1. Introduction
The COVID-19 pandemic created unprecedented pressure on healthcare systems worldwide and subsequently provoked significant changes in the organization of healthcare services. Coronavirus disease has a broad spectrum of clinical manifestations ranging from asymptomatic infection to critical illness, most frequently presenting as acute hypoxemic respiratory failure that meets the Berlin definition of acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). Patients with COVID-19-associated ARDS commonly require intensive care unit (ICU) admission and invasive mechanical ventilation and have high mortality rates [
1,
2].
It is well established that early application of prone-positioning (PP) sessions of at least 12 hours improve survival in moderate-to-severe ARDS [
3,
4]. The beneficial effect of prone ventilation is likely attributed to a better ventilation-perfusion matching, lung recruitment and protection from ventilator-induced lung injury (VILI) [
5]. Current guidelines on the management of ARDS strongly recommend the use of PP for 12 to 16 hours per day in patients with a P/F ratio ≤ 150 mmHg [
3,
4,
6]. However, the optimal duration of the intervention to gain maximum benefit is not known. During COVID-19 pandemic prone ventilation was widely adopted as a prominent therapeutic intervention for patients receiving mechanical ventilation. Retrospective data from this patient population showed that early application of PP is associated with improved oxygenation and reduced hospital mortality [
7,
8].
One of the challenges of PP is that it can increase the workload for the ICU staff in a period of crisis. To overcome this problem, it was suggested to implement a prolonged pronation protocol, beyond the usual 16 hours, aiming to reduce the number of pronation cycles per patient. Nevertheless, the intervention is not without risks. The most severe complications are accidental extubation, airway obstruction, central venous catheter or arterial catheter dislocation, pressure ulcers, peripheral nerve palsies and musculoskeletal injuries [
9]. There are reports that prolonged prone ventilation is feasible and relatively safe [
10,
11], but comparison with standard PP has been scarce.
We sought to examine the efficacy and safety of a prolonged PP protocol compared to the standard of care.
2. Materials and methods
We conducted a prospective observational study. General Hospital of Thoracic Diseases “Sotiria” is a tertiary public hospital which serves as the main referral center for COVID-19 in Athens, Greece. The study was conducted in a 12-bed COVID-19 ICU during a 6-month period. Patient demographics, clinical, and mechanical ventilation (MV) variables were entered into an electronic spreadsheet and cross-validated with source documentation in real time. The study was approved by the local Institutional Review Board (protocol number 172 /24-05-2021). The need for informed consent was waived.
Protective ventilation was applied to all patients. PP was initiated for severe hypoxemia defined as P/F ratio < 150 mmHg with FiO2>0.6 and PEEP>10cm H2O. In the prolonged PP (PPP) group patients were proned for more than 24 hours whereas the standard PP (SPP) group included patients proned for 24 hours or less. The decision for the duration of PP was at the discretion of the treating physician, according to a guiding protocol stating that return to the supine position would be performed after at least 16 hours if P/F ratio was above 150 and if experienced staff was available. For safety reasons, repositioning during the night shift was avoided, unless it was deemed necessary. Pronation cycles were stopped when P/F ratio remained > 150mmHg in supine position. Oxygenation parameters and respiratory mechanics were recorded for the first pronation cycle before PP, at the end of the cycle and 4 hours after supine repositioning. We included all the intubated patients > 18 years old, with a positive PCR for SARS-CoV-2, who underwent at least one cycle of PP during the specified time period. Patients proned for less than 4 hours were excluded from the analysis.
Prone positioning and repositioning to the supine position were performed manually by experienced ICU staff according to a standardized protocol. Alternating pressure air mattresses were used in all patients. Foam wedges, foam dressings, gel rings and pillows were used for pressure injuries prevention. Alternating arm and head repositioning in the “swimming position” were performed every 6-8 hours. Sedation and analgesia were titrated to achieve deep sedation (Richmond Sedation Agitation Scale score of 4-5) and neuromuscular blockade was administered to all patients during PP. Pressure wounds and other complications were recorded daily by bedside nurses.
