibata K, Soma A, Nakatake Y, Akiyama T, Wakabayashi S, Matsushita M, Sakota M, Kimura H, Yuzaki M, Ko SBH, Ko MSH (2017) Rapid differentiation of human pluripotent stem cells into functional neurons by mRNAs encoding transcription factors. Sci Rep 7:42367. [CrossRef]
- Hester ME, Murtha MJ, Song S, Rao M, Miranda CJ, Meyer K, Tian J, Boulting G, Schaffer DV, Zhu MX, Pfaff SL, Gage FH, Kaspar BK (2011) Rapid and efficient generation of functional motor neurons from human pluripotent stem cells using gene delivered transcription factor codes. Mol Ther 19:1905–1912. [CrossRef]
- Mazzoni EO, Mahony S, Closser M, Morrison CA, Nedelec S, Williams DJ, An D, Gifford DK, Wichterle H (2013) Synergistic binding of transcription factors to cell-specific enhancers programs motor neuron identity. Nat Neurosci 16:1219–1227. [CrossRef]
- Son EY, Ichida JK, Wainger BJ, Toma JS, Rafuse VF, Woolf CJ, Eggan K (2011) Conversion of mouse and human fibroblasts into functional spinal motor neurons. Cell Stem Cell 9:205–218. [CrossRef]
- Garone MG, de Turris V, Soloperto A, Brighi C, De Santis R, Pagani F, Di Angelantonio S, Rosa A (2019) Conversion of Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells (iPSCs) into Functional Spinal and Cranial Motor Neurons Using PiggyBac Vectors. J Vis Exp. [CrossRef]
- Liu M-L, Zang T, Zou Y, Chang JC, Gibson JR, Huber KM, Zhang C-L (2013) Small molecules enable neurogenin 2 to efficiently convert human fibroblasts into cholinergic neurons. Nat Commun 4:2183. [CrossRef]
- Blanchard JW, Eade KT, Szűcs A, Lo Sardo V, Tsunemoto RK, Williams D, Sanna PP, Baldwin KK (2015) Selective conversion of fibroblasts into peripheral sensory neurons. Nat Neurosci 18:25–35. [CrossRef]
- Hulme AJ, McArthur JR, Maksour S, Miellet S, Ooi L, Adams DJ, Finol-Urdaneta RK, Dottori M (2020) Molecular and Functional Characterization of Neurogenin-2 Induced Human Sensory Neurons. Frontiers in Cellular Neuroscience 14:.
- Nickolls AR, Lee MM, Espinoza DF, Szczot M, Lam RM, Wang Q, Beers J, Zou J, Nguyen MQ, Solinski HJ, AlJanahi AA, Johnson KR, Ward ME, Chesler AT, Bönnemann CG (2020) Transcriptional Programming of Human Mechanosensory Neuron Subtypes from Pluripotent Stem Cells. Cell Reports 30:932-946.e7. [CrossRef]
- Schrenk-Siemens K, Wende H, Prato V, Song K, Rostock C, Loewer A, Utikal J, Lewin GR, Lechner SG, Siemens J (2015) PIEZO2 is required for mechanotransduction in human stem cell–derived touch receptors. Nat Neurosci 18:10–16. [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