Outcomes
The primary clinical outcomes were changes in oxygenation and respiratory mechanics during and after PP and number of PP cycles. Secondary outcome was 28-day survival. A subgroup analysis of obese patients (BMI>30Kg/m2) was additionally performed. We also examined the safety and the complications of the procedure.
Statistical analysis
Variables were first tested for normality using the Kolmogorov-Smirnov criterion. Quantitative variables were expressed as mean (Standard Deviation) or as median (interquantile range). Qualitative variables were expressed as absolute and relative frequencies. Students’ t-tests and Mann-Whitney tests were used for the comparison of continuous variables between the two groups. For the comparison of proportions chi-square and Fisher’s exact tests were used. Pearson correlations coefficients (r) were used to explore the association of two continuous variables. Repeated measurements analysis of variance (ANOVA) was adopted to evaluate the changes observed in respiratory parameters over the follow up period, between the two groups. Logistic regression analysis in a stepwise method (p for entry 0.05, p for removal 0.10) was used in order to find independent factors associated with 28-day survival. Adjusted odds ratios (OR) with 95% confidence intervals (95% CI) were computed from the results of the logistic regression analysis. All reported p values are two-tailed. Statistical significance was set at p<0.05 and analyses were conducted using SPSS statistical software (version 26.0).
3. Results
From March 2021 to August 2021, we recorded 68 consecutive intubated patients with COVID-19-associated ARDS who underwent prone ventilation. Five patients were excluded because PP was terminated in less than 4 hours due to hemodynamic instability or worsening of oxygenation. The final study sample consisted of 63 patients (63.5% males), with mean age 63.5 years. Thirty-seven patients (58.7%) underwent prolonged prone position (PPP group) and 26 (41.3%) standard prone position (SPP group). Median PP duration for SPP group was 20 hours (IQR: 20-22) and for PPP group 46 hours (IQR: 40-48), p< 0.001. Cumulative duration of pronation was longer for PPP group. Patients’ characteristics by group are presented in
Table 1. No significant differences were found between the two groups, except for a higher proportion of obese patients among PPP group. All patients received corticosteroids while tocilizumab was administered to similar proportions in both groups.
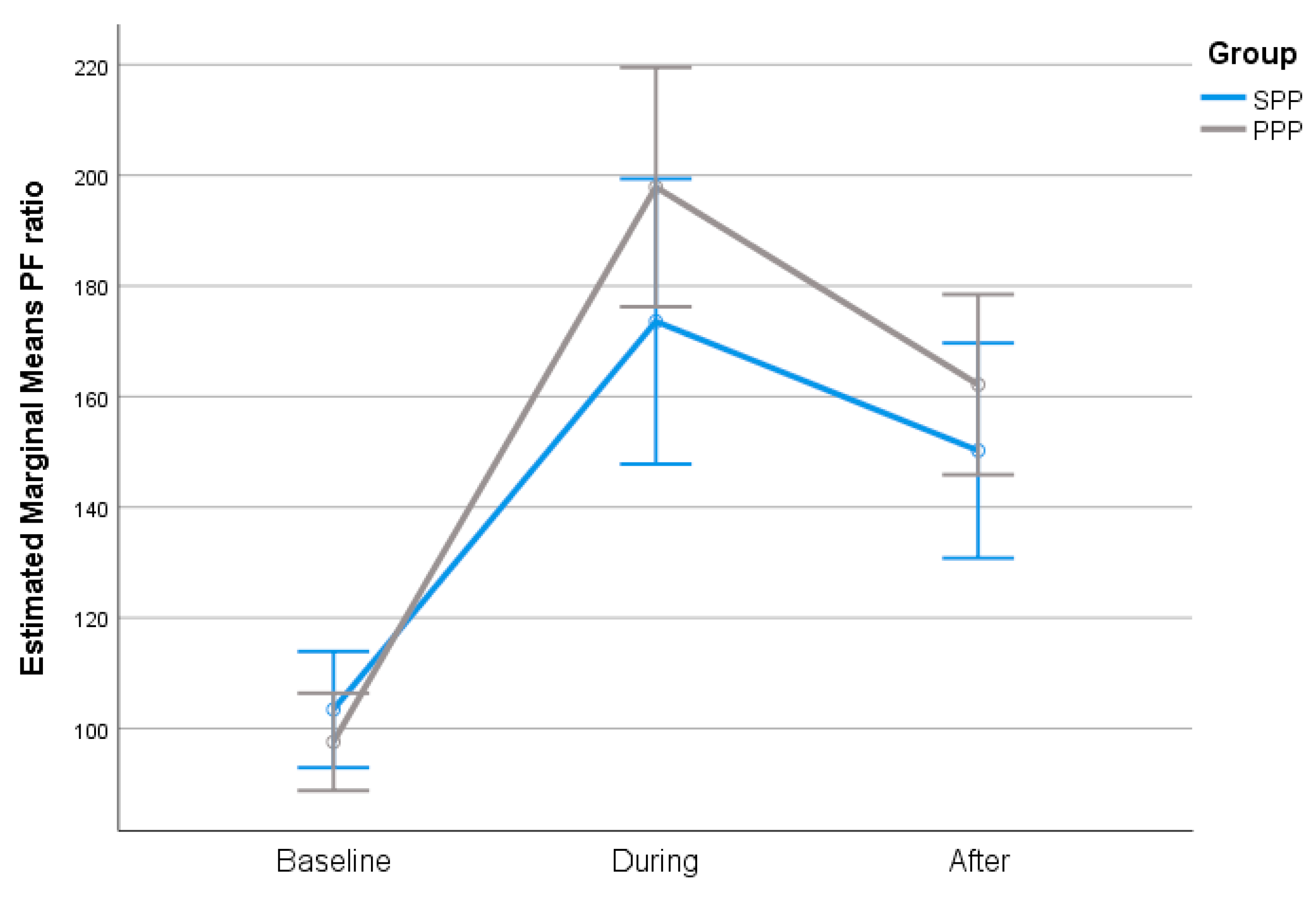
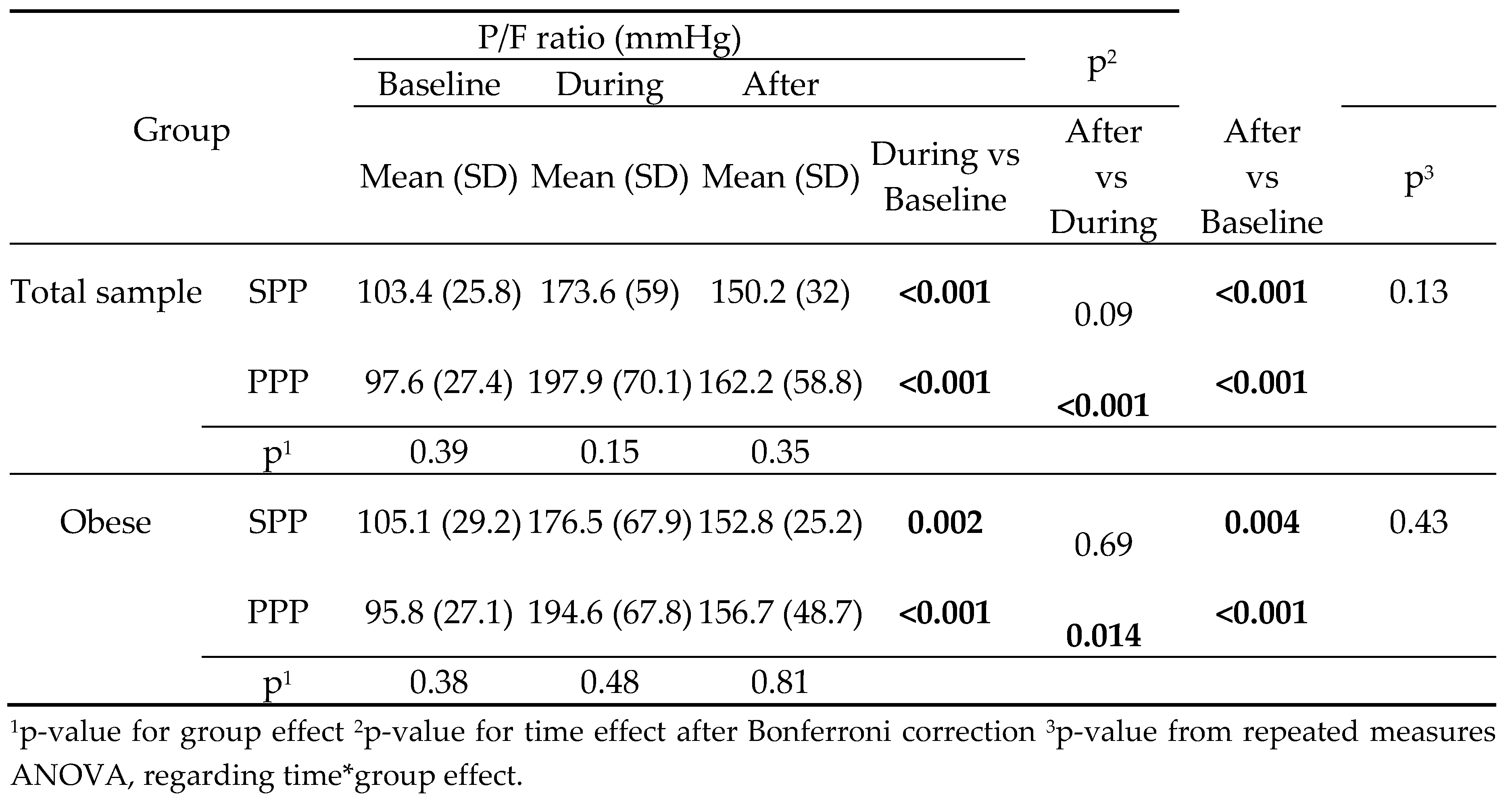
The change in P/F ratio was similar across all time points between SPP and PPP group, in the total sample and in the subgroup of obese patients. In both groups, P/F ratio during and after PP was significantly higher compared to baseline (
Table 2).
The degree of P/F ratio change across the follow-up period was similar in both groups (
Figure 1). Furthermore, PP duration was not correlated with P/F ratio (r=.18; p=.161).
The change in respiratory parameters by group throughout the follow-up period is presented in
Table 3. No significant differences were found between SPP and PPP group at any timepoint. Pplat was slightly lower during the maneuver compared to baseline in both groups, while after supination it remained lower than baseline only in the PPP group. However, because PEEP was also lower during and after the maneuver, DP and Cstat were similar throughout time.
No significant difference was found in 28-day survival between the two groups. Number of pronation cycles was also comparable. No major complications were encountered in either group. Facial edema and pressure injuries stage I were recorded in six patients during PPP and in four patients during SPP, while one patient in each group developed a stage II facial pressure ulcer and one patient in PPP group developed a stage III facial injury and periorbital edema (
Table 4). Similar results were recorded for obese patients as shown in
Table 5.
After conducting multiple logistic regression, in a stepwise method, it was found that the number of PP cycles, APACHE II and PaCO2 at baseline were independently associated with 28-day survival. Specifically, higher number of cycles, higher APACHE II score and higher PaCO2 at baseline were significantly associated with a lower probability of surviving (
Table 6).
4. Discussion
In a cohort of COVID-19 intubated patients with severe ARDS, a prolonged prone positioning protocol was not shown to confer any advantage in improving oxygenation and respiratory mechanics compared to the traditional strategy of daily prone ventilation. Furthermore, it was not associated with reduced total pronation cycles. Twenty-eight-day survival was similar between the two groups. The intervention was feasible and safe with only minor observed complications.
Prone position ventilation for at least 16 hours has been shown to reduce mortality in patients with ARDS and P/F ratio of < 150mmHg. This beneficial effect does not depend on gas exchange improvement but is rather attributed to protection from VILI by reducing overdistension of non-dependent and enhancing alveolar recruitment of dependent lung zones, leading to more homogeneous lung expansion and reducing lung stress and strain [
3]. Prone ventilation was widely adopted during COVID-19 pandemic. While LUNG SAFE study in 2016 [
12] reported application of prone positioning in only 16.3% of patients with moderate to severe ARDS, the intervention was used in more than 70% of mechanically ventilated patients with COVID-19 [
13,
14].
Early prone ventilation has been associated with improved survival among COVID-19 patients [
8]. However, it is a labor-intensive procedure requiring at least 5 highly trained ICU professionals to execute each pronation and supination maneuver [
15]. In conditions of increased workload, as was the case during the pandemic, prolongation of the duration of prone ventilation to more than 24 hours seemed an attractive option to reduce the burden of this life-saving intervention. Furthermore, prolonging PP has a physiological rationale as there is data suggesting that the beneficial effects of PP may persist at least up to 24 hours for some patients [
16], while supination is often accompanied by de-recruitment events. Prior studies in COVID-19 patients with ARDS showed that prolonged PP is efficacious and safe when performed by experienced staff [
11]. However, the efficacy of the maneuver compared to standard practice of shorter duration daily cycles has not been extensively studied. In a single-center study of patients with pneumonia and ARDS, Jochmans et al, reported that maximum physiological beneficial effect of PP was obtained between 16 and 19 hours in most patients and extending pronation for more than 24 hours offered no survival benefit [
16]. In patients with COVID-19 related ARDS, improvement of oxygenation with proning has been associated with lower mortality [
17].
In a recent retrospective study of intubated COVID-19 patients, Okin et al. [
18] reported reduced mortality and fewer pronation-supination cycles for the prolonged PP compared to the standard PP. The authors found no difference in oxygenation improvement between PPP and SPP, measured as the change of P/F ratio within 6 hours of pronation. In the present study we found a similar increase in P/F ratio between prolonged and intermittent proning during the maneuver and up to 4 hours after supination. Furthermore, there was no correlation between PP duration and P/F ratio. It seems that extending proning beyond 24 hours confers little further improvement in oxygenation. Changes in respiratory mechanics were of little clinical significance in both groups. Okin et al, attribute the beneficial effect on survival to the reduced de-recruitment events associated with fewer supination sessions. Despite similar patient characteristics and similar duration of prolonged pronation protocol between the two studies, we did not find a survival advantage of PPP over SPP. However, there are caveats that should be addressed. First, 28-day mortality rates in our cohort are similar to those in Okin’s study (21.6% vs 25.5% for PPP group and 34,6% vs 34.9% for SPP group). Therefore, lack of significance is probably due to the smaller sample size of our study. Second, although we found no difference in the total number of performed PP cycles between groups, number of cycles was an independent risk factor for mortality, lending support to the assumption that de-recruitment associated with repeated supination may be injurious to the lung and may contribute to mortality. It can be speculated that PPP may reduce mortality when it results in fewer pronation and supination events. Third, in our study a higher proportion of obese patients were included in PPP than in SPP group. Several meta-analyses have shown that obesity is associated with increased severity and higher mortality among COVID-19 patients [
19]. Moreover, a subgroup analysis of our cohort showed that obese patients had no additional benefit with PPP compared to SPP.
The rate of complications in our study was very low in both groups and almost exclusively consisted of minor facial pressure injuries. Pressure injuries are the most frequent complications of prone ventilation. In a retrospective study of 81 patients with COVID-19 who were ventilated in PP for a median of 39 hours, 26% developed pressure injuries stage II and 2.5% stage III and IV. Cumulative duration of PP sessions, but not the duration of each session, was associated with the occurrence of pressure injuries [
20]. Okin et al, reported an incidence of pressure sores of about 30%, with no difference between prolonged and intermittent PP. In our study the use of foam pads, foam dressings, gel rings and regular head repositioning probably contributed to the low incidence of this complication.
There are several limitations to our study. It was a single-center non-randomized study. The sample size was small and probably unsuitable to detect a survival benefit. We recorded only immediate complications. There was no long-term follow-up and therefore we might have missed late complications such as plexopathy and nerve damage [
21].
However, the present study confirms the feasibility and safety of prolonged prone ventilation in patients with severe ARDS caused by COVID-19 and highlights the urgent need for randomized trials comparing the efficacy of this maneuver with the standard technique of daily proning and supination in ARDS patients of various etiology. Should this approach proves to further improve mortality, it could be safely added to lung protective ventilation, which is so far the only lifesaving intervention in this patient population.
5. Conclusions
Among intubated COVID-19 patients with severe ARDS, prolonging PP to more than 24 hours was as safe and efficient as traditional PP, but it was not associated with survival benefit.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, George Karlis and Mary Daganou; Data curation, Despina Markantonaki; Investigation, George Karlis, Dimitra Bakali, Georgia Katsagani, Theodora Katsarou, Christos Kyritsis, Vasiliki Karaouli and Paraskevi Athanasiou; Methodology, Sotirios Kakavas; Supervision, Despina Markantonaki and Mary Daganou; Writing – original draft, George Karlis; Writing – review & editing, Despina Markantonaki and Mary Daganou.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the Institutional Review Board of General Hospital of Thoracic Diseases “Sotiria” (172/24-05-2021).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was waived due to the observational, non-interventional nature of the study.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- ARDS Definition of Task Force; Ranieri, V.M.; Rubenfeld, G.D.; Thompson, B.T.; Ferguson, N.D.; Caldwell, E.; Fan, E.; Camporota, L.; Slutsky, A.S. Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome: The Berlin Definition. JAMA 2012, 307, 2526–2533. [CrossRef]
- Grasselli, G.; Tonetti, T.; Protti, A.; Langer, T.; Girardis, M.; Bellani, G.; Laffey, J.; Carrafiello, G.; Carsana, L.; Rizzuto, C.; et al. Pathophysiology of COVID-19-associated acute respiratory distress syndrome: a multicentre prospective observational study. Lancet Respir. Med. 2020, 8, 1201–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guérin, C.; Reignier, J.; Richard, J.-C.; Beuret, P.; Gacouin, A.; Boulain, T.; Mercier, E.; Badet, M.; Mercat, A.; Baudin, O.; et al. Prone Positioning in Severe Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 368, 2159–2168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gattinoni, L.; Taccone, P.; Carlesso, E.; Marini, J.J. Prone Position in Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome. Rationale, Indications, and Limits. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2013, 188, 1286–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guérin, C.; Albert, R.K.; Beitler, J.; Gattinoni, L.; Jaber, S.; Marini, J.J.; Munshi, L.; Papazian, L.; Pesenti, A.; Vieillard-Baron, A.; et al. Prone position in ARDS patients: why, when, how and for whom. Intensiv. Care Med. 2020, 46, 2385–2396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffiths, M.J.D.; McAuley, D.F.; Perkins, G.D.; Barrett, N.; Blackwood, B.; Boyle, A.; Chee, N.; Connolly, B.; Dark, P.; Finney, S.; et al. Guidelines on the management of acute respiratory distress syndrome. BMJ Open Respir. Res. 2019, 6, e000420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langer, T.; Brioni, M.; Guzzardella, A.; Carlesso, E.; Cabrini, L.; Castelli, G.; Dalla Corte, F.; De Robertis, E.; Favarato, M.; Forastieri, A.; et al. Prone position in intubated, mechanically ventilated patients with COVID-19: a multi-centric study of more than 1000 patients. Crit. Care 2021, 25, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathews, K.S.; Soh, H.; Shaefi, S.; Wang, W.; Bose, S.; Coca, S.; Gupta, S.; Hayek, S.S.; Srivastava, A.; Brenner, S.K.; et al. Prone Positioning and Survival in Mechanically Ventilated Patients With Coronavirus Disease 2019–Related Respiratory Failure*. Crit. Care Med. 2021, 49, 1026–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le, M.Q.; Rosales, R.; Shapiro, L.T.; Huang, L.Y. The Down Side of Prone Positioning. Am. J. Phys. Med. Rehabilitation 2020, 99, 870–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Douglas, I.S.M.; Rosenthal, C.A.; Swanson, D.D.B.; Hiller, T.R.; Oakes, J.; Bach, J.; Whelchel, C.R.; Pickering, J.D.; George, T.R.; Kearns, M.; et al. Safety and Outcomes of Prolonged Usual Care Prone Position Mechanical Ventilation to Treat Acute Coronavirus Disease 2019 Hypoxemic Respiratory Failure*. Crit. Care Med. 2021, 49, 490–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carsetti, A.; Paciarini, A.D.; Marini, B.; Pantanetti, S.; Adrario, E.; Donati, A. Prolonged prone position ventilation for SARS-CoV-2 patients is feasible and effective. Crit. Care 2020, 24, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellani, G.; Laffey, J.G.; Pham, T.; Fan, E.; Brochard, L.; Esteban, A.; Gattinoni, L.; Van Haren, F.; Larsson, A.; McAuley, D.F.; et al. Epidemiology, Patterns of Care, and Mortality for Patients With Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome in Intensive Care Units in 50 Countries. JAMA 2016, 315, 788–800, Erratum in: JAMA. 2016 Jul 19;316(3):350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrando, C.; Suarez-Sipmann, F.; Mellado-Artigas, R.; Hernández, M.; Gea, A.; Arruti, E.; Aldecoa, C.; Martínez-Pallí, G.; Martínez-González, M.A.; Slutsky, A.S.; et al. Clinical features, ventilatory management, and outcome of ARDS caused by COVID-19 are similar to other causes of ARDS. Intensiv. Care Med. 2020, 46, 2200–2211, Erratum in: Intensive Care Med. 2020 Dec 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- COVID-ICU Group on behalf of the REVA Network and the COVID-ICU Investigators. Clinical characteristics and day-90 outcomes of 4244 critically ill adults with COVID-19: A prospective cohort study. Intensive Care Med. 2021, 47, 60–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harcombe, C.J.; Unit, C.J.H.S.I.C.; Centre, T.C.; Hospital, B. ; Liverpool Nursing patients with ARDS in the prone position. Nurs. Stand. 2004, 18, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jochmans, S.; Mazerand, S.; Chelly, J.; Pourcine, F.; Sy, O.; Thieulot-Rolin, N.; Ellrodt, O.; Rochettes, E.M.D.; Michaud, G.; Serbource-Goguel, J.; et al. Duration of prone position sessions: a prospective cohort study. Ann. Intensiv. Care 2020, 10, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scaramuzzo, G.; Gamberini, L.; Tonetti, T.; Zani, G.; Ottaviani, I.; Mazzoli, C.A.; Capozzi, C.; Giampalma, E.; Reggiani, M.L.B.; Bertellini, E.; et al. Sustained oxygenation improvement after first prone positioning is associated with liberation from mechanical ventilation and mortality in critically ill COVID-19 patients: a cohort study. Ann. Intensiv. Care 2021, 11, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okin, D.; Huang, C.-Y.; Alba, G.A.; Jesudasen, S.J.; Dandawate, N.A.; Gavralidis, A.; Chang, L.L.; Moin, E.E.; Ahmad, I.; Witkin, A.S.; et al. Prolonged Prone Position Ventilation Is Associated With Reduced Mortality in Intubated COVID-19 Patients. Chest 2022, 163, 533–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, R.; Rathore, S.S.; Khan, H.; Karale, S.; Chawla, Y.; Iqbal, K.; Bhurwal, A.; Tekin, A.; Jain, N.; Mehra, I.; et al. Association of Obesity With COVID-19 Severity and Mortality: An Updated Systemic Review, Meta-Analysis, and Meta-Regression. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 780872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walter, T.; Zucman, N.; Mullaert, J.; Thiry, I.; Gernez, C.; Roux, D.; Ricard, J.-D. Extended prone positioning duration for COVID-19-related ARDS: benefits and detriments. Crit. Care 2022, 26, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brugliera, L.; Filippi, M.; Del Carro, U.; Butera, C.; Bianchi, F.; Castellazzi, P.; Cimino, P.; Capodaglio, P.; Monti, G.; Mortini, P.; et al. Nerve Compression Injuries After Prolonged Prone Position Ventilation in Patients With SARS-CoV-2: A Case Series. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabilitation 2020, 102, 359–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).